Auditory: External Otitis, Cerumen & Foreign Bodies, Acute Otitis Media, Otitis Media with Effusion, Chronic Otitis Media &Mastoiditis, Meniere Disease, Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo, and Conductive Hearing Loss
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
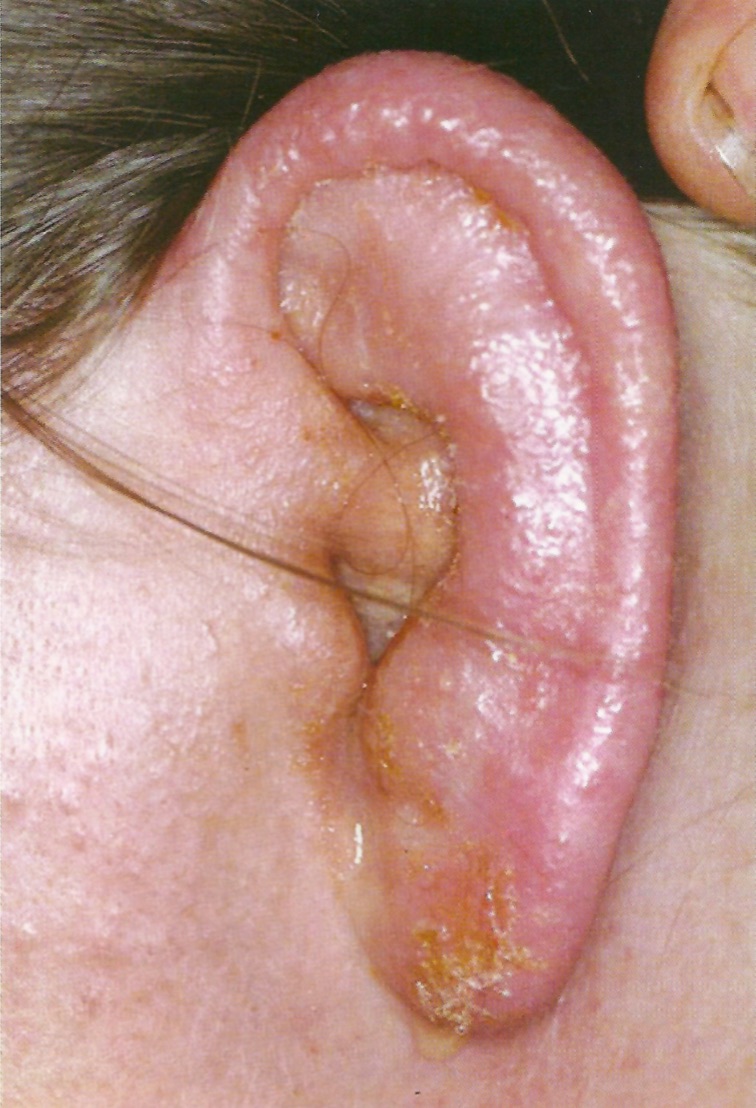
What is external otitis?
it is inflammation or infection of the auricle and ear canal
What caused external otitis?
swimming
trauma
piercings
bacterial infection
What are some signs and symptoms of external otitis?
otalgia (ear pain)
swelling of outer ear
muffled hearing
fever
What are some labs and diagnostic tests for external otitis?
otoscopic examination
culture & sensitivity tests
What are some nursing actions and interventions for patients with external otitis?
administer antibiotics when ordered
administer corticosteroids when ordered
apply moist heat to affected ear
What are some teachings for patients with external otitis?
tell pt. to take antibiotics for 7 to 14 days
tell pt. to take corticosteroids for 7 to 14 days
tell pt. to use moist heat on affected ear
tell pt. they can take ibuprofen for ear pain at home
tell pt. to apply ear drops at room temperature and the tip of the applicator cannot touch the ear
tell pt. to stay laying on their side for at least 2 minutes after applying ear drops
What is cerumen & foreign bodies in the ear?
it is a cerumen impaction or object within the ear causing blockage
What are some signs and symptoms of cerumen impaction in the ear?
discomfort in affected ear
decreased hearing in affected ear
tinnitus
vertigo
Who should remove a foreign body in a patient’s ear?
a primary health provider should remove a foreign body in a ear
What are some nursing actions and interventions for a patient with cerumen impaction?
irrigate with body temperature solution
use lubricant drops to soften cerumen before irrigation
What are some teachings for a patient with a cerumen impaction?
tell pt. to clean ear with washcloth and fingers
tell pt. to not use cotton-tipped applicators
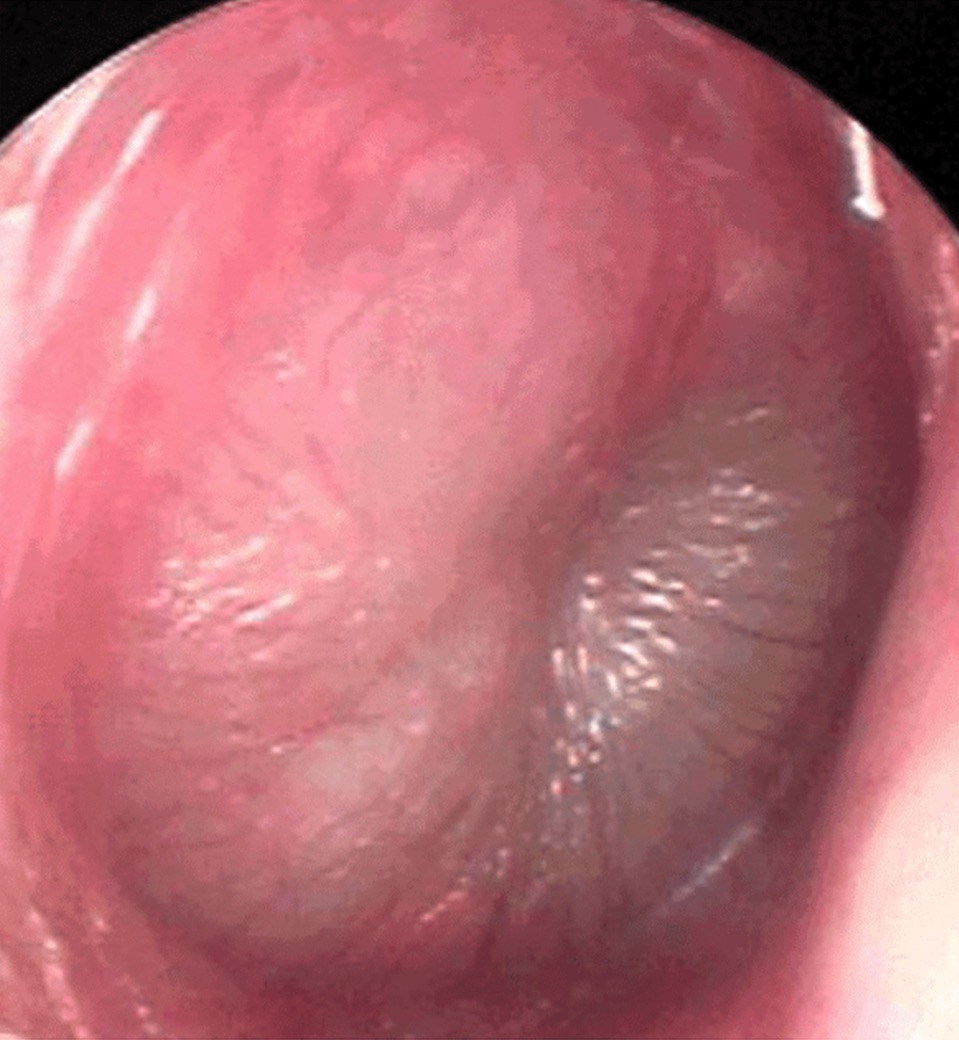
What is acute otitis media?
it is an infection of the tympanic membrane, ossicles and space of the middle ear
When does acute otitis media occur?
it usually occurs during childhood
What signs and symptoms of acute otitis media?
inflamed tympanic membrane
red, bulging tympanic membrane
pain within the ear
fever
malaise (fatigue)
drainage from ear
reduced hearing in affected ear
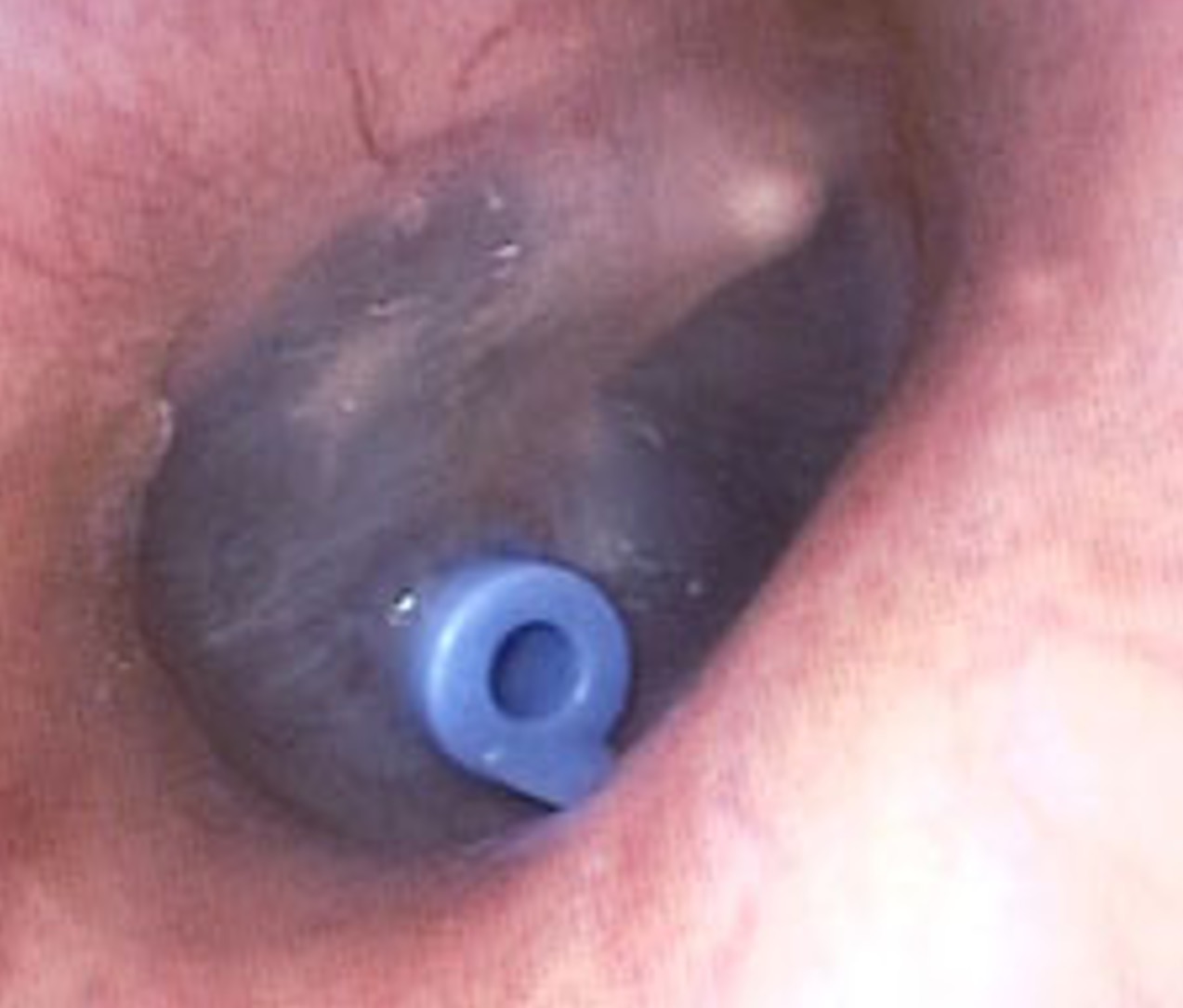
What are some surgical interventions for acute otitis media?
myringotomy
tympanostomy tube
What are some nursing actions and interventions for acute otitis media?
give oral antibiotics when ordered
apply ear drops when ordered
assess tympanic membrane
give antihistamines or corticosteroids if cause is allergies
What is some teachings for patients with acute otitis media?
tell pt. to apply ear drops when ordered
tell pt. to apply ear drops at room temperature
tell pt, to not touch applicator tip to ear
tell pt. to stay laying on their side for at least 2 minutes after applying ear drops
What is otitis media with effusion?
it is inflammation of the middle ear with collection of fluid in the middle ear space
What can cause otitis media with effusion?
acute otitis media
sinus infection
What are some signs and symptoms of otitis media with effusion?
feeling of fullness in affected ear
sounds of popping within affected ear
decreased hearing in affected ear
What are some teachings for patients with otitis media with effusion?
tell pt. that it will resolve without treatment
tell pt. that it may occur for weeks or months
What is chronic otitis media & mastoiditis?
it is purulent exudate and inflammation involving ossicles, auditory tube and mastoid bone
What are some signs and symptoms of chronic otitis media & mastoiditis?
painless
hearing loss in affected ear
nausea
vomiting
What is a complication of chronic otitis media and mastoiditis?
cholesteatoma is a complication
What are some labs and diagnostic tests for chronic otitis media and mastoiditis?
otoscopic exam
culture & sensitivity
audiogram
x-ray
CT
MRI
What are some surgical interventions for chronic otitis media and mastoiditis?
What are some nursing actions and interventions for chronic otitis media and mastoiditis?
give otic or systemic antibiotics when ordered
drain ear
during post-op, do dressing care & keep suture line dry
What are some teachings for patients with chronic otitis media and mastoiditis?
tell pt. post-op they may experience impaired hearing
teach pt. how to change packing or dressing
tell pt. to keep ear clean & dry
What is Meniere disease?
it is accumulation of endolymph in the membranous labyrinth
What are some signs and symptoms of Meniere disease?
episodic vertigo (pt. suddenly falls; pt. describes it as being pulled down by one ear)
drowsiness
tinnitus
ear pressure
feeling of fullness in affected ear
What are some surgical interventions for Meniere disease?
Decompression & shunting
vestibular nerve section
ablation of labyrinth
gentamicin injection through the tympanic membrane
What are some nursing actions and interventions for Meniere disease during acute vertigo attacks?
give antihistamines, anticholinergics, or Benzos to decrease vertigo and lessen nauseous & vomiting
make sure pt. has an IV for medications
put pt. in a quiet, dark room
put pt. on fall risk precautions
What are some nursing actions and interventions for Meniere disease between attacks?
give diuretics when ordered
administer antihistamines when ordered
What is some teaching for patients with Meniere disease?
let pt. know there is no cure
tell pt. to not make sudden head movements
tell pt. to go into a dark & quiet room
tell pt. to have a low sodium diet
tell pt. to limit caffeine intake
teach vestibular exercises
What is benign paroxysmal positional vertigo?
it is vertigo caused by free-floating debris in the semicircular canal
What can trigger benign paroxysmal positional vertigo?
it can be triggered by positional changes
What is a nursing intervention for benign paroxysmal positional vertigo?
do Epley maneuver with pt.
What is conductive hearing loss?
it is outer/ middle ear problems impair transmission of sound waves
What are the types of conductive hearing loss?
impacted cerumen
otitis media
tympanic membrane perforation
otosclerosis (bones of the inner ear harden & do not move like they should)
allergies
benign tumors
What is a diagnostic test for conductive hearing loss?
audiogram (air-bone gap)
What is presbycusis?
it is hearing loss due to aging
What is tinnitus?
it is ringing in the ears
What causes decline in balance, slowing of motor responses and musculoskeletal limitations in regard to hearing in the geriatric population?
atrophy of vestibular structures
What are some diagnostic studies done to test for hearing loss?
audiometry
electrocochleography
tympanometry
tuning fork tests
What is audiometry?
it is a screening that tests for hearing acuity to hear frequencies
What is electrocochleography?
it records electroactivity on the cochlea & the auditory nerve
What is tympanometry?
it checks the middle ear & the mobility of the tympanic membrane
What is a tuning fork?
it compares hearing by bone conduction & air conduction
What picture depicts external otitis?
What picture depicts acute otitis media?
What picture depicts tympanostomy tube for reoccurring acute otitis media?
What picture depicts otitis media with effusion?
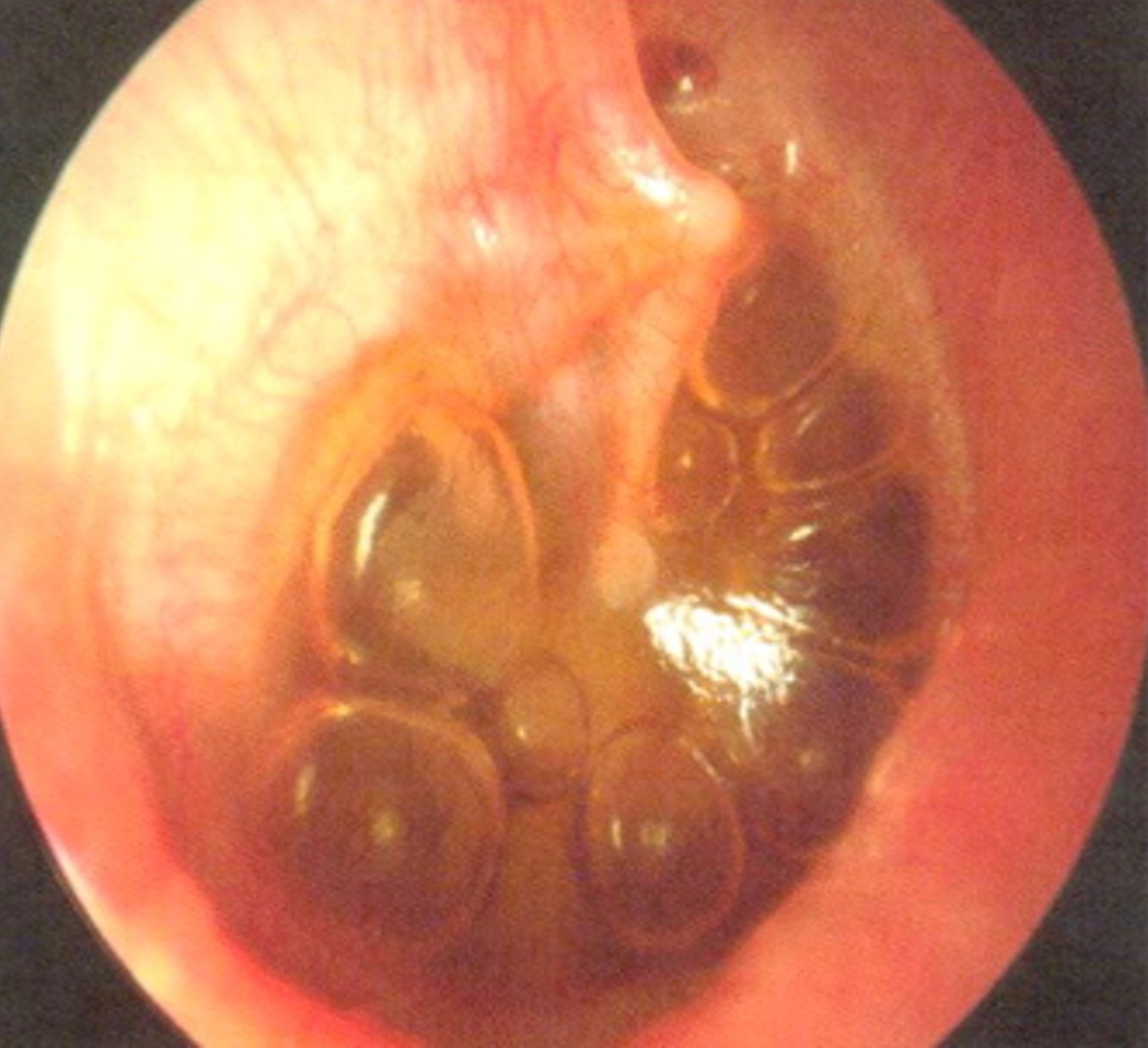
What picture depicts a cholesteatoma due to chronic otitis media and mastoiditis?
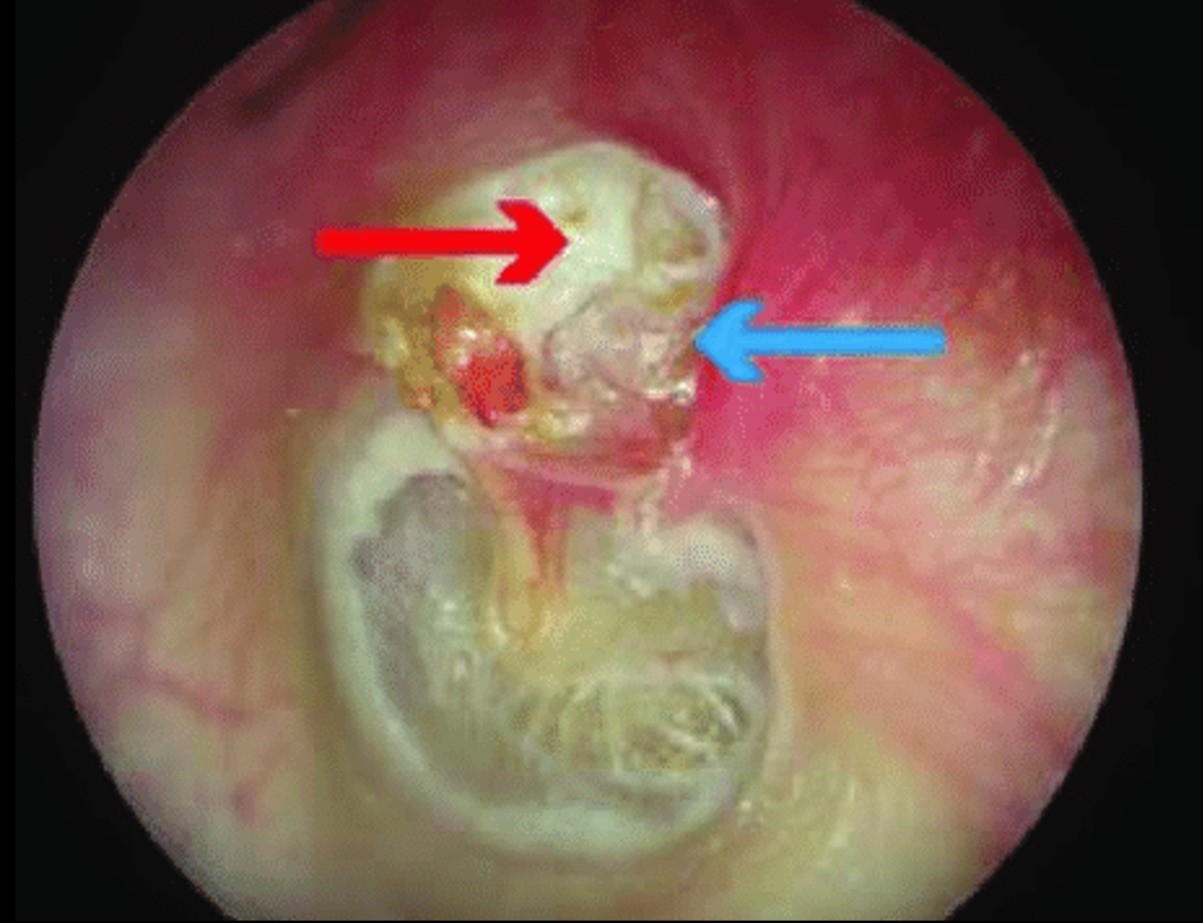
What can happen if a cholesteatoma forms due to chronic otitis media and mastoiditis?
it can cause erosion of bones around the ear
needs to be surgically removed immediately
What are some things that can cause conductive hearing loss?
impacted cerumen
otitis media
tympanic membrane perforation
otosclerosis (bones of the inner ear harden & don’t move like they are supposed to)
allergies
benign tumor(s)
What is central hearing loss?
it is the inability to interpret sound because of problem in the brain (CNS)
What is functional hearing loss?
emotional or psychologic cause
no physical reason for hearing loss but abnormal subjective hearing tests
psychologic counseling
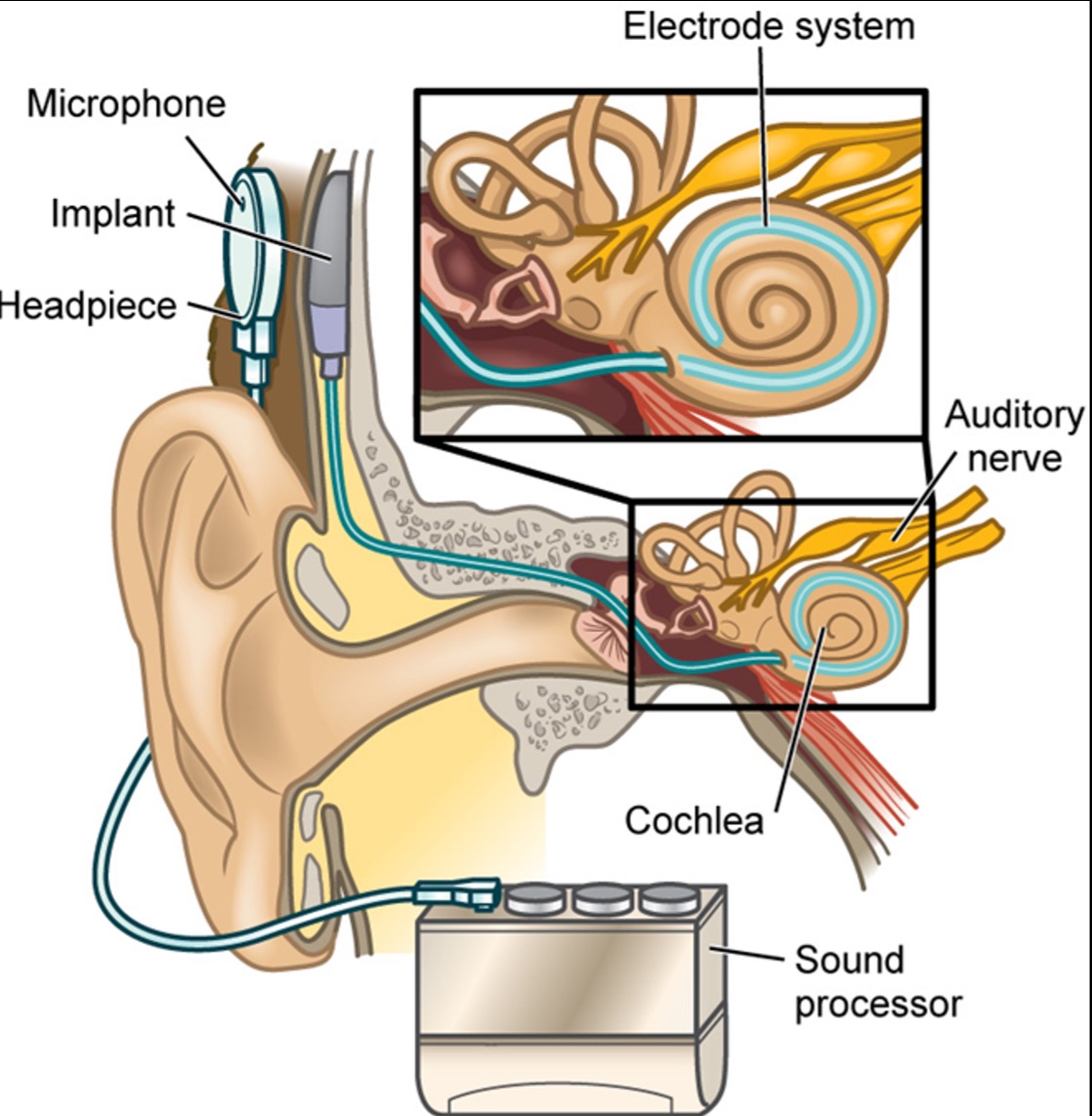
What is a cochlear implant?
it is an implant that bypasses damaged/missing portions and directly activates CN VIII
What picture depicts a cochlear implant?