CSLC 1- Ch. 3
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
Mutual Intelligibility
refers to the ability of speakers of two different languages or dialects to understand each other without having to learn the other's language.
Dialect Continuum
An interconnected group of geographically adjacent or historically related variants, some of which are mutually intelligible to different speakers, whereas others, over time, have become less comprehensible.
Dialect Atlases
a collection of maps of specific regions recording their actual speech features.
Pidgins and Creoles
Pidgins: Usually, it is the language of a colonizer that an indigenous denizen must learn, creating the pidgin as an adaptation of the colonizer’s language.
Creole: Pidgins that are passed down until they become native language are turn into creole.
Lingua Francas
A language conventionally, rather than casually, used to make communication possible among people not sharing the same native language.
Ex. English
Diglossia
refers to a linguistic situation in which two distinct varieties of a language are used by a community, but in different social contexts or for different purposes
Code Switching
Bilinguals often display a peculiar conversational habit—switching between their two codes as they communicate.
Types
Intersentential → Separate sentences.
Intrasentential → Within sentences.
Function
Fill conceptual gaps.
Allegiance to group.
Languages in Contact
phenomenon that occurs when speakers of different languages come into contact with each other.
Borrowing, Loan Words, Necessary Loans, Luxury Words, and Calquing
Borrowing → Refers to the taking-in and incorporation of the lexemes of another language into one’s own native lexicon.
Loan Word → Words that are borrowed.
Necessary Loans → Fill a gap in language.
Luxury Loans → Socially advantageous reason
Calquing → Phrases that have been translated literally from the source language.
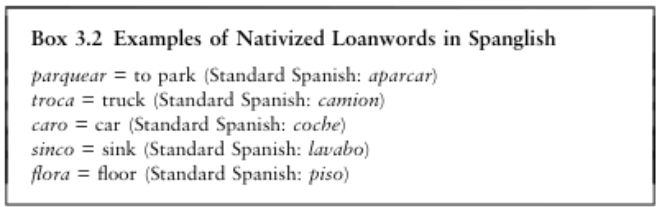
Nativization
The unconscious process of shaping the foreign lexeme to sound like a native one.
Language Loyalty
The continued usage of the local dialect for reasons of cultural solidarity, in the face of social, cultural, and linguistic change.
Language Planning
Refers to the kinds of measures taken by official (usually governmental) agencies to preserve the standard language for formal communications.
• Status Planning– Government policies ensuring the dominance of a standard
language
• Corpus Planning– Official efforts to refine and regulate the language (e.g.,
dictionaries)
• Language-in-Education Planning– Promoting the language through education
policies
• Prestige Planning– Encouraging public acceptance of the standard language (e.g.,
media campaigns)
• Revitalization & Maintenance– Policies for preserving indigenous or minority
languages
Pure Literacy and Functional Literacy
PL: Ability to read and write a language.
FL: it is the ability to use a language for knowledge-based and various intellectual purposes.