Anatomy Second Semester 1st Test
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/47
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 6:35 PM on 1/26/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
1
New cards
myology
study of muscle
2
New cards
What are the functions of muscle tissue?
1. body movement
2. stabilizing body positions
3. regulate organ volume
4. generate heat
3
New cards
What are the three types of muscle tissue?
skeletal, smooth, cardiac
4
New cards
Describe skeletal muscle tissue. Striated or nonstriated? Voluntary or involuntary? Where is it located?
\-striations
\-voluntary
\-attached to and moves bones
\-voluntary
\-attached to and moves bones
5
New cards
Describe smooth muscle tissue. Striated or nonstriated? Voluntary or involuntary? Where is it located?
\-nonstriated
\-involuntary
\-around organs that need to squeeze
\-involuntary
\-around organs that need to squeeze
6
New cards
Describe cardiac muscle tissue. Striated or nonstriated? Voluntary or involuntary? Where is it located?
\-striated
\-involuntary
\-heart
\-involuntary
\-heart
7
New cards
Draw a relaxed and contracted sarcomere and label the myosin, actin, and cross bridge, and z-line.
(make sure your drawing and labels matches this picture)
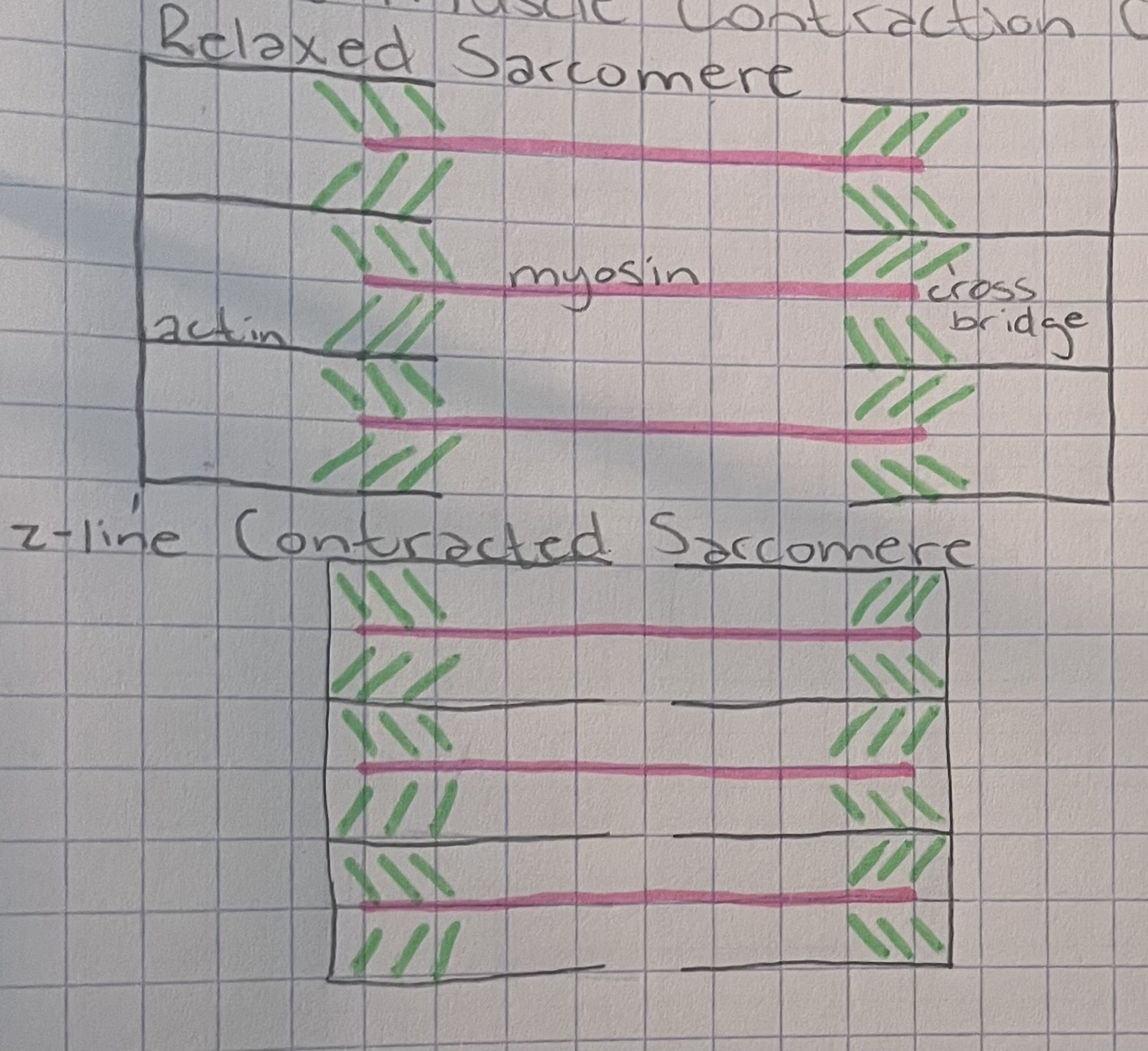
8
New cards
What is a sarcomere?
functional unit of muscle
9
New cards
What is a muscle fiber?
muscle cell
10
New cards
Describe how muscle contraction occurs.
1. stimulus arrives at neuromuscular junction
2. acetylcholine released
3. calcium released
4. ATP released
5. cross bridges on myosin release from actin
6. myosin pulled down actin by cross bridges
7. z-lines pulled closer together
8. sarcomere contracted → myofibril contracted → muscle fiber (cell) contracted → muscle fiber bundle contracted → whole muscle contracted
11
New cards
How does skeletal muscle produce body motion?
\-muscles exert force on tendons which pull on bones
\-bones act as levers (rigid rod) and joint act as fulcrums (fixed point or pivot point)
\-motion is achieved when the effort (muscle contraction) is greater than the resistance (weight of part being moved) M=E>R
\-bones act as levers (rigid rod) and joint act as fulcrums (fixed point or pivot point)
\-motion is achieved when the effort (muscle contraction) is greater than the resistance (weight of part being moved) M=E>R
12
New cards
Draw the muscle parts and label the origin, belly, and insertion.
(make sure your drawing and labels matches this picture)
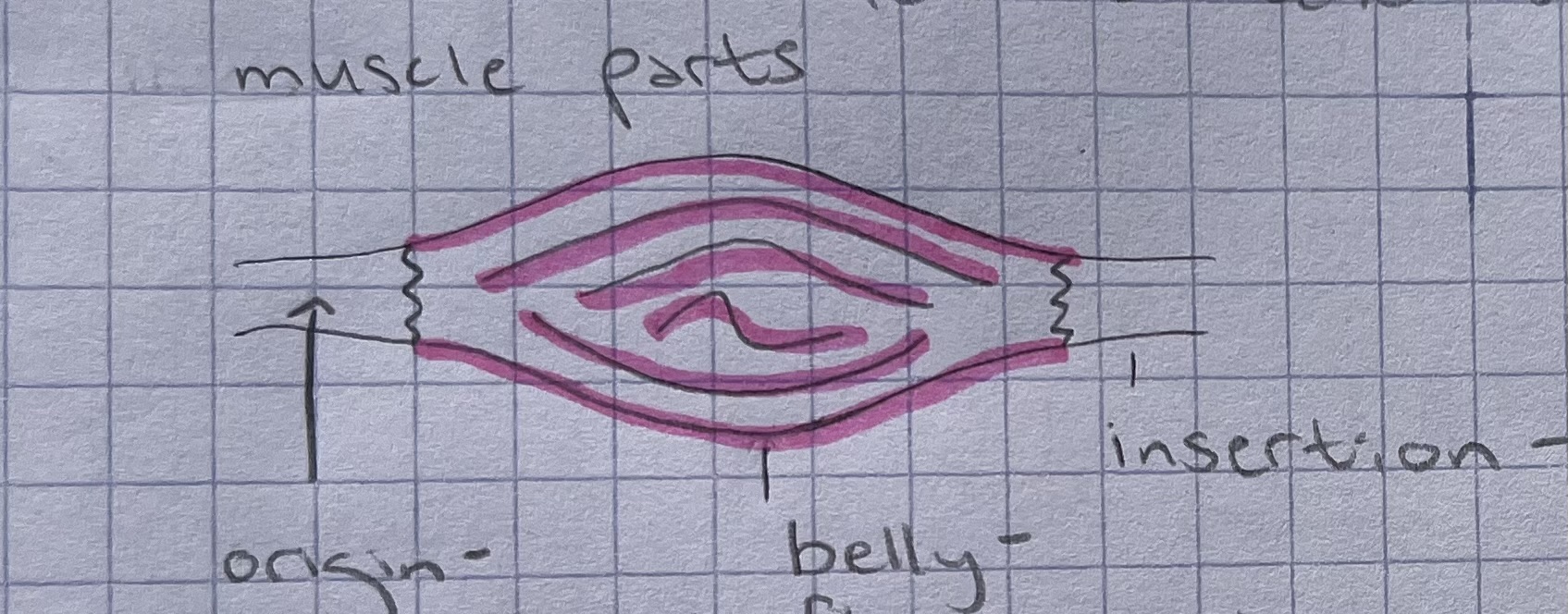
13
New cards
What is the origin of a muscle?
attachment of muscle tendon to stationary bone
14
New cards
What is the belly of a muscle?
fleshy part between origin and insertion
15
New cards
What is the insertion of a muscle?
attachment of a muscle tendon to the moving bone
16
New cards
What does high strength mean?
low range of motion (ROM)
17
New cards
What does low strength mean?
high range of motion (ROM)
18
New cards
What is the prime mover?
muscle causing desired movement
19
New cards
What is the antagonist?
opposite action to prime mover
20
New cards
What is the synergist?
muscles that help steady movement
21
New cards
What does rectus mean?
fibers run parallel to midline
22
New cards
What does transverse mean?
fibers run perpendicular to midline
23
New cards
What does oblique mean?
fibers run at an angle to midline
24
New cards
What does location have to do with muscle names?
sometimes muscles named for a structure near where they are found in the body
25
New cards
What does maximus mean?
largest of muscle group
26
New cards
What does minimus mean?
smallest of muscle group
27
New cards
What does longus mean?
longest of muscle group
28
New cards
What does brevis mean?
shortest of muscle group
29
New cards
How many origins does a bicep have?
two
30
New cards
How many origins does a tricep have?
three
31
New cards
How many origins does a “quadricep” have? (group of muscles)
four
32
New cards
What shape is a deltoid?
triangle
33
New cards
What shape is a trapezius?
trapezoid
34
New cards
What shape is a rhomboideus?
rhomboid
35
New cards
What does a flexor do?
decrease the angle of the joint
36
New cards
What does an extensor do?
increase the angle of the joint
37
New cards
What does an abductor do?
move away from midline
38
New cards
What does an adductor do?
move toward midline
39
New cards
What does a levator do?
lifts body part
40
New cards
What does a depressor do?
lowers body part
41
New cards
What does a supinator do?
turns palm upward
42
New cards
What does a pronator do?
turns palm downward
43
New cards
What does a tensor do?
makes body part rigid/tight to stabilize position
44
New cards
What does a sphincter do?
muscle that encloses an opening
45
New cards
What is fascia?
white connective tissue binding muscle together
46
New cards
Describe thumb movements.
most dexterous in terms of muscle movement
47
New cards
Name the different types of thumb movements.
\-flexion
\-extension
\-abduction
\-adduction
\-circumduction
\-opposition
\-extension
\-abduction
\-adduction
\-circumduction
\-opposition
48
New cards
What is opposition?
\-thumb can touch each finger tip
\-most important movement
\-most important movement