Psych. Perspectives and Research
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
psychoanalytic perspective
emphasizes the influence of an unconscious mind; childhood, past experiences, dreams affect behavior; difficult to test scientifically
cognitive perspective
mental activities like knowing, thinking, remembering affect behavior; includes perception, language, memory
behavioral perspective
learning process, observable behaviors and responses; includes empiricism, or belief that path to scientific knowledge is systematic and experimental
humanistic persepctive
behavior based on fact that we are rational beings with potential for growth, individual choice, free will; not easily or scientifically tested
evolutionary perspective
a.k.a Darwinian perspective; behavior based on natural selection, adaptive behaviors, and maximizing reproductive success
biopsychology perspective
behavior based on brain structure, sensation and perception from genes, hormones, and neurotransmitters
socio-cultural perspective
behavior shaped by history, society, social norms, and culture; cultural variance of thoughts and behaviors
eclectic perspective
all perspectives are complimentary; as research continues, some perspectives might be combined
theory
explanation; a way of organizing and explaining behavior that generates a number of hypotheses, eg. cell phones affect performance and attention
hypothesis
prediction; testable prediction of a theory, eg. students who have their phones our during a lecture will score lower on a quiz about lecture material
correlational study
examines the relationship between two variables (does NOT prove causation)
case study
in-depth study of a specific individual or small group of people
naturalistic observation
studying behavior in authentic, natural settings without manipulating variables
meta-analysis study
summarizes previous studies on a topic to find one overall conclusion
hindsight bias
tendency to exaggerate our ability to foresee something after learning an outcome; eg. “I knew all along!”
overconfidence bias
tendency to overestimate the accuracy of our own current knowledge; eg. a student who does very well in high school and thinks they’re brilliant does not study in college, and fails their exam
random sampling/selection
method by which subjects are chosen, giving each member of the group an equal chance; increases the likelihood that the sample is representative of the population being studied; larger = more representative
sampling bias
technique used to choose a sample group that favors one part of the population over another
stratified sample
population is divided into groups and a random sample is taken from each group; helps with sampling bias
random assignment
process by which subjects are put into groups; each subject has an equal chance of being placed into any group, ensuring composition of experimental and control groups is consistent
operational definition
the quantification of a variable that allows it to be measured and replicated
Likert scale
rating scale that uses a range of options from extreme to neutral
test validity
applicability/legitimacy; degree in which measuring device is actually measuring what we intended to measure; eg. measuring psych on a psych test, not calculus
test reliability
consistency; can the study be done by someone else with the same result?
confounding/extraneous variables
any factors other than the IV that seem likely to influence the DV in the study; difficult to sort out specific effects (random assignment helps)
experimenter bias
tendency for researches to treat members of the experimental/control groups differently to increase changes of confirming hypothesis
demand characteristics
subjects respond to cues about the purpose of the study; eg. researchers tell experimental group that his new teaching method is very effective, so the subjects try harder and perform better
social desirability bias
responses are based on society’s expectations; eg. people often exaggerate how much they exercise or eat healthy
single blind procedure
research staff OR participants are unaware of experimental conditions
double blind procedure
research staff AND participants are unaware of experimental conditions
confirmation bias
tendency to gather evidence that supports pre-existing expectations, and fail to gather evidence that is contradictory
belief perseverance
tendency to maintain a belief or opinion even after evidence that supports it has been refuted or proven inaccurate
Hawthorne effect
subjects perform differently (usually in a positive way) when they know they are being observed
placebo effect
a response to a placebo, or fake substance, caused by the subject’s belief that they are being exposed to the real substance
false consensus effect
tendency to assume one’s own opinions, beliefs, attitudes, or behaviors are more widely shared than is actually the case
illusory correlation
appearance of a relationship that does not actually exist; superstitions arise from random conincidences
confederates
research staff that pose as a participant, but actually rehearsed prior to the experiment
informed consent
participants must be informed of the risk of the study and choose to participate
voluntary/right to withdrawl
participants must be informed that participation is voluntary and they have a right to withdrawl
confidentiality
anonymity must be protected unless subjects give permission to release their data
protection from harm
physical safety must be guaranteed, and researchers must minimize psychological distress
debriefing
researchers must provide full explanation of goals and procedures afterwards and allow for participant feedback
deception
may be used if deemed essential and benefits outweigh risks
institutional review board
ethical oversight and risk assessment for human and animal studies
animal experimentation
animals must be given adequate care beyond the boundaries of testing, researchers must minimize psychological and physical harm
mean
average of all the numbers in a set
median
score that falls in the middle of all the numbers in a set
mode
score that occurs most frequently in a set
range
lowest score subtracted from the highest score
standard deviation
the average distance of any score in the distribution from the mean
variance
a measure of how spread out scores are in a sample
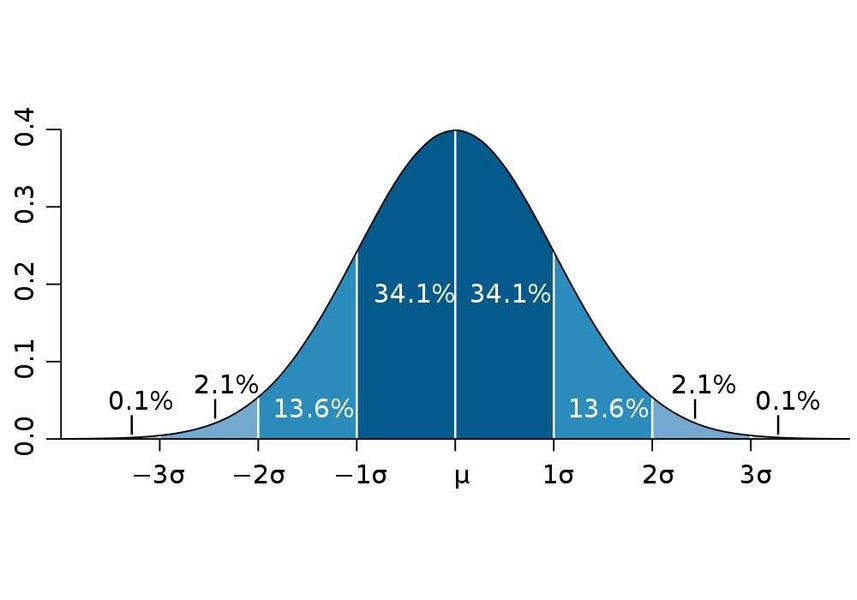
normal distribution
bell-shaped curve representing a typical spread of scores (68% fall within ± 1 SD, 95% fall within ± 2 SD, and 99.7 fall within ± 3 SD)
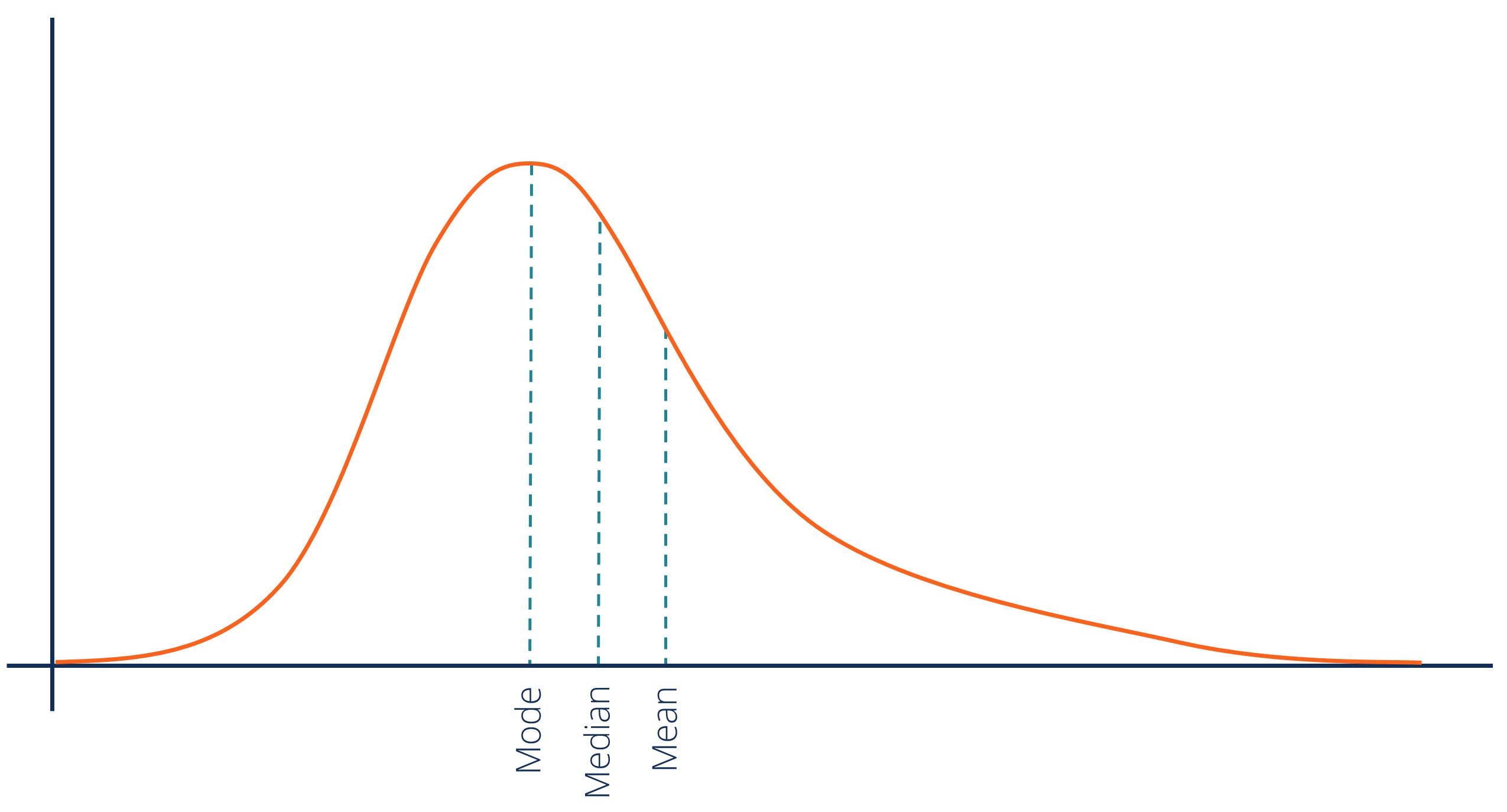
positive skew
includes an extreme score in the high, a.k.a. left skew
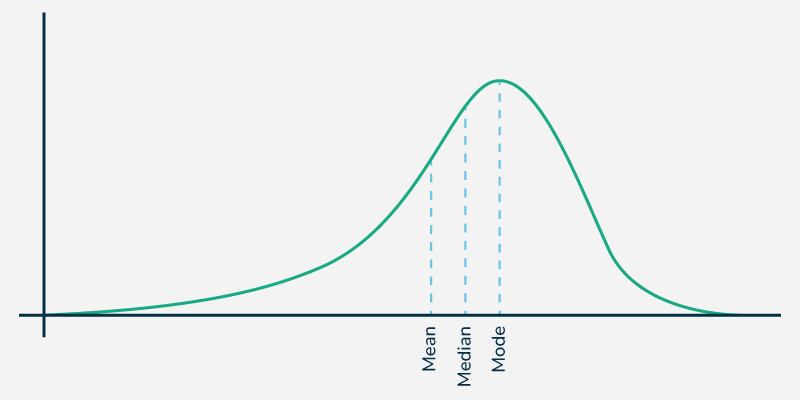
negative skew
includes an extreme score in the low, a.k.a. right skew
0.00 to 1.00
strength of correlational relationship
positive correlation
presence of one variable predicts the presence of another variable, and vice versa
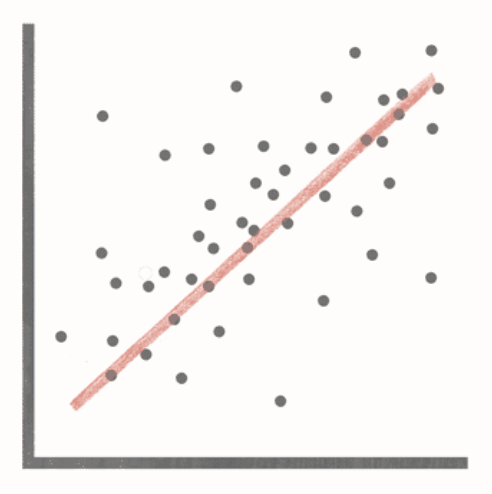
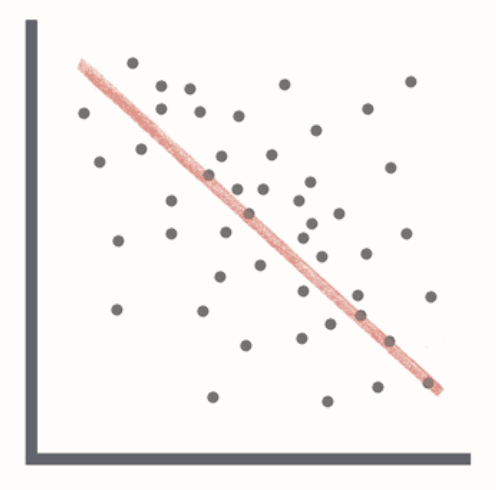
negative correlation
presence of one variable predicts absence of another
no correlation
scores do not show a clear trend line or direction, and are scattered everywhere