Anthropology Chapter One
1/137
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
138 Terms
Cultural, Linguistics, Archaeology, Biological
Four subcategories of anthropology
Carolus Linnaeous
Binomial Nomenclature and Taxonomy
Jean Baptiste de Lamarck
Documents fossil record in Paris Bason
Charles Darwin
“Descent with Modification”
Microevolution
Change within a species over time
Macroevolution
Changes above the species level, or in the patterning over time
Lamarchianism
Inheritance of acquired characteristics
Conditions for Natural Selection, and eventually adaption
Variation, Heritable, Competition with Selective Pressure, Differential Reproductive Success
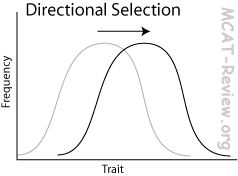
Directional Selection
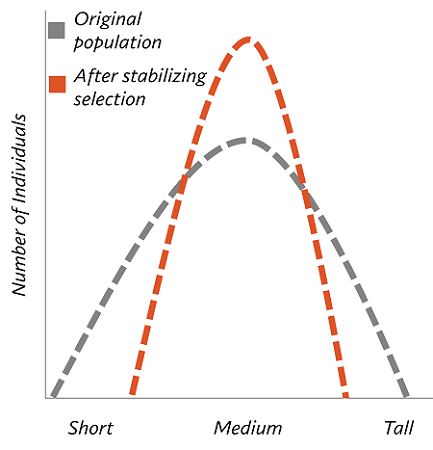
Stabilizing Selection
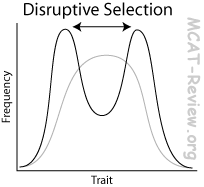
Disruptive Selection
Particulate Inheritance
The idea that heredity is based on the transmission of alleles
Structural Genes
Encode for protein synthesis
Regulatory Genes
Guide expression of structural genes
Mendel Postulate 1.
Hereditary characteristic is controlled by existed by particulate unit factors that exist in pairs. What is their name?
Mendel Postulate 2.
An individual has 2 different unit factors responsible for a characteristic, and only one is expressed and said to be dominant to other. Is this always true?
Mendel Postulate 3. (Mendel’s Law of Segregation)
During fertilization, the pair units seperate so that each cell may recieve a unit factor with an equal liklihood
Mendel Postulate #4 (Mendel’s Law of Independent Asssortment)
Genes found on different chromosomes are sorted into gametes independently of each other. What if they’re on the same chromosome, what is this called?
Point Mutation
A single base change
Insertion
Insertion of nucleotide base pair
Deletion
Deletion of nucleotide base-pair
Quantitative Variation
Phenotypic variation that is distributed across some scale
Qualitative Variation
Phenotypic traits that can be easily grouped into distinct categories
Polygenic Traits
Traits determined by 2+ genes
Pleiotropy
Single gene having multiple phenotypic effects
Heritability Equation (explain it)
H=(Genetic Variability)/ (Genetic Variability + Enviornmental Variability )
Evolution is occuring if
there are changes to the allele frequencies over time
Hardy Weinberg Equilibrium
q²+2pq+p² = 1.0
p+q=1.0
The hardy weinberge equilibrium will be altered when
there is mutation, there is gene flow, genetic drift, natural selection, and individuals do not differential reproductive success
Mutation
Change in organism’s genome
Gene Flow
The movement of alleles from one population to another, i.e. migration
Genetic Drift
Change in allele frequency due to random chance, what population size is this more likely to happen in?
Found Effect
An isolated population caries only genetic variation from a few amount of ancestors
Sexual selection
Differential Reproductive sucess
Sexual Dimorphism
Difference in traits between sexes as a result of sexual selection
Reproductive Potential
Possible output of offspring by one sex
Systemics
Study of taxonomy
Convergent Evolution
More or less parallel evolution. No shared common ancestor. Two similar features that evolved independently in seperate organisms
Cladistics
Classifying species on the basis of ancestral/derived traits → to distinguish lineages
Biological Species Concept
Species are defined as two populations that cannot interbreed with each other
Evolutionary Species Concept
Defines species as lineages with unique ancestral lineage
Ecological Species Concept
Defines species on ecological niche
Recognition Species Concept
Species are defined on unique traits or behaviors that allow mating to materialize (Pheremones, bird song, plumage, ect.)
Reproductive Isolating Mechanism
A factor preventing two species from hybridizing
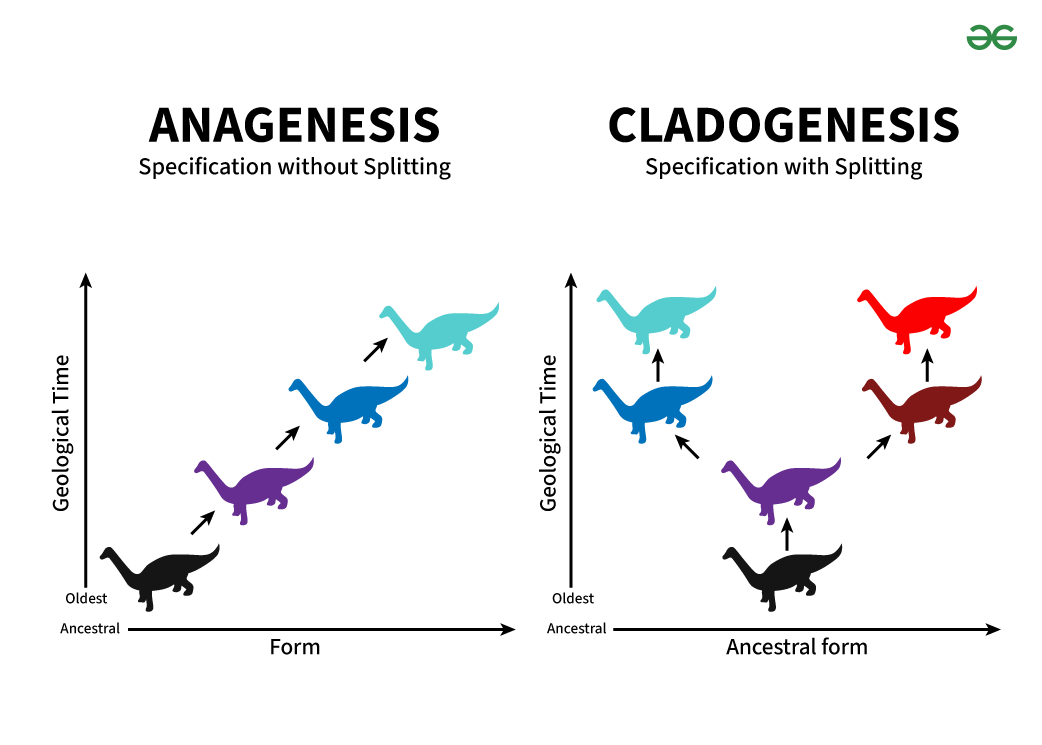
Anagenesis
evolution of trait into another
Cladogenesis
Evolution over time into two new species
Allopatric Speciation
Speciation due to geographic seperation
Parapatric Speciation
Gene flow occurs, but 2 sepearate populations are created in adjacent areas because of some niche
Sympatric Speciation
Population in the same area, but some force of evolution still causes two new species to be produce (think disruptive evolution)
Gradualism
Fossil record indication evolution happens in a steady rate over time
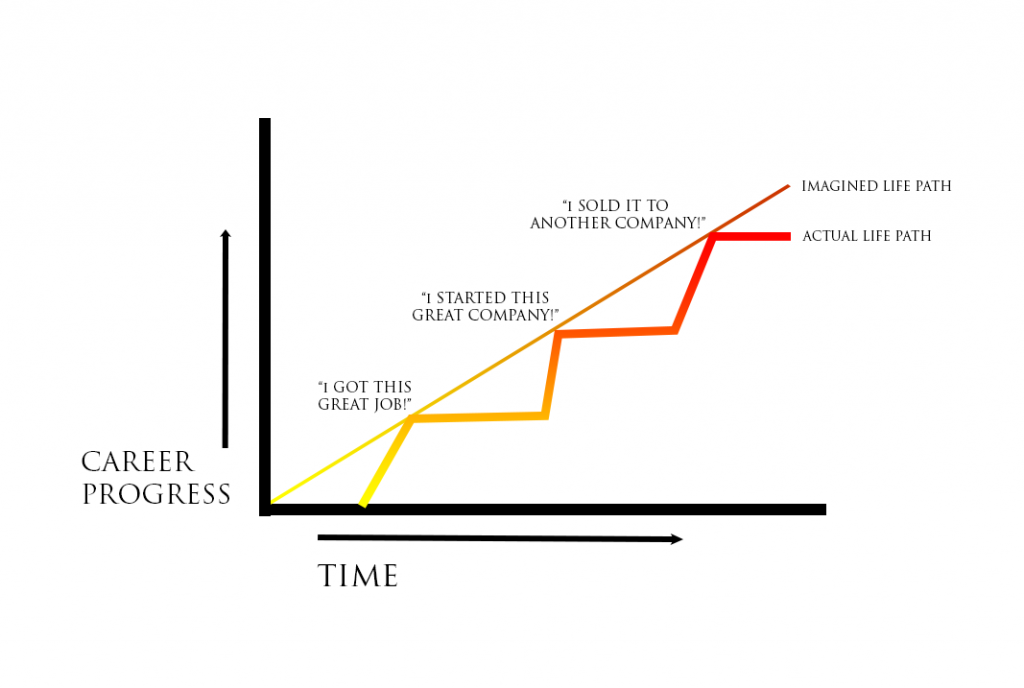
Punctuated Equilibrium
Major phenotypic change over short periods of time
Adaptationism
The believe that all aspects of organism have been molded by natural selection
Reductionism
The theory that an organism is the sum of of many evolved parts
Kin Selection
rb>c what does each variable mean?
Systematics
The science of diversity
Phylogeny
Pattern of evolutionary relationships between species
Clades
A chunck of some phylogenetic tree
Synapomorphy
Shared, derived character inherited from a least common ancestor
Homology
Character shared by taxa that is inherited
Homoplasy
A shared character that is not inherited from a common ancestor
Symplesiomorphy
A “primitive” characteristic inherited from a distant common ancestor
Igneous Rocks
Rocks formed under volcanic pressure
Sedimentary Rocks
Rocks formed under pressure of weight
Metamorphic Rocks
Rocks formed under the pressure without melting/transformation of other rocks
Paraphyletic Group
A group that does not include an LCA, but resembles each other
George Gaylord Simpson
Evolutionary Species Concept: Speciies is an unbroken lineage of populations linked by ancestory and descent
Kingdom
Animalia/Metazoa
Phylum
Chordata
Sub phylum
Vertebrata
Class
Mamamillia
Order
Primates
Suborder
Haplorhini
Superfamily
Hominidea
family
hominidae
tribe
hominini
genus
homo
species
sapiens
Era
Cenozoic P
Period
Quatenary, Tertiary(Paleogene, Neogene)
Epoch
Halocene, Pleistocene, Piocene, Miocene, oligiocene, eocene, paleocene
Lithostratigraphy
Study of geologic deposits and their formation
Biostrigraphy
Correlations based on ages of other organisms
Tephrostratiagraphy
Identifying volcanic ash by fingerprint
Radiometric dating
Use of radioactive decay to estimate age
Lacustrine/Fluvial Sediments
Sediments from lake shores
Cave Deposits
Sinkholes (How are these good for fossils? )
Stratiagraphy
Relative dating techniques → tells us age of fossils
Absolute Dating Methods
Carbon Dating (Explain Process), K/Ar Dating (volcanic rock, explain)
Oxygen isotopes
Explain Process and relation to climate change
Antitilopini, Alcelaphini
Open Dry Habitats
Tragelaphini, Apeyceretoni
Closed, Dry habitats
Reducini, Bovini
Closed, Wet, Habitats
Caborn 13 Paleoecology Paleoecology
explain
Mendel’s Assumptions
Each trait controlled by a single gene
Genotype does NOT equal phenotype
Inheritance is particulate (Mendel’s Law of Segregation)
Mendel’s Law of Independent Assortment (Multiple allele types for genes)
Name experiments in which scientists discovered mechanisms of inheritance
Sperm Cells by Leeuvonhoek
Mammalian egg cells by von Baer
Contents of nucleus discovered to be high in phosphorus by Miescher
“Nuclein”
DNA
Rosalind Franklin
Took photograph 51, the closer the spots, the larger the distance → Informed double helix
X-Ray Crystal Diffraction
Molecule Gets stretched out and molecule gets shot down it
James Watson + Francis Crick
Proposed structure of DNA
Credited for the biological Species Concept
Ernst Mayr