simplified midterm diagrams
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
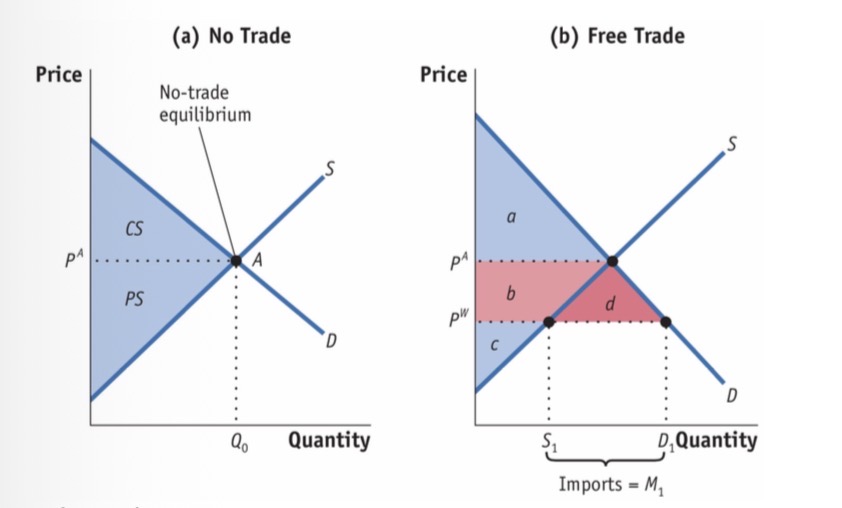
Basic gains of trade
CS: a+b+d
PS: c
HW: a+b+c+d
import demand curve
Determined by home market (small OR the other country) ‘s no trade equilibrium and the (D1-S1=M1)
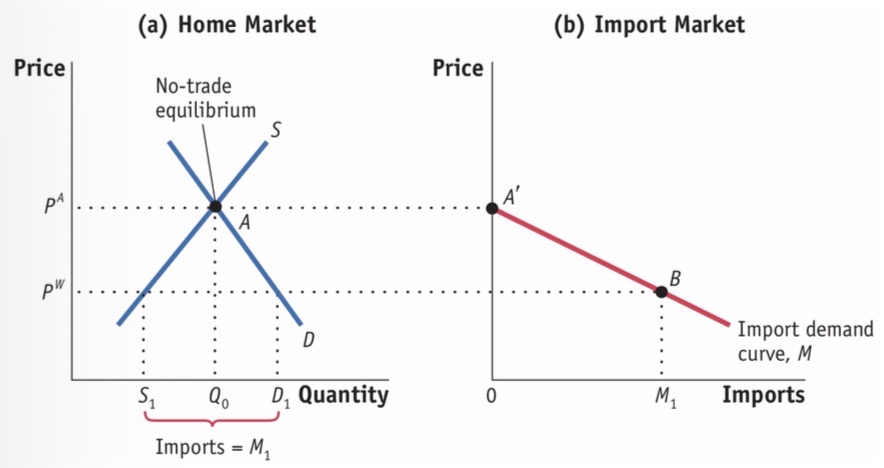
Foreign export supply curve
Determined by large / foreign country’s no trade equilibrium and the world price
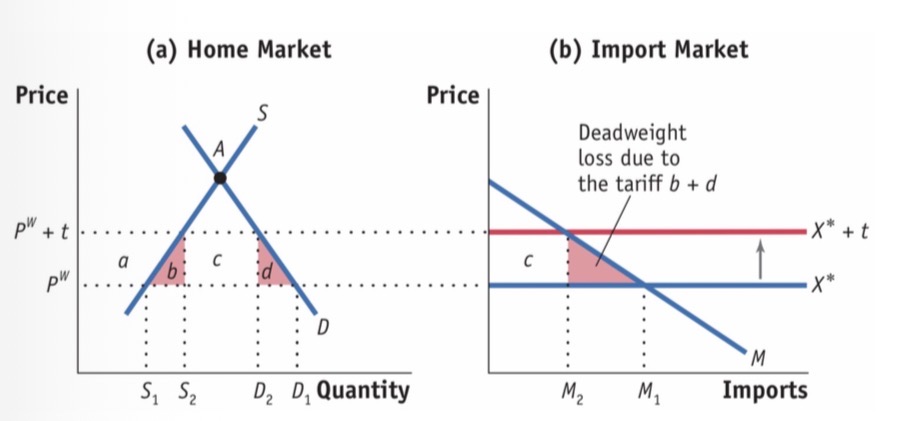
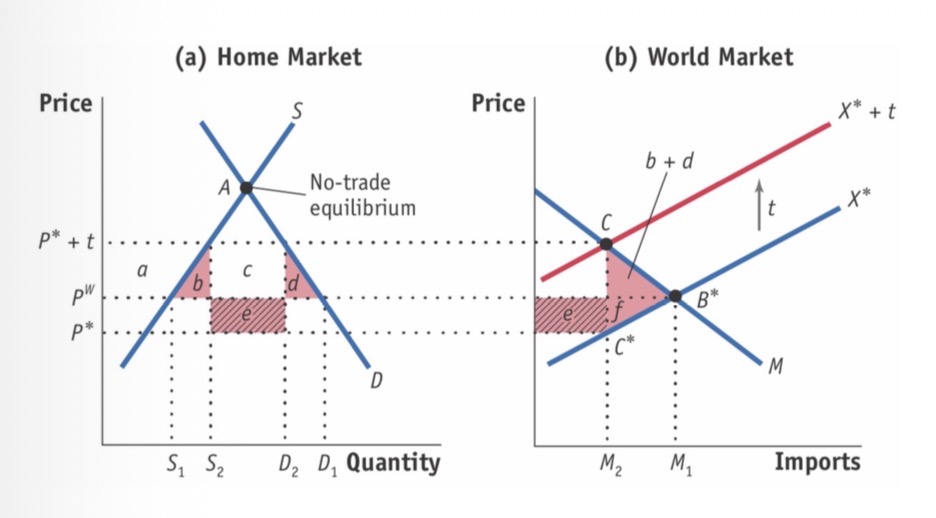
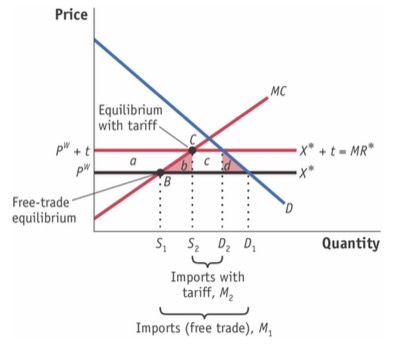
Smal country tariff
Small country so flat export supply curve
X* shifts up to X* + t
CS: - (a+b+c+d)
PS: + a
GR: + c
HW: -(b+d)
Large country tariffs
Large country so non-flat foreign supply
CS: -(a+b+c+d)
PS: +a
GR: + (c+e)
HW: + e -(b+d) if e>(b+d), benefit.
Optimal tariff
t = 1/E*x
Small country optimal tariff
E*x is infinite hence t must be = 0
Large country optimal tariff
E*x < infinite, as E*x decreases, the optimal tariff is higher. Since low elasticity = low fall in import demand
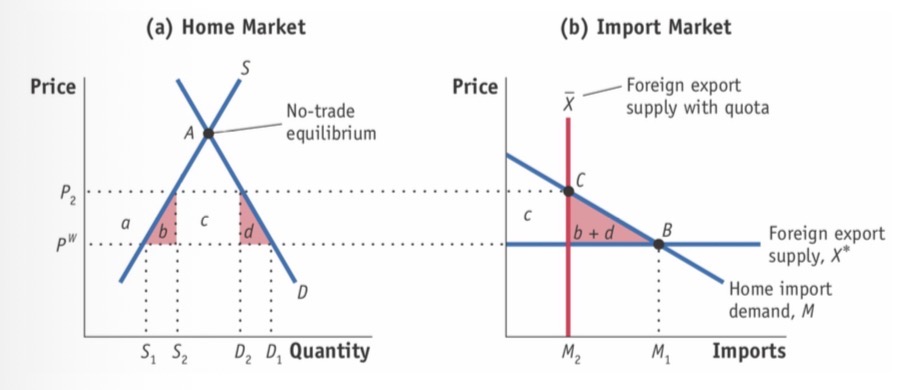
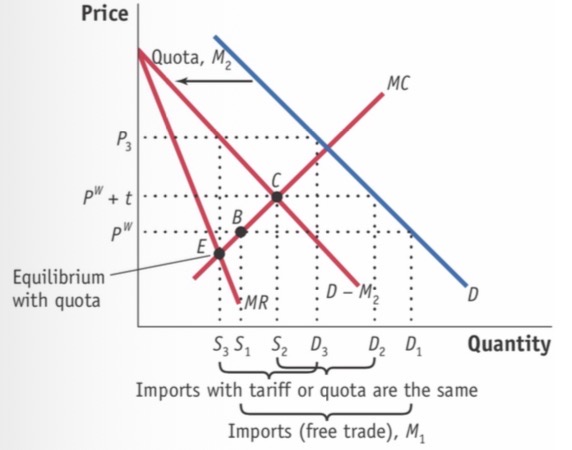
Import quota small & large
Home is assumed small, quota is imposed by world/foreign
Vertical supply curve with quota
CS: - (a+b+c+d)
PS: + a
QR: +c
HW: - (b+d)
Equivalent effect with tariff
Quota rents
Quota licenses can be given to Home firms, which are then able to import at the world price p" and sell locally at P2, earning the differences between these as rents.
Rent seeking
Rent seeking occurs when firms engage in inefficient activities to obtain quota licenses. (e.g. a firm produce more batteries to obtain the import licenses for the chemicals the following years). If rent seeking occurs, the welfare loss due to the quota would be:
Auctioning the quota
when the govt of the importing country auctions off quotas licenses to foreign firms. The revenue collected should equal the value of the rents so that area c is earned by the govt.
VER
Voluntary export restraint
to avoid quota/tariff war
Importer still loses more than exporter but is a political tool
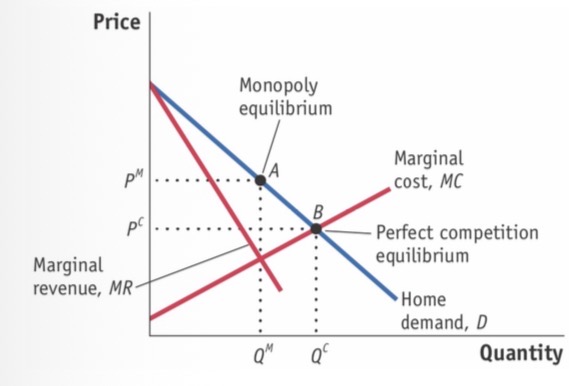
Home monopoly (imperfect) diagram
ME is where MC=MR
PCE is where MC=Dhome
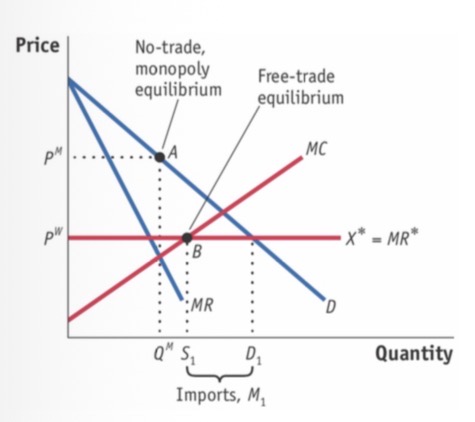
Free trade monopoly equilibrium
F-TE is where MC=X*
Home = small country, hence X* is flat
Monopoly equilibrium + tariff (small country)
X* shifts up
CS: -(a+b+c+d)
PS: +a
Auction revenue/quota rents?: +c
HW: -(b+d)
Monopoly equilibrium + quota (small country)
MR becomes non-flat cause quota
Shifts D backwards by quota size
Even when t=quota in terms of import change, quota means less output, means less employment
Dwl quota > dwl tariff as monopolists charge higher p
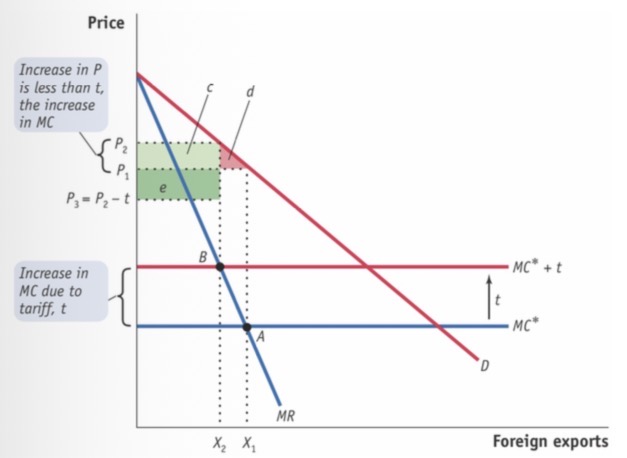
foreign Monopoly equilibrium + tariff
D is entirely supplied by foreign
MC* is the supply curve
MC* shifts upwards
CS: -(c+d)
GR: + (c+e)
HW: +(e-d)
Monopoly equilibrium foreign country
Exports at MC*=MR
Sells locally at local MR & P*
Since AC < P*, but higher than P, dumping
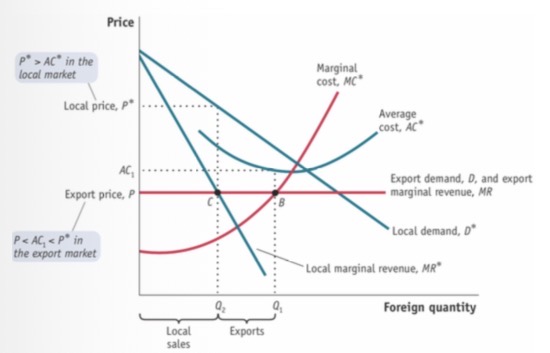
Dumping
If the average cost AC < local price P* but > export price P, must be dumping since they’re selling at a unprofitable price & are hence trying to just get rid/ sell cheap
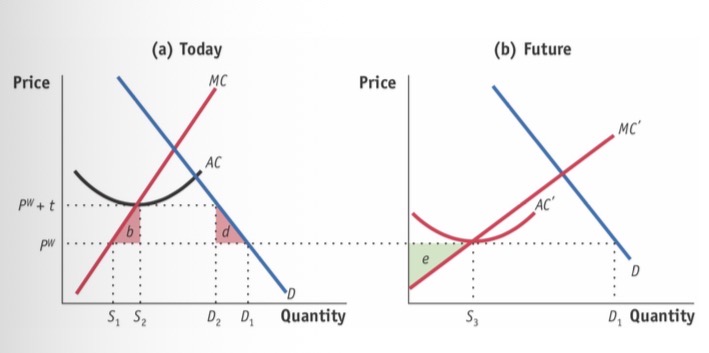
Infant industry protection
Technological advances based:
Set up import tariff (not quota as it would just mean less production and no progress) which allows industry time to advance technologically, hence reduce price and hence minimise/erase shutdown/losses.
Only works if tariff can be removed
PS future must > than current dwl