Module 3.2 Electromagnetism
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
95 Terms
Volta
Invented the Voltic pile - first battery - (pile of copper & zinc), attached to a wire
Oersted
discovered that electric current produces magnetic field
Faraday
discovered that current is induced by a moving magnetic field
First Law of Electromagnetism
a changing magnetic field induces an electromotive force (EMF) in a conductor
Strength of Magnets
↑ M = ↑ I (current/ amps)
Speed of Motion
↑ S = ↑ I (current/ amps)
Direction of Motion
The way the wire is moved through the magnetic field influences its strength
MOST current
↑ 90◦
LESS current
↗ 45◦-50◦
ZERO current
→ same direction as magnetic field
Shape of Conductor
a. Straight wire will give some current
b. Loop coil, will give more
More coils =
More current
↑ _____ = ↑ ____ = more current
turns, loops
Control Magnitude of Induced Current by:
Strength of Magnets
Speed of Motion
Direction of Motion
Shape of Conductor
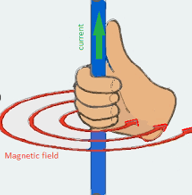
Right thumb rule
when you grab a wire, the way your hand wraps is an indication of the direction the magnetic field is going
Current flows
N to S
Helix
Coil with Wire
Solenoid
Helix with a current
What is a coil of wire?
Helix
What is a coil of wire with a current?
Solenoid
Electromagnet
Solenoid with an iron core
Ferromagnetic material ___ the magnetic strength
↑
2nd Law of Electromagnetism
the magnitude of the induced EMF is equal to the rate of change of magnetic flux linkage
Lenz Law
o The induced current flows in the opposite direction of the applied current
o Called Back EMF (Electromotive Force) or Principle of Self Induction
Self-Induction
The induction of an opposing EMF in a single coil by its own changing magnetic field
Mutual Induction
Magnetic field induces a current in a nearby helix
o Only in an alternating current
How do we get electricity?
Having a loop of wires being turned
How do Windmills work?
Rotating multiple loop wires through magnetic field
How does the Hoover Dam work?
Turbines create energy with water
How does the San Onofre Power Plant work?
Takes plutonium rods, submerging them into water creating steam. The steam will rise, causing turbines to generate energy
What are Generators?
Converts mechanical energy into electrical energy
Components of a generator
Wire coil between magnetic poles
How does a generator work?
1. Coil is mechanically turned within field (armature)
2. As coil moves it cuts through field
3. Current induced
What are Slip rings?
attached to end of the wires so the wires don’t get tangled up
What does 1 slip ring mean?
→ Direct current
What does 2 slip rings mean?
→ Alternating current
What are Brushes?
Contacts, attached to slip rings when they are stationary while the rings turn to keep the contact with the circuitry
Example if a resistor?
Light bulb
In the US, what is the frequency of an AC generator operator?
60 Hz, 120 alternations
What does a motor do?
Converts electrical energy to mechanical energy
Components of a motor
Same as generator
How do motors operate?
1. I (current/ amps) is passed through the coil
2. Magnetic Field of the I interacts with permanent magnetic field causing coil to move
BIG difference between generator and motor:
Motor has a current that is passed through the coil
Types of motors
Synchronous
Induction
Synchronous motor
a. coil rotates at same frequency as current (60 Hz)
b. used in timing circuits in older machines
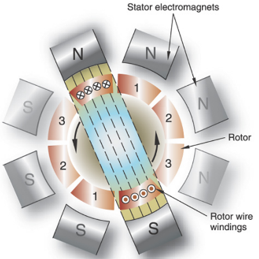
Induction motor
a. Stator and Rotor
b. Uses electromagnets to create magnetic field to interact with current's magnetic field
c. Type used to rotate anode in an x-ray tube

These wires carry electricity that is ___ voltage but ___ amperage.
HIGH, LOW
↑ V (voltage), ↓ I (current/ amp) → due to
resistance
Types of Transformers
Step Up
Step Down
Step Up & Step Down - both are
Used to change the magnitude of current & voltage
Transformers operate on the
Principle of Mutual Induction
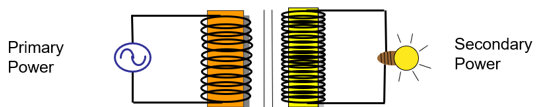
Step Up
Found in tube circuit (also know as High Voltage Transformer – HVT)
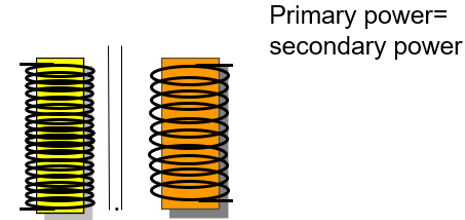
Step Down
Found in filament circuit (used to heat up cathode to boil off electrons)
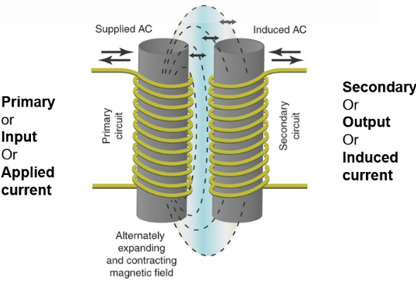
Transformers Mutual Induction
where the magnetic flux of two or more inductors are “linked” so that voltage is induced in one coil proportional to the rate-of-change of current in another
Transformer Law Voltage
Vp/Vs = Np/Ns
The primary side of a step-up transformer has 500 turns, and the secondary side has 1000 turns. If the voltage on the primary side is 200, what is the voltage on the secondary side?
X = 400 V
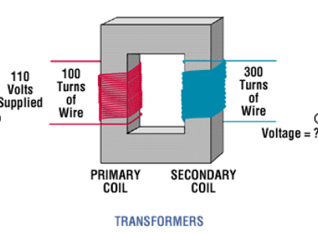
X = 330 V
Transformer Law Amperage
Is/Ip = Np/Ns
V =
Voltage
N =
# turns of the coils
P =
Primary
S =
Secondary
I =
Amperage/ Current
If the number of turns on the primary side is 50 and the number of turns on the secondary side is 150 and the amperage at the input is 10 A, what is the amperage on output?
X = 3.33 I
Transformer Law Amperage formula is
Inversed!
Auto Transformers (SELF) AKA -
The Variable Transformer
Auto Transformers
Able to accomplish Voltage regulation by the Principle of Self Induction
Step Up Transformer =
Mutual induction
Different Auto Transformers
Air Core
Open Core
Closed Core
Shell Type
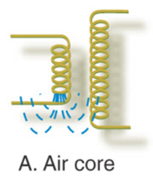
Air Core:
1. coil & wire
a. First auto transformer
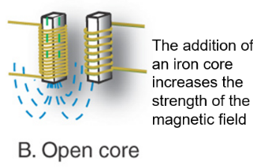
Open Core:
1. Adds iron core (bar), inside
a. Iron core increases the strength of magnetic field
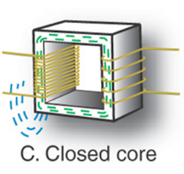
Closed Core:
Inefficient because it still loses energy at the bottom
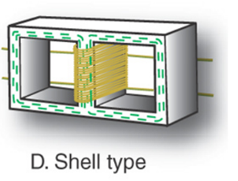
Shell Type:
1. Used in the field today
a. 95% efficient
b. In between the shell is insulated
What type of transformers with two coils of wire?
Air Core
What type of transformer with two coils of wire AND iron bar?
Open Core
What transformer is used in modern x-ray?
Shell Type
List Power Losses
Copper (conductor resistance)
Hysteresis
Eddy Current
Copper (conductor resistance)
↑ distance = ↑ resistance / ↑ cross section = ↓ resistance
Hysteresis
Rearranging magnetic domains
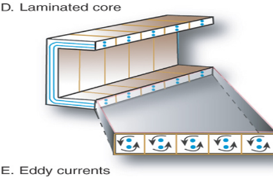
Eddy Current
o Swirling currents in the core
o Minimized by lamination of plates
What makes a transformer work?
Alternating Current – A/C
What does the addition of an iron core do to the magnetic field?
increases the strength of the magnetic field
What are some details about the Autotransformer? (voltage, what induction and current, sent to)
incoming line voltage of 110 V/220 V, operates on self-induction with alternating current, sent to the HVT submerged in oil to reduce shock
Why do wires carry electricity that is high voltage, low amperage?
if the voltage is lower, than the amperage will be higher due to the transformers
How does the strength of magnets control the magnitude of the induced circuit?
if the magnetic field increases, the current increases
How does the speed of motion control the magnitude of the induced circuit?
if the speed of the magnetic influence increases, the current increases
How does the direction of motion control the magnitude of the induced circuit?
90 degrees to the magnetic field = the most current
How does the shape of the conductor control the magnitude of the induced circuit?
the more loops the conductor has, the more current
What is an Electromagnet?
a solenoid with an iron core (ferromagnetic material with magnetic strength)
What is the Lenz Law (2nd Law of Electromagnetism)?
the induced current flows in the opposite direction to the applied current, called Back EMF or Principle of Self Induction
What is Self-Induction?
the induction of an opposing EMF in a single coil by its own changing magnetic field
What is Mutual Induction?
a magnetic field induces a current in a nearby helix, only in an alternating current
What are some details about the Autotransformer? (voltage, what induction and current, sent to)
incoming line voltage of 110 V/220 V, operates on self-induction with alternating current, sent to the HVT submerged in oil to reduce shock
What does the addition of an iron core do to the magnetic field?
increases the strength of the magnetic field
What are the three things that cause power loss?
copper is a conductor with resistance hysteresis rearranges the magnetic domain eddy current swirls current in the core, minimized by lamination of plates