Thyroid and Parathyroid Hormone Functions and Disorders
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
T3
Potent thyroid hormone increasing metabolism.
T4
Weak thyroid hormone maintaining steady metabolism.
TSH
Thyrotropin from pituitary regulating thyroid hormones.
Calcitonin
Lowers blood calcium by depositing in bones.
Serum Free T4
Measures unbound thyroxine
Serum T3 & T4
Measures bound and free thyroid hormone levels.
T3 Resin Uptake Test
Indirect measurement for thyroid hormone levels for
patients that have received Iodine for testing or treatment
Hashimoto Disease
Autoimmune thyroiditis attacking the thyroid gland.
Myxedema
Severe skin swelling with waxy consistency (hypo)
Hypothyroidism
Condition of decreased thyroid hormone production.
Synthetic Levothyroxine
Daily dosage 75-150 mcg for hypothyroidism.
Thyroid Storm
Life-threatening acute complication of hyperthyroidism.
Graves Disease
Autoimmune disorder causing excessive thyroid hormone.
Hyperthyroidism
Excessive thyroid hormone production increasing metabolism.
Dexamethasone
Medication suppressing thyroid hormone release.
Hyperparathyroidism
Overproduction of parathyroid hormone elevating calcium.
Tetany
Muscle spasms due to low calcium levels.
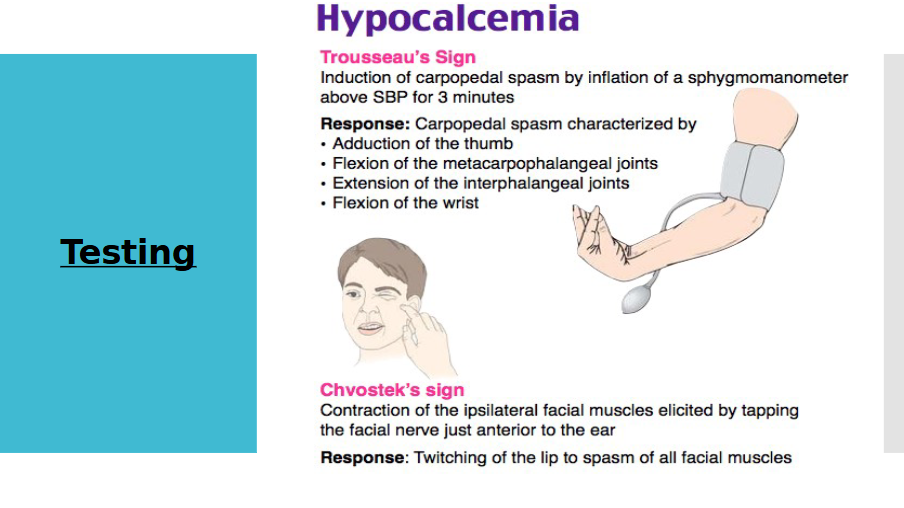
Trousseau Sign
Carpopedal spasm from blood flow occlusion.
Chvostek Sign
Facial twitching from nerve stimulation.
Hypoparathyroidism
Insufficient parathyroid hormone causing low calcium.
Addison's Disease
Adrenal insufficiency leading to various symptoms.
Addisonian Crisis
Severe adrenal insufficiency requiring immediate treatment.
ACTH
Hormone levels increased in primary Addison's.
Renal Calculi
Kidney stones due to calcium imbalance.
Medical Management
Includes hydration therapy and surgical interventions.
Weight Gain
Common symptom of hypothyroidism.
Cold Intolerance
Increased sensitivity to cold in hypothyroidism.
Bradycardia
Slow heart rate associated with hypothyroidism.
How to check pancreas function
amylase and lipase levels
Radiologic study of abdomen’
subjective pain history
What does thyroid regulate
basal metabolic rate, tissue thermogenesis, cholesterol level/resistance
what stimulates release of TSH
low t3 and T4
When is calcitonin released
When ca is high, reducing plasma levels
symptoms of hypothyroidism
lethargy, slow mentation, weight gain, constipation, cold intolerance, slowing of body systems
Levothroxine
hypothyroidism, must be taken on empty stomach, no food for at least an hour after
symptoms of hyperthyroidism
increased metabolic rate, goiter, anxiety, nervousness, tremor, irritability, tachycardia, weight loss, elevated systolic BP, cardiac dysrhythmias, skin flushed, warm, soft, and moist
What does serum free T4 tell you
metabolic status
Why is it important to assess for iodine allergy
iodine is used for a lot of diagnostic studies
what is normal range for serum free T4
0.7 - 2.0 ng/dL
Normal T4 levels
5.4 - 11.5 ug/dL
Normal T3 levels
260-480 pg/dL
Causes of hypothyroidism
Autoimmune disease
Atrophy due to Aging
Infiltrative Disease: Amyloidosis, Scleroderma,
Lymphoma
Iodine deficiencies or excess
Medications (Lithium)
Radioactive Iodine
Therapy or surgery for hyperthyroidism
Radiation
Pt has angina taking Levothyroxine (Synthroid)
stop immediately
Prevention of Cardiac Dysfunction with hypo
Decrease Serum Cholesterol, Monitor and treat atherosclerosis and CAD
hyperthyroidism nursing care
maintain adequate CO, improve nutrition, maintain normal body temp
Nursing care for thyroid cancer
Post-op:
- Monitor for bleeding
- Monitor Airway and breathing
- Vitals
- Pain control
- Fluids
- Keep patient to whispers and limited talking
hyperparathyroidism
Characterized by bone decalcification and formation of Renal
Calculi (Kidney Stones)
what does parathyroid do?
Parathormone regulates calcium and phosphorus balance
- Increased parathormone elevates blood calcium by increasing
calcium absorption from the kidney, intestine, and bone
- Parathormone lowers phosphorus level
Symptoms of hyperparathyroidism
No symptoms possible
- Apathy
- Fatigue
- Muscle weakness
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Constipation
- Hypertension
- Cardiac Arrhythmias
- High Calcium Blood levels (monitor for Hypercalcemic
Crisis – Serum Calcium > 13 mg/dL)
what is hypercalcemic crisis
serum calcium greater than 13 mg/dl
Hypoparathyroidism
Vitamin D deficiency, Decreased intestinal absorption of calcium, Decreased reabsorption of calcium from bone and through renal
tubules
Manifestations of Hypoparathyroidism
tetany, numbness, tingling in extremities, stiffness of hands and feet, bronchospasm, Laryngeal spasm, Carpopedal spasm, anxiety, irritability, depression, delirium, ECG changes
Testing hypocalcemia
Trousseau sign and Chvostek sign
Treatment of hypoparathyroidism
The goal is to increase serum Ca+ to 9 – 10 mg/dL
- Possible combination treatment of Calcium,
Magnesium, and Calcitriol
- Thiazide Diuretic ( help decrease urinary calcium
excretion)
- Treatment for Bone loss
Manifestations of Addison’s Disease
Muscle weakness
- Anorexia
- GI symptoms
- Fatigue
- Dark pigmentation of skin and mucosa
- Hypotension
- Low blood glucose
- Low serum sodium
- High serum potassium
- Apathy
- Emotional lability
- Confusion
ACTH in Addison’s
high
Nursing Management of Addison’s
Health History collection
- Assess for fluid imbalance
- Assess patient level of stress
- Monitor BP and HR
- Do Orthostatic BP’s
- Assess skin often for any change in color
- Restore fluid balance
- Improve activity as tolerated