LO4: Anatomical Landmarks and Anomalies
1/137
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
138 Terms
what is radiopaque
Shows white on the film
What is radiolucent?
black or dark areas
what are the prominences of bone
ridge, spine, tubercle, tuberosity
What are spaces & depressions of bone
canal, foramen, fossa, sinus
what are the two types of bone
cortical and cancellous
what is cortical bone
the dense outer layer of bone
how does cortical bone appear in a radiograph
radiopaque
what is cancellous bone
soft, spongy bone located between two layers of dense cortical bone
how does the cancellous bone appear in a radiograph
padiolucent
why is anatomic order important in mounting radiographs
for correct identification and preservation of images
what is radiographic interpretation
an explanation of what is viewed on a dental radiograph
what is the importance of interpretation
a lot of information about teeth and supporting bone is obtained from radiographic interpretation
what information does interpretation state
state of health, presence of disease, baseline information, evaluation/change, cause of symptoms
what is the difference between inerpretation and diagnosis
an interpretation is an explanation and diagnosis is the identification of disease
who can interpret radiographs
any dental professional with training
what do we identify when we interpret
normal anatomy, dental caries, periodontal disease, traumatic injuries, periaplical lesions
what are the landmarks seen in maxillary radiographs
max sinus, max tuberosity, zygomatic process, nasal sinus, nasal septum, lateral fossa, medial paltine suture
where can you see the max sinus in a radiograph
apices of max molars
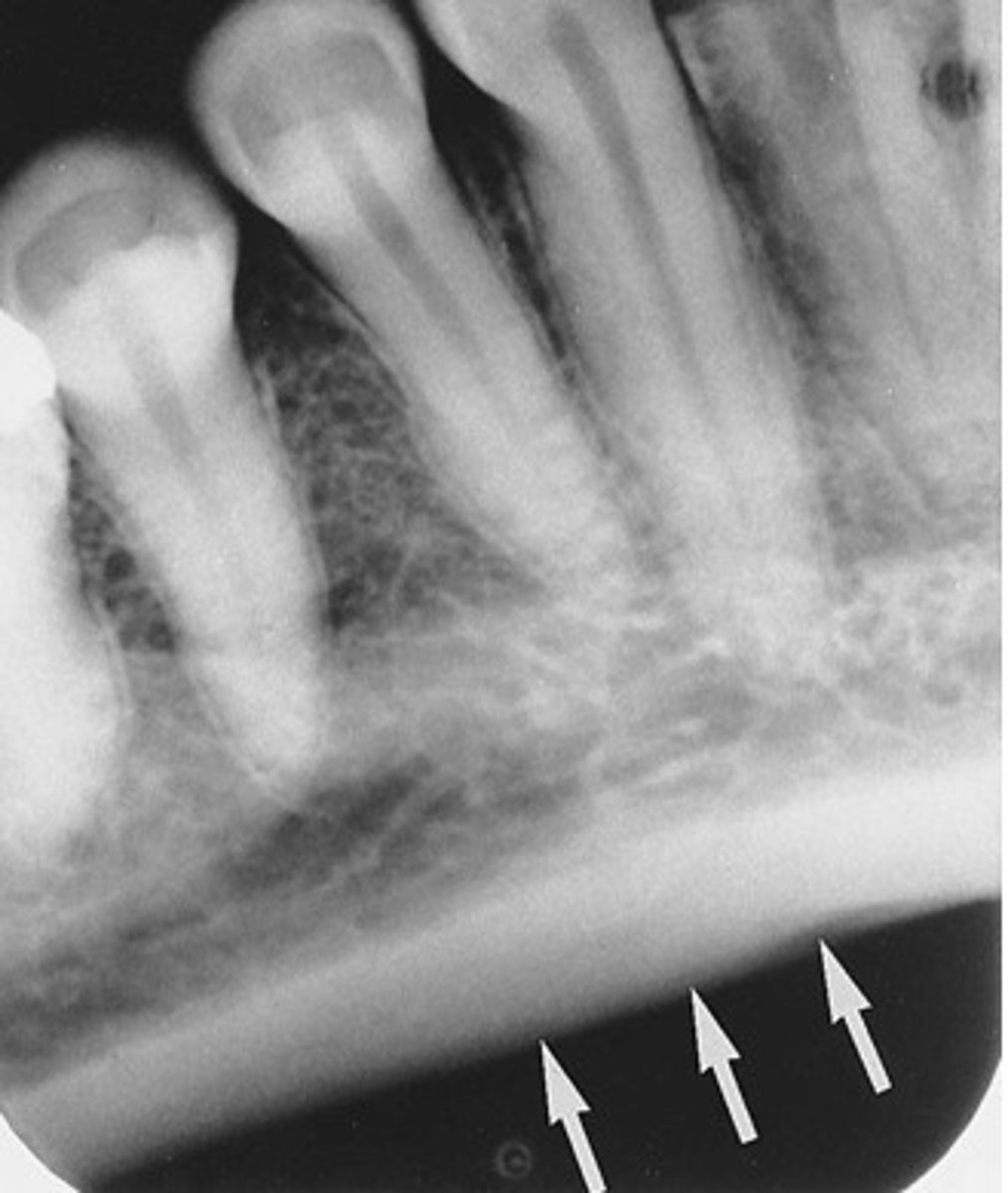
where can you see the max tuberosity in a radiograph
18/28 area
where can you see zygomatic process in a radiograph
apices of max molars
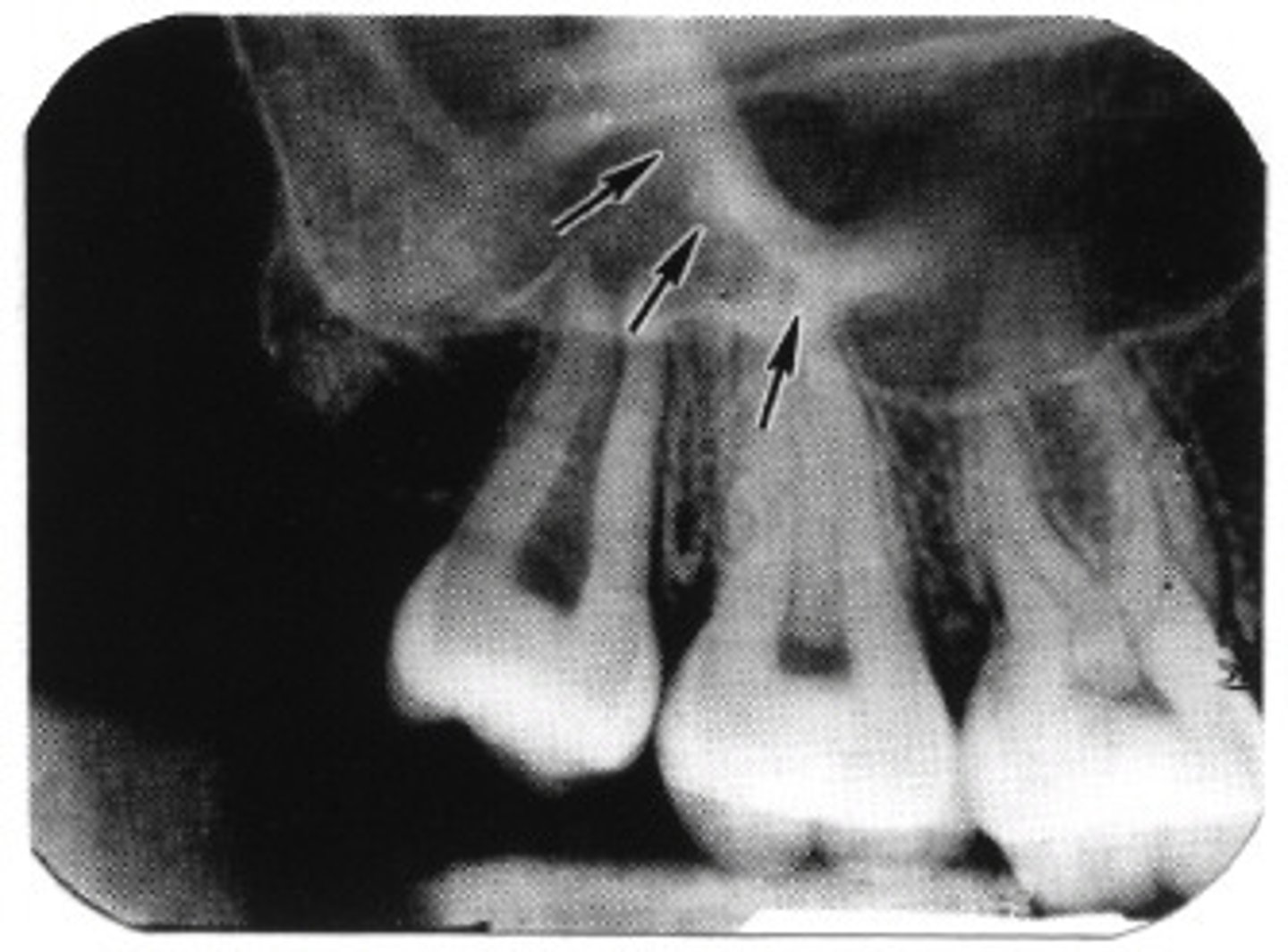
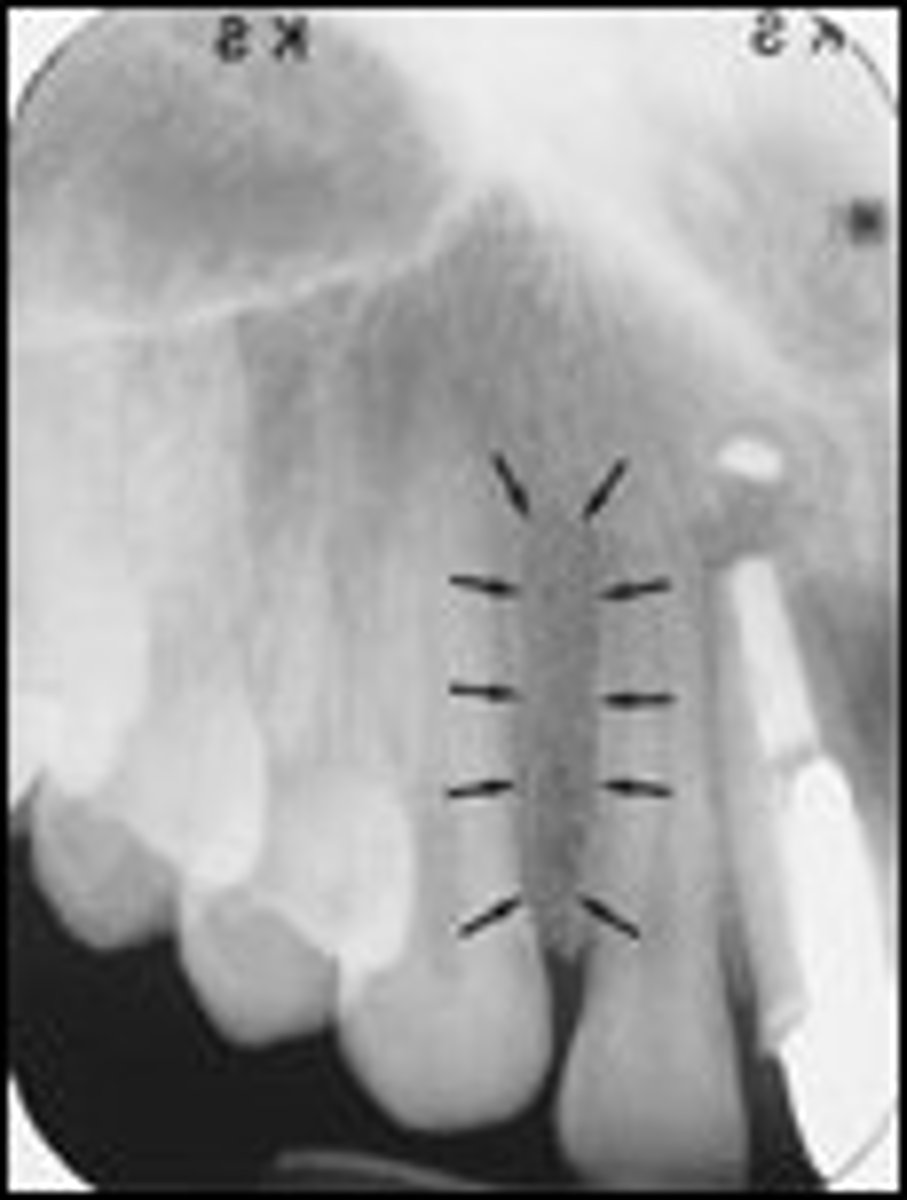
where can you see the nasal sinus in a radiograph
apices of 11/21
where can you see the nasal septum in a radiograph
apices of 11/21
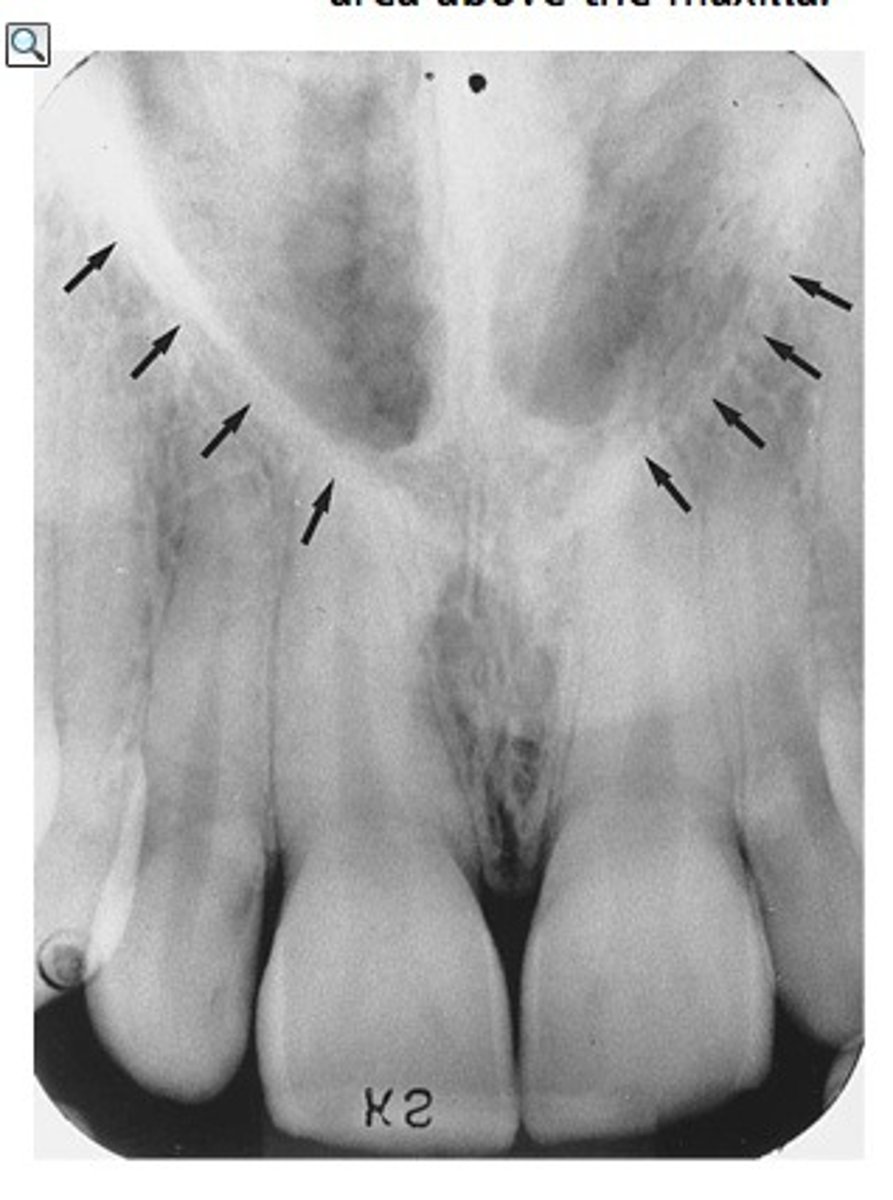
where can you see the lateral fossa in a radiograph
between lateral and canines
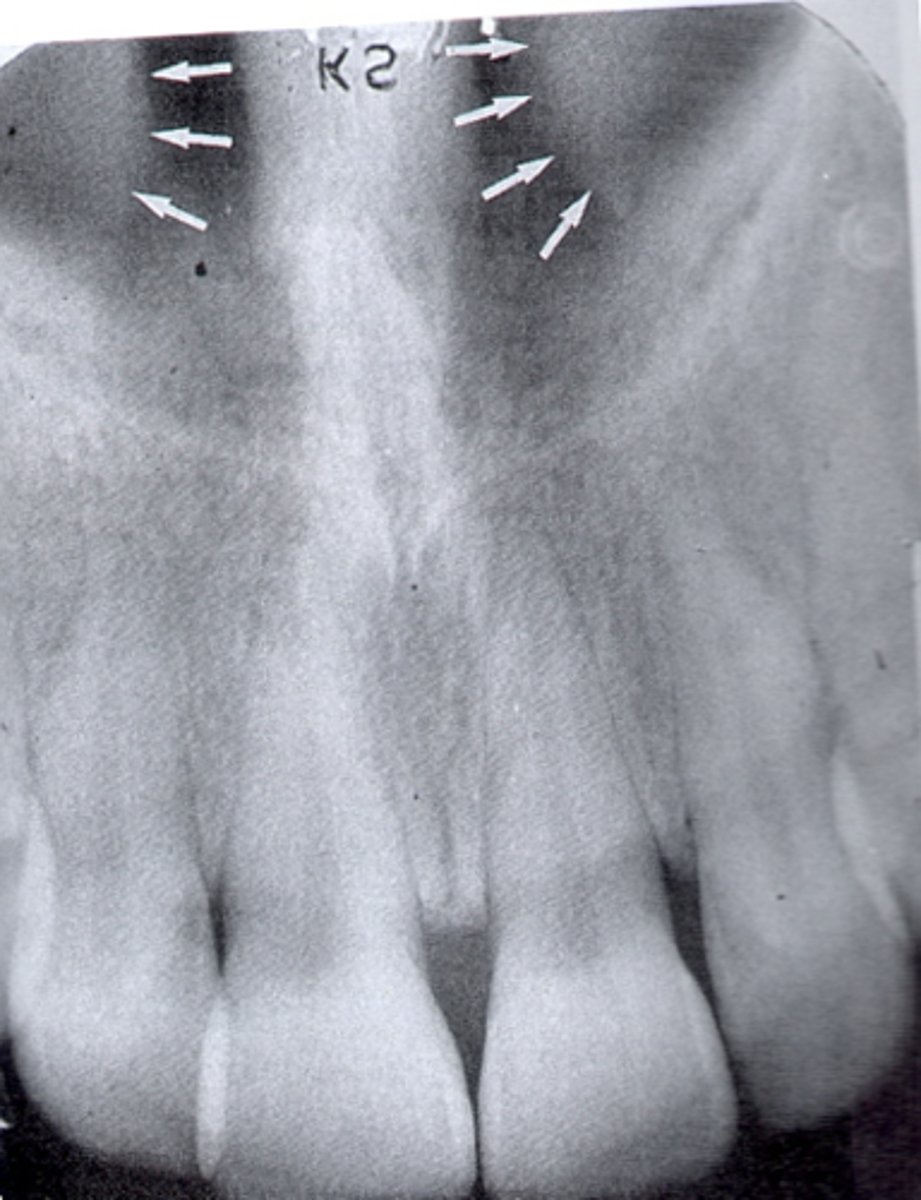
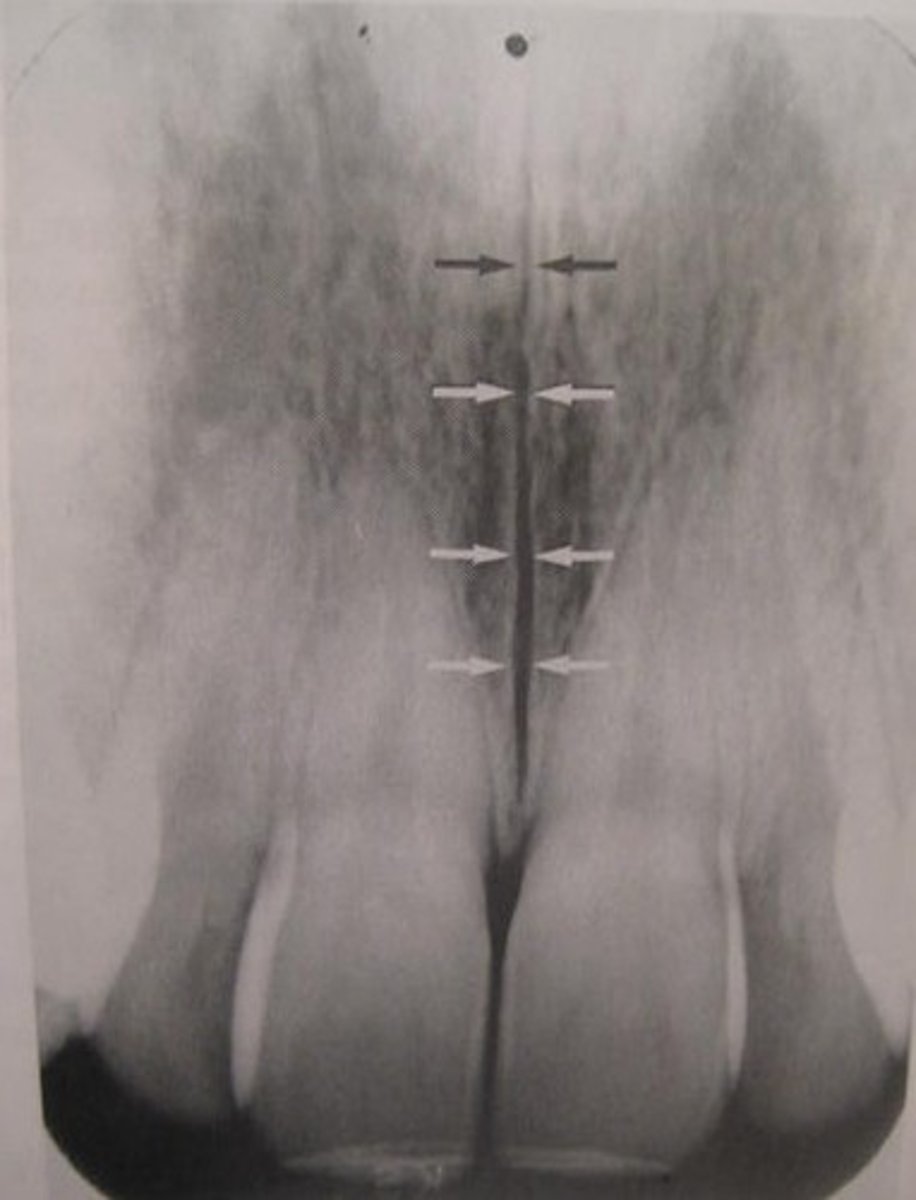
where can you see the median palatine suture in a radiograph
line running the length of a palate
does the maxillary sinus appear radiolucent or radiopaque in a radiograph
radiolucent
does the maxillary tuberosity appear radiolucent or radiopaque in a radiograph
radiopaque
does the zygomatic process appear radiolucent or radiopaque in a radiograph
radiopaque
does the nasal sinus appear radiolucent or radiopaque in a radiograph
radiolucent
does the nasal septum appear radiolucent or radiopaque in a radiograph
radiopaque
does the lateral fossa appear radiolucent or radiopaque in a radiograph
radiolucent
does the median palatal suture appear radiolucent or radiopaque in a radiograph
radiolucent
what are the landmarks seen in radiographs of the mandible (change maybe)
external oblique ridge, internal oblique ridge, submandibular fossa, mand canal, mental foramen, genial tubercles, lingual foramen
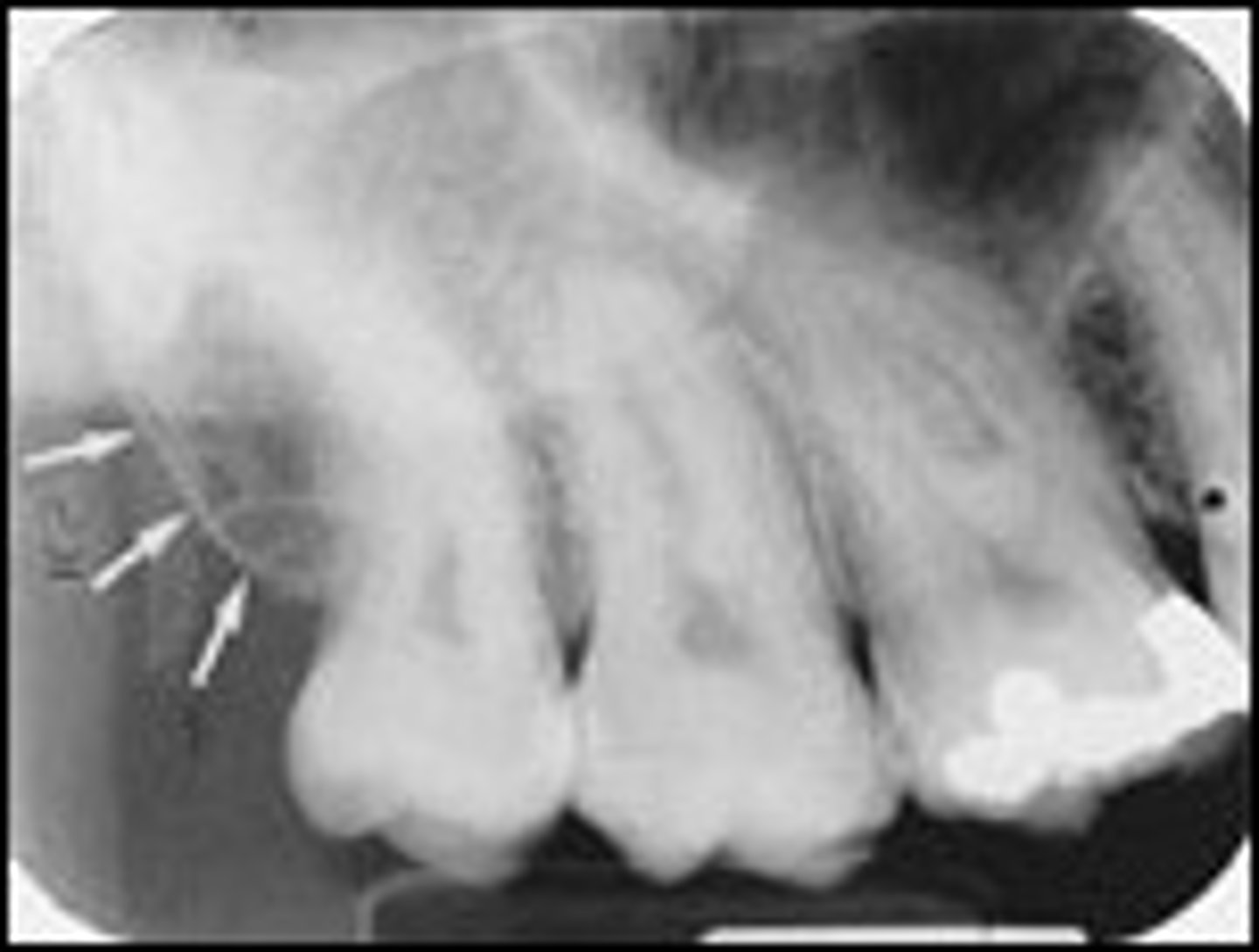
where can you see the mylohyoid ridge in a radiograph
posterior molar region at apices
where can you see the external oblique ridge in a radiograph
posterior mand molars
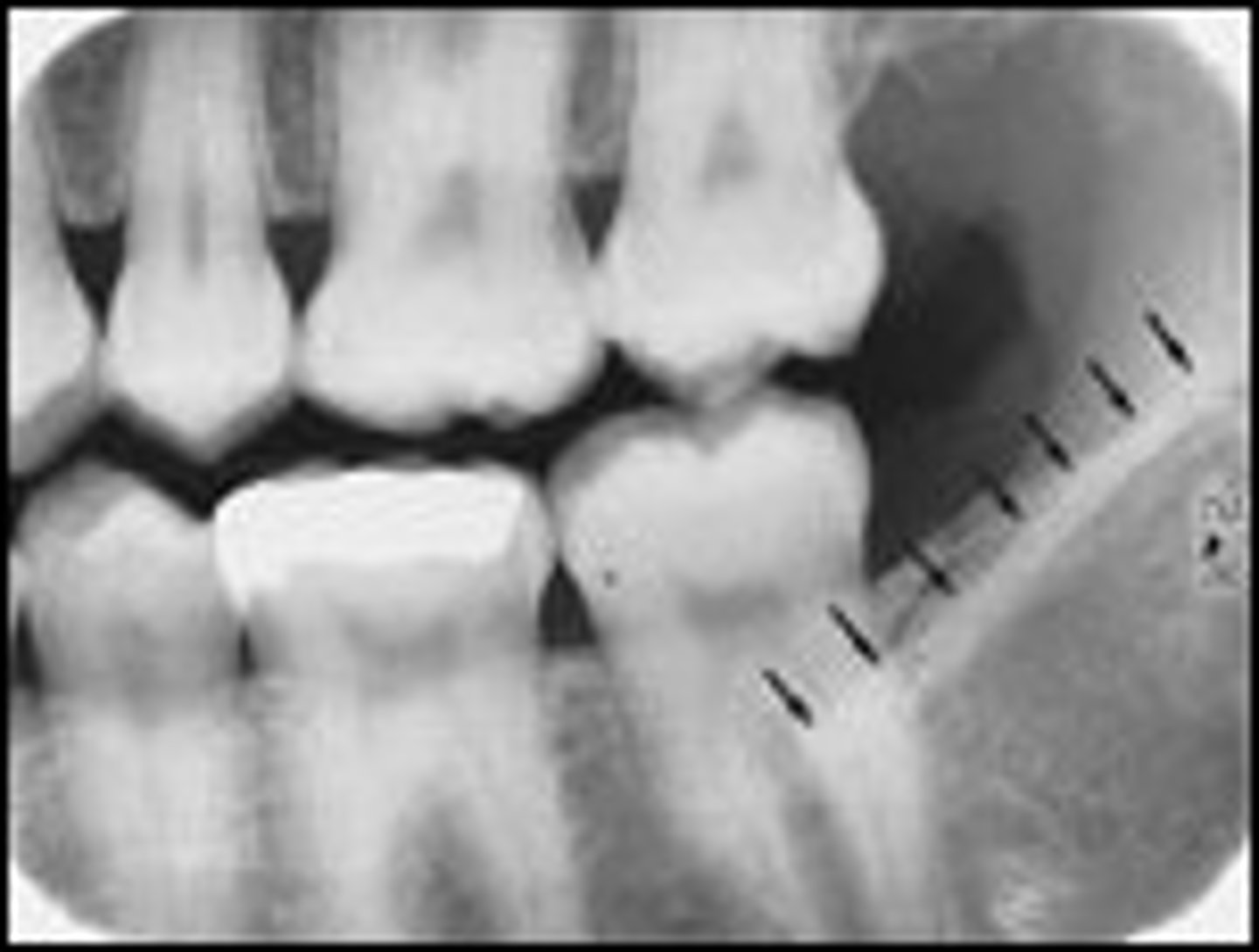
where can you see the internal oblique ridge in a radiograph
apicies of molars, inferior to external oblique ridge
where can you see the submandibular fossa in a radiograph
apices of molar teeth, inferior to interal oblique ridge
where can you see the mandibular canal in a radiograph
apcies of molars
where can you see the mental foramne in a radiograph
apices of premolars
where can you see the genial tubercles in a radiograph
apices of 41/31
where can you see the lingual foramen in a radiograph
apcies of 41/31
does the enternal oblique ridge appear radiopague or radiolucent in a radiograph
radiopaque
does the the submandibular fossa appear radiopaque or radiolucnet in a radiograph
radiolucent
does the mandibular canal appear radiopque or radiolucent in a radiorgraoh
radiolucent
does the mental foramen appear radiopaque or radiolucent in a radiograph
radiolucent
does the genial tubercles appear radiopaque or radiolucent in a radiograph
radiopaque
does the lingual foramen appear radiopaque or radiolucent in a radiograph
radiolucent
what normal tooth anatomy appears radiopauw
enamel, dentin, cementum, DEJ, lamina dura, alveolar bone, deciduous and permanent teeth
what normal tooth anatomy appears radiolucent
pulp cavity and periodontal ligament space
what are the characteristics of a good pan
symetrical, uniform density, teeth are sharp in focus, slight smile in occlusal plane
what structures do you need to view to interpret a pan correctly
condyles, maxilla, sinuses, jaw, and all teeth
what are the common pan errors
client position, clients head tilt, client not entered, tongue position, client moved, metal objects, lead apron
how does a carious area appear
radiolucent
what provides a dental professional with the greatest amount of diagnostic information
bite wing
what are facors influencing caries interpretation
radiographs must be of diagnostic quality
what are the different classications of caries
interproximal, occlusal, buccal and lingual, root surface, recurrent, and rampant caries
what are interproximal caries
caries between the teeth often at or below the contact point
what is a class I interproximal caries
extends less than halfway through enamel
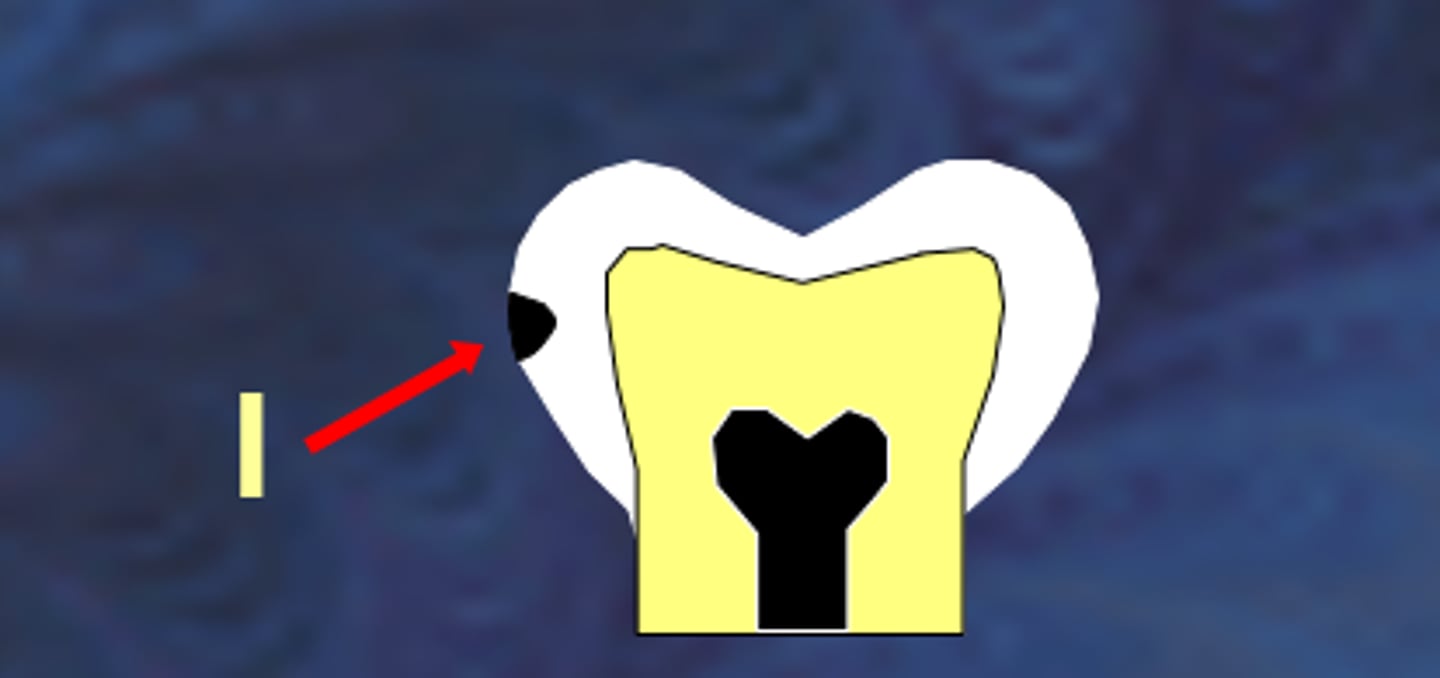
what is class II interproximal caries
extends more than half way through the enamel
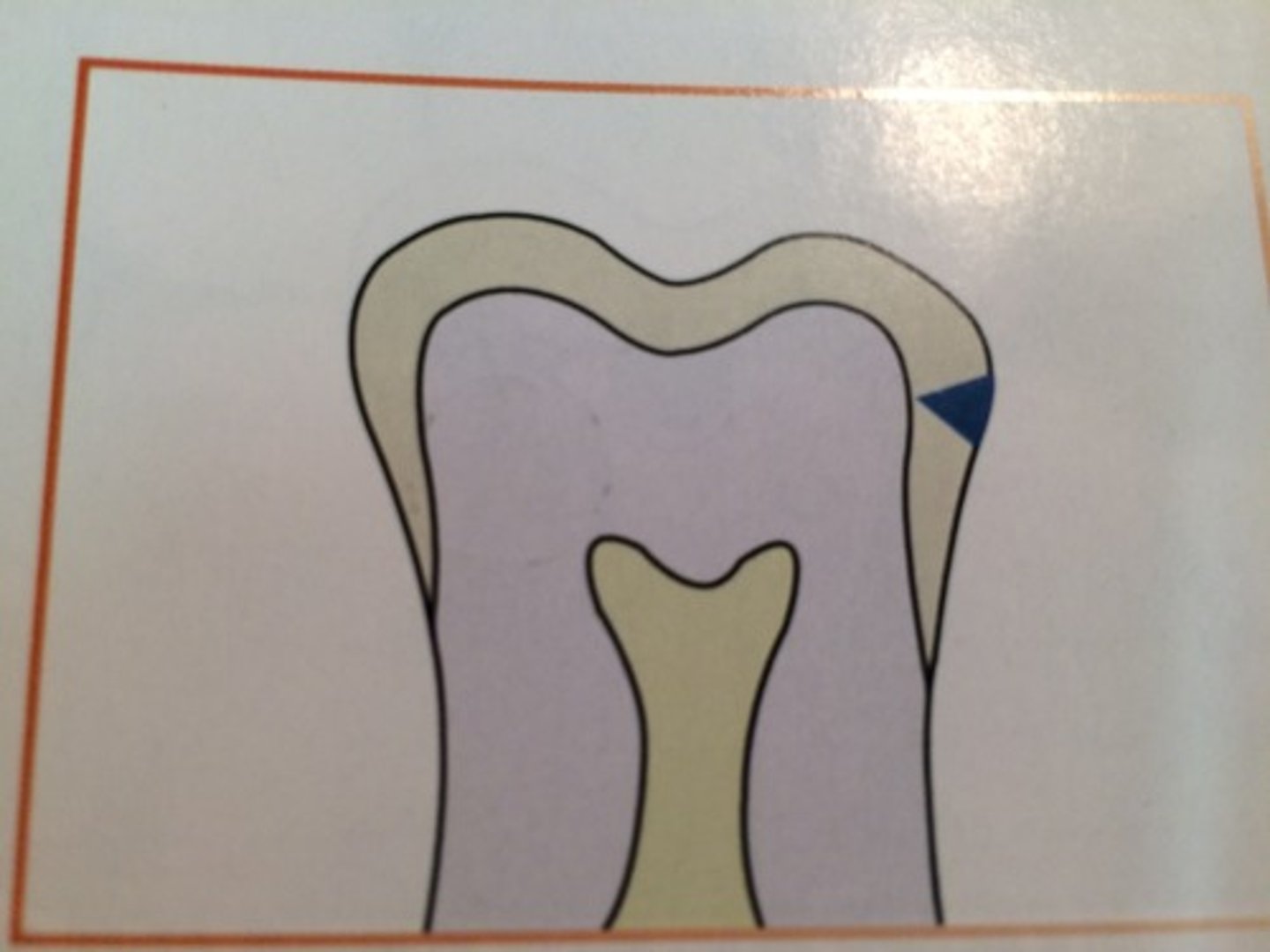
what is a class III interproximal caies
extends to or through the DEJ and into dentin
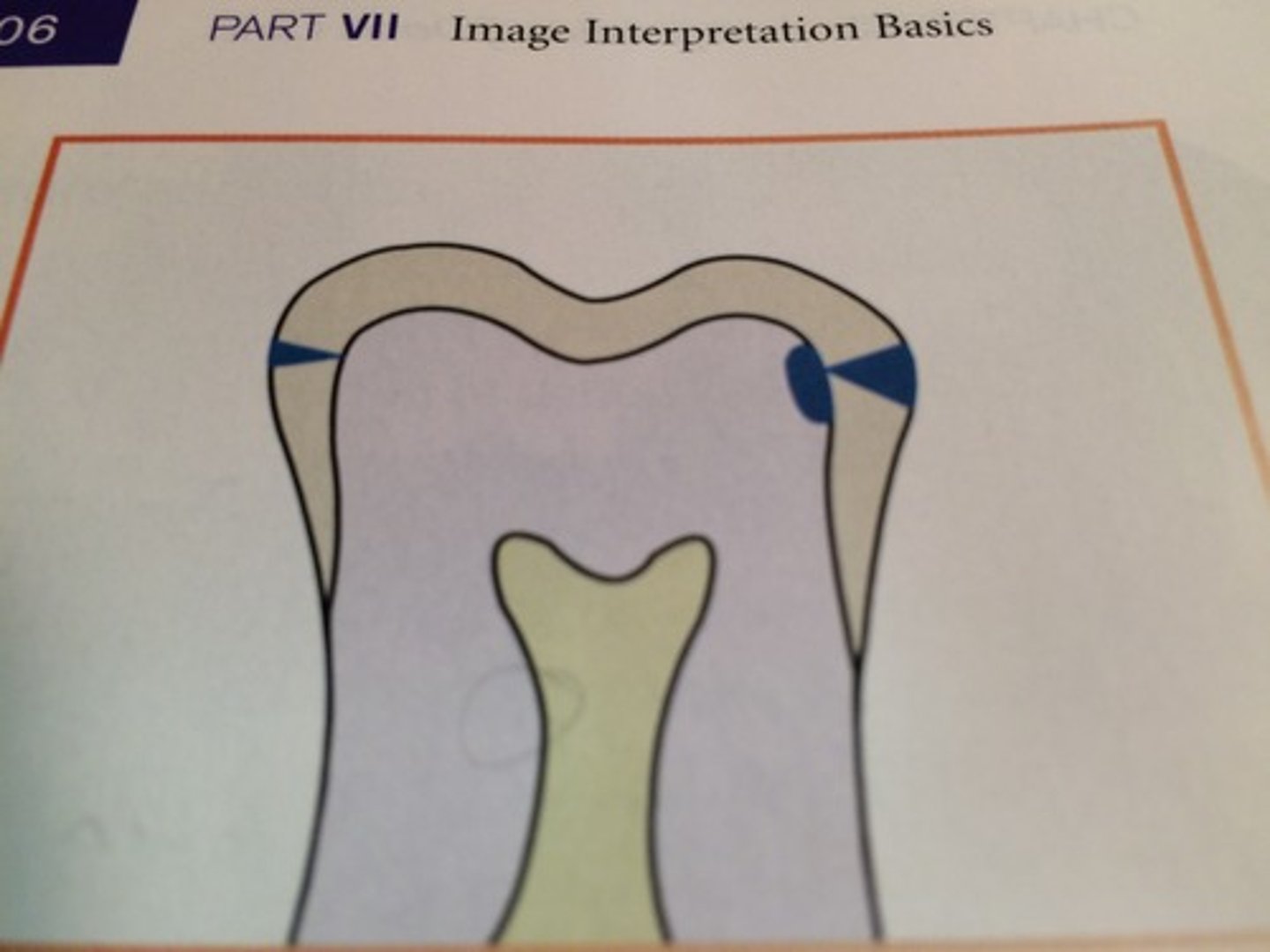
what is class IV inerproximal caries
extends through enamel and dentin more than half distance towards the pulp
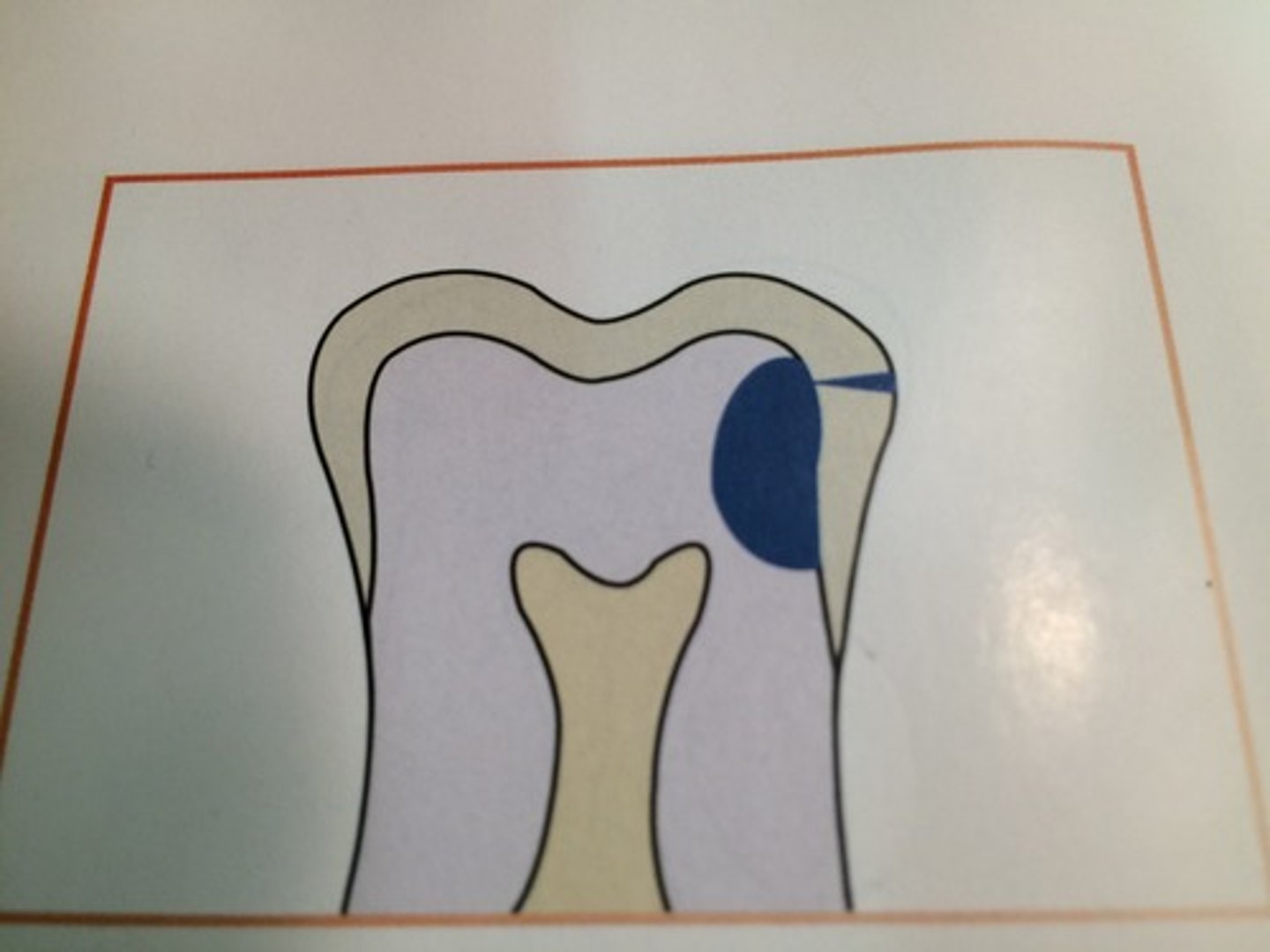
what is the best way to detect occlusal caries
a clinical exam
how do you detect a incipent occlusal caries
cannot be seen on dental radiograph and must be detected with an explorer
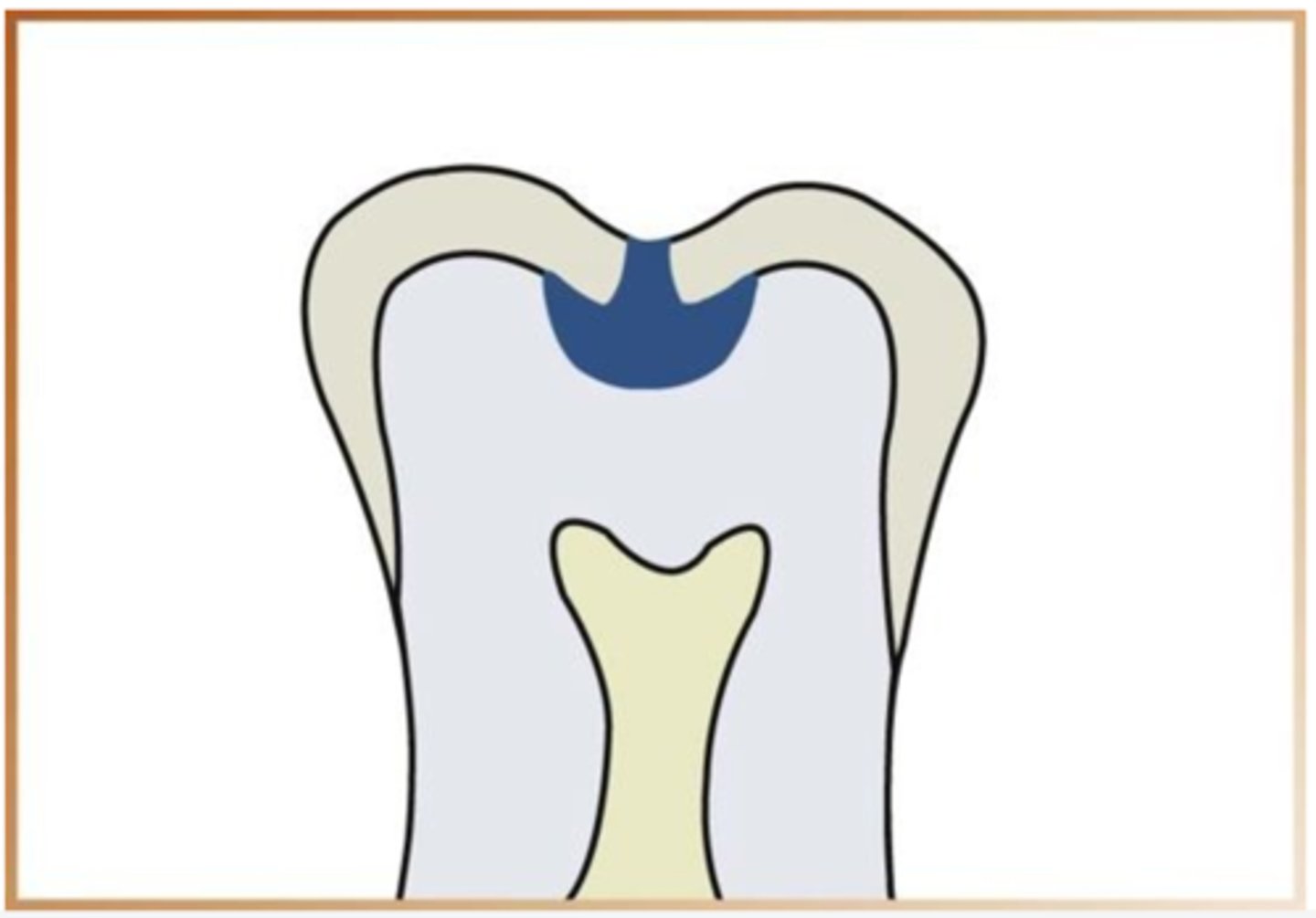
what are moderate occlusal caries
extends into the dentin
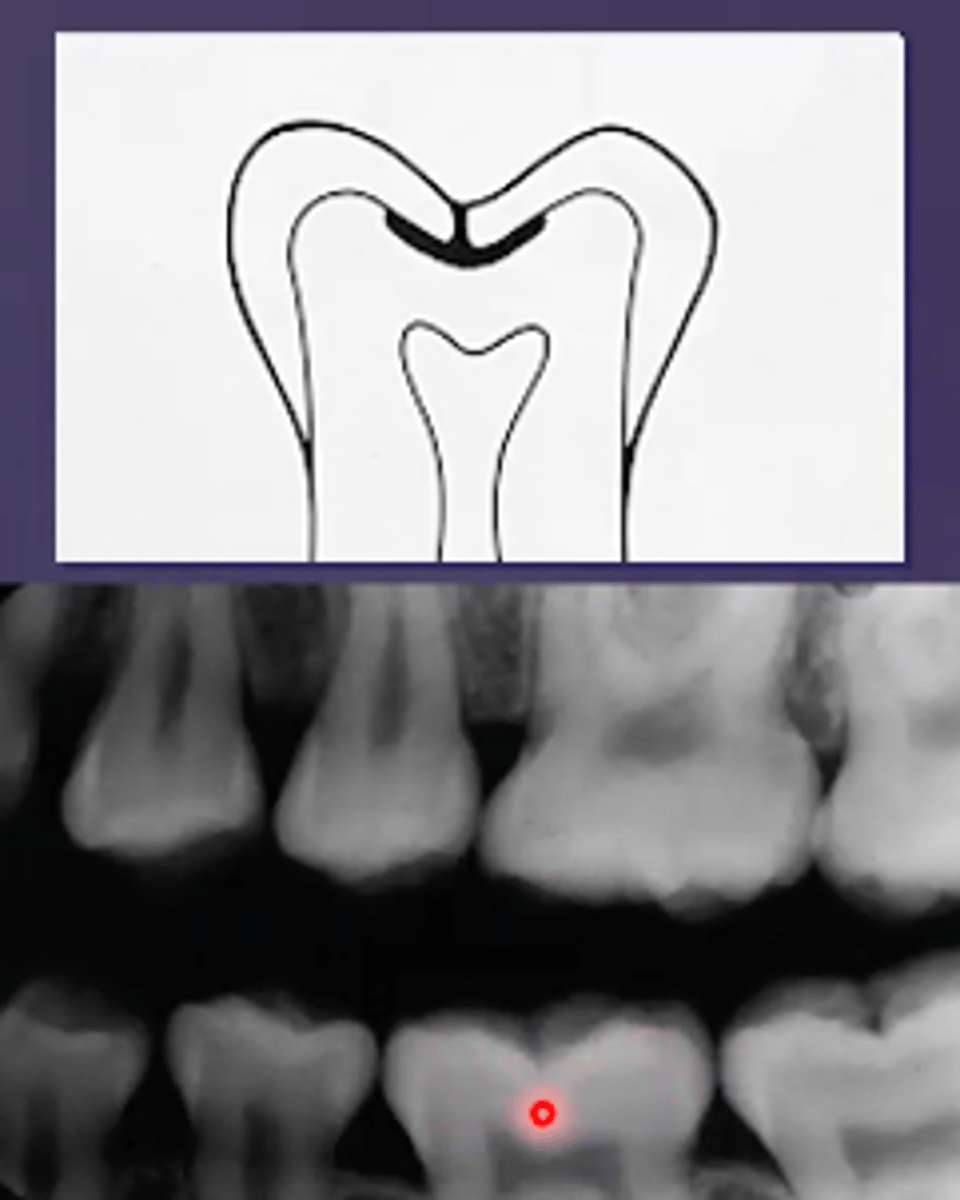
what are severe occlusal caries
extends into dentin and appears radiolucency
can you detect buccal and lingual caries on a radiograph
difficult to detect on radiograph due to location but appear as a circular radiolucent area
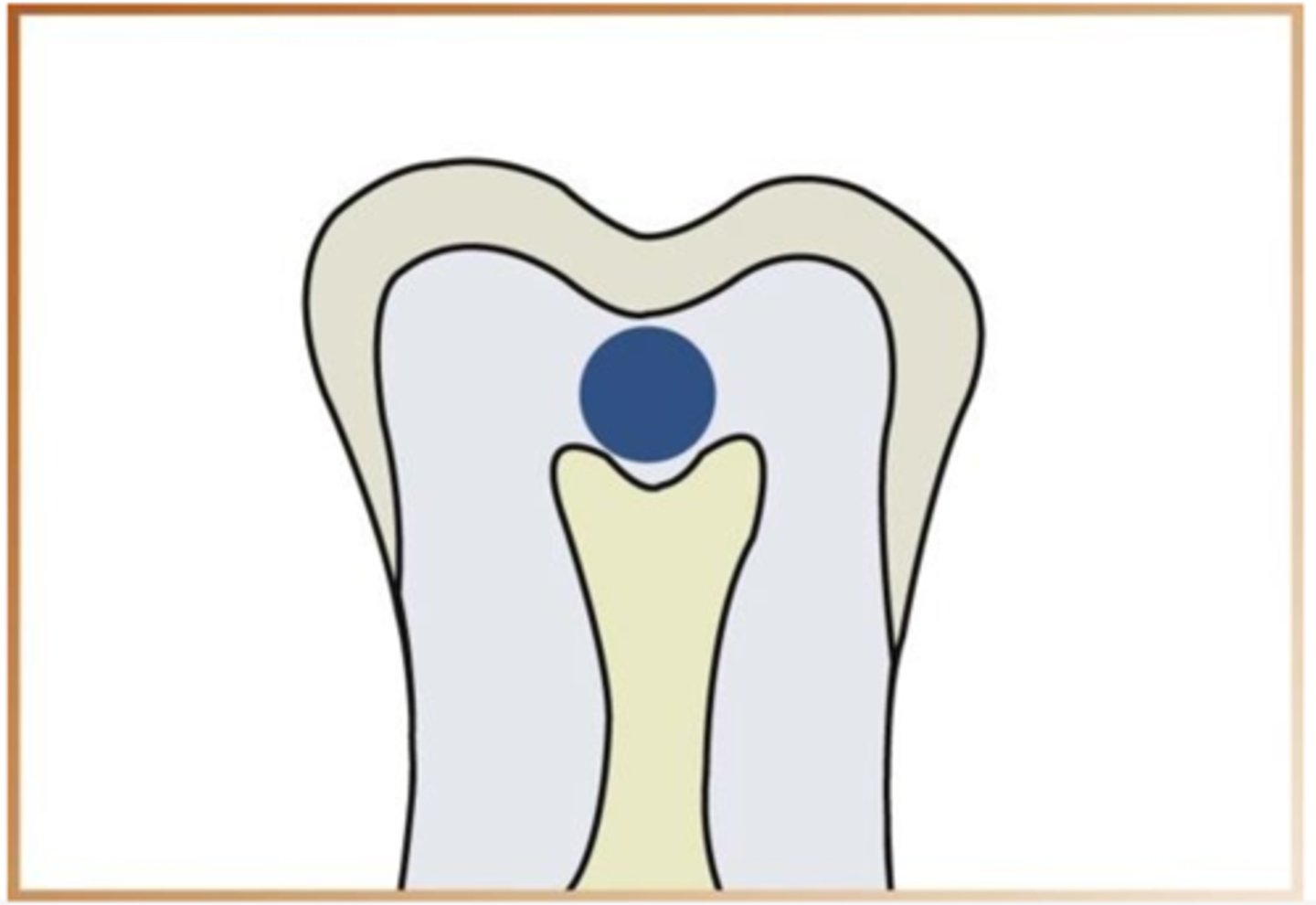
what are root surface caries
involves only the roots of teeth appear as a cupped out shape beflow the CEJ
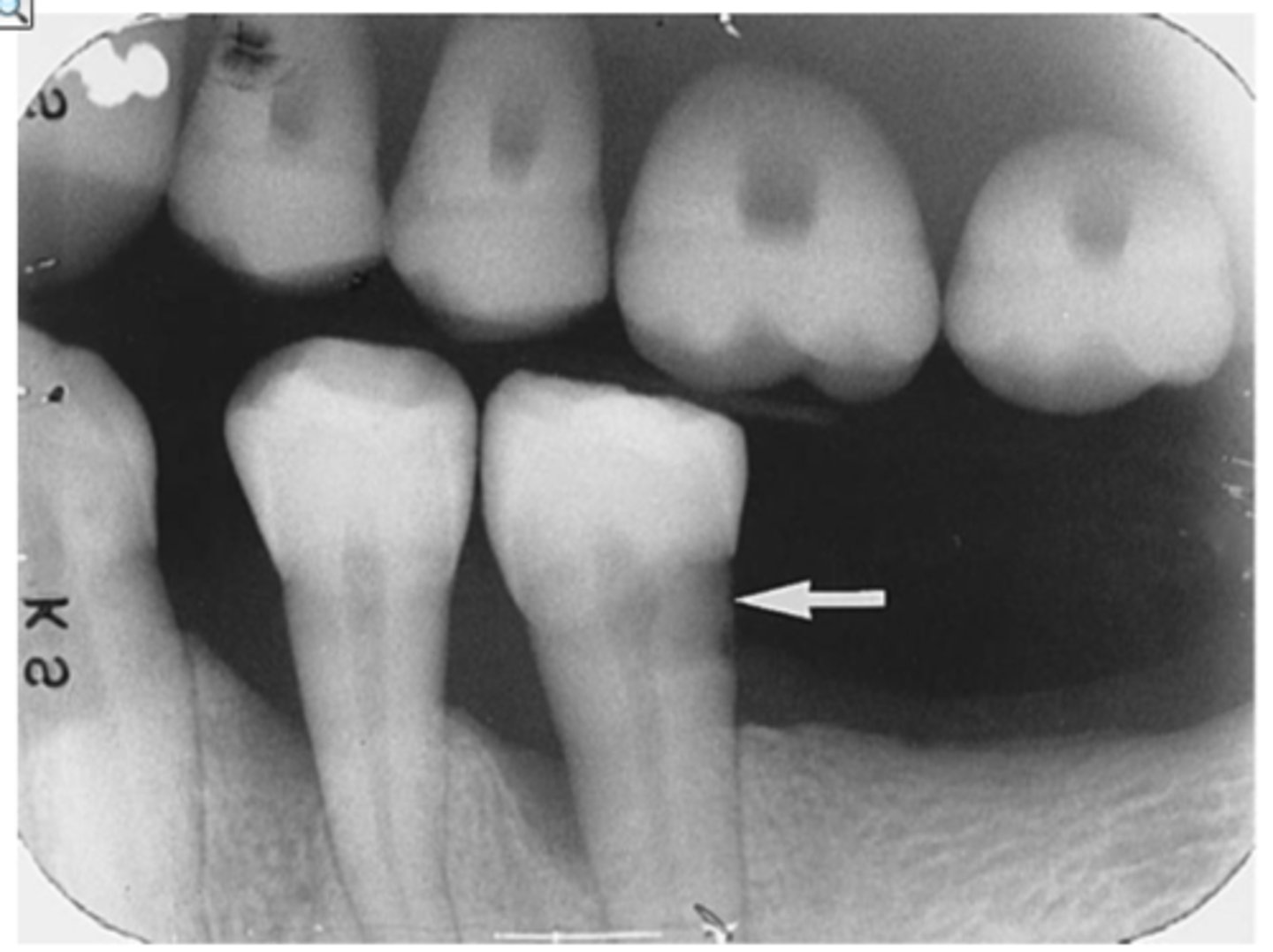
what are recurrent caries
decay adjacent to an existing restoration
what are rampant caries
advance and severe caries affecting multiple teeth
who are rampant caries most common in
children with poor diet and adults with decreased salivary flow
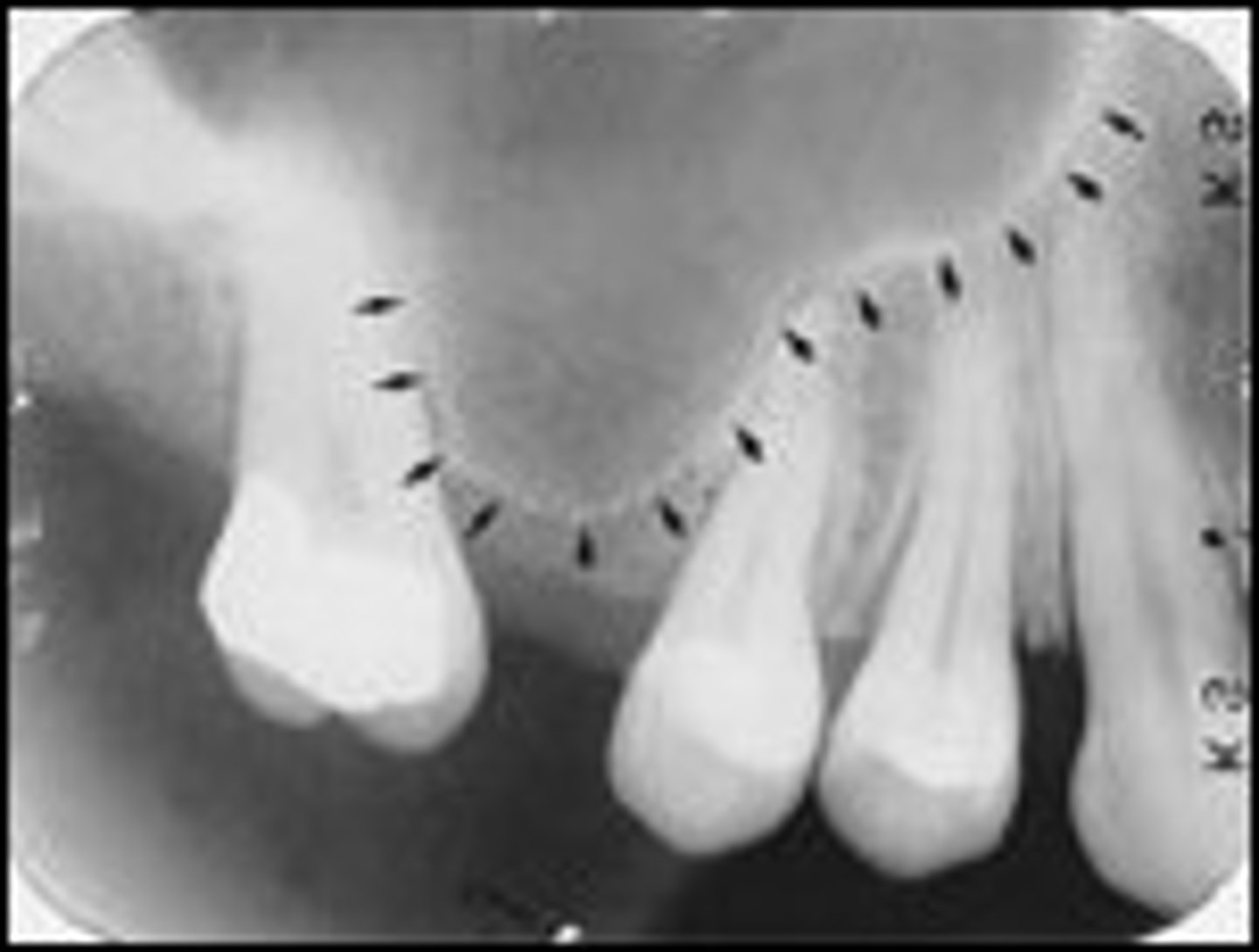
how should the alveolar crest look on a radiograph of healthy teeth
1.5-2mm apical to the CEJ of adjacent healthy teeth
what is the description of periodontium of anterior teeth
alveolar crest is pointed, sharp, and very radiopaque
what is the decription of periodontium of posterior teeth
alveolar crest is flat, smooth, and parallel to a line between CEJ, less radiopaque than anterior teeth
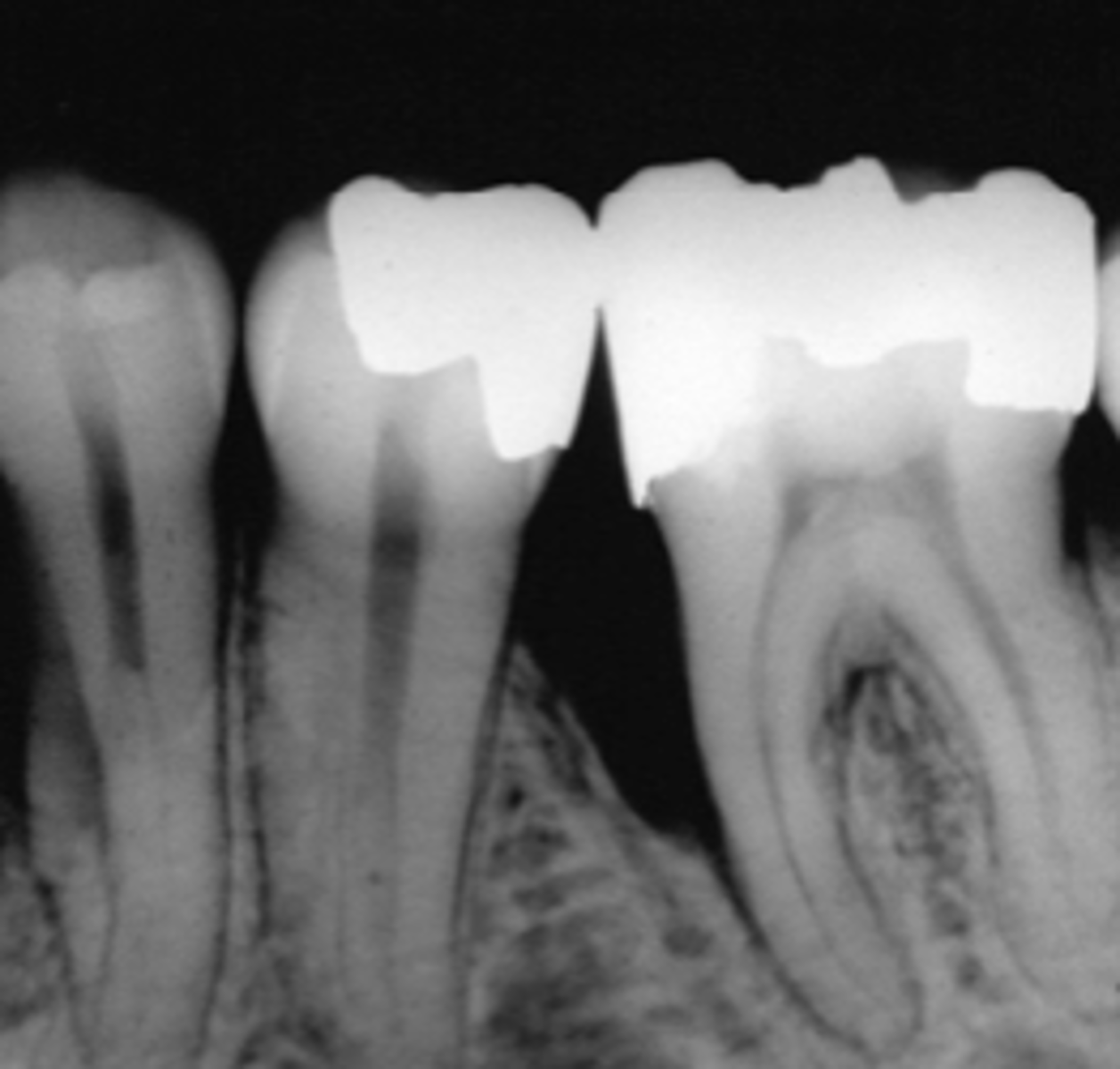
how does the lamina dura appear on a radiograph
dense radiopaque line
how does the periodontal ligament space look in a radiograph
thin radiolucent line between the root and lamina dura
what is periodontal disease
bacterial infection of the periodontium
how does periodontal disease appear
swollen, red, bleeding gingiva with pocket formation
what does the detection of periodontal disease require
both clinical and radiographic examination
what does a clinical examination include
evaluation of soft tissues for signs of inflammation, and a thorough clinical assessment that involves periodontal probing
how are radiographs helpful in evaluating periodontal disease
provide an overview of the amount of bone present, and indicate the pattern and severity of bone loss
what is the best type of radiograph for detecting the periodontium
parallel PA
why does a radiograph need to be paired with a clinical examination to diagnose periodontal disease
they are two dimensional representations of three dimensional objects
what are the ways to describe bone loss
pattern, severity, and distribution
what is pattern of bone loss
described as either horizontal or vertical
what is severity of bone loss
the amound of bone lost
what is mild severity of bone loss
1-2mm bone loss
what is moderate severity of bone loss
3-4mm bone loss
what is severe severity of bone loss
5mm or more bone loss
what is distribution of bone loss
is it localized or generalized bone loss
what are the classifcations of periodontal disease
gingivitis, slight periodontits, moderate periodontitis, severe periodontitis
what is gingivitis
inflammation of the gums that has no assocaition with bone loss
what is slight periodontitis
mild crestal changes with 1-2mm of bone loss
what is moderate periodontitis
3-4mm of bone loss that may involve furcation
what is severe periodontitis
33% or more of the bone is gone
what are predisposing factors that contribute to periodontal disease
calculus, defective restorations, malpositioned teeth, supernumerary teeth, impacted teeth, caries, fusion, gemination, dilacerations
how can defective restorations affect periodontal disease
act as food traps and accumulate food debris and bacteria
how can malpositioned teeth affect periodontal disease
attracts more plaque, irregular contacts, thickness variations
how can supernumerary and impacted teeth affect periodontal disease
bone densitiy and thickness, can develop cysts, affects teeth around them
how can caries affect periodontal disease
food impaction in the decayed area
how can fusion and gemination affect periodontal disease
more occlusal strain and difficult to keep clean
how can dilacerations affect periodontal disease
more occlusal strain and can affect surrounding teeth