Reproductive & Excretory Systems
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
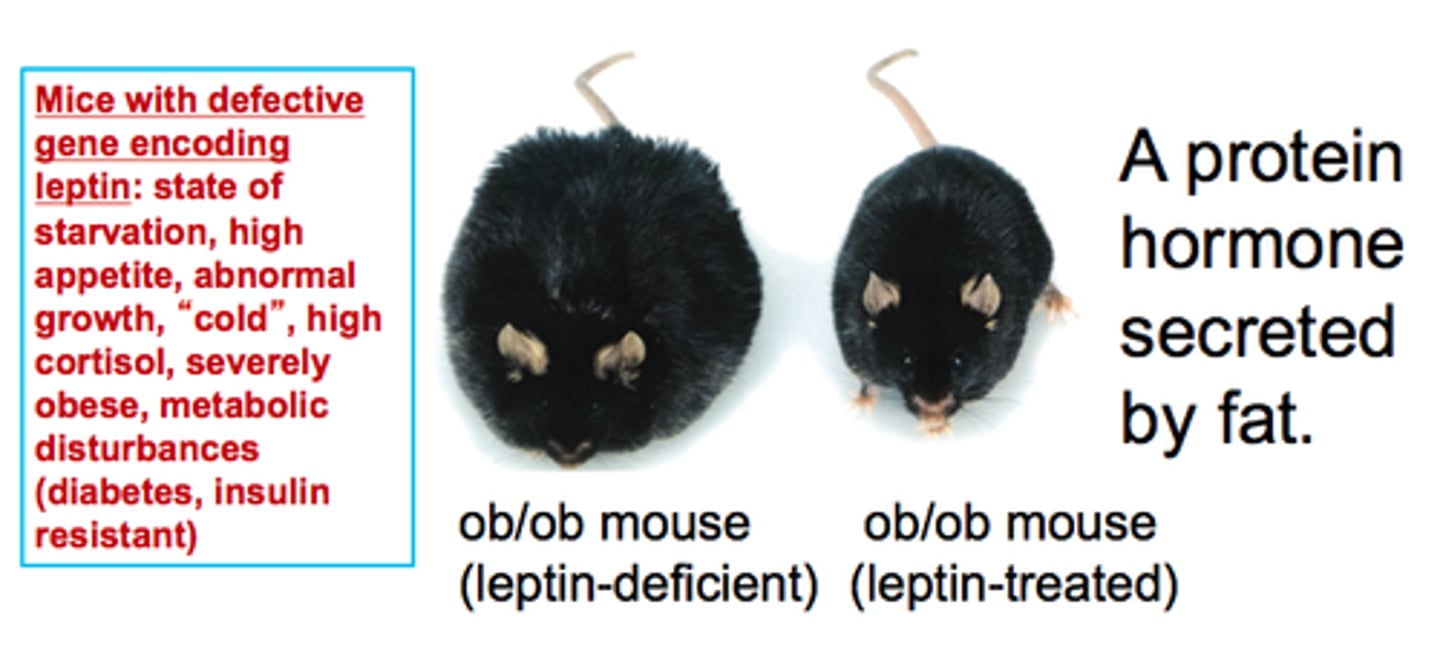
leptin
secreted by adipose (fat) tissue, targets hypothalamus, suppresses hunger
- obesity (too much adipose) -> desensitization to leptin
ghrelin
secreted by empty stomach, targets hypothalamus, causes hunger

melatonin
secreted by pineal gland, regulates circadian rhythms (day-night sleep cycle), causes sleepiness

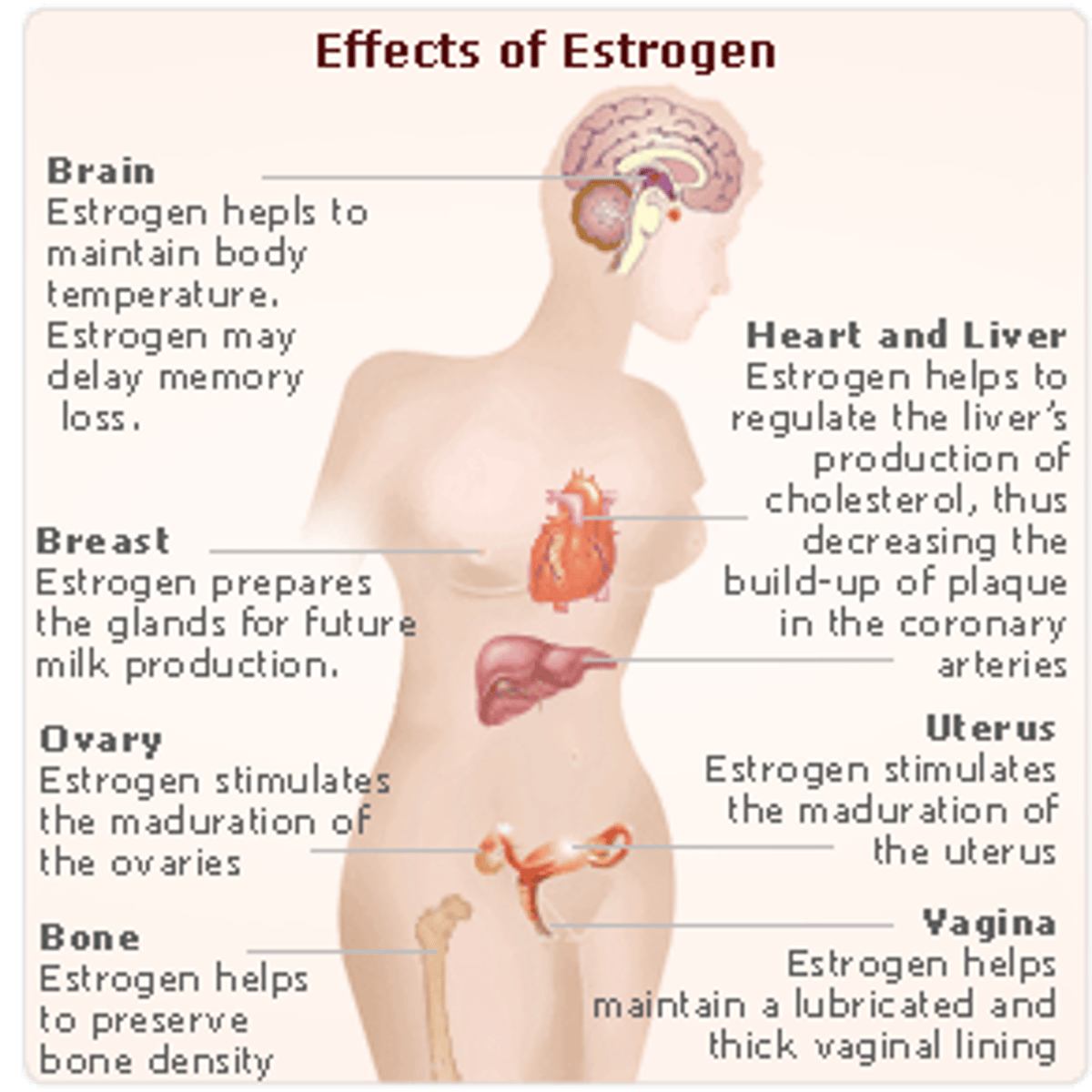
estrogen
- female sex hormone, produced by ovary
- stimulates development and THICKENING of endometrium
- promotes development of reproductive organs & secondary characteristics of female
FSH
follicle-stimulating hormone
- produced by pituitary gland
- development of mature eggs
LH
luteinizing hormone; stimulates ovulation
progesterone
- produced by the corpus luteum (or placenta in pregnant women)
- maintains the endometrium
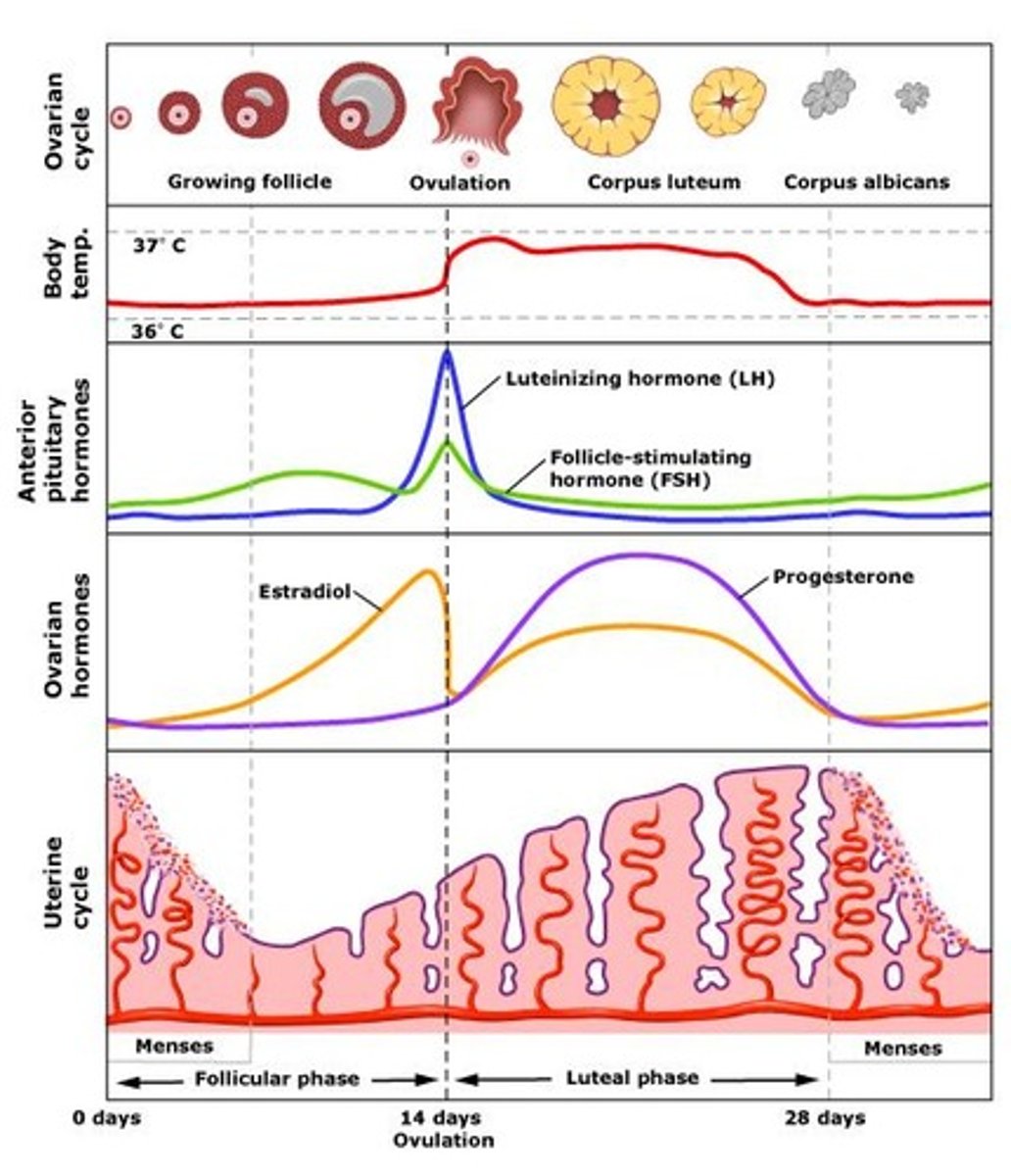
key events in menstrual cycle
approx. 28 days long
Day 1: bleeding
Day 14: ovulation
1. follicular phase: FSH stimulates follicles to develop, dominant follicle -> 1 mature egg secretes estrogen (thickens endometrium)
2. ovulation (egg release): triggered by LH, corpus luteum created
3. luteal phase: corpus luteum (leftover follicular tissue) makes estrogen/progesterone, stimulates endometrial growth and inhibits FSH/LH
- corpus luteum degrades over time, so estrogen/progesterone levels drop & endometrium is shed
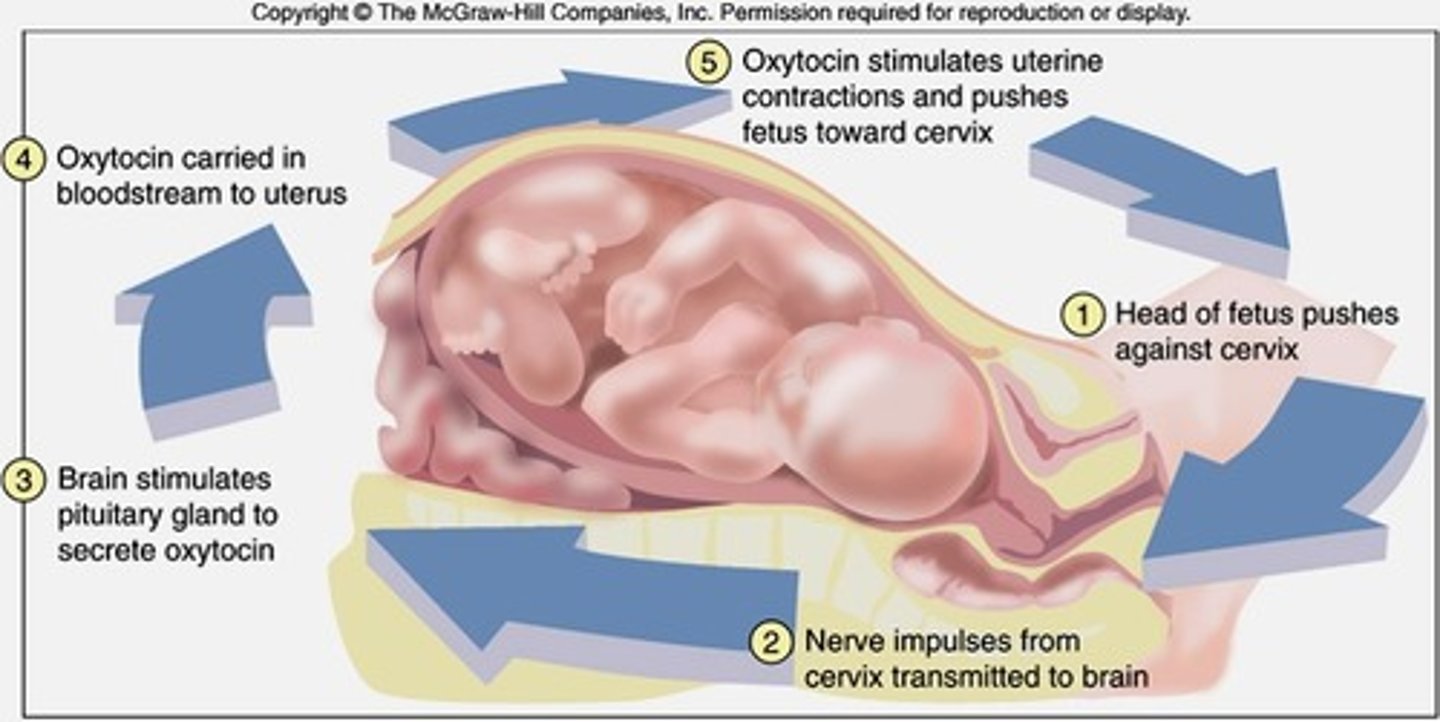
oxytocin in childbirth
secreted during childbirth when levels of progesterone fall; triggers uterine contractions
- positive feedback loop
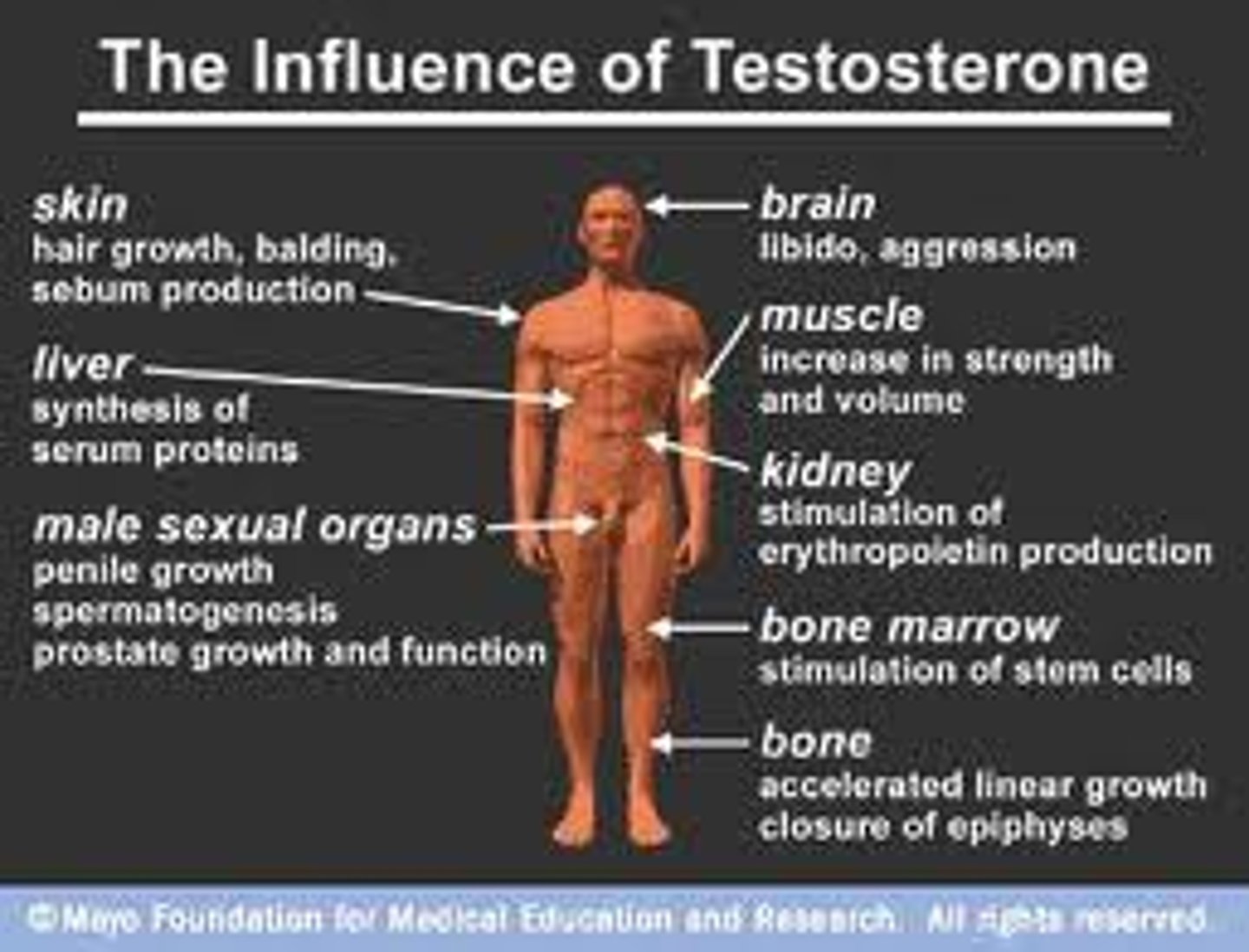
testosterone
male sex hormone
- development of male genitalia & male secondary sexual characteristics
- maintains sex drive
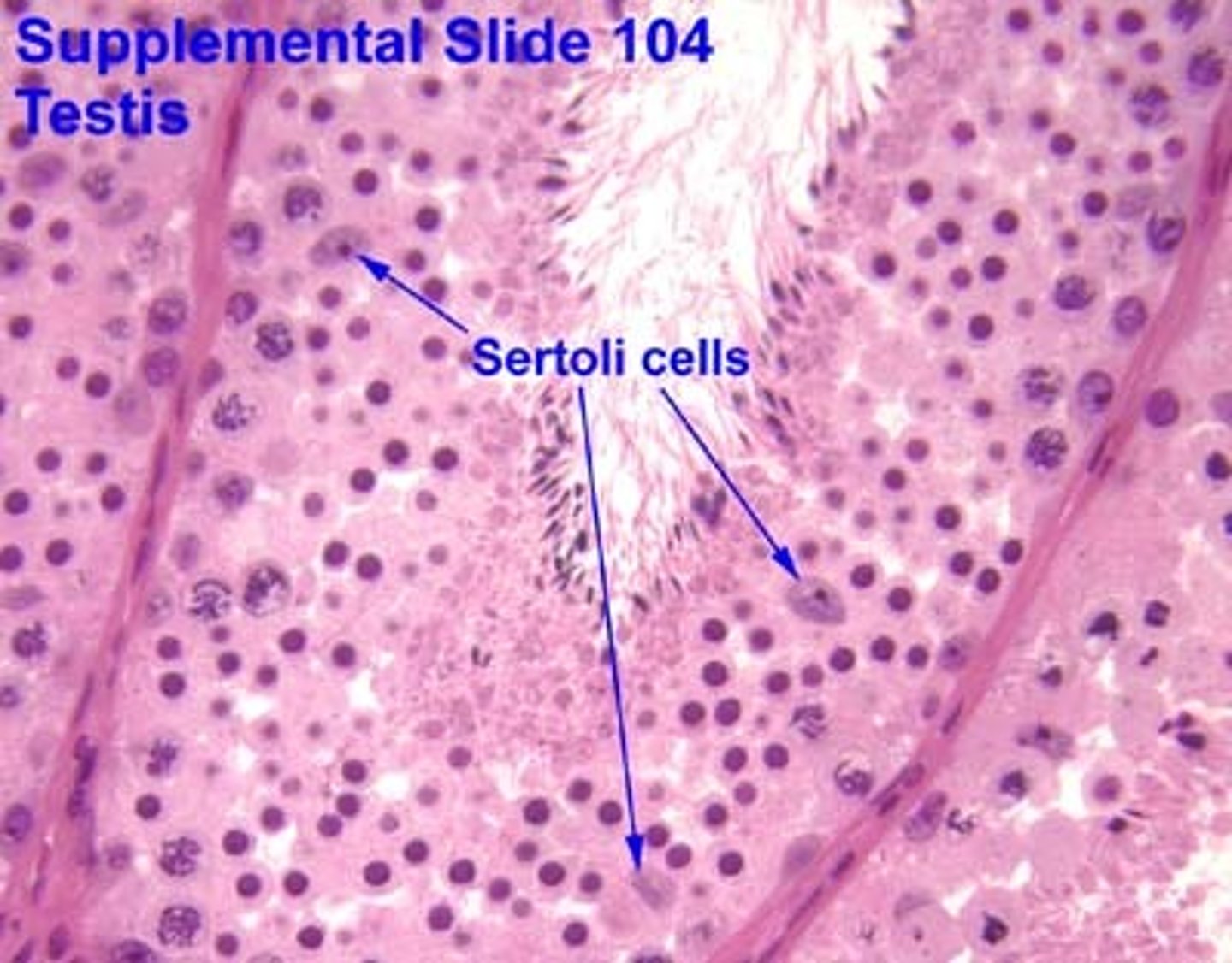
Sertoli cells
secrete fluids to nourish and support the developing sperm cells
- "nurse cells" (in seminiferous tubules)
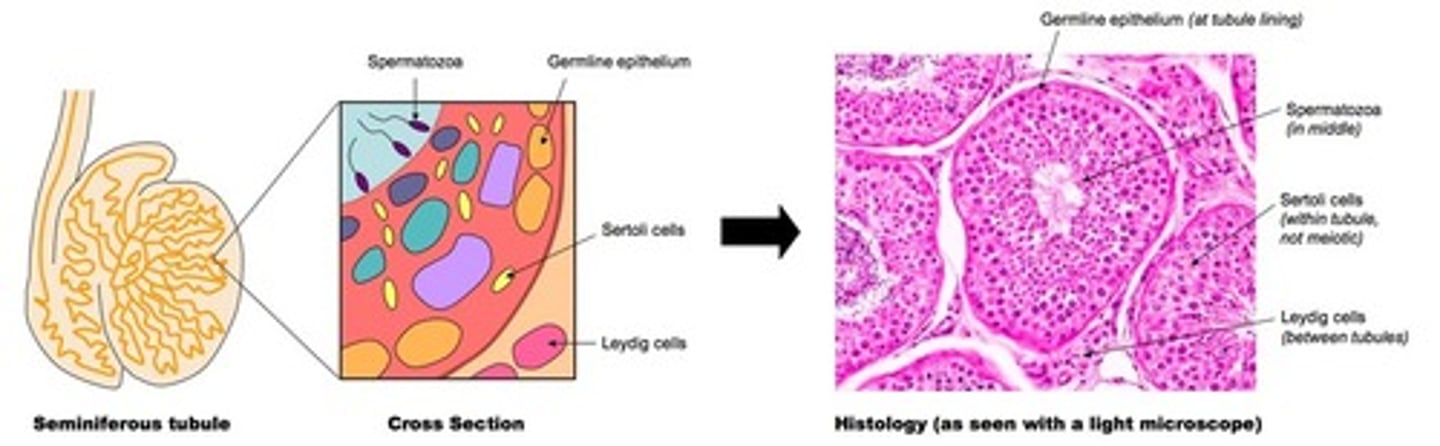
Leydig cells
secrete testosterone - outside seminiferous tubules, in testes
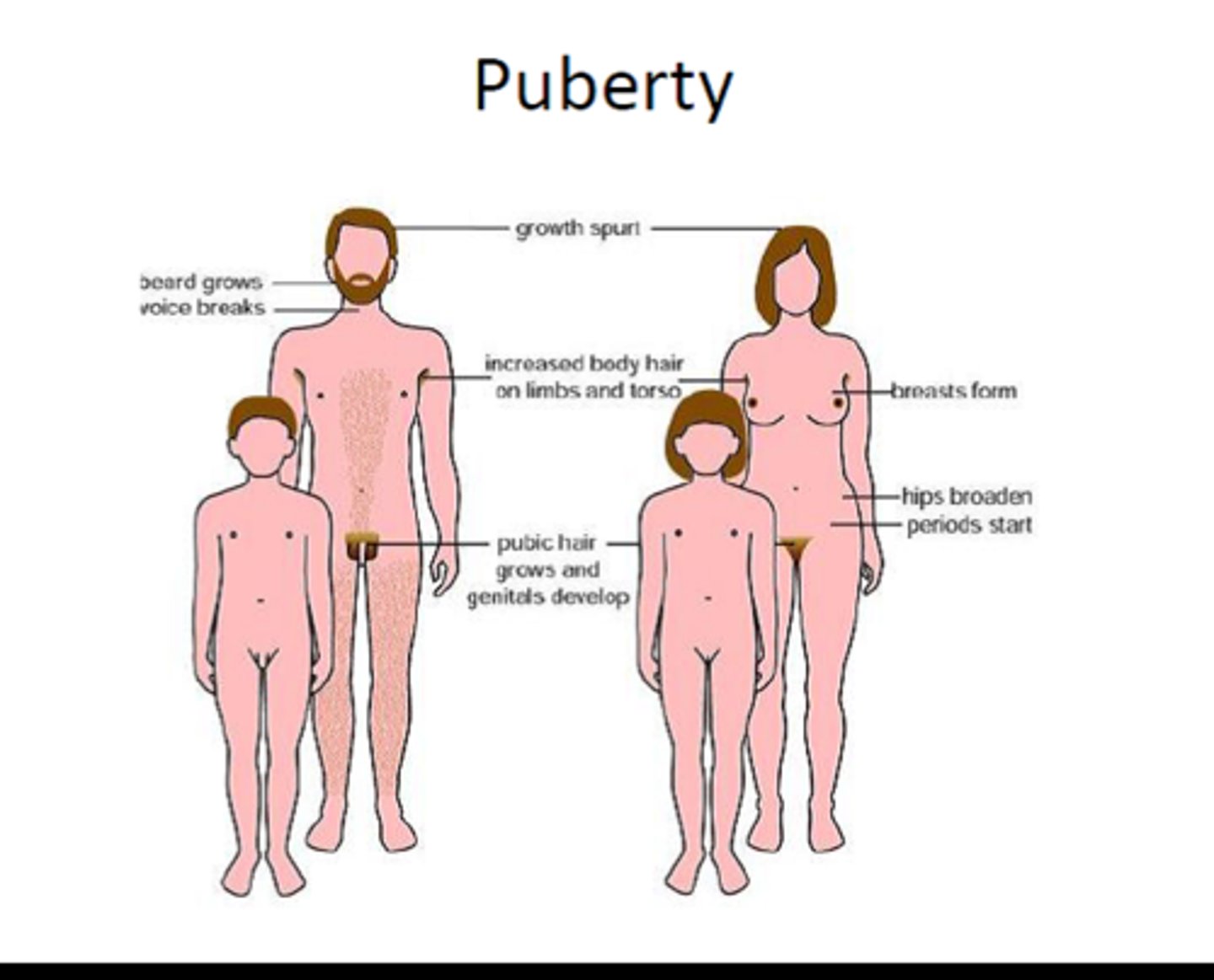
secondary sexual characteristics
sexual features not directly linked to reproduction
- males: facial hair, deep voice
- females: breast development, wider hips
blastocyst
hollow ball of cells that has the capability to "burrow" into the endometrium

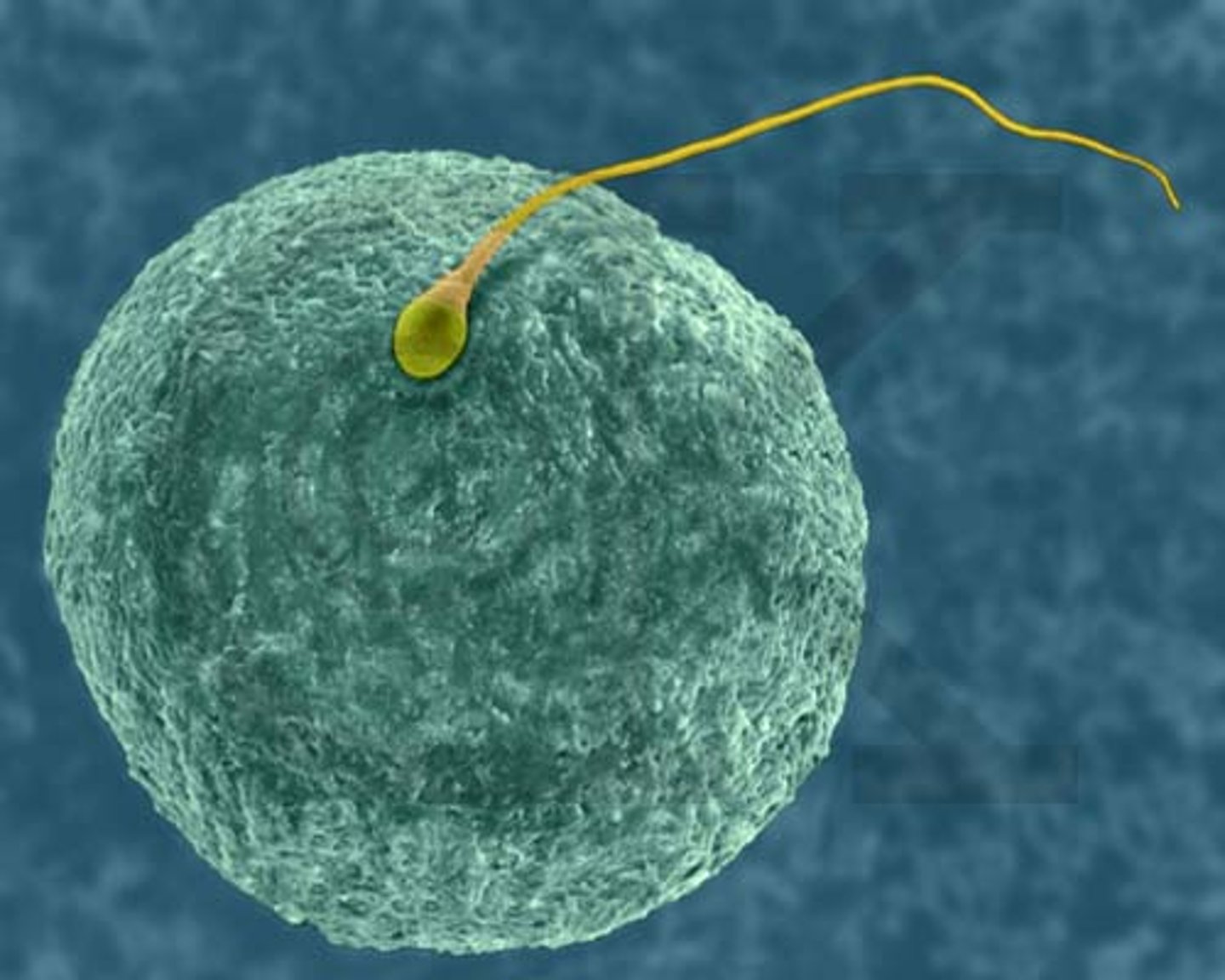
fertilization
Occurs in the oviducts/fallopian tubes
1) many sperm arrive at the egg and begin to push through the follicular cells surrounding the egg (corona radiata)
2) first sperm to reach the zona pellucida binds & begins acrosome reaction (hydrolytic enzymes digest zona pellucida)
3) plasma membranes of the egg & sperm fuse; sperm nucleus enters the egg
4) cortical reaction occurs (cortical granules release enzymes & calcify zona pellucida, preventing polyspermy - fertilization by multiple sperm - ensuring diploidy
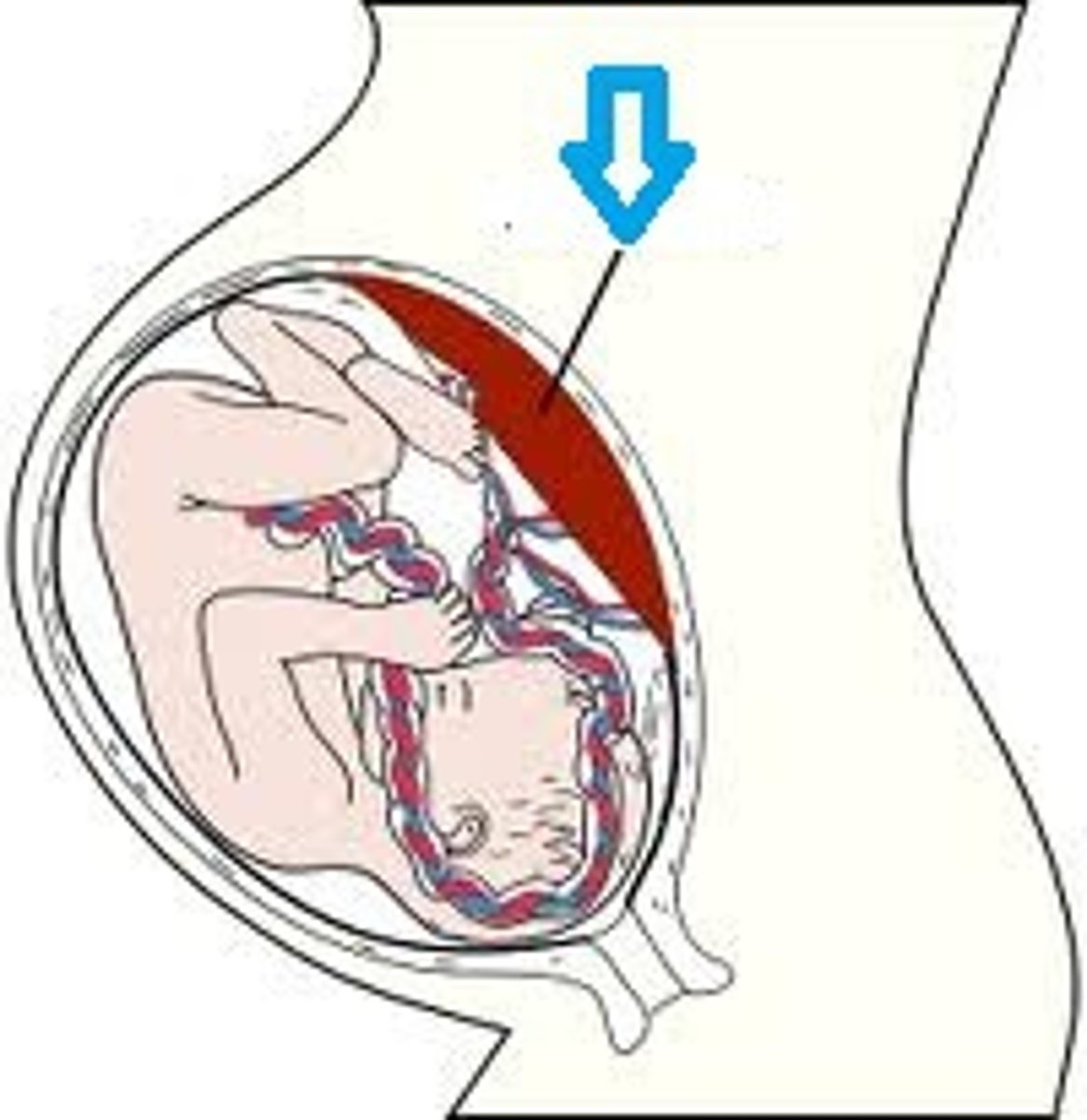
placenta
structure that facilitates the exchange of material between the mother and fetus
- CO2, H2O, urea, waste and hormones from fetus
- O2, H2O, macronutrients, drugs, hormones and viruses/pathogens from the mother)
takes over the role of the ovary in producing estrogen/progesterone; corpus luteum degenerates
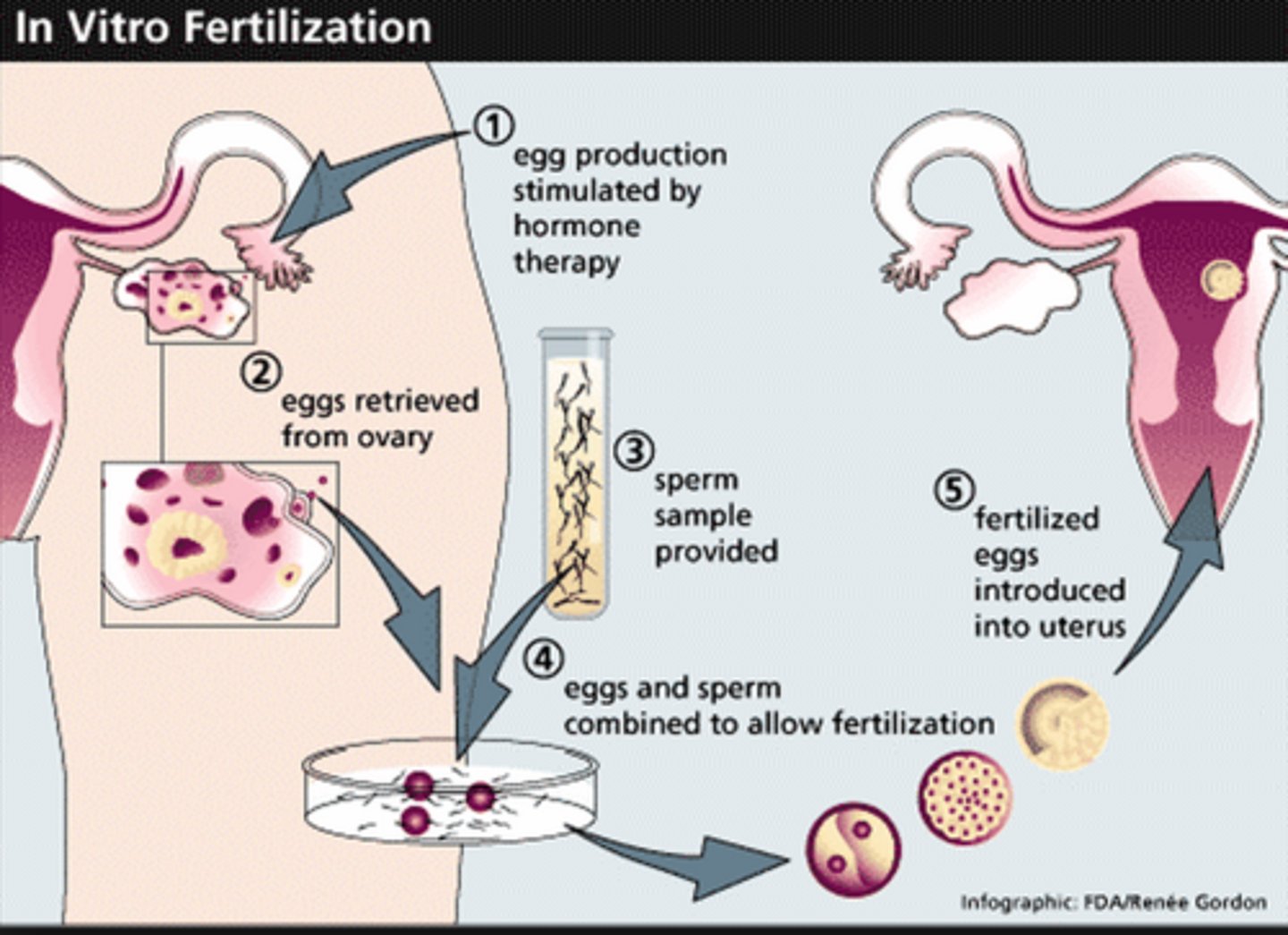
IVF
1. Female is injected with hormones to stop menstrual cycle
2. FSH is injected to stimulate production of many eggs in the ovaries
3. LH given -> ovulation of multiple eggs, egg retrieval
4. Estrogen is given to develop the endometrium
5. Sperm is collected and combined w/ the eggs (fertilization) to produce viable blastocysts
5. Blastocysts develop -> embryo (~5 days), transferred into uterus -> implantation
6. Progesterone is given to maintain endometrium
7. After 2 weeks, HCG levels are checked to determine pregnancy
Pros: Increased control of conception timing, higher chance of healthy baby due to increased screenings, decreased chance of miscarriage, fertility preservation
Cons: It is expensive, embryos are destroyed, low success rate and it can lead to multiple births
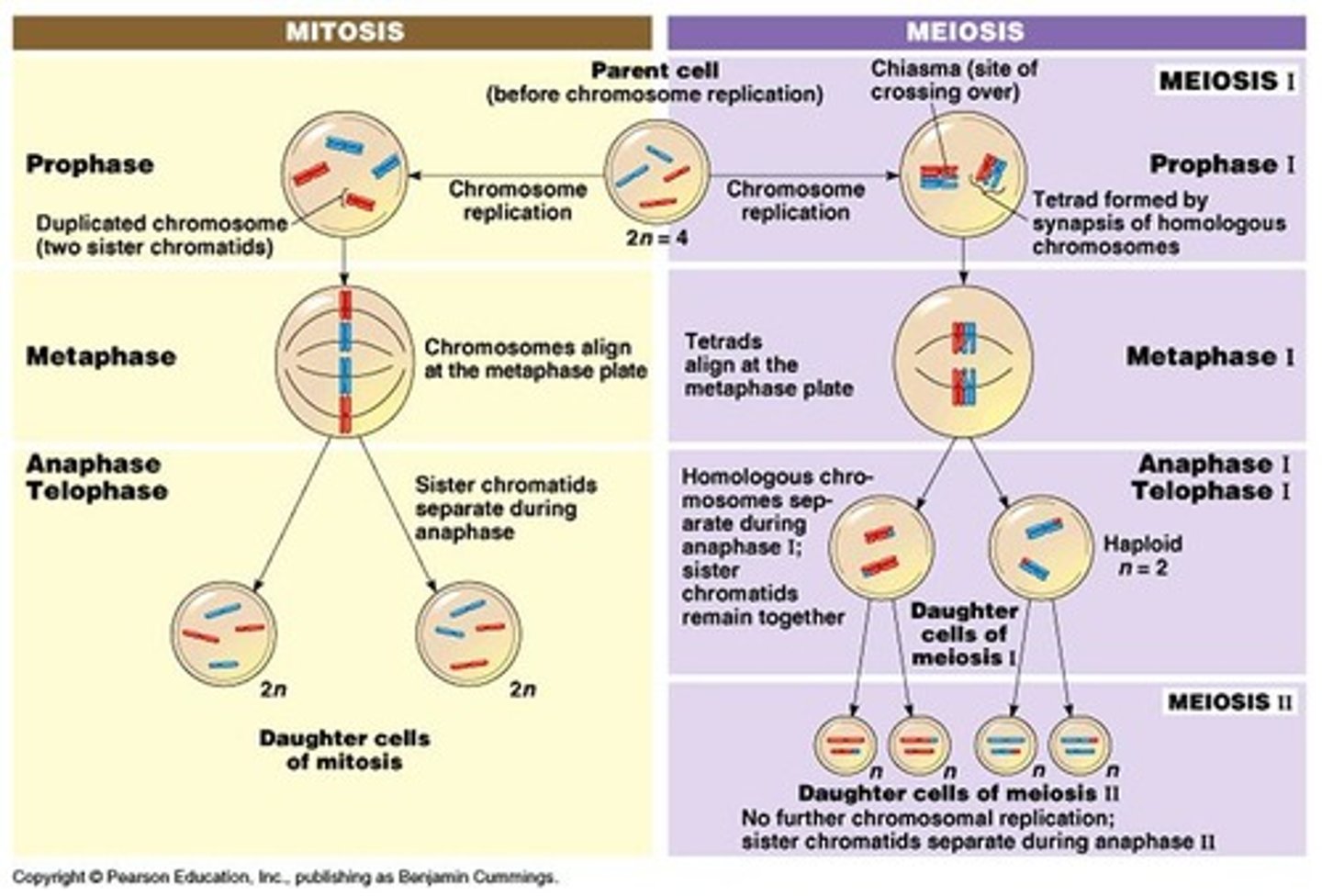
mitosis VS meiosis
MITOSIS
- somatic cells
- 1 division -> 2 genetically identical daughter cells
- diploid (2n)
MEIOSIS
- gametes
- 2 divisions -> 4 genetically different daughter cells
- haploid (n)
HCG
produced by fetus/blastocyst - maintains corpus luteum, which keeps progesterone levels high & preserves endometrium
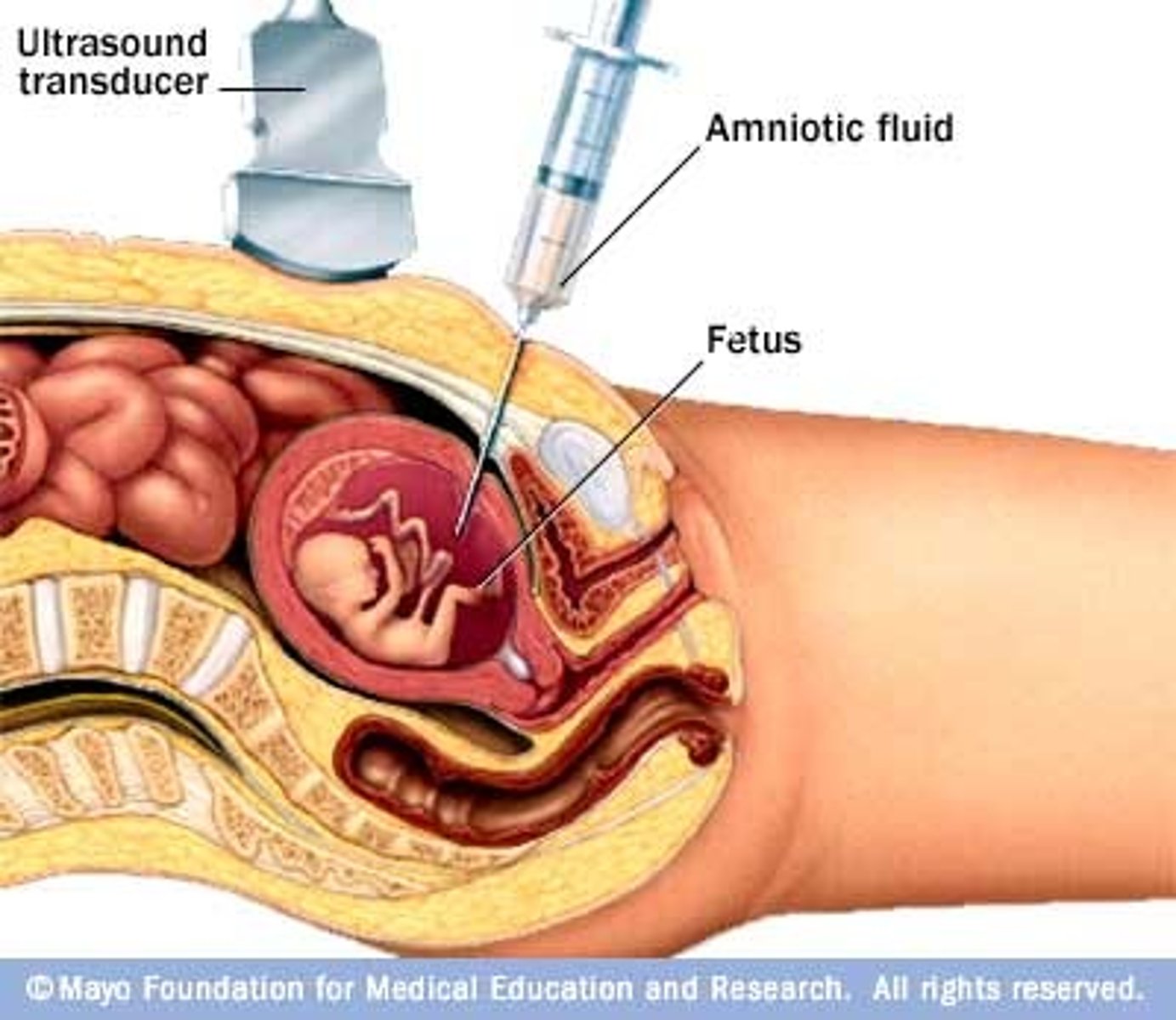
amniocentesis
removal of some of the amniotic fluid, which contain ONLY CELLS FROM THE FETUS, in order to create a karyotype (cells must be undergoing mitosis to see chromosomes)
podocytes
wrap around capillaries in glomerulus; secure basement membrane
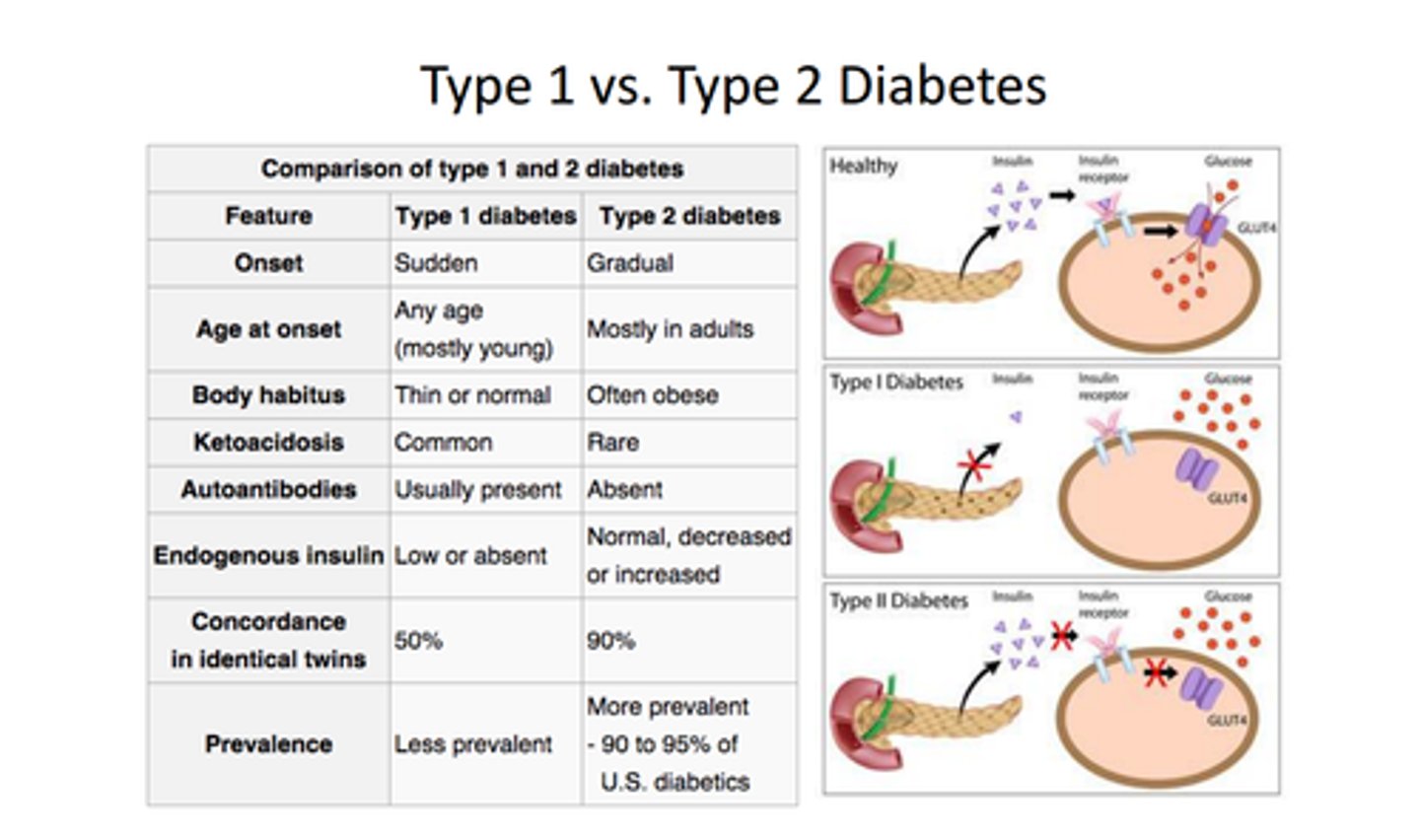
Diabetes Type I vs Type II
Type I: genetic/autoimmune cause, increased hunger/thirst/urination, insulin injections (irreversible, usually childhood onset) - do not produce insulin
Type II: genetic/obesity cause, no symptoms (insidious); reversible w/ diet & exercise (manage w/ insulin) - resistant to insulin
meaning of proteins/blood or glucose in urine
proteins/blood: glomerulus is damaged (improper filtration)
glucose: diabetes (hyperglycemia - too much glucose in blood/filtrate to be reabsorbed)
glands involved in semen production
prostate (largest): produces seminal fluid - buffers pH so sperm can survive vagina's acidity
seminal vesicles: add fructose - energy so sperm can swim
epididymis: "swim school" - sperm mature & learn to swim, become concentrated
mitosis
division of the nucleus into 2 genetically identical, diploid daughter nuclei
GATE: growth, asexual reproduction, tissue repair, embryonic development
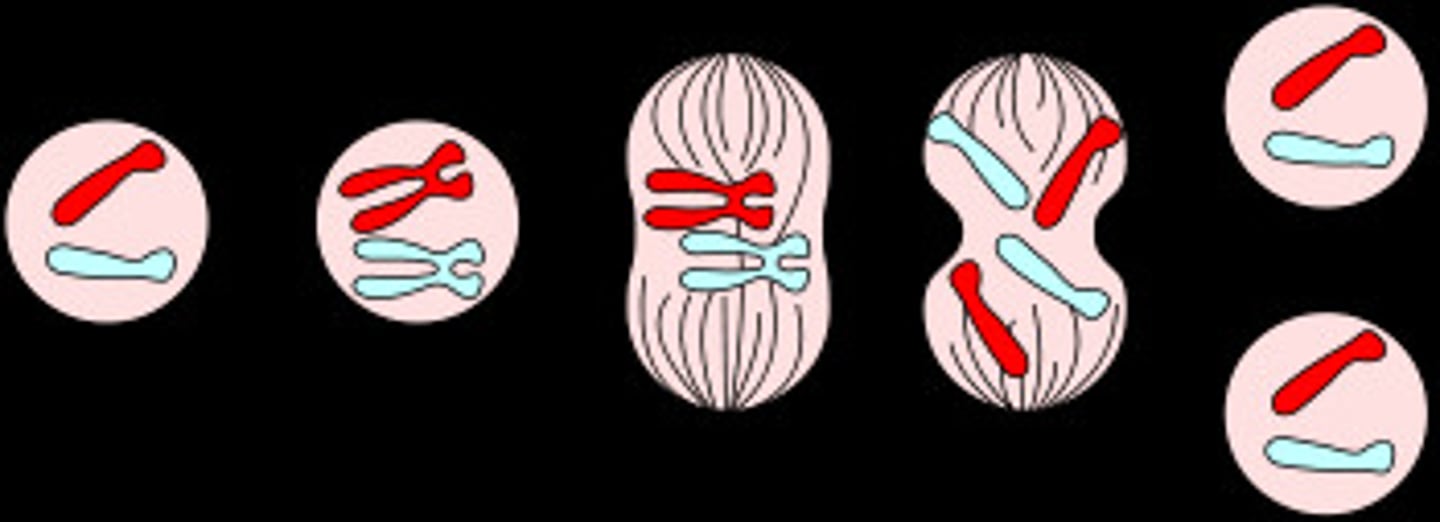
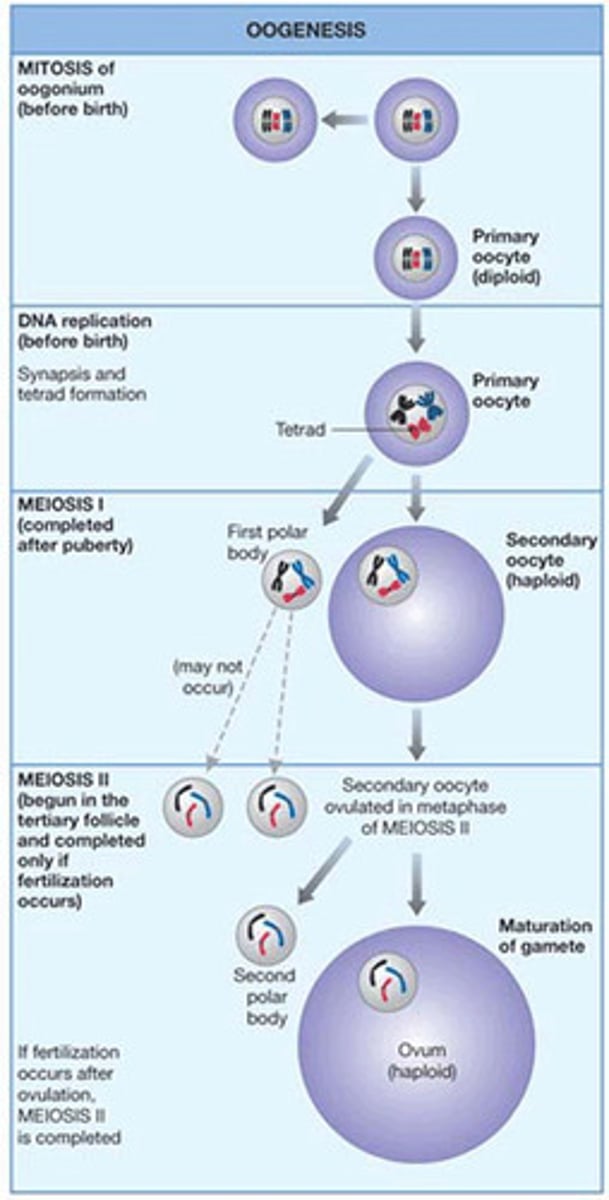
oogenesis
1 produced in ovaries monthly, starts while embryo, ends at menopause
- released in ovulation
- 1 functional egg produced per meiotic division (3 polar bodies)
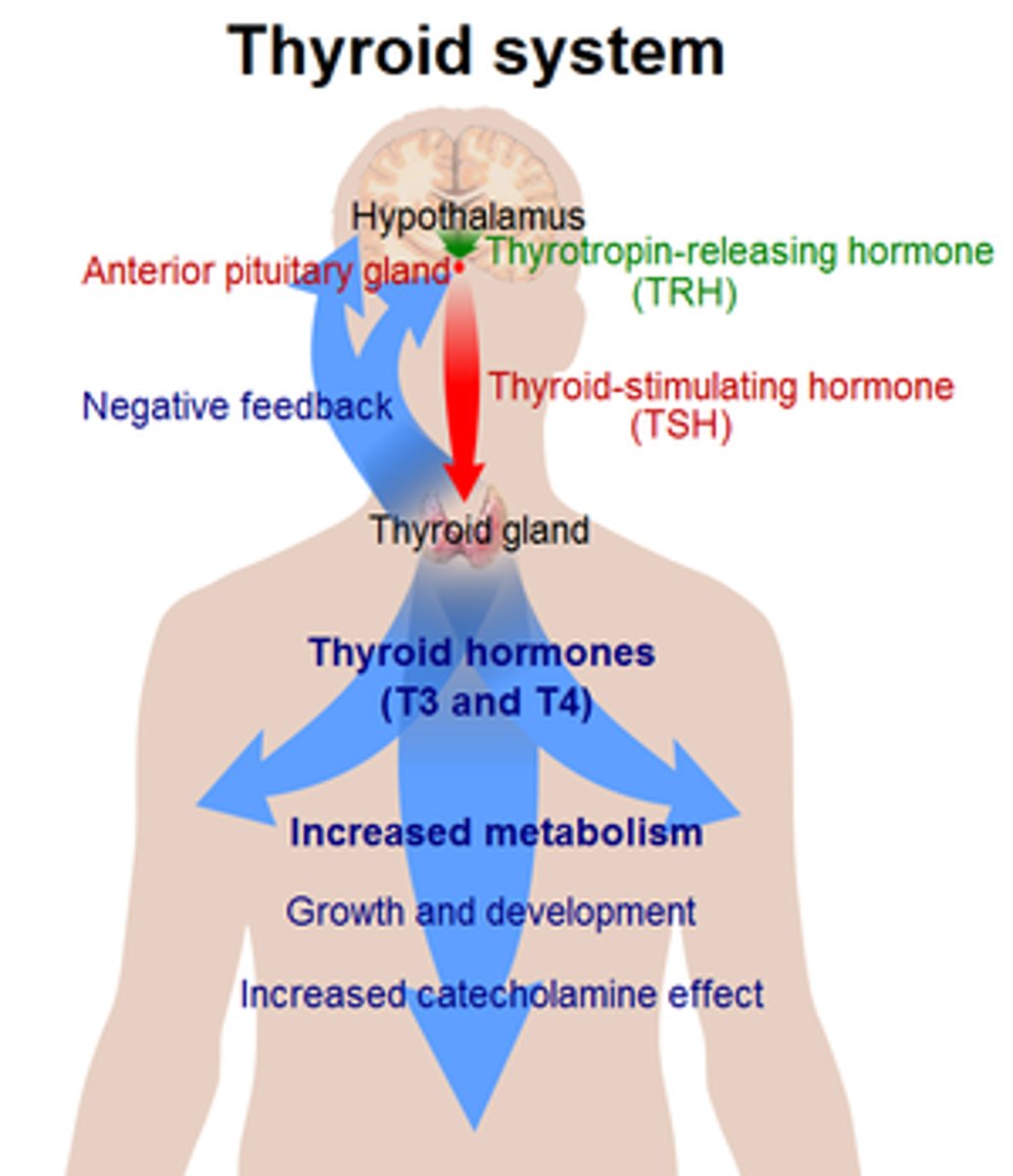
thyroxine
secreted by thyroid gland, targets all cells in the body, increases metabolic rate (which produces heat, raises body temp - thermoregulation)
homeostasis (define + processes of thermoregulation & blood sugar regulation)
maintenance of stable internal environment despite external changes
thermoregulation: thyroxine increases metabolic rate, which produces heat, raising body temp
hyperglycemia (BS too high): liver beta cells make insulin, which opens protein channels for glucose to enter cells & triggers liver to store glucose as glycogen
hypoglycemia (BS too low): alpha cells make glucagon, triggers liver to hydrolyze glycogen -> glucose
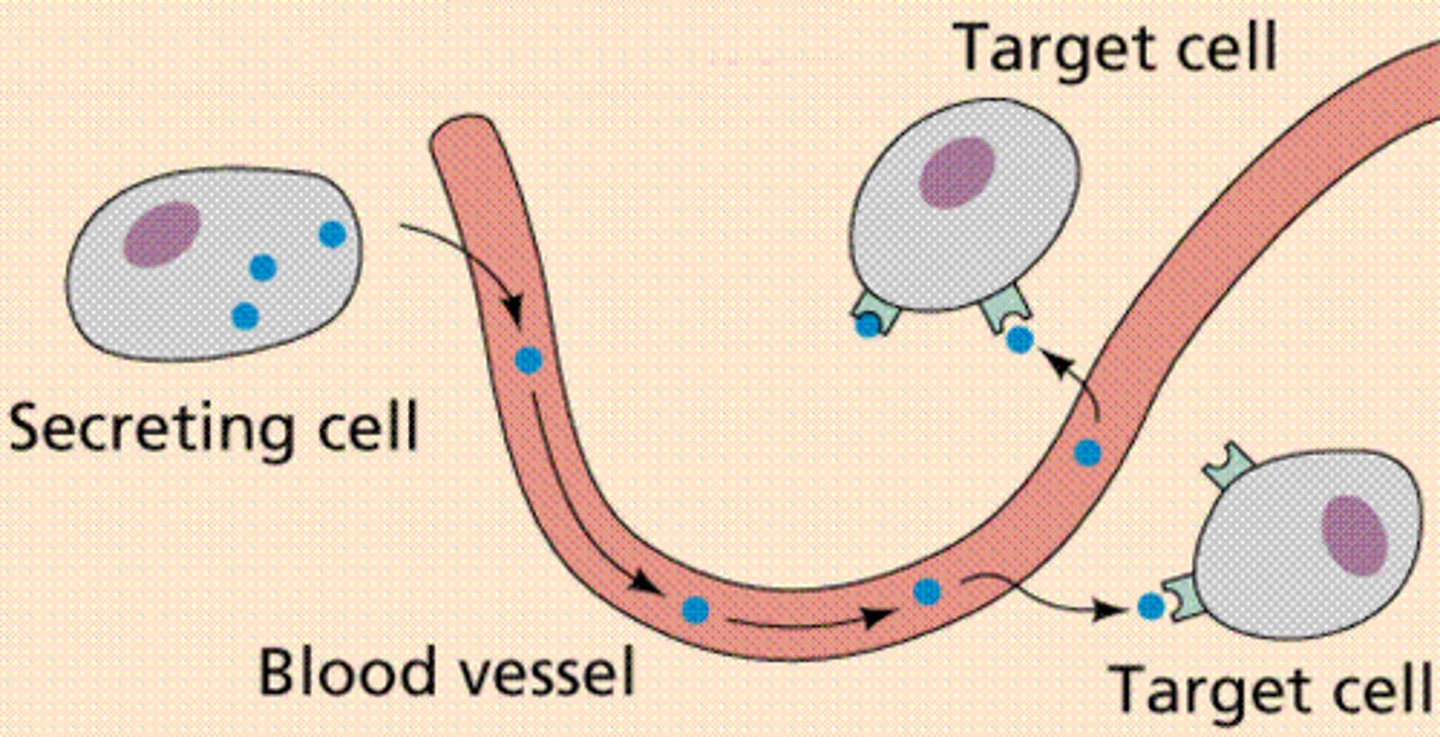
hormone
chemical messengers, made by endocrine glands, travel through blood & have specific effect on another tissue
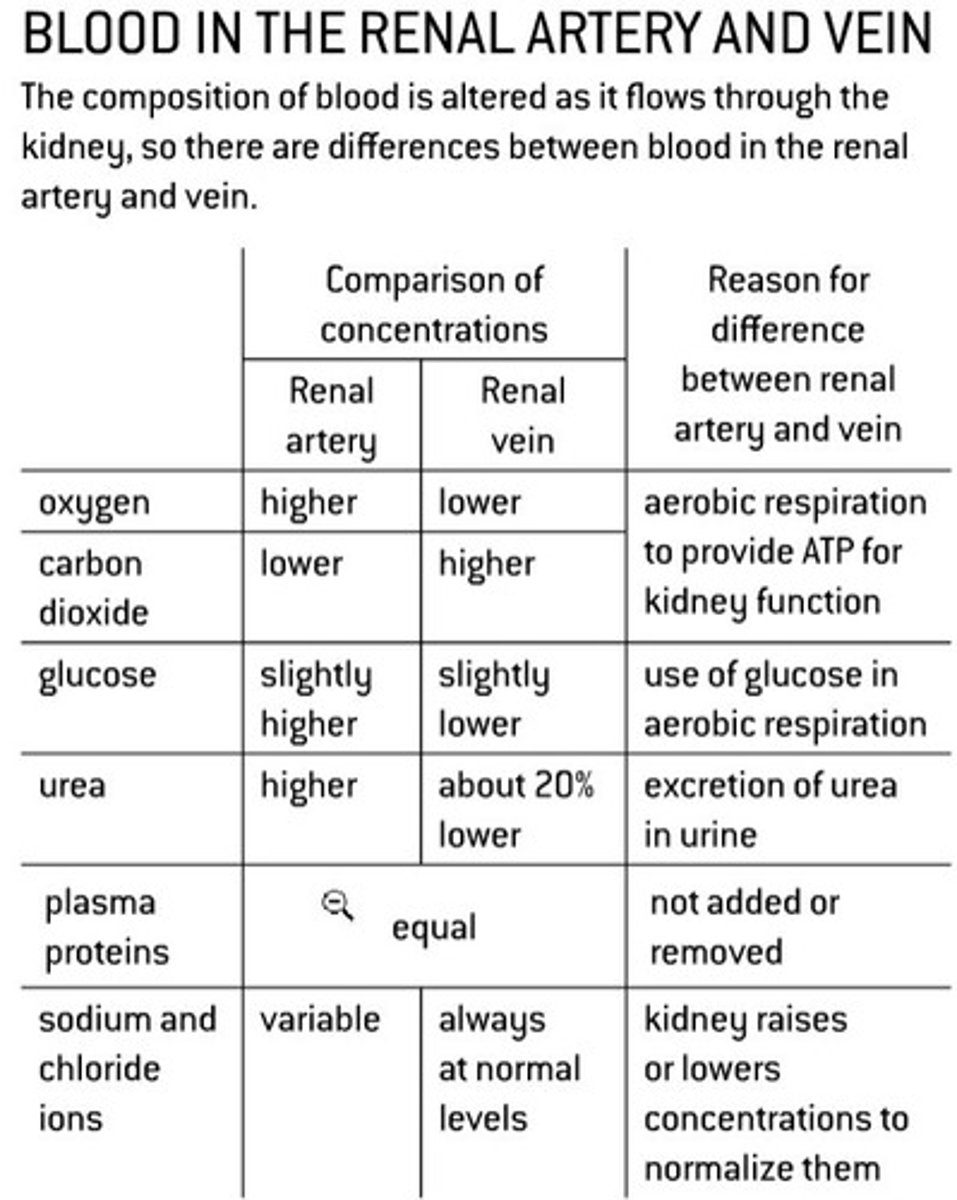
blood composition in renal artery VS vein
blood in vein (leaving after filtration): lower in urea, glucose, O2; higher in CO2; balanced H2O/salts
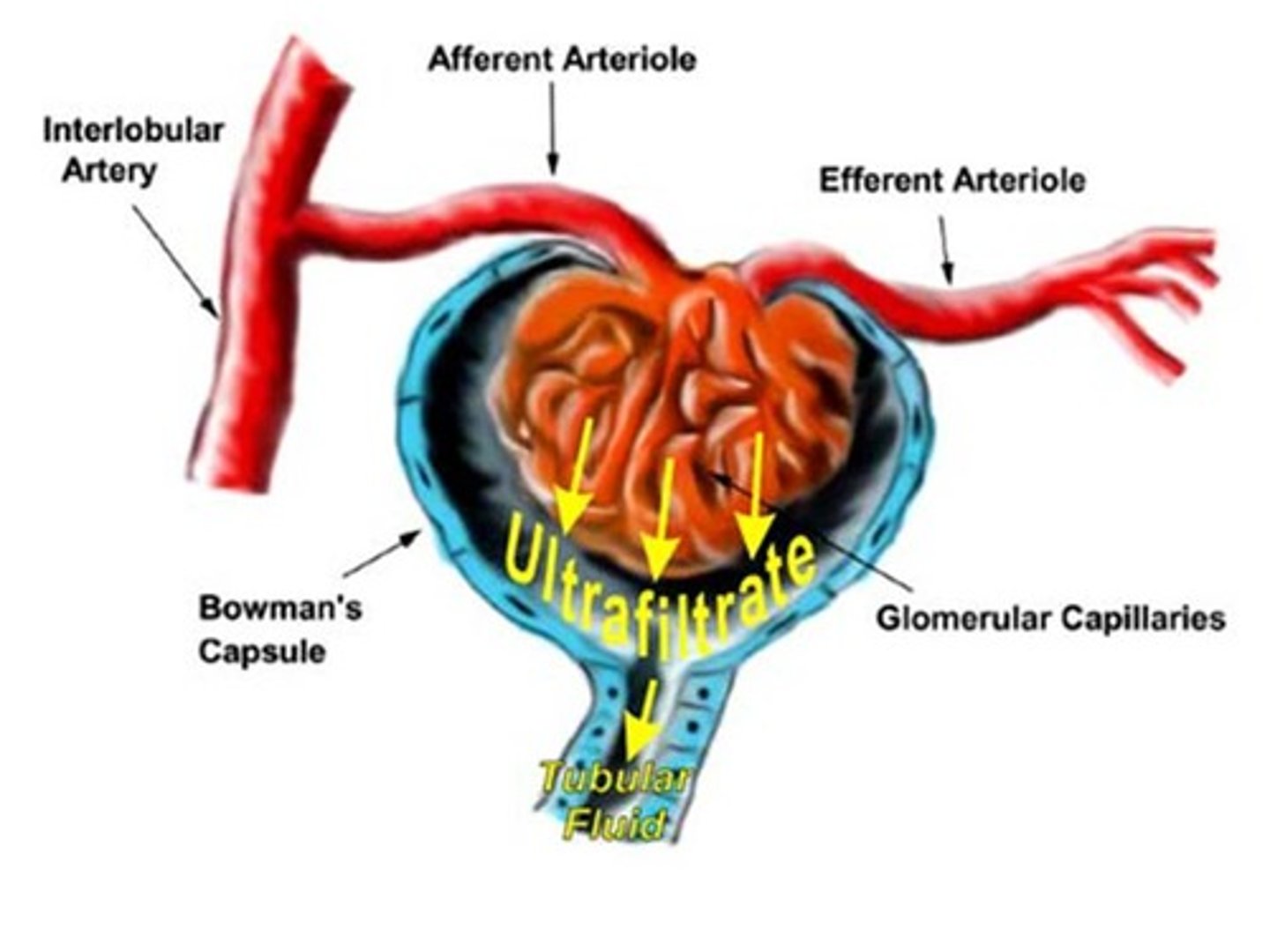
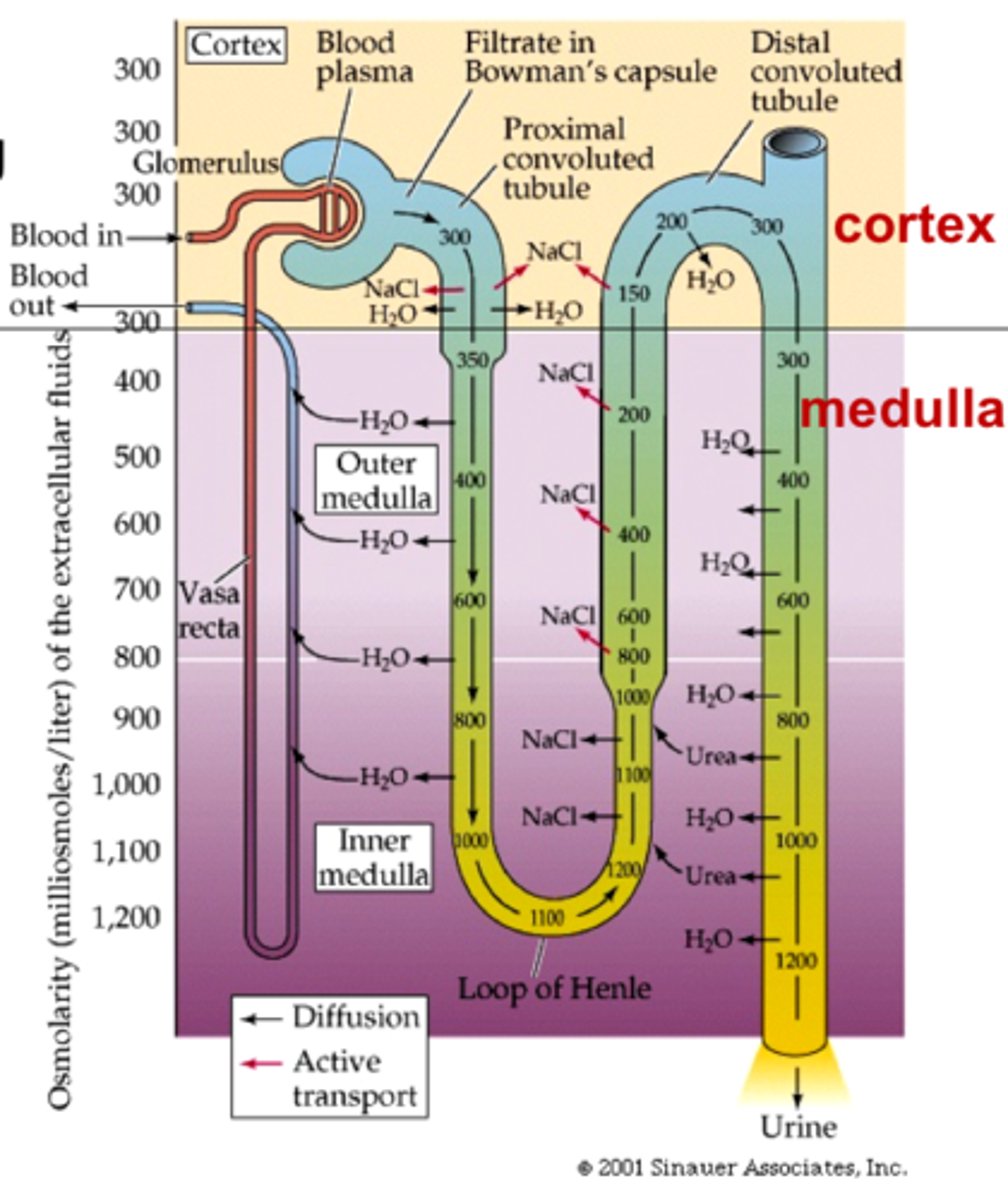
ultrafiltration
efferent (exiting) arteriole is smaller than afferent (entering) arteriole -> high pressure; small molecules in blood forced out of the capillaries (glomerulus) into Bowman's capsule
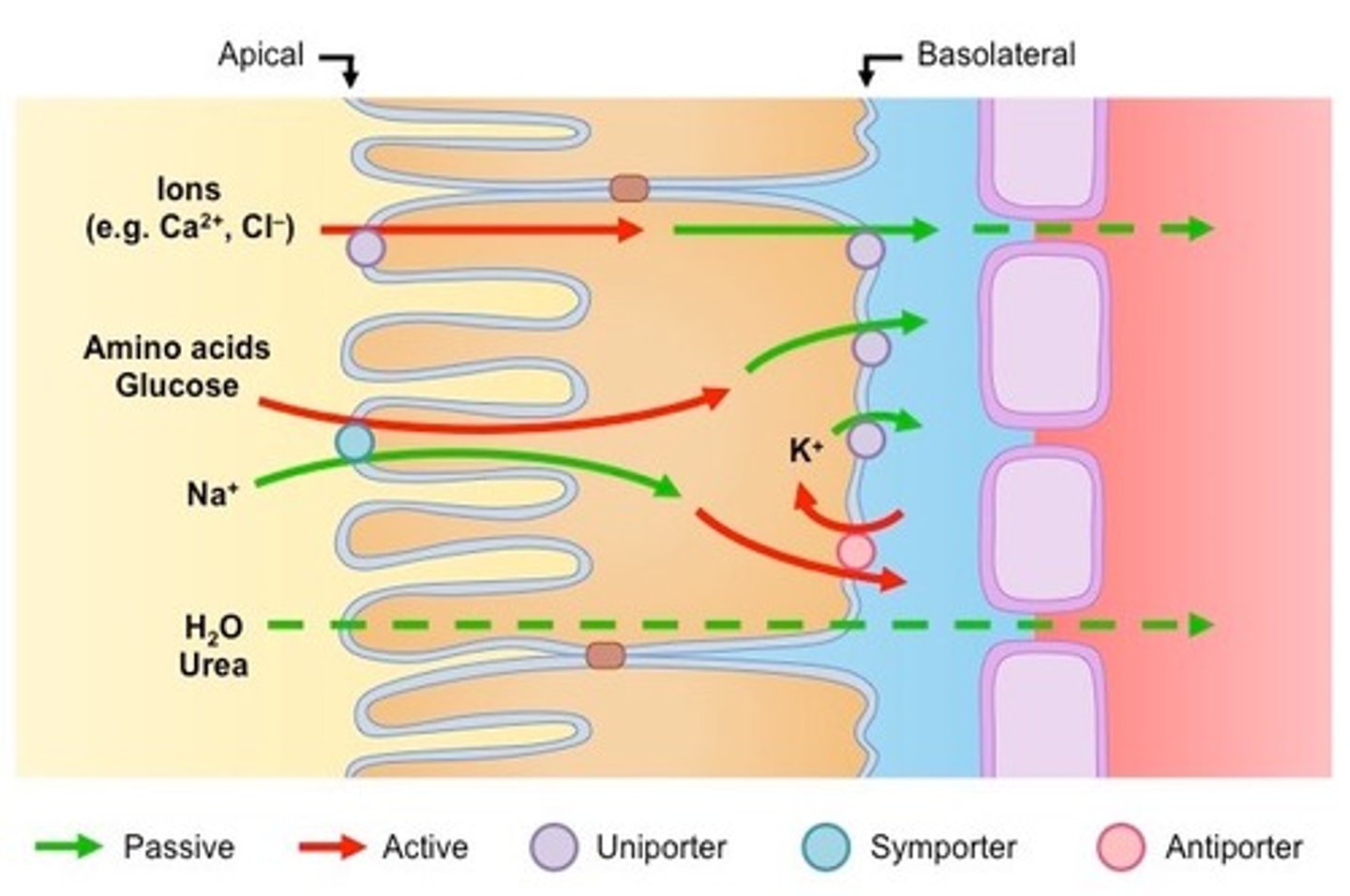
selective reabsorption
proximal convoluted tubule: glucose, amino acids, salts are reabsorbed actively, water follows passively (osmosis)
secretion
distal convoluted tubule: salts, waste/toxins secreted into urine
excretion
process by which wastes are removed from the body
ADH
released by pituitary, opens aquapores in collecting duct so water leaves urine -> body
-> more concentrated, small amount of urine
- produced when you Are DeHydrated (need to retain water)
osmoregulation (osmoconformers vs osmoregulators)
controlling water balance
- occurs in renal medulla: hypertonicity (created by Loop of Henle -> concentration gradient so water leaves collecting duct) & ADH
osmoconformers: isotonic (match salinity) to environment; no active regulation (ex. marine invertebrates)
osmoregulators: active regulation (ex. marine vertebrates)
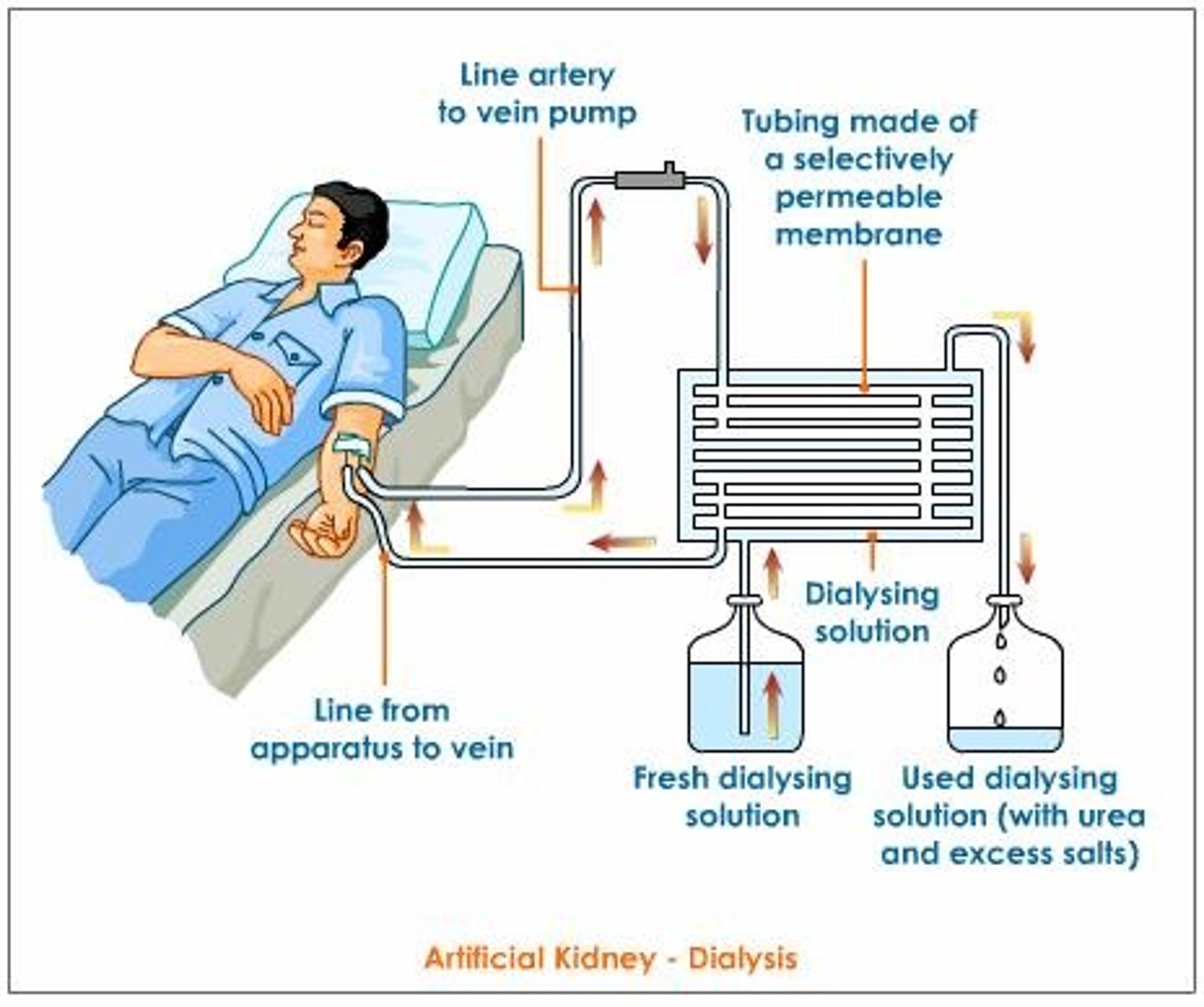
kidney dialysis
replacement for lost kidney function (filtration)
- blood taken out of body, passed through dialysis tubing & continually-replaced dialysis fluid (isotonic to glucose/salt, no urea so that urea will diffuse down concentration gradient out of blood), returned to body
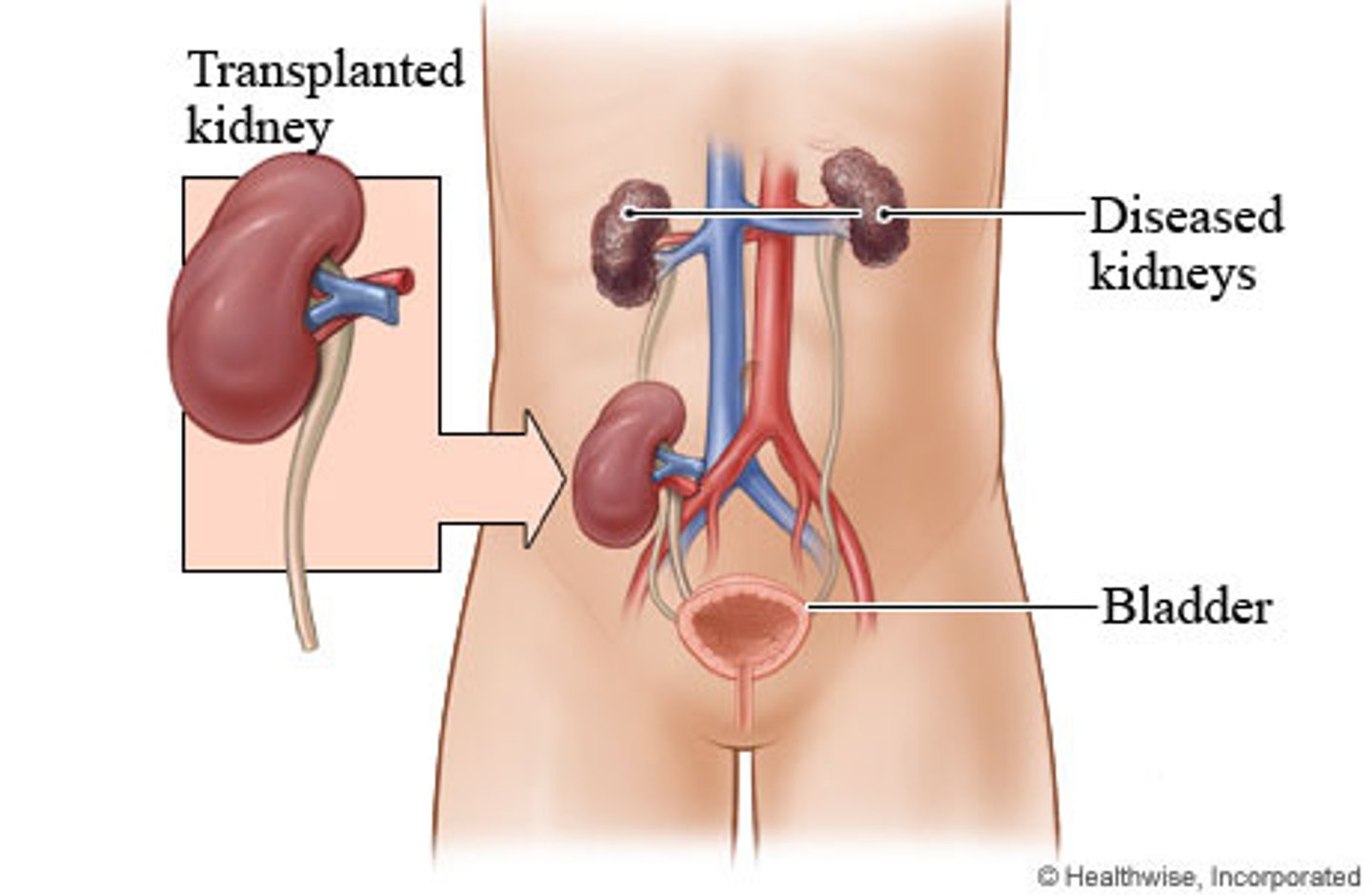
kidney transplant
replacement of a diseased kidney with a healthy one from compatible donor (close genetic match to lower risk of rejection)
basement membrane
separates blood in capillaries from filtrate in Bowman's capsule (like a coffee filter)
Loop of Henle (ascending/descending)
part of nephron involved in osmoregulation, makes the medulla hypertonic (salty) - conserves water
- descending is permeable to water (aquapores) and not salt -> high salt concentration
- ascending is permeable to salt & not water (salt leaves into medulla -> hypertonicity)
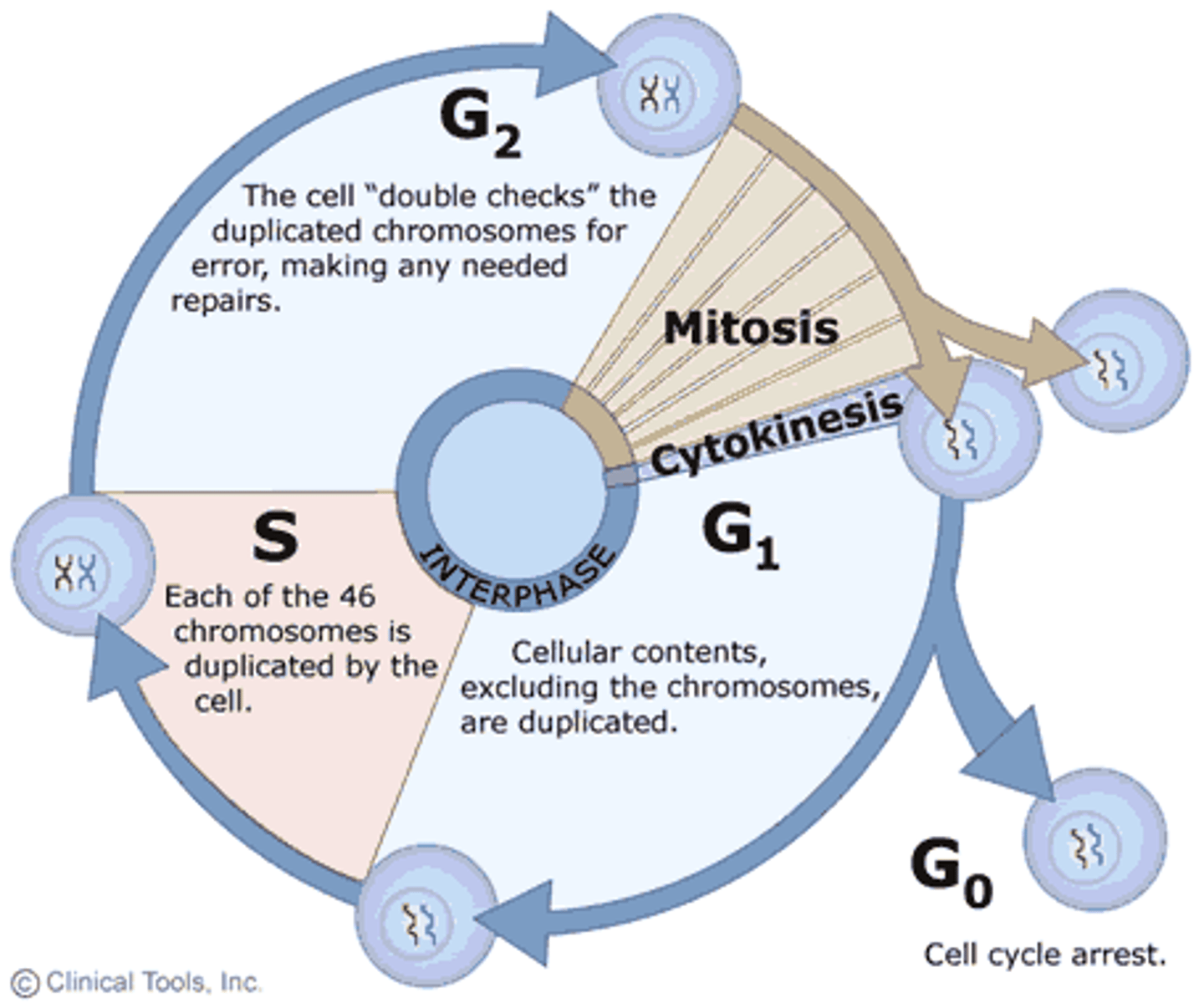
cell cycle
INTERPHASE
Gap 1: growth, protein/organelle synthesis
Synthesis: DNA replication
Gap 2: more growth, final prep for mitosis
MITOSIS
Prophase: chromatin -> chromosomes
Metaphase: chromosomes align in middle of cell
Anaphase: spindle fibers pull chromosomes apart
Telophase: nuclei reform
CYTOKINESIS (cytoplasm divides -> 2 daughter cells)
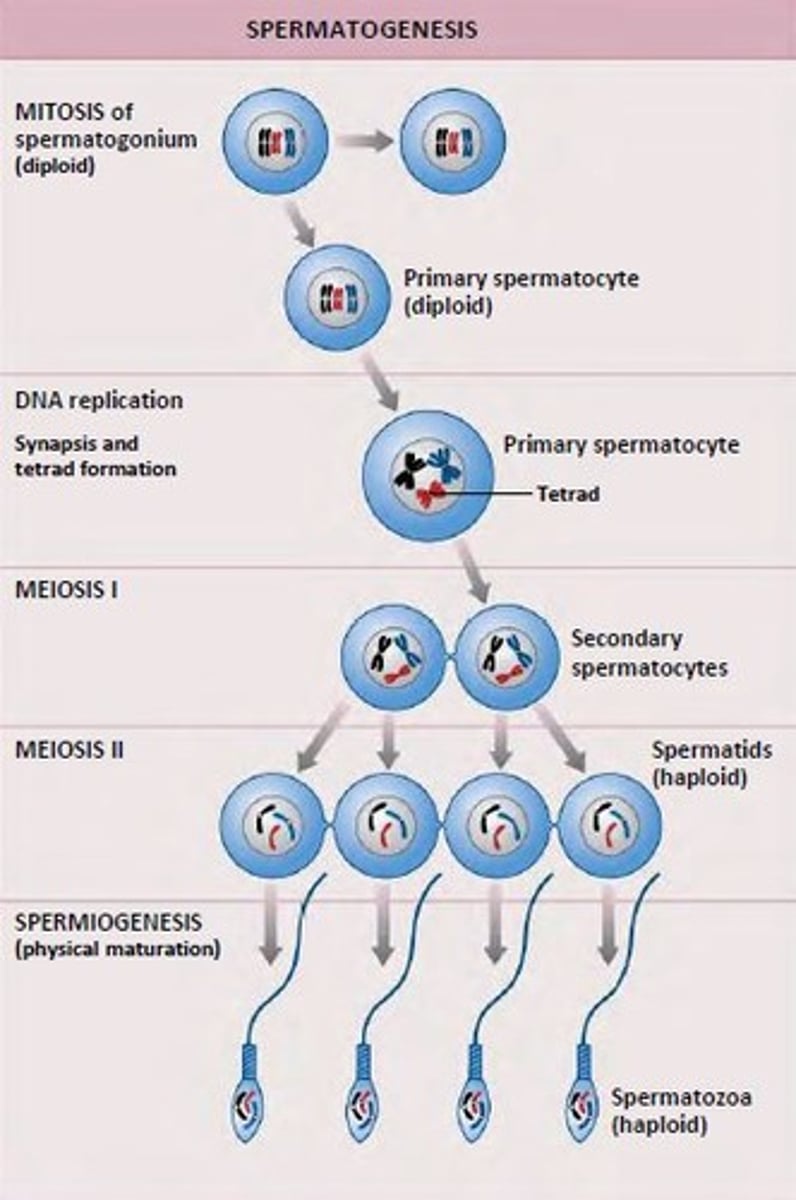
spermatogenesis
millions produced in testes continuously, starts at puberty, ends at death
- released in ejaculation
- 4 functional sperm produced per meiotic division