OSCE
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
Method/technique: Bristles are directed apically at 45 degrees (up for maxillary and down for mandibular) to long axis of tooth, mostly it is difficult to place at 45 degrees so placing parallel to teeth is also beneficial
Now press the bristles slightly so that they enter the gingival sulcus and embrasures.
Vibrate the brush back and forth with short strokes for 10-15 strokes for each position and move to the next teeth
bass
Method/technique: Bristles are directed apically at 45 degrees (up for maxillary and down for mandibular) to long axis of tooth, mostly it is difficult to place at 45 degrees so placing parallel to teeth is also beneficial
Now press the bristles slightly so that they enter the gingival sulcus and embrasures.
Vibrate the brush back and forth with short strokes for 10-15 strokes for each position and move to the next teeth
END WITH A MOTION ROLLING CORONALLY
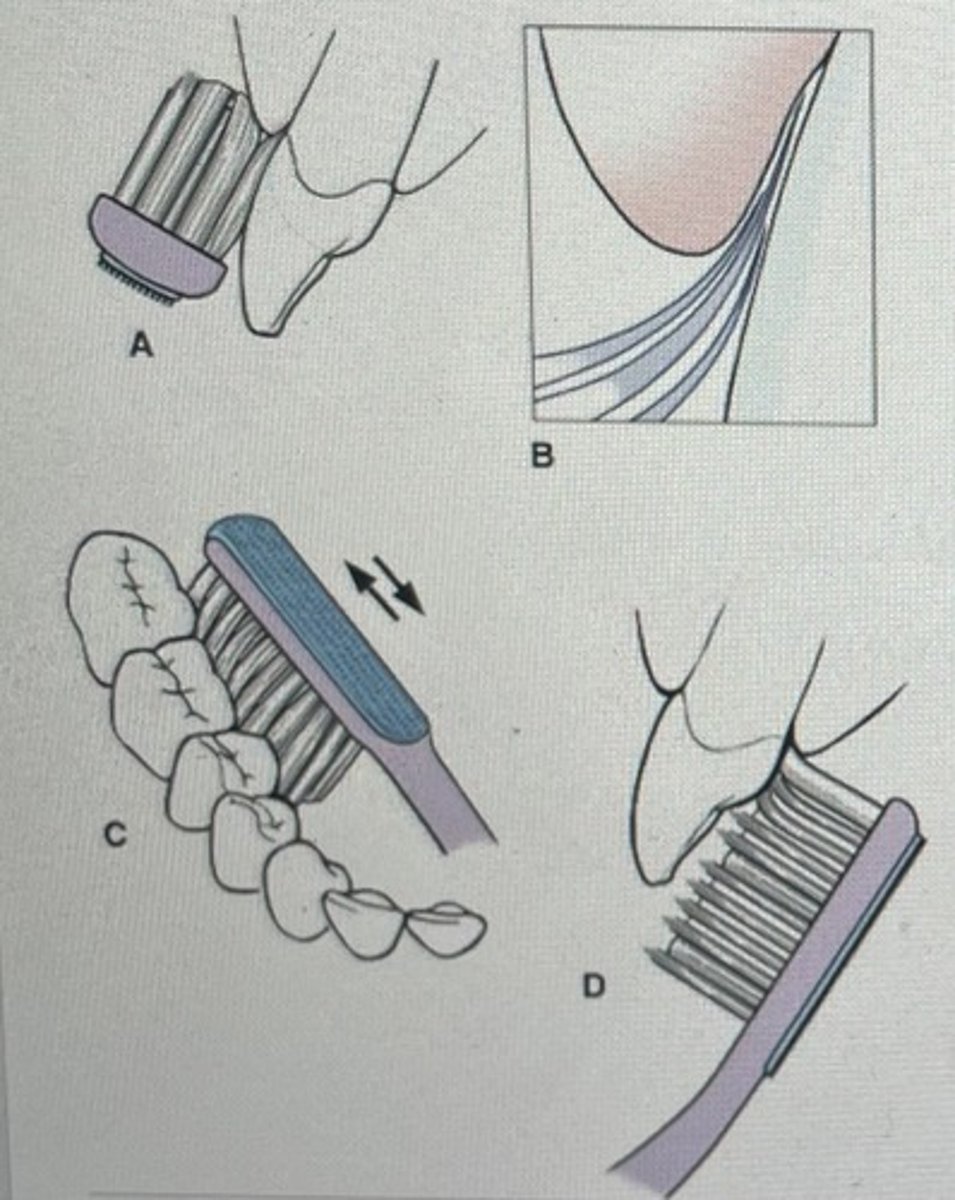
modified bass
apply pressure on the gingival margin to produce blanching. Then do 20 short back and forth motion on attached gingiva, gingival margin and tooth simultaneously. Roll occlusally to end the stroke
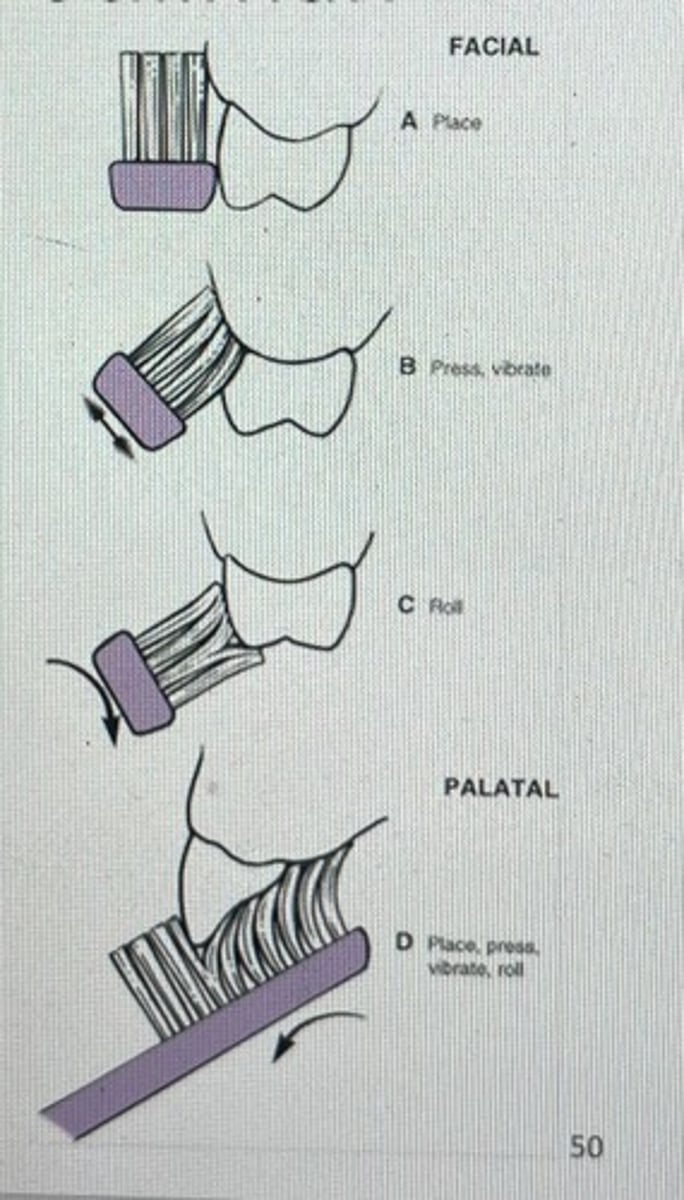
modified stillman
Place bristles on the gumline at a 45-degree pointing toward the chewing surface or crown of the tooth.
Gently vibrate the brush for 15 to 20 counts, using short circular strokes or small back and forth motions, and then reposition the brush to the next area.
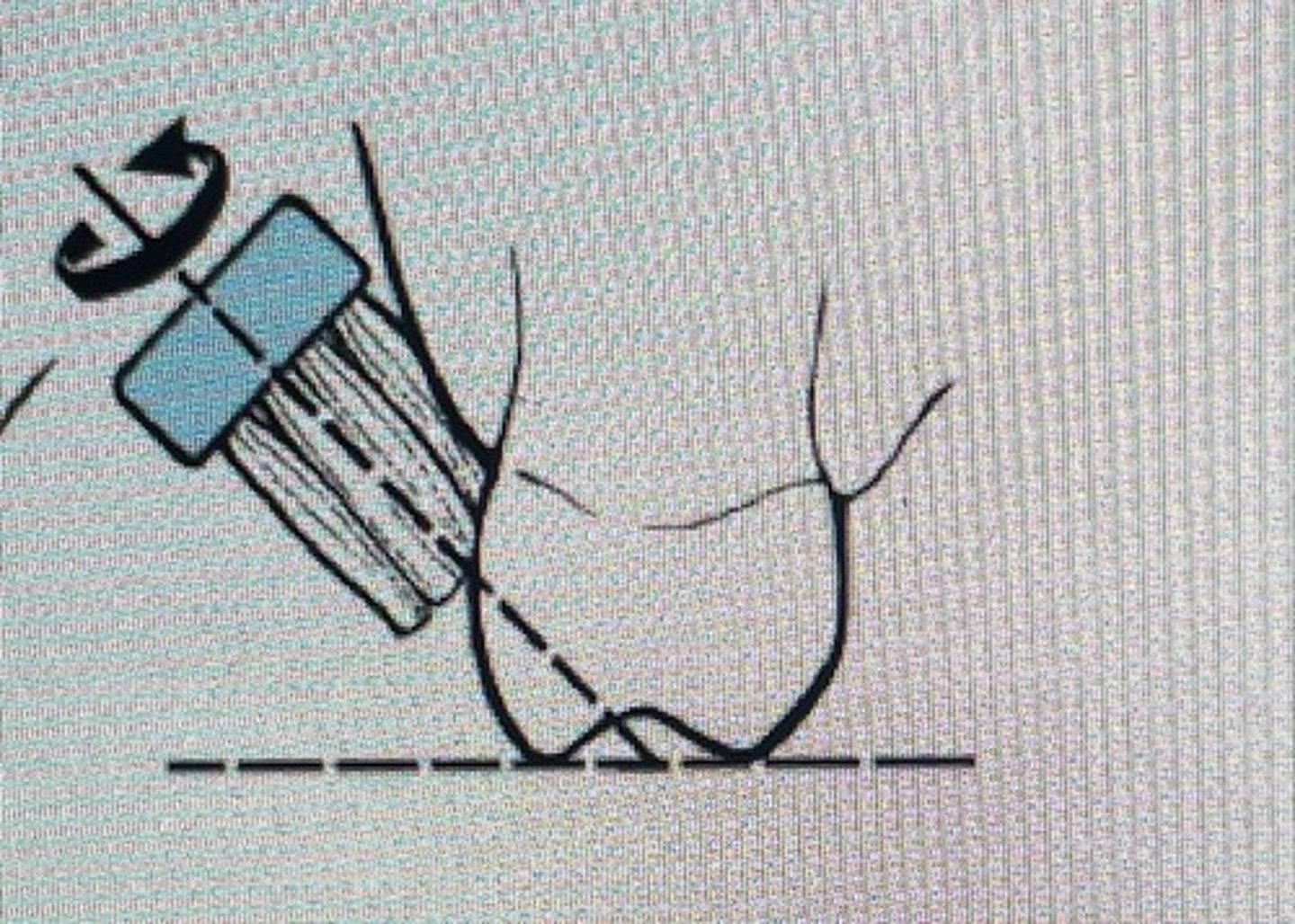
charters
apply pressure on the gingival margin to produce blanching. Then do 20 short back and forth motion on attached gingiva, gingival margin and tooth simultaneously
stillman
It is the simplest of all methods of brushing, all you have to do is move the brush in a circular motion around a set of teeth and move on to the next set
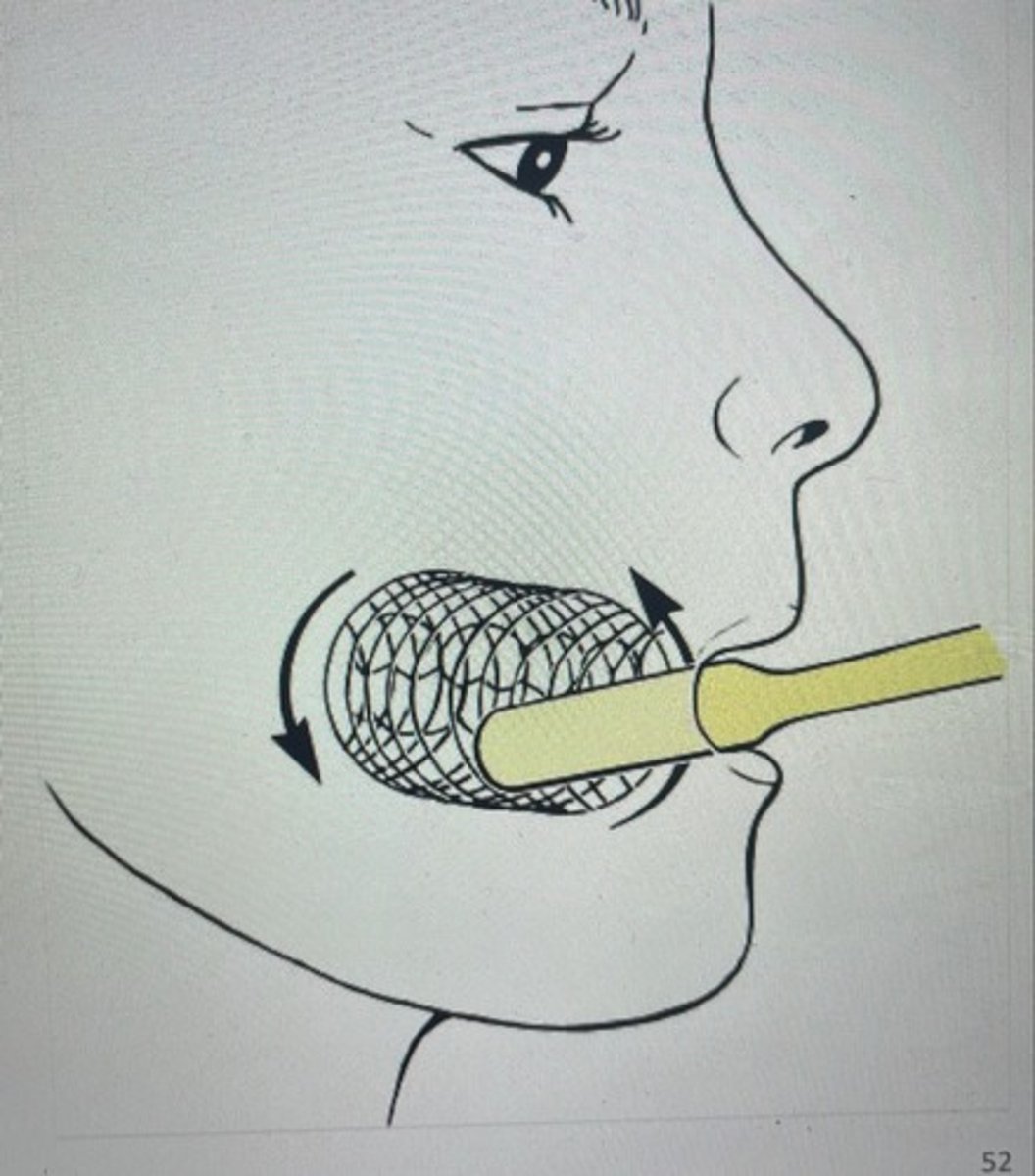
fones
this technique involves rigorous vertical & horizontal motions for every surface of your teeth.
horizontal (or scrub)
modified stillman
charters
modified bass
fones
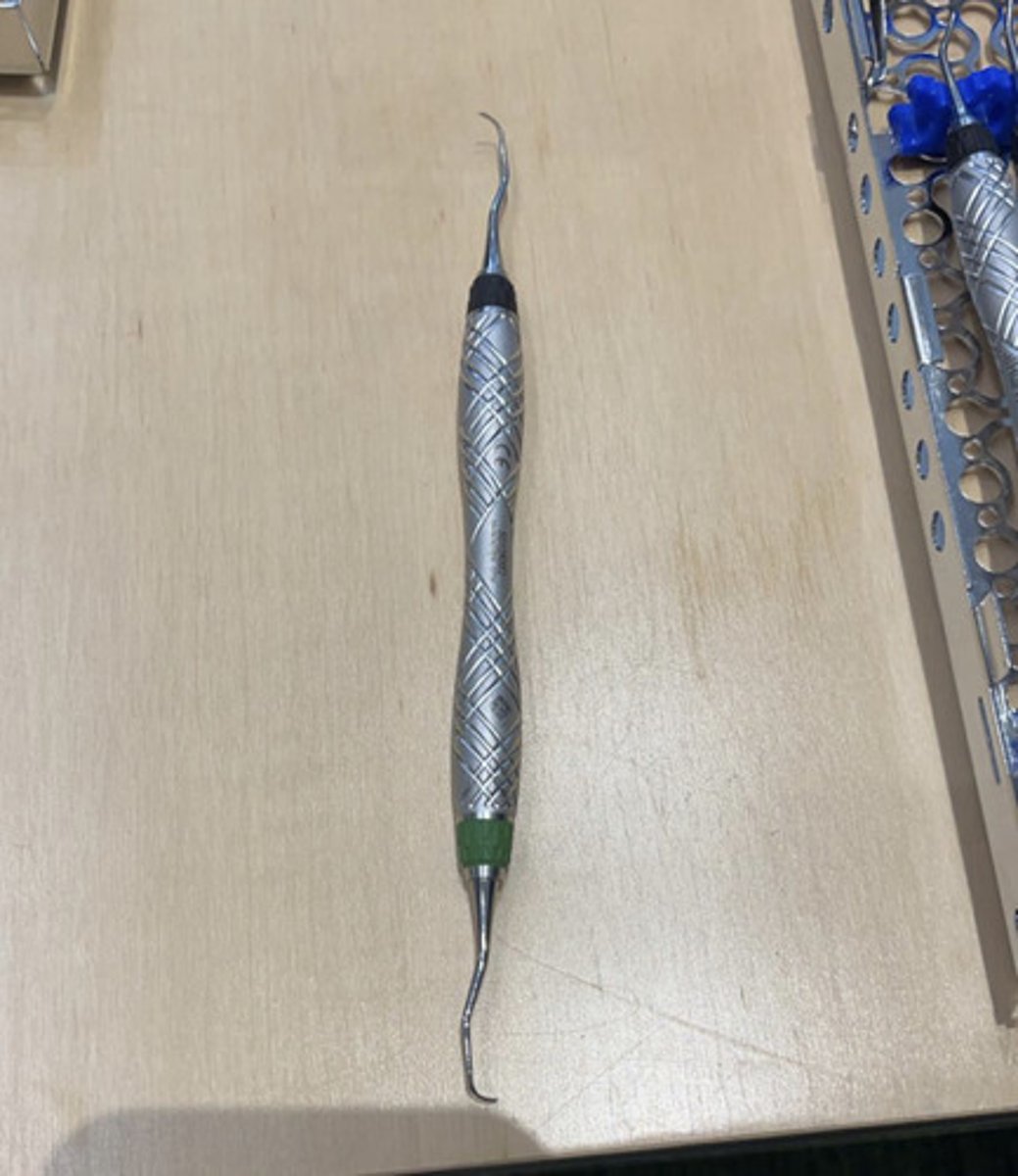

anterior currette
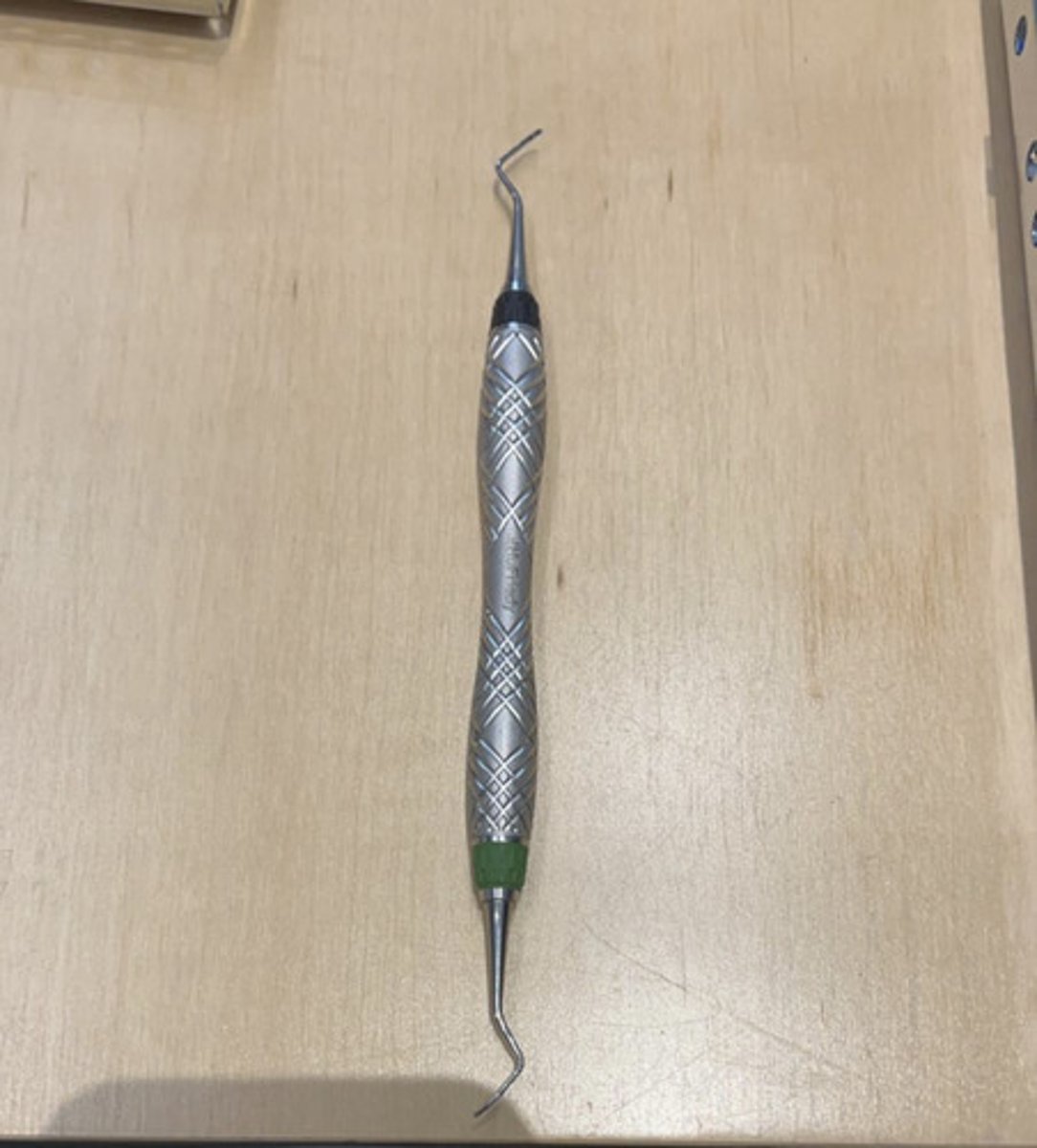

universal curette
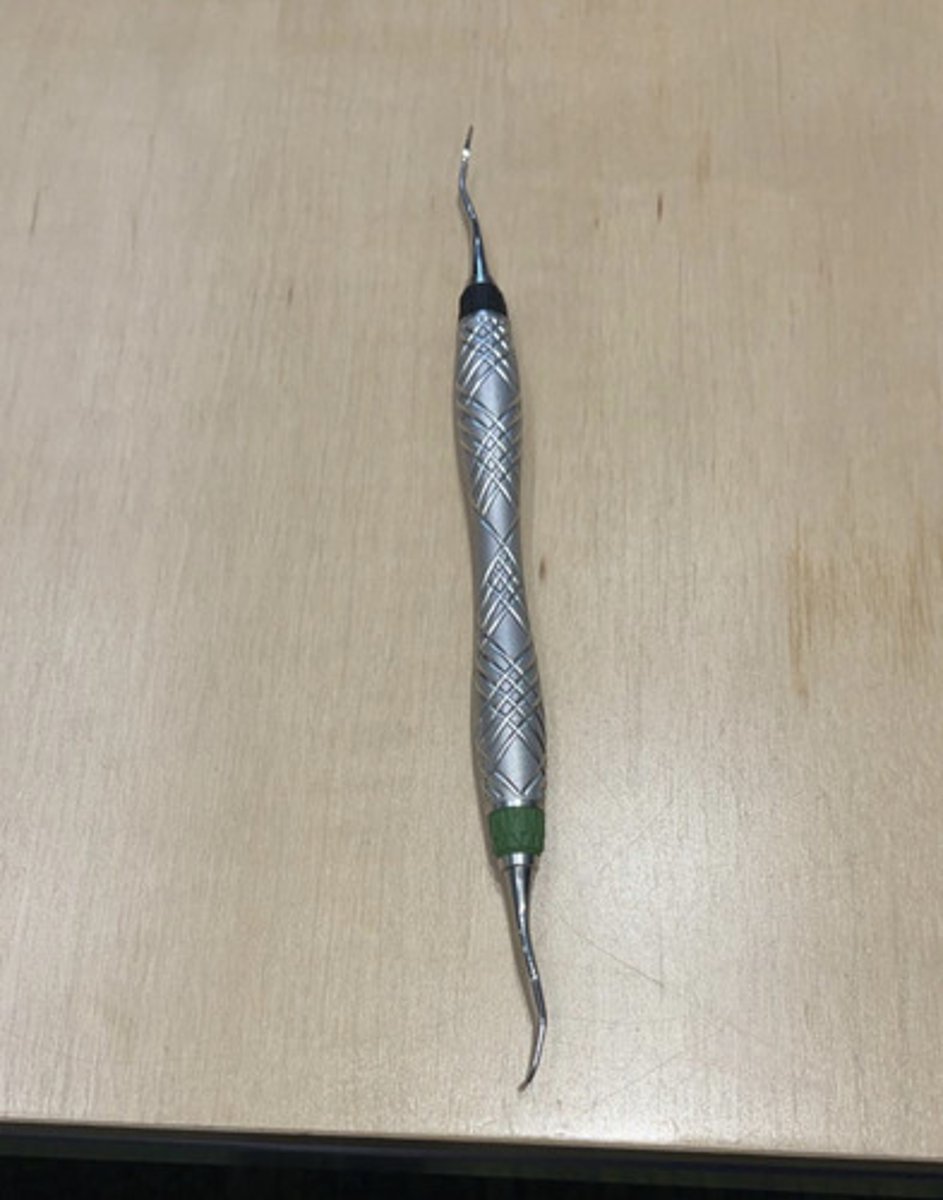

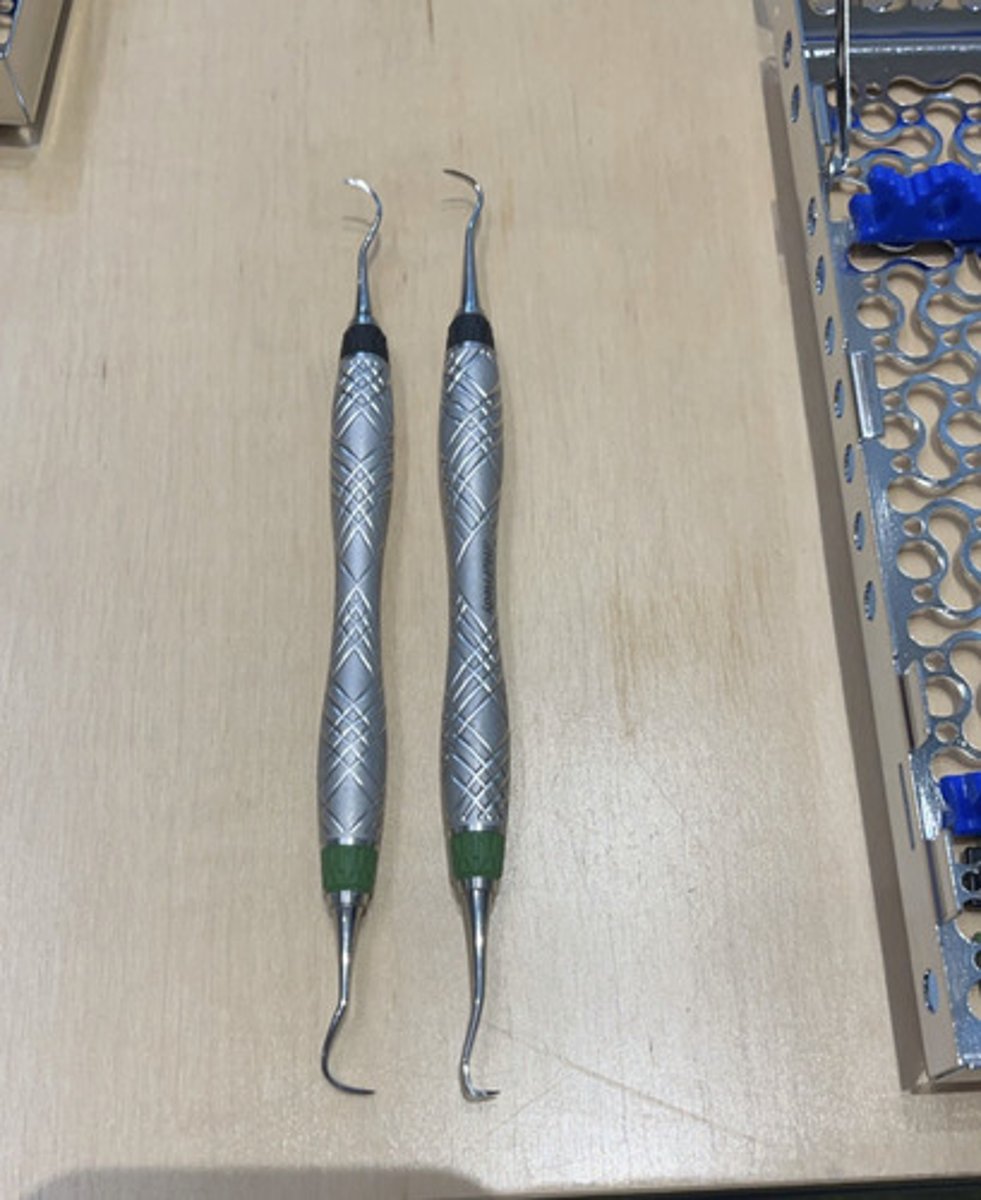
area specific currette (mesial)
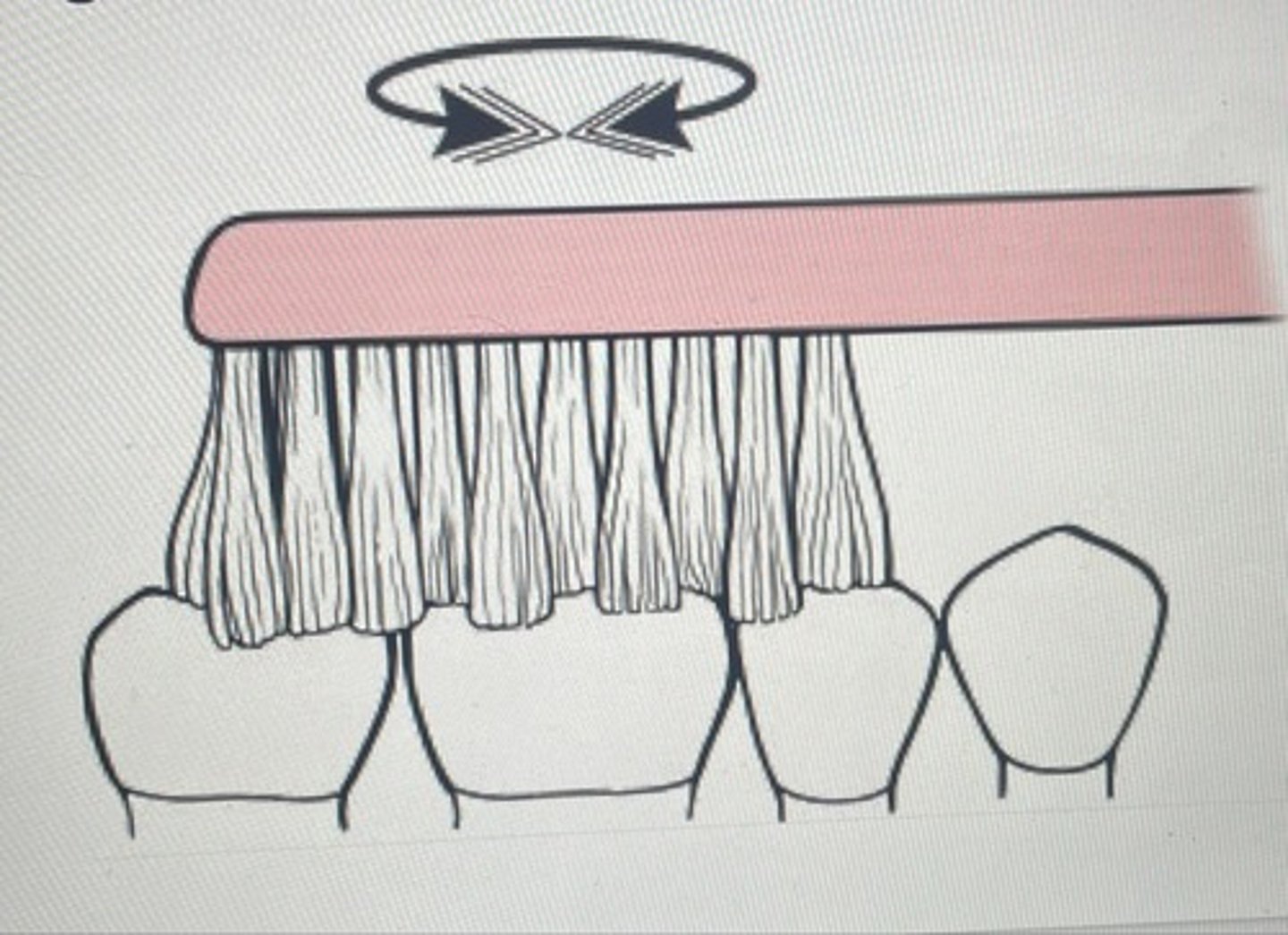
horizontal (scrub)

area specific currette (distal)

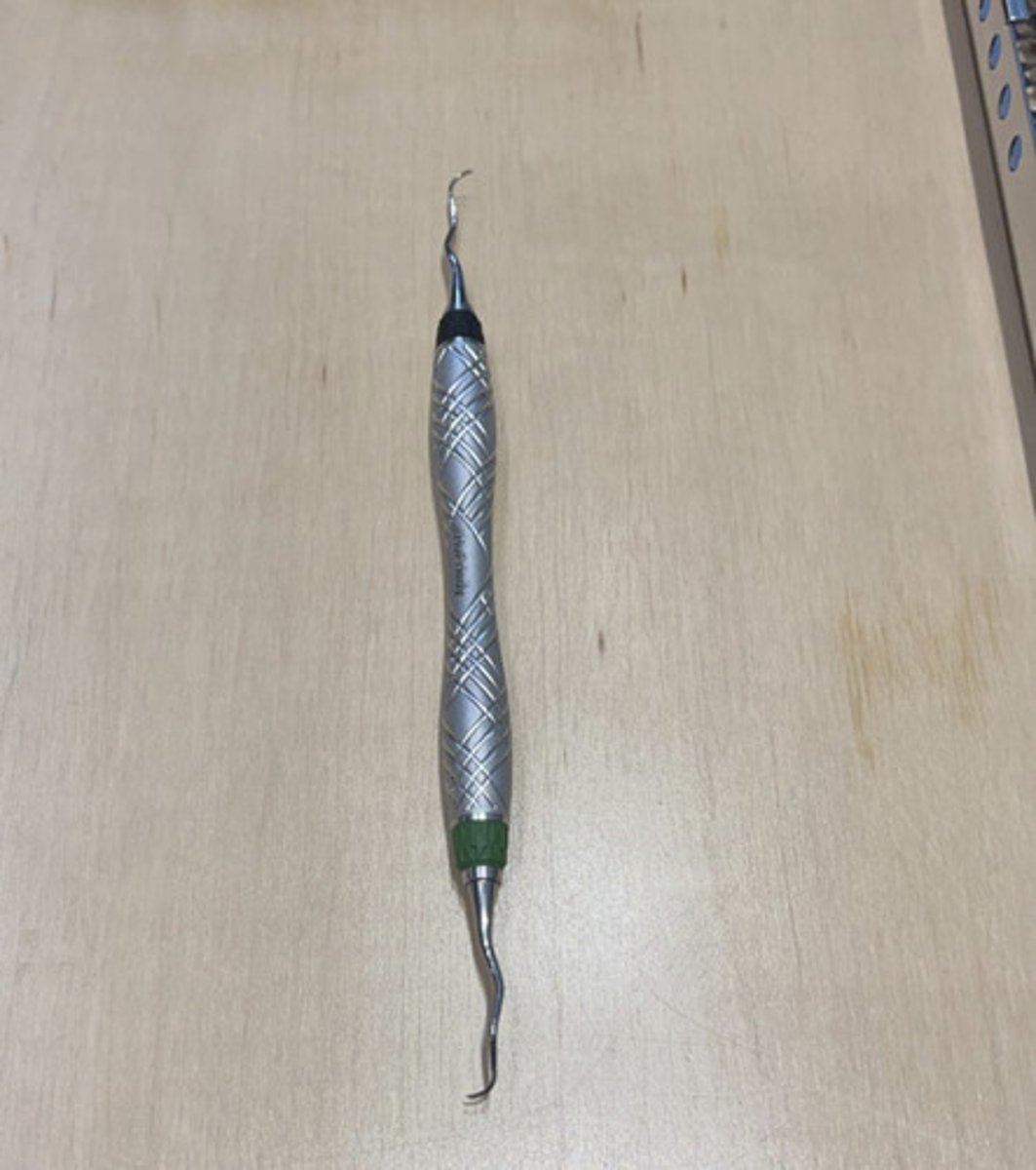
sickle
pink
pigmented
pigmented
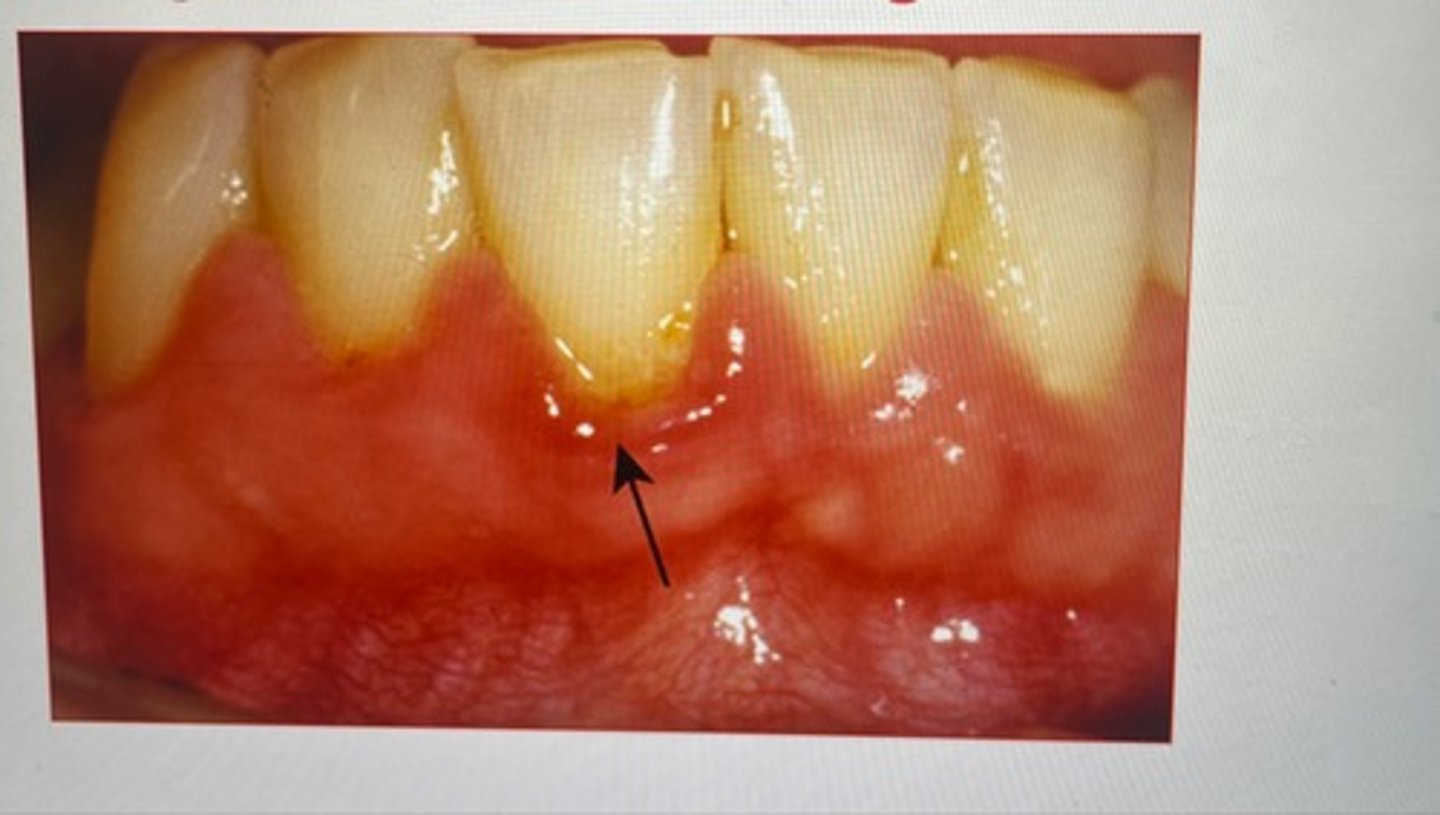
erythematous
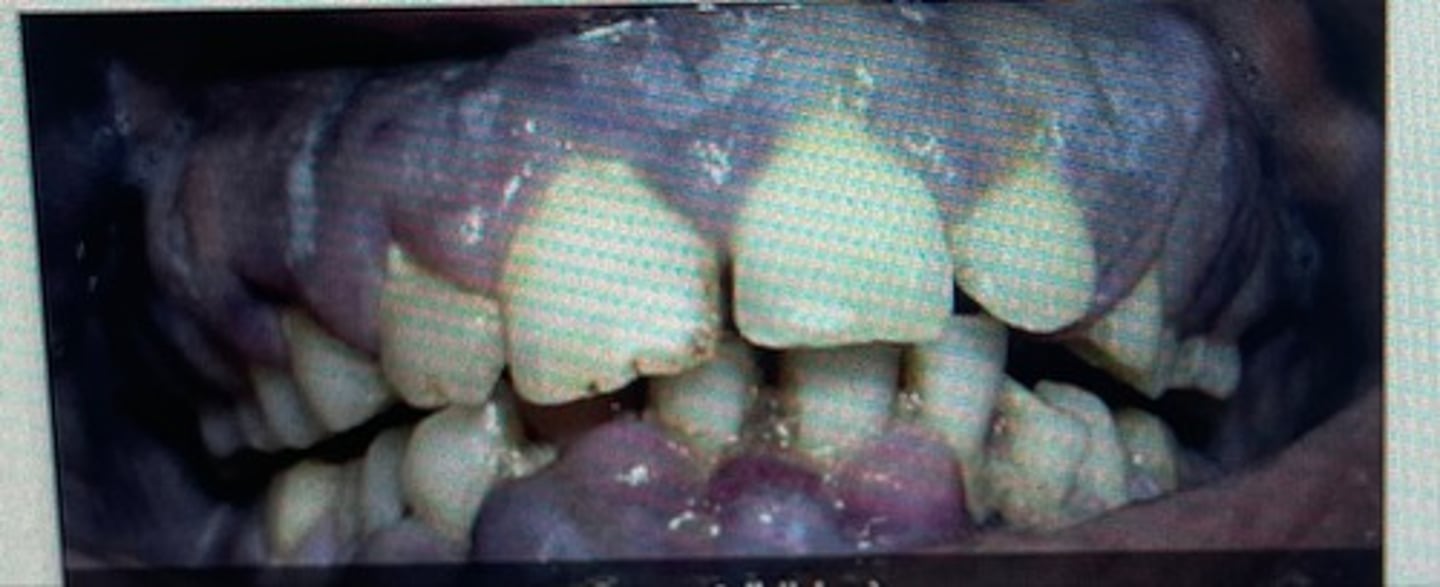
cyanotic
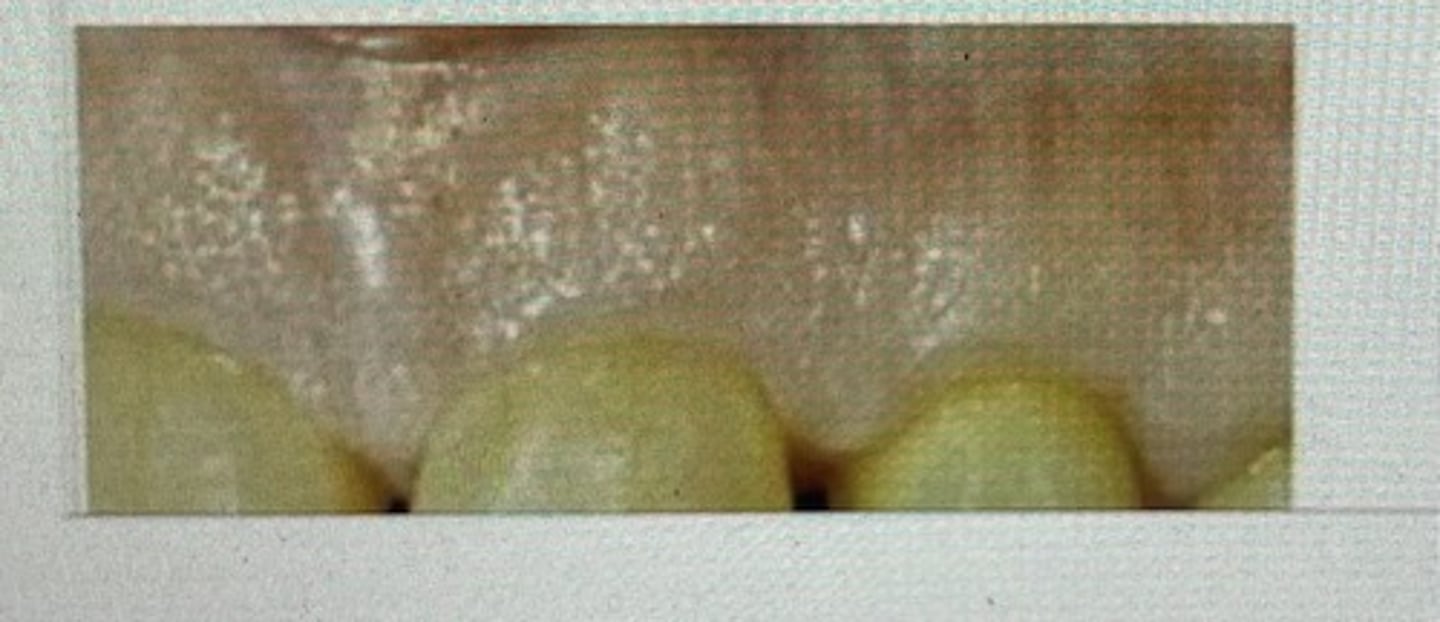
pale pink
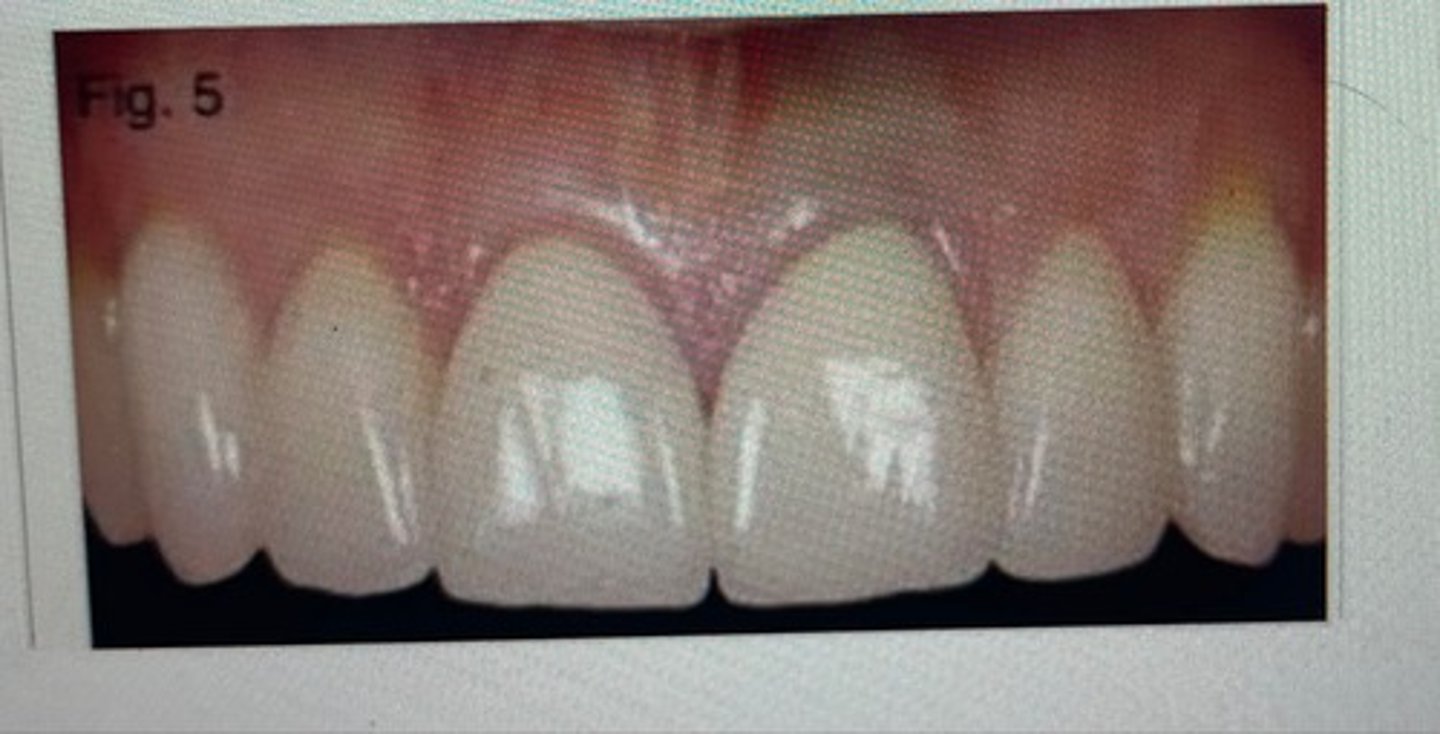
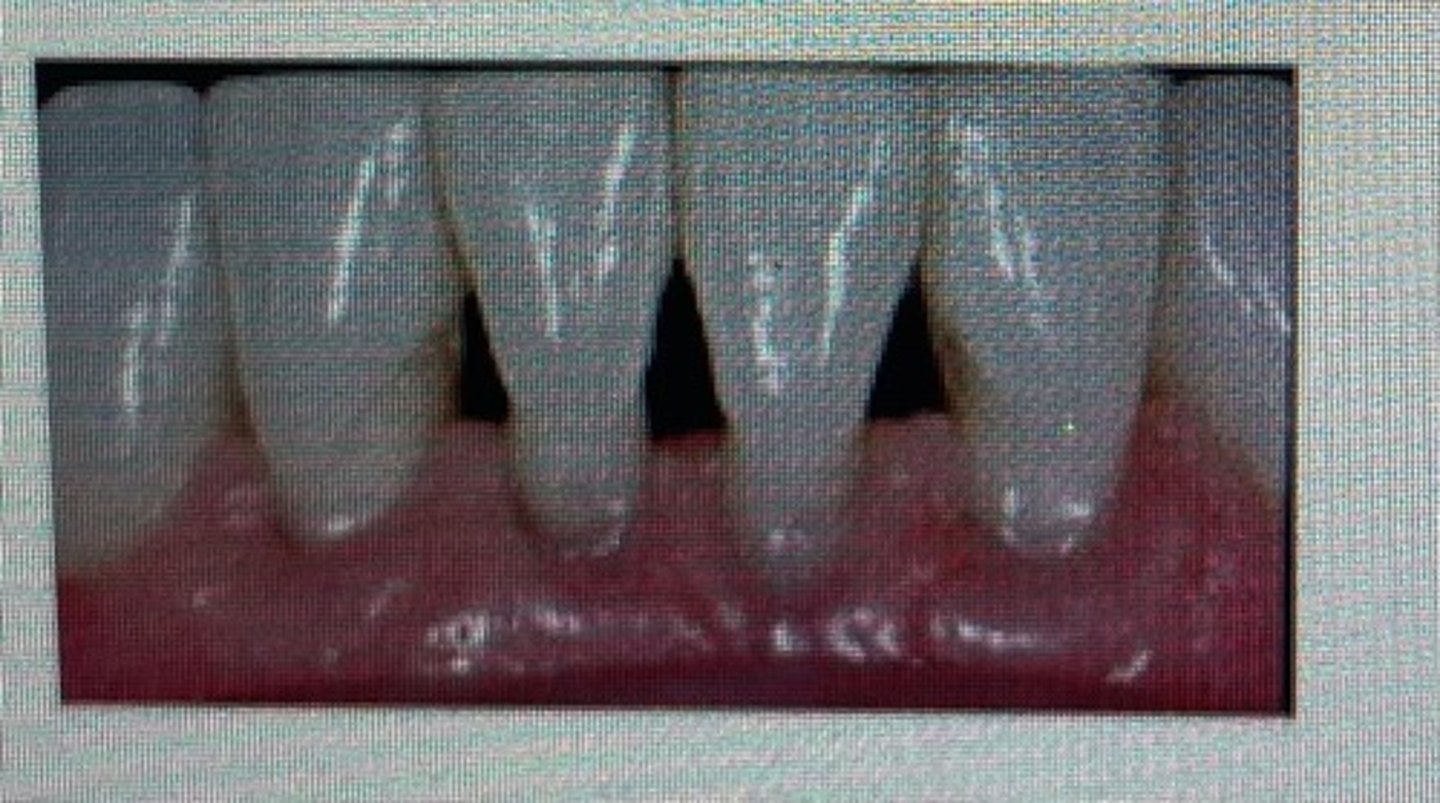
pointed papilla
blunted papilla
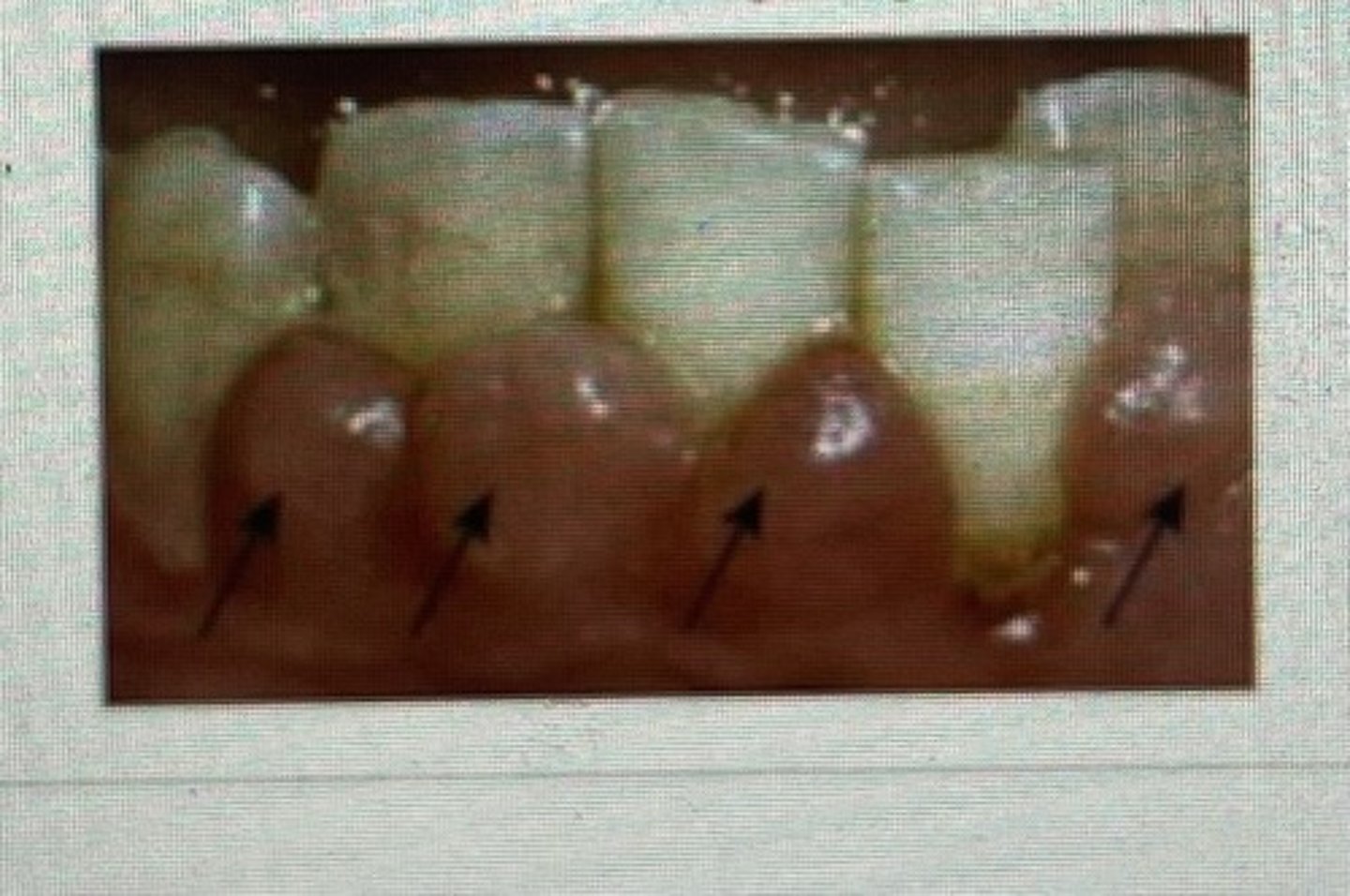
bulbous papilla
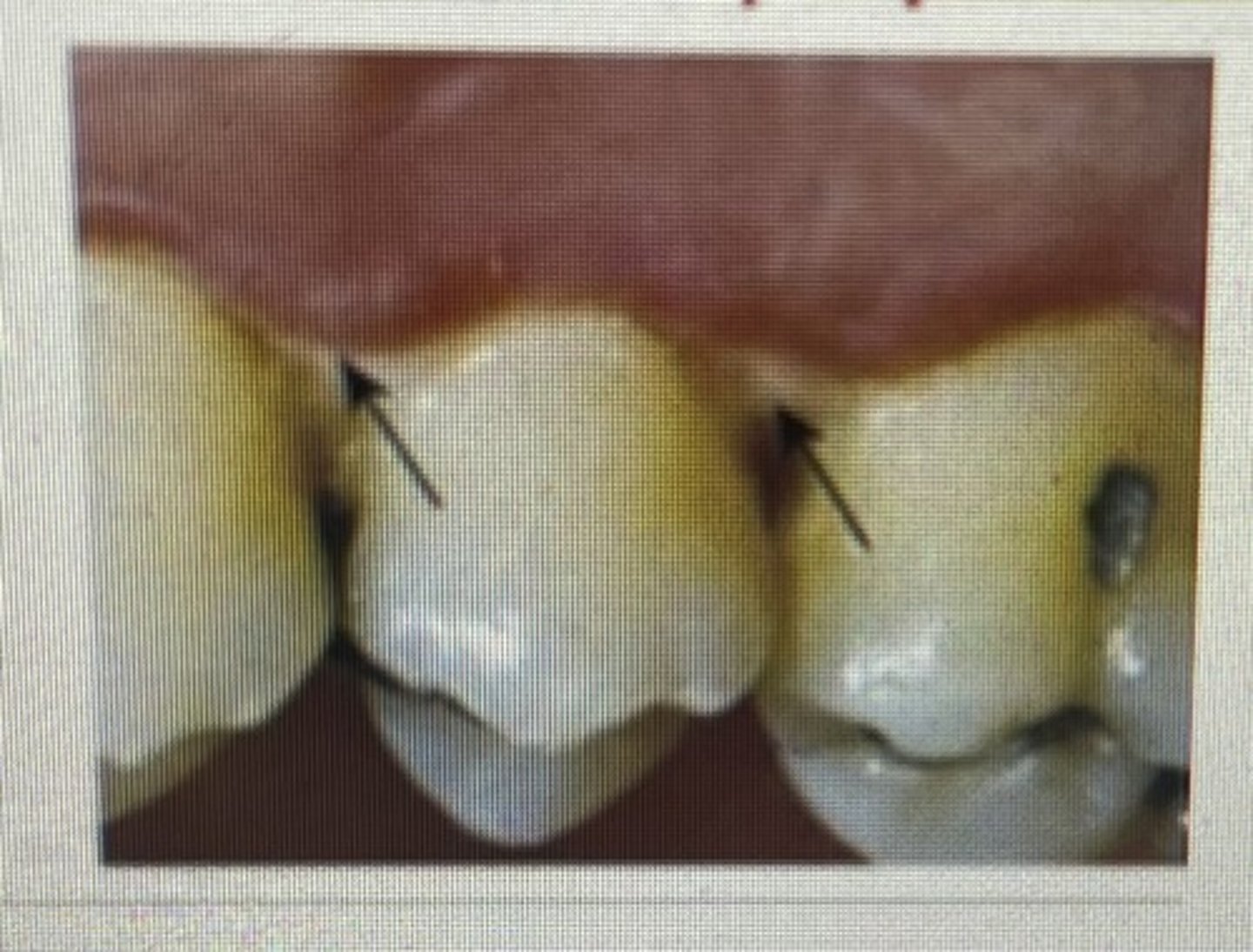
cratered papilla
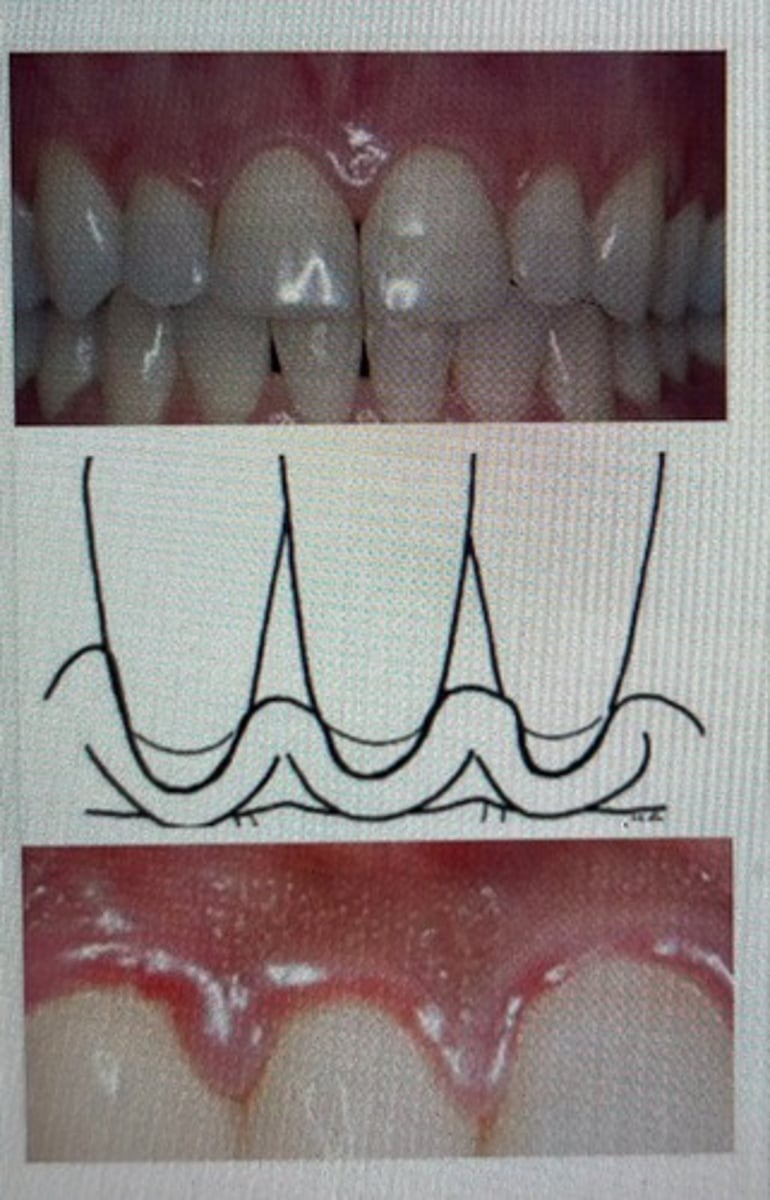
rolled margins
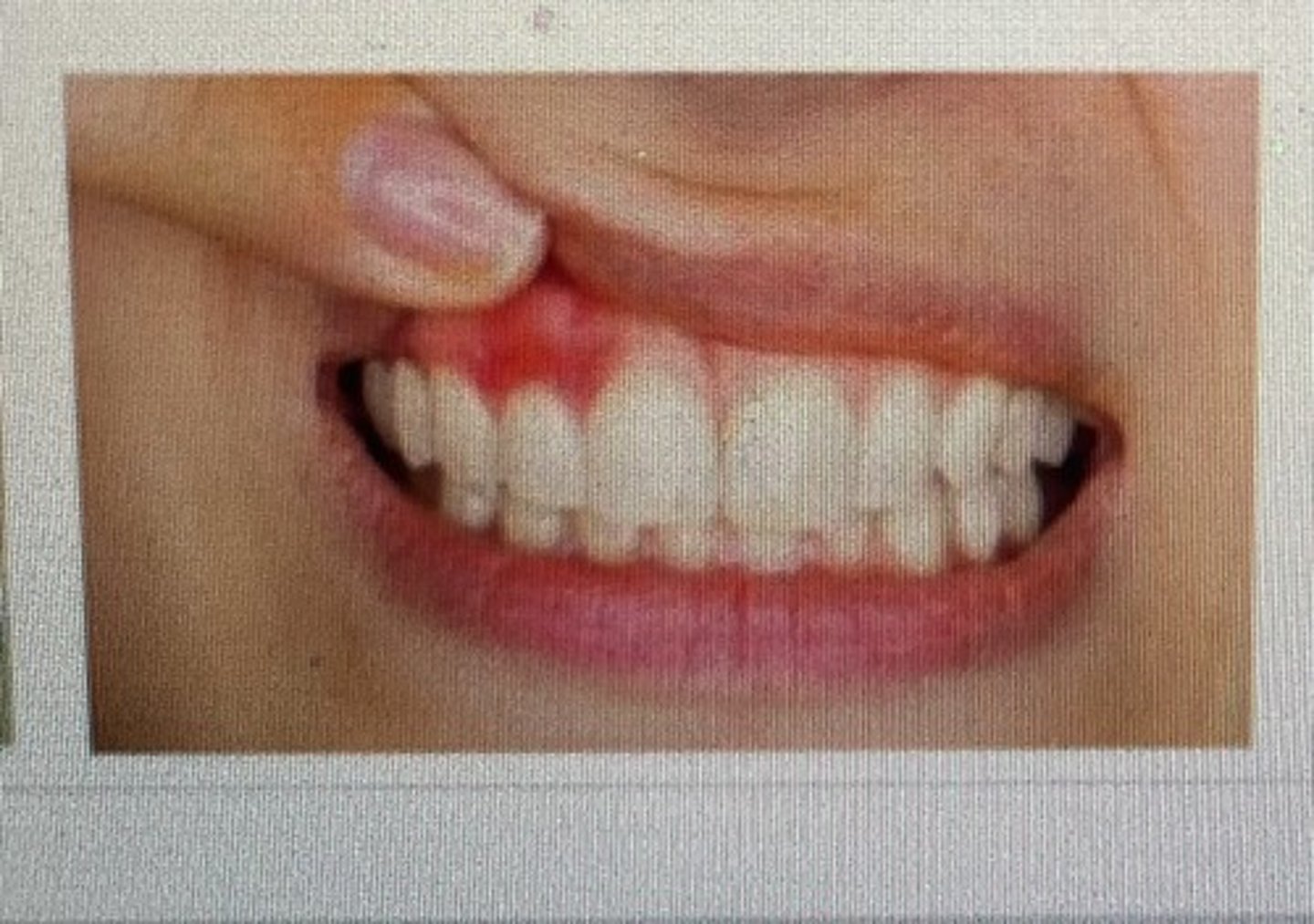
edematous

flaccid
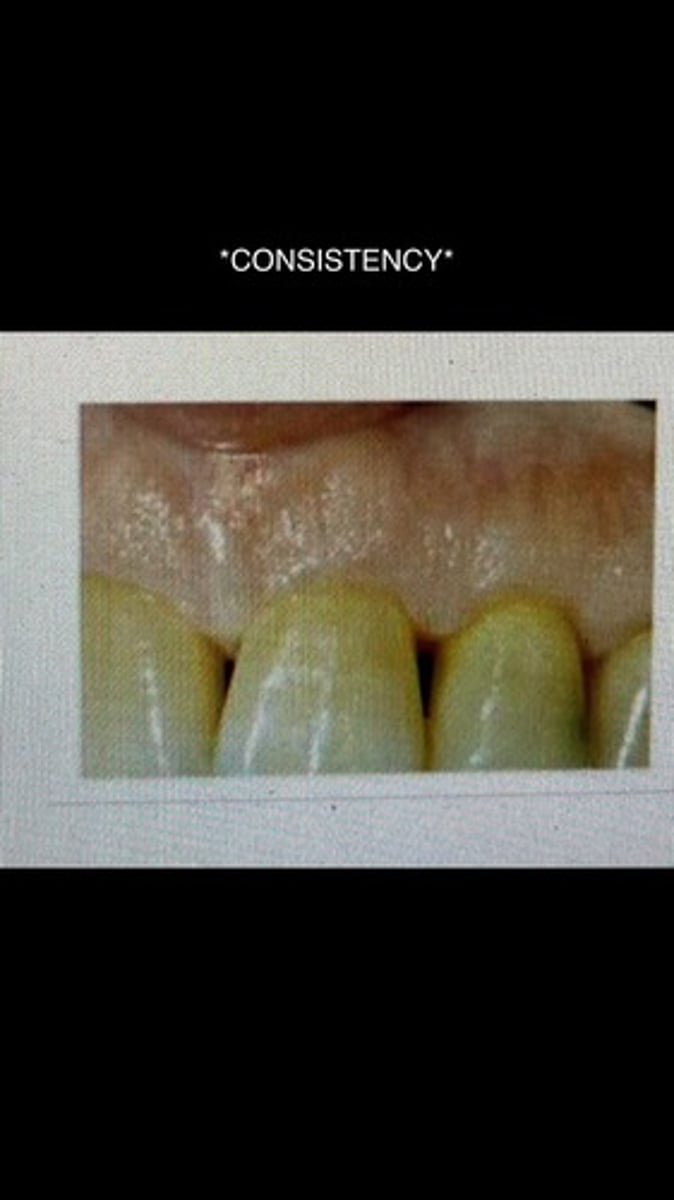
fibrotic
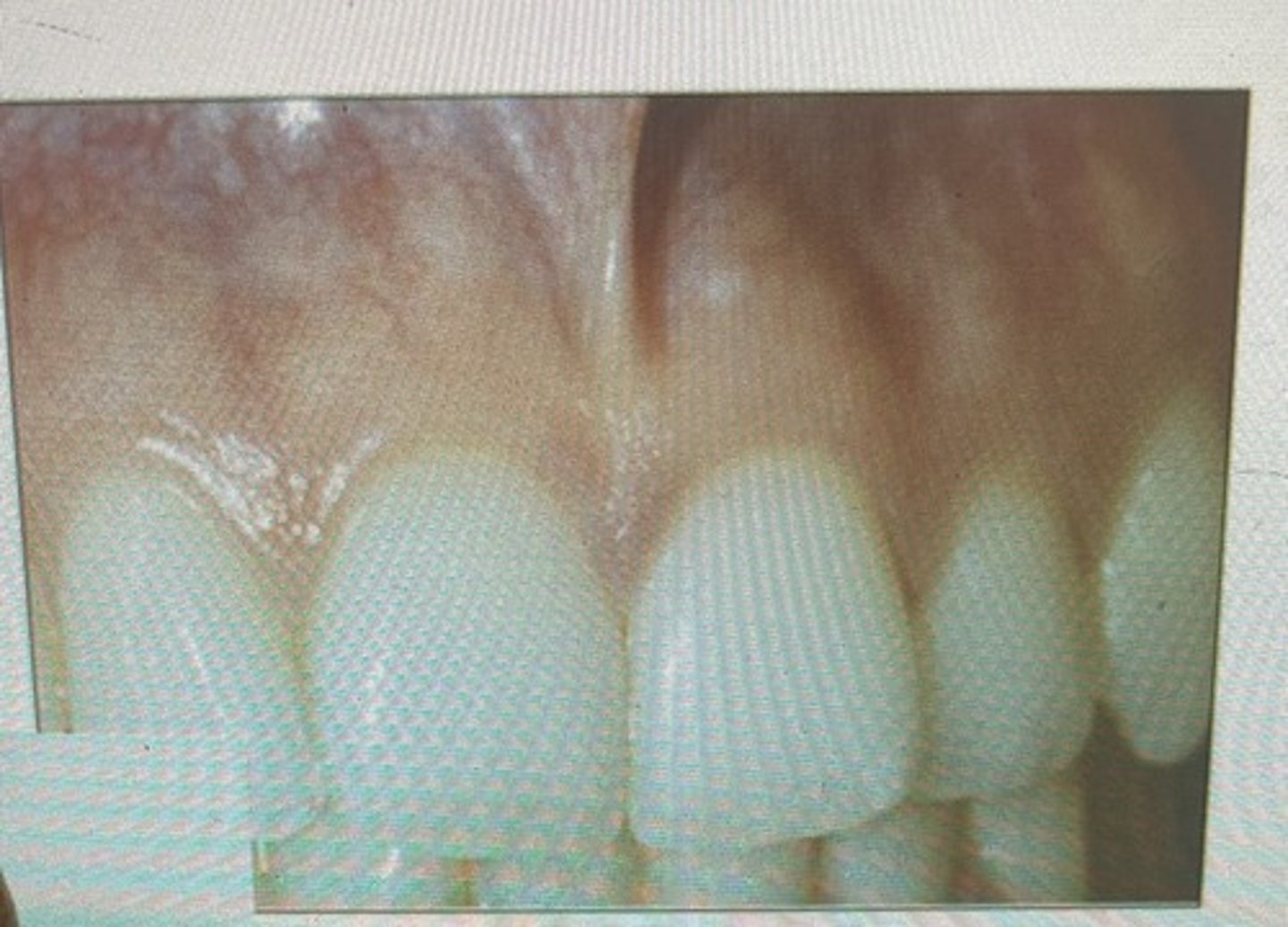
stippled
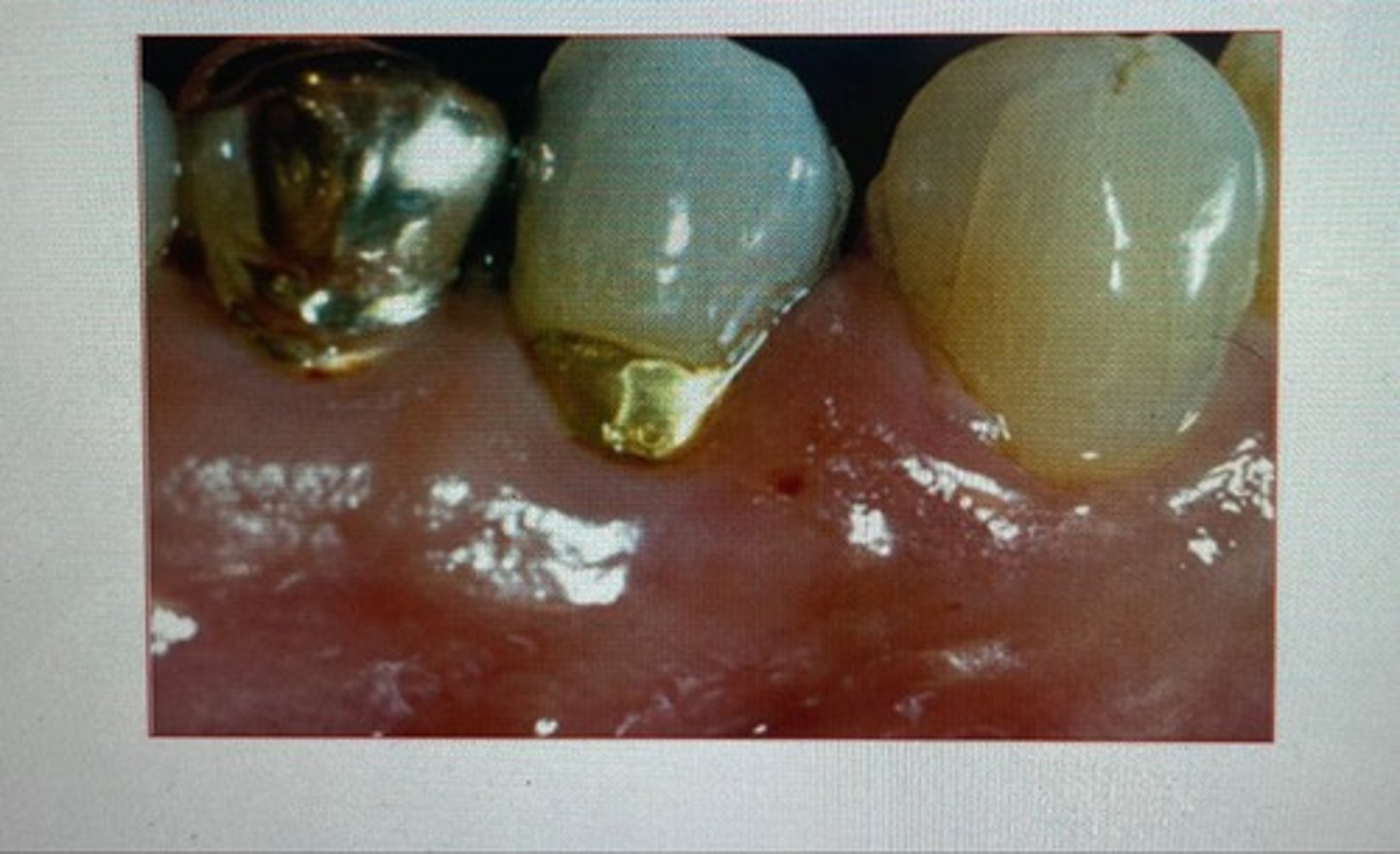
smooth shiney tissue
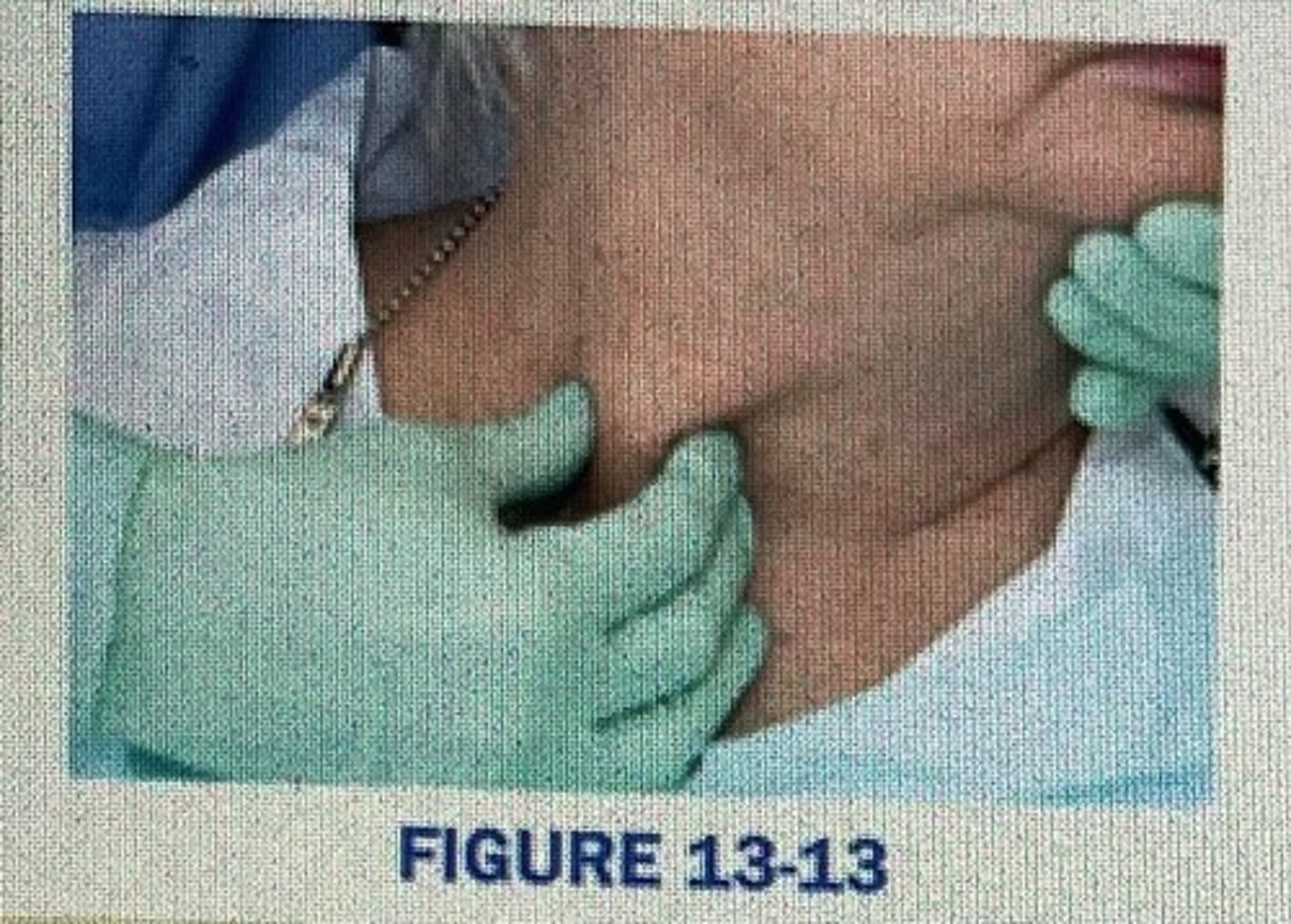
compressing the sternomastoid muscle
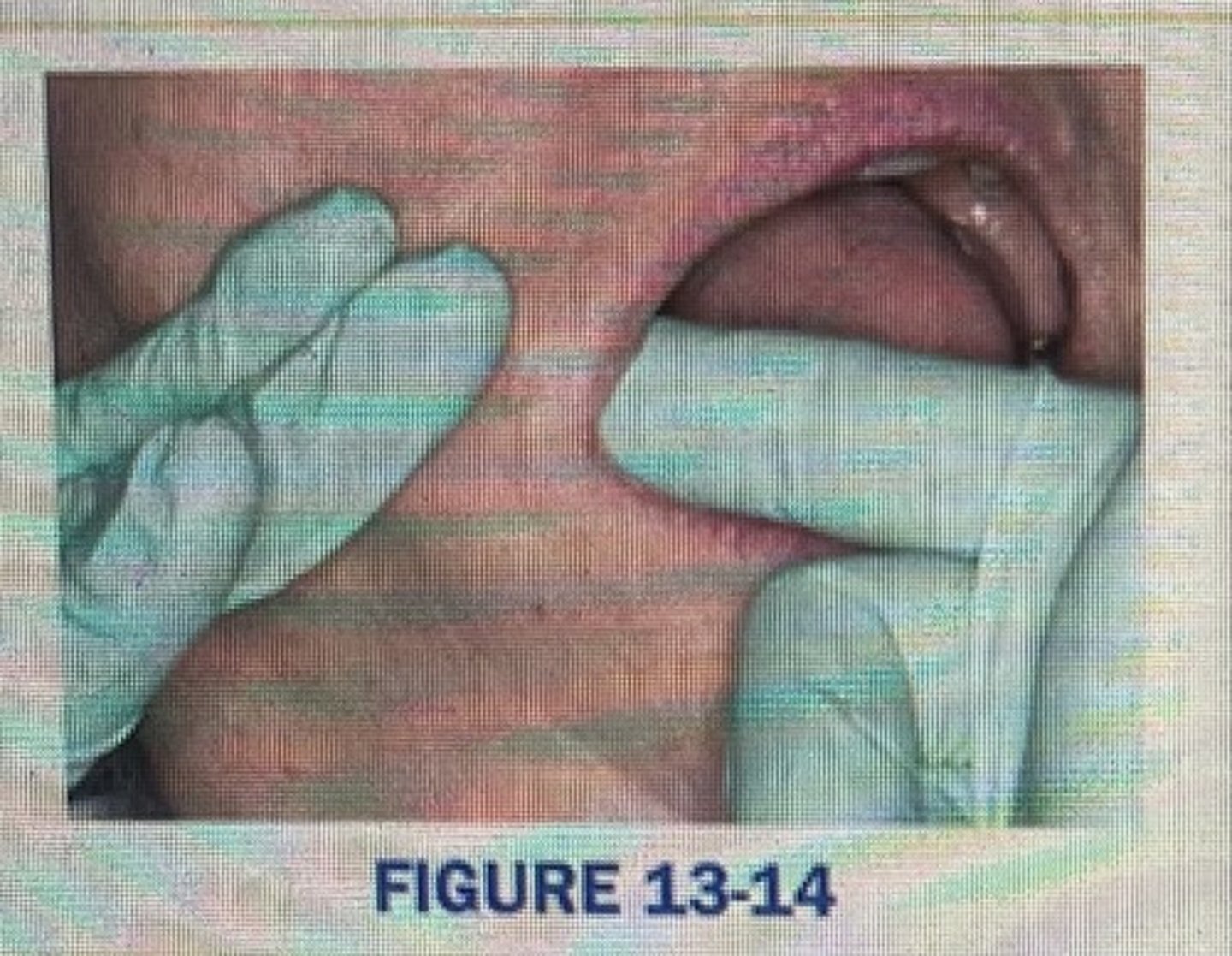
compressing the buccal mucosa
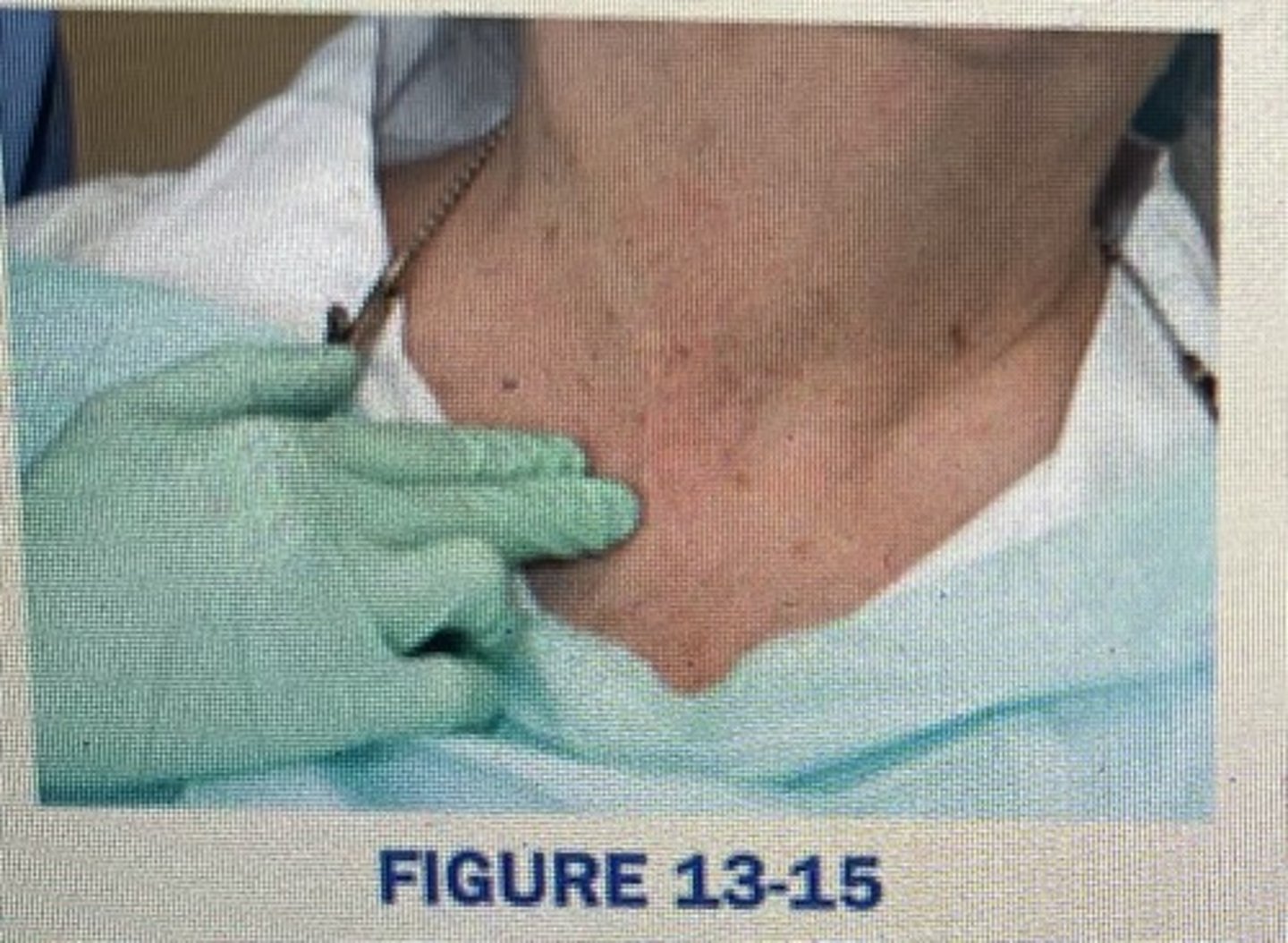
compressing supraclavicular lymph nodes
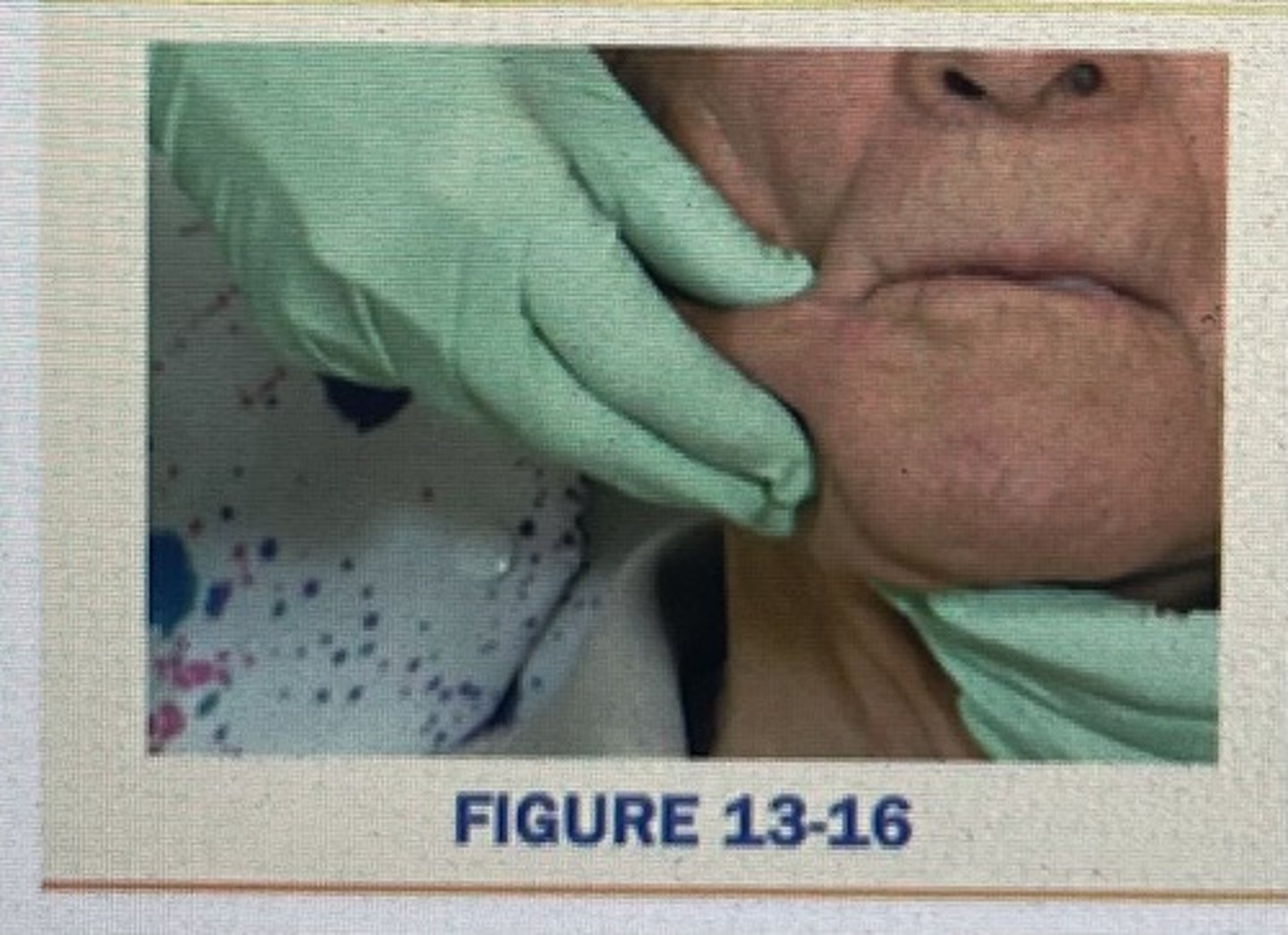
roll the tissue from under the chin up and over the inferior border of the mandible
class I occlusion
considered neutral. the mesiobuccal cusp of the maxillary first molar aligns with the buccal groove of the mandibular first molar
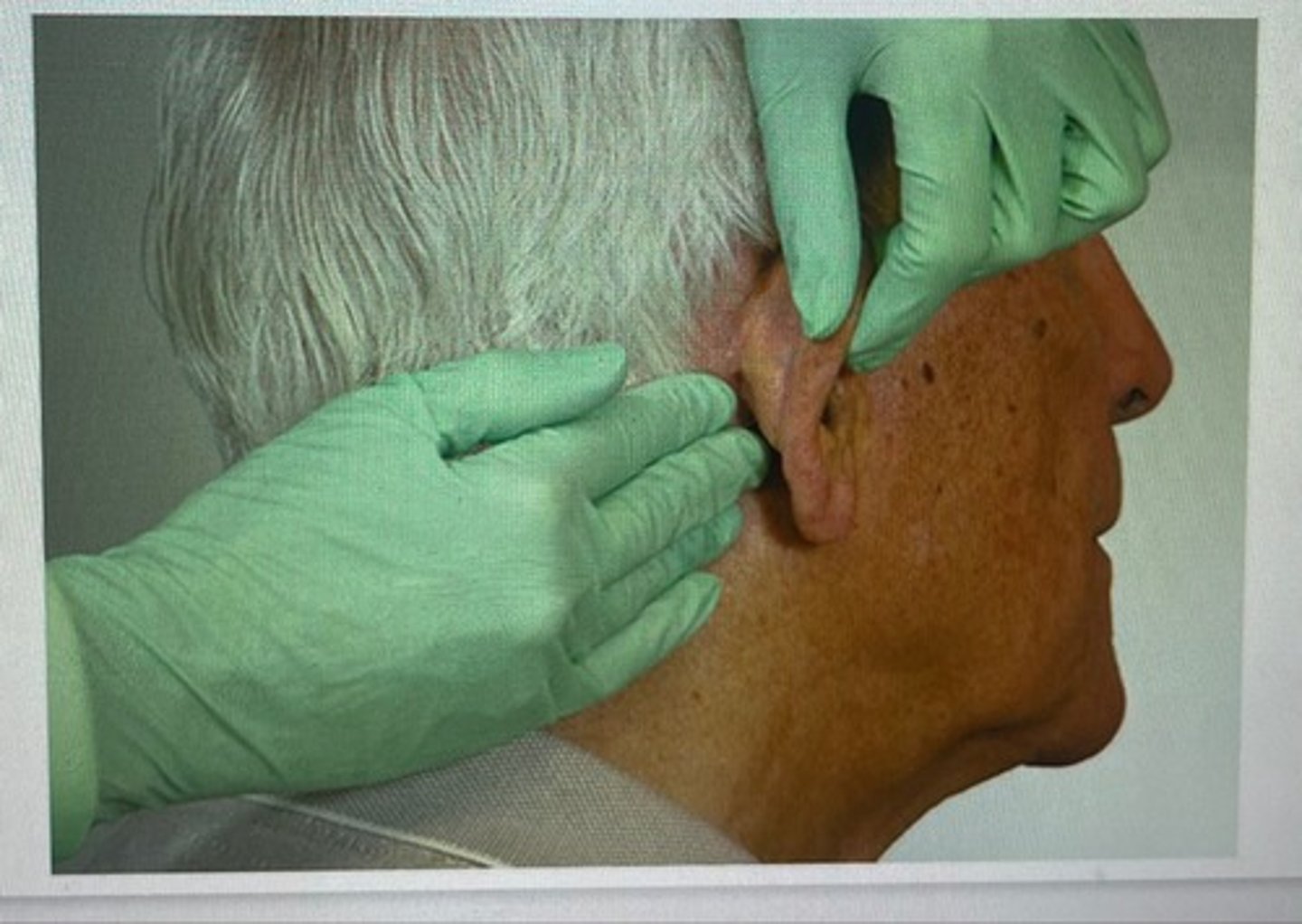
posterior auricular lymph nodes
class II malocclusion
The mesiobuccal cusp of the maxillary first molar is mesial to the buccal groove of the mandibular first molar
Class I blacks
pits and fissures
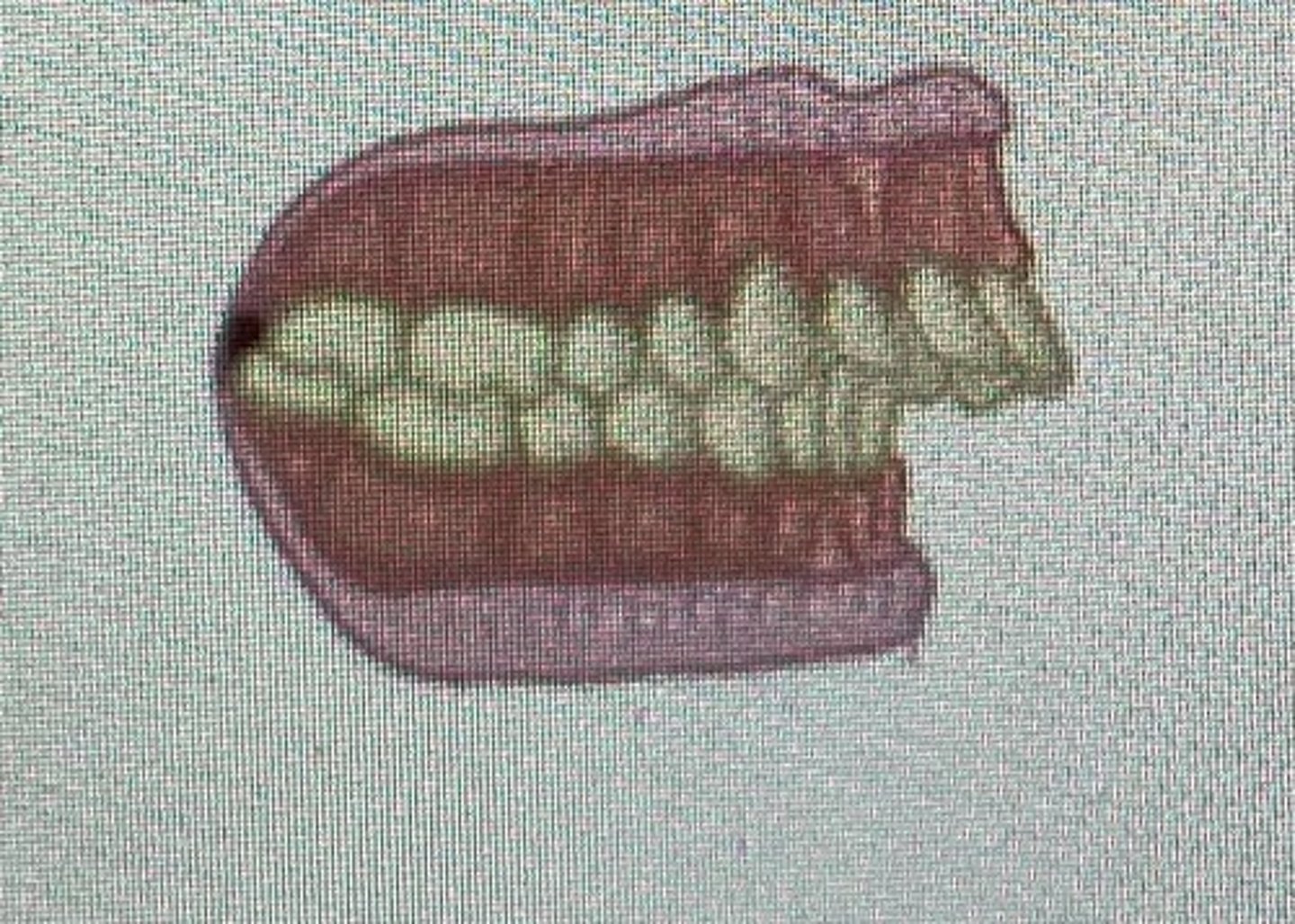
class II malocclusion division 1
class II blacks
proximal surfaces of posterior teeth
class III blacks
proximal surfaces of anterior teeth
Class IV blacks
proximal surfaces of anterior teeth and the incisal angle
Class V blacks
Cervical 1/3 of the facial or lingual surface
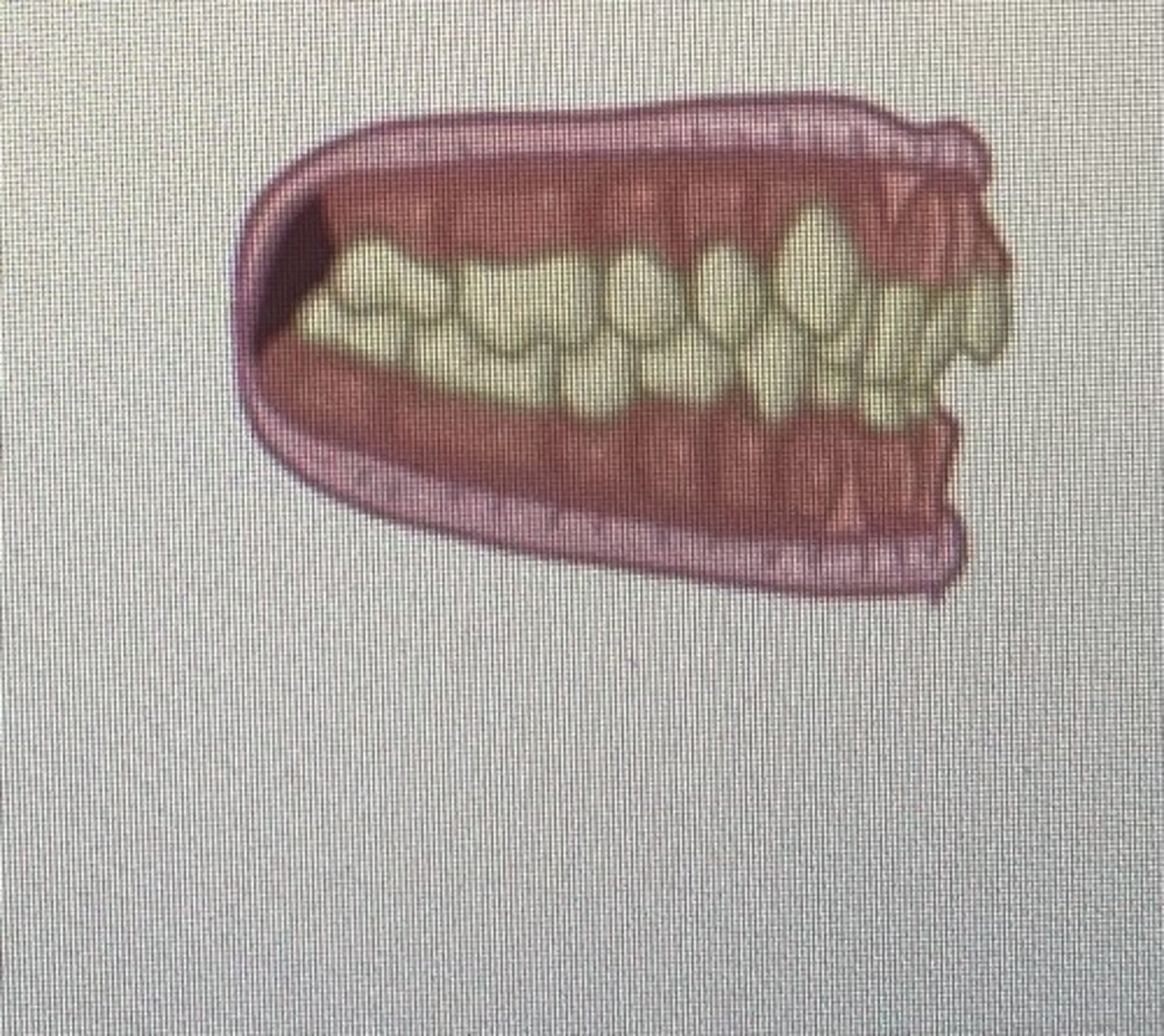
class II malocclusion division 2
class III malocclusion
The mesiobuccal cusp of the maxillary first molar is distal to the buccal groove of the mandibular first molar
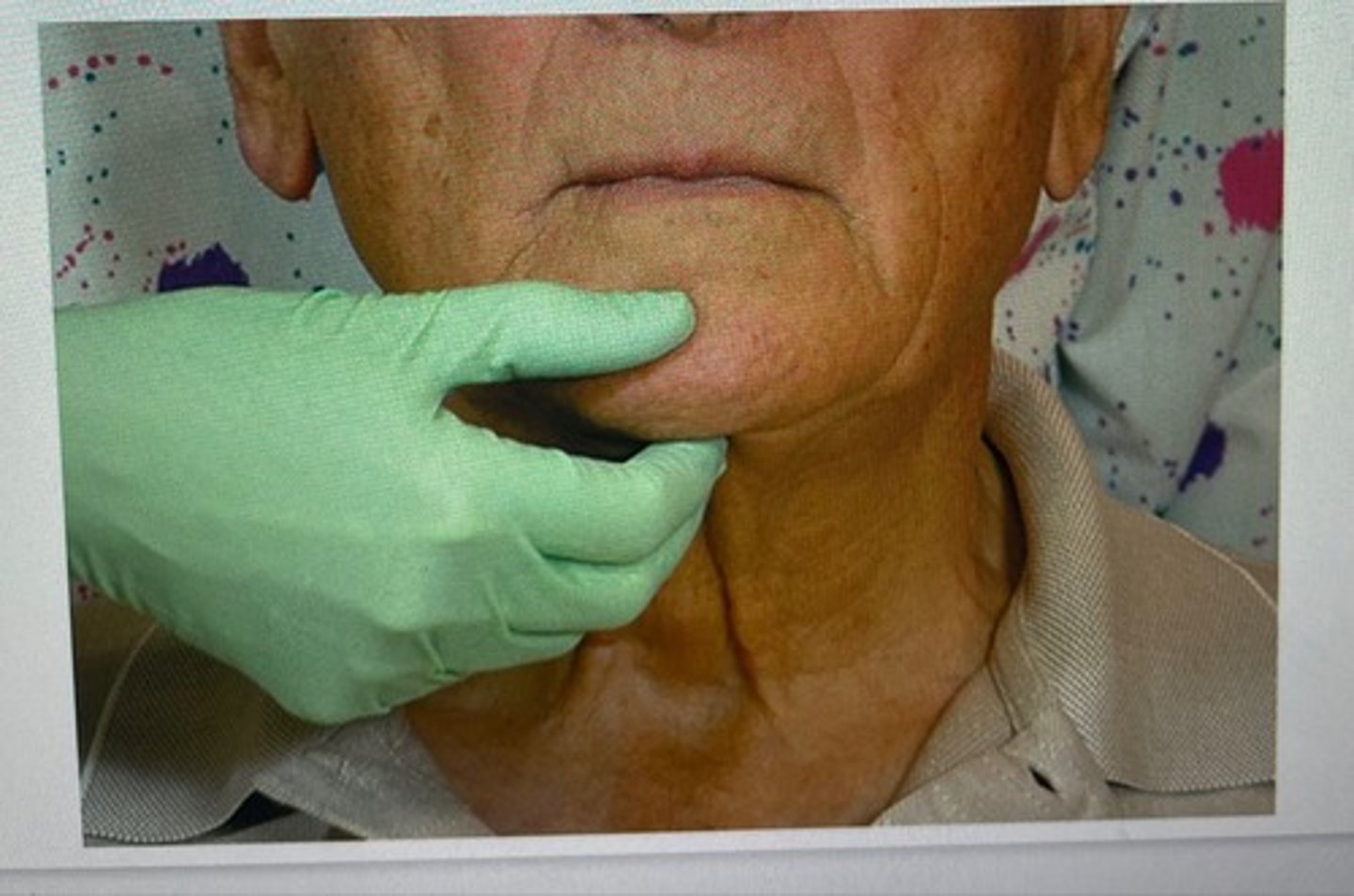
submental lymph nodes
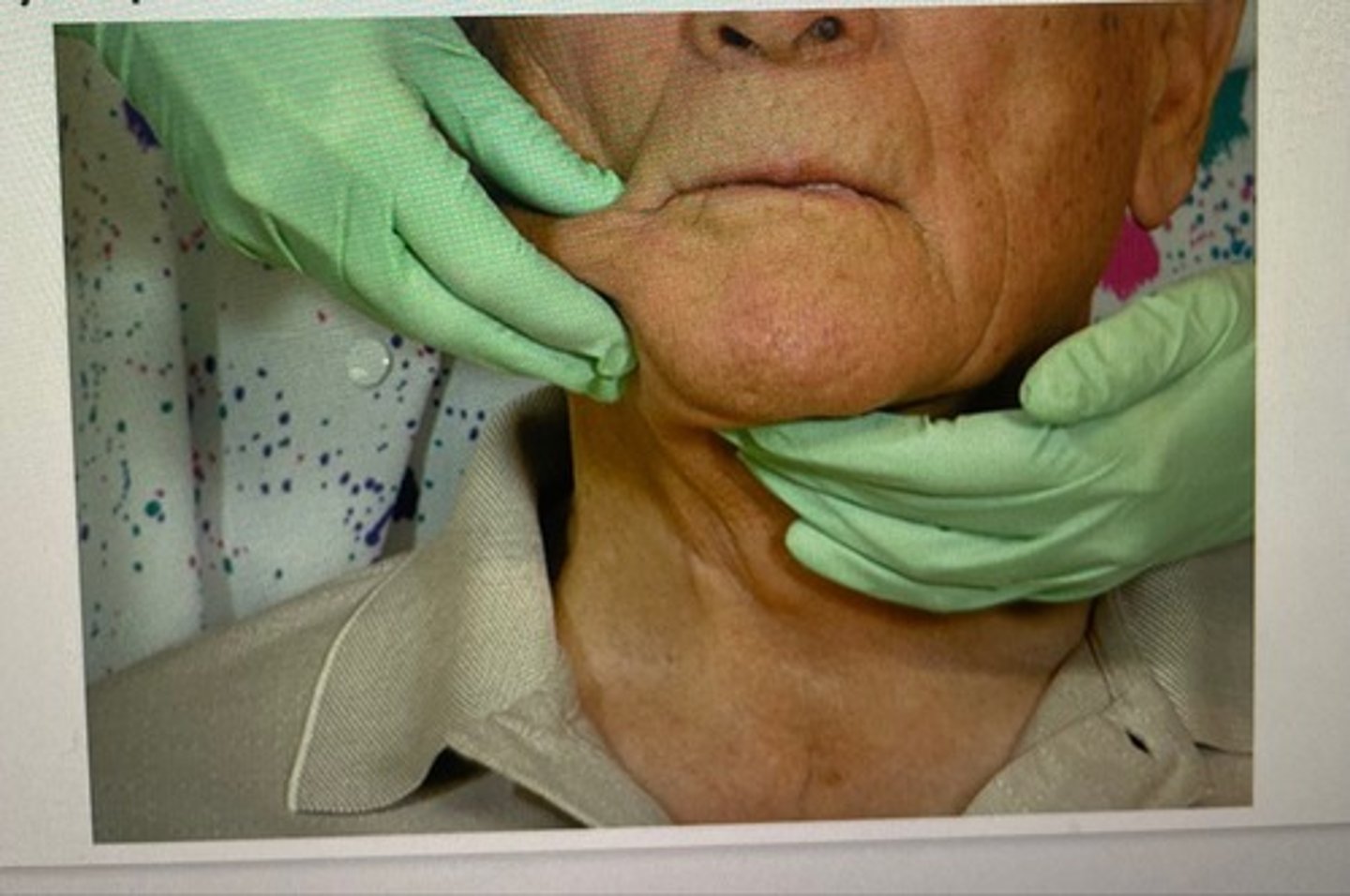
submandibular lymph nodes
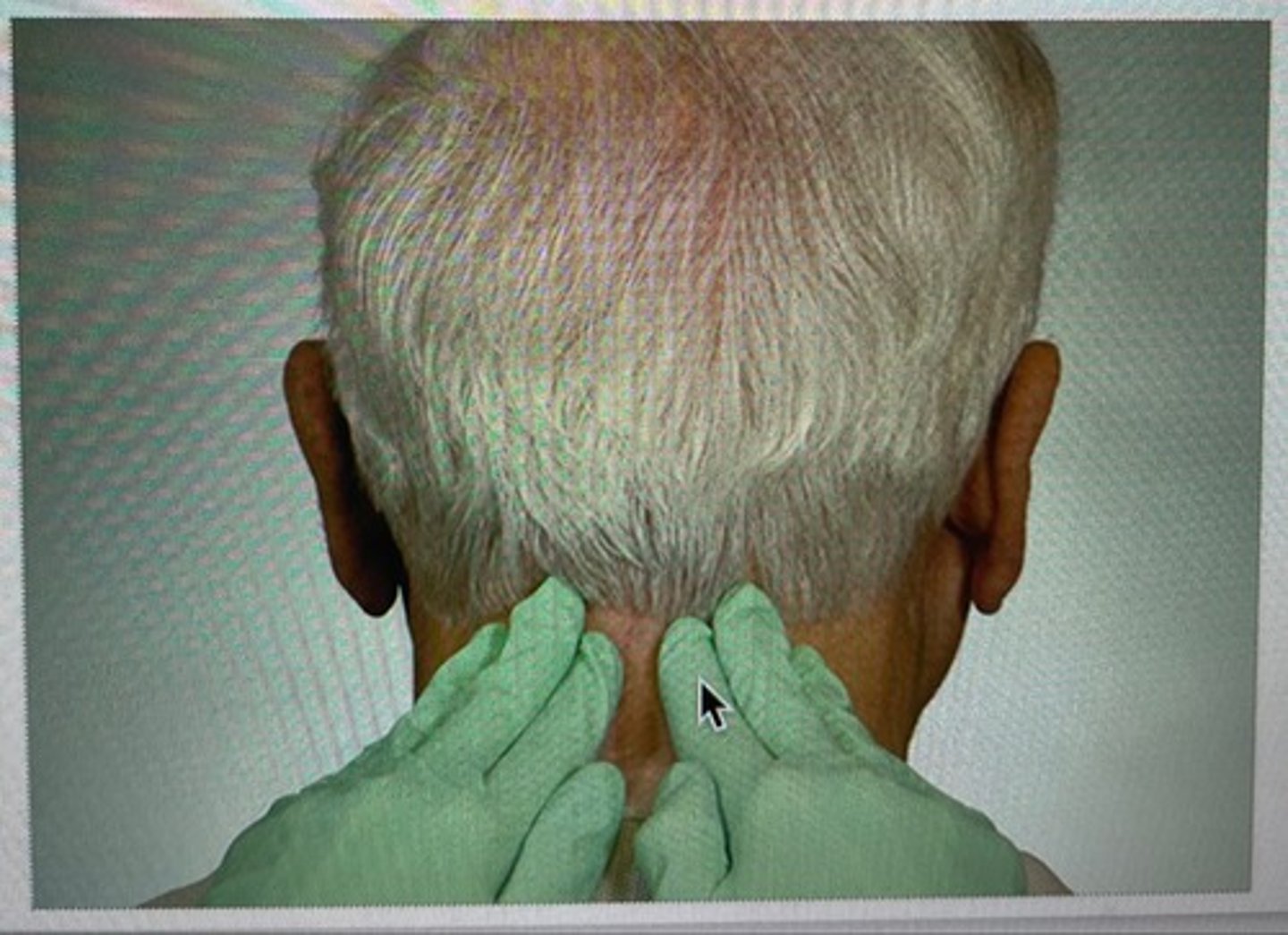
occipital lymph nodes
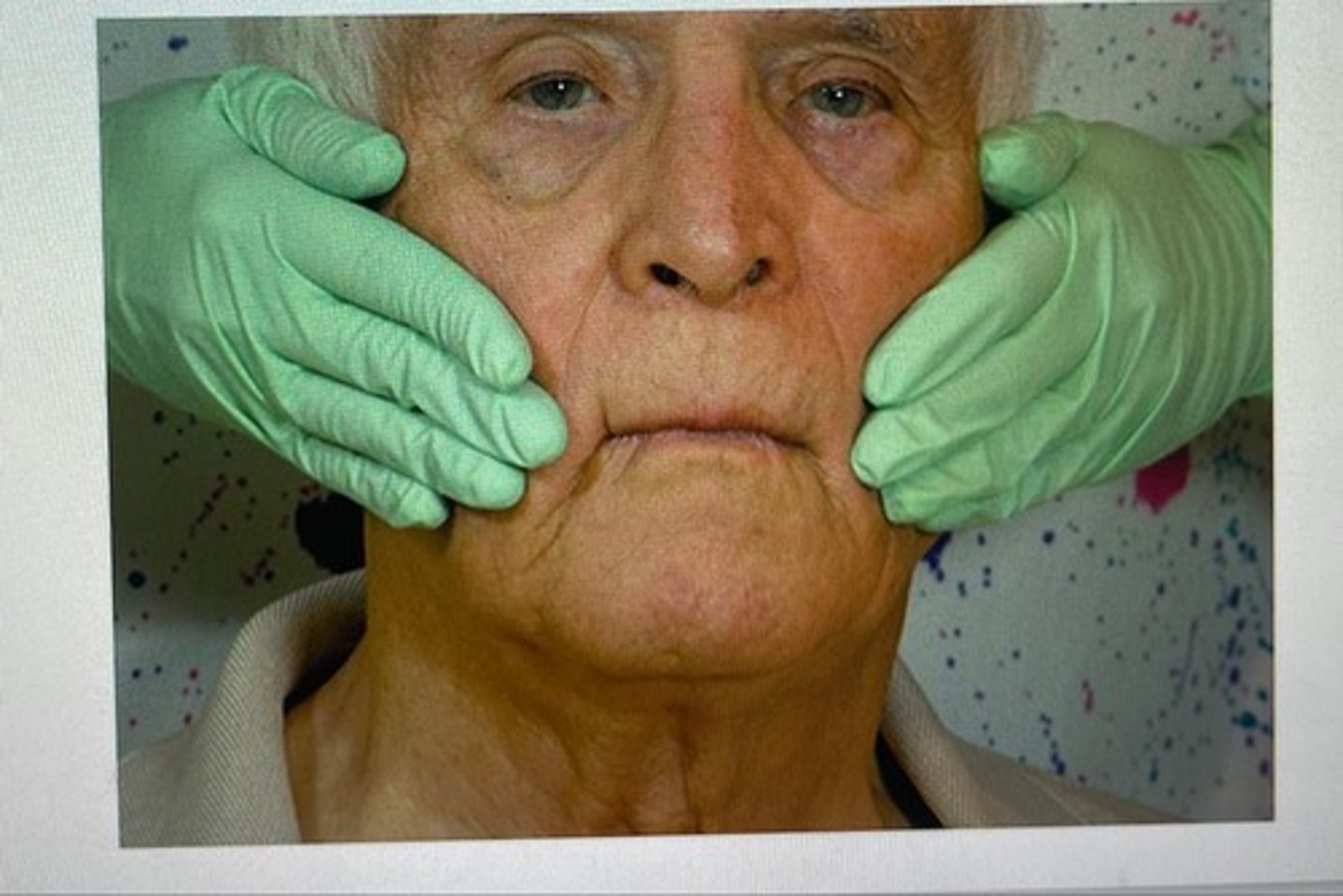
parotid glands
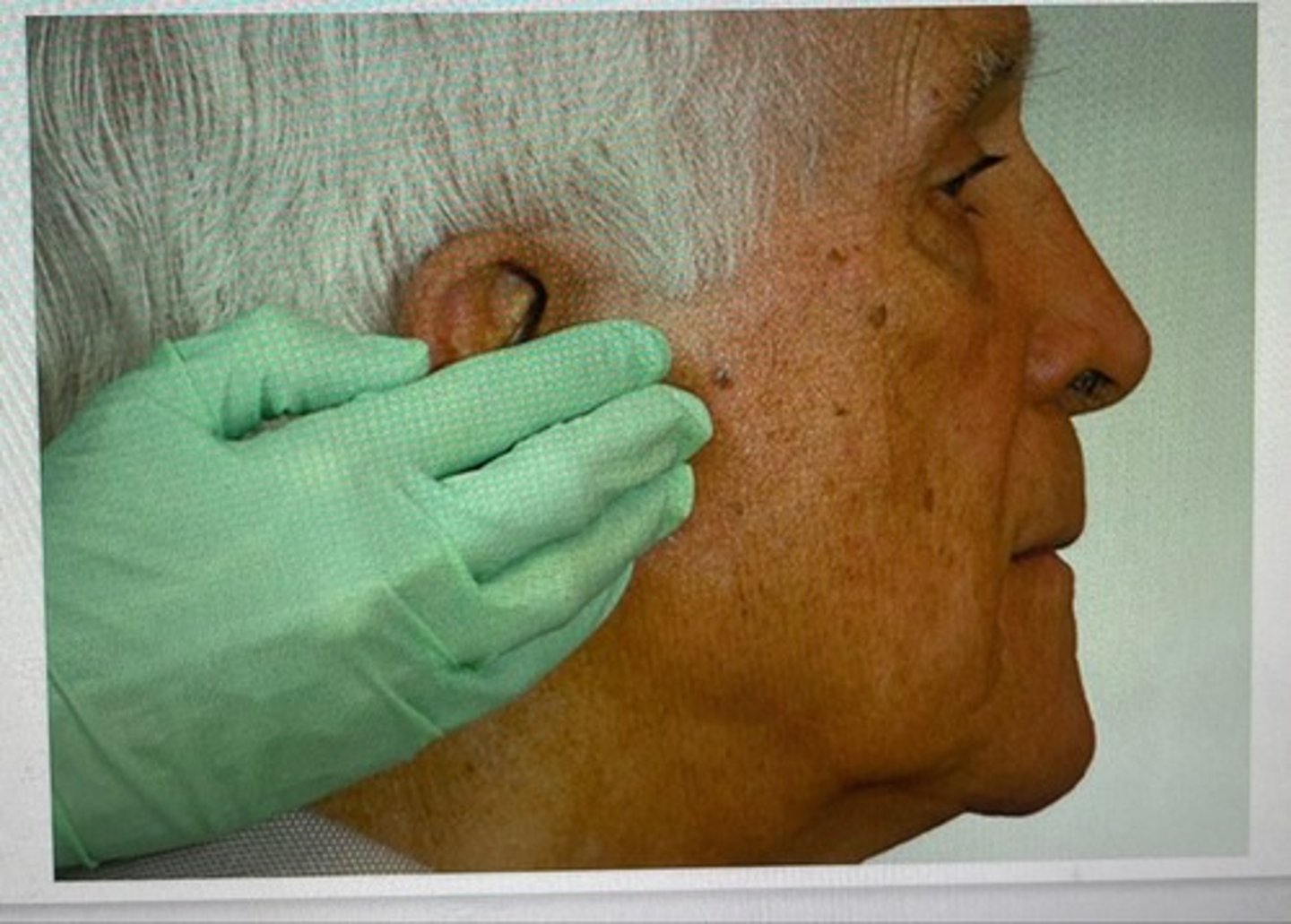
pre auricular lymph nodes
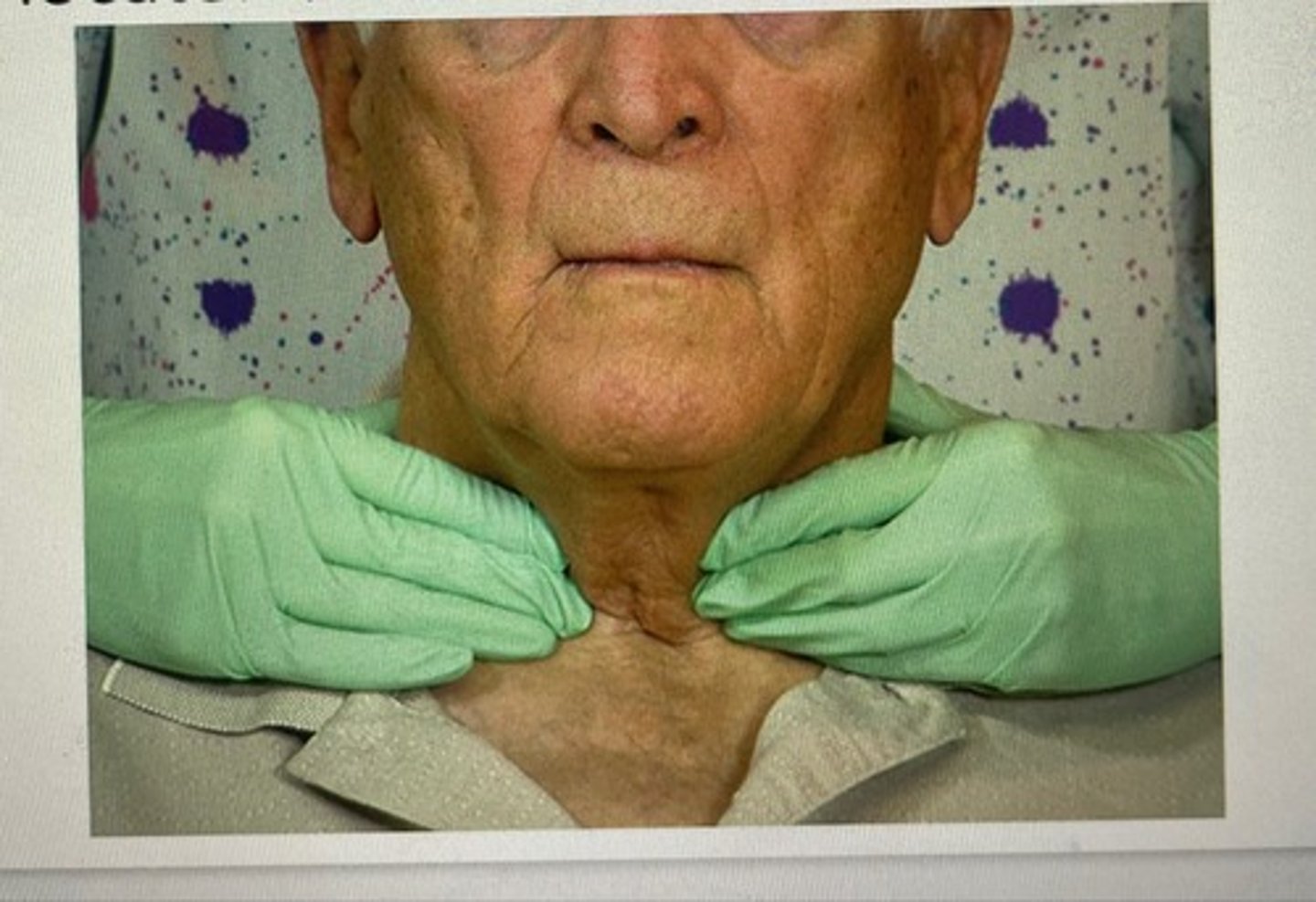
thyroid gland
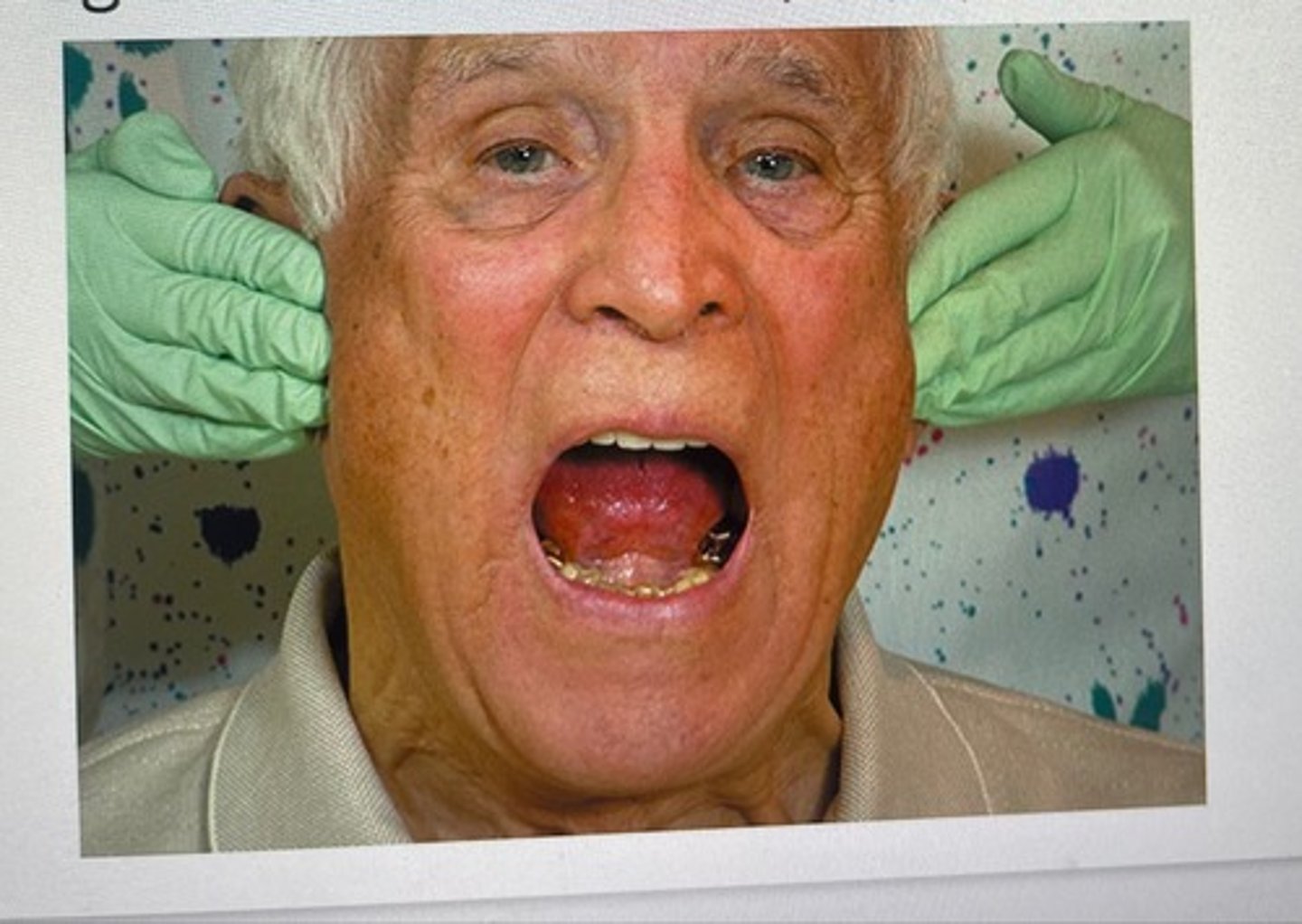
tmj
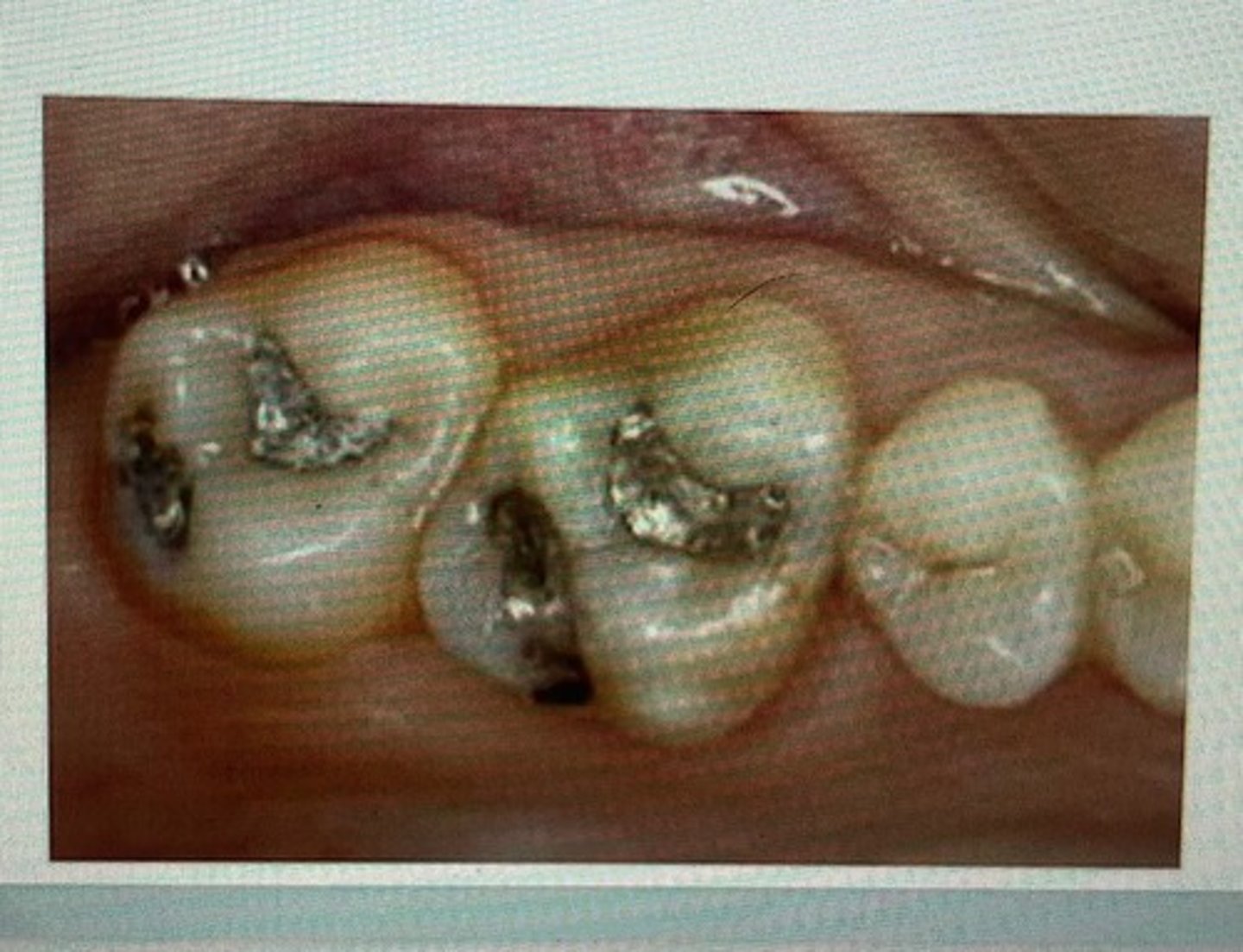
class I restoration
class I restoration
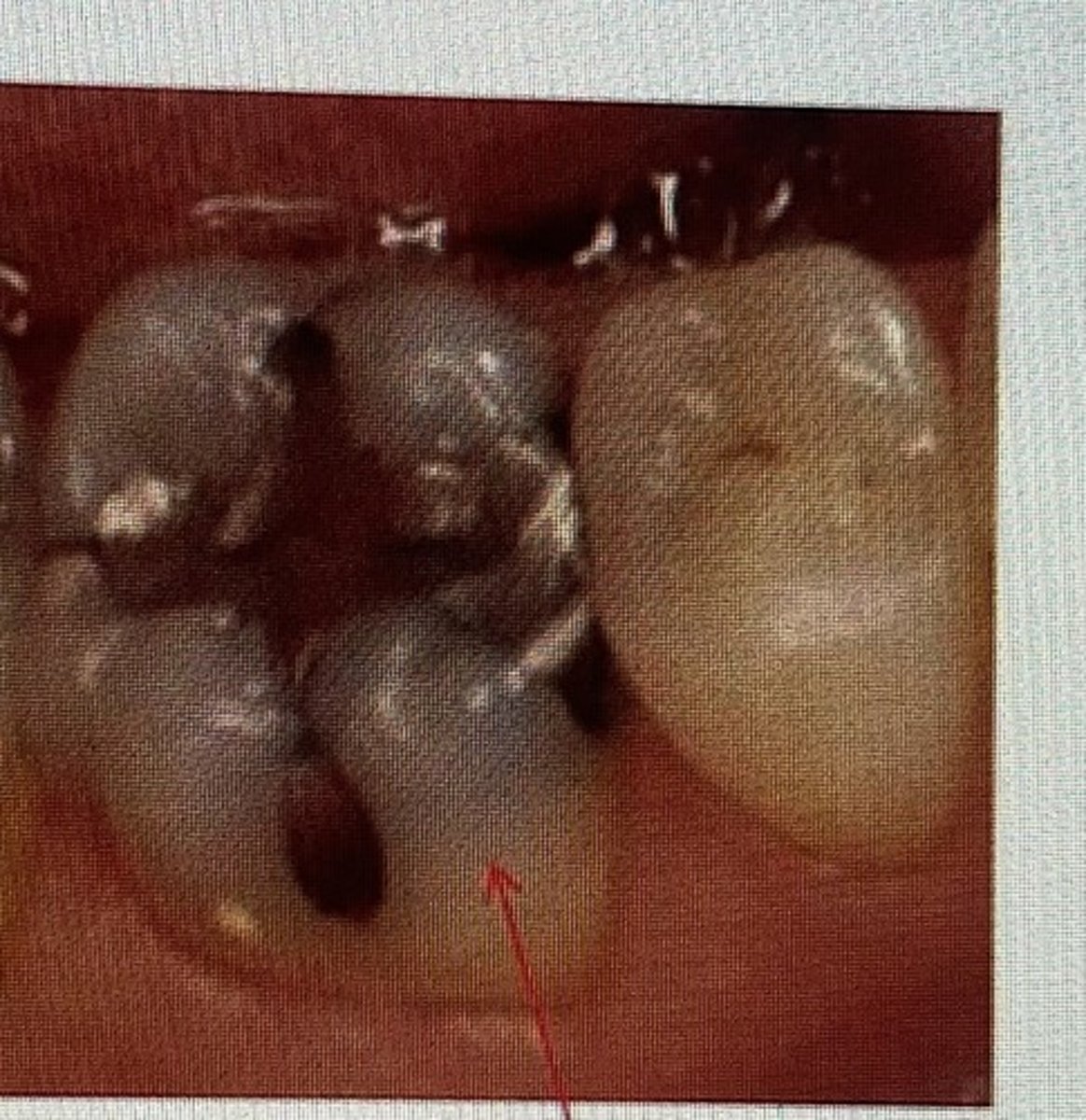
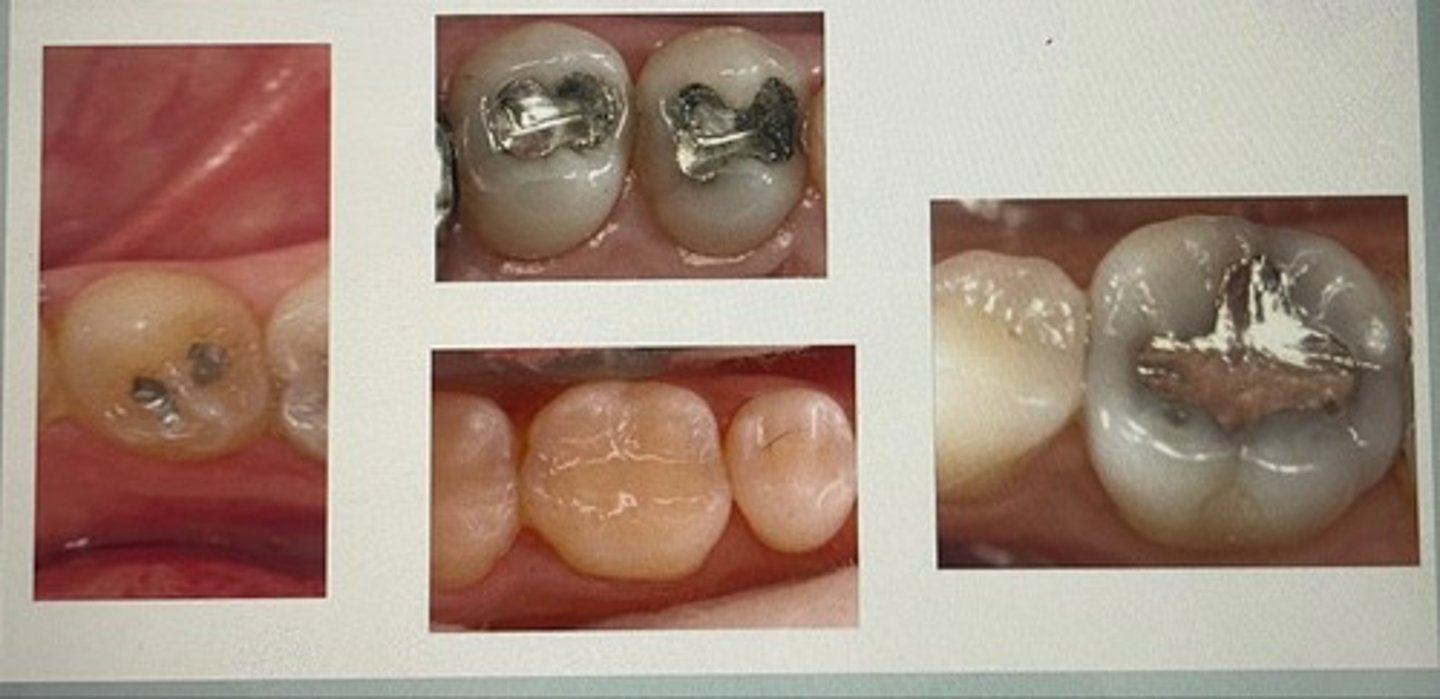
class II restoration
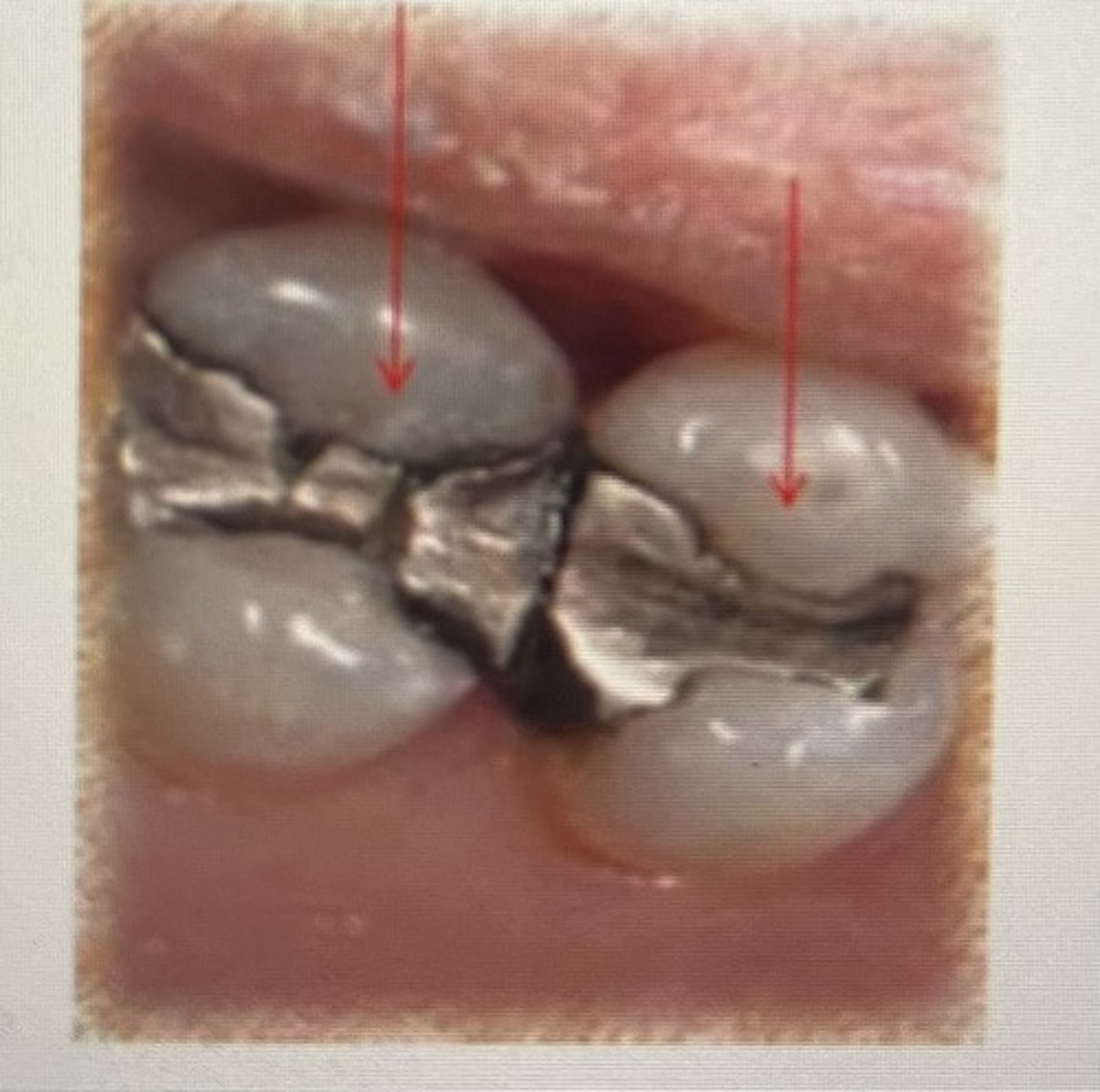
Class II restoration
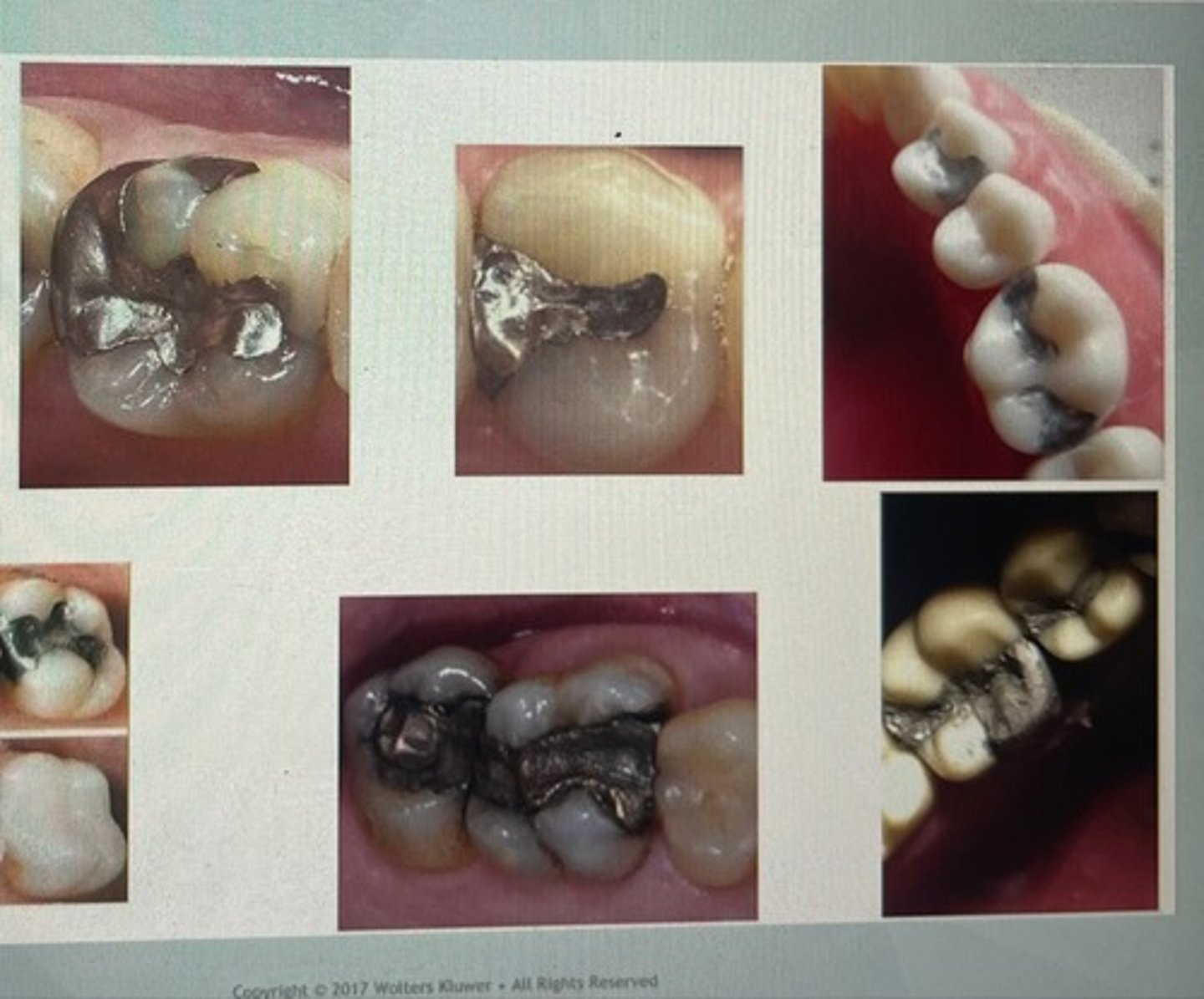
class II restoration
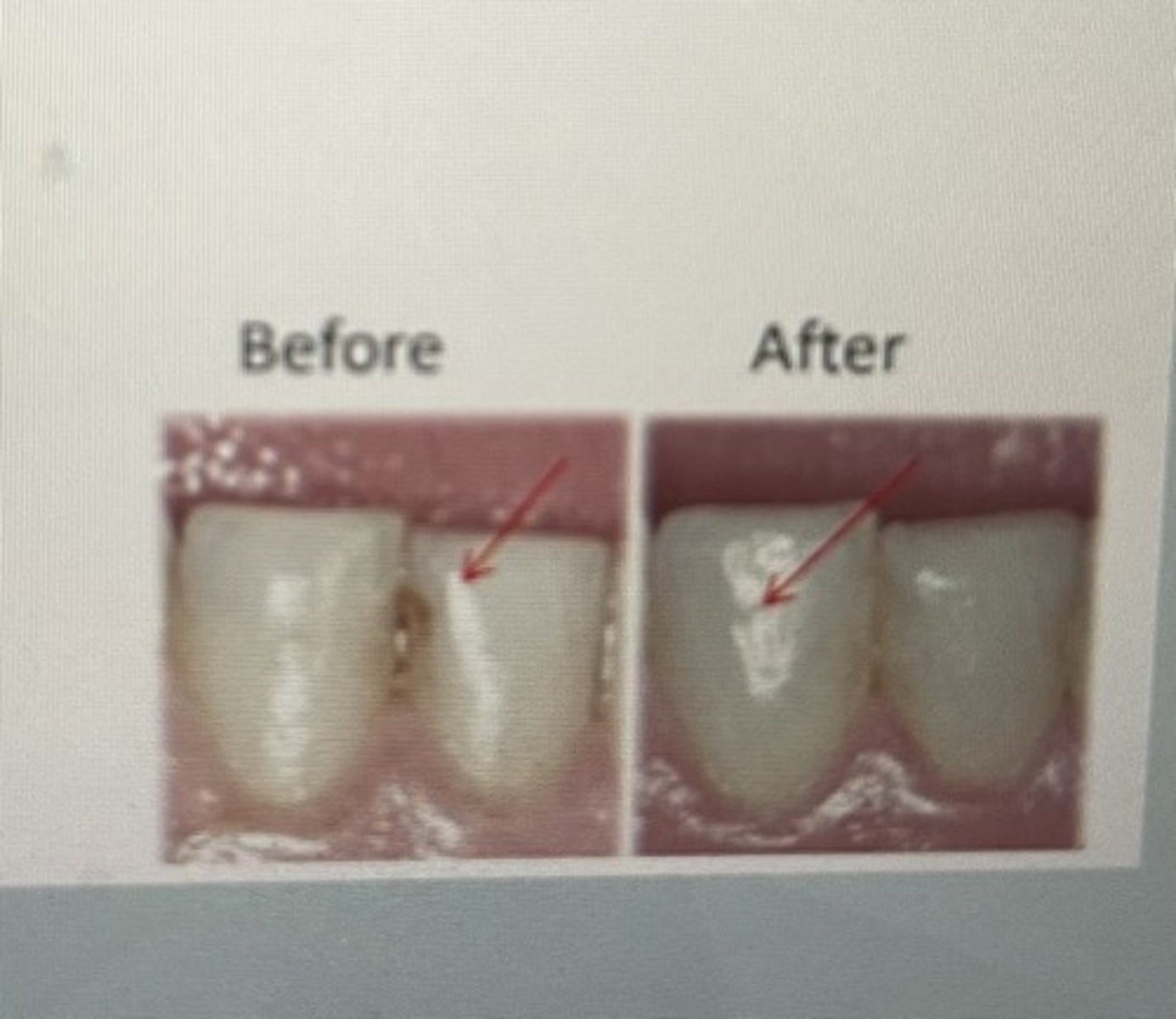
class III restoration
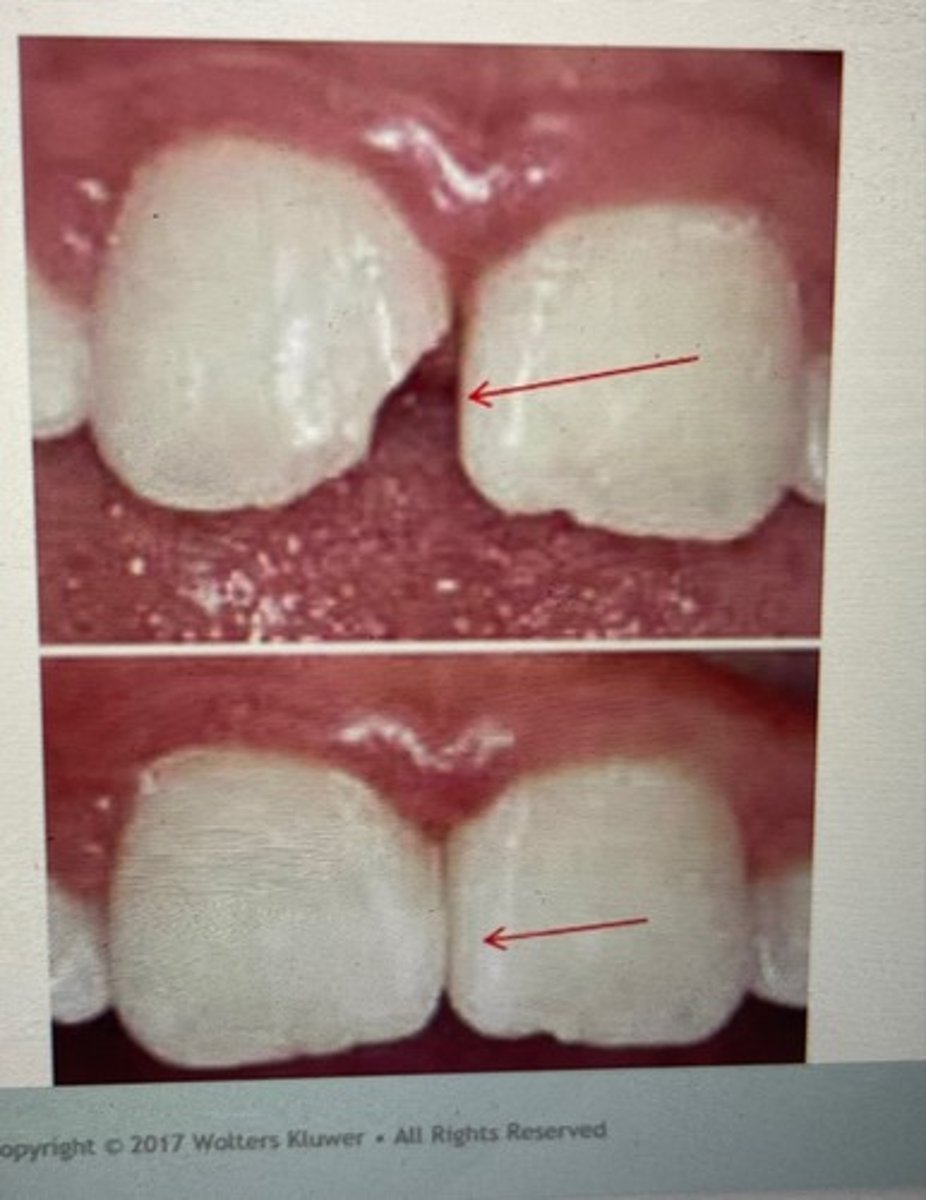
class IV restoration
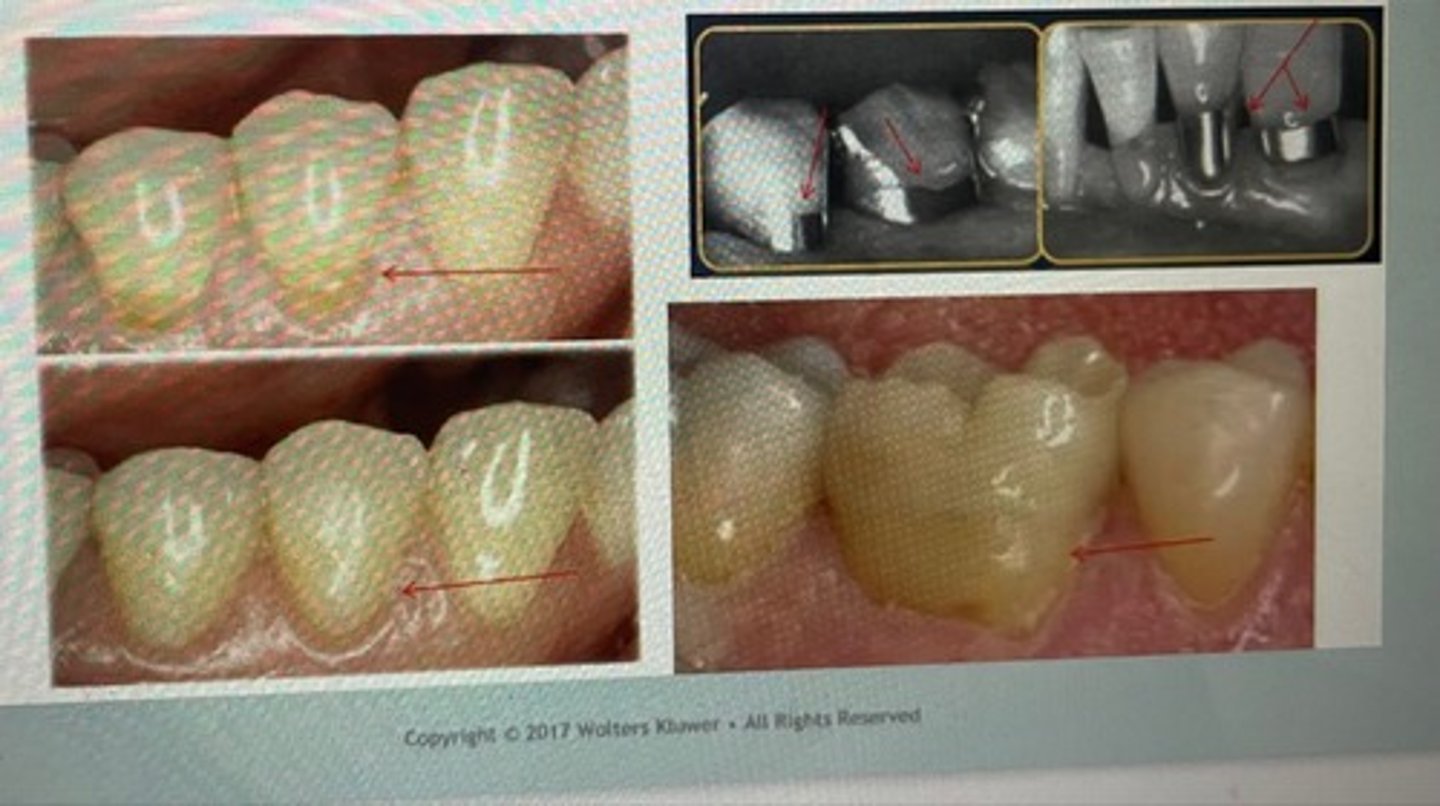
class V restoration