INFO 3234 Ch1
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 11:31 PM on 9/12/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
1
New cards
Information Systems Analysis and Design
the complex, challenging, and simulating organizational process that a team of business and systems professionals uses to develop and maintain information systems
2
New cards
Application Software
software designed to support organizational function or process
3
New cards
Systems Analyst
organizational role most responsible for analysis and design of information systems
4
New cards
Present
\
Continued focus on developing systems for the Internet and for firm’s intranets and extranets
– Implementation involving three-tier design
▪ Database on one server
▪ Application on second server
▪ Client logic located on user machines
– Move to wireless system components (access from anywhere)
– Continuing trend toward assembling systems from programs and components purchased off the shelf
Continued focus on developing systems for the Internet and for firm’s intranets and extranets
– Implementation involving three-tier design
▪ Database on one server
▪ Application on second server
▪ Client logic located on user machines
– Move to wireless system components (access from anywhere)
– Continuing trend toward assembling systems from programs and components purchased off the shelf
5
New cards
Systems development methodology
a standard process followed in an organization to conduct all the steps necessary to analyze, design, implement, and maintain information systems
6
New cards
Systems development life cycle (SDLC)
the traditional methodology used to develop, maintain and replace information systems
* features several phases that mark the progress of the systems analysis and design efforts
* Circular= never ending
* iterative= back up if needed
* features several phases that mark the progress of the systems analysis and design efforts
* Circular= never ending
* iterative= back up if needed
7
New cards
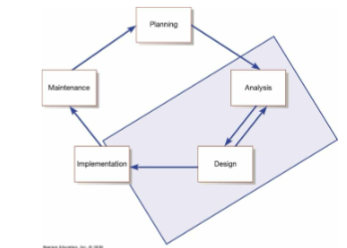
5 phases of SDLC
* Planning
* Analysis
* Design
* Implementation
* Maintenance
* Analysis
* Design
* Implementation
* Maintenance
8
New cards
Planning
– Need for a new or enhanced system is identified
– Needs are identified, analyzed, prioritized, and arranged
– Determine the scope of the proposed system
– Baseline project plan is developed
– Needs are identified, analyzed, prioritized, and arranged
– Determine the scope of the proposed system
– Baseline project plan is developed
9
New cards
Analysis
– System requirements are studied from user input and structured
– Requires careful study of current systems, manual and computerized, that might be replaced or be enhanced
\-Two sub phases:
\-==Requirement determination==
==-Study the req and structure them according to their interrelationships and eliminate any redundancies==
– Output is description of the alternate (new) solution recommend by the analysis team
– Requires careful study of current systems, manual and computerized, that might be replaced or be enhanced
\-Two sub phases:
\-==Requirement determination==
==-Study the req and structure them according to their interrelationships and eliminate any redundancies==
– Output is description of the alternate (new) solution recommend by the analysis team
10
New cards
Design
– Analyst converts the alternate solution into logical and physical specifications
– Logical Design
▪ The design process part that is independent of any specific hardware or software platform
▪ Concentrates on business aspect- high level
– Physical Design
▪ The logical specifications of the system from logical design are transformed into technology-specific details from which all programing/system construction can be accomplished
– Logical Design
▪ The design process part that is independent of any specific hardware or software platform
▪ Concentrates on business aspect- high level
– Physical Design
▪ The logical specifications of the system from logical design are transformed into technology-specific details from which all programing/system construction can be accomplished
11
New cards
Implementation
– Occurs when the information system is coded, tested, installed, and supported in the organization
– New systems become part of the daily activities of the organization
– New systems become part of the daily activities of the organization
12
New cards
Maintenance
– The phase in which an information system is systematically repaired and improved
– Organization’s needs may change over time requiring changes to the system based on user’s needs
– Organization’s needs may change over time requiring changes to the system based on user’s needs
13
New cards
When to replace systems (SDLC)
* when the info system is no longer performing as desired
* when maintenance costs become prohibitive
* when the org needs have substantially changed
* not just when the system has reached an arbitrary time limit
* when maintenance costs become prohibitive
* when the org needs have substantially changed
* not just when the system has reached an arbitrary time limit
14
New cards
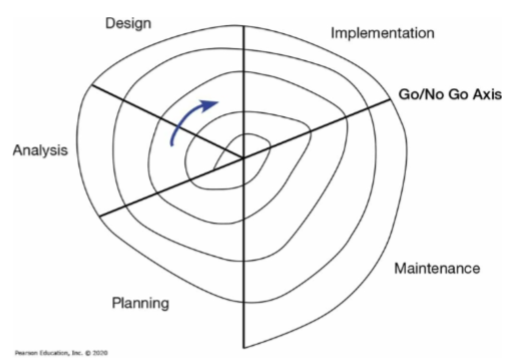
Analysis Design Code Test Loop
an example of traditional practice
15
New cards
HOSD
encompasses analysis, design, and partially implementation phase to indicate combination of their respective activities into a single process
16
New cards
Heart of Systems Development
current practice combines analysis, design, and implementation into a single process
17
New cards
Why is waterfall good?
Timing, scope determined, limit scope creep
18
New cards
Why is waterfall bad?
not as easy to go back phases or back up, users-assume requirements established in advance, focused on deadlines
19
New cards
SDLC Traditional Waterfall problems
* once one phase ends another begins, going downhill until complete
* makes it diff to go back
* results in great expense to make changes
* ==r**ole of system users or customers narrowly defined**==
* focus on deadlines
* makes it diff to go back
* results in great expense to make changes
* ==r**ole of system users or customers narrowly defined**==
* focus on deadlines
20
New cards
Agile Methodologies (3 principles)
1. a focus on adaptive rather than predictive methodologies
2. a focus on people rather than roles
3. a focus on self-adaptive processes
21
New cards
eXtreme Programming
* short, incremental development cycles
* focus on automated tests written by programmers
* emphasis on two-person programming teams
* customers to monitor the development process
* focus on automated tests written by programmers
* emphasis on two-person programming teams
* customers to monitor the development process
22
New cards
Scrum
* primary unit is the sprint (runs two weeks to a month)
23
New cards
Criticisms of SDLC include
* forced timed phases on intangible and dynamic processes were doomed to fail
* life-cycle reliance has resulted in massive amounts of process and documentation
* cycles are not necessarily waterfalls
* life-cycle reliance has resulted in massive amounts of process and documentation
* cycles are not necessarily waterfalls
24
New cards
Evolutionary Model
a spiral process in which one is constantly cycling through phases at different levels
\-start small: min risk
\-early feedback from users
downside: complex to manage
\-start small: min risk
\-early feedback from users
downside: complex to manage