1- Orthodontics concept
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
What does the concept of orthodontics deal with?
Growth of facial cranial complex, development of dentition and occlusion, treatment of anomalies
Etymology of orthodontics?
Ortho- right/straight
Odonto- tooth
In the German/ + - system how do you identify teeth?
+ on upper
- on lower
Sign on side it’s part of
0 before primary dentition
What are the 4 categories included in malocclusion?
Overcrowded teeth
Space between teeth
Improper bite
Disproportionate size and alignment
What are the 3 classifications of malocclusion?
Intra arch
Inter arch
Skeletal
What does an intra arch malocclusion involve?
Inclination, displacement, rotation, transposition of individual tooth
What is inclination and the types?
Abnormal tilting of the crown, if apex in same point but tooth surface position changes
Buccal, lingual, mesial, distal
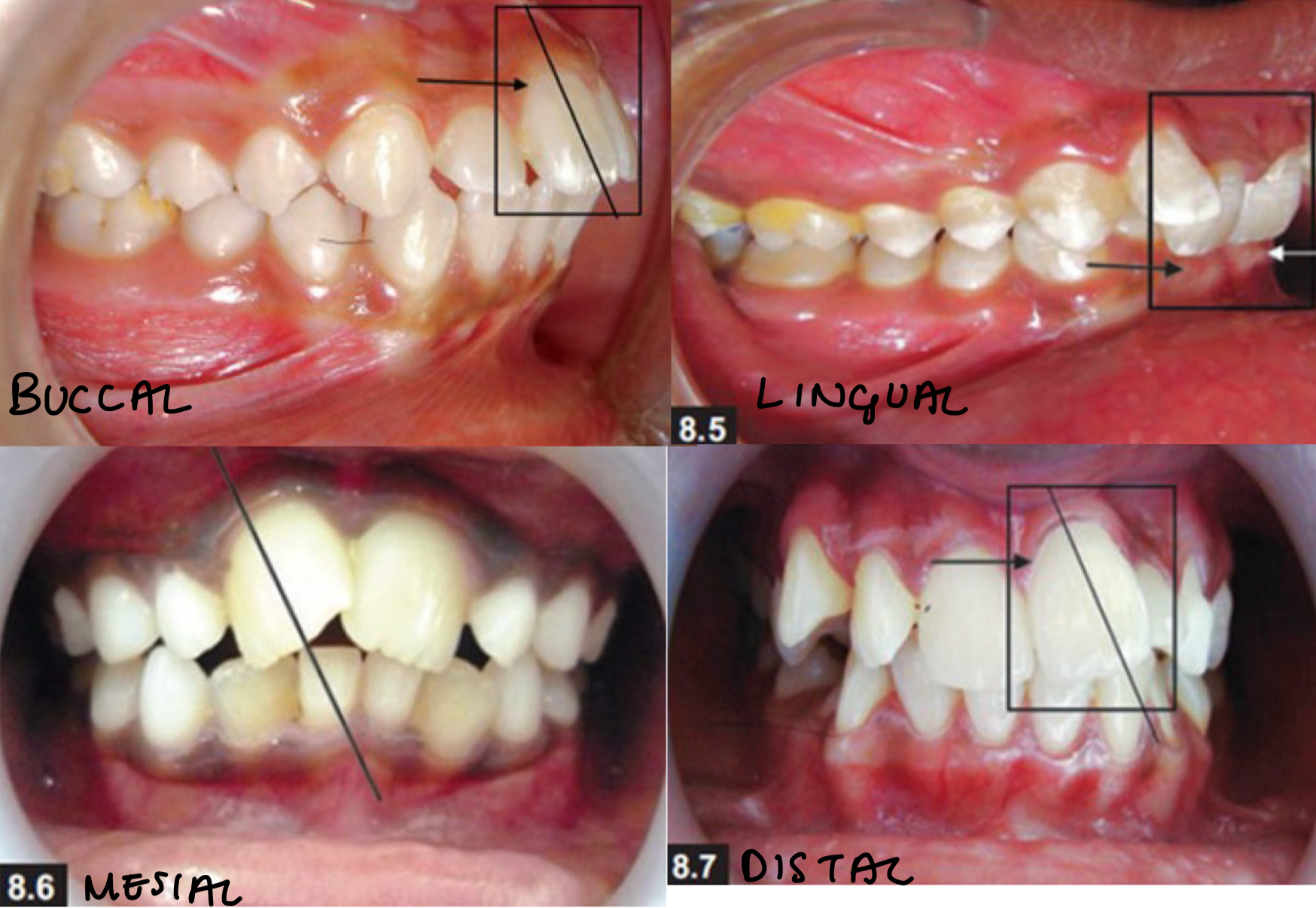
What is displacement?
Bodily movement of crown, apex position changes
Buccal, lingual, mesial, distal
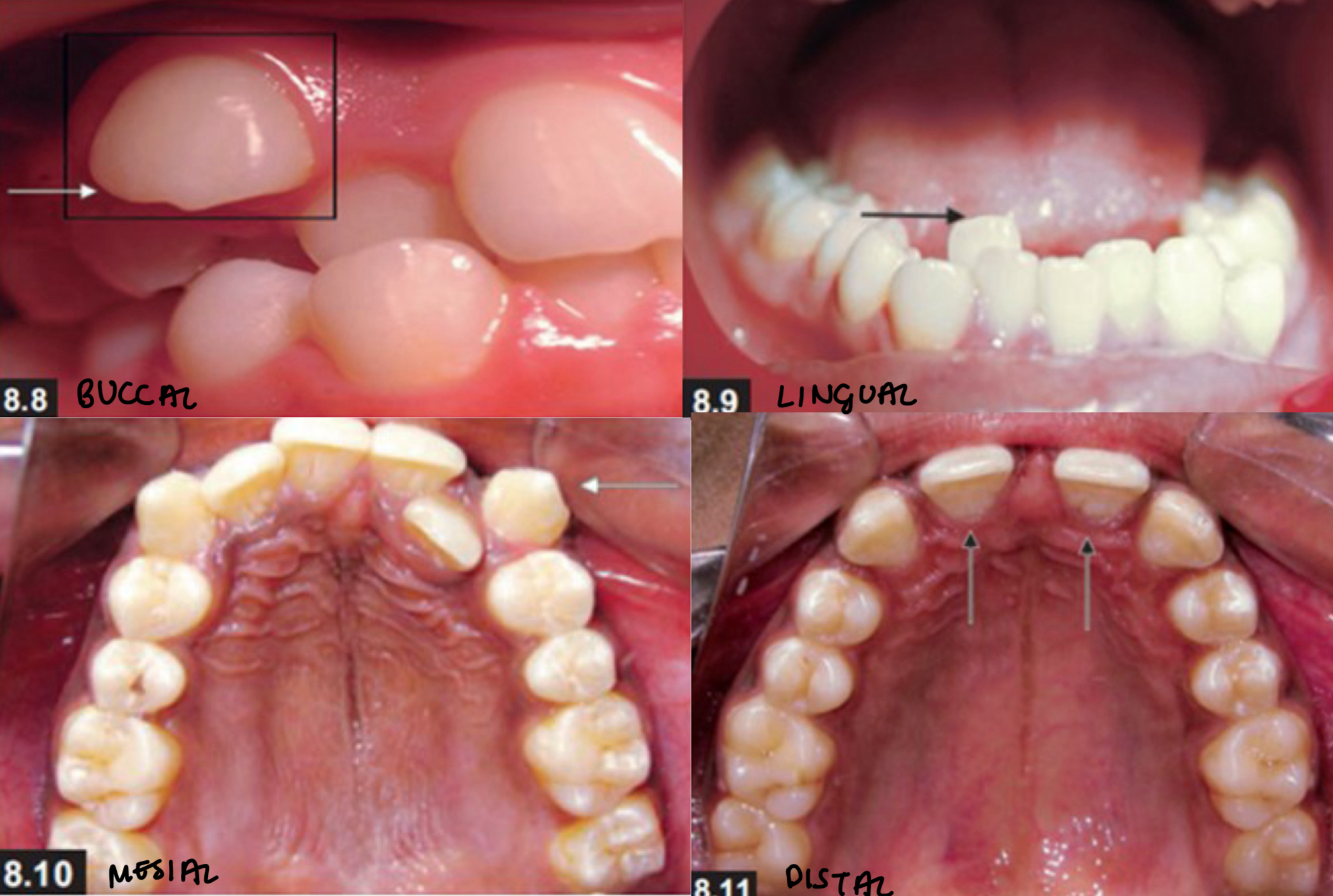
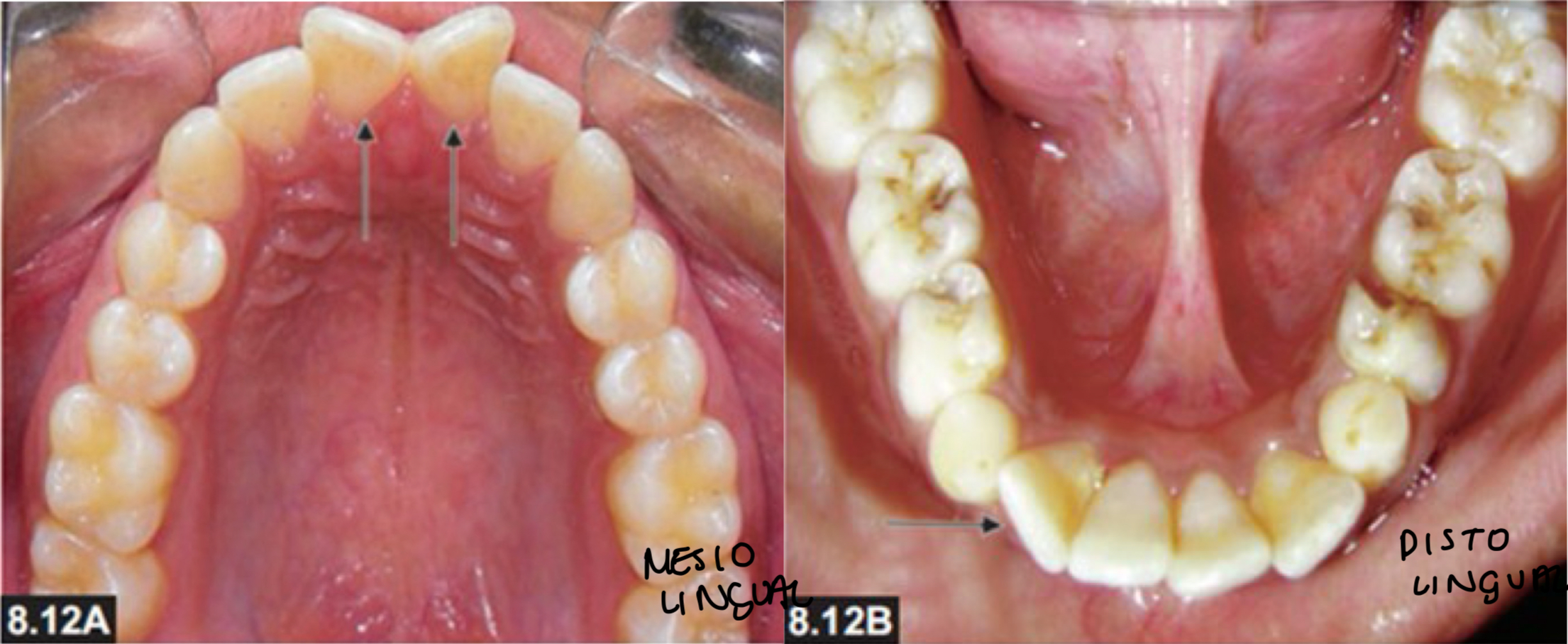
What is rotation and the types?
Movement of tooth around its long axis- described in 2 ways depending on which surface
Mesiolingual (distolabial)
Distolingual (mesiolabial)
What is transposition?
Two teeth swapped position
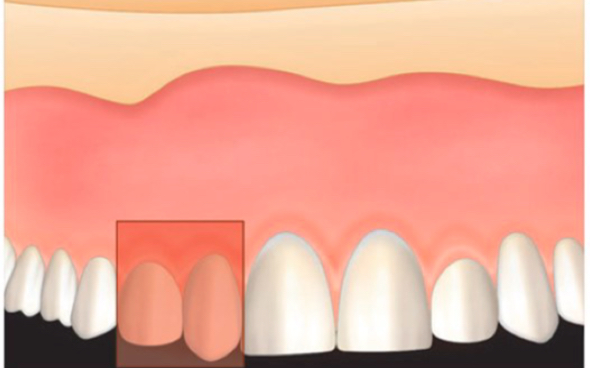
What is infra/supraversion (intrusion,extrusion)?
Tooth not at level of occlusion
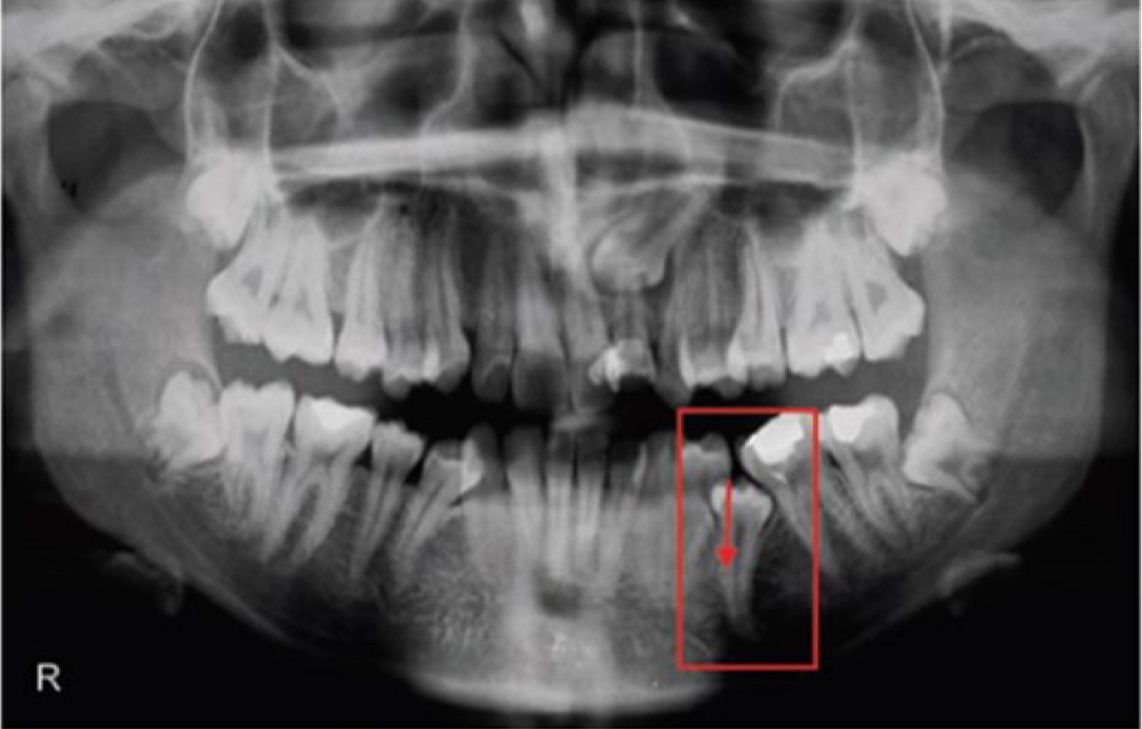
What are the 3 types of inter arch malocclusions?
Sagittal, vertical, transverse plane
In the sagittal plane malocclusions, what is the difference between pre and post normal occlusion?
Mandible more anterior in centric occlusion vs more posterior
(Maxilla in fixed position)
What is the relationship between molars in the sagittal plane?
Mesiobuccal cusp of upper 1st molar falls in buccal groove of lower 1st molar
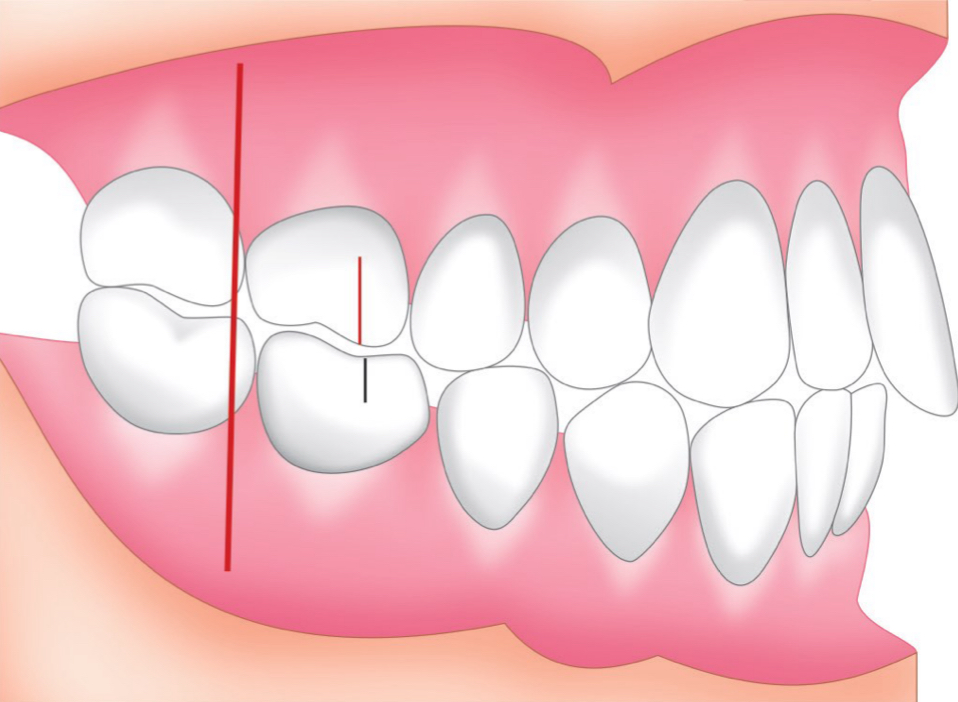
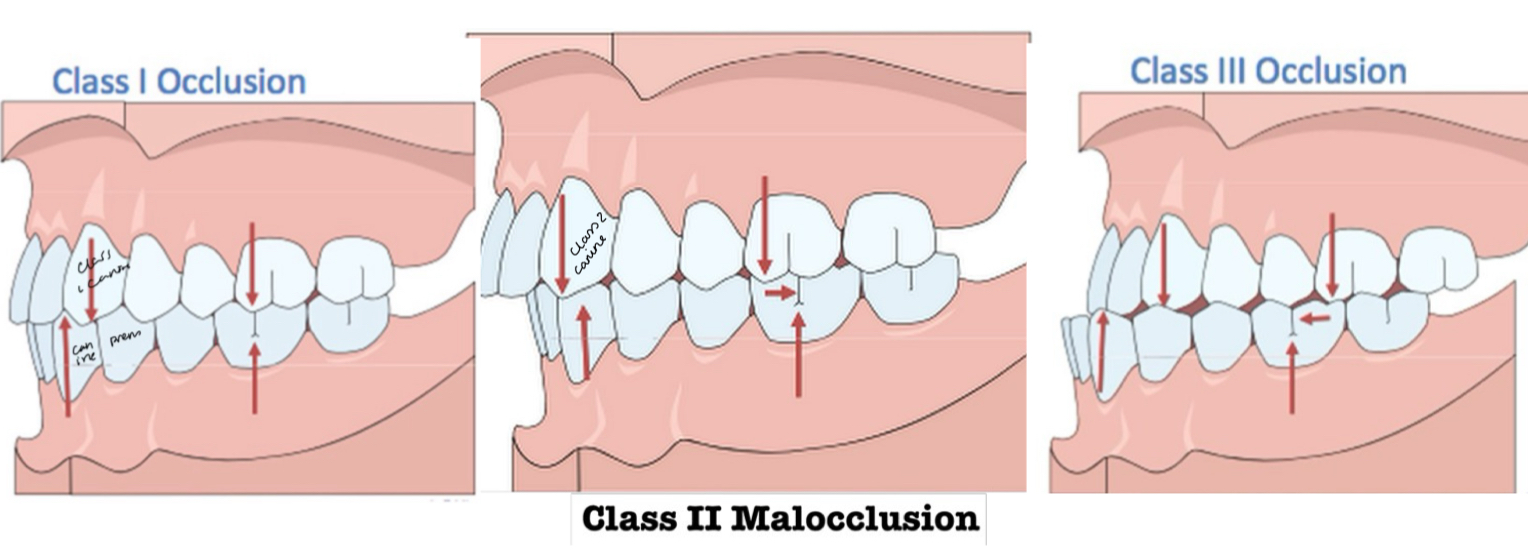
what is the difference between class angle 1, 2 and 3 malocclusions?
Mesiobuccal cusp of upper 1st molar falls within vs in front of vs behind the Buccal groove of the lower 1st molar
What are the types of vertical plane (interarch and skeletal) malocclusions?
Deep bite
Open bite
Anterior open bite
Posterior- uni or bilateral open bite
What are the 2 types of transverse plane (interarch and skeletal) malocclusions?
Crossbite- teeth are misaligned but they contact
Scissor bite- teeth don’t contact
What can skeletal malocclusions be caused by vs interarch malocclusions?
Defects in size, position or relationship between jaws vs is how the teeth fit together
What do skeletal malocclusions in the sagittal plane present as?
Prognathism- forward placement of the jaw
Retrognathism- backward placement
Both can occur
What are the aims of orthodontic treatment?
Functional efficiency- chewing, speech
Structural balance- consider soft tissues and associated structures
Aesthetic balance
Makes up Jackson’s triad
What are the branches of orthodontics?
Preventive- before onset of malocclusion- parent eduction, caries control, care of temp teeth
Interceptive- in early stage to lessen severity
Corrective- after, need appliance
What are 6 preventive orthodontic procedures?
Space maintainers
Manage ankylosis and prolonged retention of temp teeth
Extract supernumerary teeth
Manage oral habits
Treat premature contacts
Abnormal frenums- diagnose with blanch test and notch like radiolucency between max ci
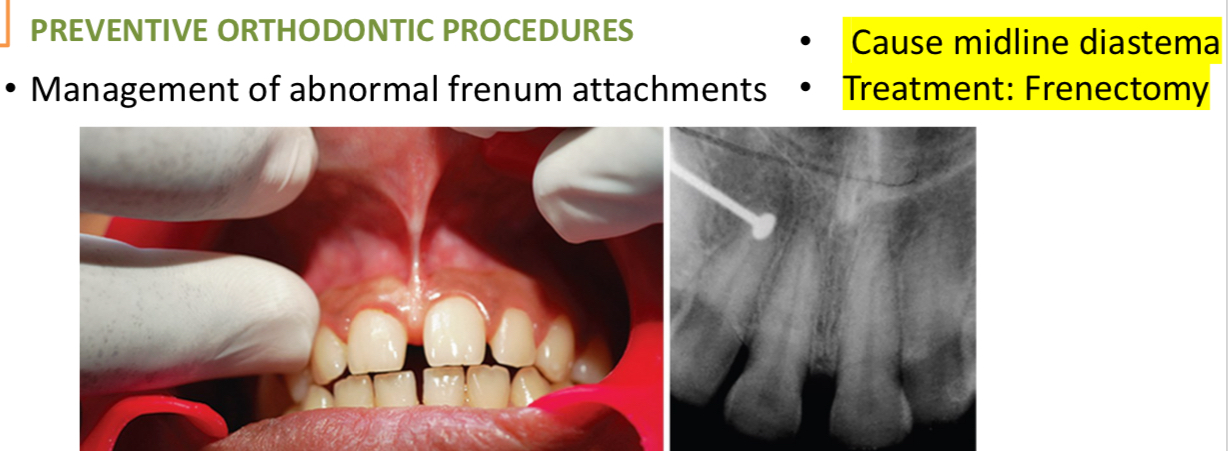
What is interceptive orthodontics?
Serial extraction
Correcting a developing anterior crossbite
Eliminate bony or tissue barriers of erupting teeth
What is needed for an orthodontic appliance and what are the types?
A good diagnosis
Removable
Fixed- need multiple movements for correction
Functional- mandible away from normal resting position, uses forces of circumoral muscles
Orthopedic/extraoral force appliance