Oxidative Phosphorylation/ Electron Transport Chain
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
Oxidative phosphorylation
also know as the electron transport chain. takes place in the inner mitochondrial membrane
Electron donor
NADH and FADH2, these to olceules stor energy in the proton graient
ATP synthesis
This enzyme uses the protons in NADH and FADH2 to generate ATP
Electron acceptor
Oxygen
FMN
acts like FAD+
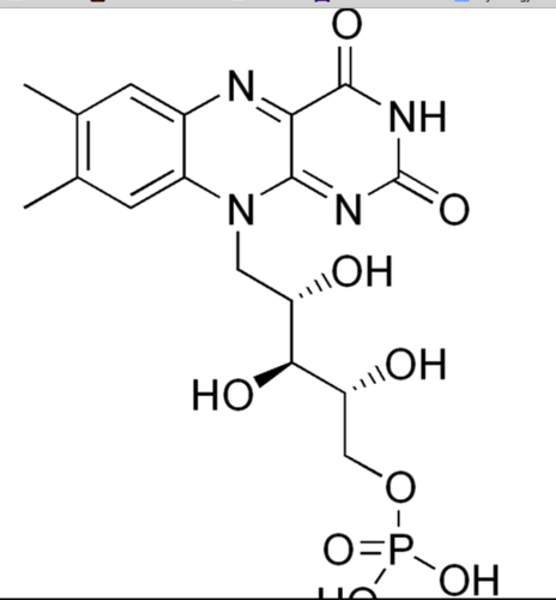
Iron-Sulfur proteins
example of these proteins are in a variety of metalloproteins, such as the ferredoxins, as well as NADH dehydrogenase, hydrogenases, coenzyme Q - cytochrome c reductase, succinate - coenzyme Q reductase and nitrogenase.[1] Iron-sulfur clusters are best known for their role in the oxidation-reduction reactions of mitochondrial electron transport.
![<p>example of these proteins are in a variety of metalloproteins, such as the ferredoxins, as well as NADH dehydrogenase, hydrogenases, coenzyme Q - cytochrome c reductase, succinate - coenzyme Q reductase and nitrogenase.[1] Iron-sulfur clusters are best known for their role in the oxidation-reduction reactions of mitochondrial electron transport.</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/2ed92fa5-9c7a-44eb-9d8b-7435ecbfcc0d.image/jpeg)
cytochrome b, c1
cytochrome b has heme b.
Coenzyme Q - cytochrome c reductase ("Complex III")
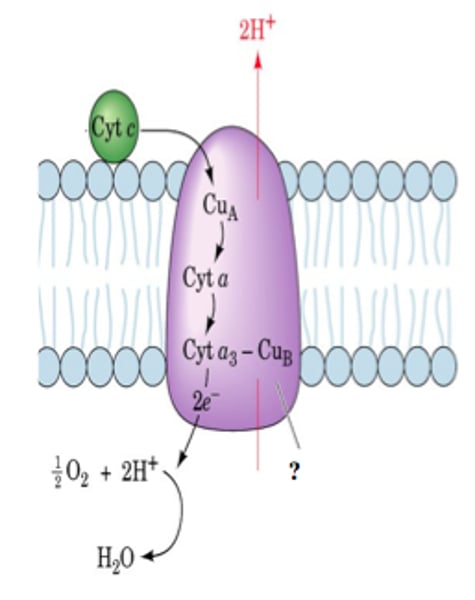
cytochrome a, a3
this cytochrome has heme A.
its also called Cytochrome c oxidase
("Complex IV") with electrons delivered to complex by soluble cytochrome c (hence the name)
Whats the complex order in oxisative phosphorylation pathway?
complex 1 to 3 to 4 or complex 2 to 3 to 4
NADH CoQ reductase
Complex I in ETC, reduces coQ oxidizes NADH, transports 4H+ to inner mitochondrial space, 44 components, L shape, bound FMN + 7 Fe-S centers primarily in matrix domain
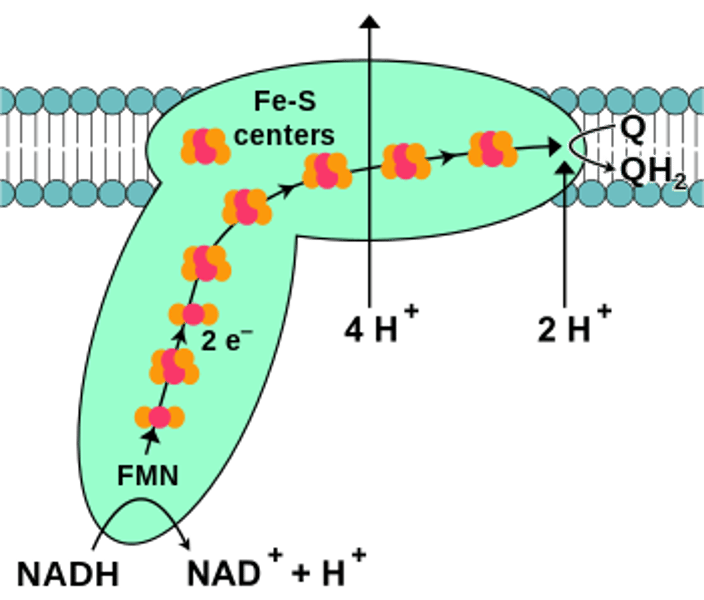
Succinate CoQ Reductase
Complex II in ETC, reduces coQ and oxidized FADH2, no proton transfer, connects TCA to ETC. Contains bound FAD, 3 Fe-S clusters + a heme
Is the only enzyme of the 4 complexes of oxidative phosphorylation to not pump protons into the mitochondrial inner membrane space.
is in the Citric Acid Cycle and in oxidative phosphorylation.
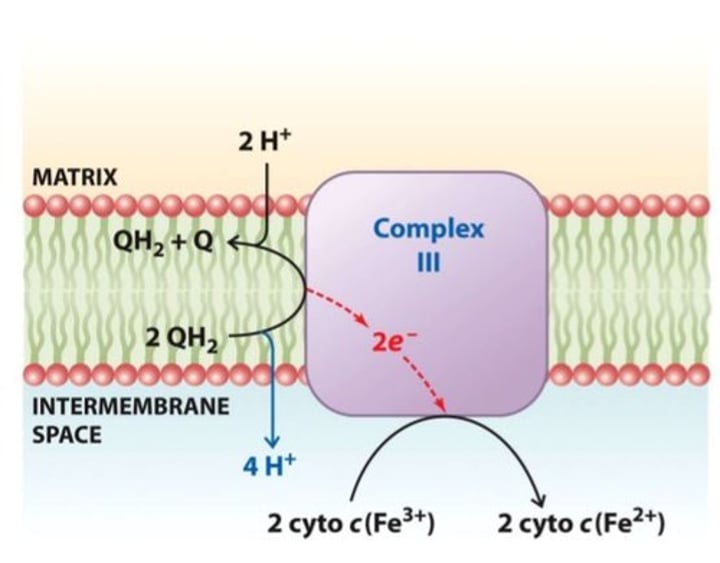
CoQ Cytochrome c Reductase
Cytochrome c is a component of the electron transport chain in mitochondria. The heme group of cytochrome c accepts electrons from the bc1complex and transfers electrons to the complex IV. Cytochrome c is also involved in initiation of apoptosis.
Soluble mobile Electron carrier
Complex III in ETC
Cytochrome C Oxidase
Complex IV in ETC, oxidizes coQ, reduces oxygen to water, 2 H+ to intermembrane space (but 4 H+ transfer), cyanide is deadly because it inactivates cytochrome c oxidase.
Standard Reduction Potential
E= E0' + RT/ (nF) ln (ox)/(red)
n= numer of electrons transferred (equvilent/mol)
F= 96.5 kJ/V mol or 24.06 kcal/V m (Faraday)
Out of the 14 polypeptides encoded in Mitochondrial DNA, which are a part of the Electron Transport Chain?
13
ADP translocase
is an integral membrane protein
Uniporter
s an integral membrane protein that is involved in facilitated diffusion
Synporter
Transports both ADP and ATP into the mitochondria
Antiporter
Transpoerts ADP into the mitochondria and ATP out
Outer mitochondrial Membrane
permeable to compounds with molecular weights < 10,000
Inner Mitochondrial Space
H+ pumped here via the action of the electron transport chain
is the positively charged side which become more acidic
Inner Mitochondrial Membrane
impermeable to most compounds, Including H+; home of electron transport chain and ATP synthase
Matrix
site of NADH production via citric acid cycle and where H+ is removed.
this is also a negitively charged space which becomes more basic
pH of the mitochondrial matrix
7.9-8.0, H+ pumps out of it so pH raises
pH of cytoplasm
7.4
pH inside the golgi
6.6
pH inside the lysosome
4.5-5.0
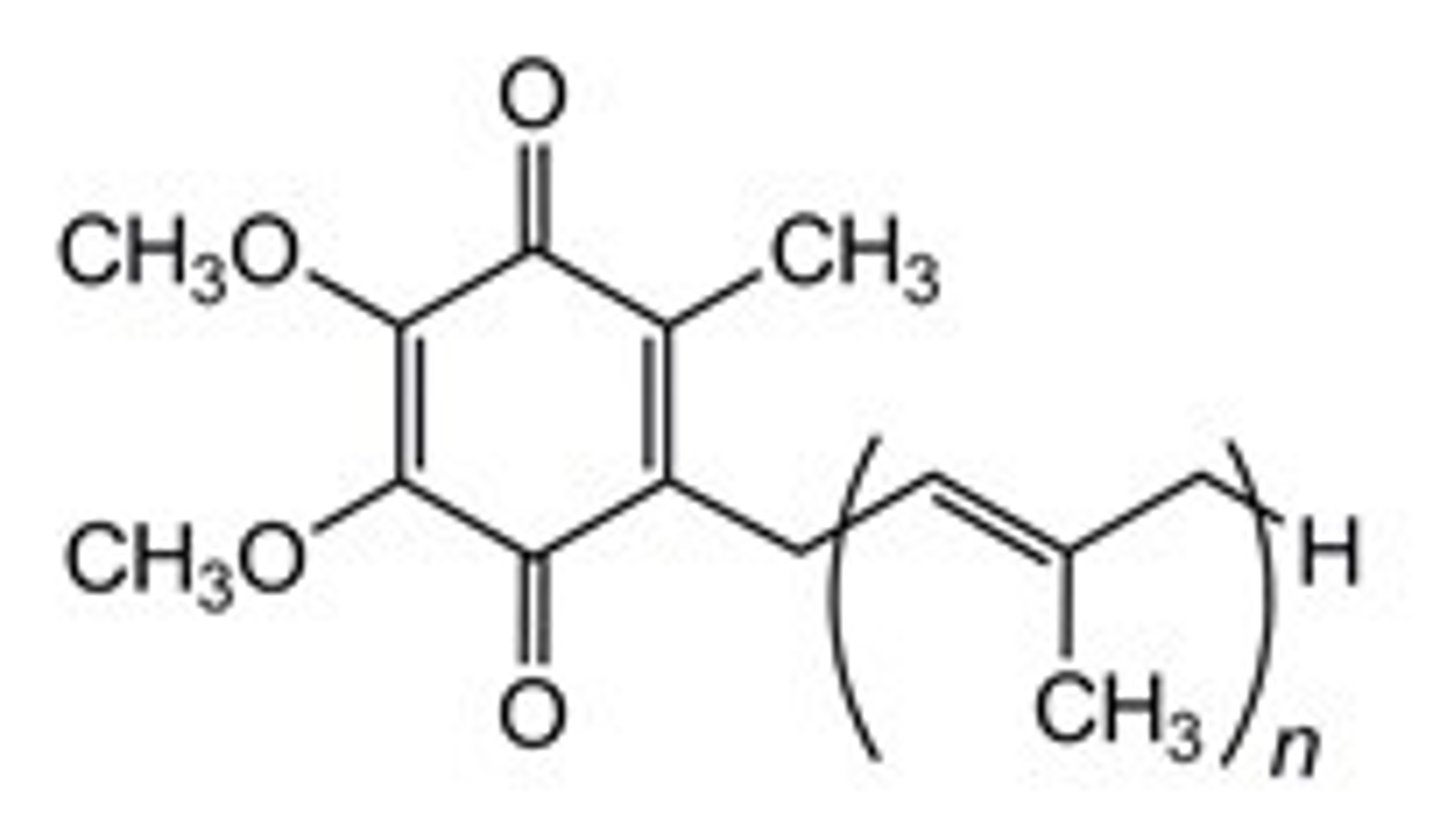
Co-enzyme Q (notecard)
is a mobile electron in the INNER MITOCHONDRIAL MEMBRANE made in (n=10)
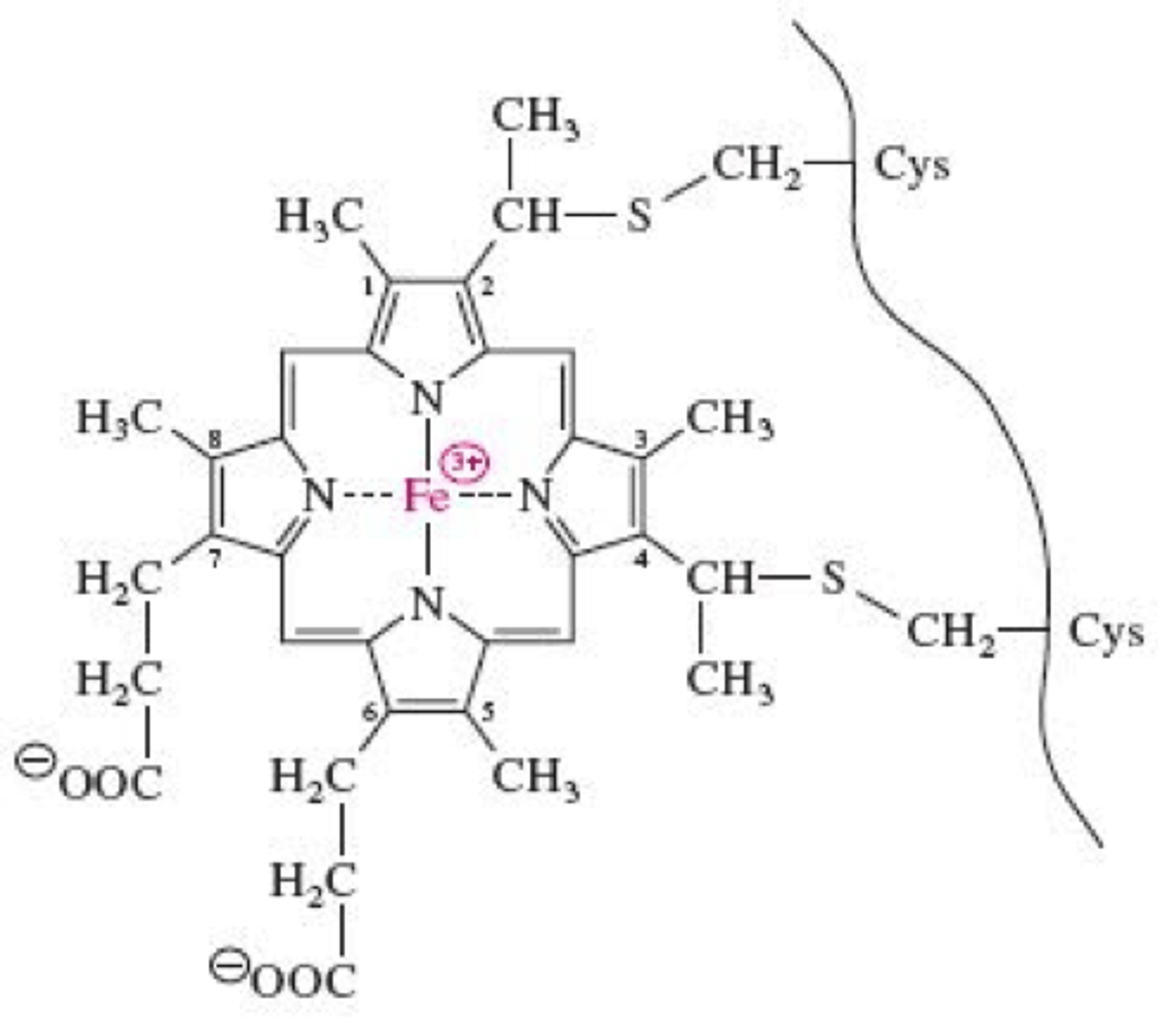
Cytochrome c (notecard)
is a moble electron carrier in the INNER MITOCHONDRIAL SPACE made in cytoplasm
Inner membrane space
is the positively charged side which become more acidic
Matrix
is the negitively charge side which become more basic
Q cycle
This happen in complex III, it explains the movement of protons
summarize, the first reaction of Q cycle is:
CoQH2 + cytochrome c1 (Fe3+) → CoQ−• + cytochrome c1 (Fe2+) + 2 H+ (intermembrane)
Then the second reaction of the cycle involves the reduction of the transient semiquinone by another electron to give CoQH2:
CoQH2 + CoQ−• + cytochrome c1 (Fe3+) + 2 H+ (matrix) → CoQ + CoQH2 + cytochrome c1 (Fe2+) + 2 H+ (intermembrane)
Combining the two equations, we have the overall reaction of Q cycle:
CoQH2 + 2 cytochrome c1 (Fe3+) + 2 H+ (matrix) → CoQ + 2 cytochrome c1 (Fe2+) + 4 H+ (intermembrane)
Approximately how many protons are transported to the intermembrae space per NADH oxidized
10 H+
ATP synthase
Makes ATP from proton gradient,F0 is the integral membrane subunit a1b2c10
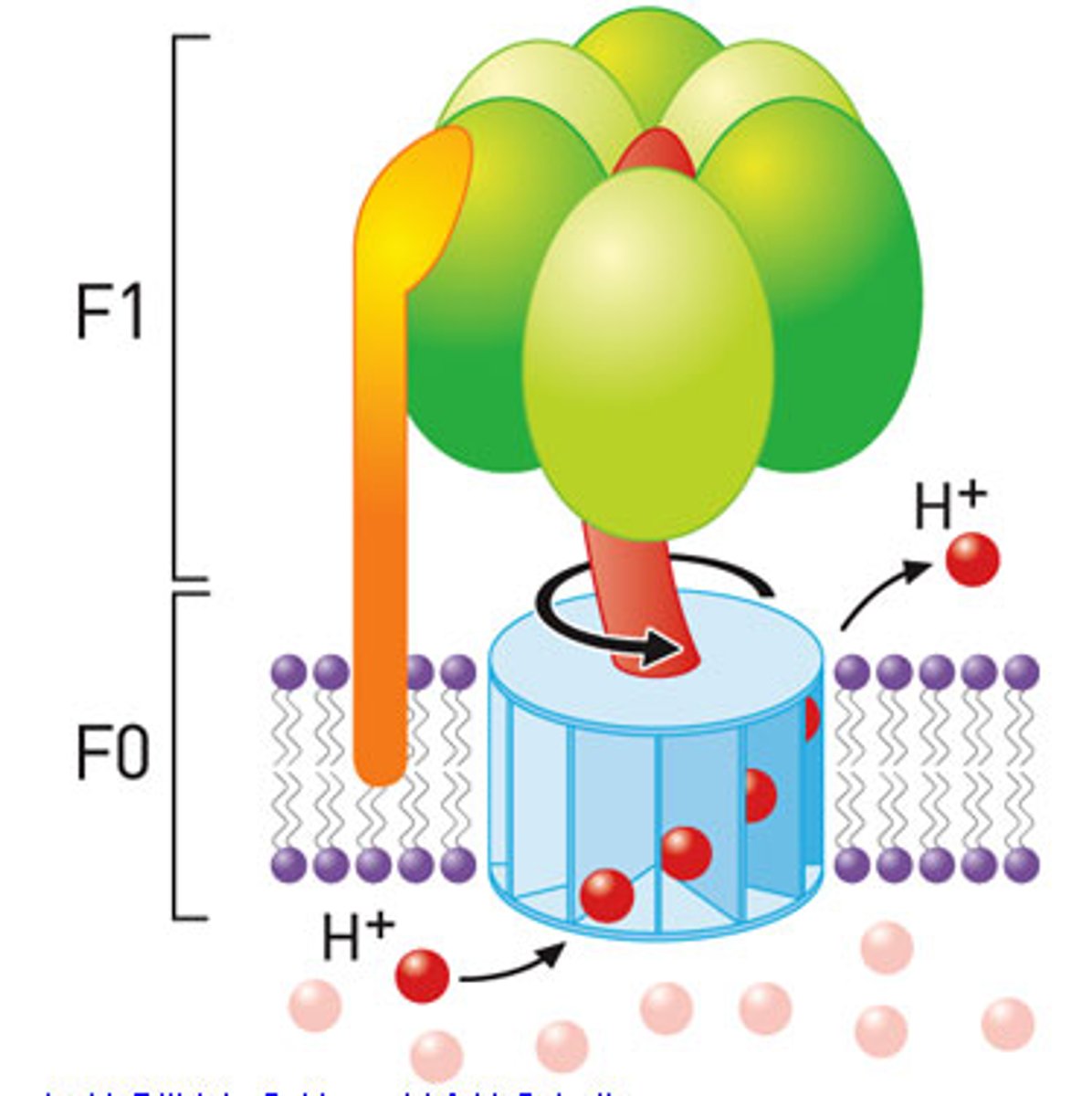
ATP synthase - F1
complex attached to F0 and faces the matrix.
-consists of a3B3Se
-Y-c complex rotate together relative to the (ab)3 complex and cause the confrontational changes in B that drive ATP synthesis
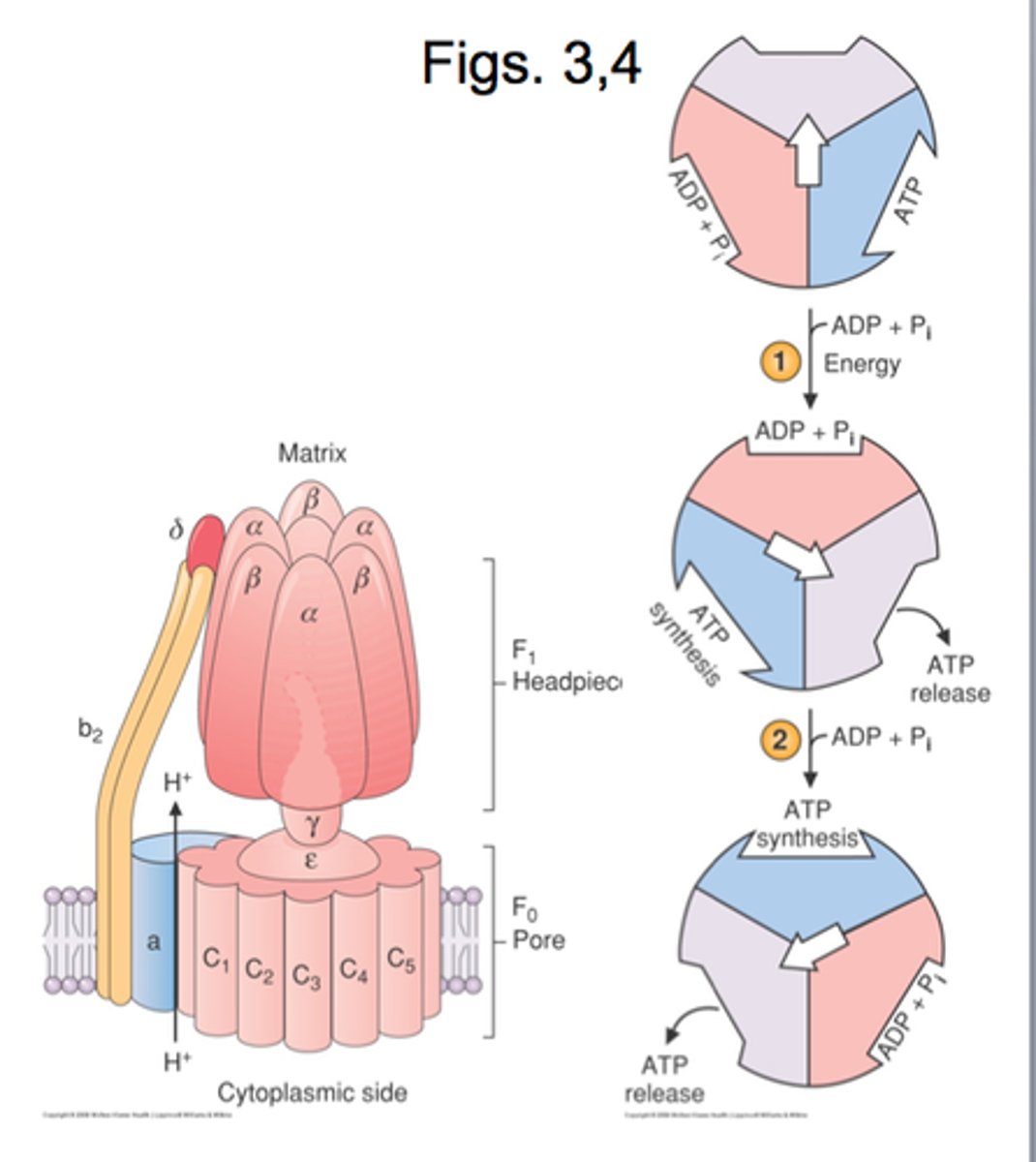
F0
integral membrane protein complex
-a1b2c10
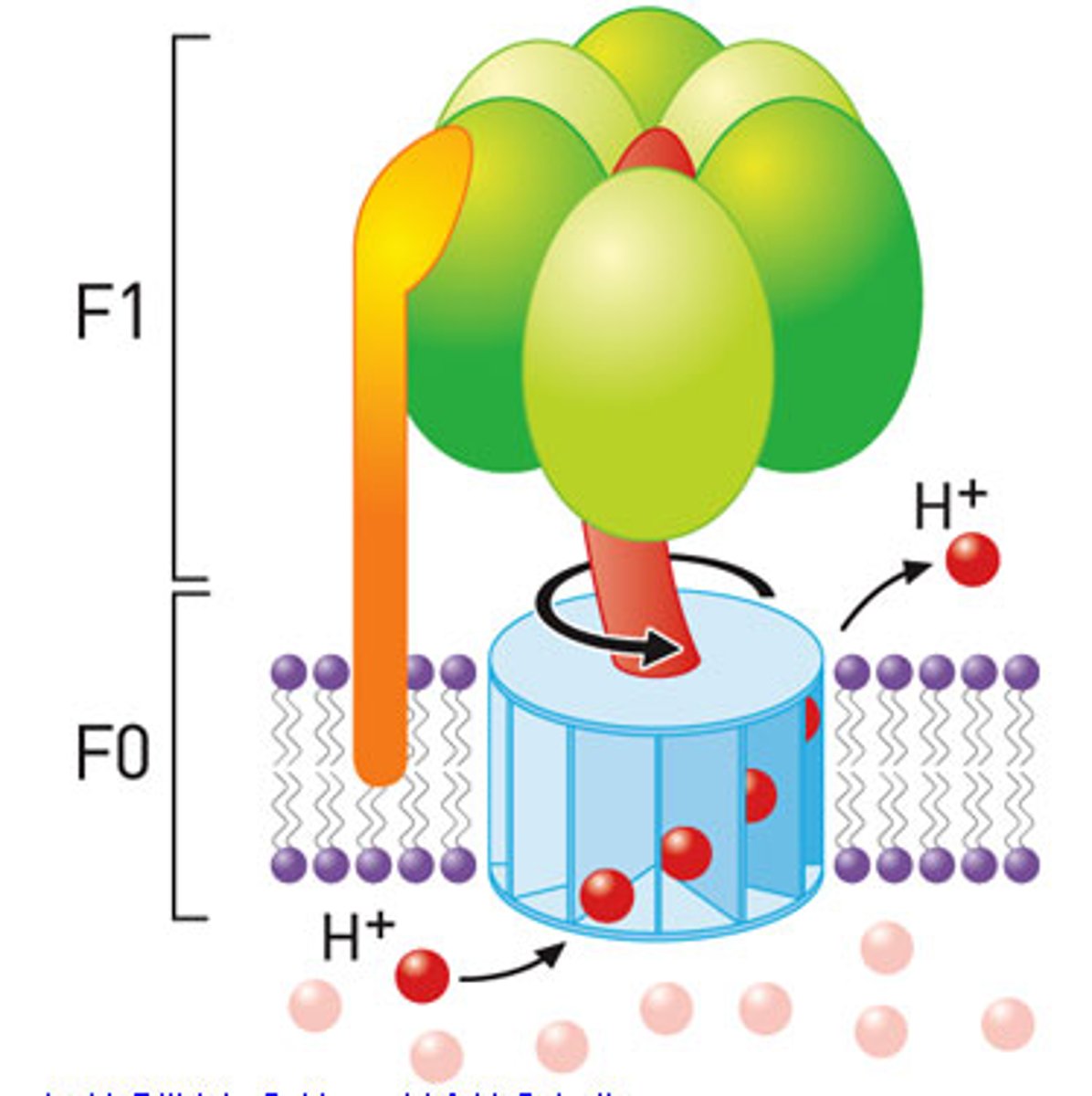
subunit a
holds proton and transfers them to subunit C as it rotates around
c (10)
the c subunit has carboxylated side chains of a highly conserved Asp and Glu residue on each subunit that serves as a proton bonding site.
a3 and B3
in F1 of ATP synthesis there are 3 total ab complexs that make 3 different form L-T-O
ySe
S and E subunit of F1 are small and Y is composted of two long alpha helices the Y interacte with the ab complex for as it rotate t=so does the ab complex.
whats the number of ATP formed per 2e- tranfered, in eukaryotes?
when converting NADH to ATP you generate 2.5 ATP
when converting FADH2 to ATP you generate 1.5 ATP
What is the number of ATP formed per 2e- transfer in prokaryotes?
When converting NADH to ATP you get 3 ATP
when converting FADH2 to ATP you get 2 ATP
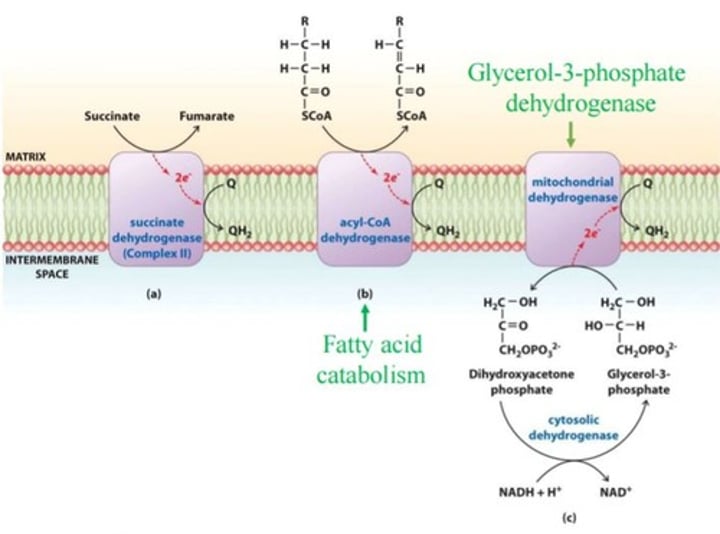
How Does NADH get into Mitochondria?
through either the glycerol Phopshate shuttle or the Malate-Aspartate Shuttle
Oxaloaceate
this molecule is not an intermediate of the citric acid cycle
The Net ATP yield per glucose?
32