Spleen, GI, Hernia, FAST, Thyroid For Final Pt 1
1/123
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
124 Terms
General GI approach uses a ______ high frequency transducer
Linear
For a general GI exam, the patient is in the _________position, though _______ positions may also be used.
supine, decub
What scanning technique is used for GI
“Mowing the Lawn”
Normal sonographic findings of the GI Tract
Bowel is compressible, shows a layered appearance, peristalsis is present
Large intestine wall thickness
<4mm
Small intestine wall thickness
3-4mm
The appendix is a remnant of the __________ of the cecum, and is a long __________ structure
apex; tubular
The appendix is located in the ________________ point and can extend in any direction
McBurney’s
Appendix length
9cm - 3-3.5 inches
Appendix is covered in proximal ______ w/peritoneum
2/3
Appendicitis is an _____________process of the appendix
inflammatory
Appendicitis is most common in _______________
children/young adults
Appendicitis is caused by:
Obstruction which leads to infection
Complication of appendicitis:
Peritonitis which can lead to perforation (life-threatening)
S/S of appendicitis:
N/V, fever, diarrhea, elevated body temperature, elevated WBC, REBOUND TENDERNESS, + McBurney’s sign
Appendicitis pain begins in the ____________ region and radiates to the RLQ
Periumbilical
Crohn’s disease is an _________ GI process with unknown cause and can effect ____ part of the GI tract
Inflammatory; any
Crohn’s Disease occurs most commonly in:
young adults
Most common site for Crohn’s
Terminal ileum
S/S for Crohns
Painful right iliac mass, crampy abdominal pain, intermittent diarrhea, weakness, fever, elevated WBC, poor malabsorption
Crohn’s disease is often associated with a narrowed _______
lumen
Evaluation for Crohn’s disease includes:
Monitoring the wall for thickness, evaluate for abscess and FF, look for lymph adenopathy, increased vascularity may be seen, attempt to evaluate for FISTULAS to skin, bladder or other bowel
Ulcerative Colitis does NOT result in ____________ formation
fistula
Ulcerative Colitis is a similar inflammatory process to Chron’s disease and shows a ________ bowel wall, with ____________ vascularity compared to Crohn’s, appearance is ________ ___________
thickened; increased; worm-like
USA of appendicitis
Targetoid or bulls-eye appearance, non-compressible, lacks peristalsis, fat surrounding appendix, may or may not have appendicolith, hypoechoic w/blunted end
In appendicitis, the diameter is more than _____ mm
6
FAST stands for:
Focused Abdominal Sonography for Trauma
Purpose of FAST exams:
Evaluate for life-threatening FF/Blood in trauma patients within the peritoneal cavity
How long does a FAST exam take and who is it performed by?
5 minutes, by a resident/physician
FAST views
Morrison’s pouch, Peri splenic view, Paracolic Gutters (2), Pericardium, pelvic
Morrison’s pouch is located between the
liver and kidney
RUQ fluid pathology often involves:
RUQ fluid collection
Perisplenic view evaluates interface between _________ and ___________. Common findings include FF at the ______ ________
spleen; kidney; splenic hilum
Pelvic view is evaluated with a _____ bladder, at a ______ view, and is sensitive to detecting ____ in the posterior cul-de-sac
full; midline; FF
Paracolic gutters are located along the ________ abdomen borders, FF may collect here and float _________
bilateral; intestines
Pericardial view is typically imaged with a _________ approach, but you can also use a ________ view. This evaluates for ____ around the heart
sub-xiphoid; parasternal; FF
eFAST evaluates for chest emergencies such as:
Hemothorax, pleural effusion, and pneumothorax
Perinephric hematoma may occur post-________
biopsy
Parenchyma injuries are common in the _______ and _____ due to trauma
liver; spleen
Parenchymal injuries appearance changes over time, initially: ___________ w/low-level echoes, as coagulation occurs: __________, Eventually_________ due to hemolysis
hypoechoic; echogenic; anechoic
Urolithiasis Clinical S/S:
Spasmodic flank pain that radiates to the pelvis, fever, syncope
Urolithiasis USA:
Echogenic foci w/shadowing, hydro may be seen
Aortic Dissection Clinical S/S:
Sudden chest pain, syncope
Aortic Dissection USA:
Aneurysm, intimal flap, false lumen
Paraumbillical Hernia Clinical S/S:
Lower abdominal mass, visible w/Valsalva maneuver
Paraumbillical Hernia USA:
Bowel peristalsis in mass, reducible w/pressure
Time out:
Immediately before a procedure, performed w/everyone in the room, confirm patient, procedure, location and reason
FNA
Fine needle aspiration, thin needle
Core Bx:
Thicker needle, samples a larger area, can be an option when FNA isn’t sufficient
Lab values to review before a Paracentesis
Platelet count, coagulation factors
Adrenal Cyst
Uncommon, female prevalence, asymptomatic, incidental finding, incidental findings, unilateral
Adrenal hemorrhage
Rare in adults, common in neonates w/traumatic delivery
S/S of adrenal hemorrhage
Abdominal mass, anemia, hyperbilirubinemia
USA of adrenal hemorrhage
Hyperechoic mass like initially, cystic and complex as regresses and gets reabsorbed
Adrenal Adenoma
Benign, usually less than 2.5cm, increased prevalence in older patients w/diabetes or HTN
USA of adrenal adenoma
Well defined, round, homogeneous, hypoechoic, symmetrical
Malignant adrenal tumors
rare, female prevalence, can cause Cushing’s (change in function)
Malignant adrenal tumors USA:
Small, well defined, homogeneous, hypervascular
METS in adrenals
4th most common site, from liver, lungs, and bone
Adrenal medulla tumor: Pheochromocytoma
Mass than secretes excess epinephrine and norepinephrine, usually benign
Adrenal Pheochromocytoma S/S:
HTN, headaches, heart palpations
USA of Pheochromocytoma
Homogeneous poor transmission, unilateral, large and bulky, hyperechoic surrounding area
Most common malignancy of adrenal in childhood?
Adrenal neuroblastoma
USA Adrenal Neuroblastoma
Heterogeneous, poorly defined borders, calcifications and necrosis, color will show capsular flow, doppler analysis demonstrates low resistance arterial flow
Most common Primary retro tumor?
Lymphoma
Lymphnodes suspicious if …
Greater than 2cm, round, RI greater than 0.7
Urinoma
Walled off collection of extravated urine, trauma, surgery or obstruction, usually around kidney or perinephric space
Urinoma USA
Sonolucent unless complicated or long standing
A neck ultrasound is ordered to evaluate a patient with hypercalcemia. What is the first pathology that you would evaluate for?
Parathyroid ademoma
A patient has been referred for a parathyroid ultrasound for a suspected parathyroid adenoma in the superior parathyroid gland. Where would you look for this pathology?
Posterior to mid thyroid
According to TI-RAD, what defines a very hypoechoic nodule?
Darker than the surrounding muscles.
The right and left lobes of the thyroid gland are connected across the midline by the _________.
Isthmus
The most common thyroid carcinoma is:
Papillary
True/False: Thyroid carcinoma is a rare entity.
True
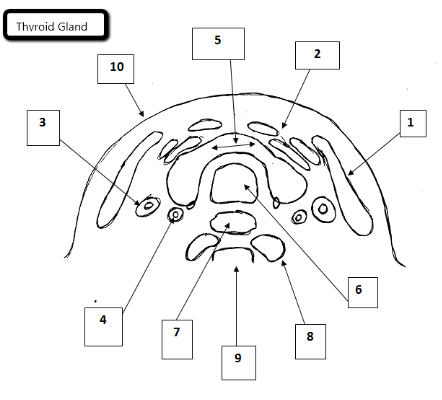
1
Sternocleidomastoid
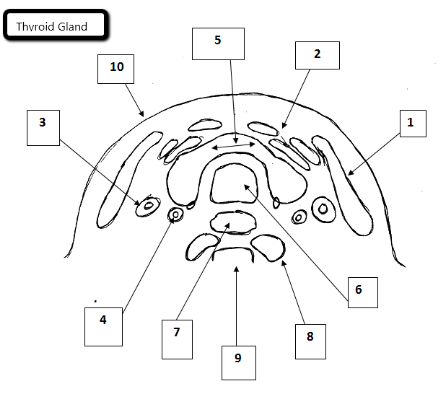
2
Strap muscles
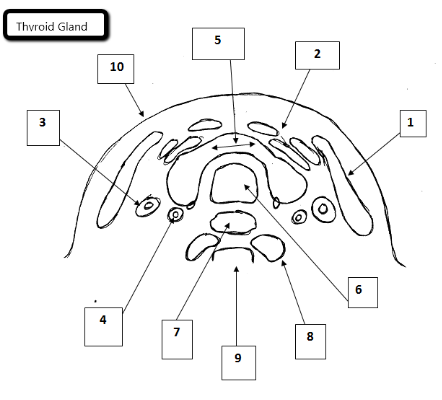
3
Jugular vein
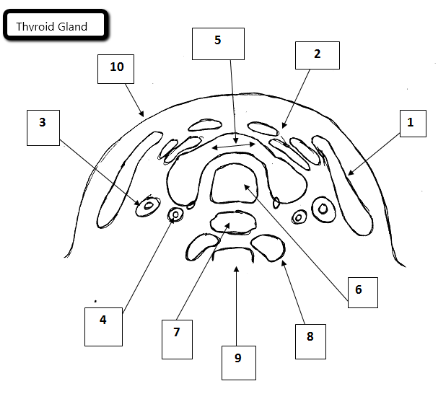
4
Carotid artery
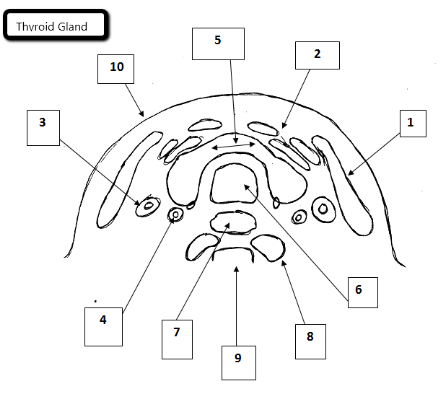
5
Thyroid gland
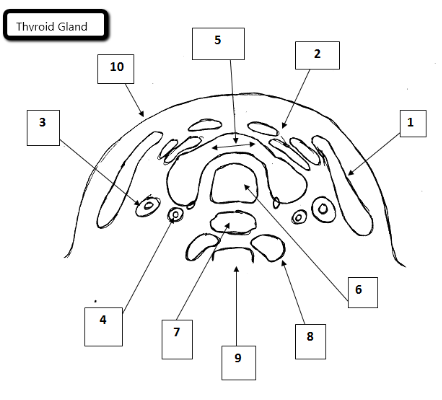
6
Trachea
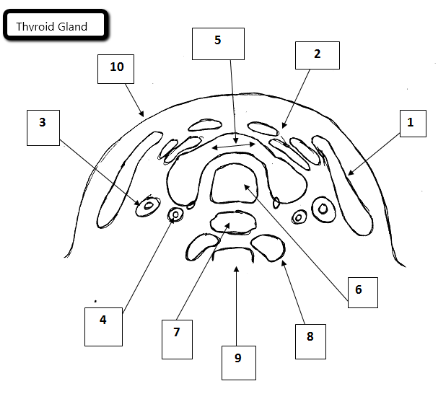
7
Esophagus
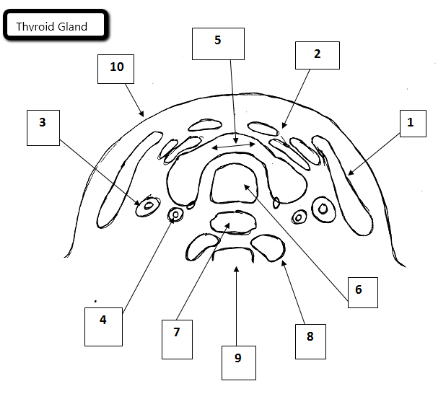
8
Longus Coli Muscles
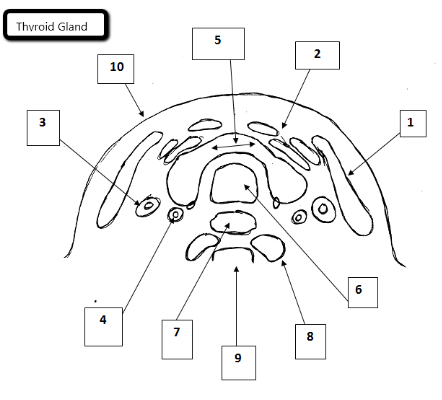
9
Cervical spine
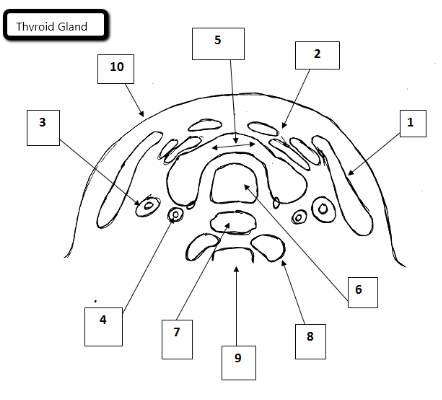
10
Skin
List 2 indications to perform a lymph leveling exam.
Assist tumor staging and evaluate the neck region
hypoechoic gland with fibrous strands
Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis
Cystic nodule with comet tail artifact
Colloid Cyst
hypoechoic nodule with multiple microcalcifications
Papillary carcinoma
homogeneous gland that measures 6cm in length
Goiter
Adenoma
solid, peripheral halo
Cyst
Smooth wall, sonolucent w/enhancement
Goiter
enlargement of thyroid gland, wt gain, hair loss, deep voice
Caricnoma
irregular contour, echodense
Hypothyroidism
Lethargic, sluggish
Hyperthyroidism
wt. loss, nervousness
What is the USA of a normal thyroid gland?
Homogeneous with mid-high level grays
What are the 3 main lab values that we look for when correlating for thyroid exams?
T3, T4, TSH
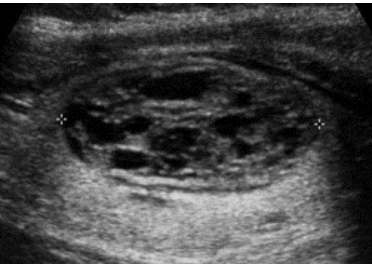
What type of composition is this? Does it have a benign or malignant correlation according to TI-RADS
spongiform, benign
When evaluating a lymph node in the neck which of the following criteria that would signify a benign process
wider than tall, centralized hilum, centralized vascularity
Hyperthyroidism
Hypermetabolic state, increased amount of thyroid hormones (Grave’s)