Vibrio, Aeromonas, Plesiomonas, and Campylobacter Overview
1/145
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
146 Terms
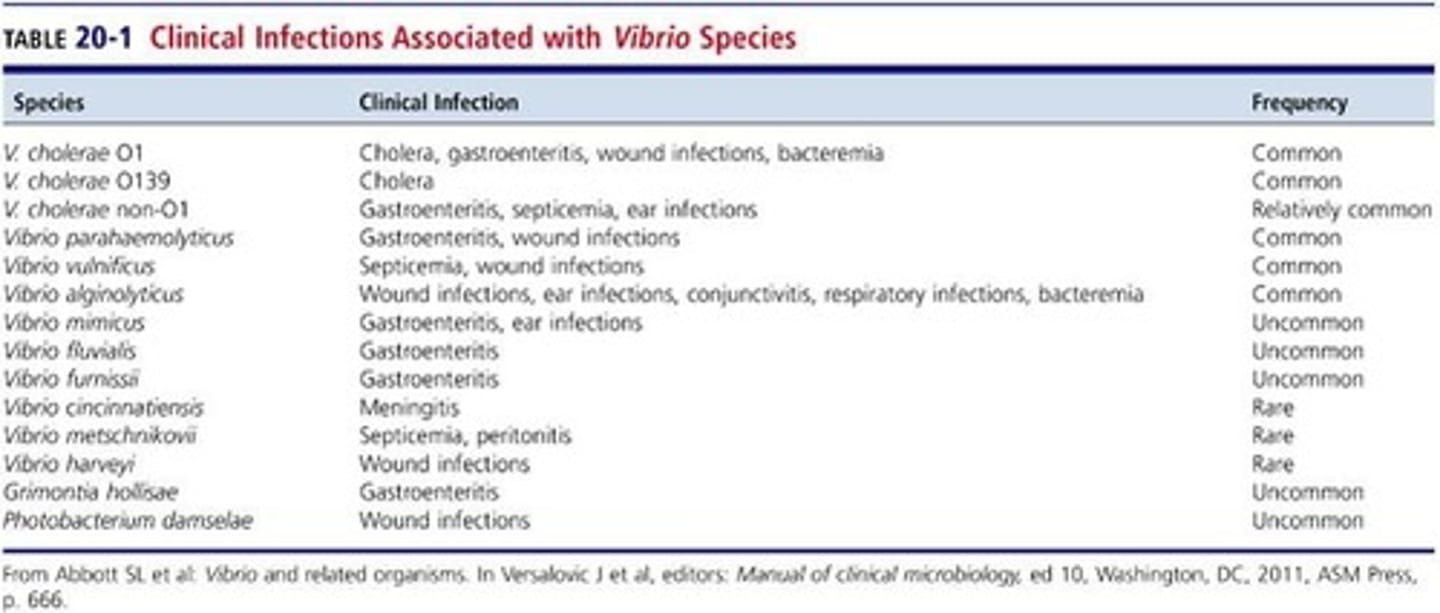
Vibrio species
10 species involved in human infections.
Habitat of Vibrio
Found in fresh, brackish, and salt water.
Temperature preference
Prefers warmer water environments.
Epidemic involvement
Usually associated with cyclical epidemics.
Vibrio cholerae
Causative agent of cholera disease.
Vibrio parahemolyticus
Commonly associated with seafood-related infections.
Vibrio vulnificus
Linked to severe infections from seafood.
Vibrio alginolyticus
Associated with marine environments and infections.
Isolation increase factors
Rising ocean temperatures and seafood consumption.
Risk factors for infection
Raw seafood consumption, travel, and trauma.
Gastroenteritis symptoms
Cholera-like or rice-water stools observed.
General characteristics
Facultatively anaerobic, gram-negative, small rods.
Size of Vibrio
1.4 to 2.6 µm long.
Morphology
Pleomorphic shapes, curved in Gram stain.
Biochemical tests
Catalase and oxidase positive, nitrate reduction.
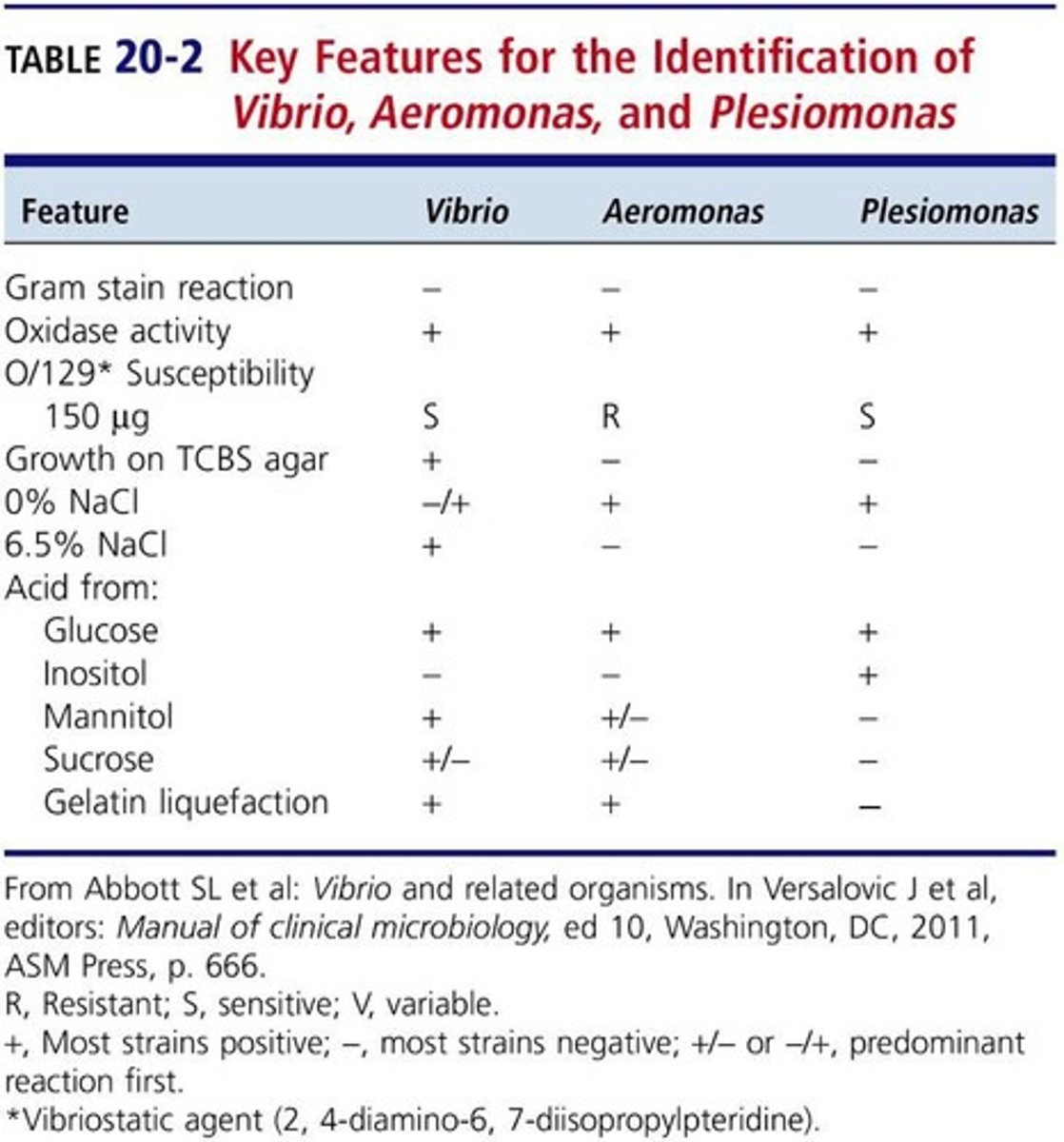
Vibriostat disk
Used to differentiate Vibrio from others.
O/129 susceptibility
Separates Vibrio from Aeromonas and Plesiomonas.
String test
Identifies Vibrio by emulsifying colonies.
Halophilic nature
Most Vibrio species are salt-loving.
V. cholerae subgroups
Three major subgroups with common antigens.
Epidemic cholera serotypes
V. cholerae O1 and O139 are epidemic.
Epidemiology of cholera
Seven pandemics since 1817, last in 1975.
Cholera in the US
Last outbreak occurred 1910-1911.
Common cholera regions
Bengal region of India and Bangladesh.
Imported cholera cases
Most US cases considered imported.
Infection prevention
Quarantine measures historically used to control outbreaks.
Recreational water exposure
Increased risk of Vibrio infections.
Immunocompromised population
Higher susceptibility to Vibrio infections.
Clinical specimen isolation
Low frequency except in coastal areas.
Cholera
Bacterial infection causing severe diarrhea and dehydration.
2010 Haiti Earthquake
Natural disaster affecting 3 million people.
Artibonite River
Major drinking water source in Haiti.
Nepalese UN Peacekeepers
Stationed in Haiti during cholera outbreak.
Fecal Contamination
Primary cause of cholera outbreak in Haiti.
Cholera Symptoms
Rice-water stool and large fluid loss.
Hypovolemic Shock
Condition from severe fluid loss.
Cholera Toxin
Causes diarrhea by stimulating cAMP production.
cAMP
Cyclic adenosine monophosphate, increases fluid secretion.
Cholera Transmission
Spread through contaminated water and food.
V. cholerae O1
Most common strain causing cholera outbreaks.
V. cholerae O139
Causes cholera outbreaks in India and Bangladesh.
V. cholerae non-01
Non-toxigenic strain causing milder gastroenteritis.
V. parahaemolyticus
Bacteria causing summer diarrhea from seafood.
Serotype O3:K6
Major cause of foodborne outbreaks worldwide.
Kanagawa Phenomenon
Heat-stabile hemolysin associated with V. parahaemolyticus.
Self-limiting Diarrhea
Watery diarrhea resolving without treatment.
V. vulnificus
Lactose-positive Vibrio causing severe infections.
Septicemia
Blood infection with high mortality rate.
Specimen Collection
Collect fluids, pus, tissues for Vibrio testing.
Cary-Blair Medium
Transport medium preventing desiccation of samples.
Raw Seafood Risk
Source of V. vulnificus infections.
Electrolyte Loss
Significant loss during cholera infection.
Diarrhea Frequency
10-30 movements per day in cholera.
Dehydration Treatment
IV and oral fluids with electrolytes.
Antibiotic Resistance
Reported resistance to tetracycline and doxycycline.
Extraintestinal Infections
Wound, eye, ear infections from V. parahaemolyticus.
Marine Animal Association
V. parahaemolyticus linked to 30 species.
Vibrio Species
Bacteria primarily found in aquatic environments.
Blood Agar Plate (BAP)
Culture medium suitable for Vibrios.
MacConkey Plates
Selective agar for Gram-negative bacteria.
Lactose Negative
Characteristic of most Vibrio species except V. vulnificus.
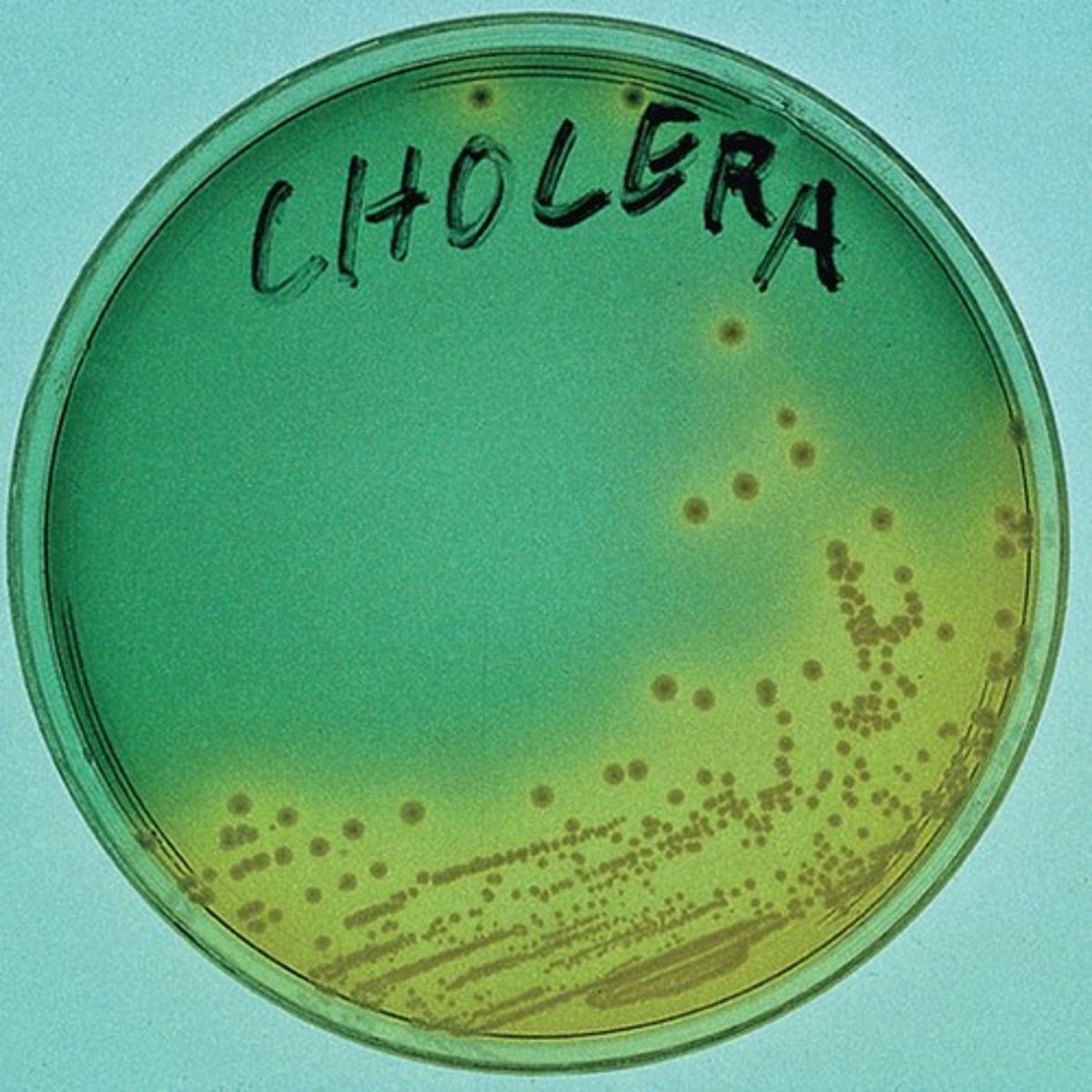
Thiosulfate-Citrate-Bile Salts-Sucrose (TCBS)
Medium for isolating Vibrio species.
V. cholerae
Causes cholera, appears yellow on TCBS.
V. parahaemolyticus
Green on TCBS, associated with seafood.
Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
Evaluates bacteria's resistance to antibiotics.
Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI)
Sets standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing.
Doxycycline
Commonly effective antibiotic against Vibrio species.
Ciprofloxacin
Fluoroquinolone effective against Vibrio infections.
Aeromonas
Gram-negative rods, oxidase positive, glucose fermenting.
Mesophilic Aeromonas
Optimal growth at 37°C, includes A. hydrophila.
Psychrophilic Aeromonas
Optimal growth at 22°C, includes fish pathogen.
Gastroenteritis
Infection causing diarrhea, often from contaminated water.
Acute Secretory Diarrhea
Diarrhea with watery stools, often viral or bacterial.
Cholera-like Disease
Presents with rice-water stools, similar to cholera.
Wound Infection
Infection from injuries in contaminated water.
Septicemia
Blood infection, can be caused by A. veronii.
Osteomyelitis
Bone infection, can be caused by Aeromonas.
Indole Positive
Characteristic of most clinically relevant Aeromonas species.
String Test Negative
Differentiates Aeromonas from Vibrio species.
Plesiomonas
Similar to Aeromonas, grows well in 0% NaCl.
Inositol Negative
Aeromonas does not ferment inositol.
Trimethoprim/Sulfamethoxazole
Effective against Aeromonas infections.
A. hydrophila
Commonly associated with wound infections and gastroenteritis.
A. veronii
Associated with septicemia in immunocompromised patients.
Beta Hemolysis on SBA
Characteristic of Aeromonas hydrophila on sheep blood agar.
Lactose Fermentation
Aeromonas caviae can ferment lactose on MAC.
Plesiomonas
Gram-negative rod, formerly in Vibrionaceae.
Enterobacteriaceae
Family of bacteria including Plesiomonas.
Gram-negative
Bacteria with thin peptidoglycan layer.
Oxidase positive
Indicates presence of cytochrome c oxidase.
Glucose fermenting
Can metabolize glucose without gas production.
Facultatively anaerobic
Can grow with or without oxygen.
Motile
Capable of movement, often via flagella.
Vibriostat (O/129) disks
Used to test susceptibility of Plesiomonas.
Gastroenteritis
Inflammation of stomach and intestines.
Watery diarrhea
Common symptom of Plesiomonas infection.
Dysenteric form
Severe diarrhea resembling colitis.
Inositol brilliant green bile salts (IBB)
Special media for culturing Plesiomonas.
Lactose fermenter
Ability to ferment lactose, distinguishes bacteria.
High salt tolerance
Vibrio species grow in high salt concentrations.