lab 21: spinal cord, nerves, + reflexes
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/120
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 12:47 AM on 4/29/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
121 Terms
1
New cards
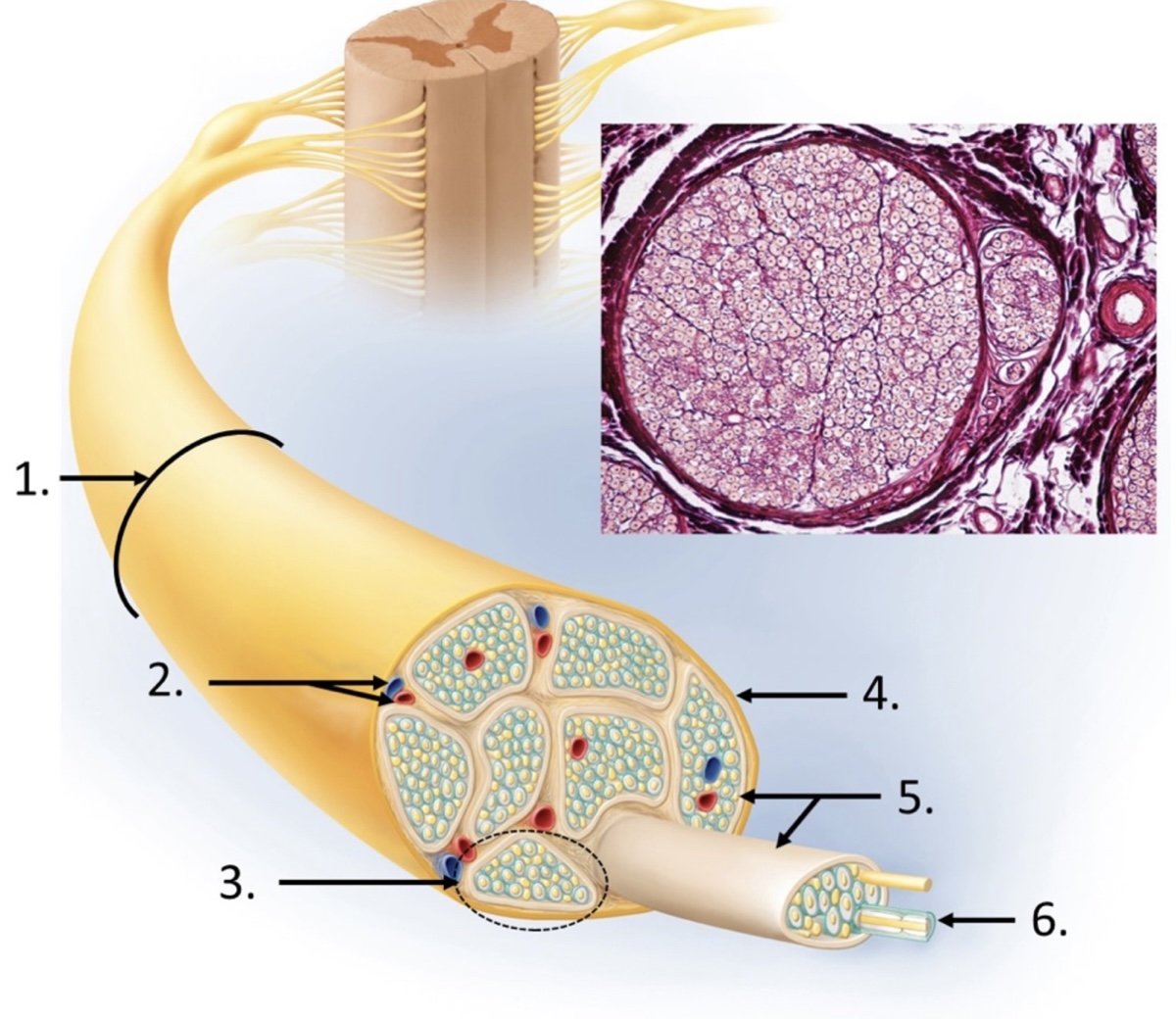
1
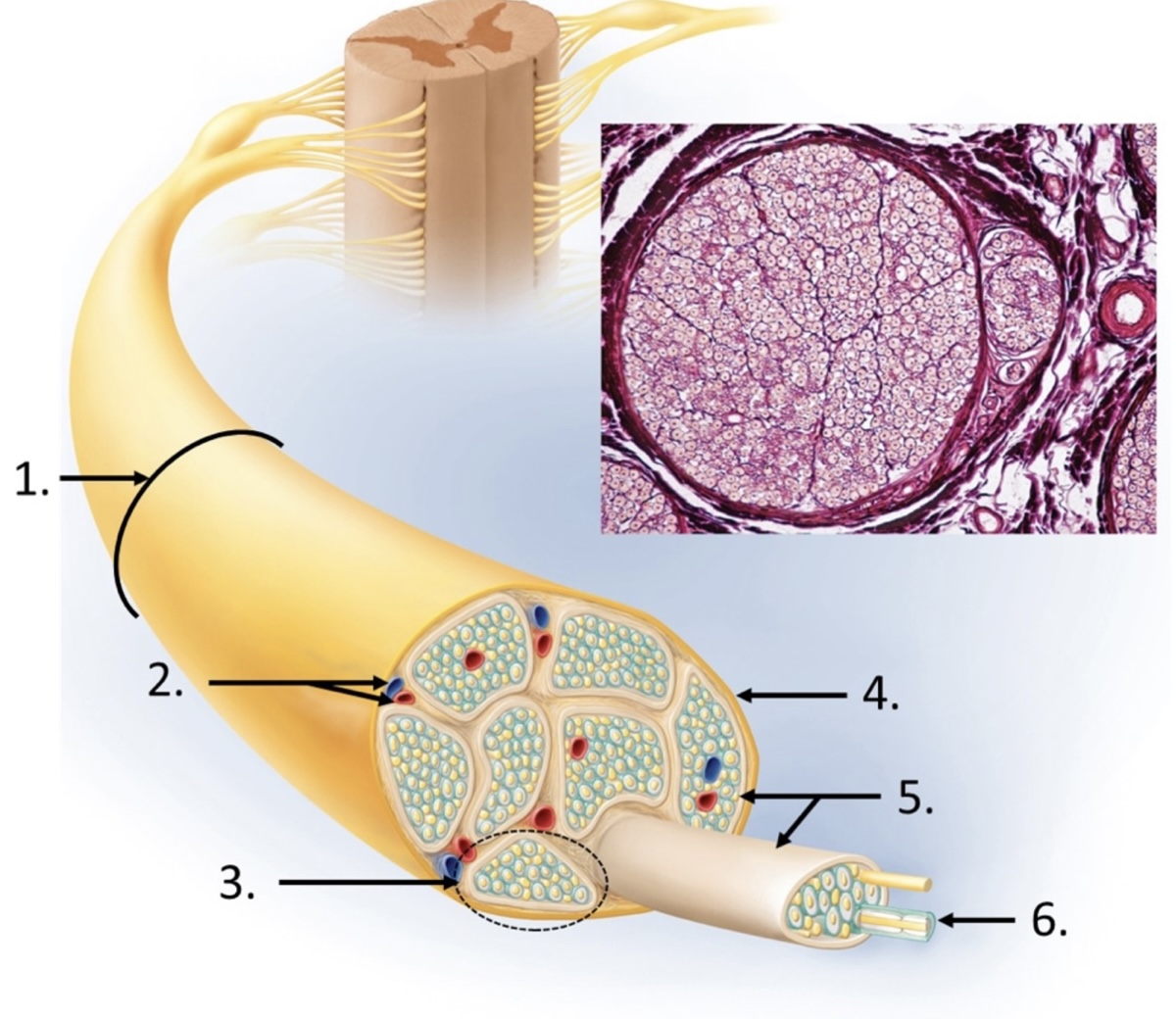
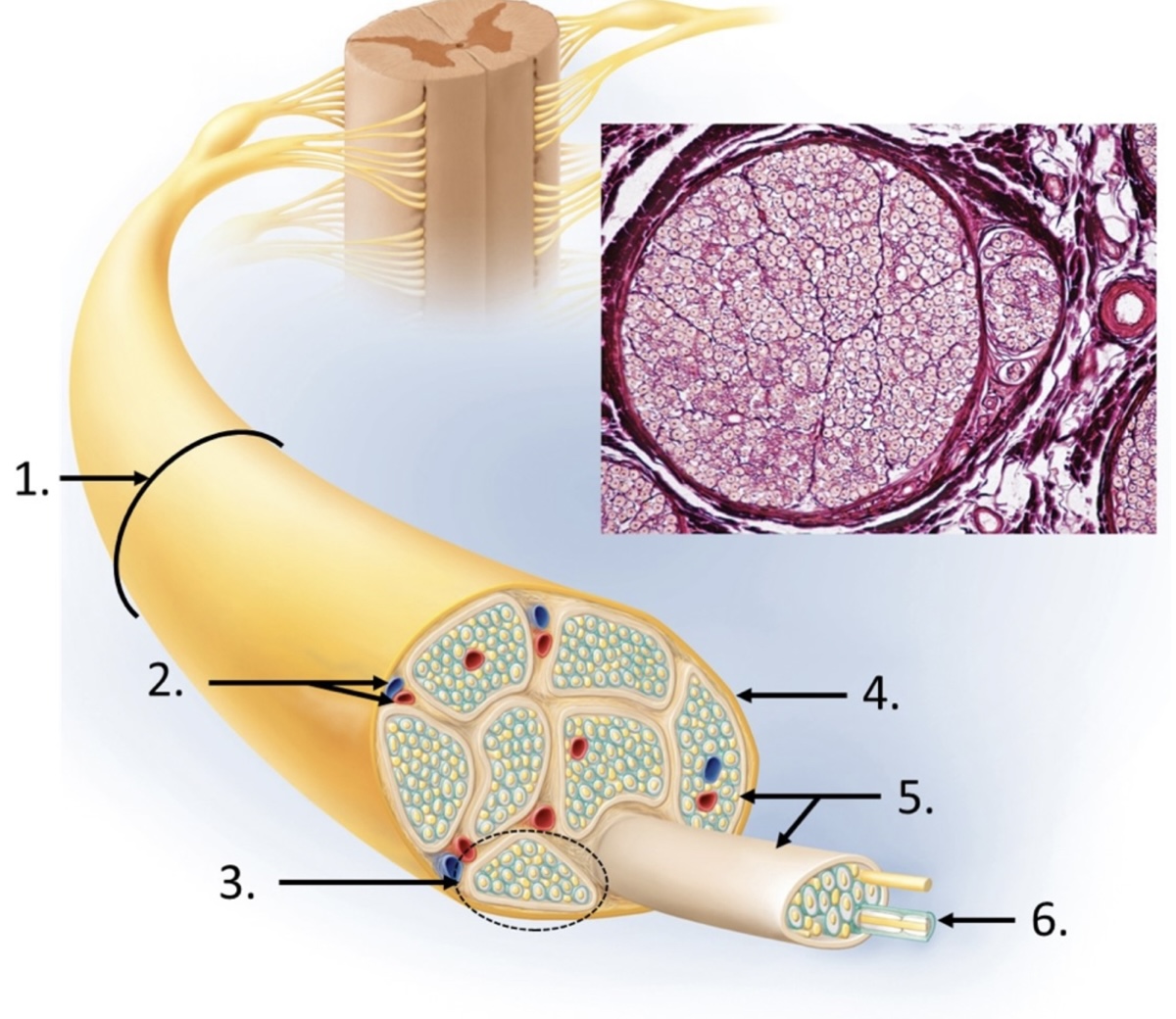
nerve
2
New cards
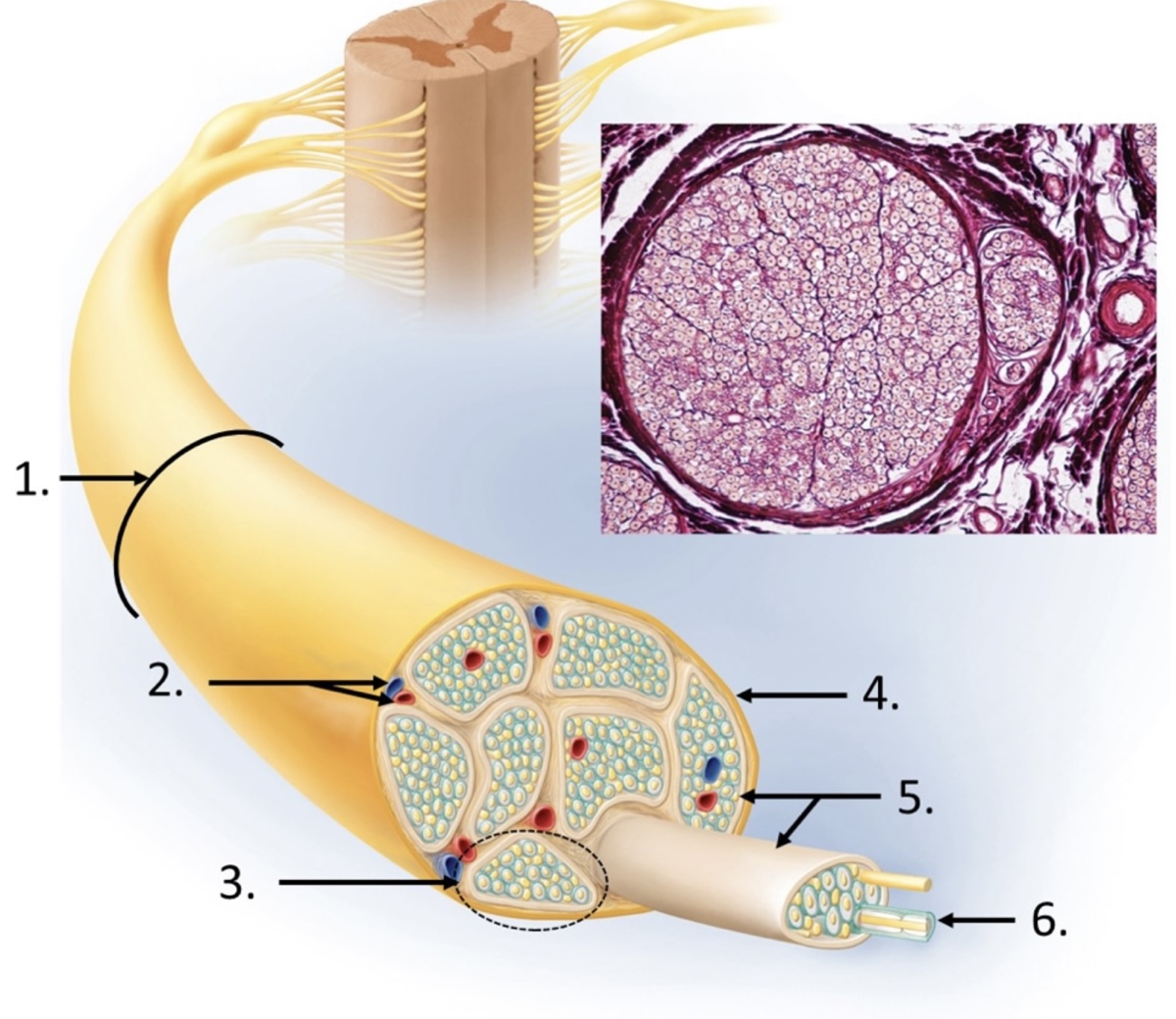
2
blood vessels
3
New cards
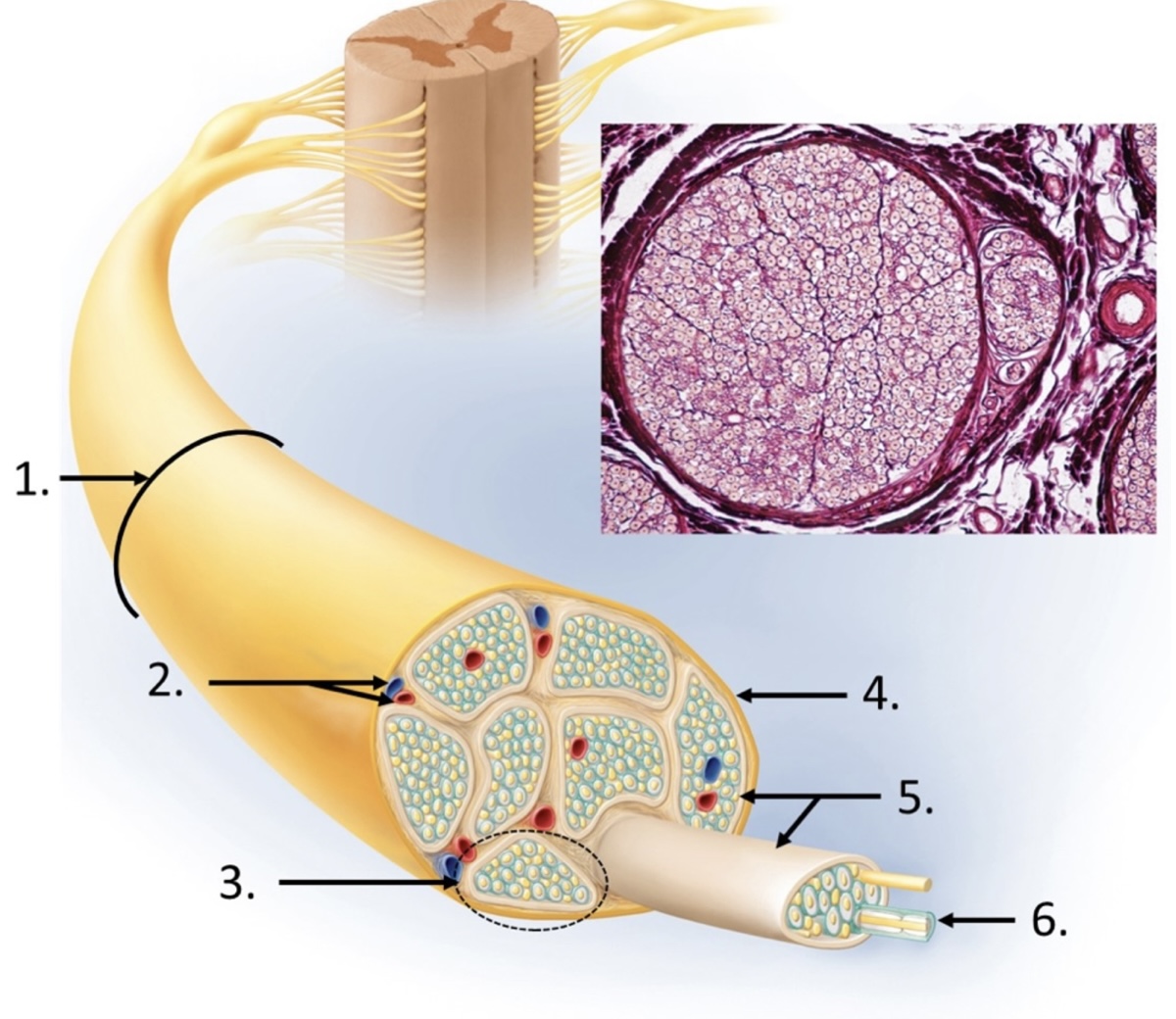
3
fascicle
4
New cards
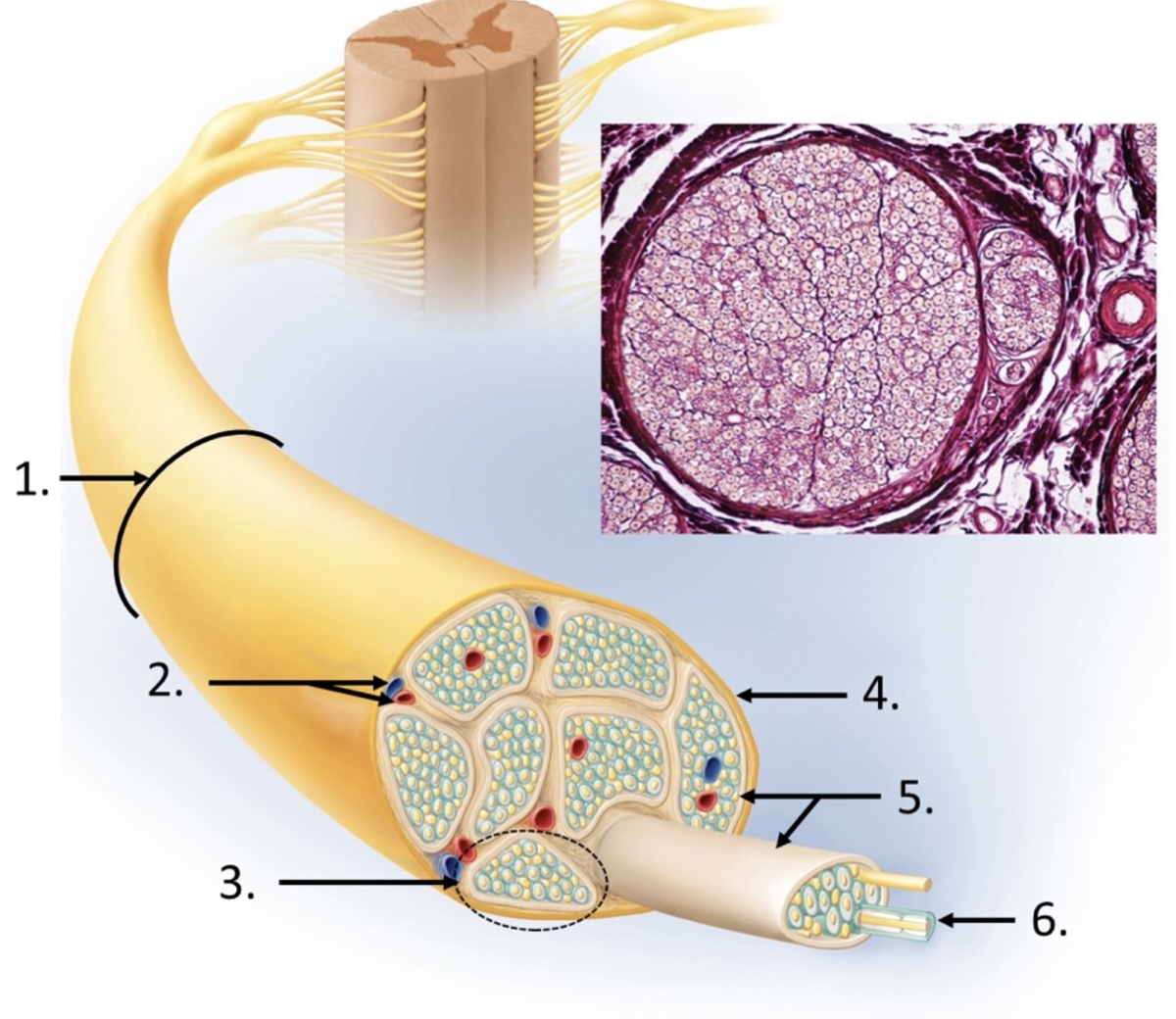
4
epineurium
5
New cards
5
perineurium
6
New cards
6
endoneurium
7
New cards
1
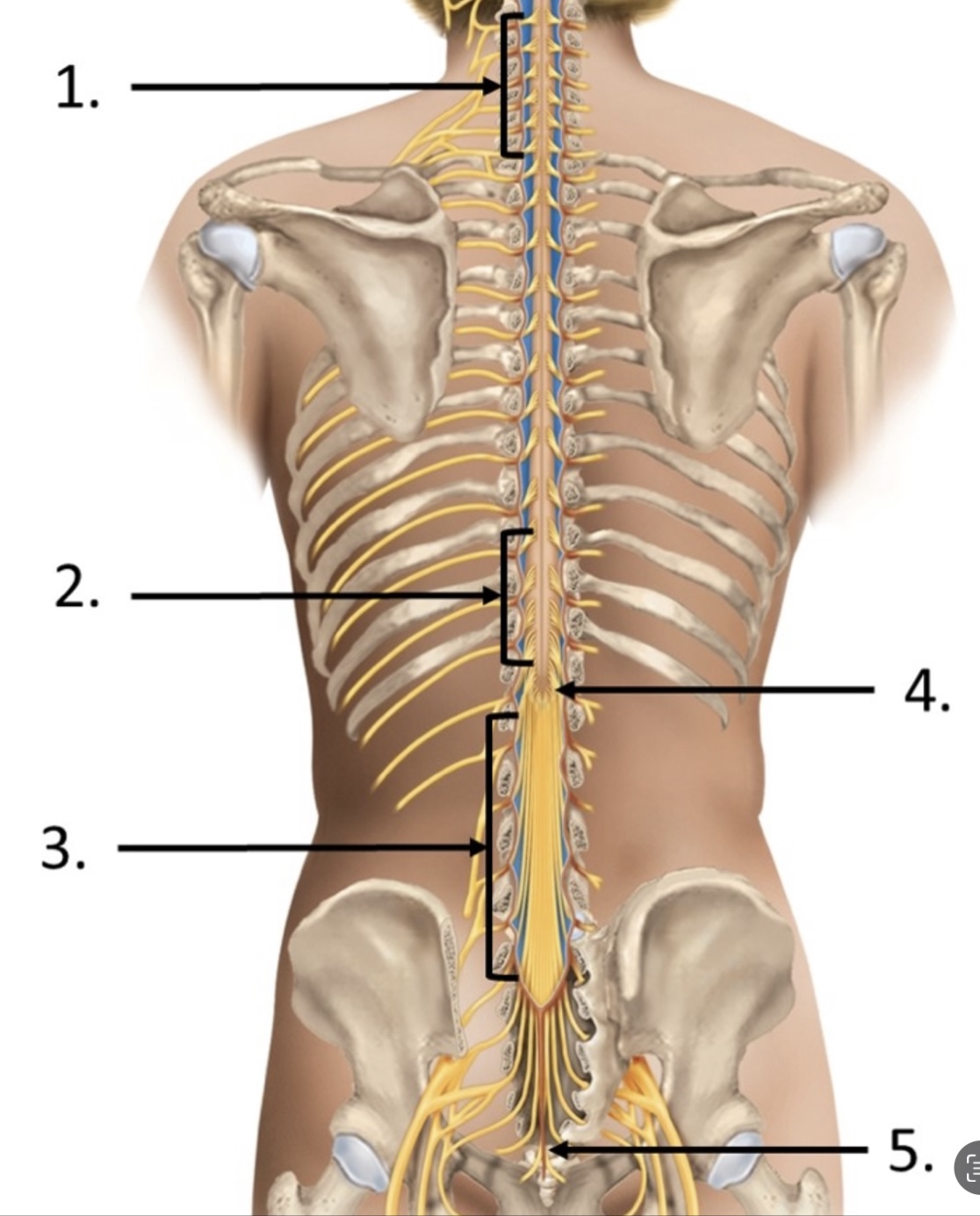
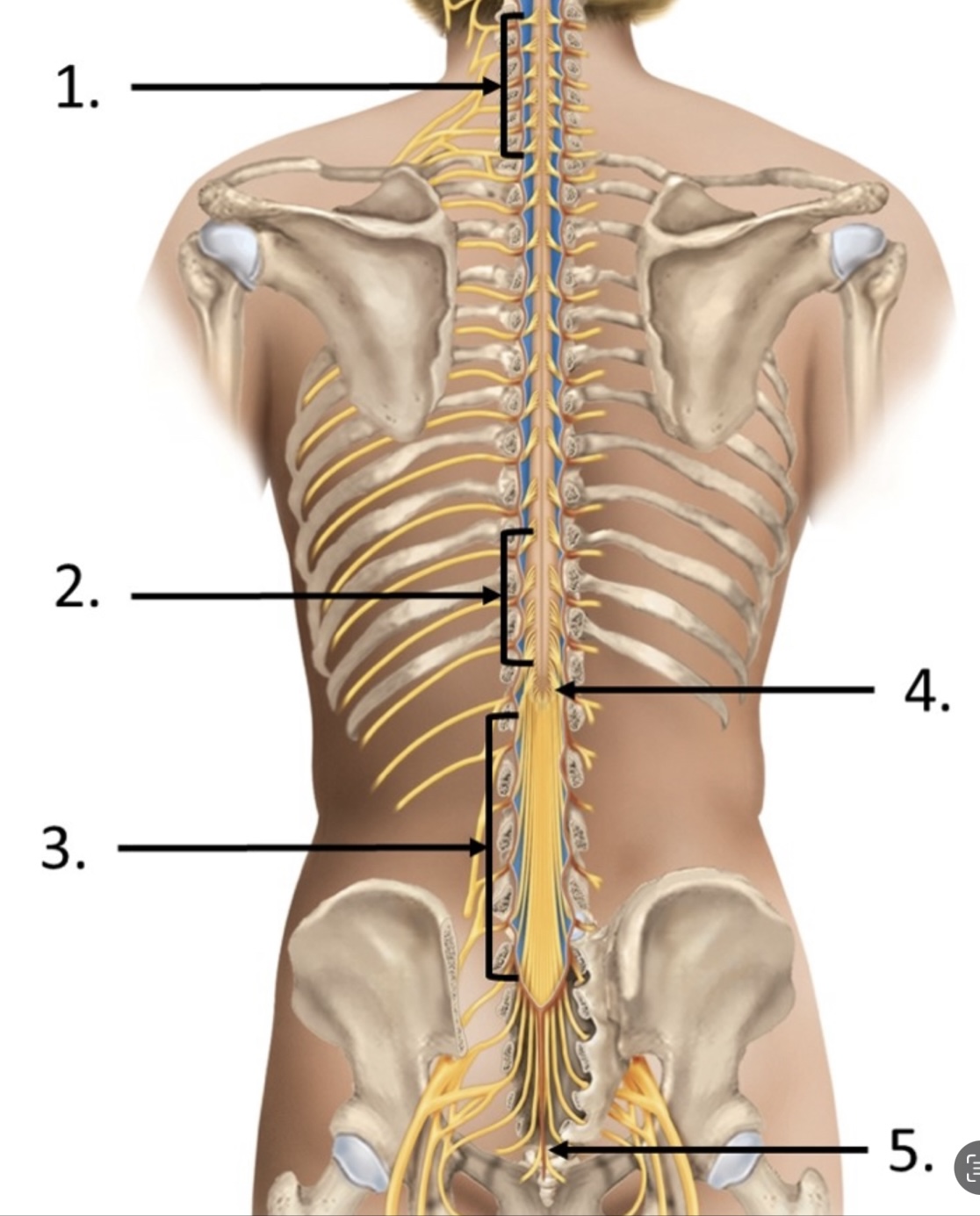
cervical enlargement
8
New cards
2
lumbar enlargement
9
New cards
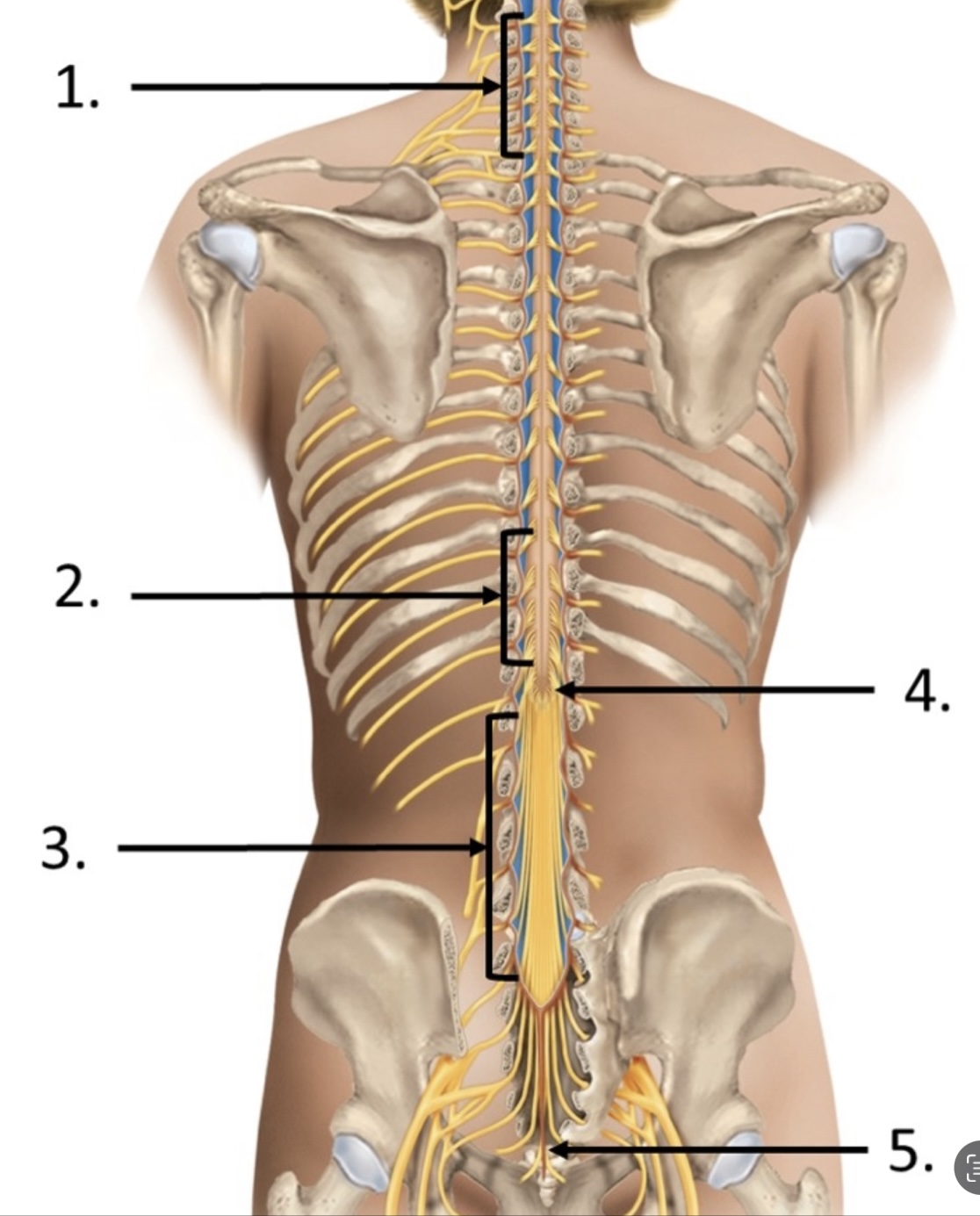
3
cauda equina
10
New cards
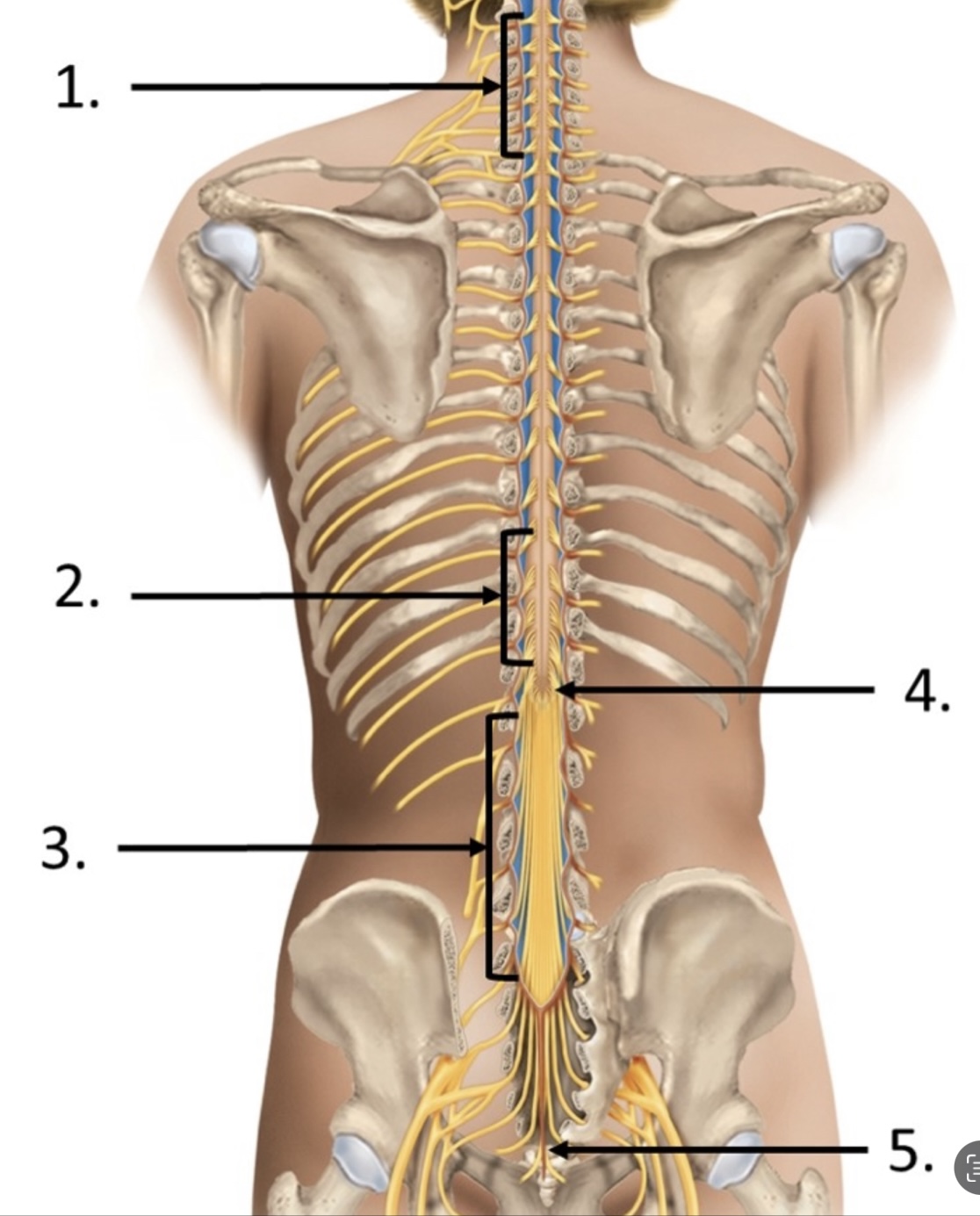
4
conus medullaris
11
New cards
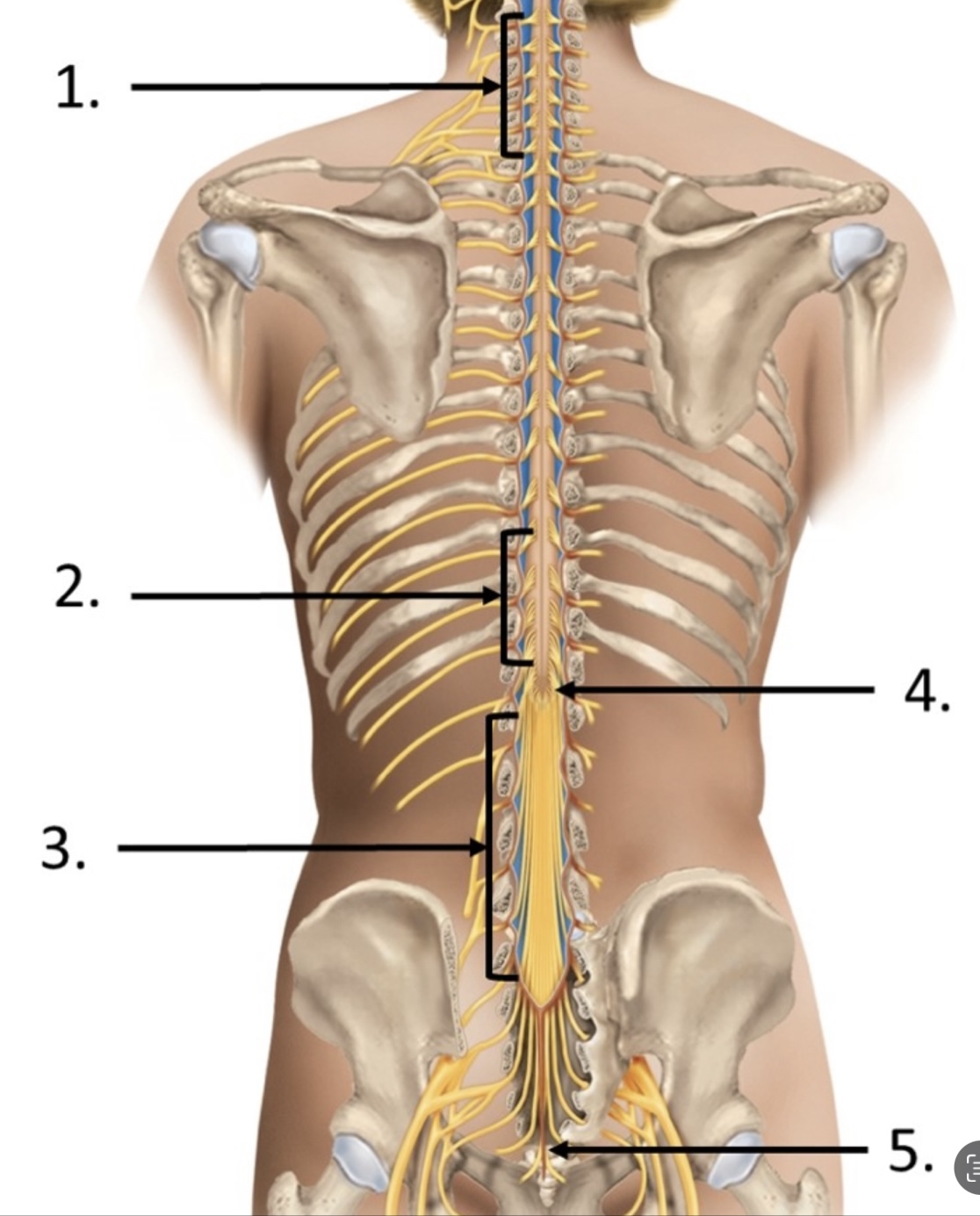
5
filum terminale
12
New cards
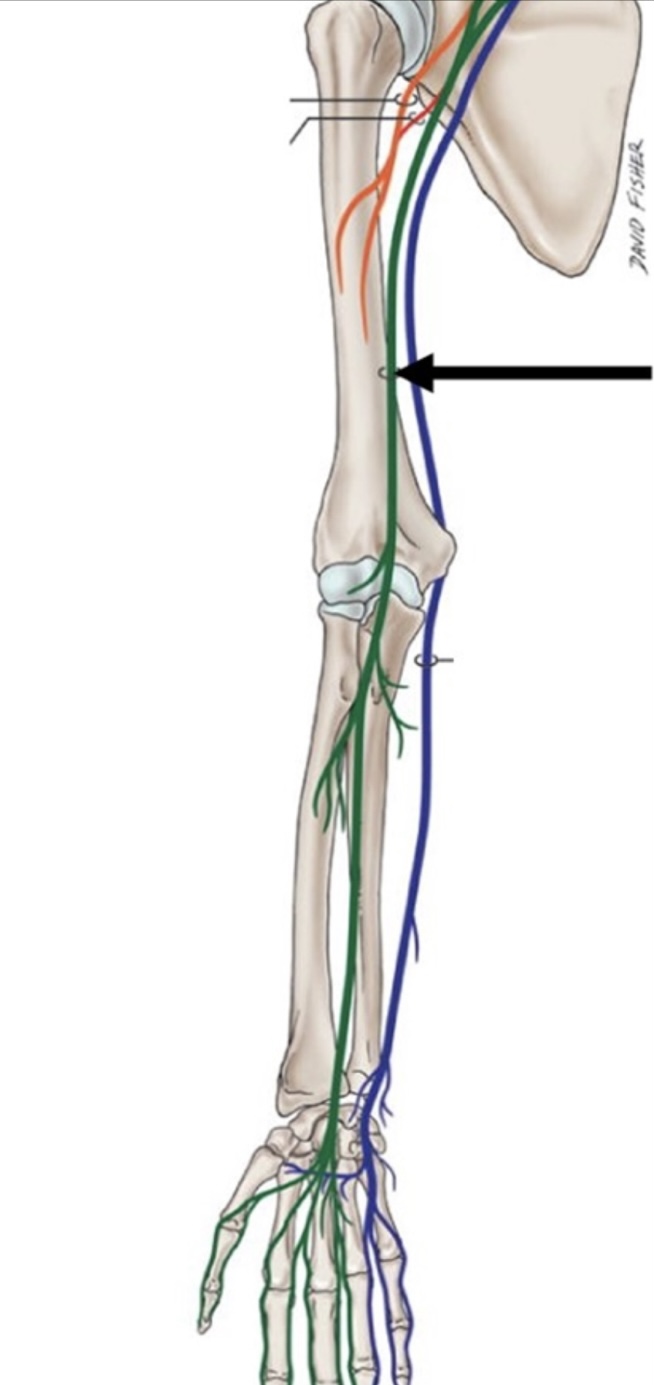
identify this nerve
median nerve
13
New cards
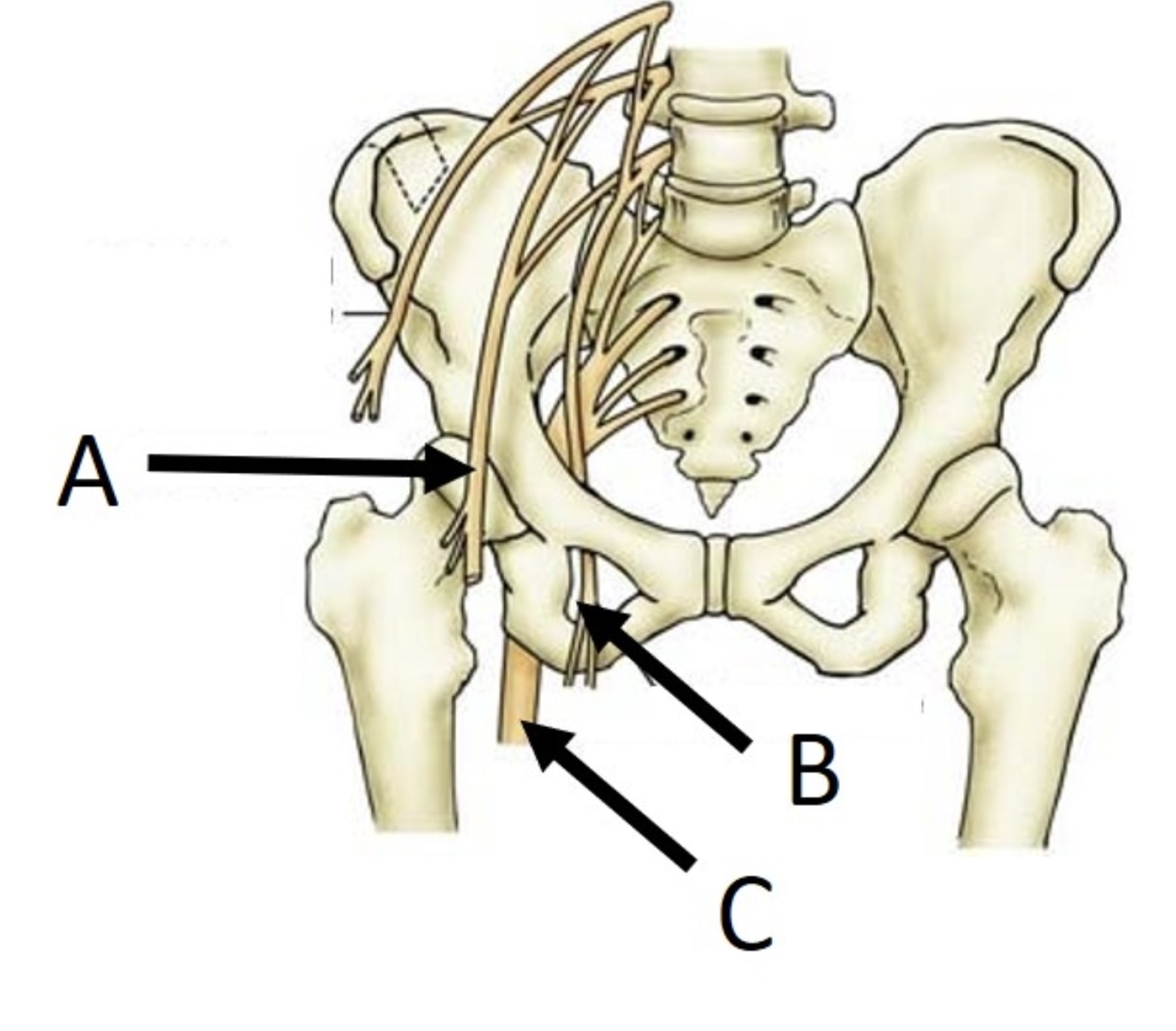
B
obturator nerve
14
New cards
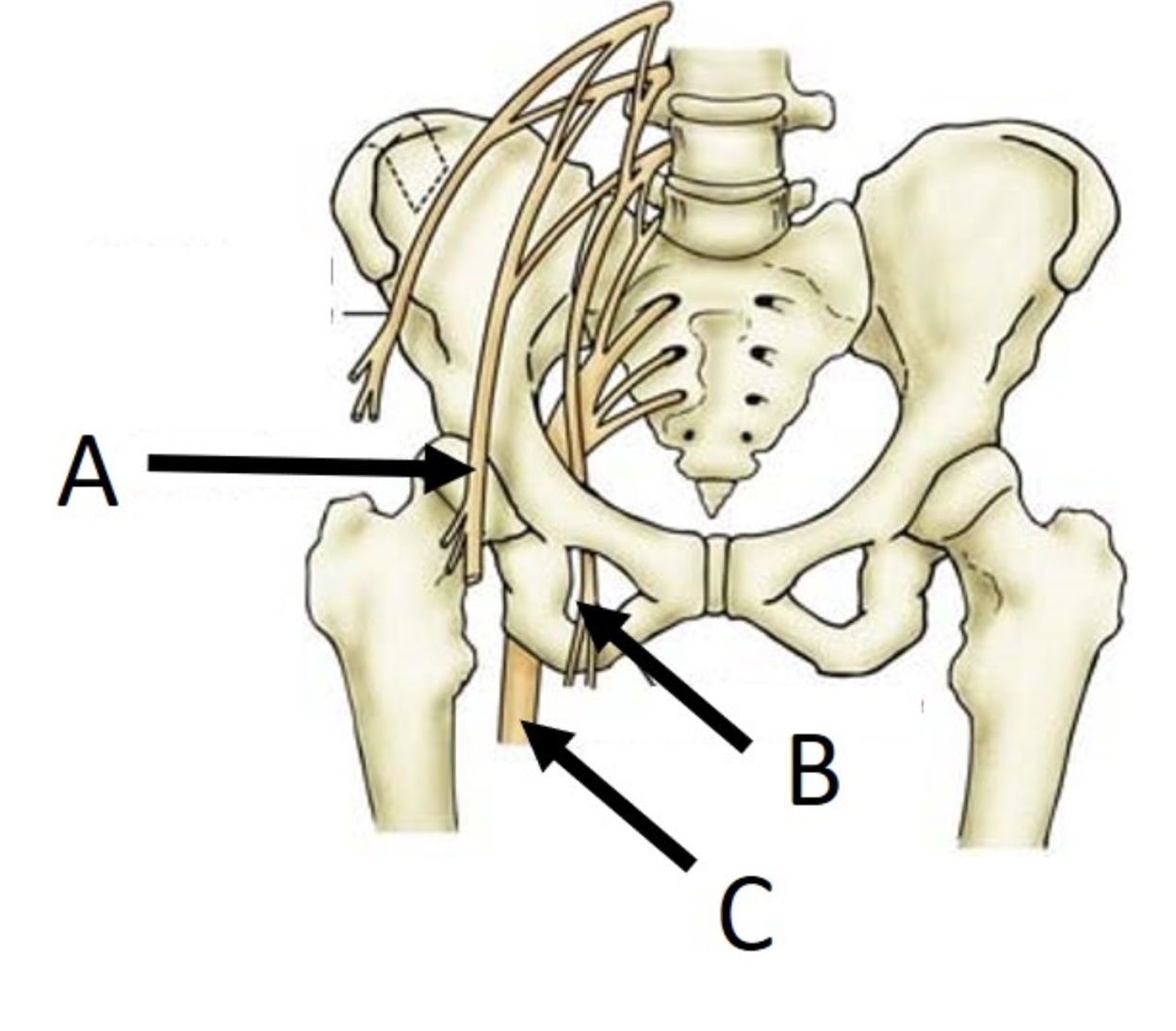
A
femoral nerve
15
New cards
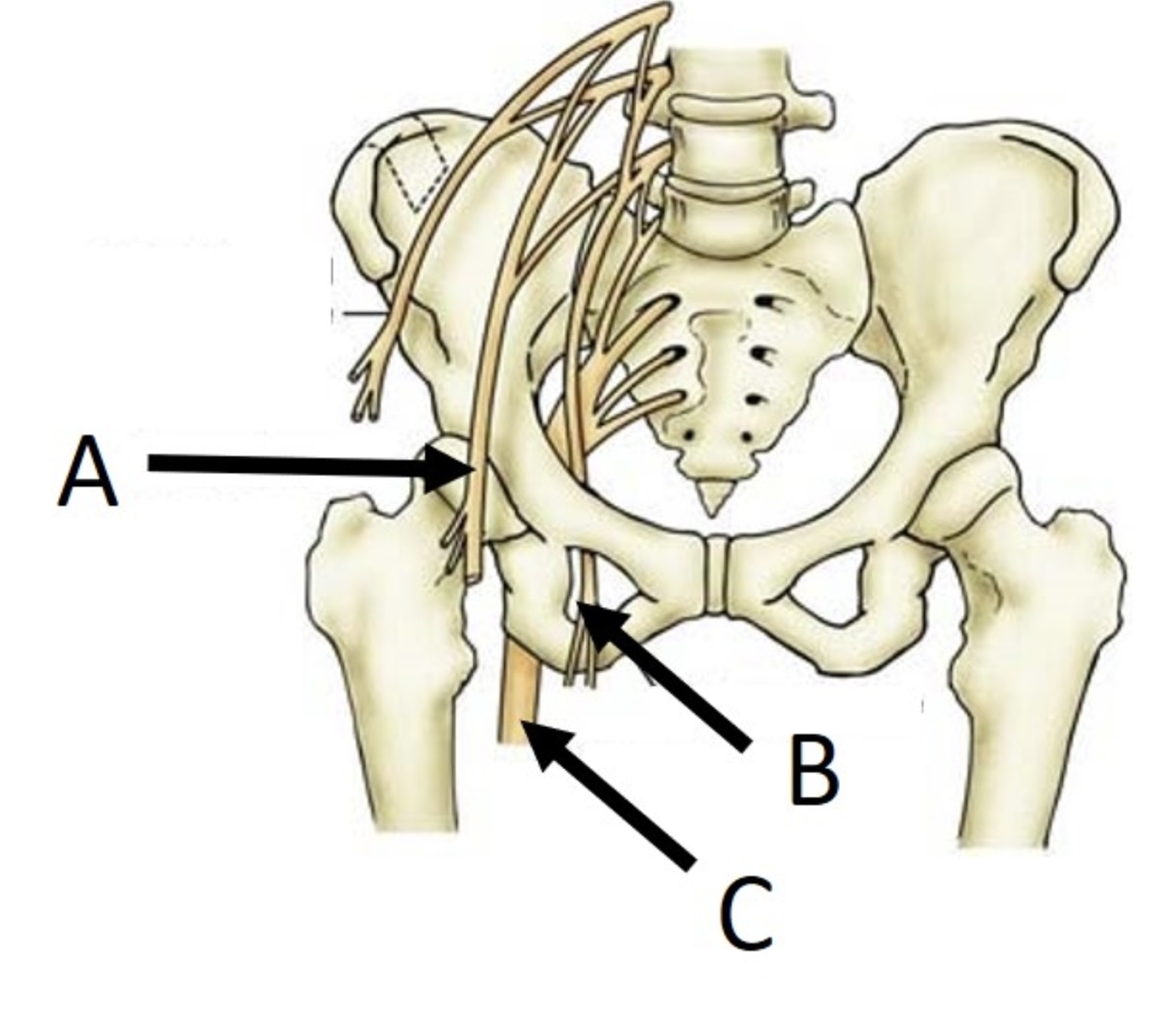
C
sciatic nerve
16
New cards
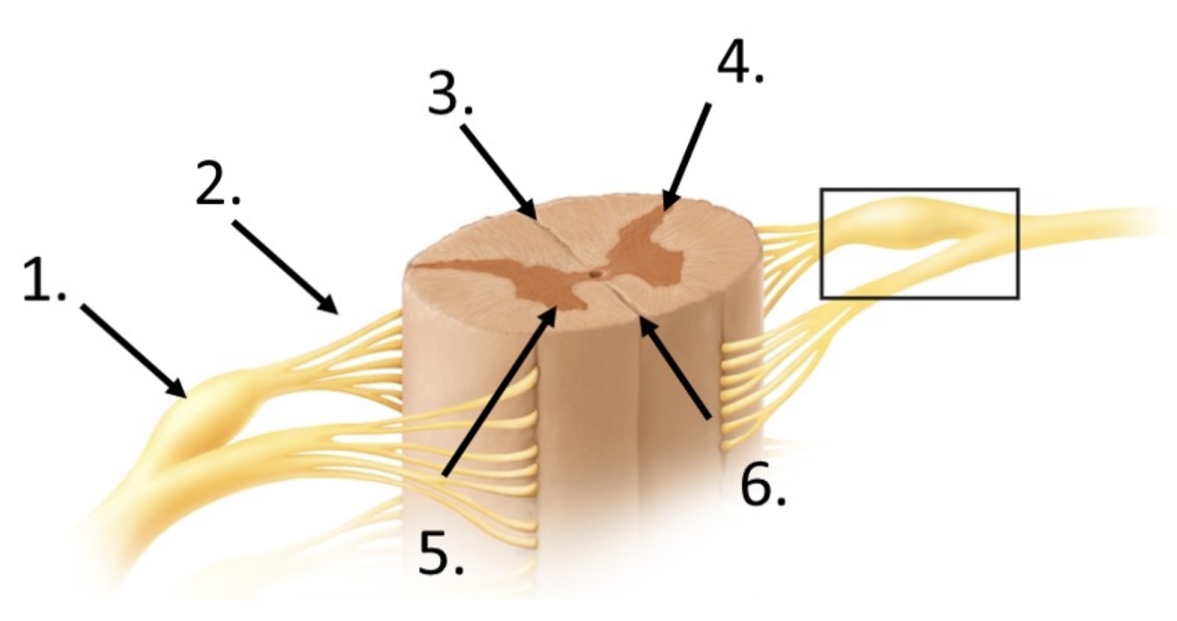
1
posterior root ganglion
17
New cards
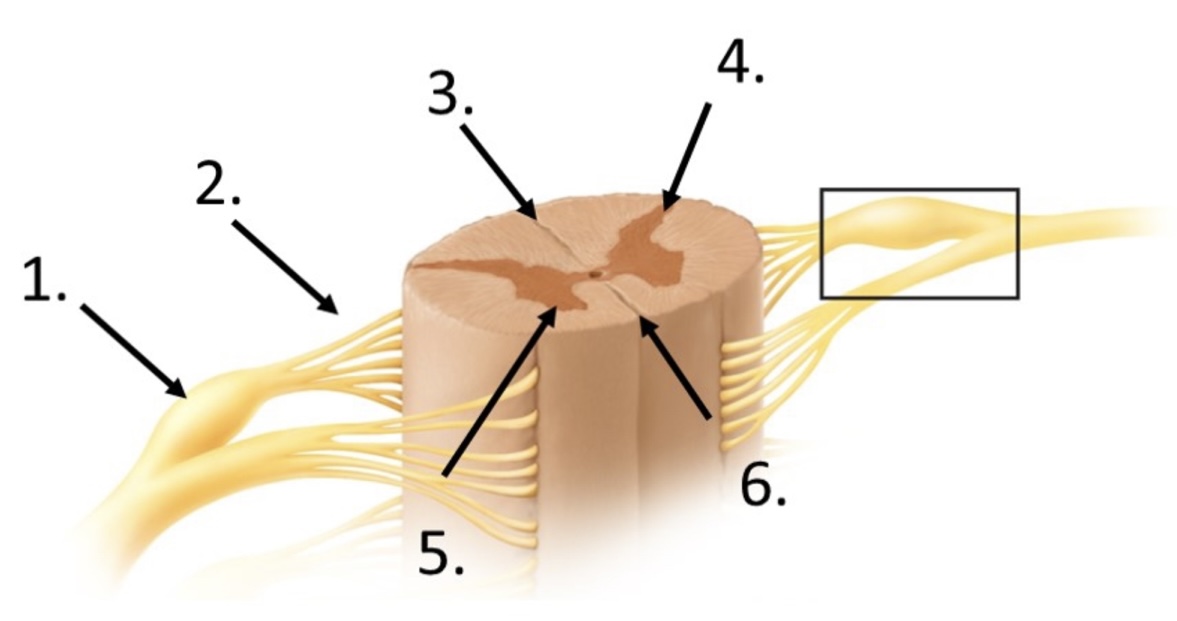
2
posterior rootlets
18
New cards
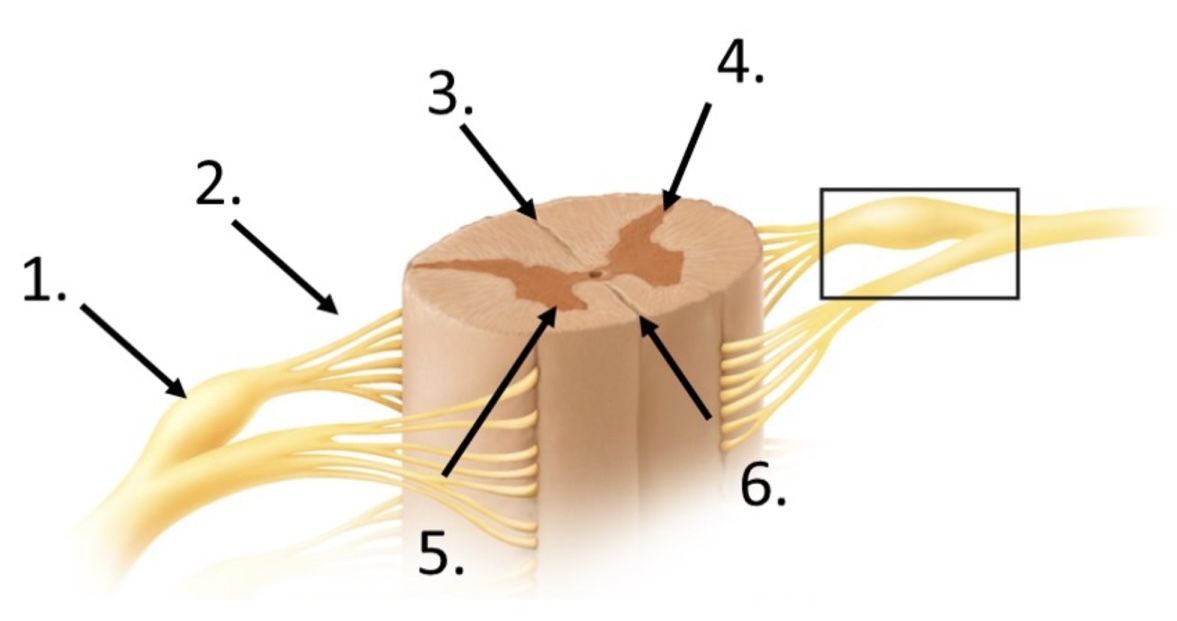
3
posterior median sulcus
19
New cards
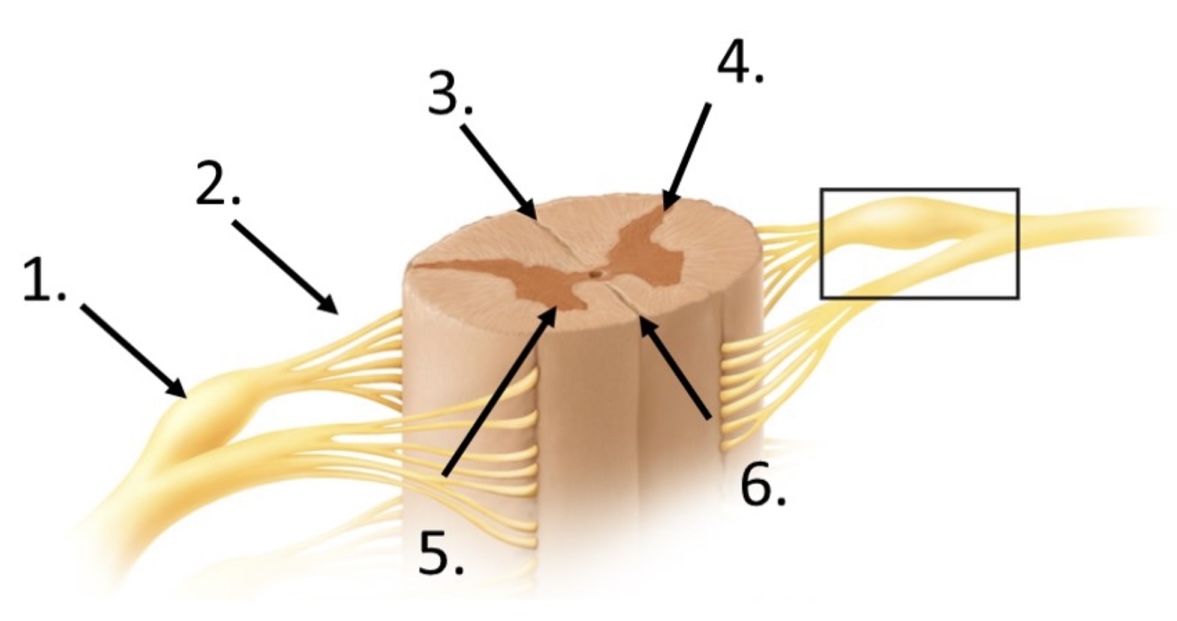
4
posterior horn
20
New cards
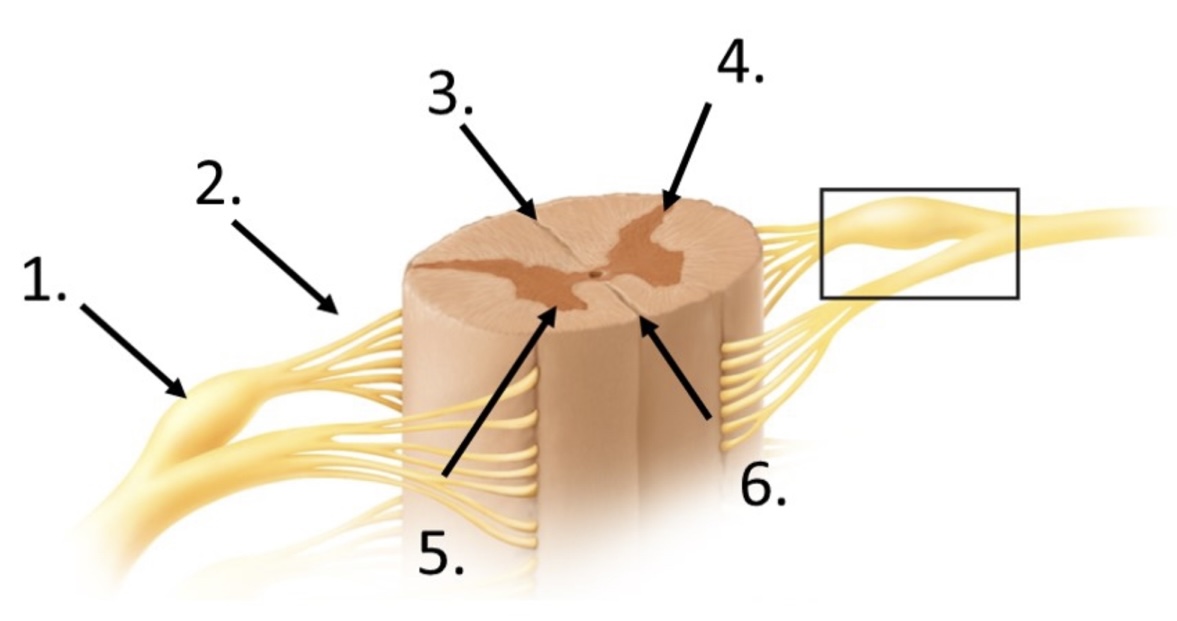
5
anterior horn
21
New cards
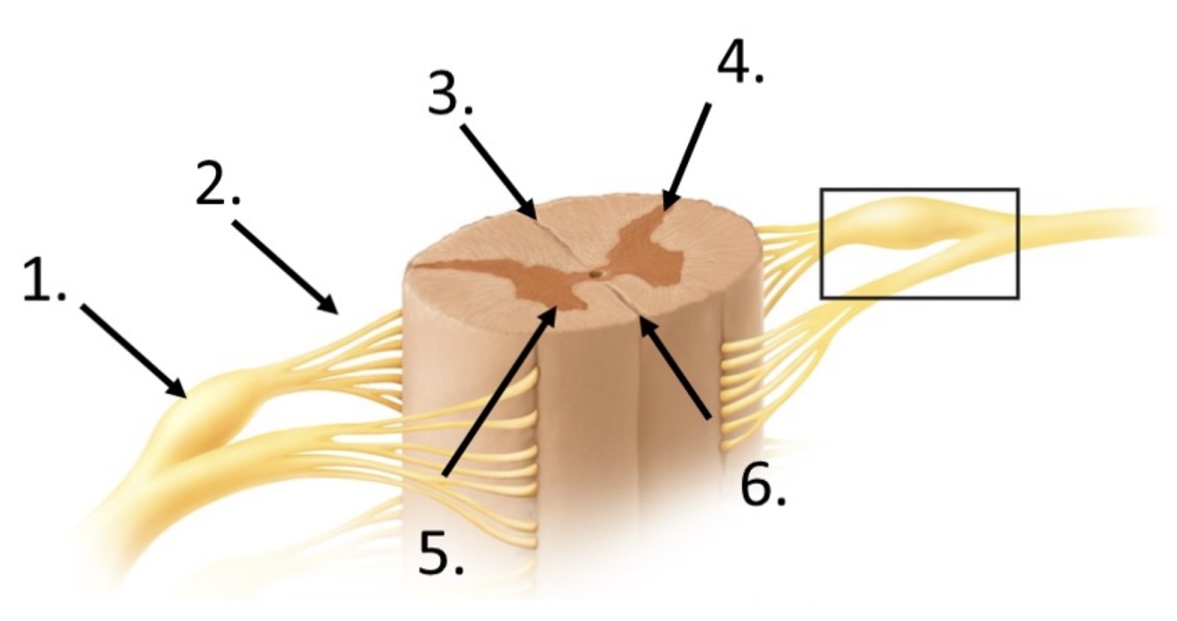
6
anterior median fissure
22
New cards
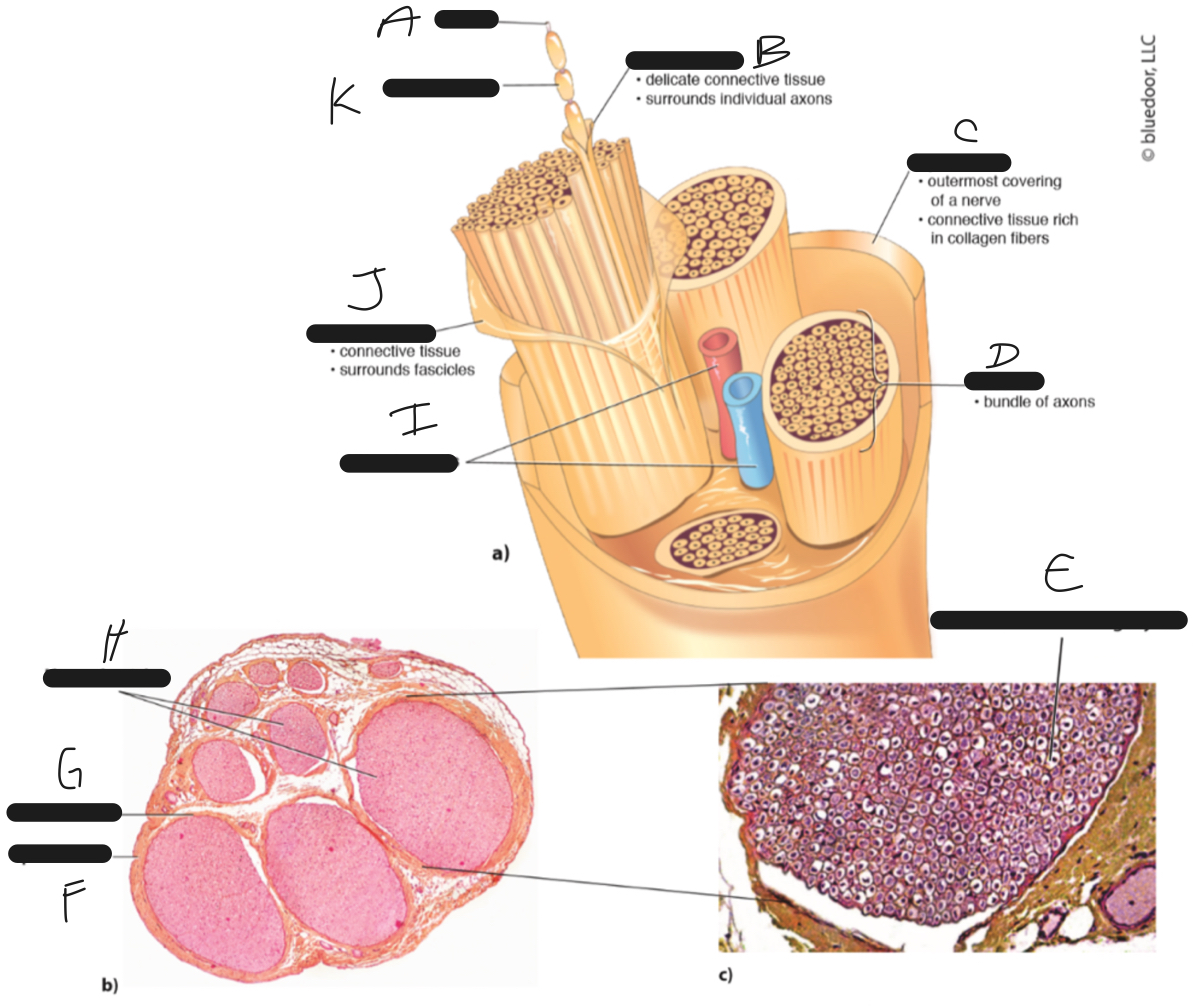
K
myelin sheath
23
New cards
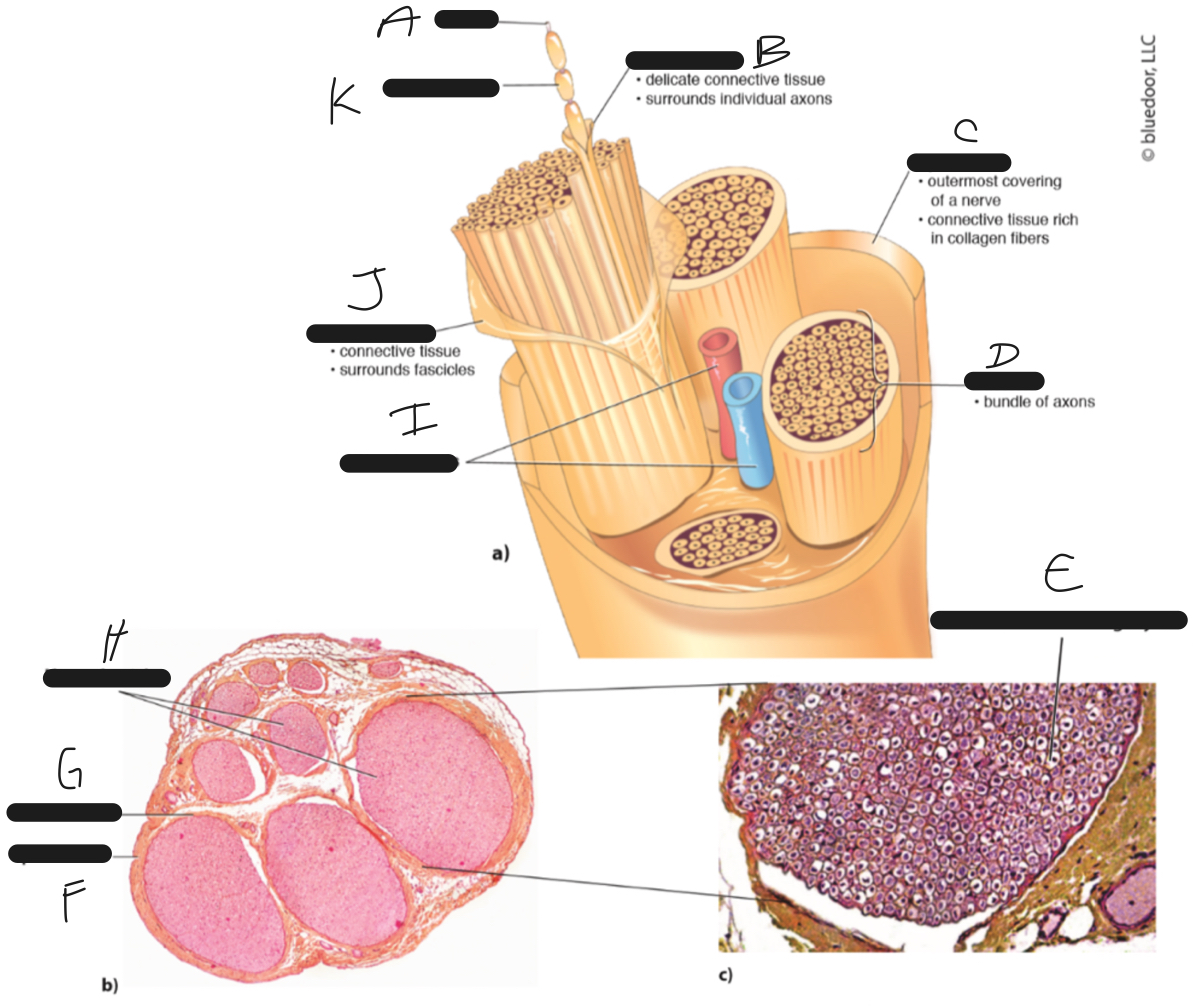
J
perineurium
24
New cards
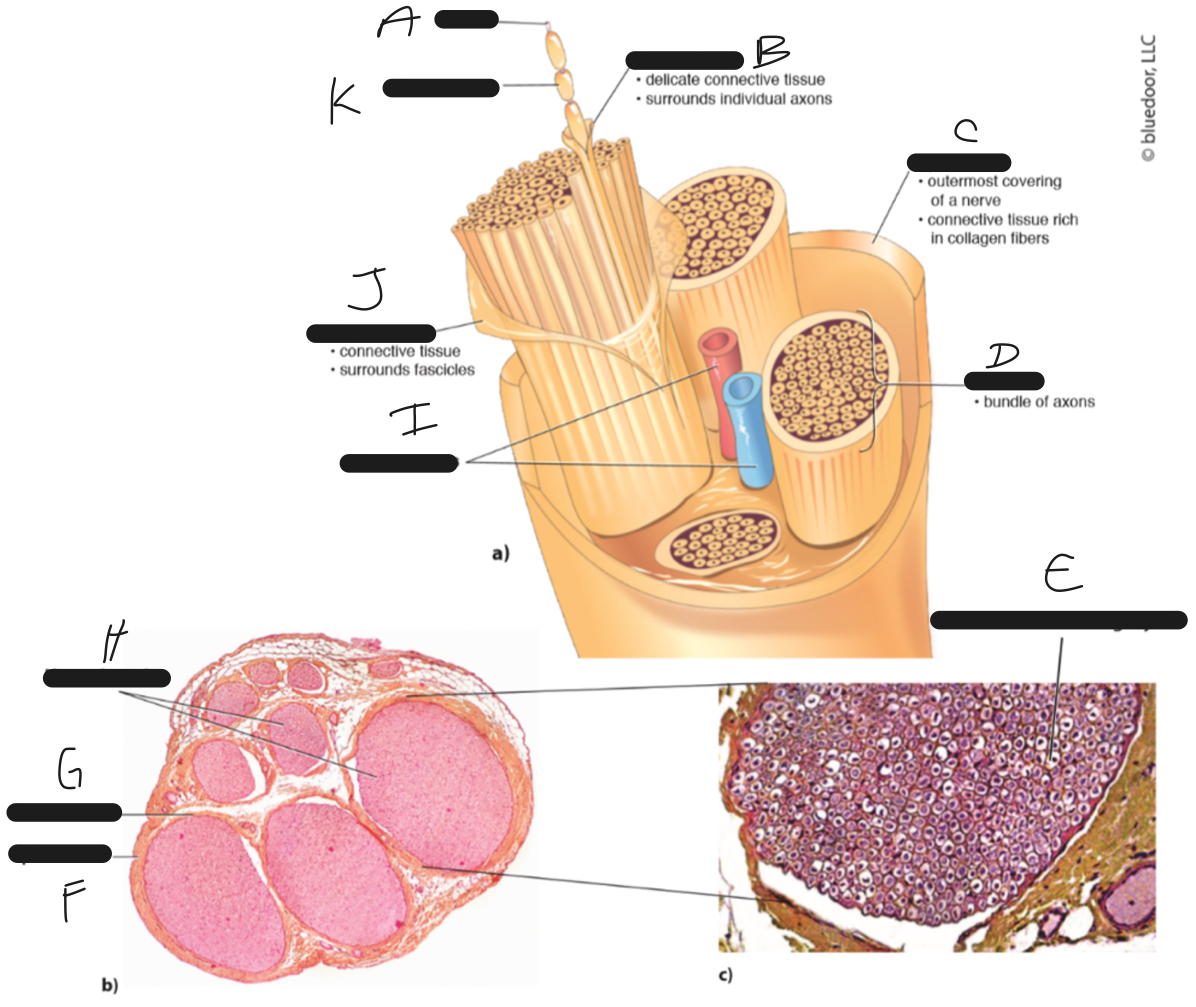
I
blood vessels
25
New cards
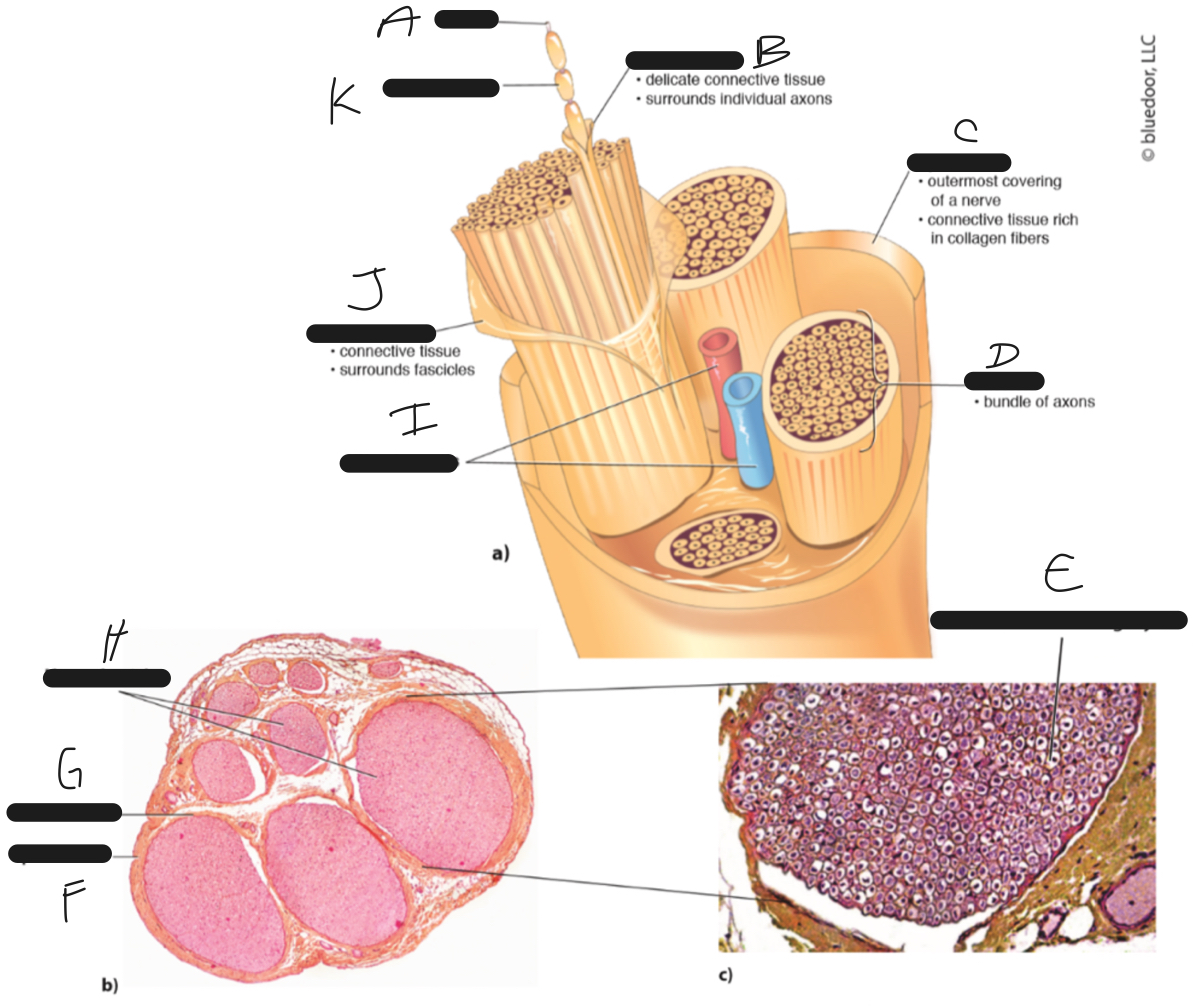
H
nerve fascicles
26
New cards
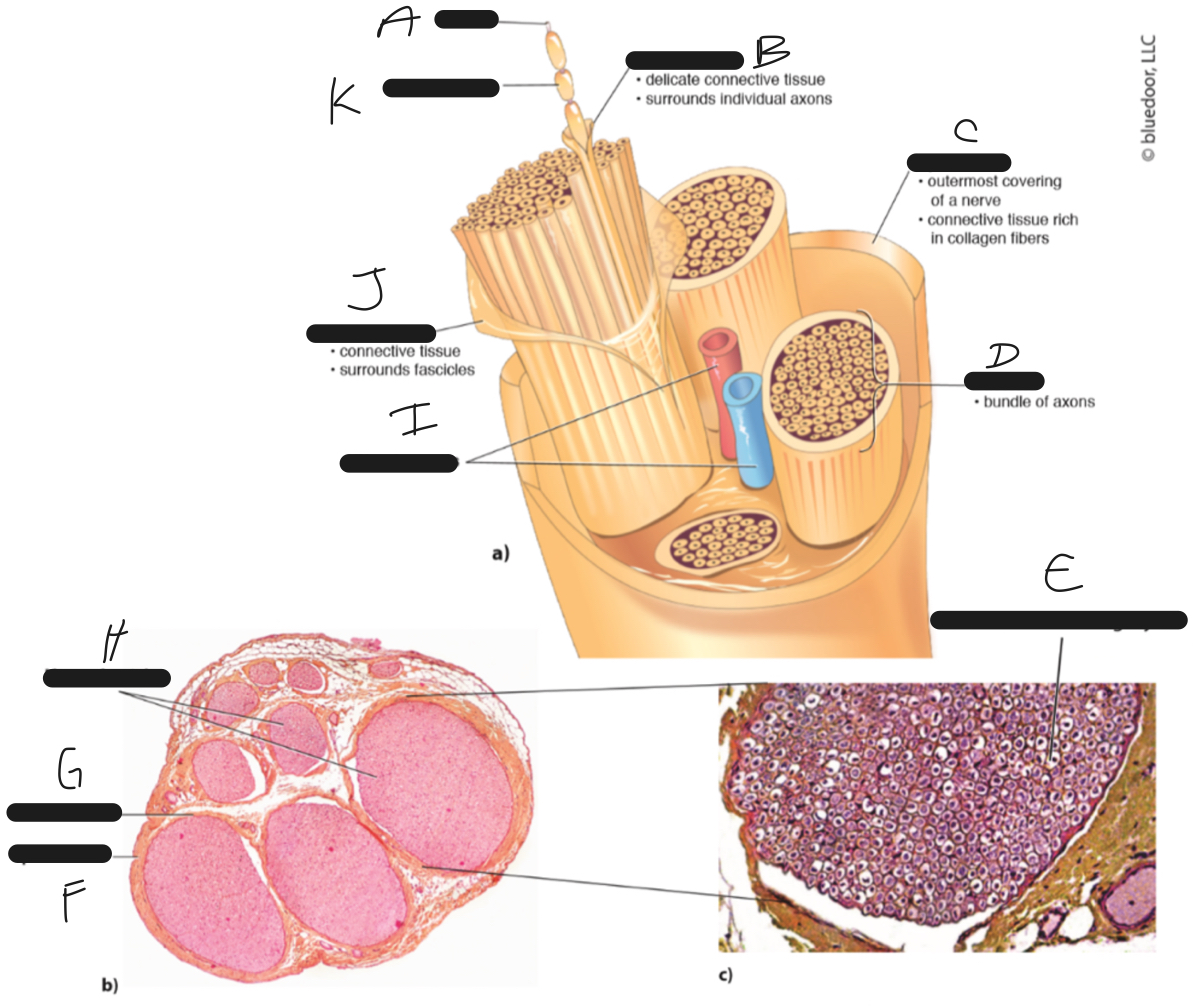
G
perineurium
27
New cards
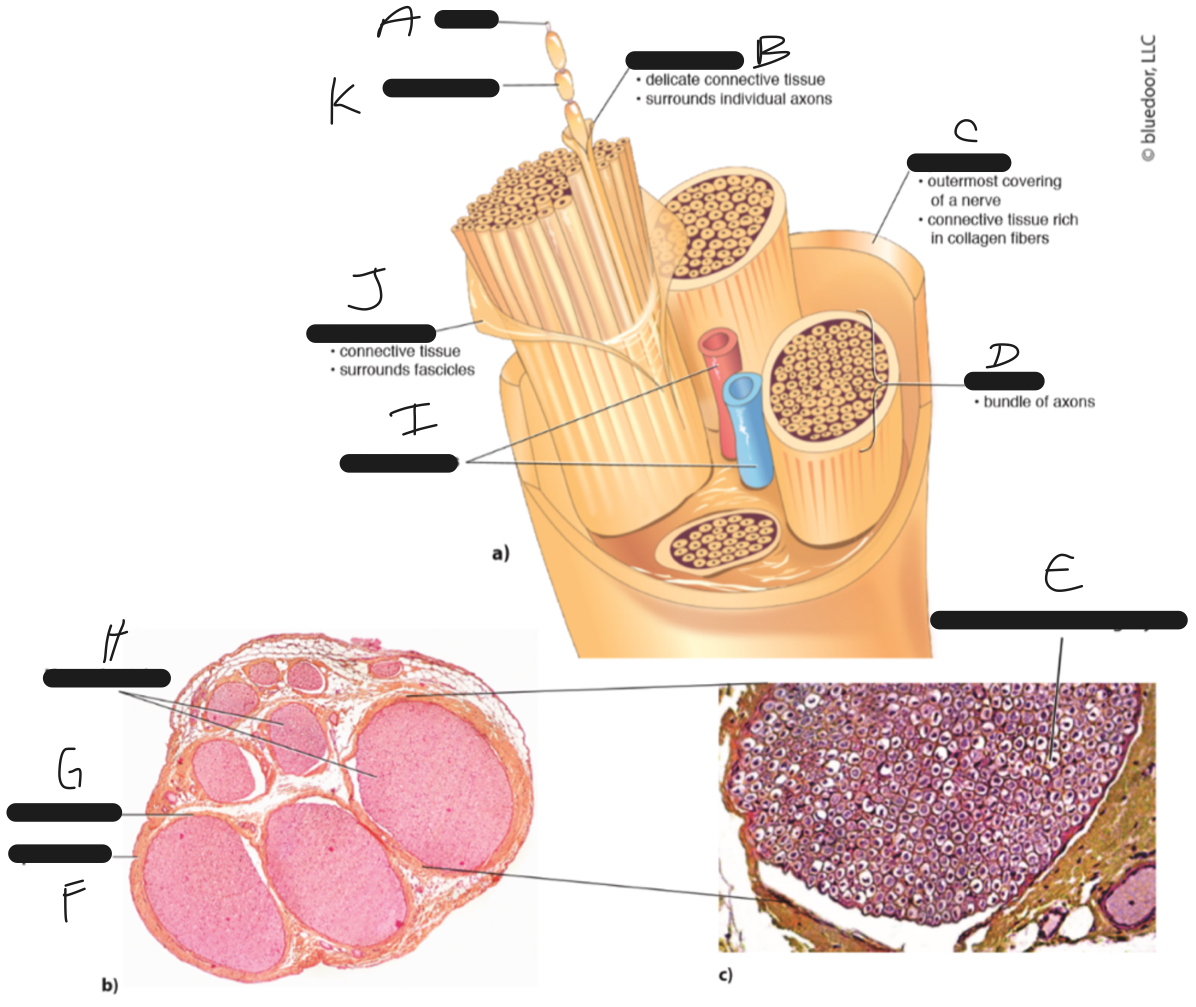
F
epineurium
28
New cards
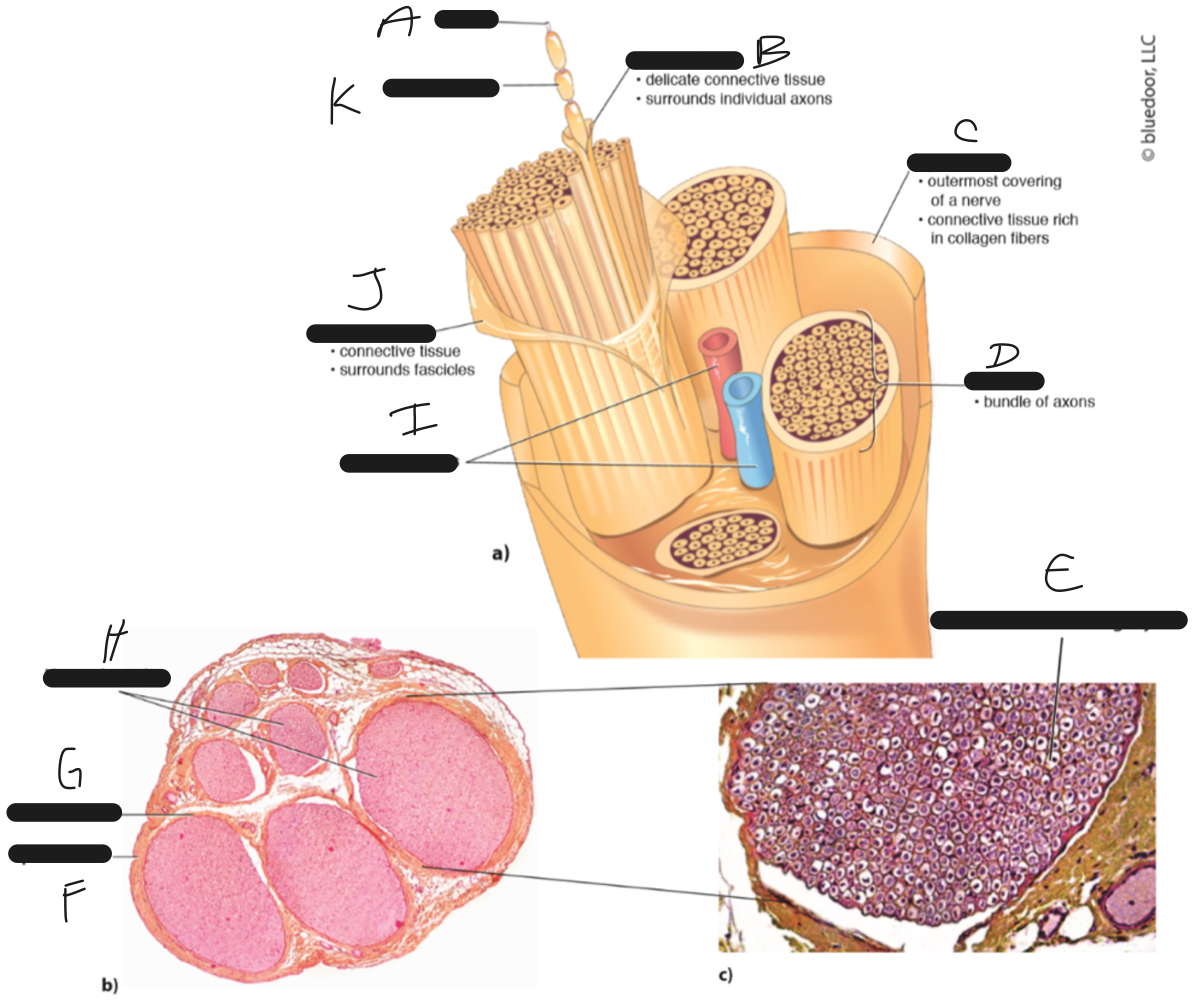
E
axon and surrounding myelin
29
New cards
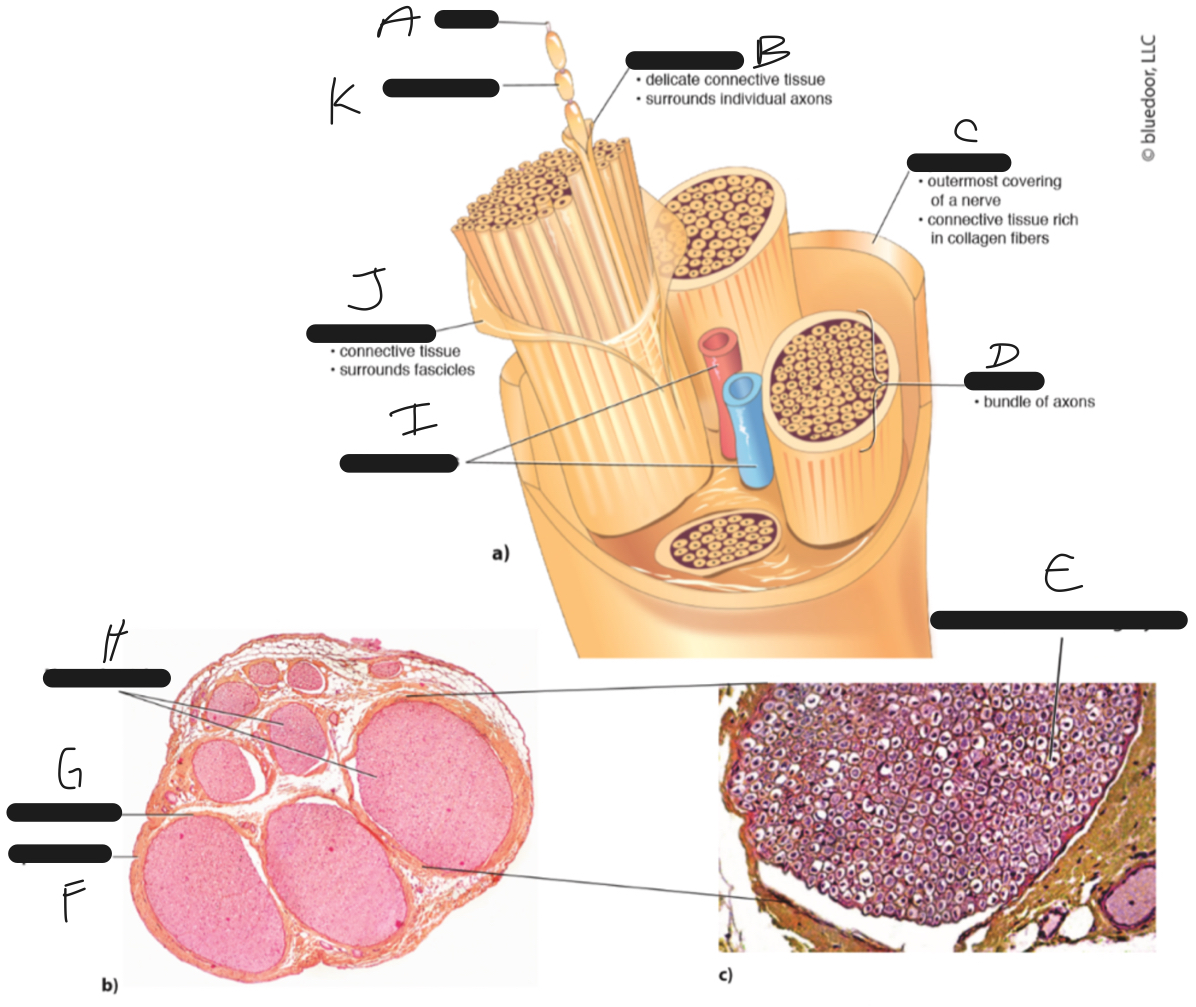
D
fascicle
30
New cards
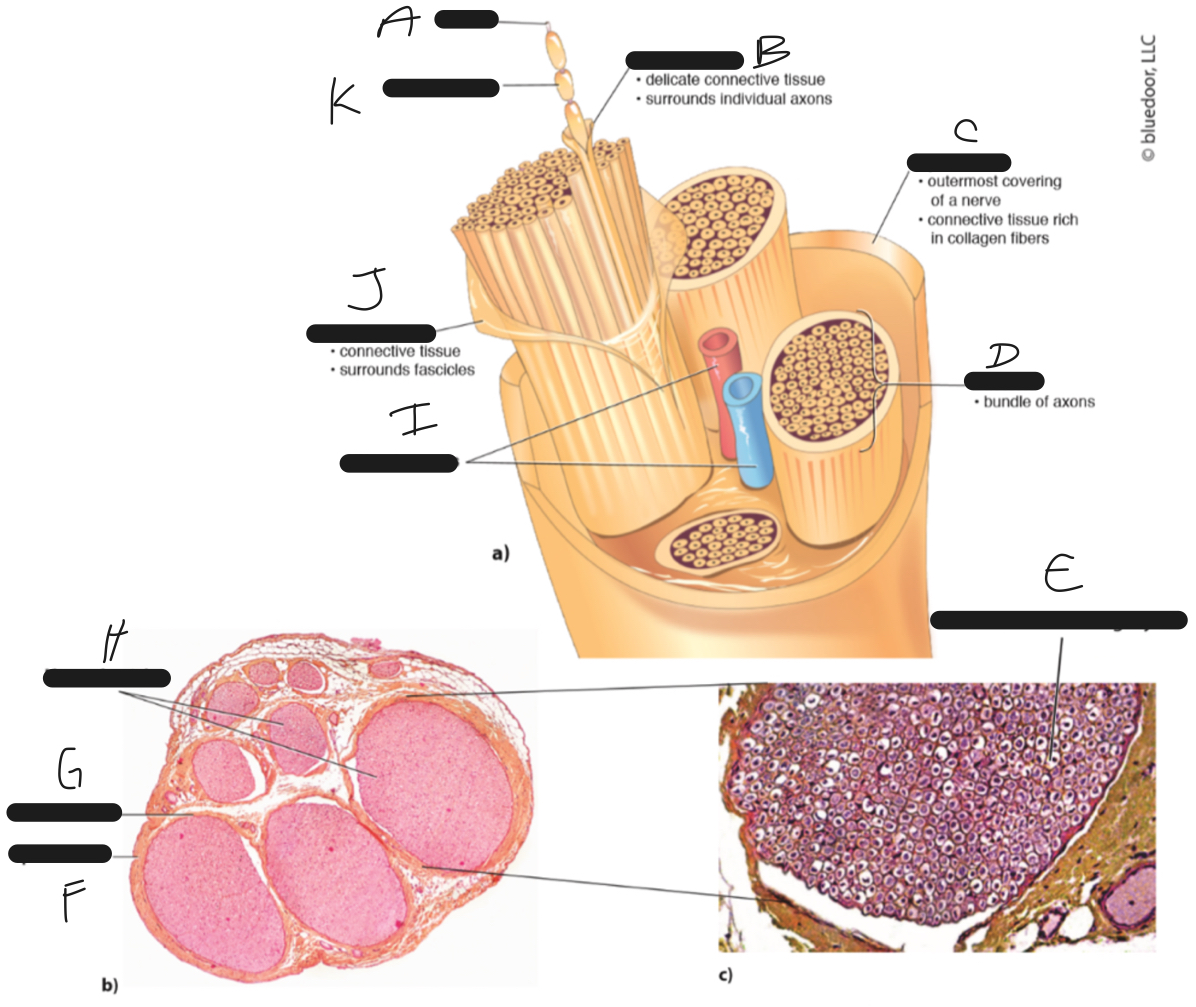
C
epineurium
31
New cards
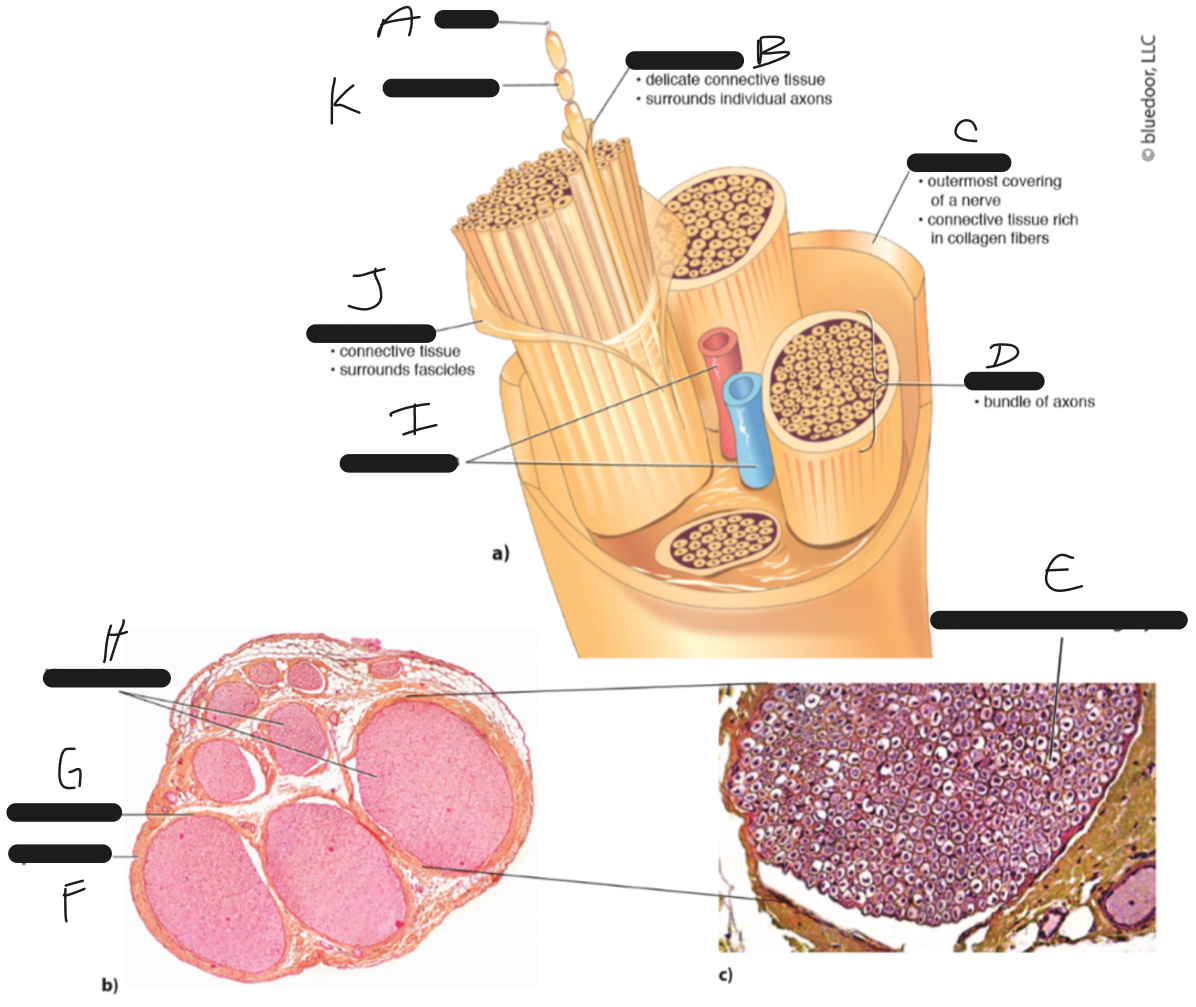
B
endoneurium
32
New cards
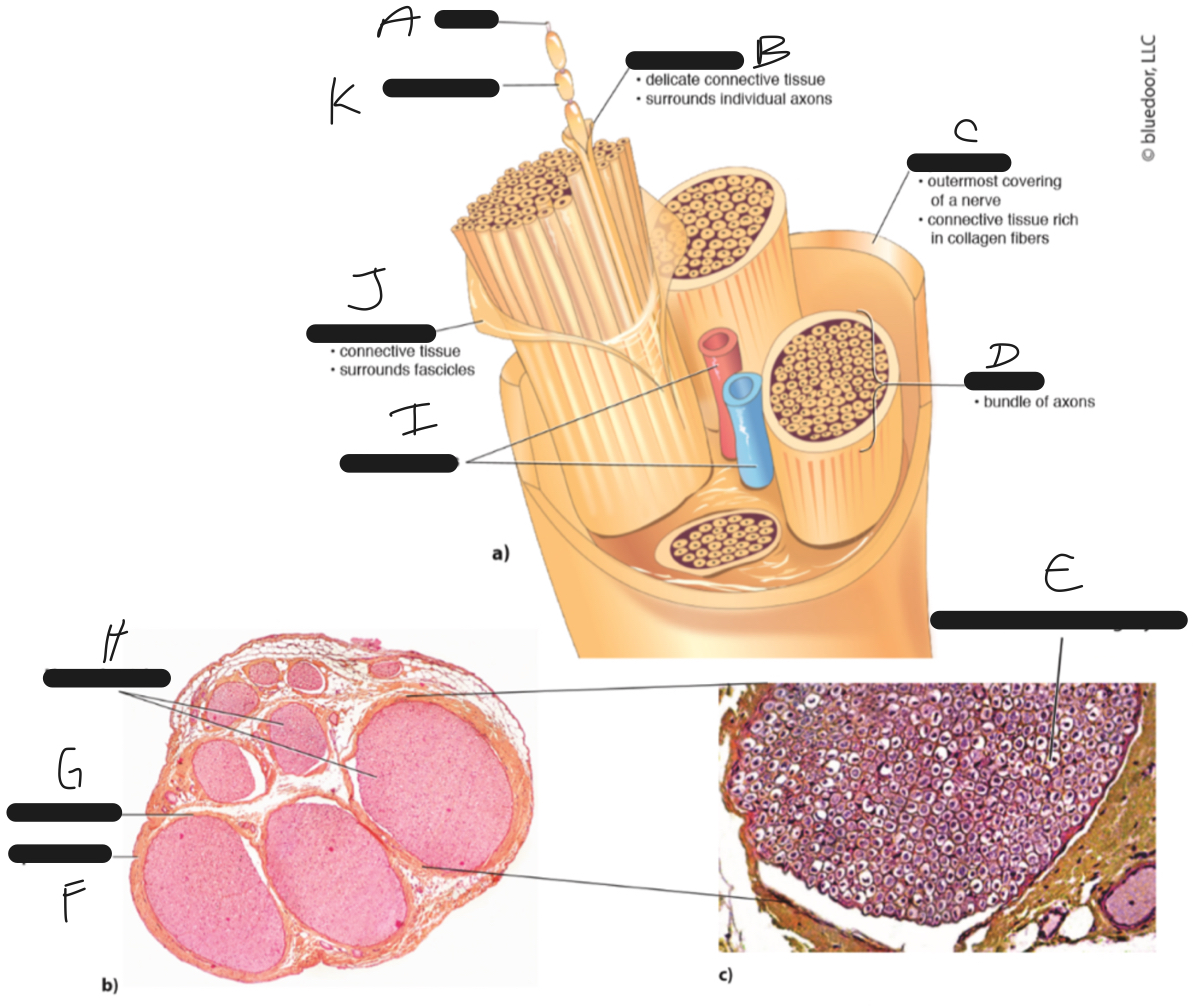
A
axon
33
New cards
fanning of the toes up is the
babinski sign
34
New cards
babinksi sign (plantar reflex) is the abnormal response that helps reveal..
damage to the motor tracts of the spinal cord.
35
New cards
reflex
an involuntary motor response
36
New cards
reaction
a planned motor response
37
New cards
reflex arc
nerve pathway for a reflex
38
New cards
stimulus
activates a sensory receptor
39
New cards
sensory receptor
the first step in a reflex arc
40
New cards
sensory neuron
also called an afferent neuron
41
New cards
integrating center
found only in gray matter of CNS
42
New cards
interneuron
neuron found only in polysynaptic reflexes
43
New cards
motor neuron
also called an efferent neuron
44
New cards
effector organ
carries out a motor response
45
New cards
monosynaptic reflex
has only one synapse
46
New cards
polysynaptic reflex
always has one or more interneurons
47
New cards
somatic reflex
effector organ is skeletal muscle
48
New cards
autonomic reflex
effector organ may be a gland
49
New cards
cranial reflex
integrating center is the brain
50
New cards
spinal reflex
integrating center is the spinal cord
51
New cards
patellar reflex
also called the knee jerk reflex
52
New cards
plantar reflex
can reveal babinski’s sign
53
New cards
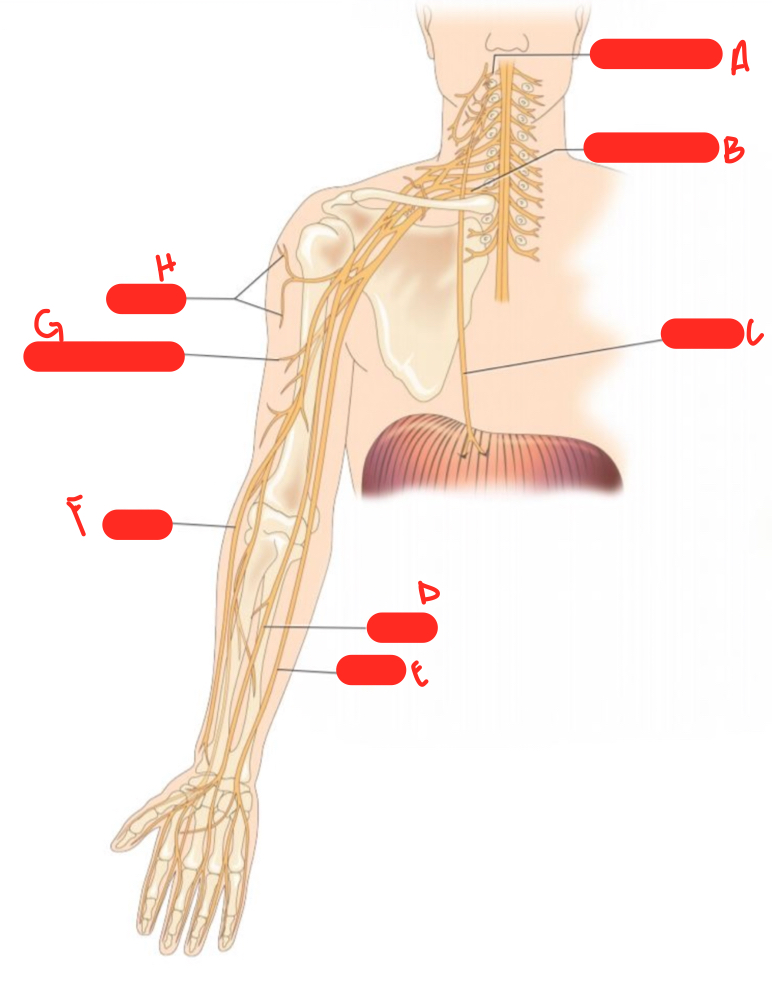
A
c1 spinal nerve
54
New cards
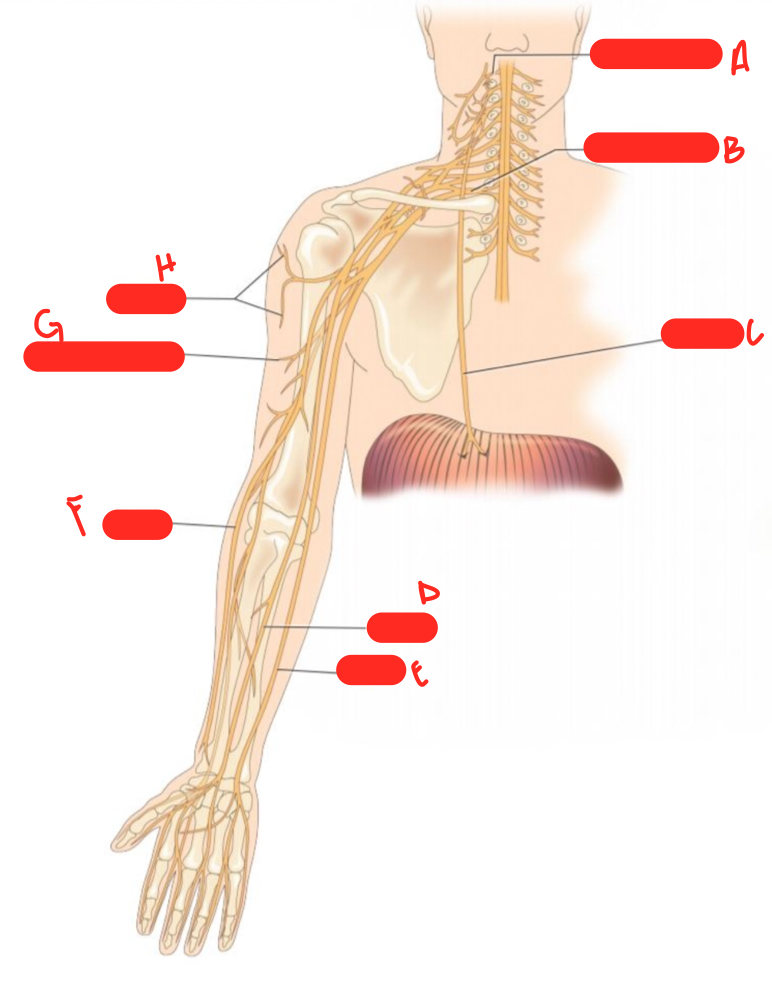
B
c8 spinal nerve
55
New cards
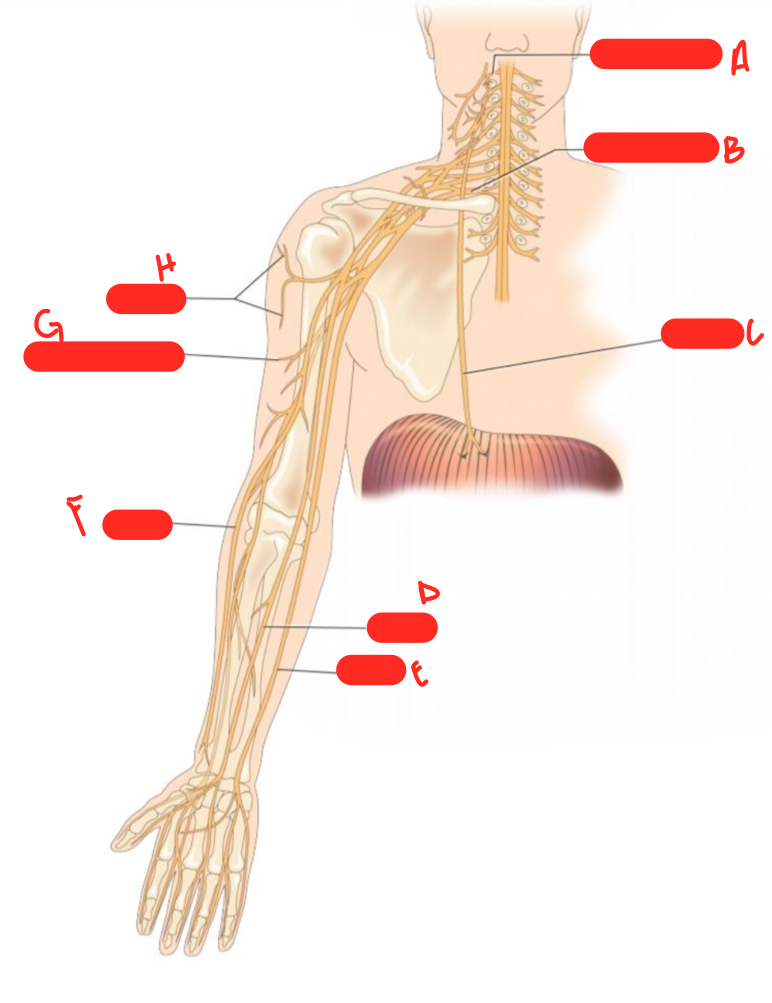
C
phrenic nerve
56
New cards
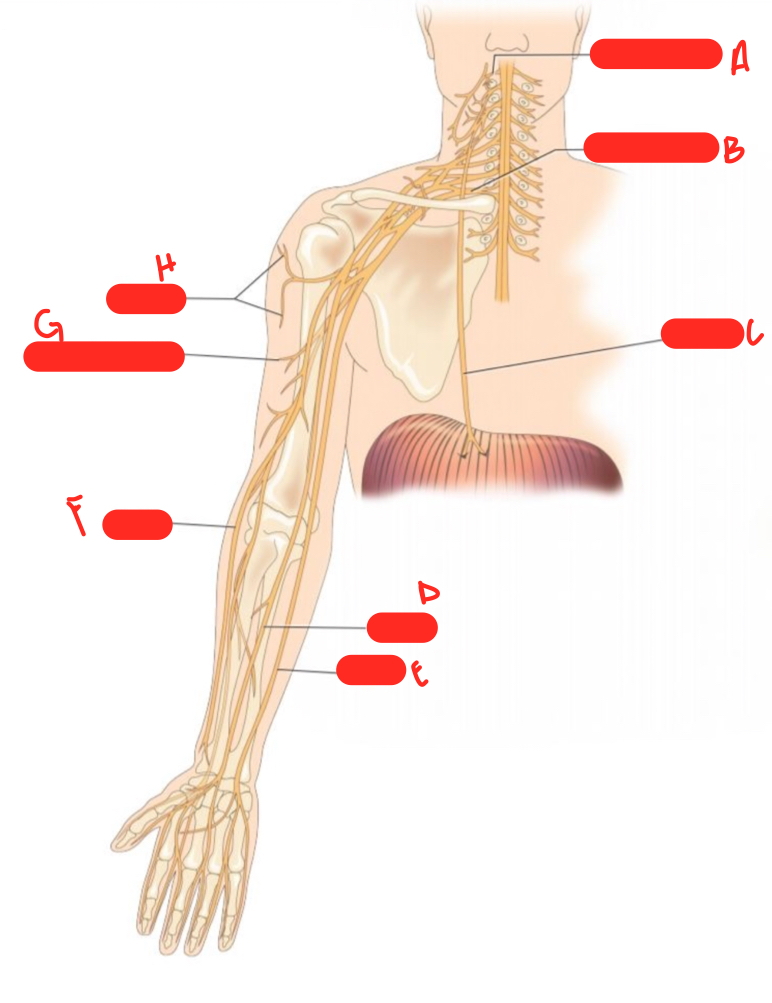
D
median nerve
57
New cards
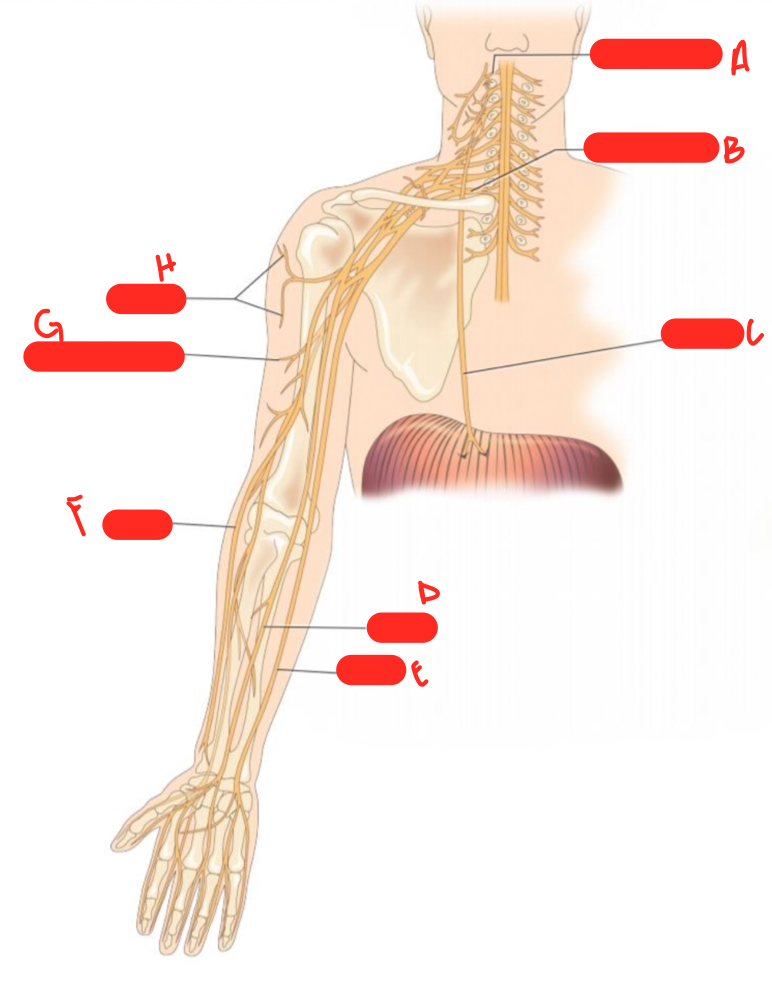
E
ulnar nerve
58
New cards
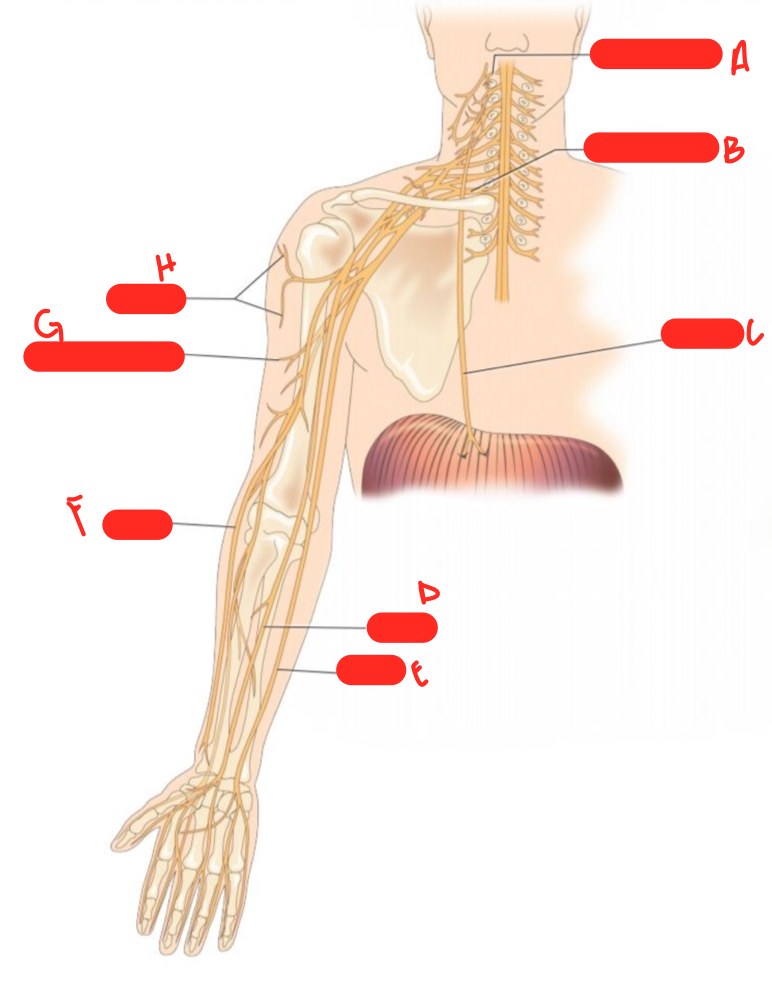
F
radial nerve
59
New cards
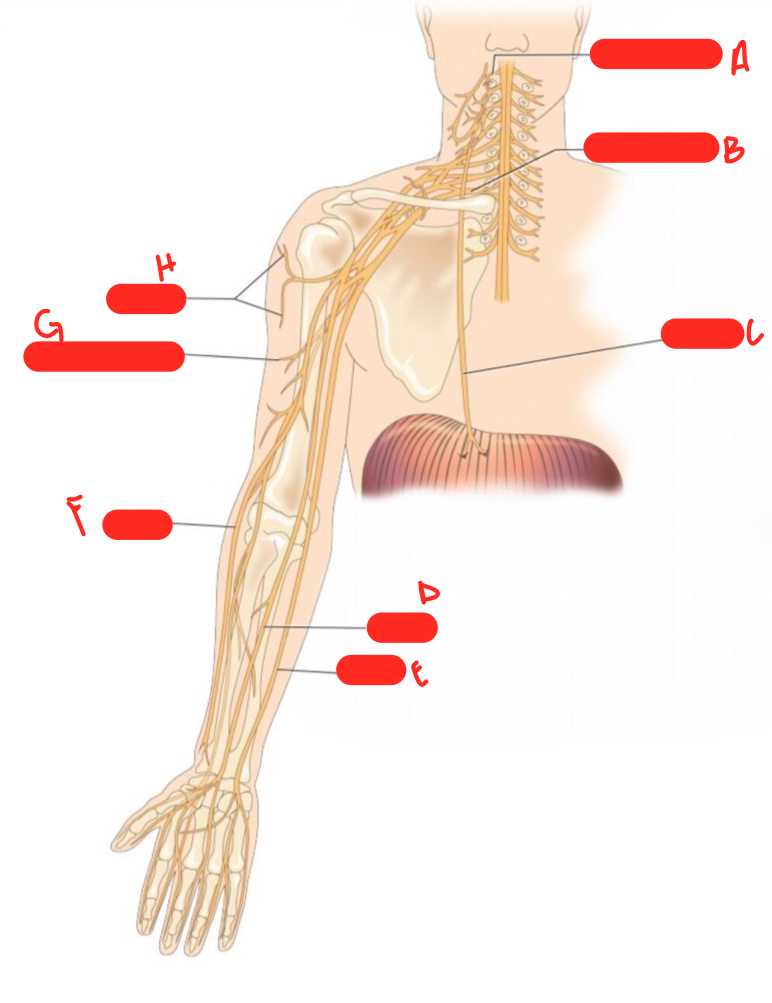
G
musculocutaneous nerve
60
New cards
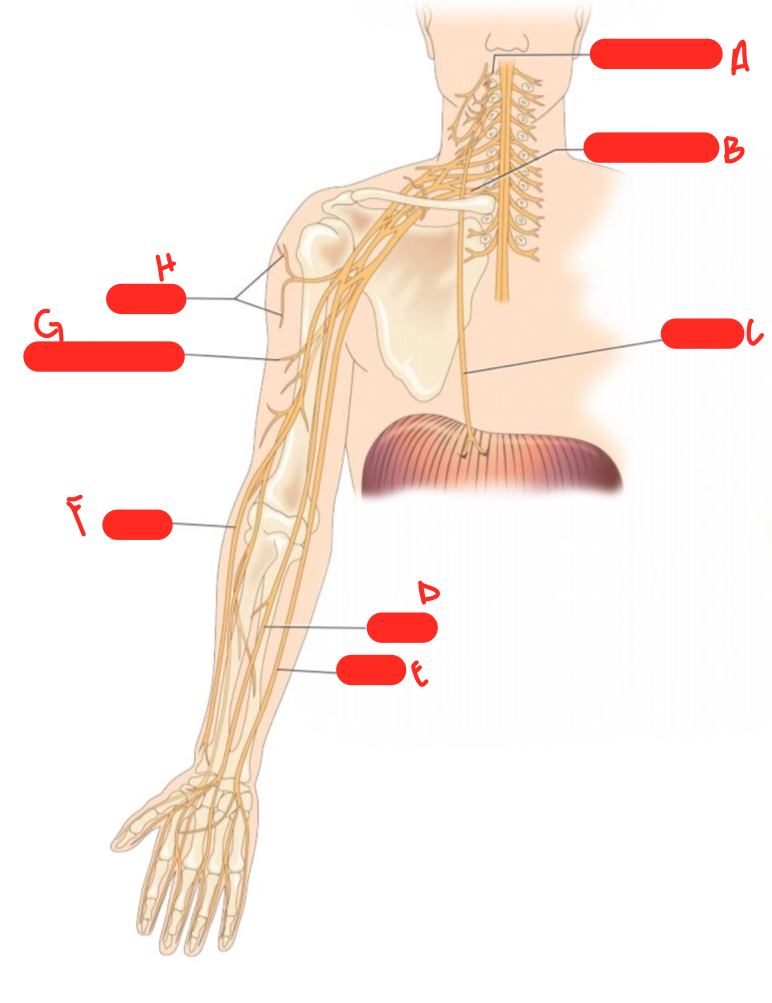
H
axillary nerve
61
New cards
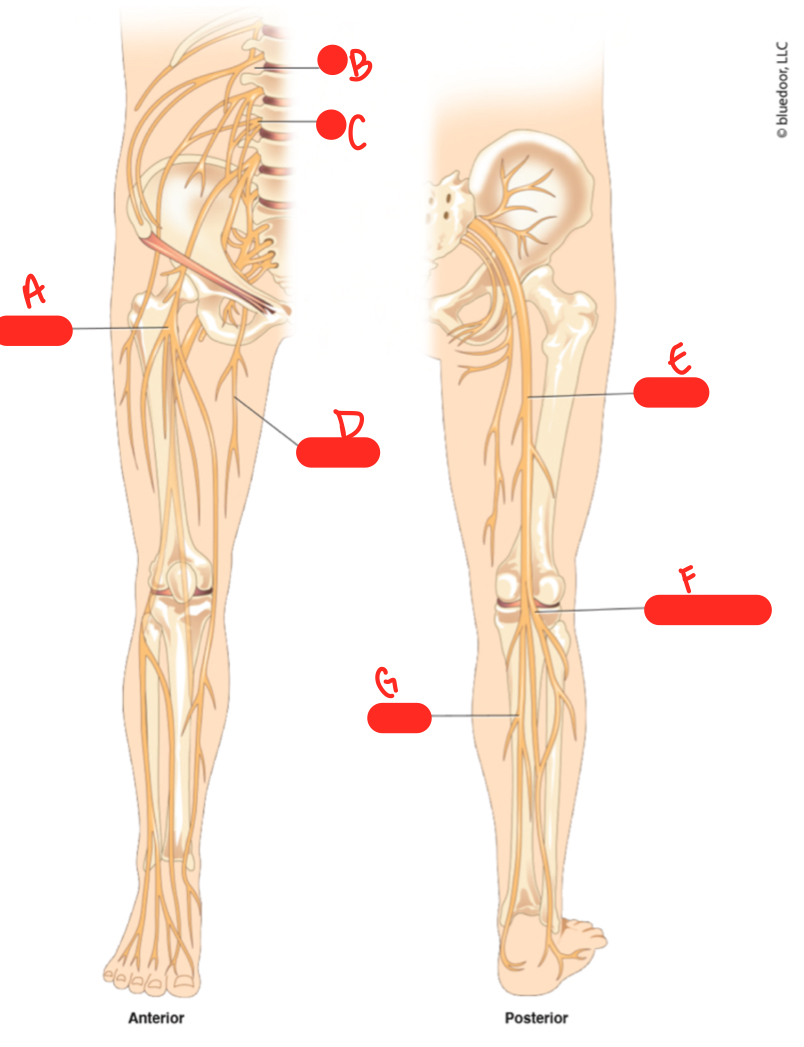
A
femoral nerve
62
New cards
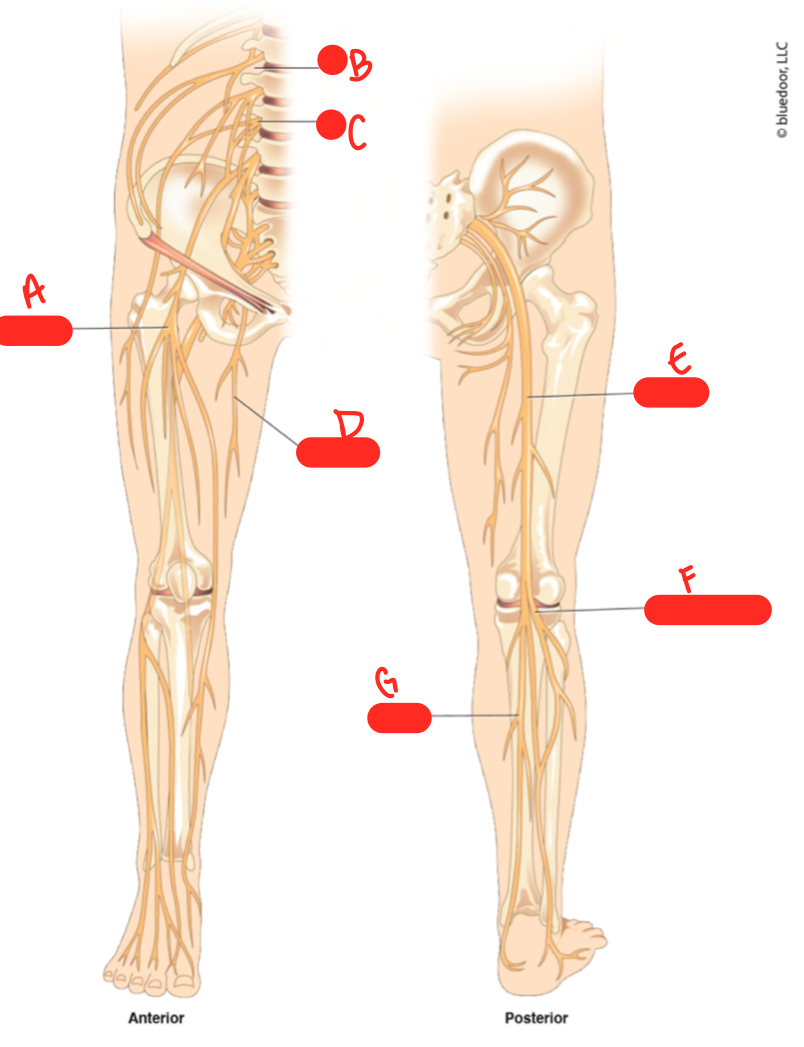
B
L1
63
New cards
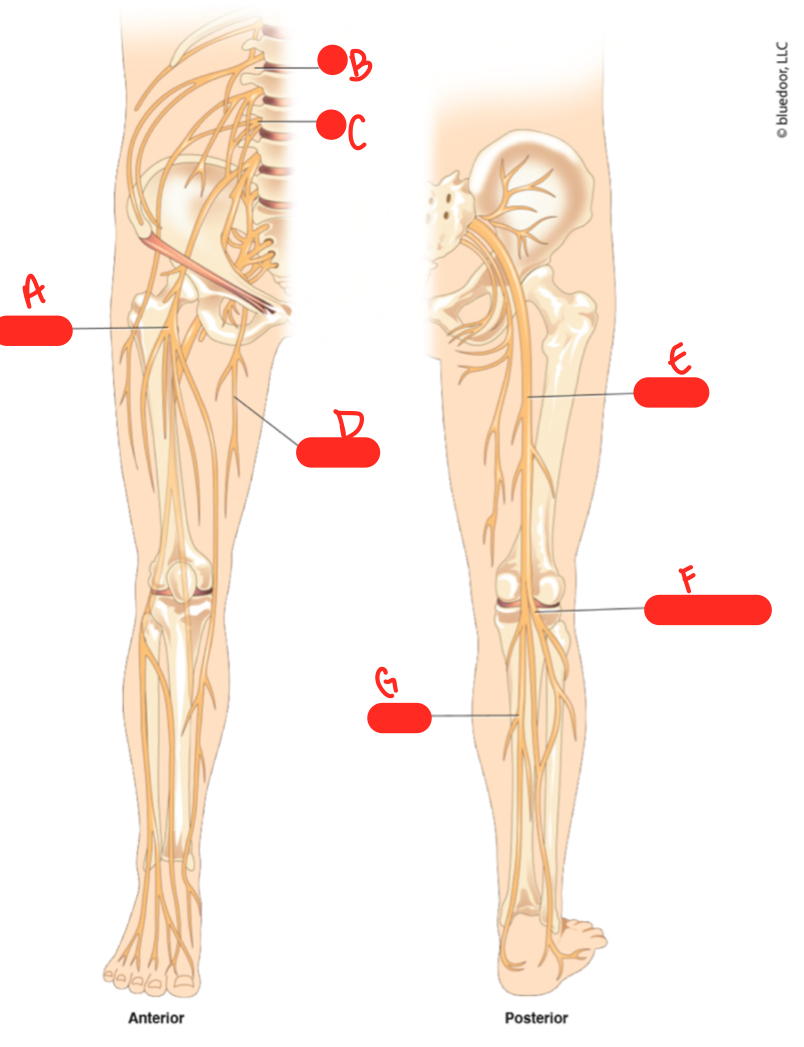
C
L3
64
New cards
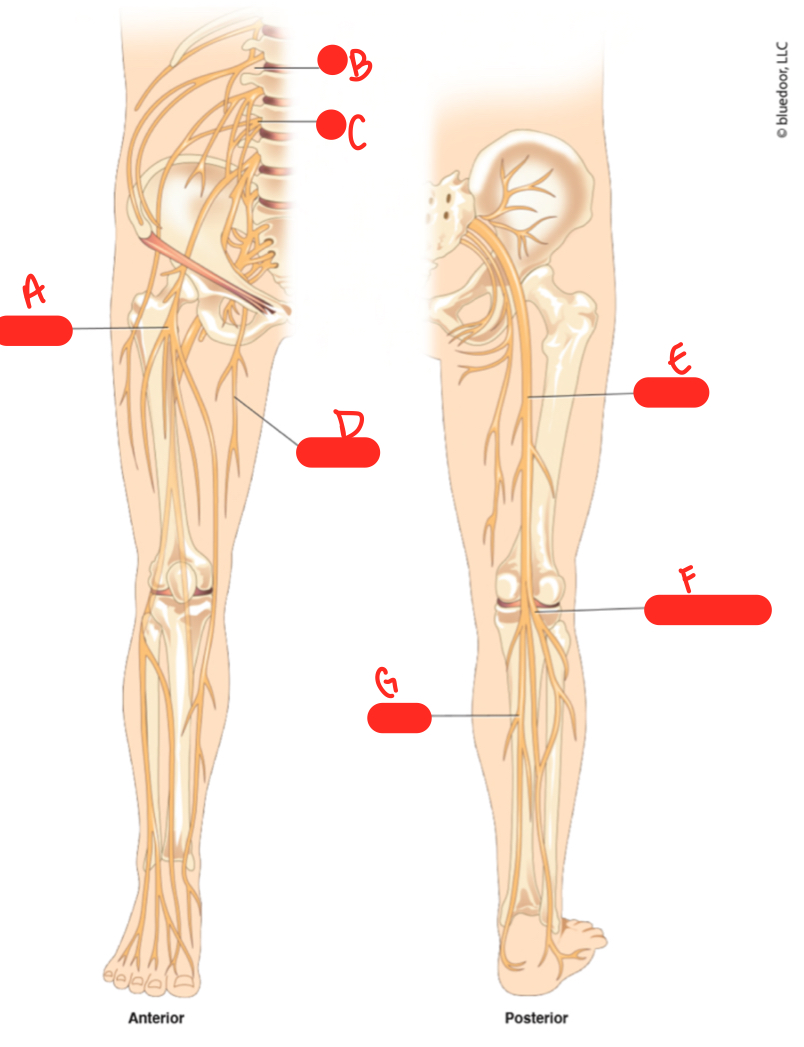
D
obturator nerve
65
New cards
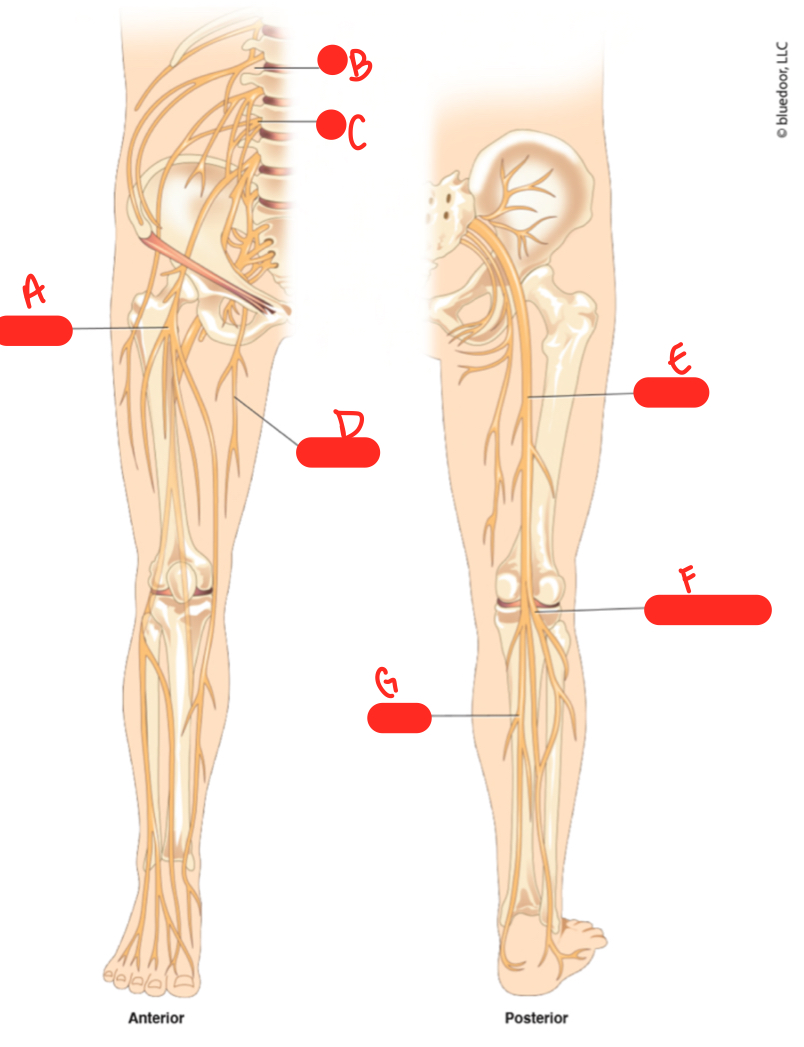
E
sciatic nerve
66
New cards
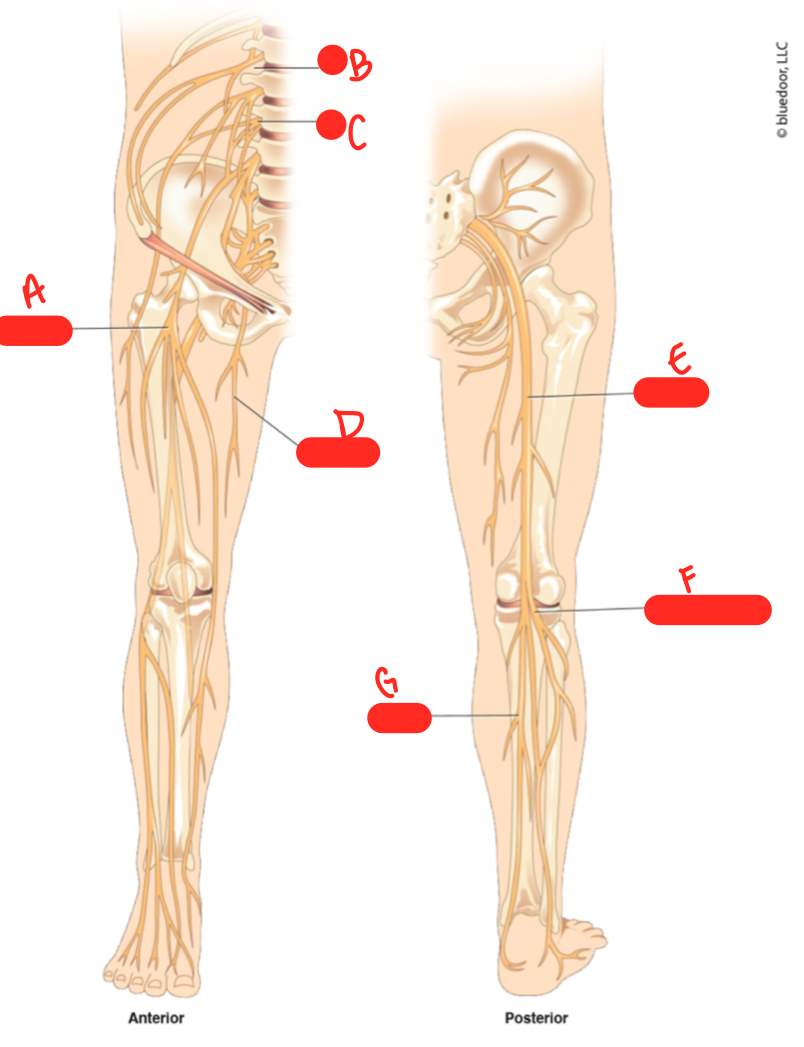
F
common fibular nerve
67
New cards
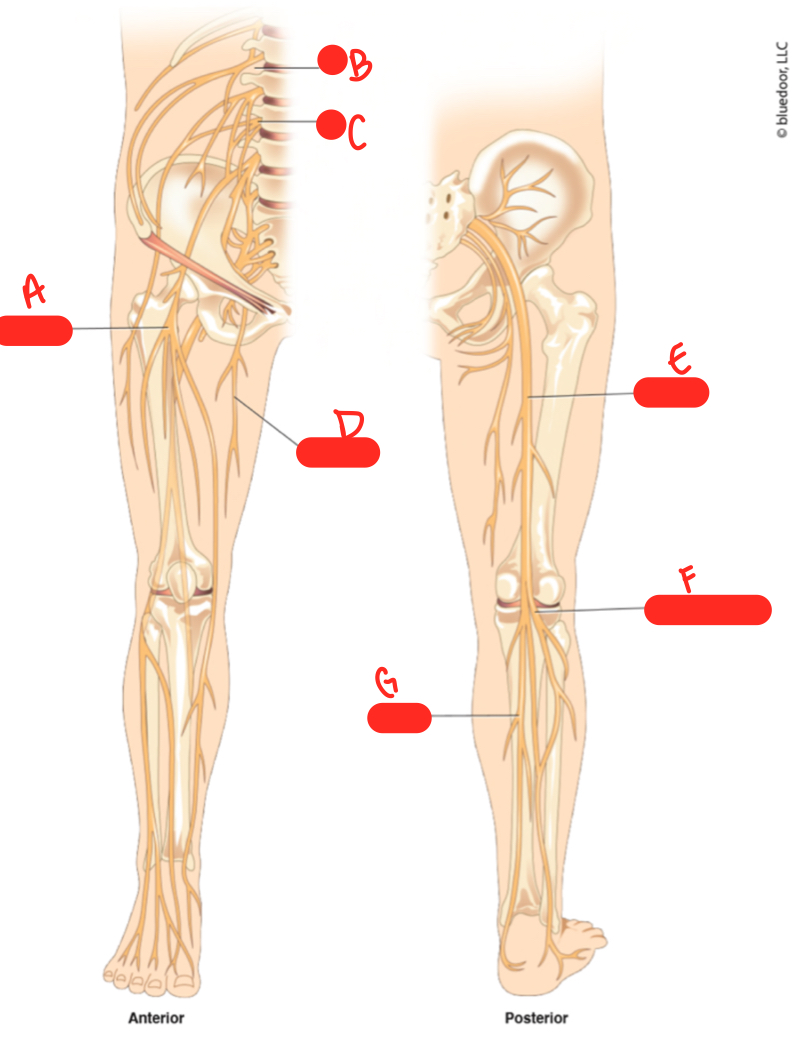
G
tibial nerve
68
New cards
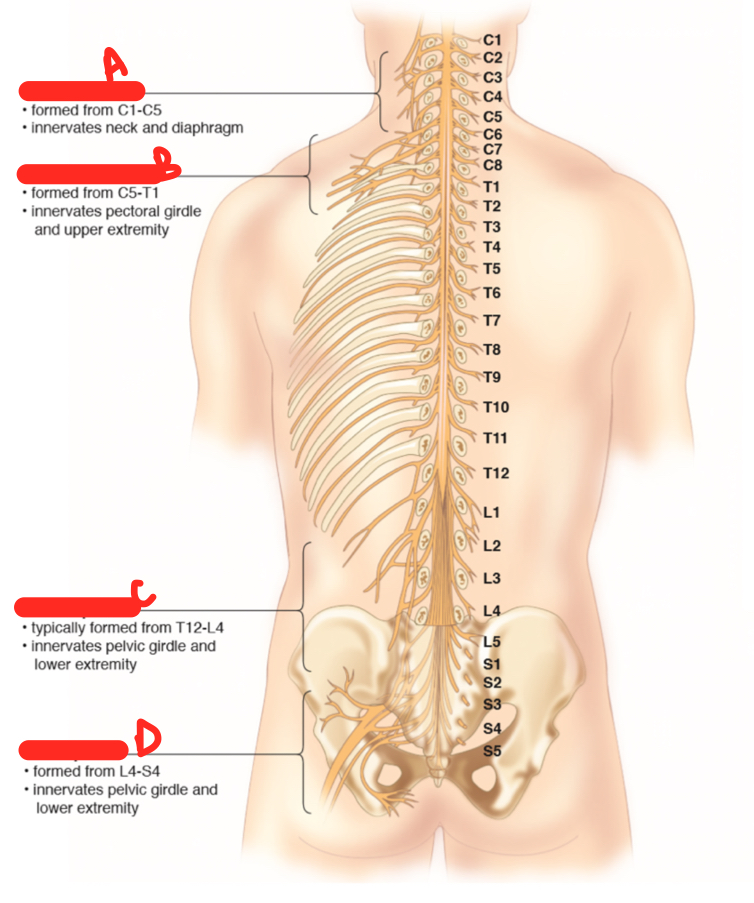
A
cervical plexus
69
New cards
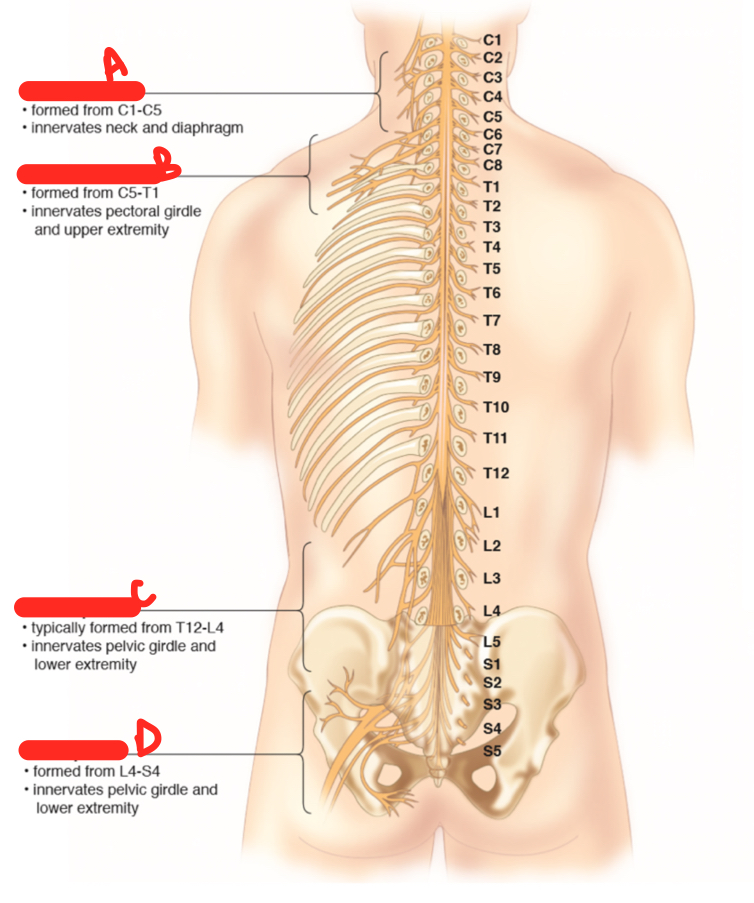
B
brachial plexus
70
New cards
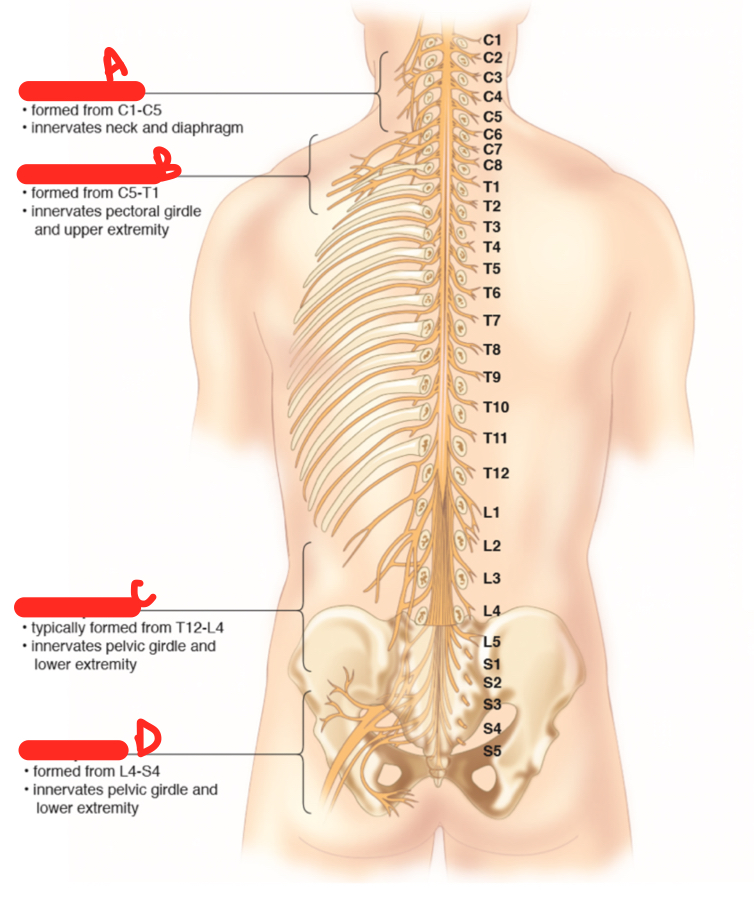
C
lumbar plexus
71
New cards
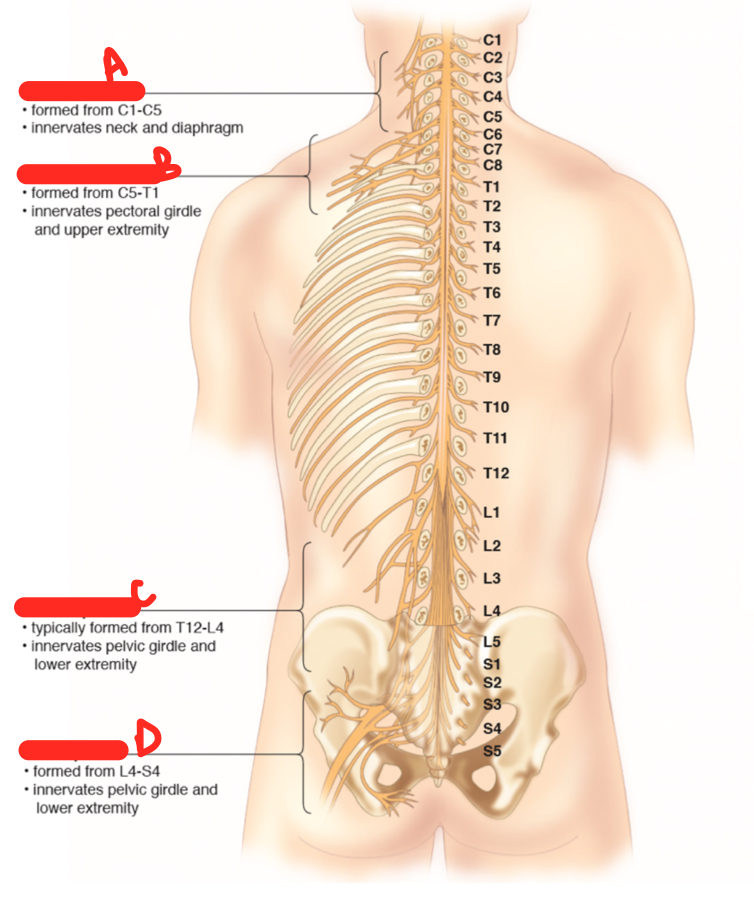
D
sacral plaexus
72
New cards
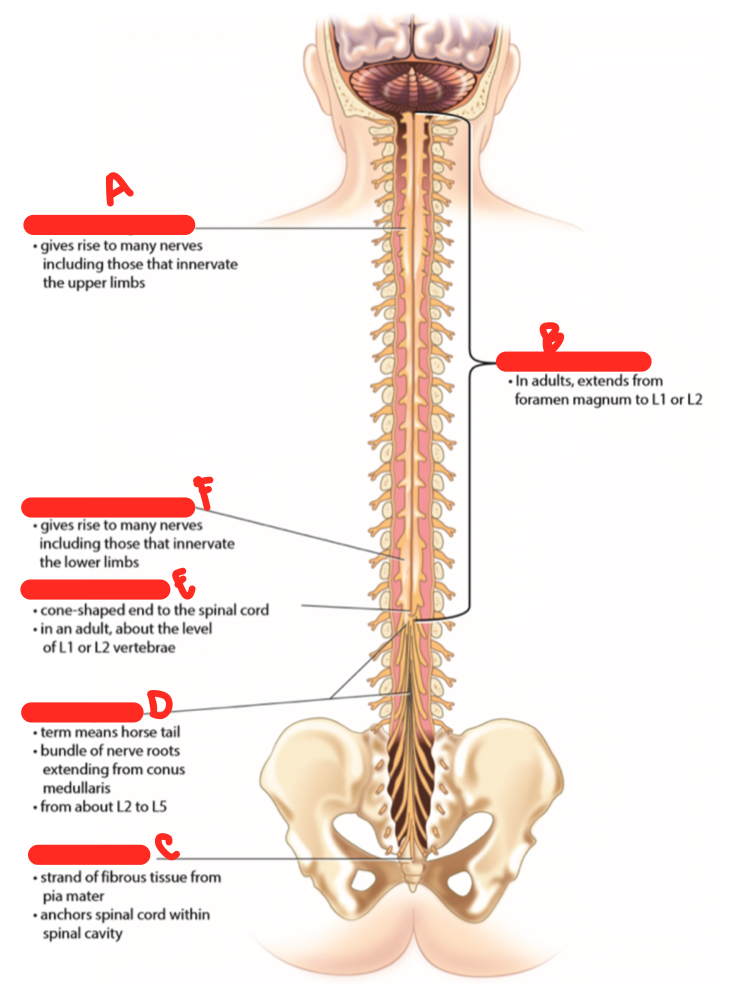
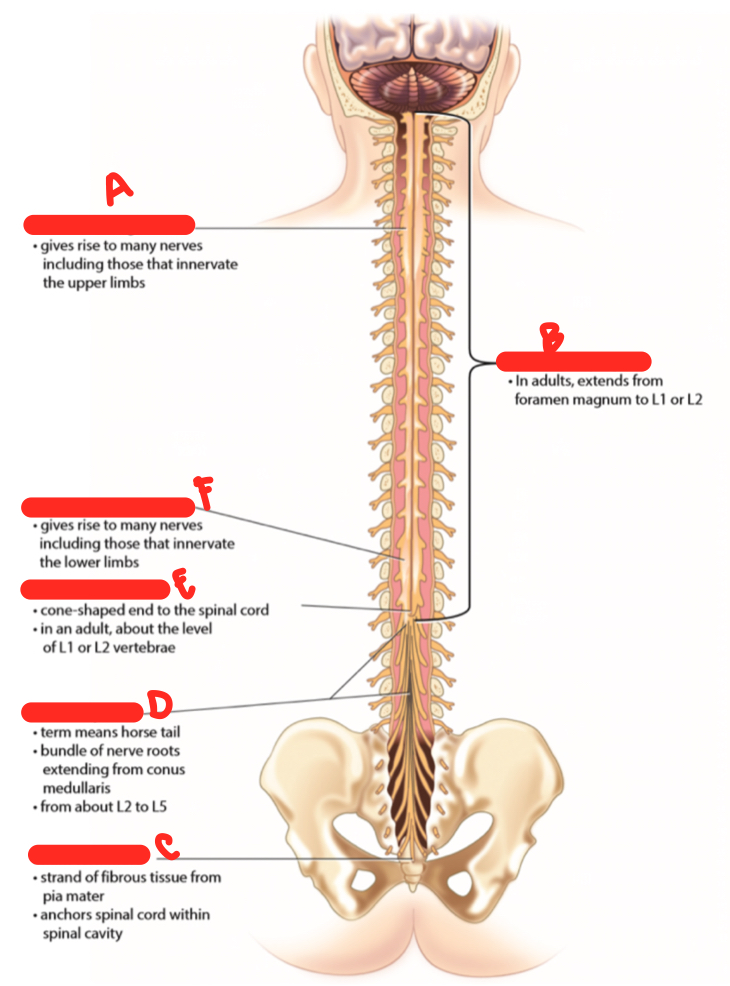
A
cervical enlargement
73
New cards
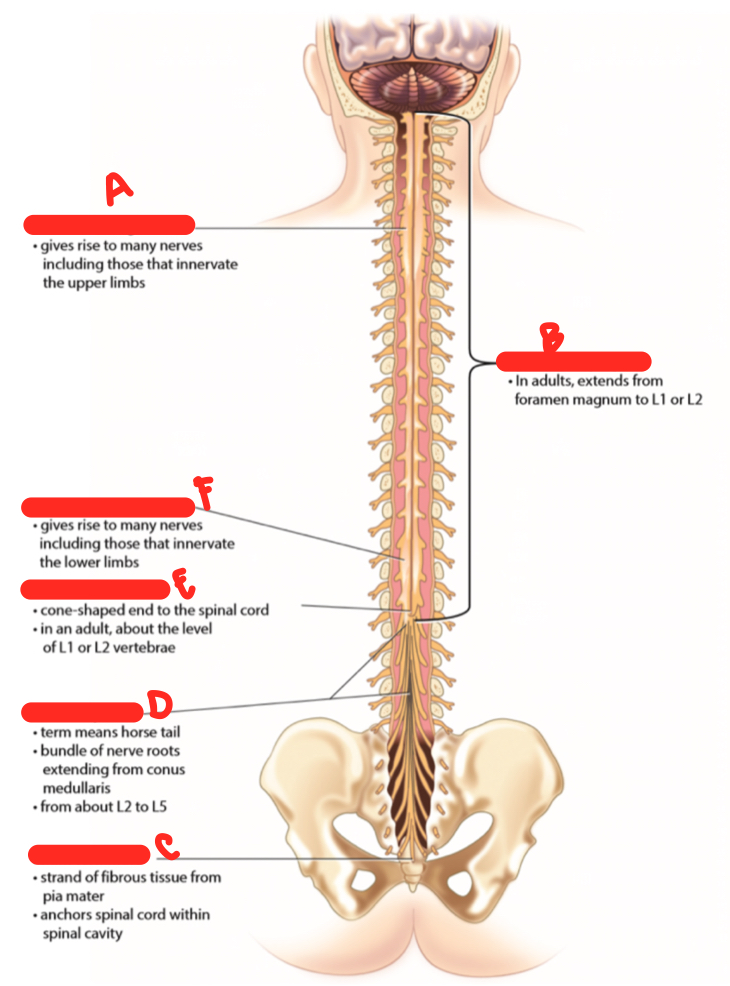
B
spinal cord proper
74
New cards
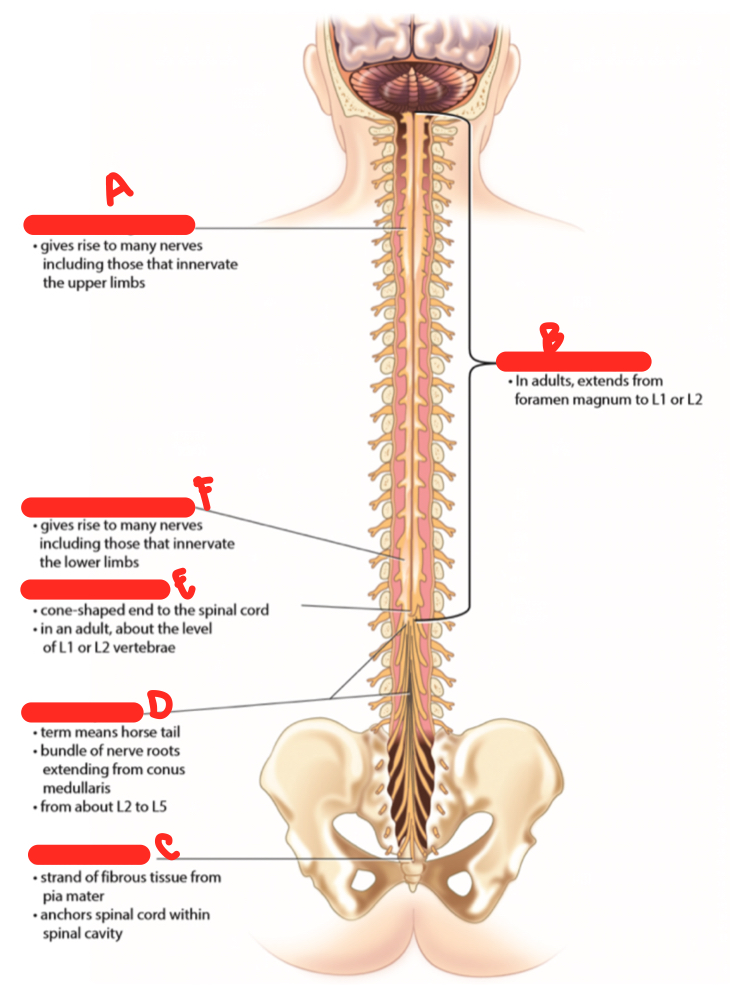
C
filum terminale
75
New cards
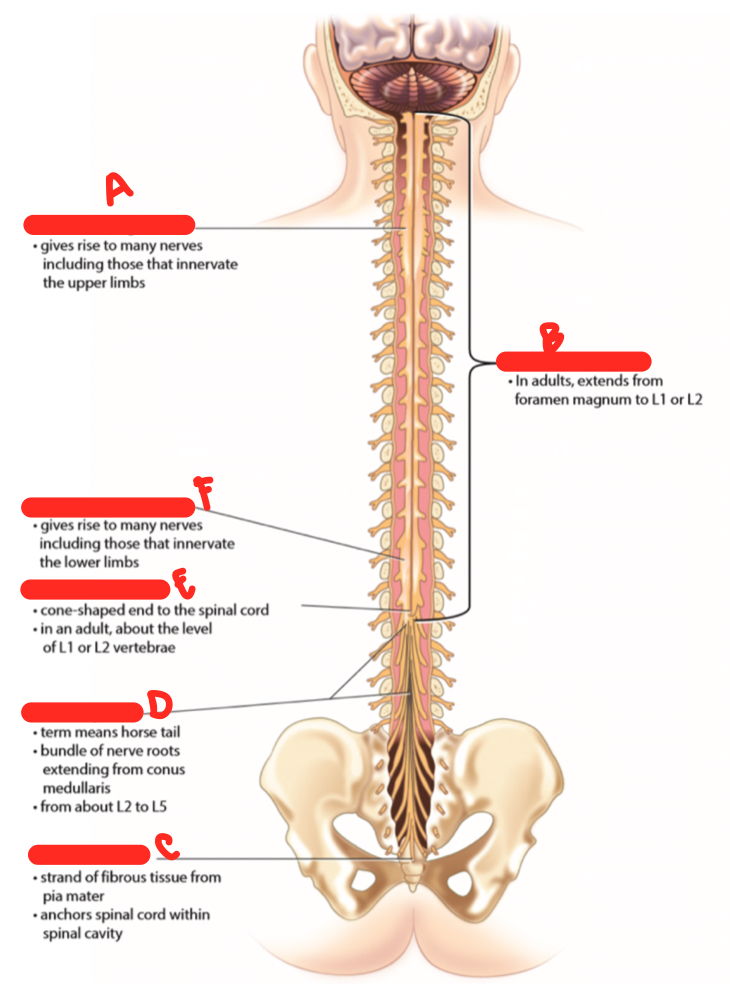
D
cauda equina
76
New cards
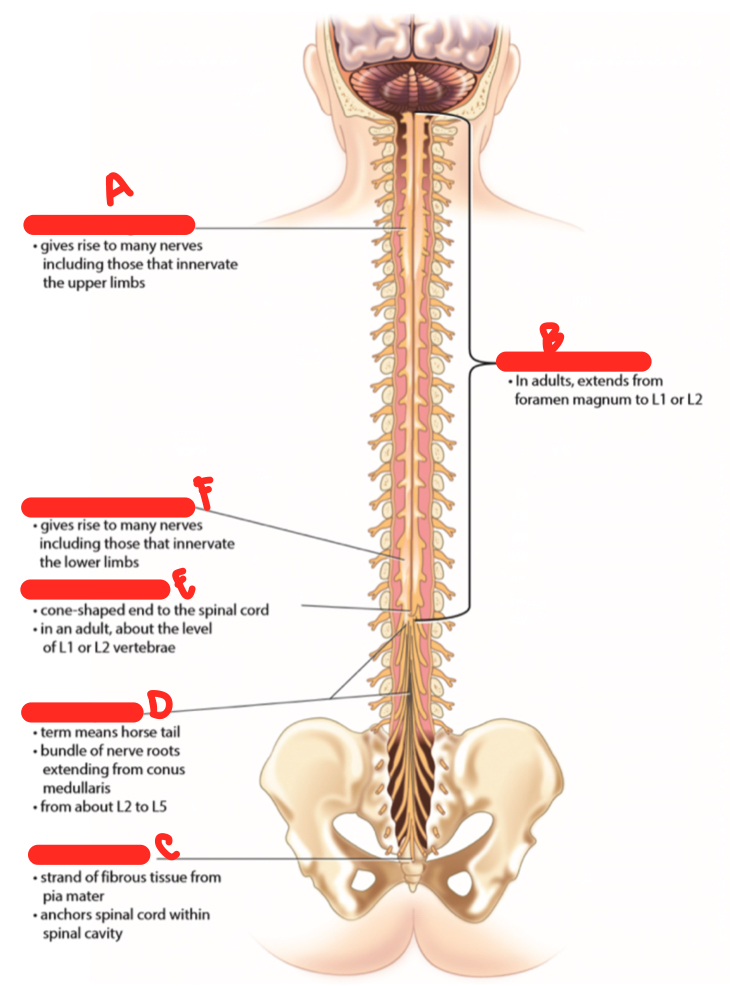
E
conus medullaris
77
New cards
F
lumbar enlargement
78
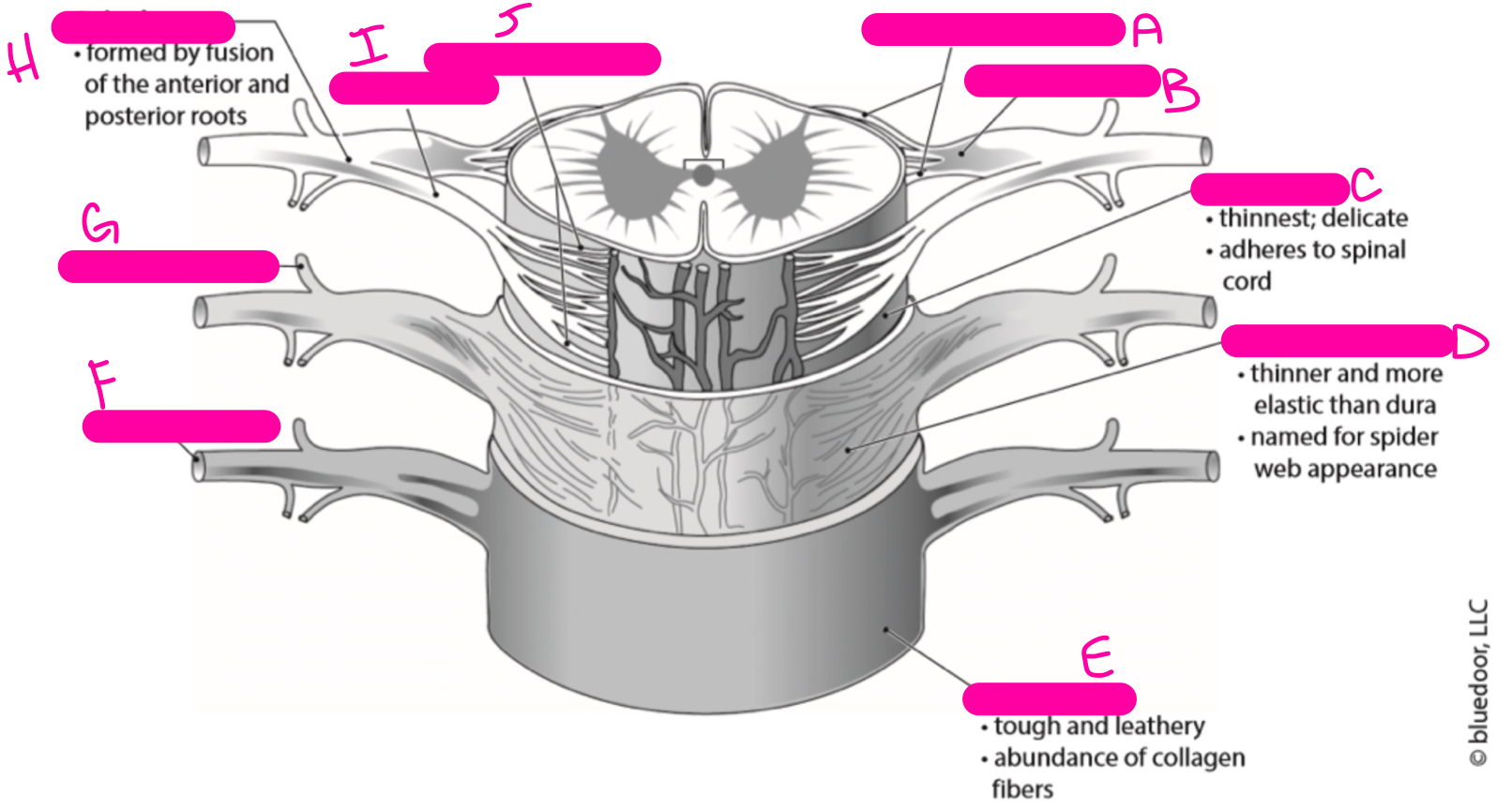
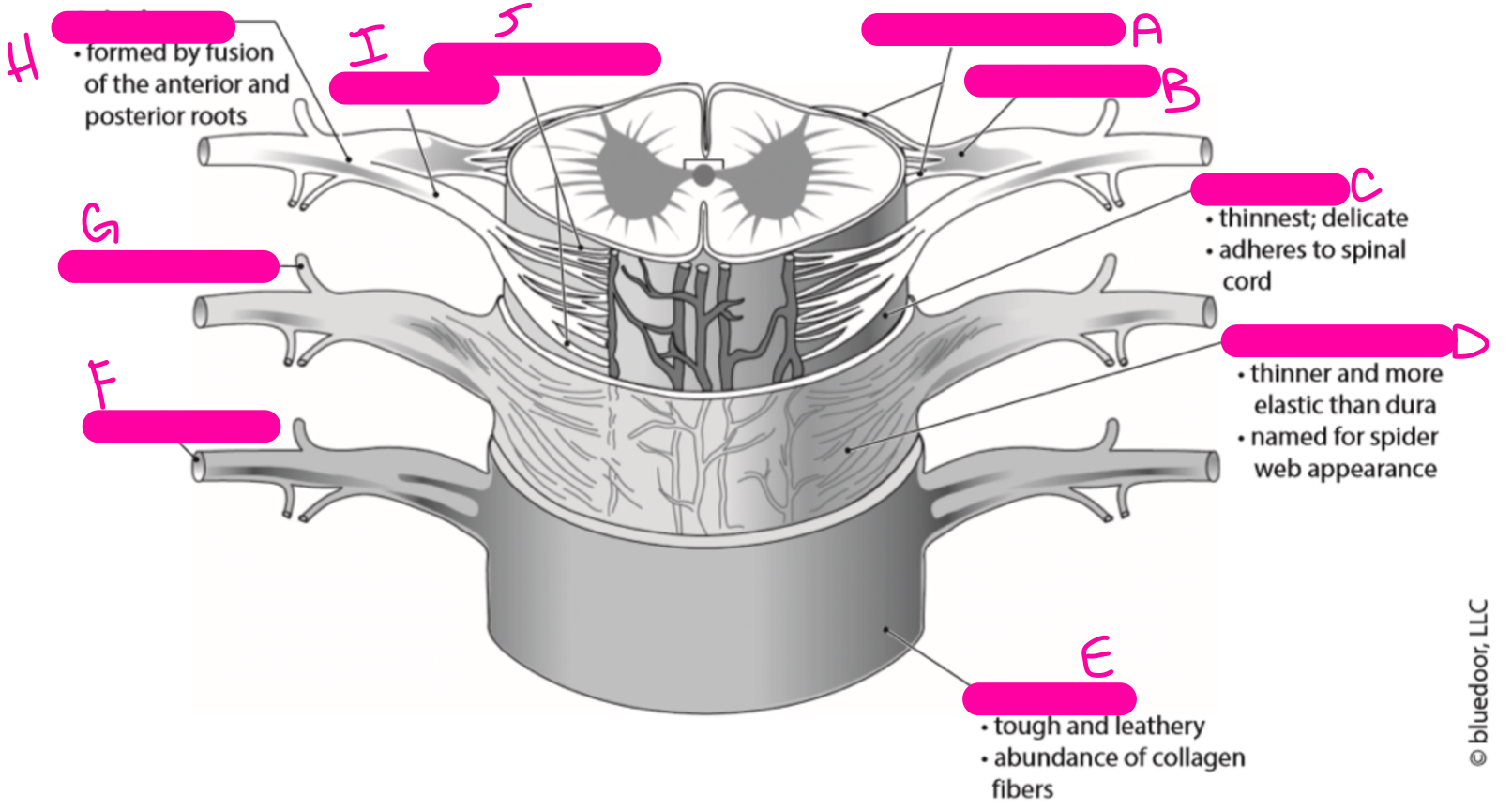
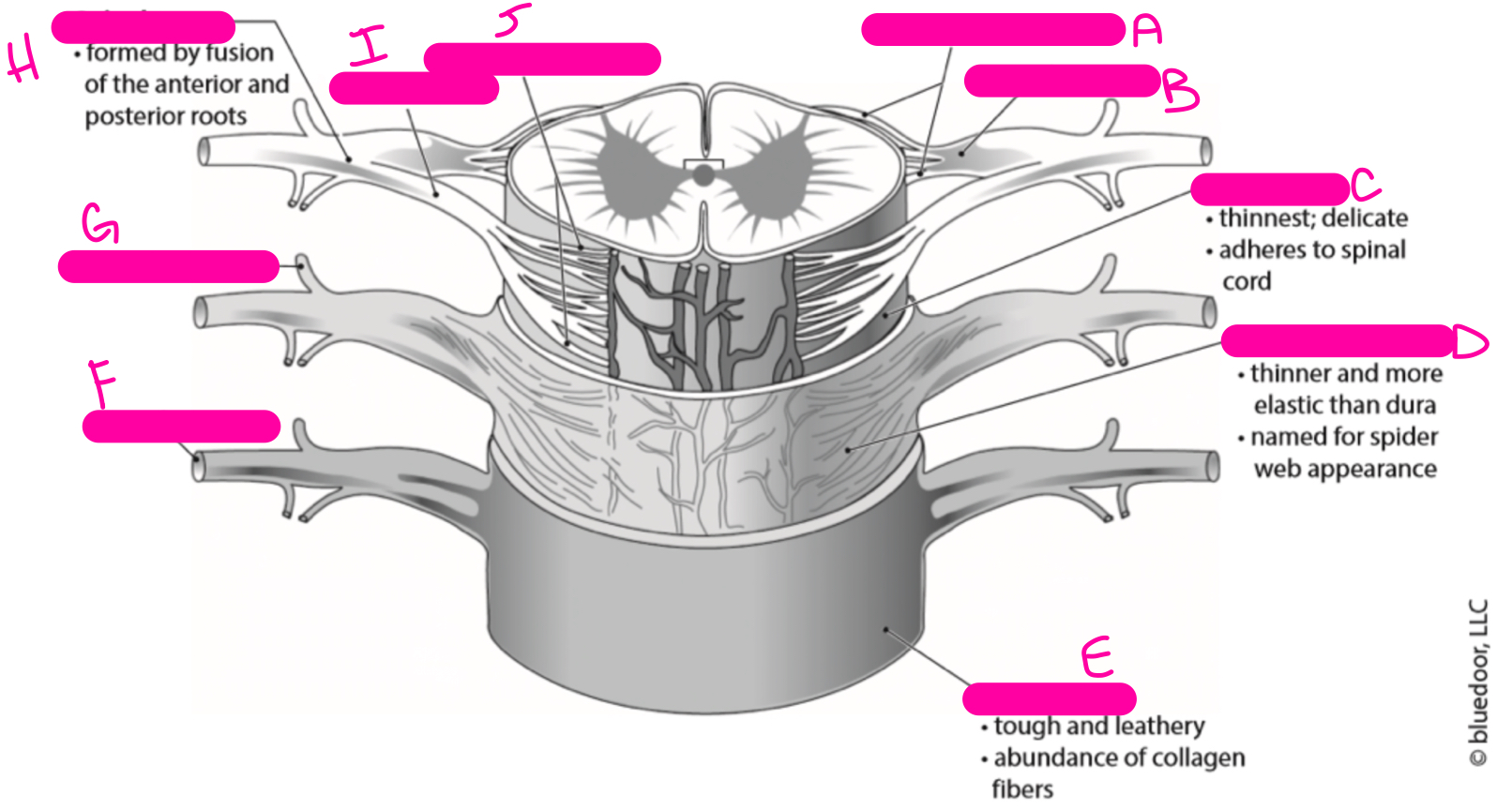
New cards
A
posterior rootlets
79
New cards
B
posterior root
80
New cards
C
pia mater
81
New cards
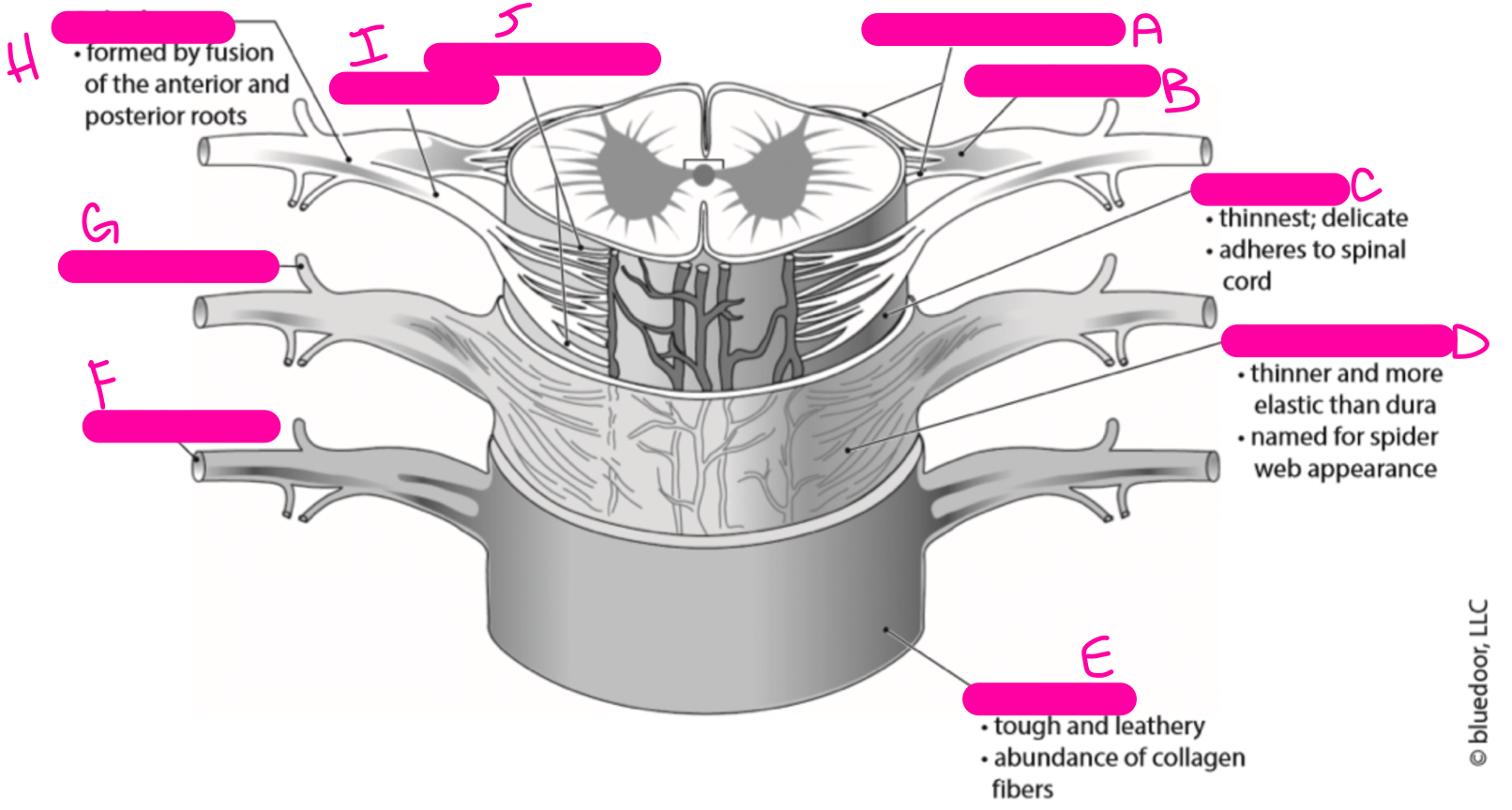
D
arachnoid mater
82
New cards
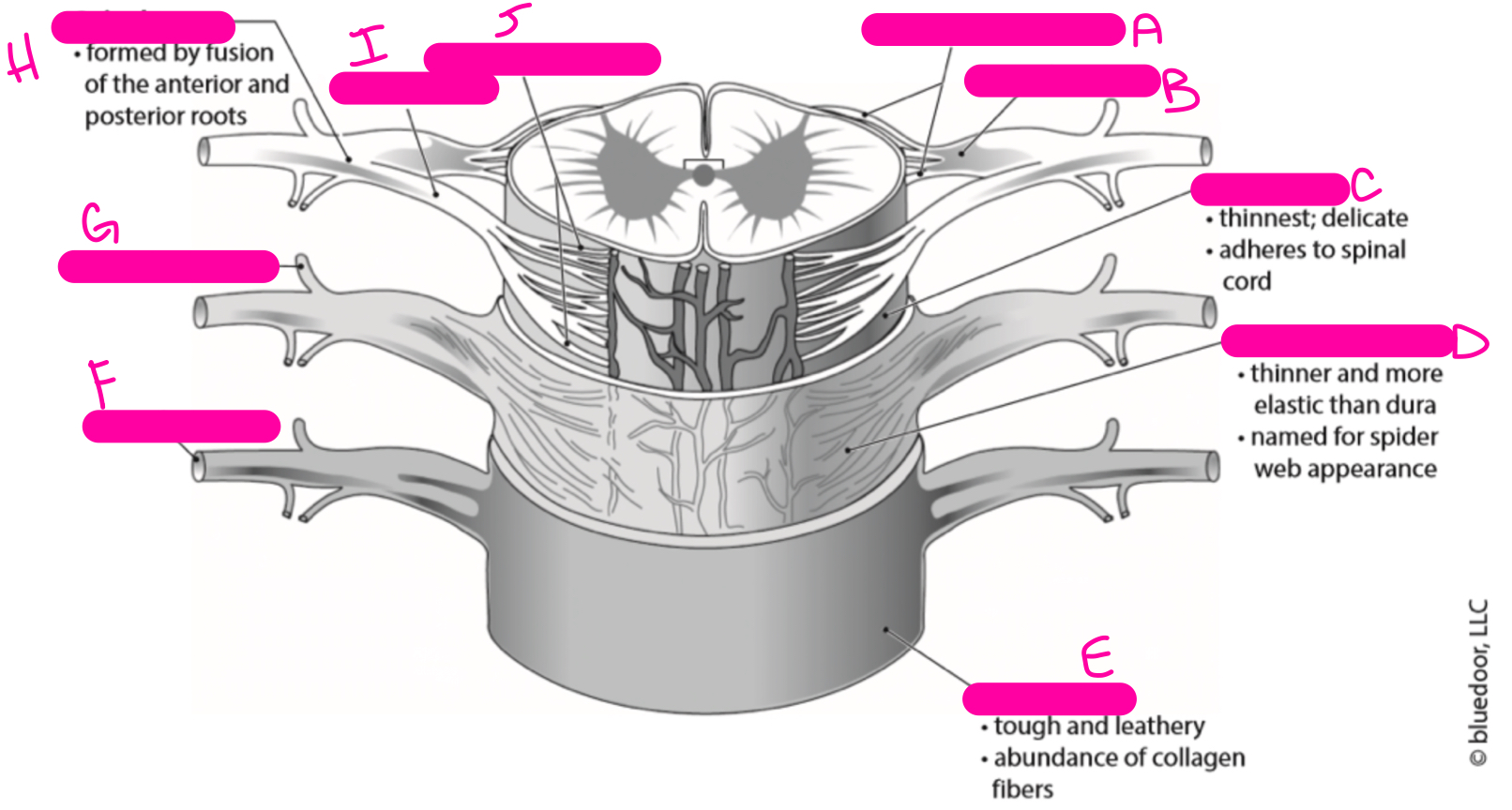
E
dura mater
83
New cards
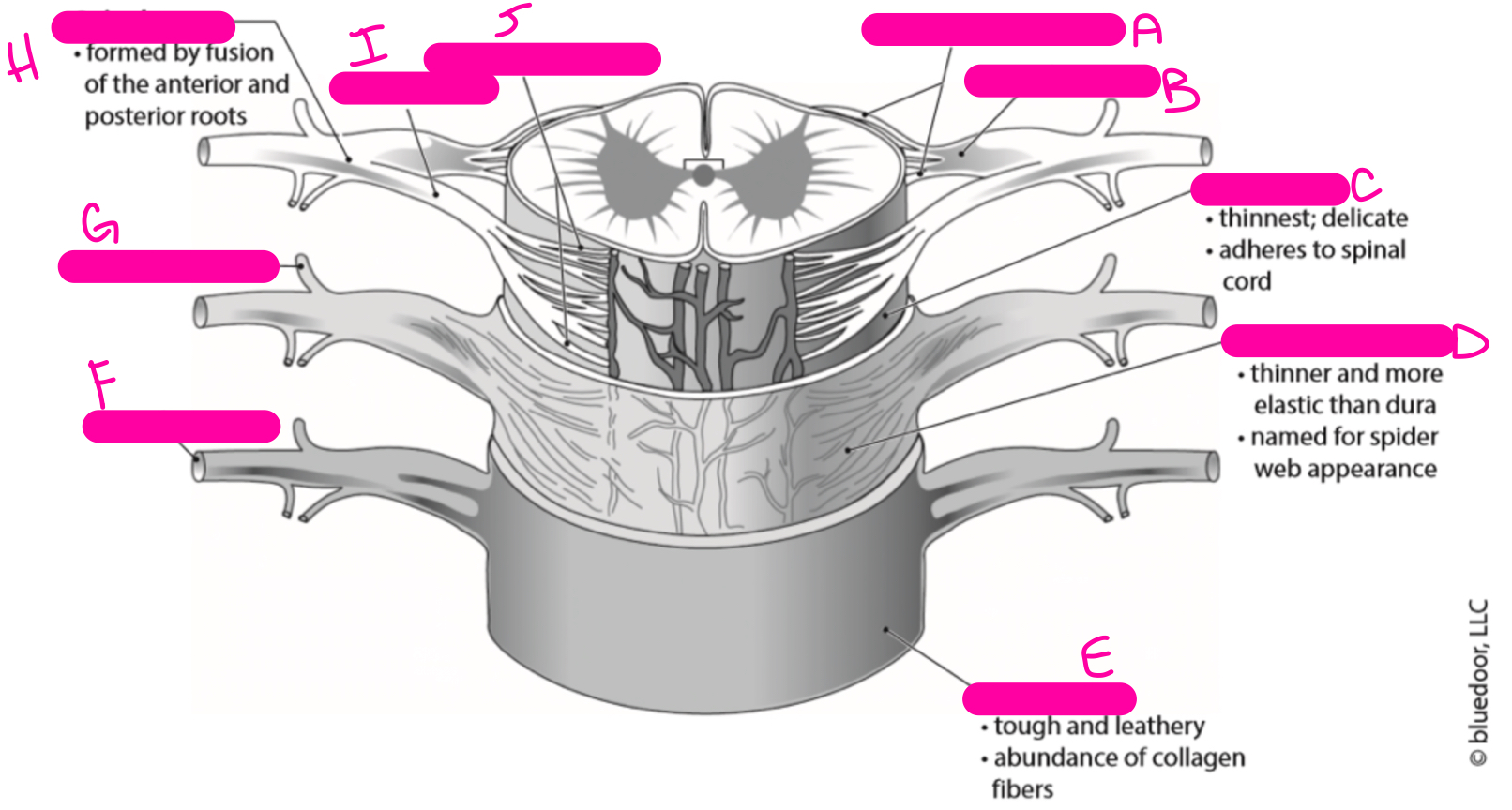
F
anterior ramus
84
New cards
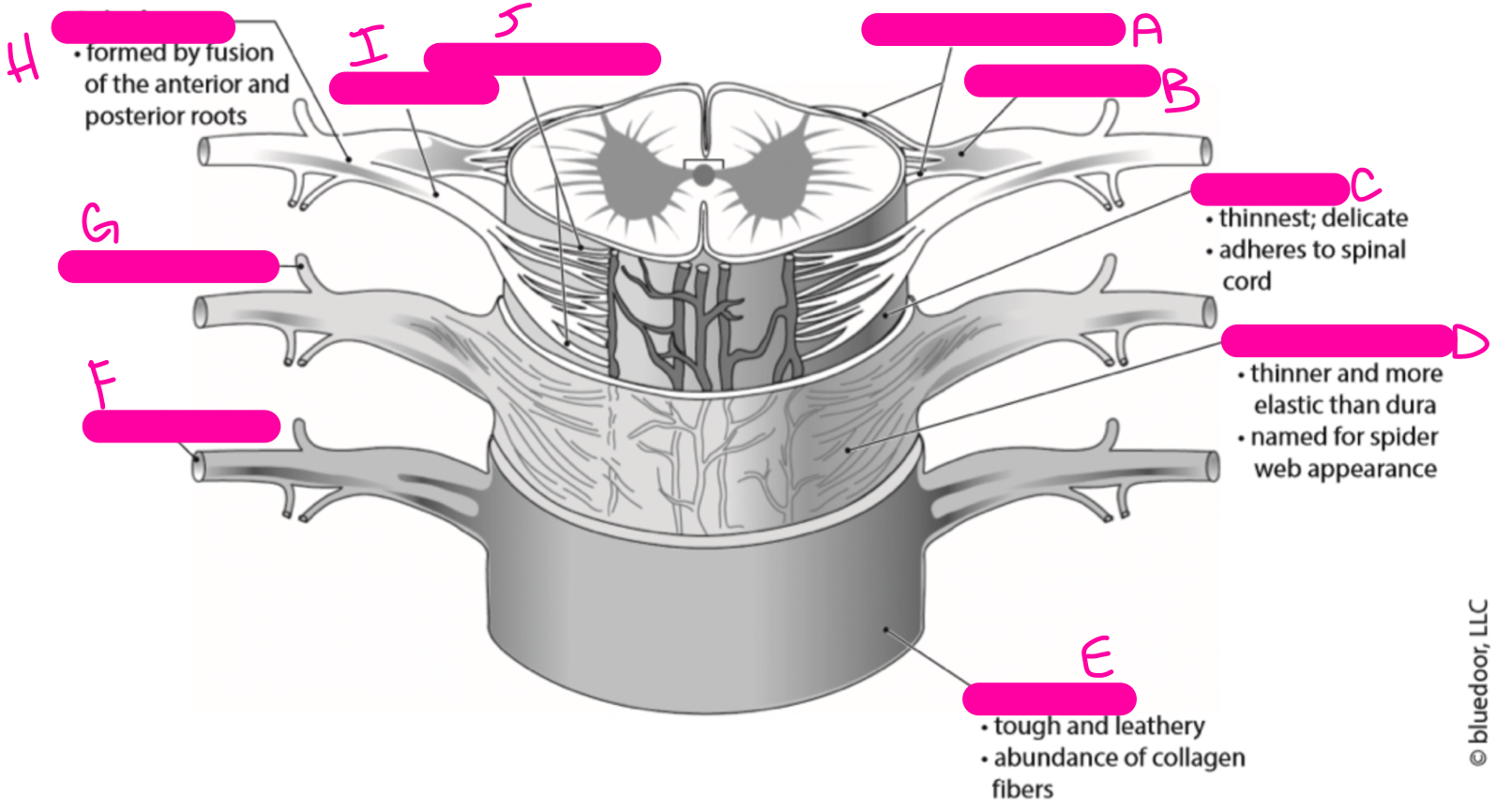
G
posterior ramus
85
New cards
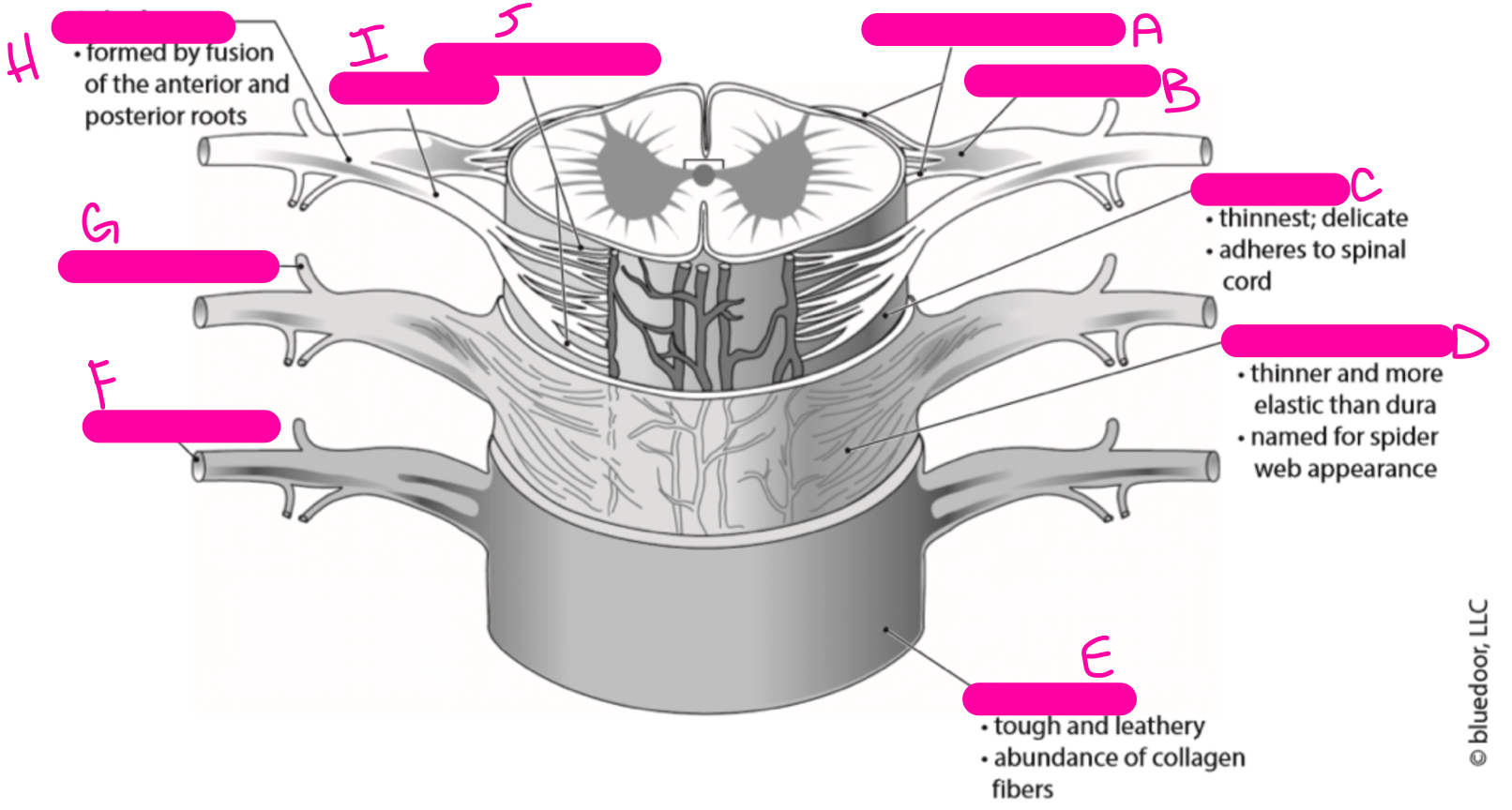
H
spinal nerve
86
New cards
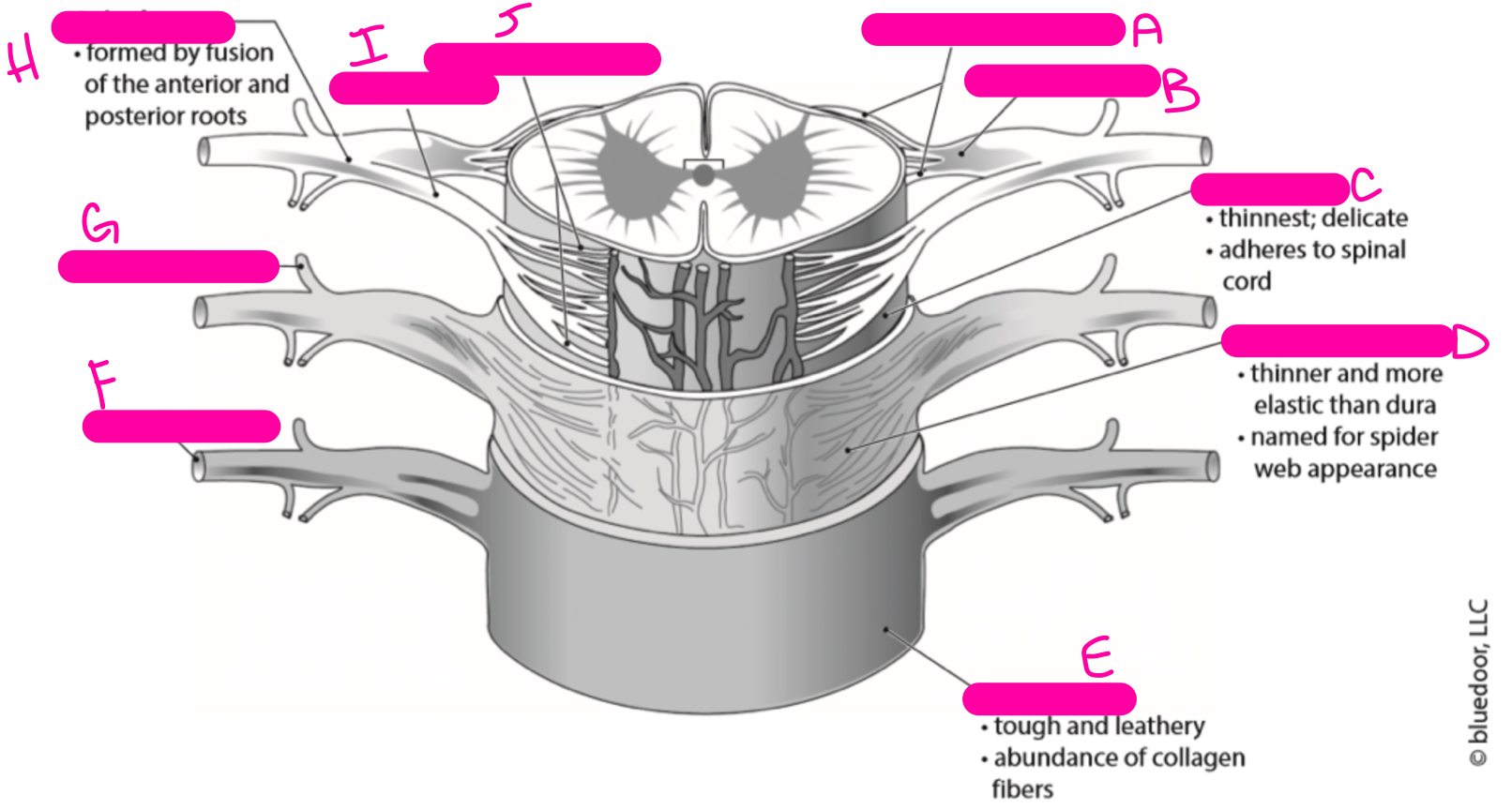
I
anterior root
87
New cards
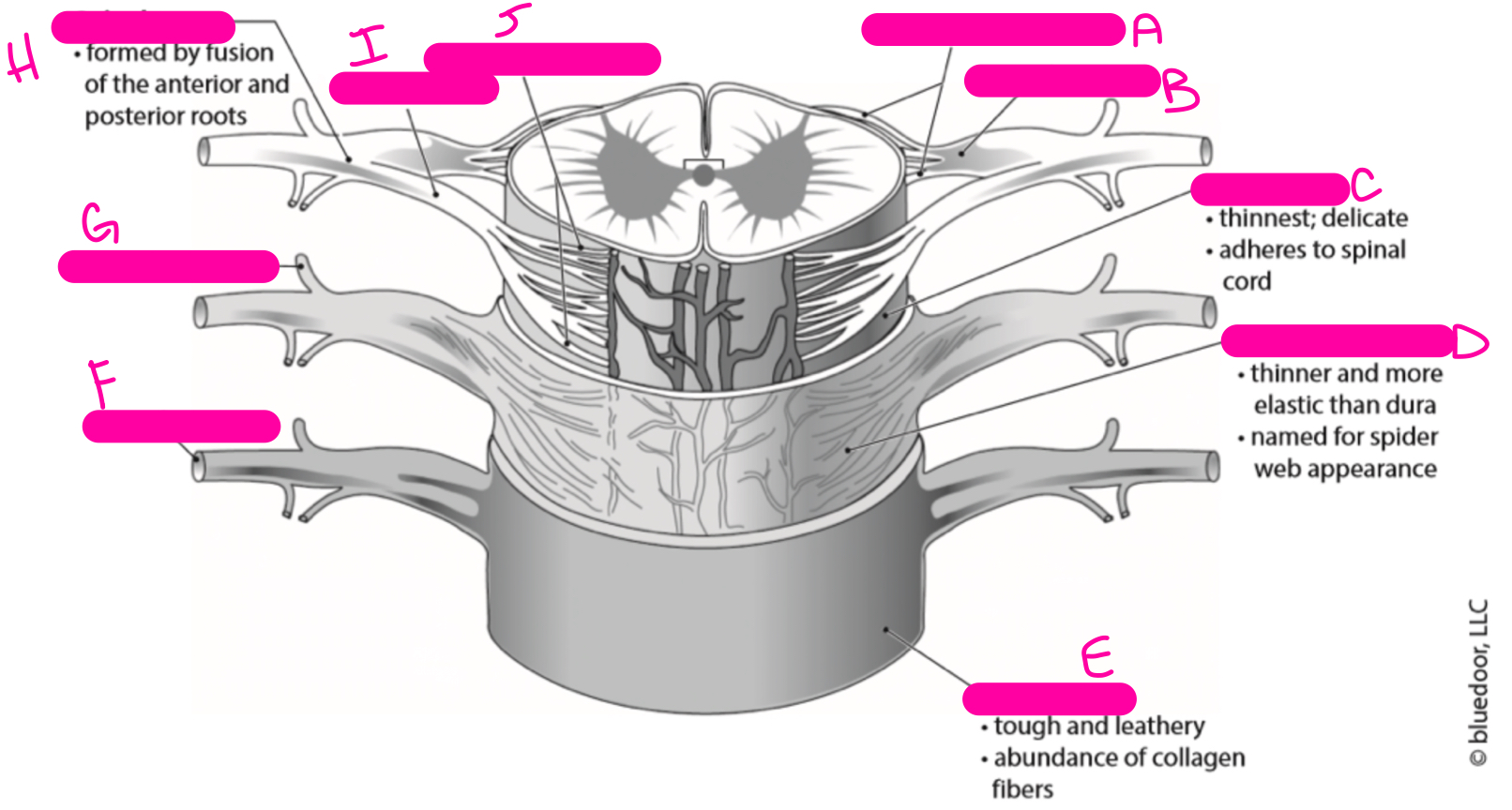
J
anterior rootlets
88
New cards
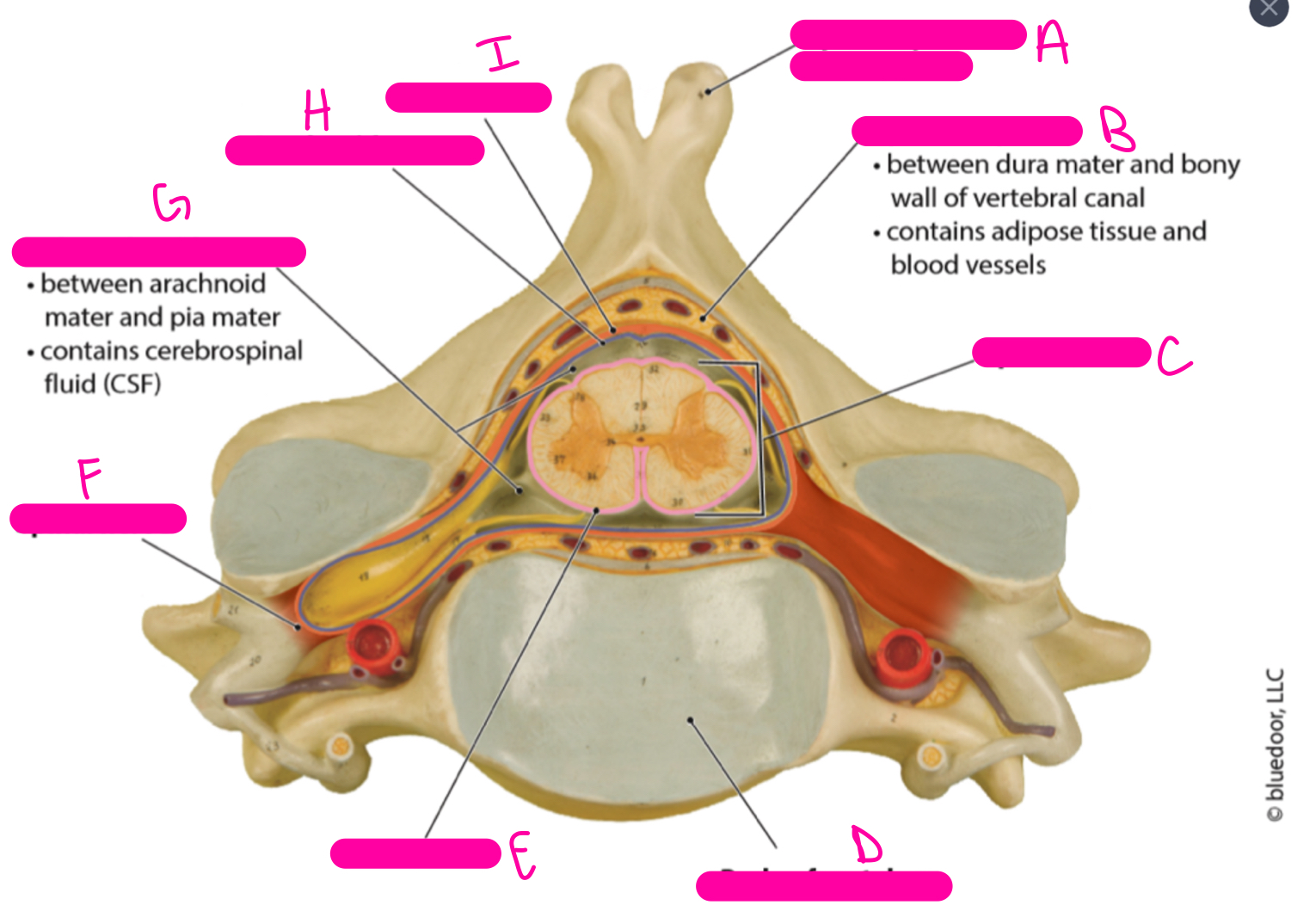
A
spinous process of vertebra
89
New cards
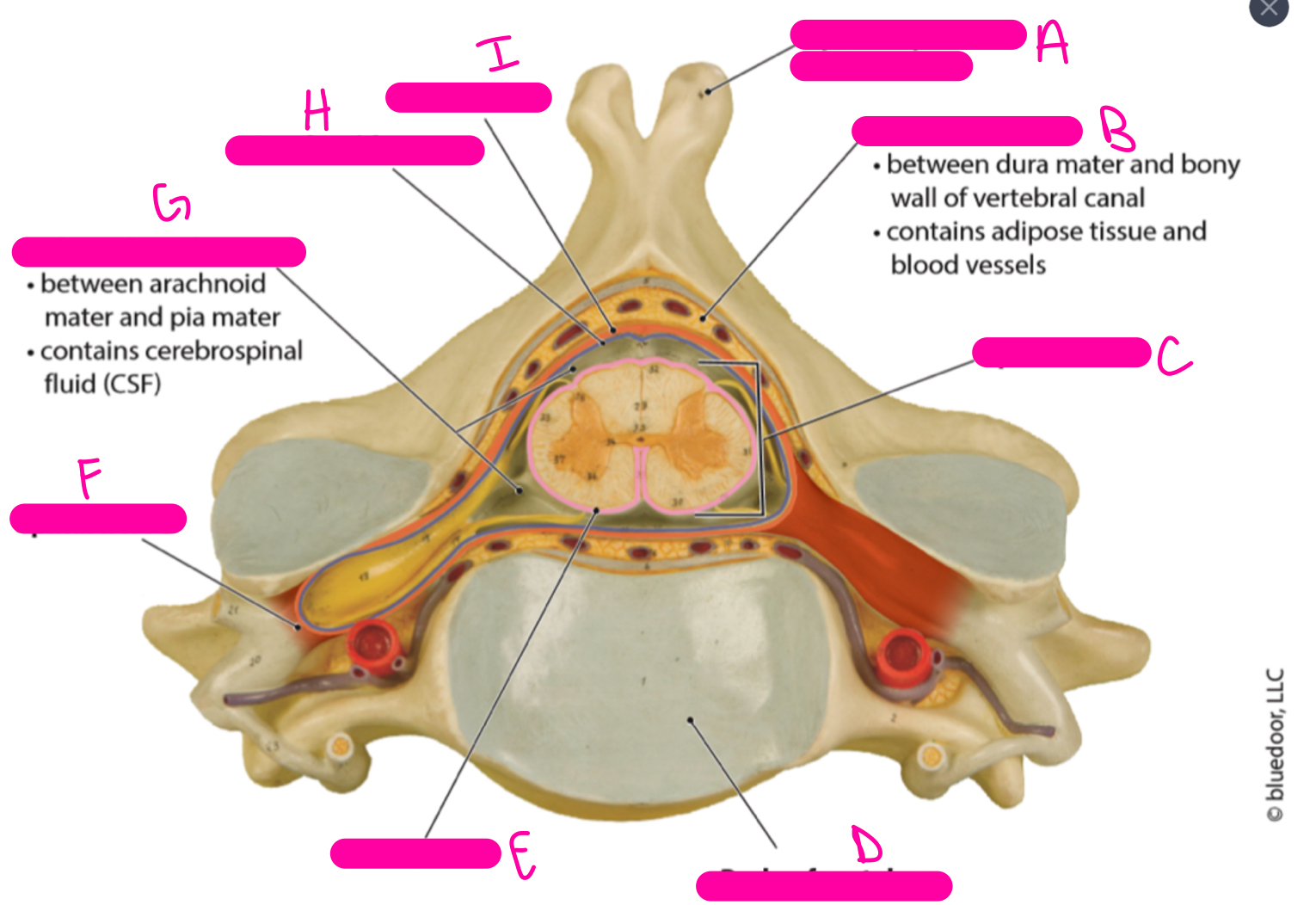
B
epidural space
90
New cards
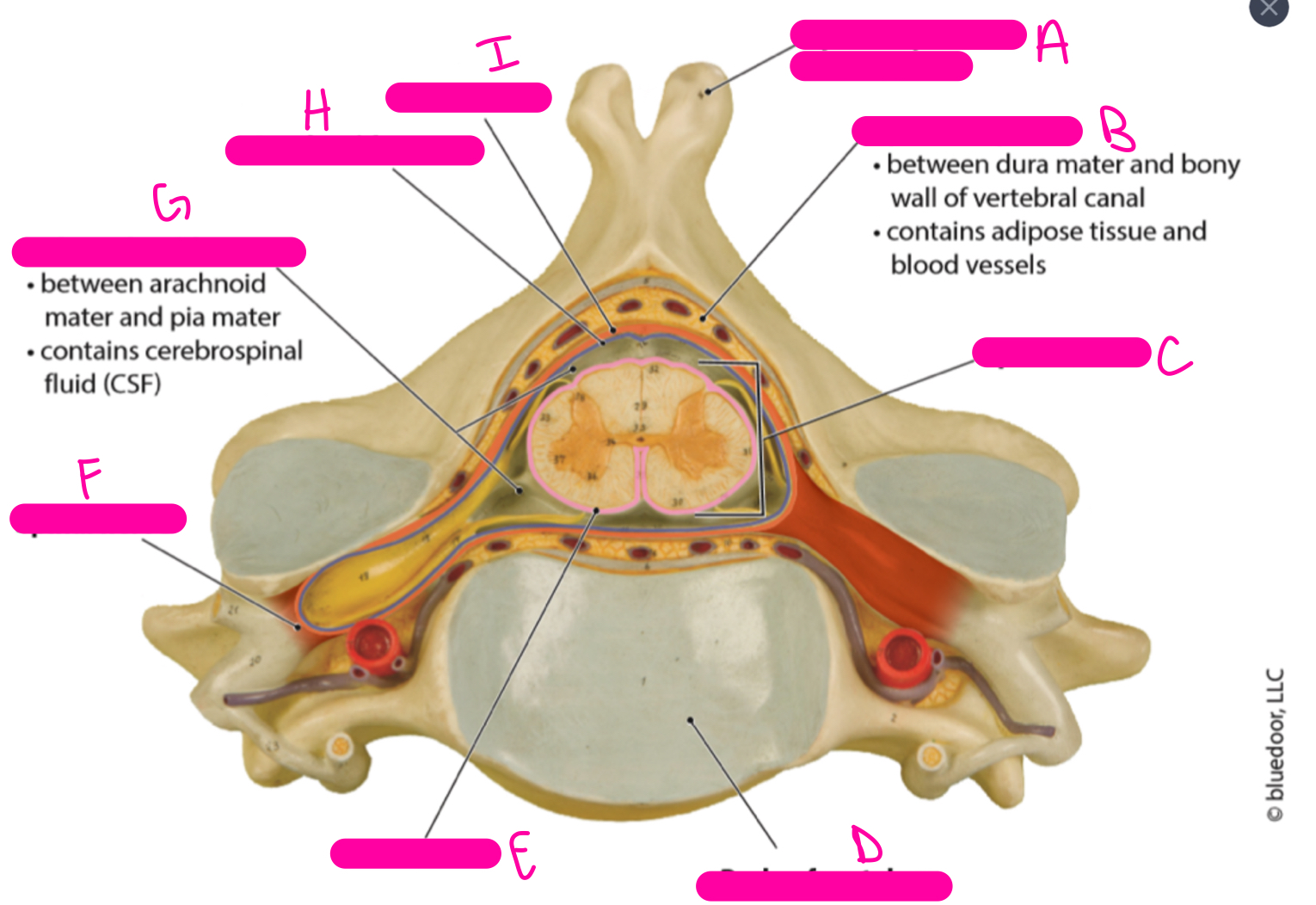
C
spinal cord
91
New cards
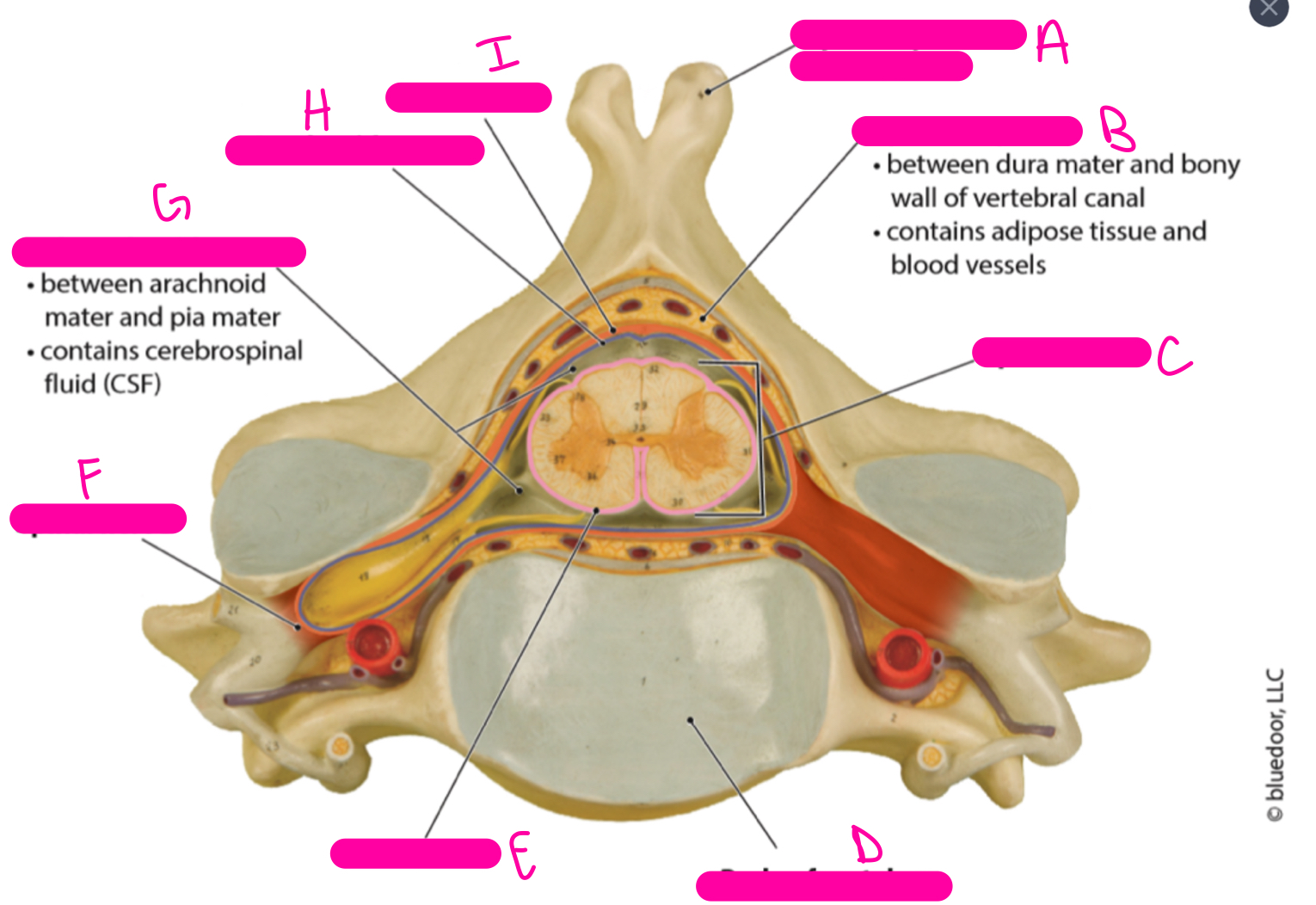
D
body or vertebra
92
New cards
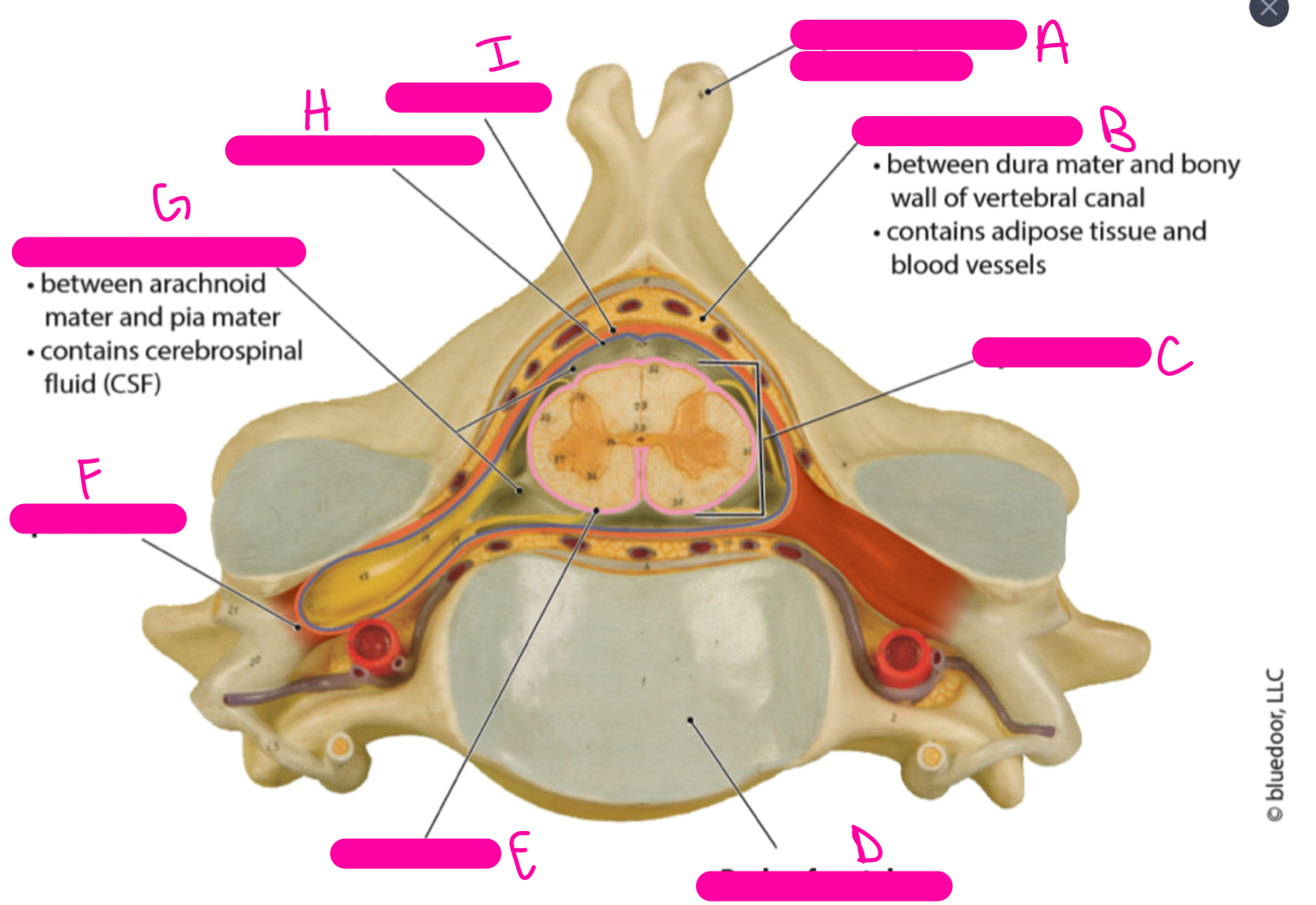
E
pia mater
93
New cards
F
spinal nerve
94
New cards
G
subarachnoid space
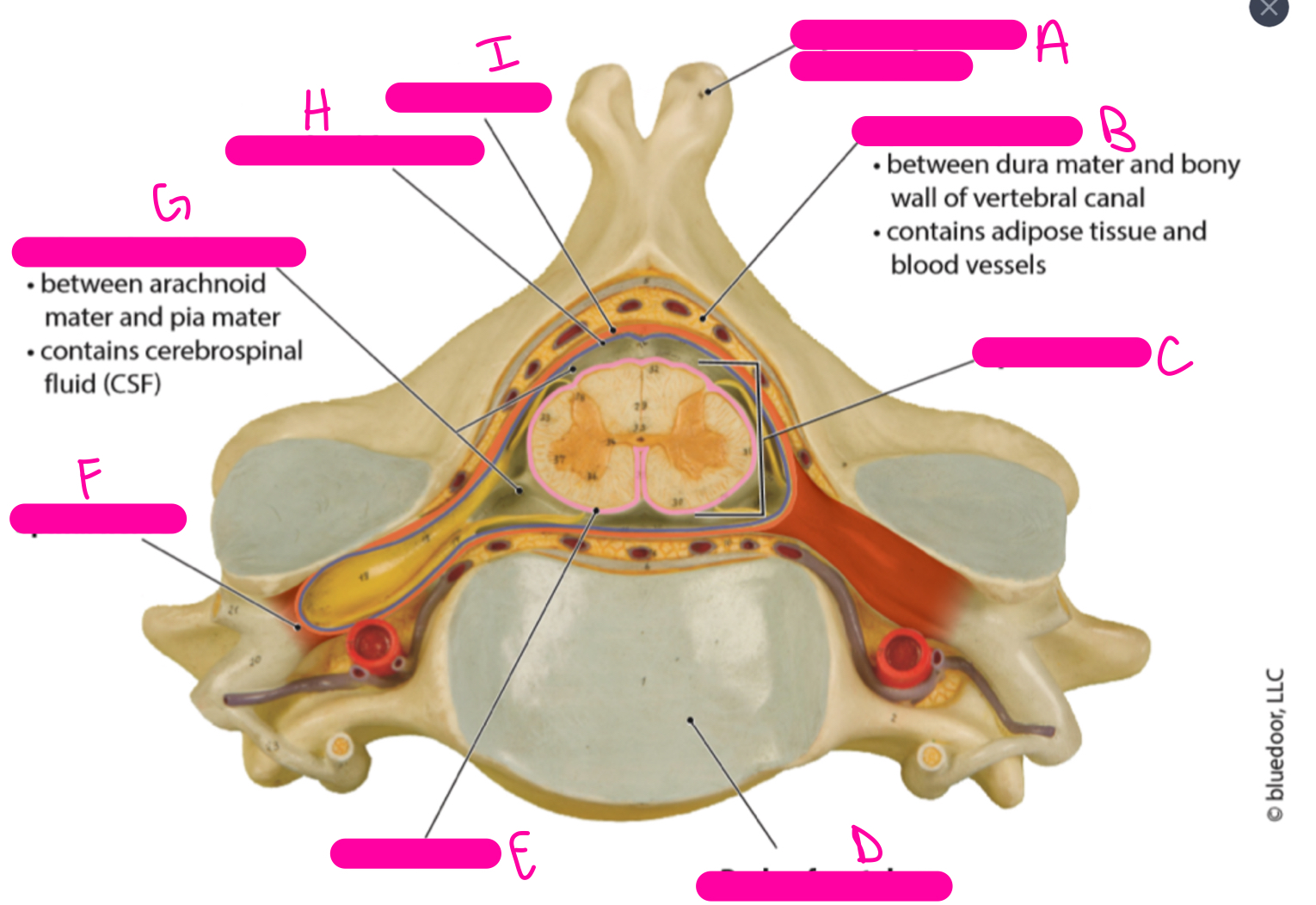
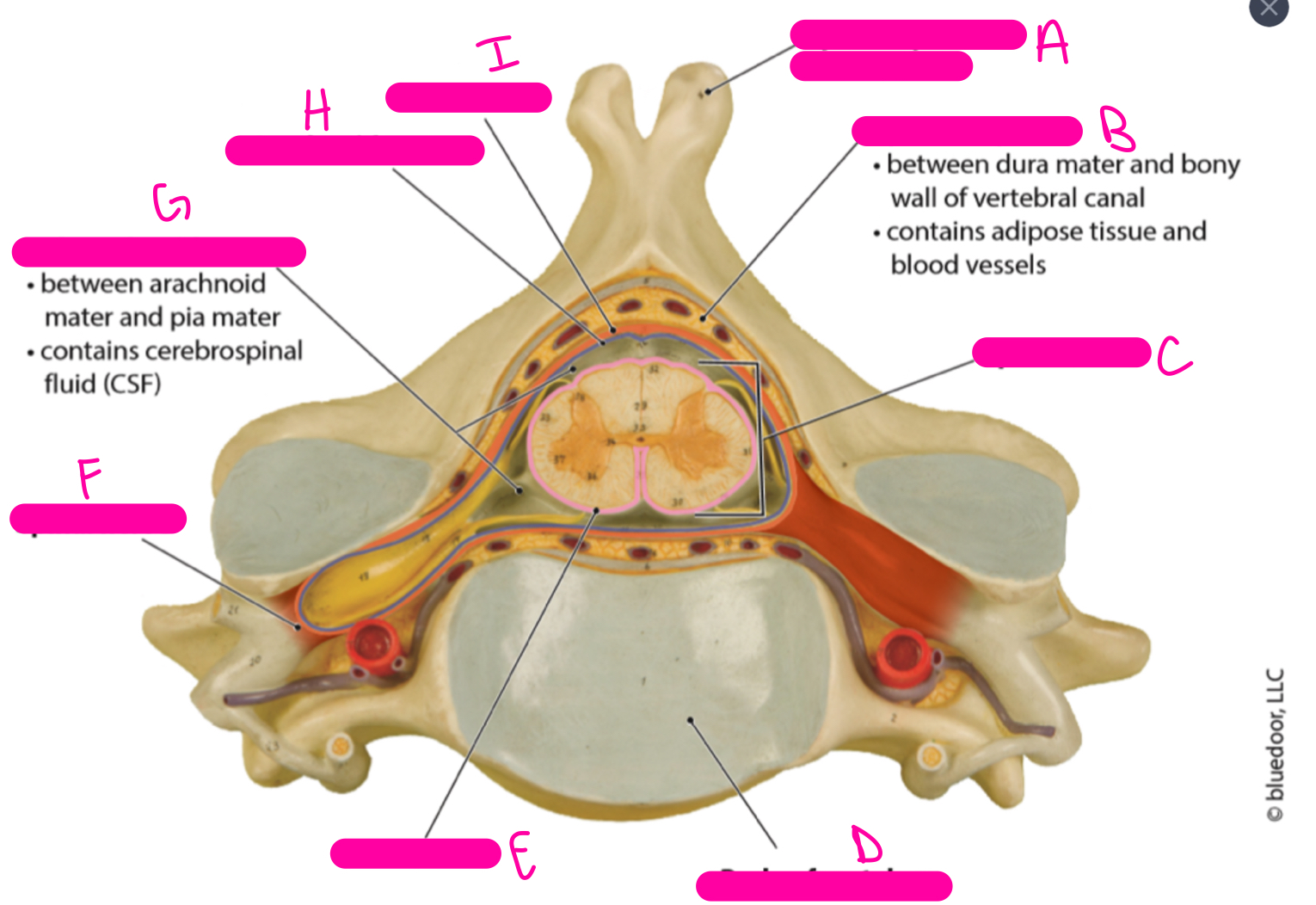
95
New cards
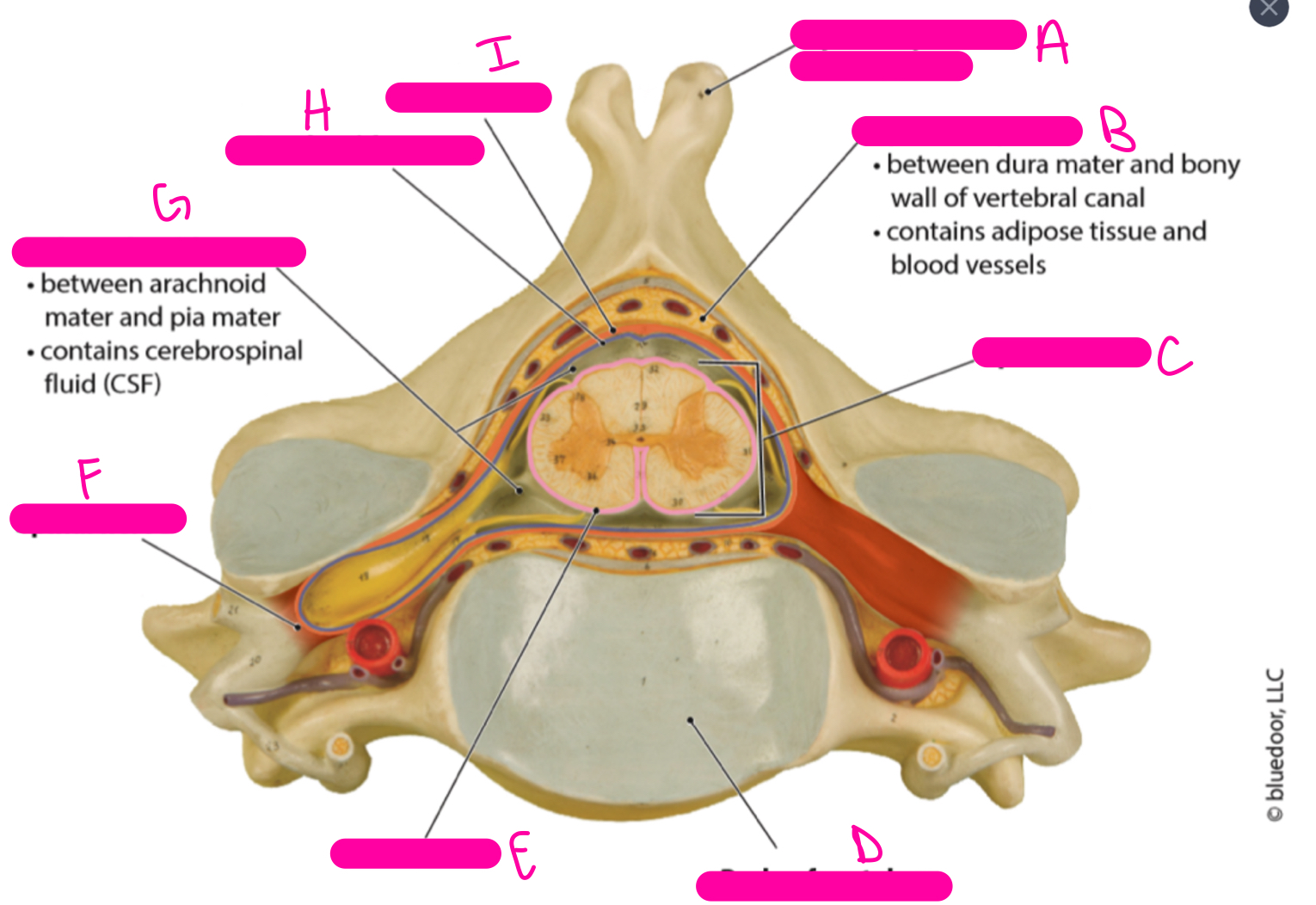
H
arachnoid mater
96
New cards
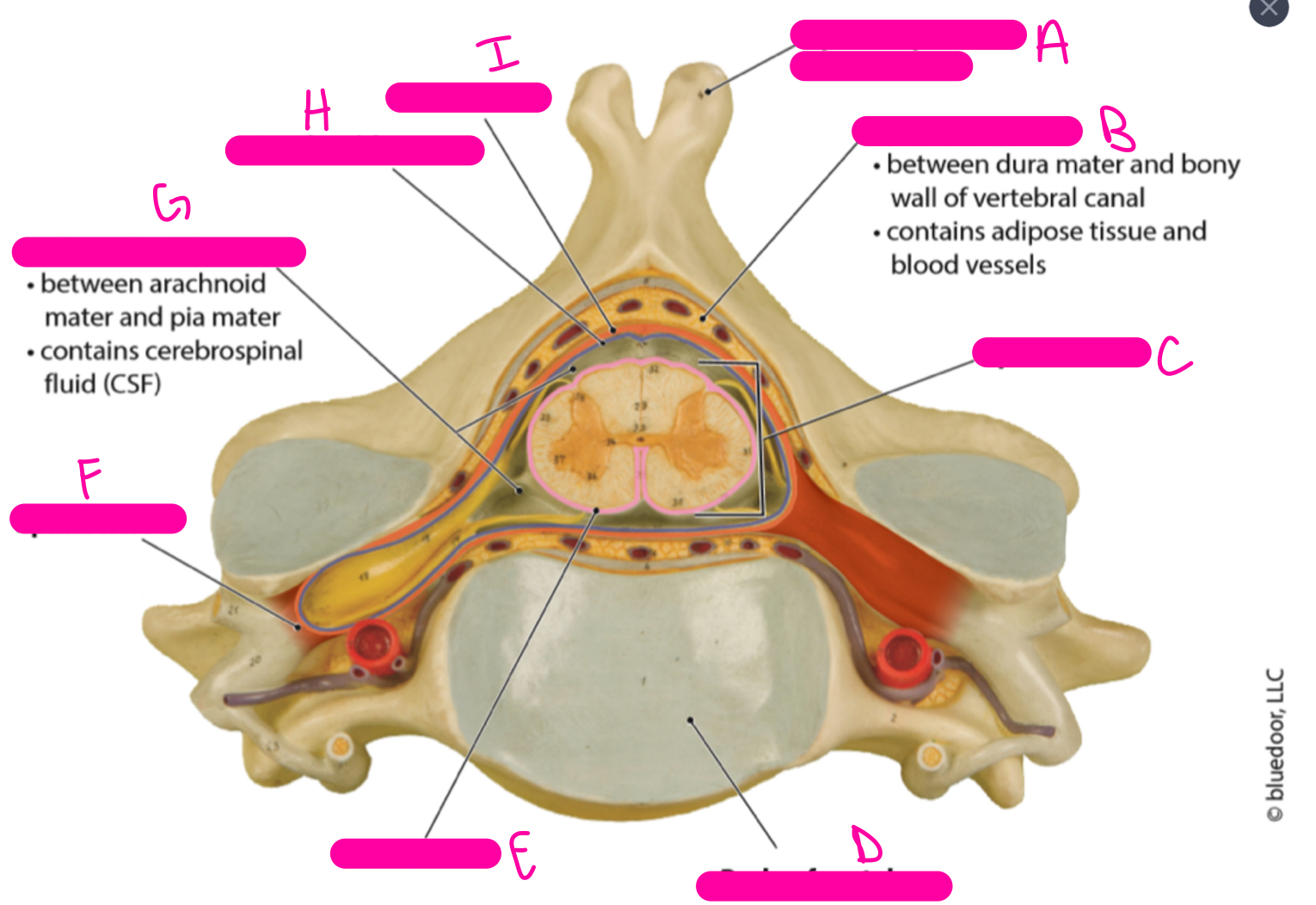
I
dura mater
97
New cards
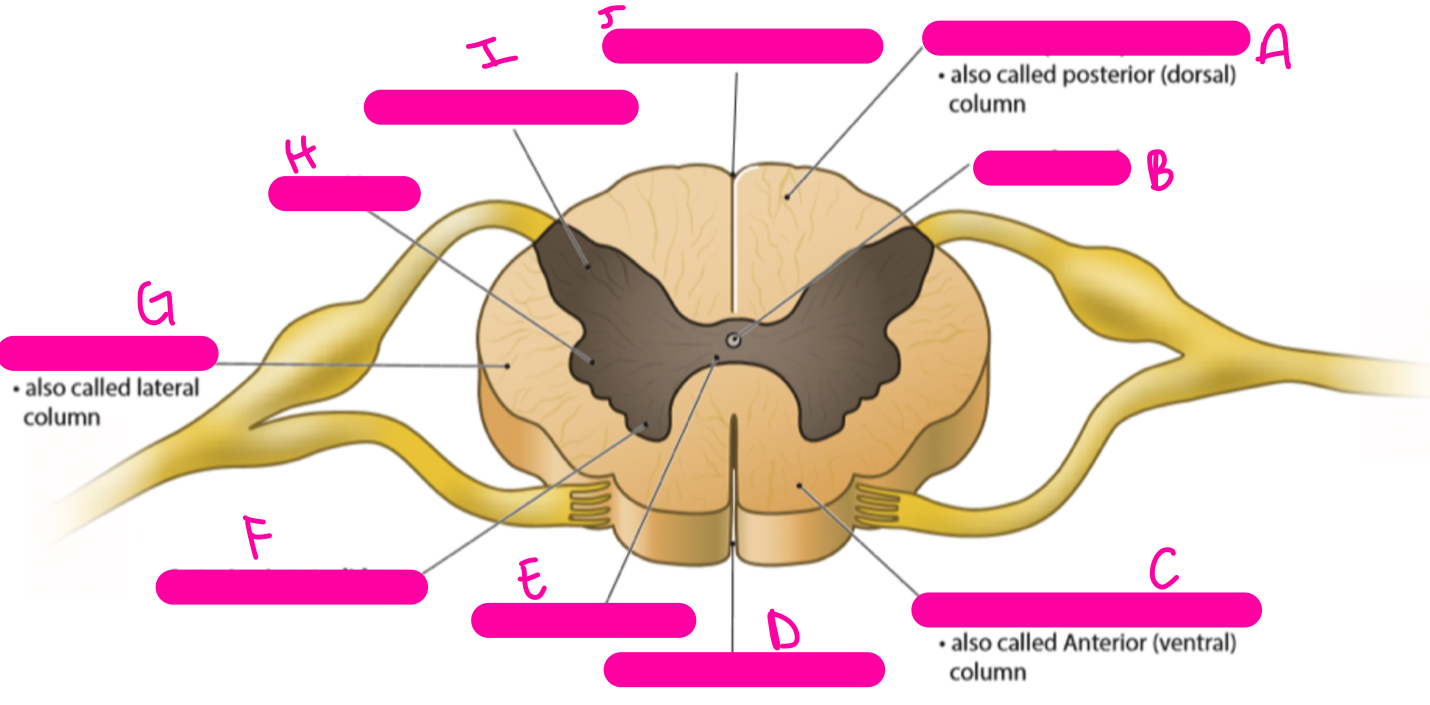
A
posterior (dorsal) funiculus
98
New cards
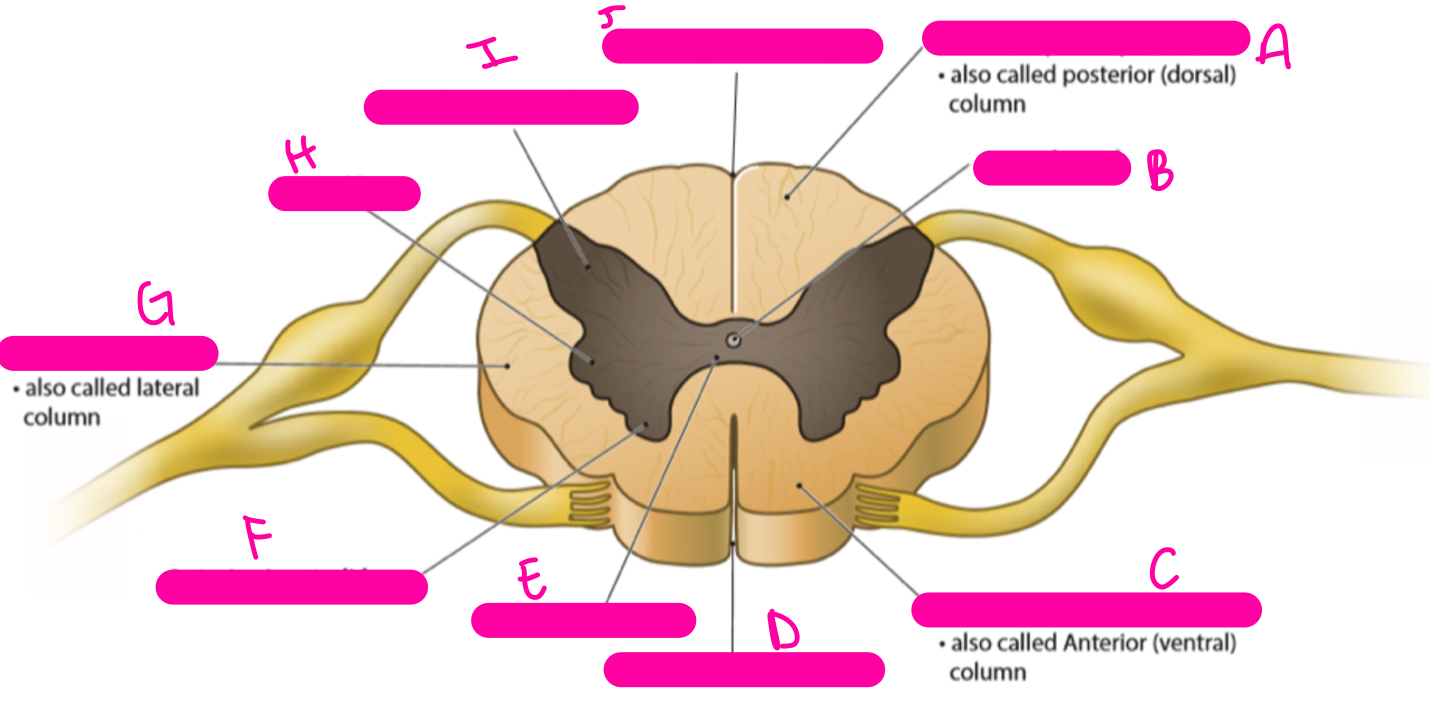
B
central canal
99
New cards
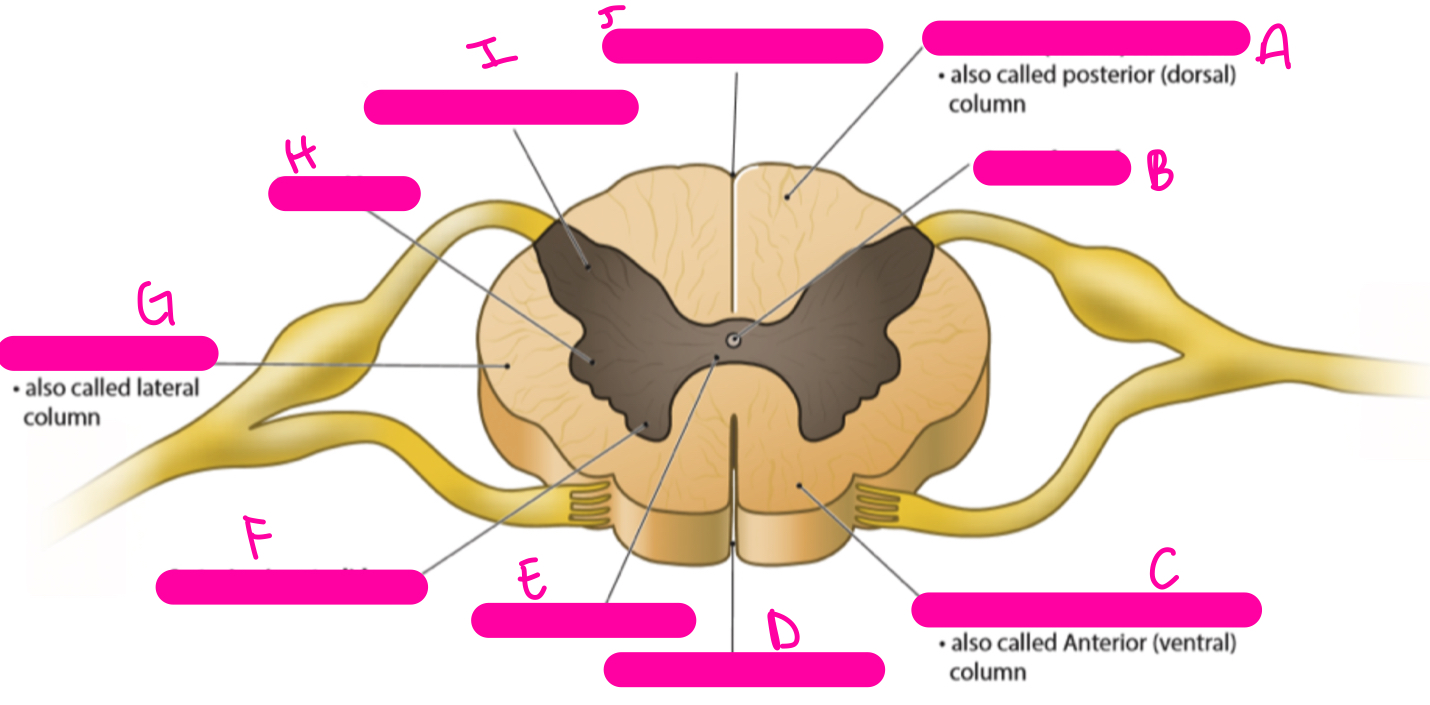
C
anterior (ventral) funiculus
100
New cards
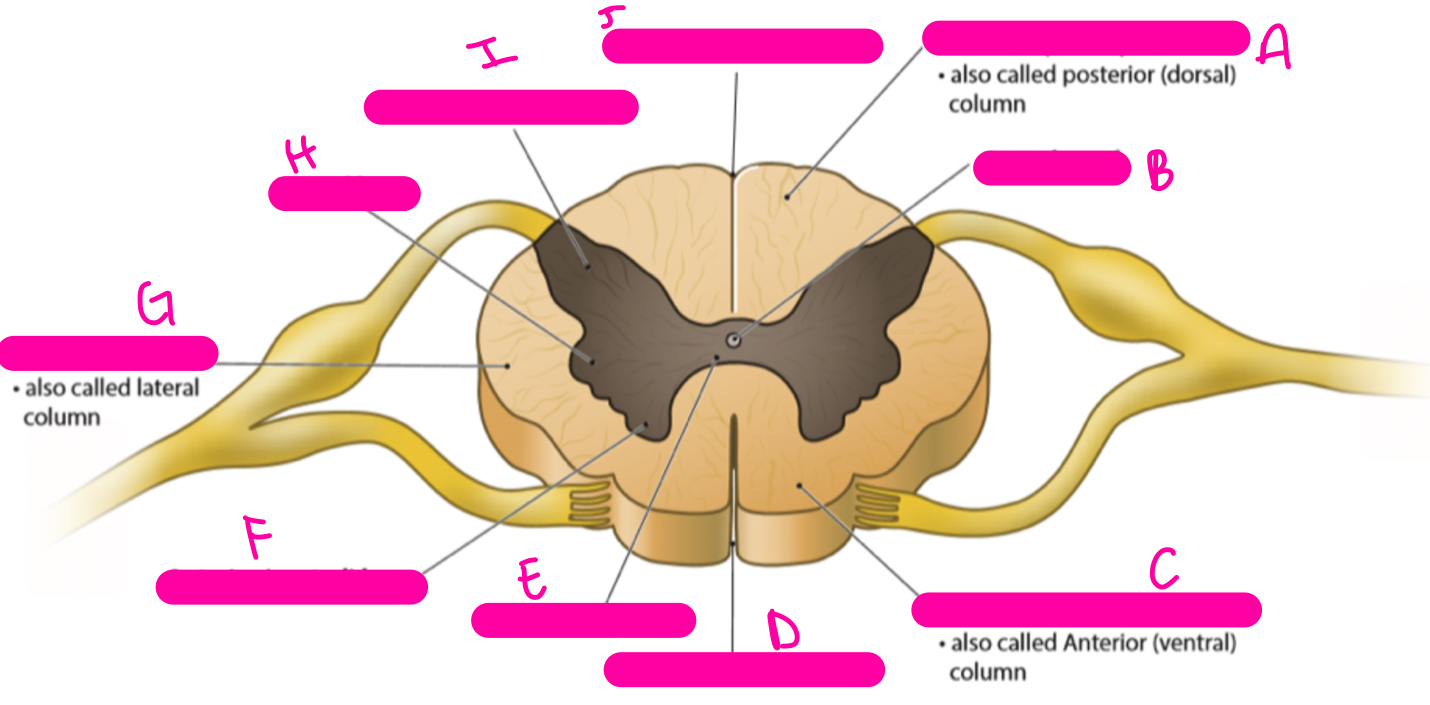
D
anterior median fissure