GN 301 Module 2: Cell Cycle and Chromosomes
Chromosome Structure
==Chromosome parts:== A chromosome is 15% DNA, 10% RNA and 75% Protein
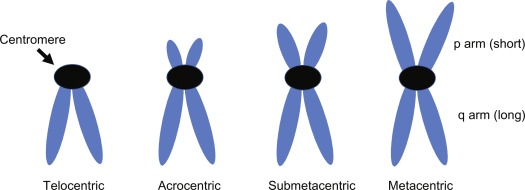
- Label the parts of a chromosome and centromere positions (Draw them)
Metacentric, Submetacentric, Acrocentric, Telocentric
- Metacentric: the centromere is in the middle of the chromosome
- Submetacentric: the centromere is slightly off-center
- Acrocentric: the centromere is very off-center
- Telocentric: the centromere is at the top of the chromosome
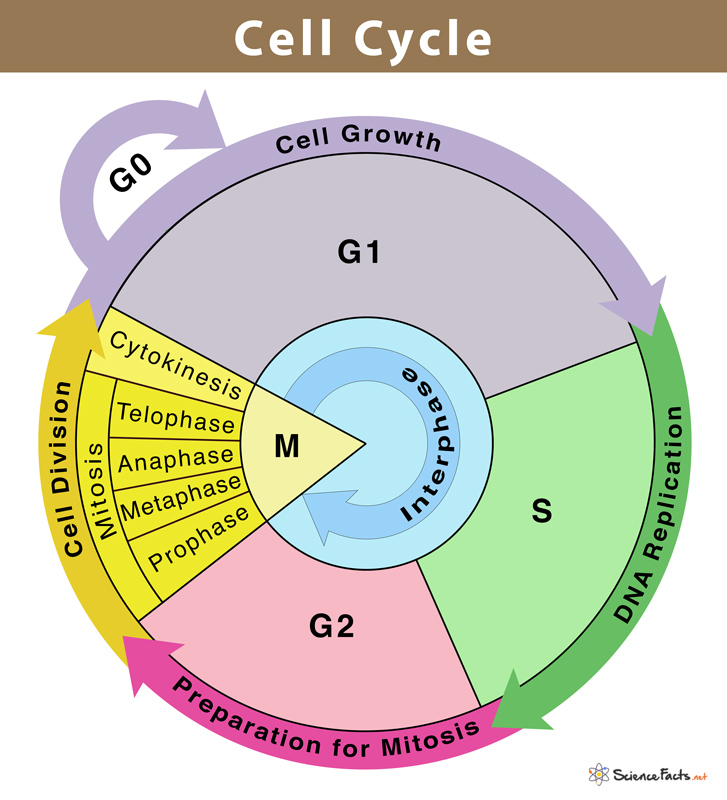
 \n The Cell Cycle
\n The Cell Cycle
- ==G1==
Gap 1. Cells accomplish much of their growth, growing larger and making proteins and organelles needed for DNA synthesis.
- ==S==
S-phase. The cell synthesizes a copy of the DNA in its nucleus.
- ==G2==
Gap 2. The cell grows more as it makes more proteins and organelles, reorganizing its contents in
preparation for mitosis.
- ==M==
M-phase. Nuclear division (mitosis) followed by cytoplasmic division (cytokinesis)
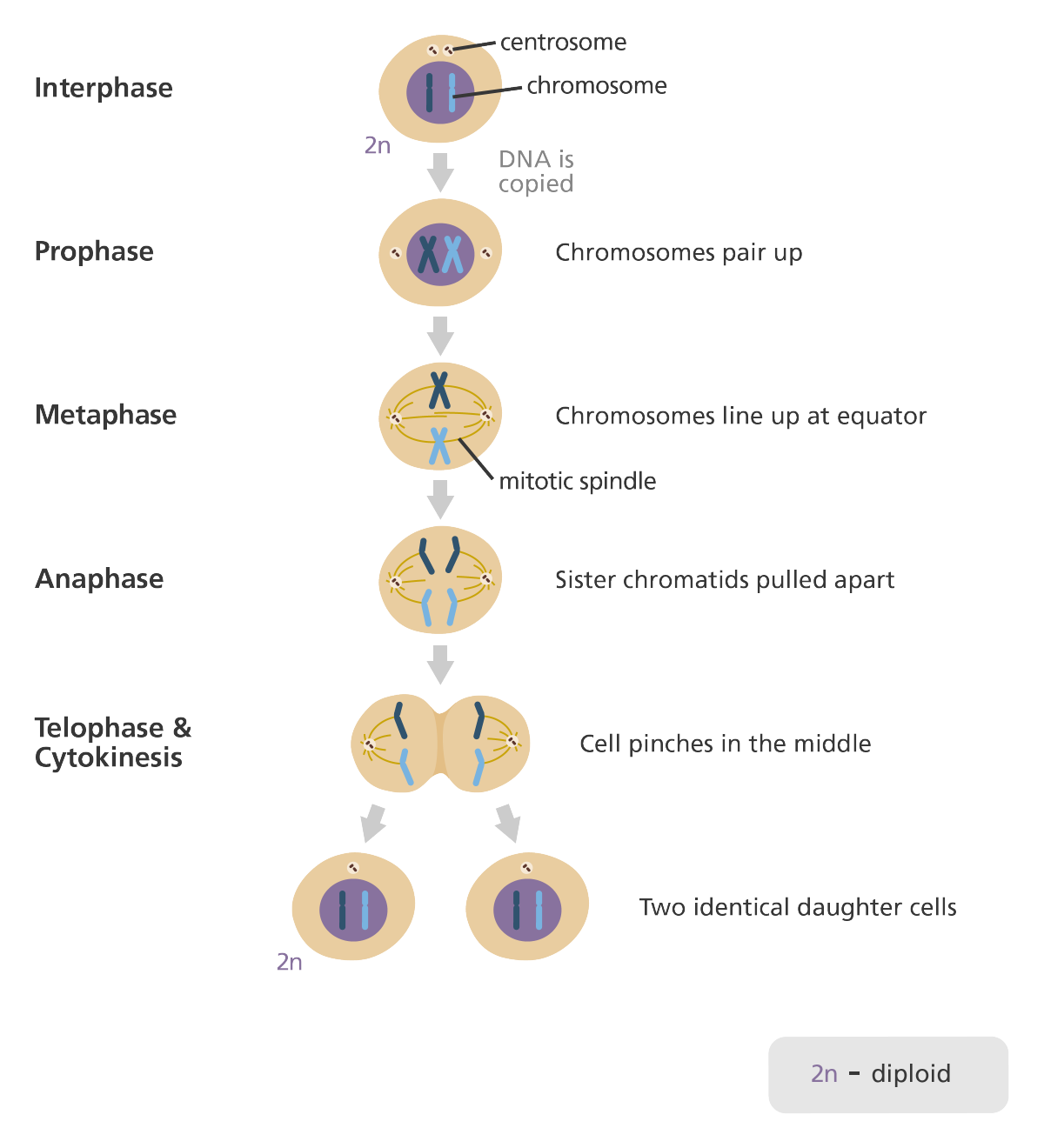
Mitosis
==Prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase==
- What is ==Cytokinesis?==
The cytoplasmic division of a cell at the end of mitosis or meiosis, bringing about the separation into two daughter cells.
Interphase = G1 + S + G2
When is there one chromatid and when are there 2 chromatids (sister chromatids) on the centromere?
During anaphase, there are two chromatids on the centromere. During Telophase, there is just one chromatid on the centromere. \n
Chromosome Preparation
- Colchicine does… destroy spindle fibers in a cell so the view of chromosomes is unobstructed
- Hypotonic Salt solution does ….. increase the cell volume
- Dropping cells from height does …. splinter them apart by force, which reveals chromosomes
==Homologous Chromosomes== have the same: length, centromere, position, banding pattern, and genetic loci.
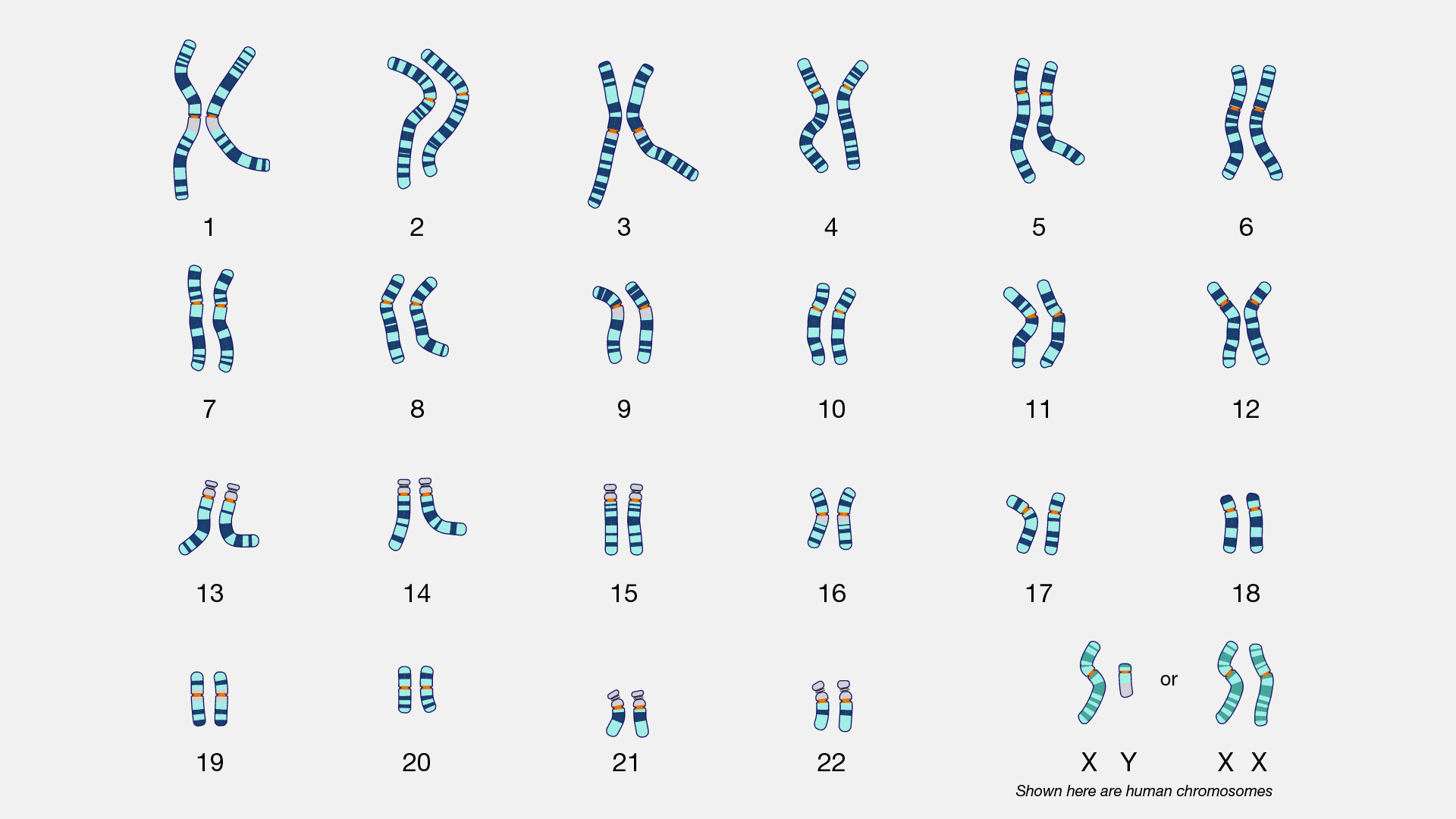
Karyotype
- Define: an organized array of a cell’s chromosomes
- Autosomes: non-sex chromosomes
- Sex Chromosomes: X or Y chromosomes
- Describe arrangement in karyotype: homologous chromosomes are matched together
Karyotypes can show whether an individual has a genetic disorder based on the appearance or absence of chromosomes.
FISH technique
- FISH stands for … Fluorescent in situ Hybridization
- Purpose: to use fluorescent DNA probes to target specific chromosomal locations within the nucleus, resulting in colored signals that can be detected using a fluorescent microscope