Chem Unit 1
1/48
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
atomic structure
protons and neutrons form nucleus, electrons orbit the nucleus
atomic number
the number of protons
atomic mass
the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus
average atomic mass
the average atomic mass of all known atoms of that element; most stable with a mass of the nearest whole number
unit for atomic mass
amu
ion
atom with a charge (# electrons ≠ # protons)
cation
positively charged ion (more protons than electrons)
anion
negatively charged ion (more electrons than protons)
isotope
atoms that have the same number of protons, but have a different number of neutrons
nuclear notation
mass number on top left, atomic number on bottom left, element symbol on the right
how to calculate average atomic mass
add (percent abundance) * (mass) for each isotope
Schrodinger
developed quantum wave equation
Bohr
found that electrons move in specific orbits around the nucleus
Chadwick
discovered neutrons
Dalton
created dalton atomic theory
Rutherford
gold foil experiment; proposed protons & neutrons are in the nucleus of an atom
Thomson
plum pudding model; discovered electrons
nuclear fission
splitting of nucleus into smaller fragments, releasing energy
example of nuclear fission
nuclear power plants
nuclear fusion
light mass nuclei combine together and releases more energy than fission
example of nuclear fusion
hydrogen bomb, sun
nuclear half life
time required for half the atoms of a particular radioisotope to decay into another isotope
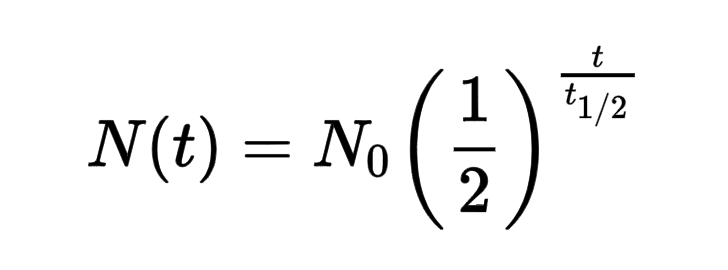
alpha decay
emits helium
beta decay
emits an electron
gamma decay
emits energy with no charge or mass
positron/beta plus decay
emits positron (positive electron)
neutron emission
neutron emitted
band of stability
line showing where elements are most stable (neutrons vs protons)
where do you undergo beta decay
elements above the band of stability
where do you undergo positron decay
elements below the band of stability
when do you undergo alpha decay
when the element has more than 82 protons
electromagnetic spectrum
range of all types of radiation
what type of radiation has the longest wavelength and lowest frequency
radio
what type of radiation has the shortest wavelength and highest frequency
gamma
what happens when the electrons of an element is heated up?
the electrons get excited and jump up an energy level, when they fall back down light is produced
what are the orbitals and how many electrons can they hold
s (2 electrons), p (6 electrons), d (10 electrons), f (14 electrons)
aufbau principle
electrons enter lowest energy orbitals first
pauli exclusion principle
atomic orbital may have up to 2 electrons, spins must be paired in opposite directions
hund's rule
fill orbitals halfway first, then pair electrons
what are exceptions to electron configuration?
silver and chromium have the s and d swapped at the end
atomic radius
how large the radius of an atom is (how big the atom is)
atomic radius trend
increases as you go down, decreases as you go across
proton pulling
as protons increase, they pull the electrons closer to the nucleus
ionization energy
the amount of energy required to remove a valence electron
electron shielding
outer electrons have less of an attraction to the nucleus because the inner electrons “shield” them
ionization energy trend
decreases as you go down, increases as you go across
electronegativity
ability of an atom to attract an electron
electronegativity trend
decreases as you go down, increases as you go across, noble gases have an electronegativity of 0
what element is the most electronegative?
fluorine