Chemistry-Nuclear Reactions
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
7 Terms
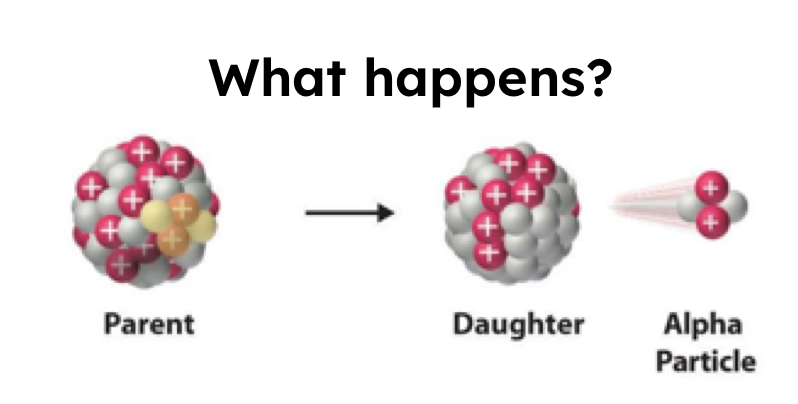
Alpha Decay
4/2 (fish) or 4/2 He
Too big and too unstable nucleus
1 reactant —> 2 products
Protons and neutrons decrease
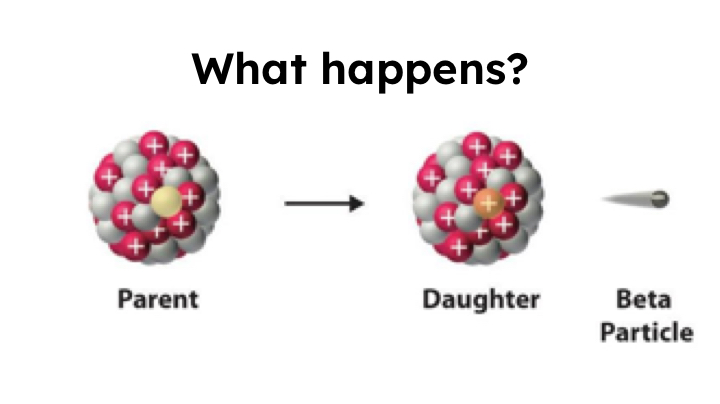
Beta Decay
0/-1 e or 0/-1 B
Too many protons to be stable, so an electron is ejected from the nucleus. A neutron converts to a proton.
1 reactant —> 2 products
Protons increase, neutrons decrease
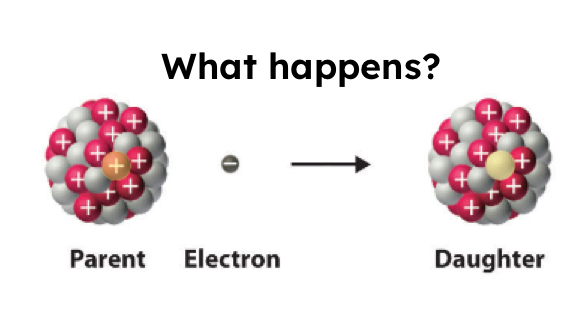
Electron Capture
Too many protons in the nucleus, so a proton captures an electron. This changes the proton to a neutron.
2 reactants —> 1 product
Protons decrease, neutrons increase.
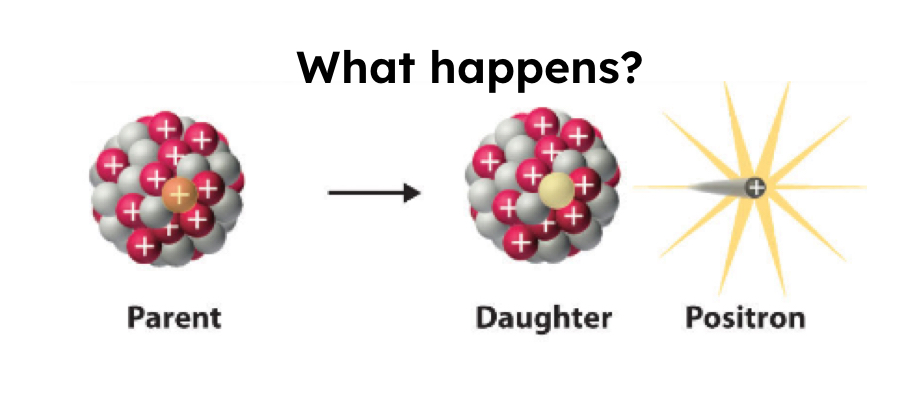
Positron Emission
0/+1 e or 0/+1 B
Too many protons, so a POSITIVE electron is ejected from the nucleus to change it to a neutron (antimatter, negative electron flips charge)
1 reactant —> 2 products
Protons decrease, neutrons increase.
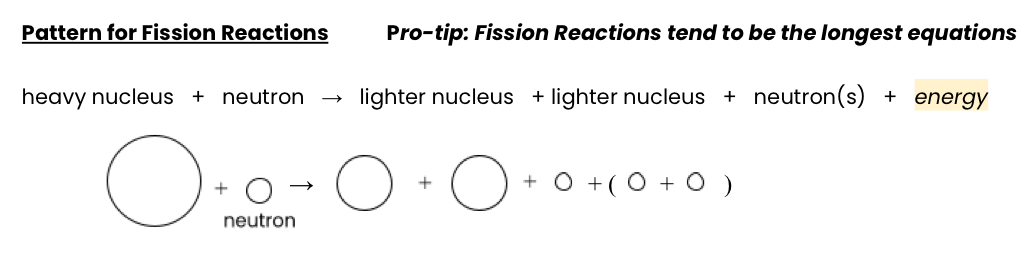
Fission
Large nuclei split into smaller nuclei of equal size
Used in atomic bombs and power plants
Releases tremendous amounts of energy
Occurs because nucleus is too large and too unstable
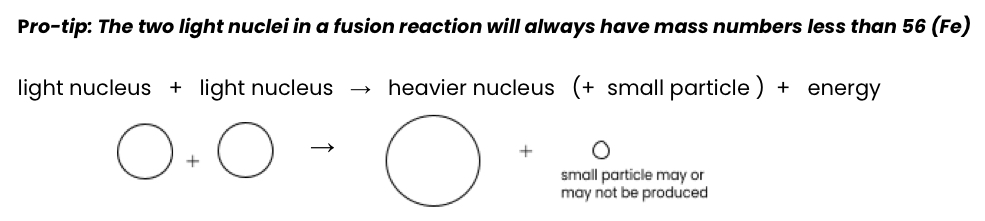
Fusion
Two smaller nuclei combine to make a bigger nucleus
Found in the stars and the sun
Produces the most energy out of all the reactions (High temp required)
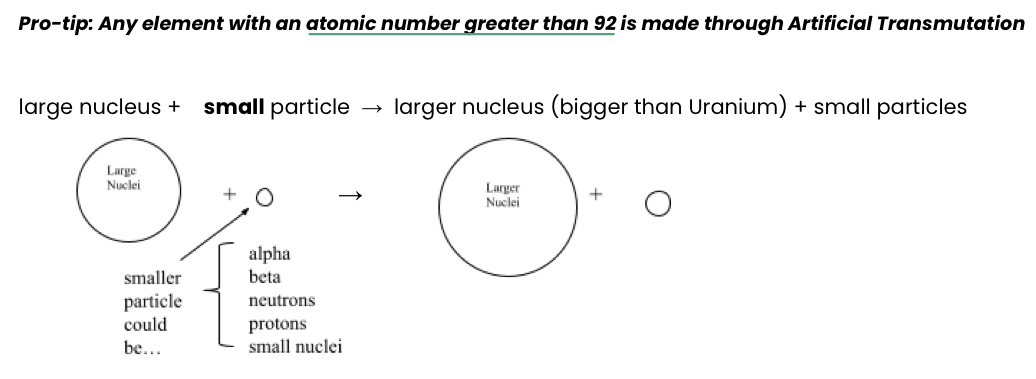
Artificial Transmutation
The process that mimics the natural fusion process on the sun to create new elements
A large nucleus is bombarded by a smaller nucleus
Any element with atomic number >92 is made through this process