Biochemistry Quiz 1 + r groups
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
80 Terms
Glycine
Group A - Nonpolar Amino Acids (Hydrophobic)
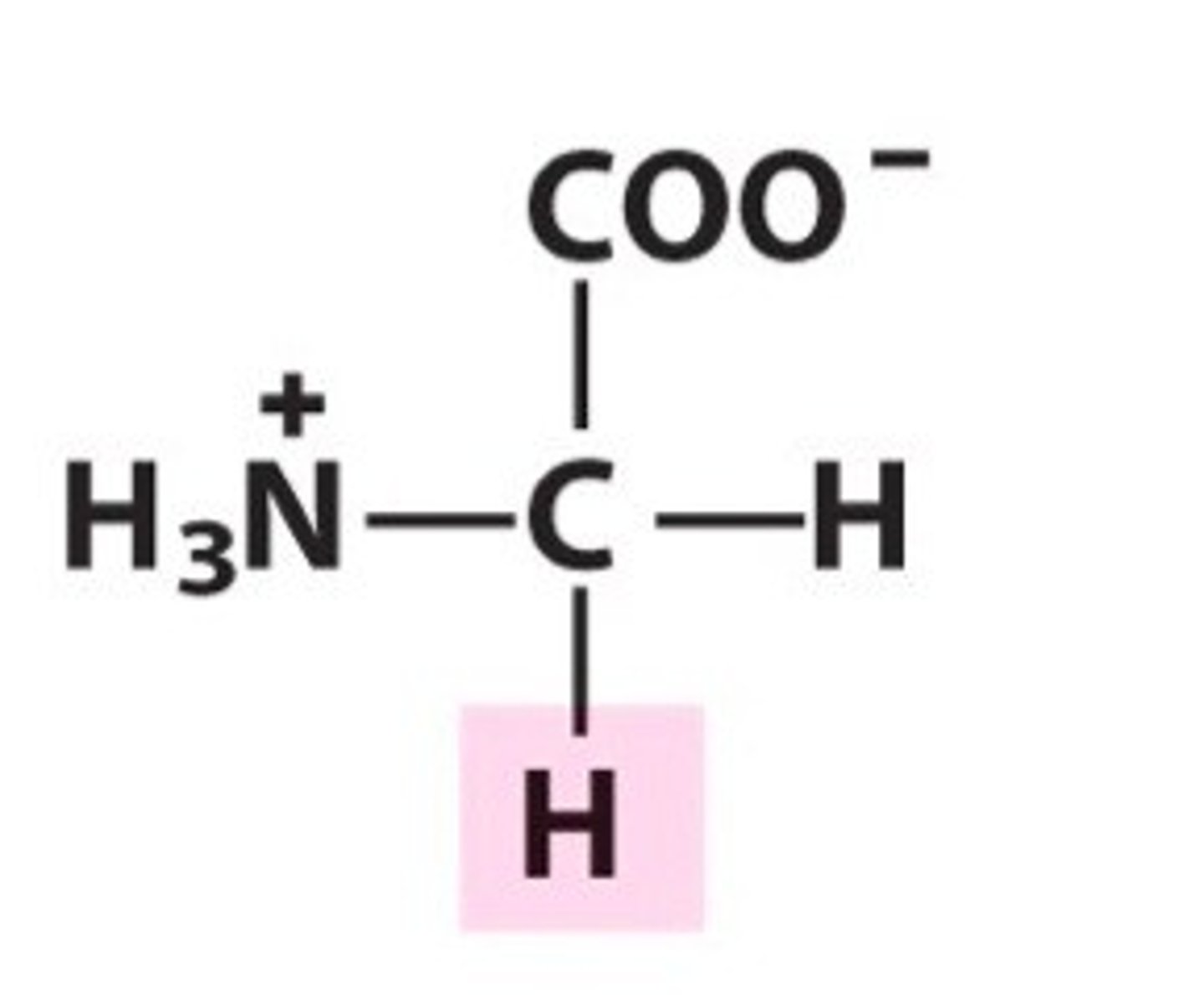
Alanine
Group A - Nonpolar Amino Acids (Hydrophobic)
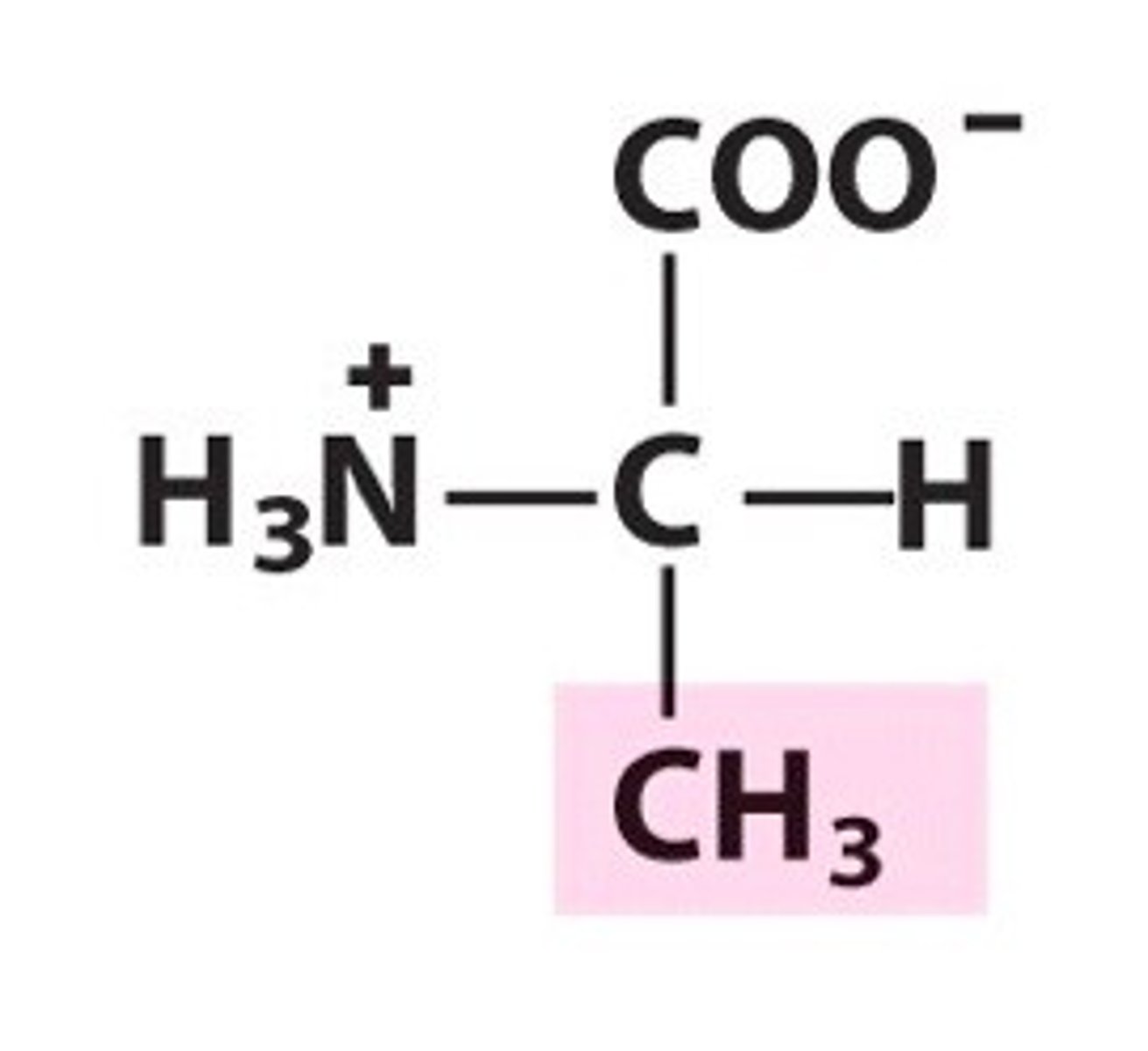
Valine
Group A - Nonpolar Amino Acids (Hydrophobic)
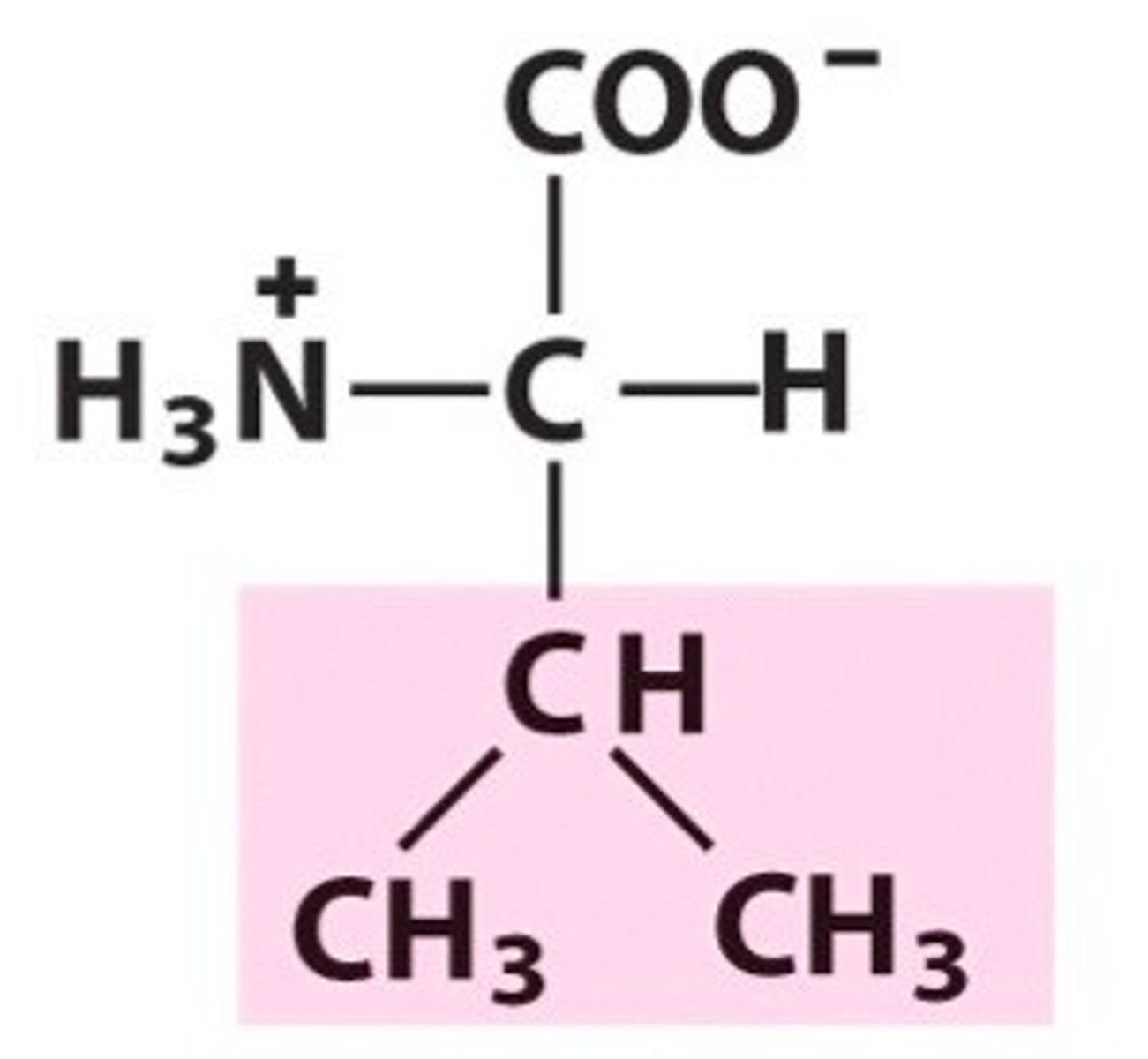
Leucine
Group A - Nonpolar Amino Acids (Hydrophobic)
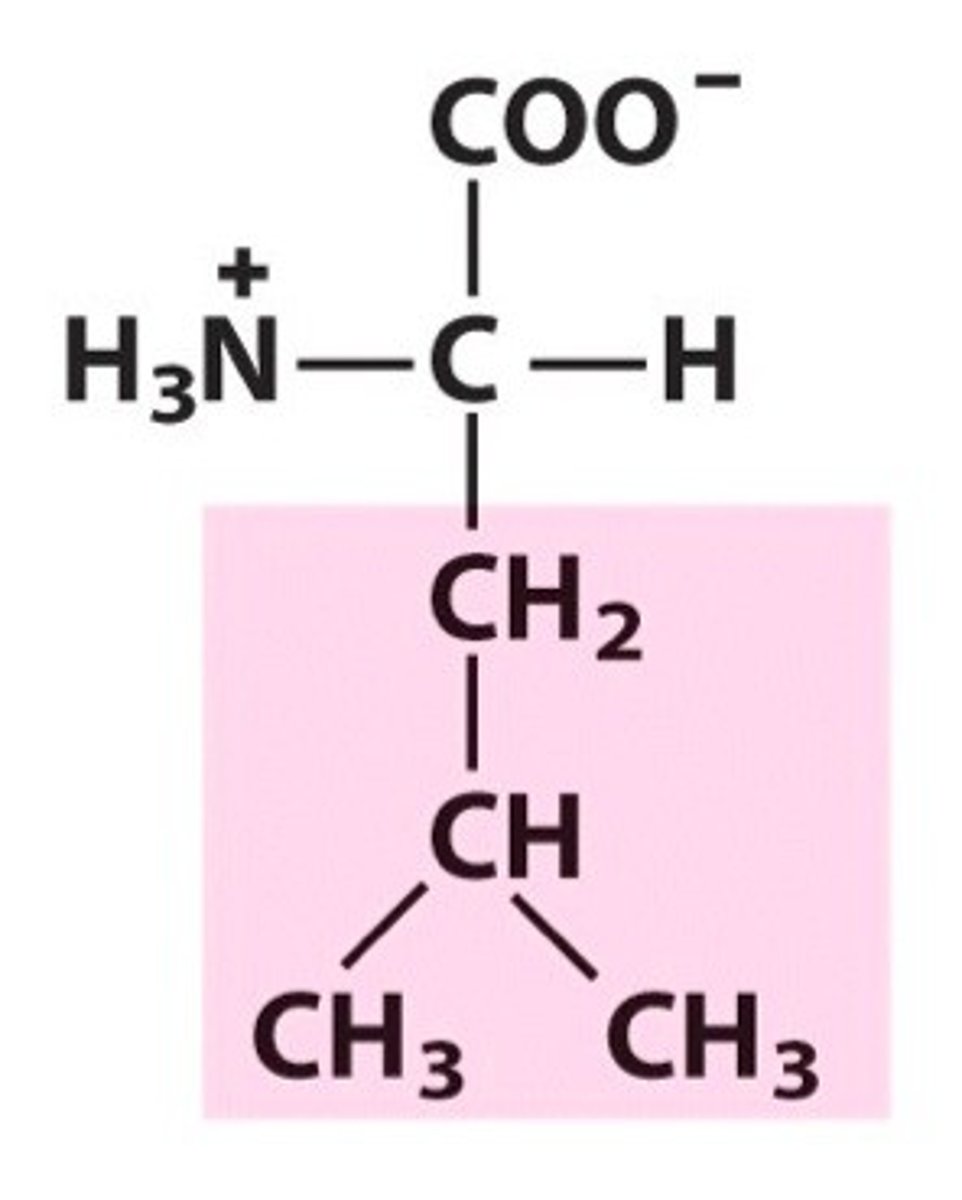
Isoleucine
Group A - Nonpolar Amino Acids (Hydrophobic)
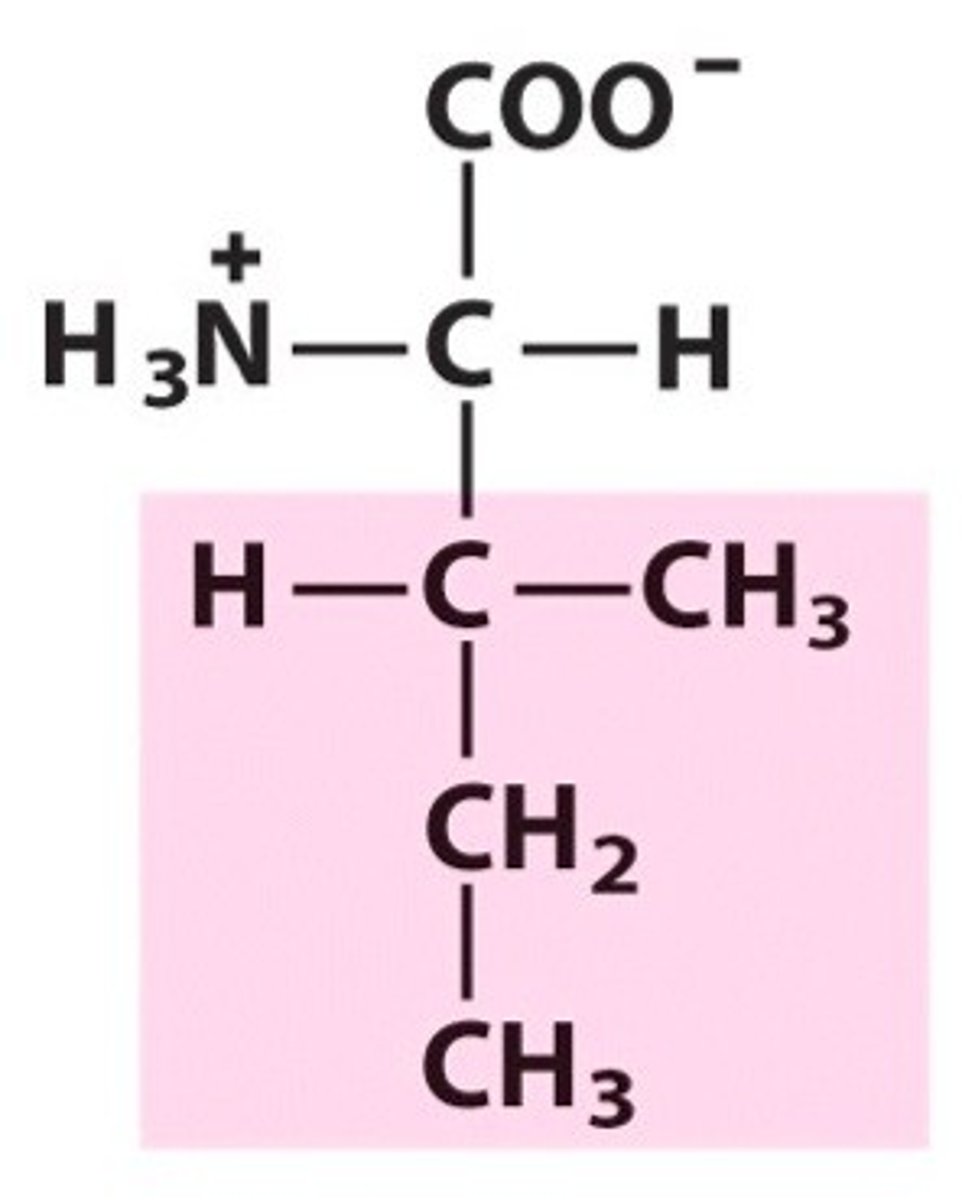
Methionine
Group A - Nonpolar Amino Acids (Hydrophobic)
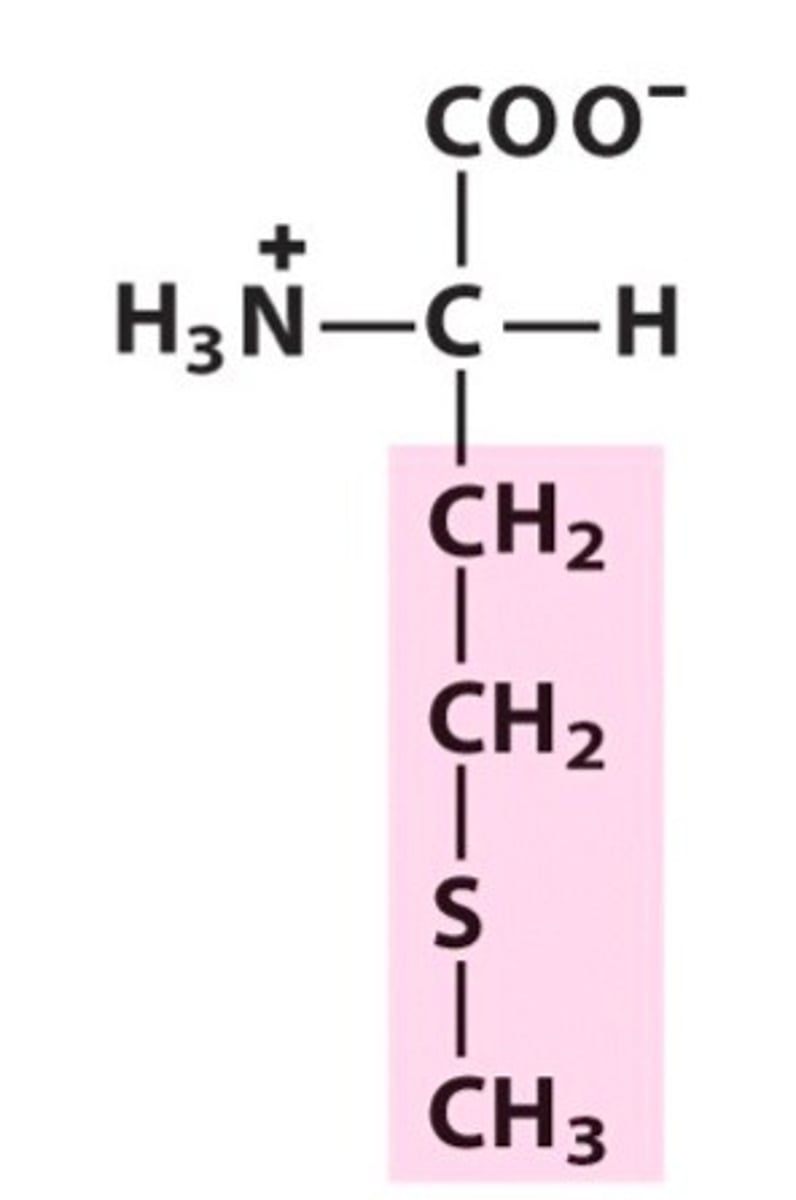
Phenylalanine
Group A - Nonpolar Amino Acids (Hydrophobic)
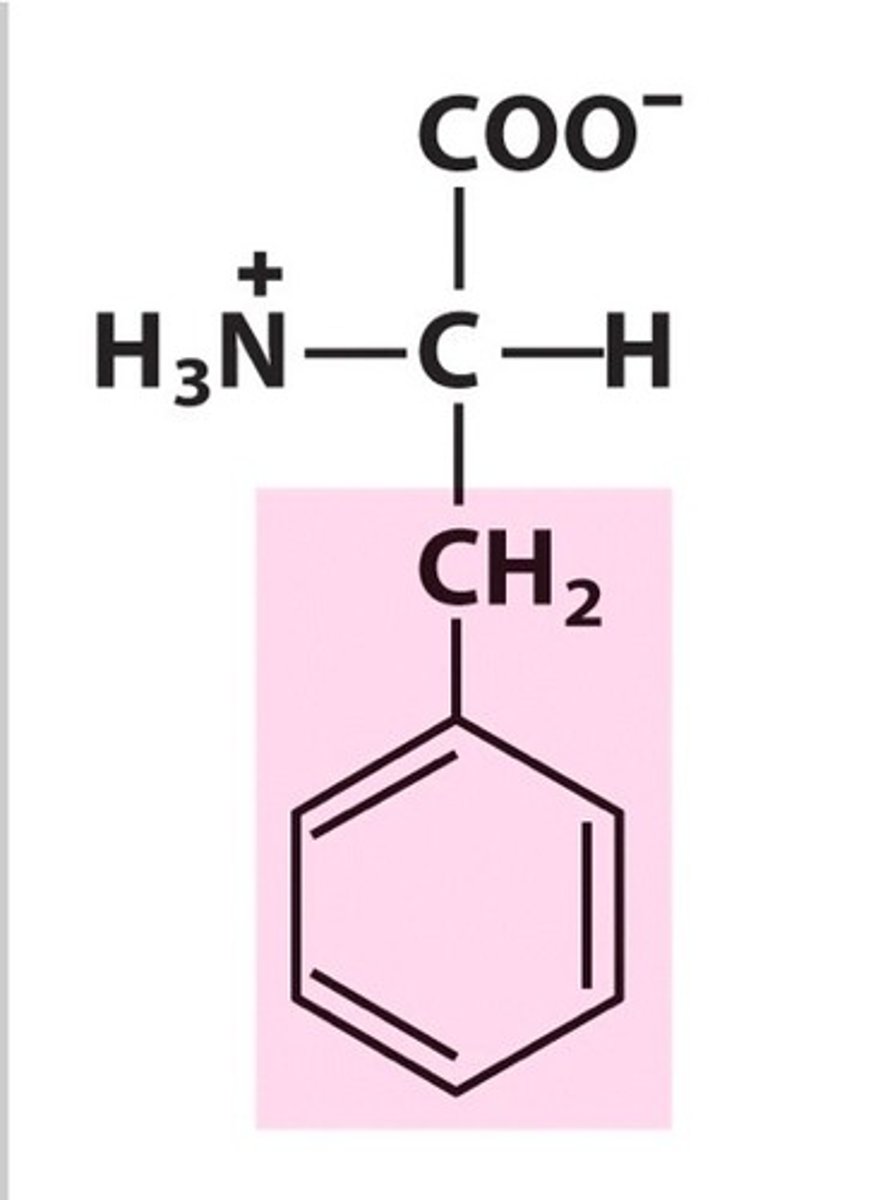
Tryptophan
Group A - Nonpolar Amino Acids (Hydrophobic)
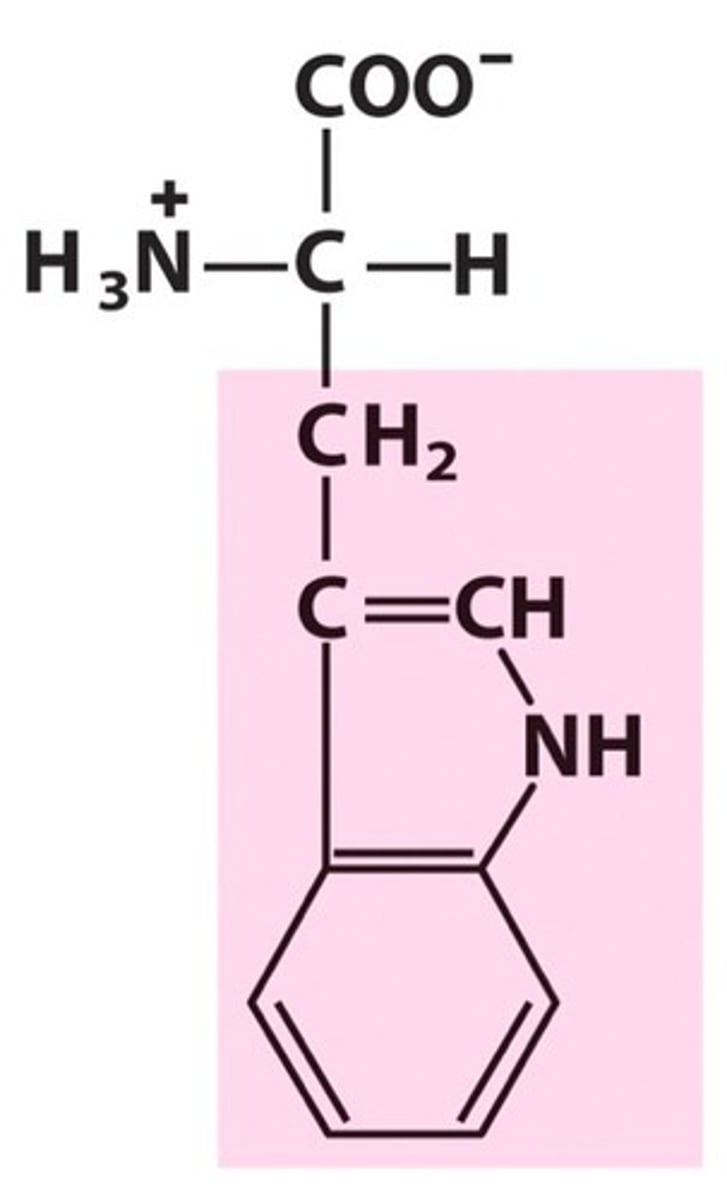
Proline
Group A - Nonpolar Amino Acids (Hydrophobic)
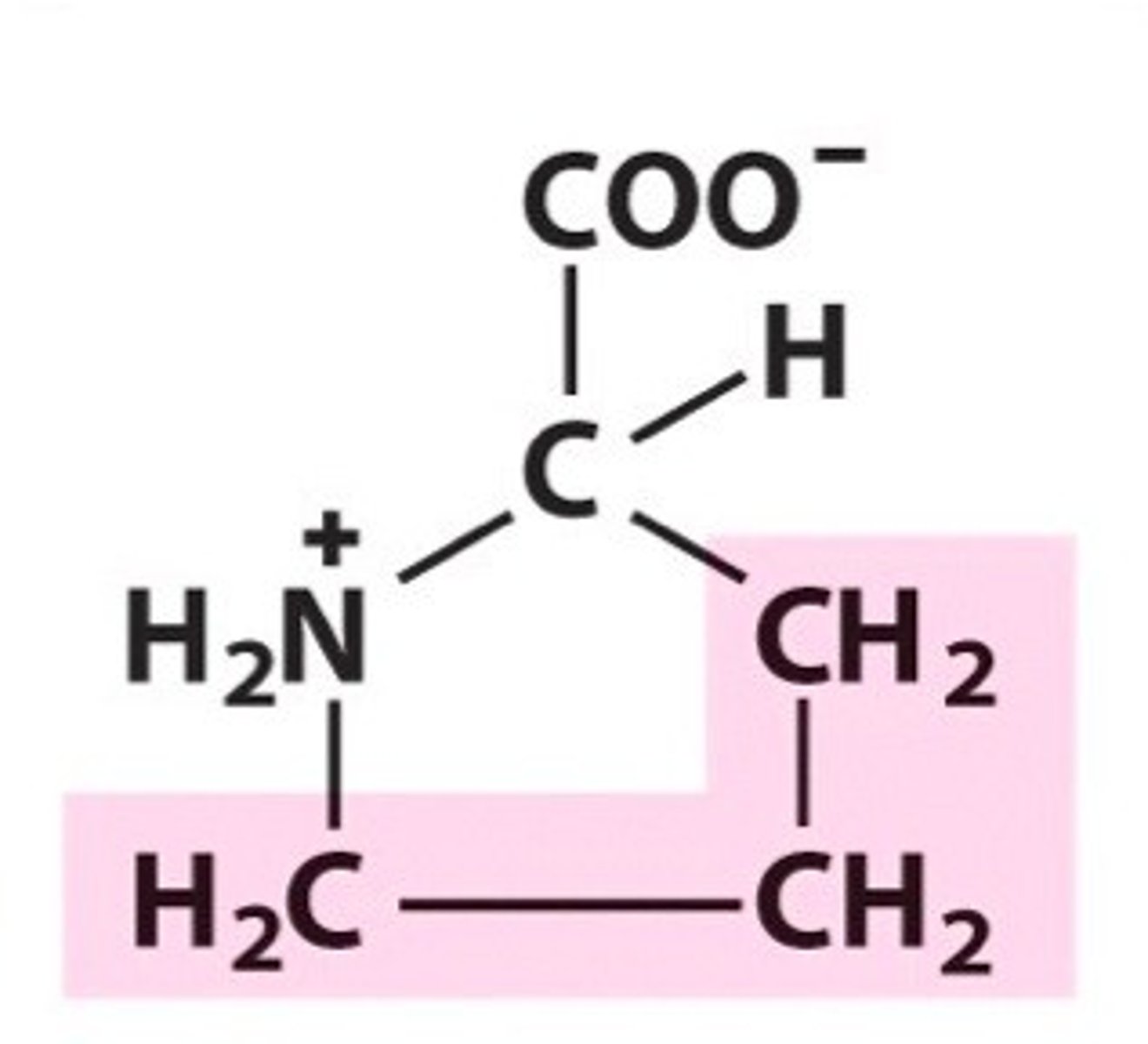
Serine
Group B - Polar Uncharged Amino Acids (Hydrophillic)
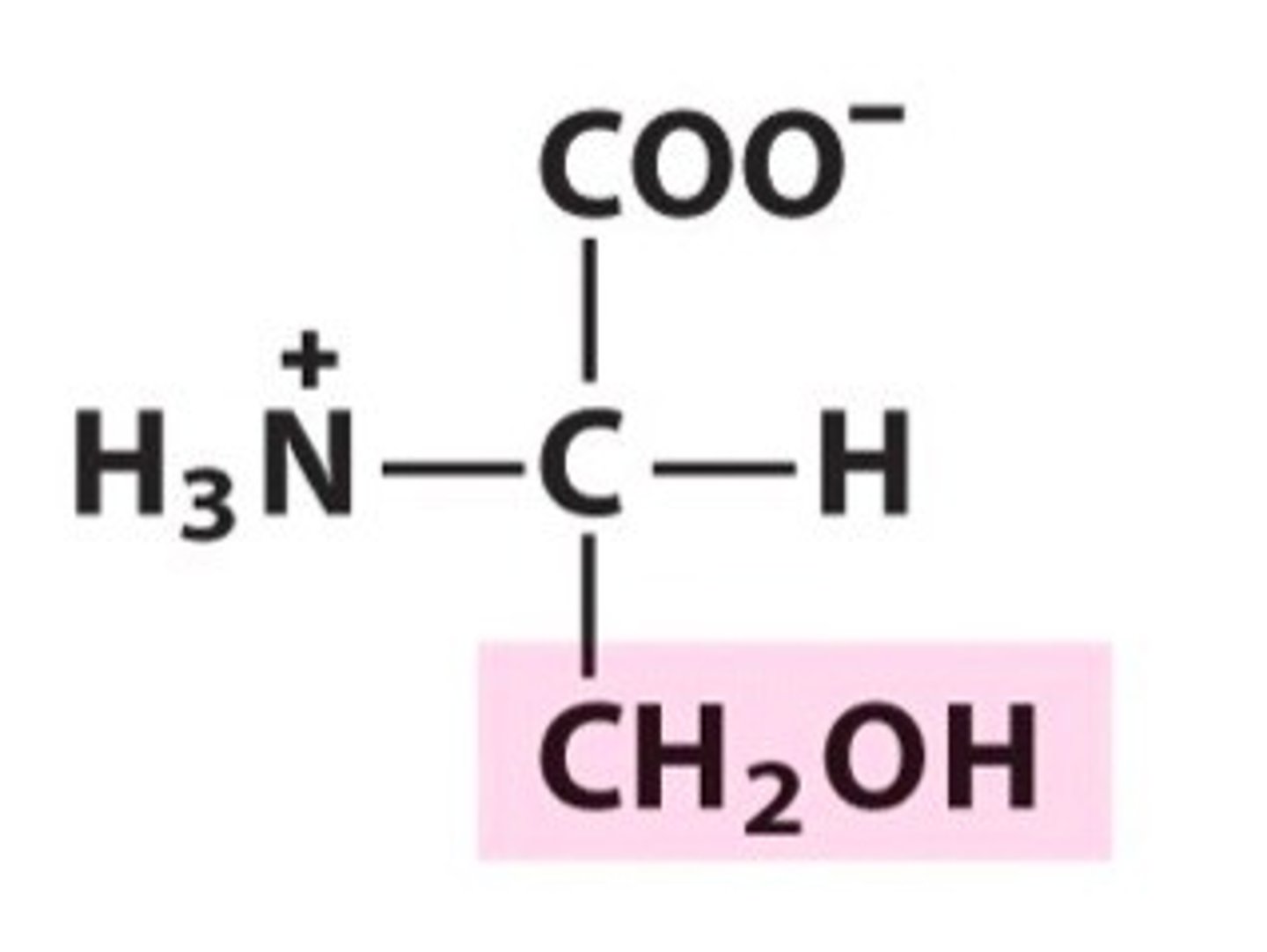
Threonine
Group B - Polar Uncharged Amino Acids (Hydrophillic)
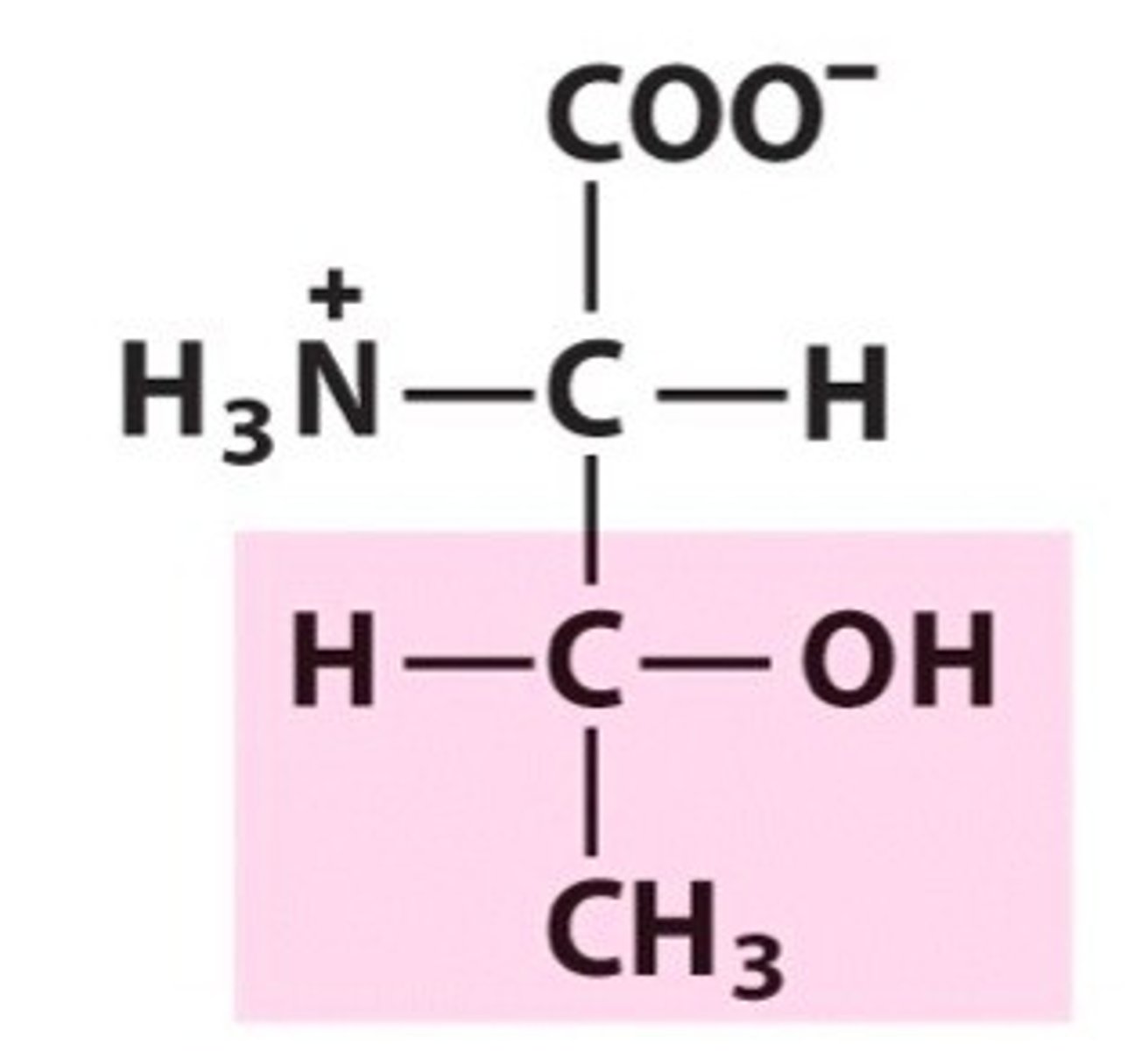
Cysteine
Group B - Polar Uncharged Amino Acids (Hydrophillic)
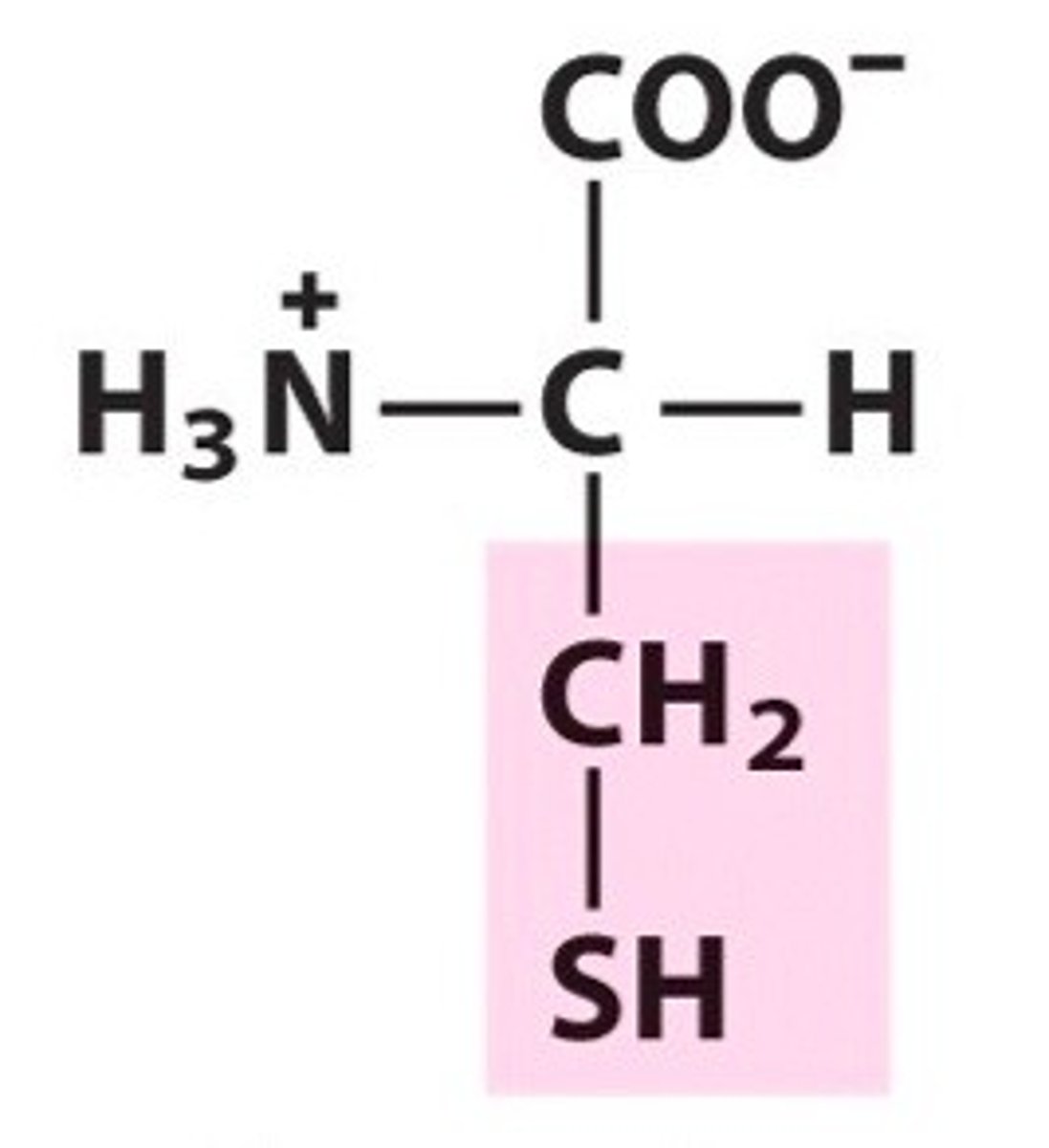
Tyrosine
Group B - Polar Uncharged Amino Acids (Hydrophillic)
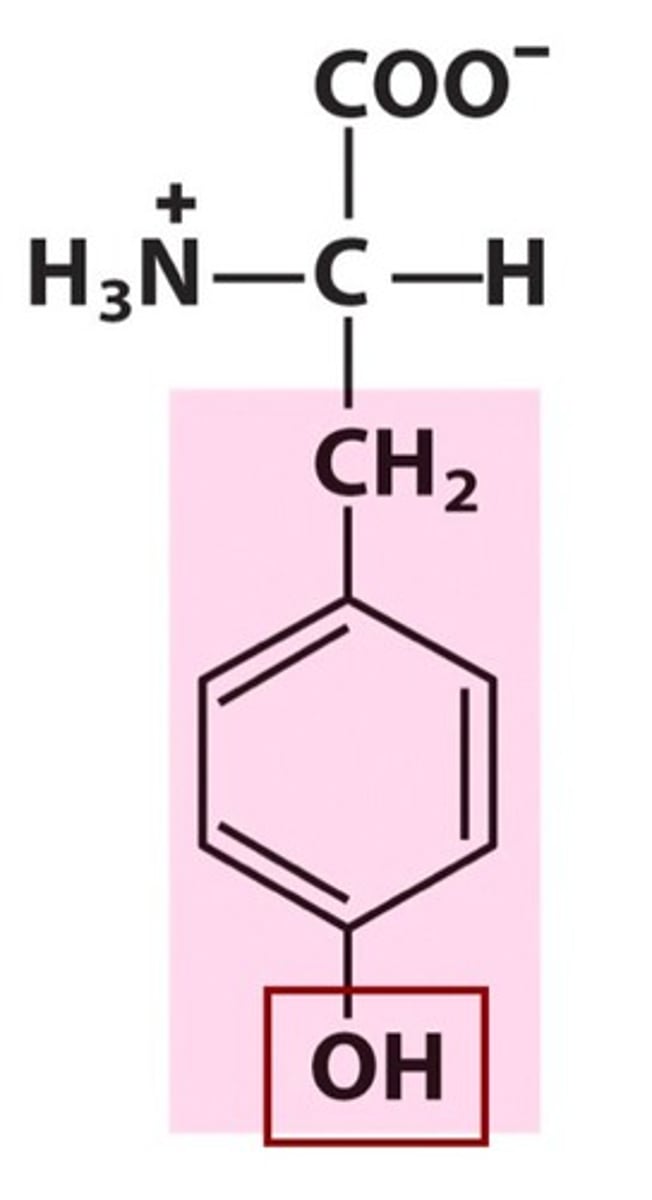
Asparagine
Group B - Polar Uncharged Amino Acids (Hydrophillic)
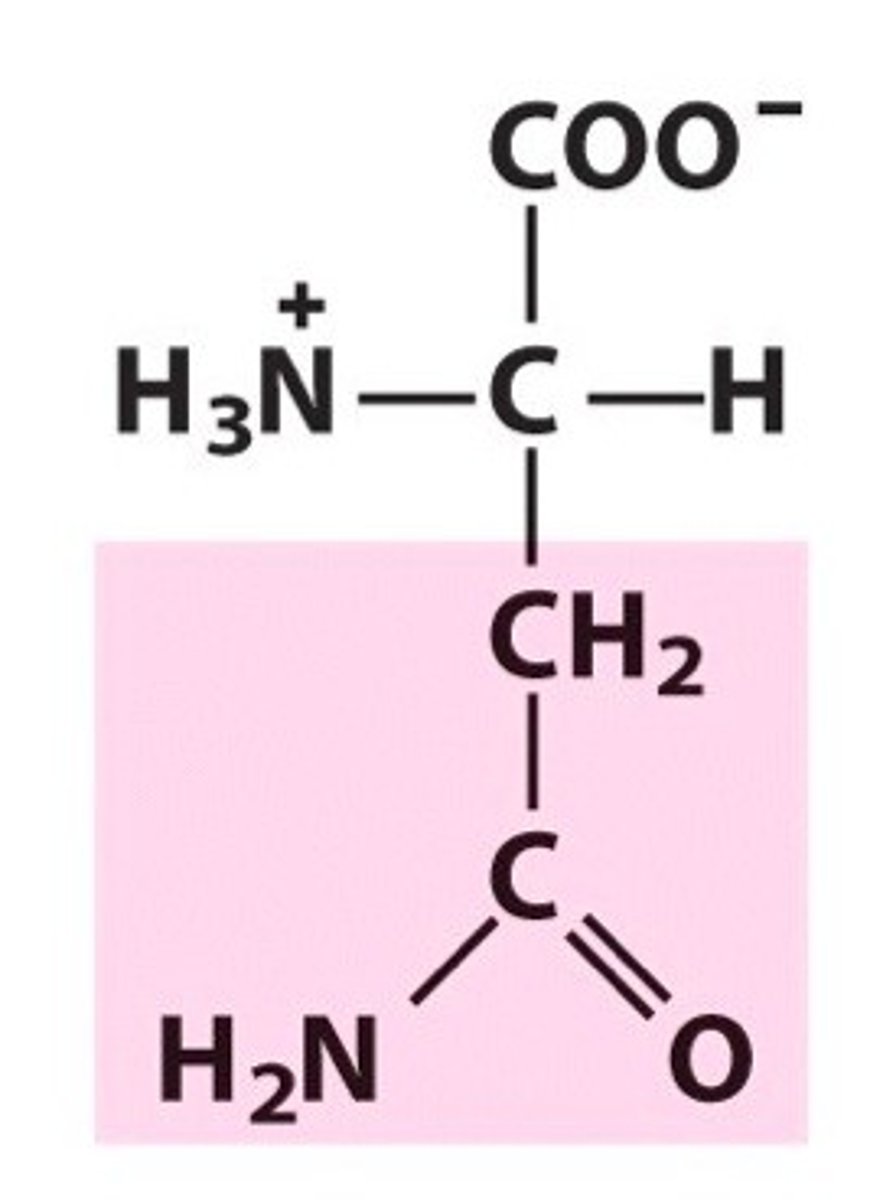
Glutamine
Group B - Polar Uncharged Amino Acids (Hydrophillic)
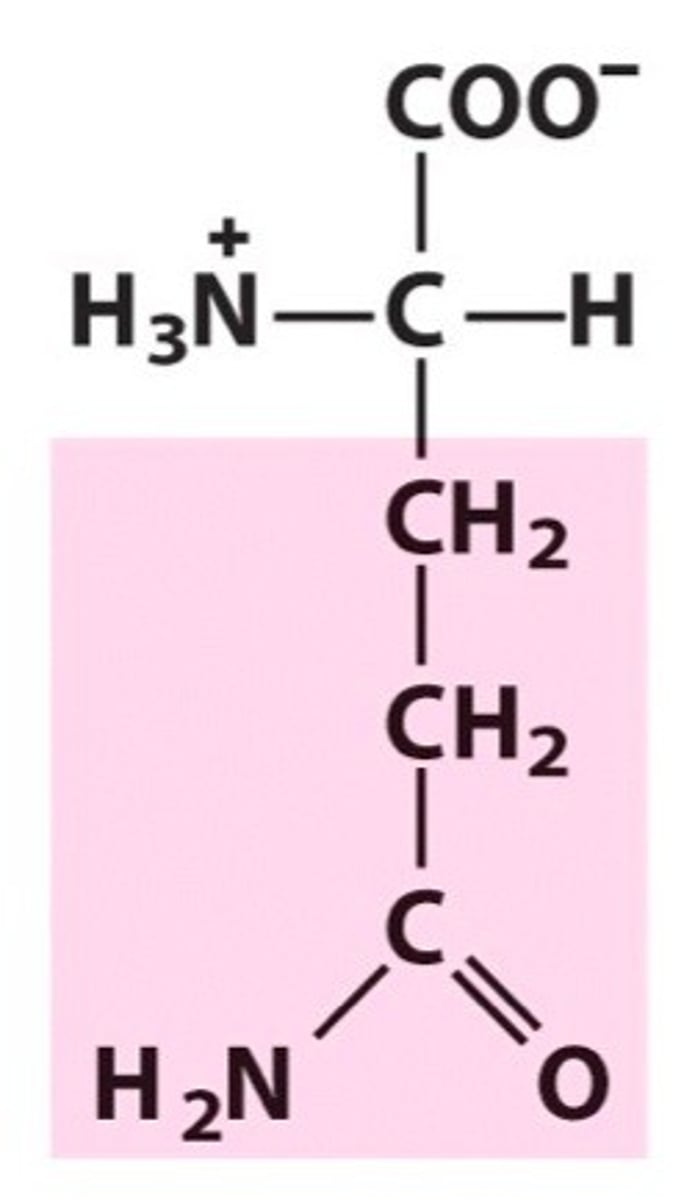
Aspartate
Group C - Polar charged Amino Acids (Hydrophillic) (Acidic)
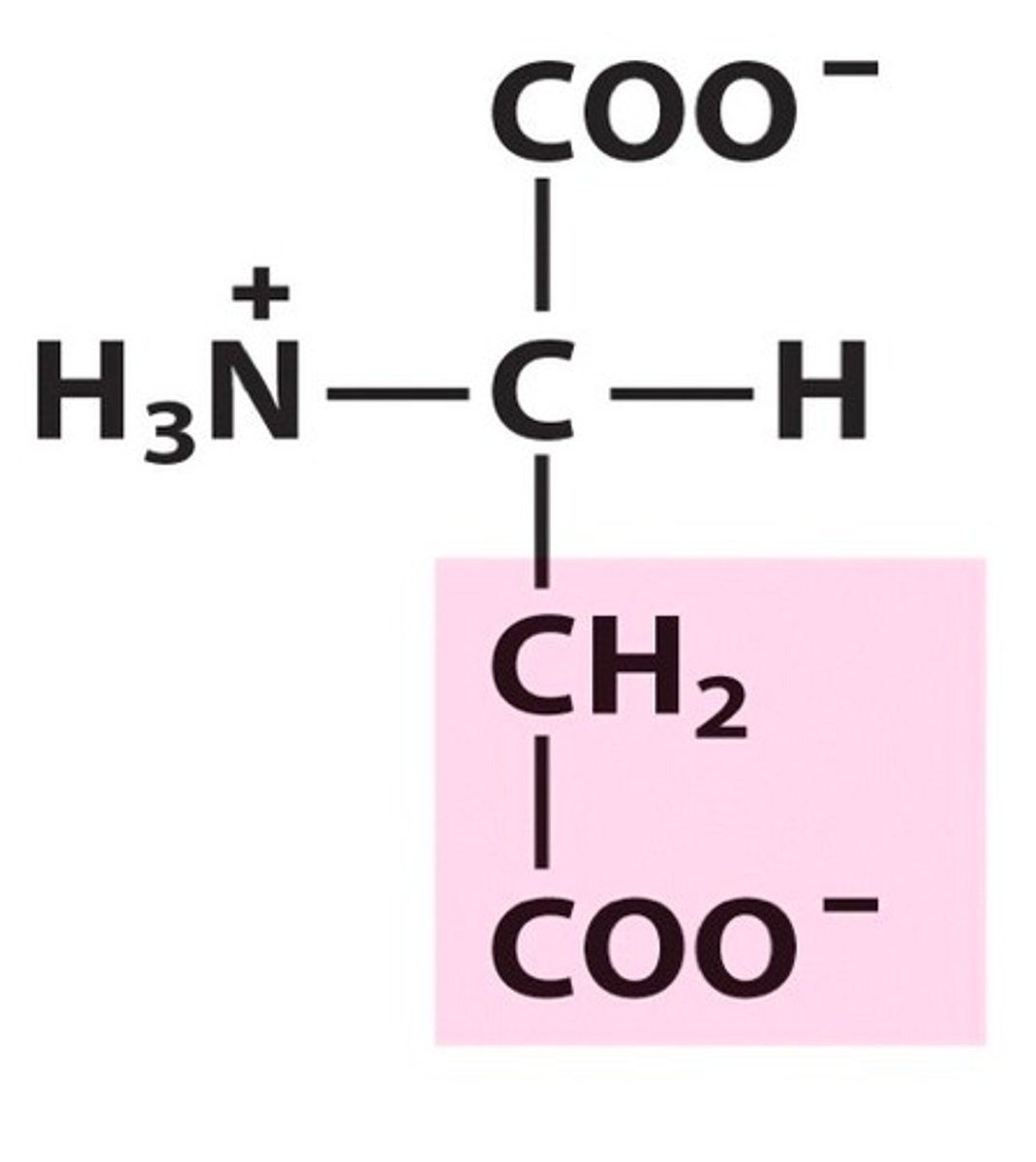
Glutamate
Group C - Polar charged Amino Acids (Hydrophillic) (Acidic)
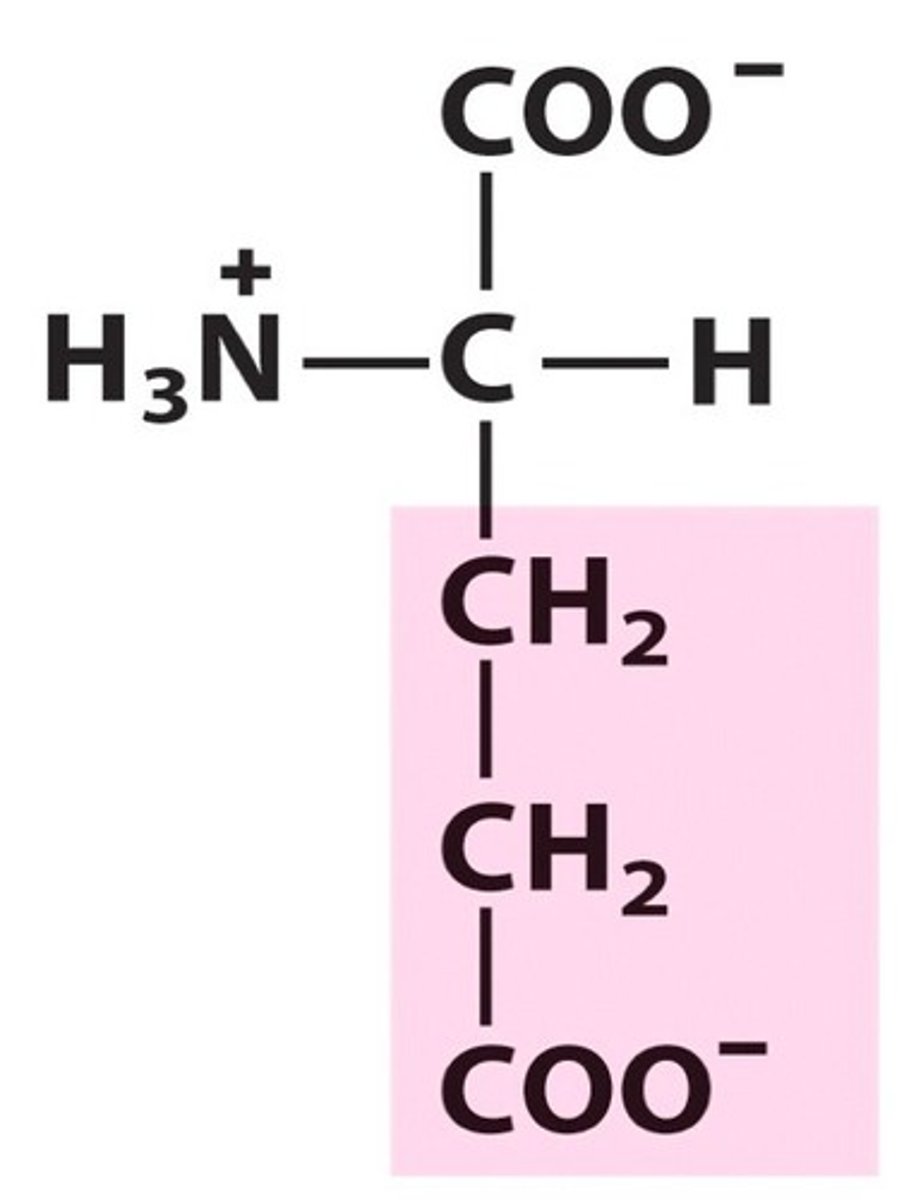
Lysine
Group C - Polar charged Amino Acids (Hydrophillic) (Basic)
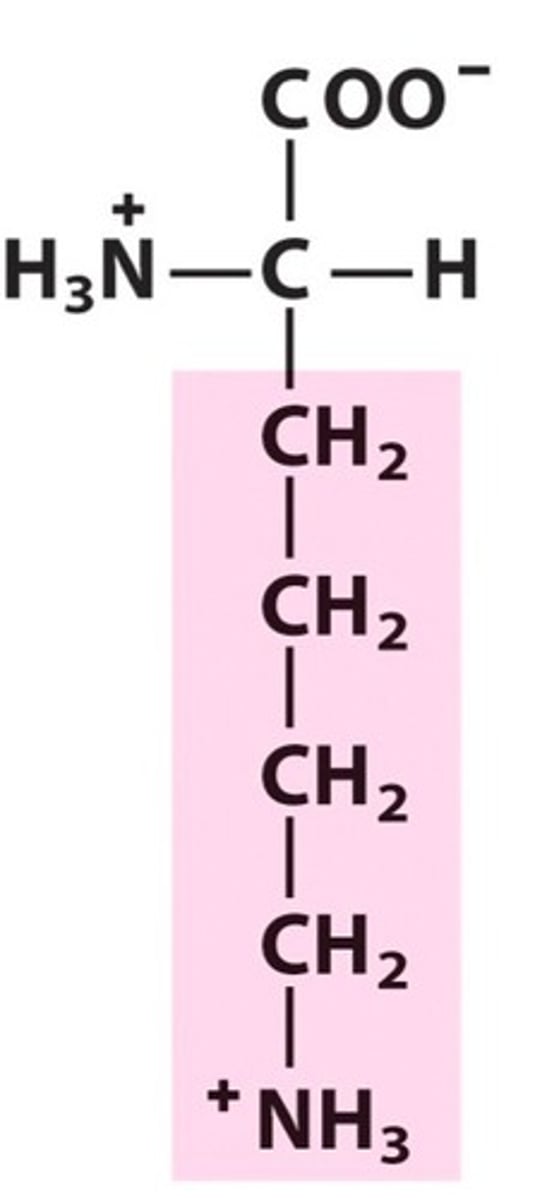
Arginine
Group C - Polar charged Amino Acids (Hydrophillic) (Basic)
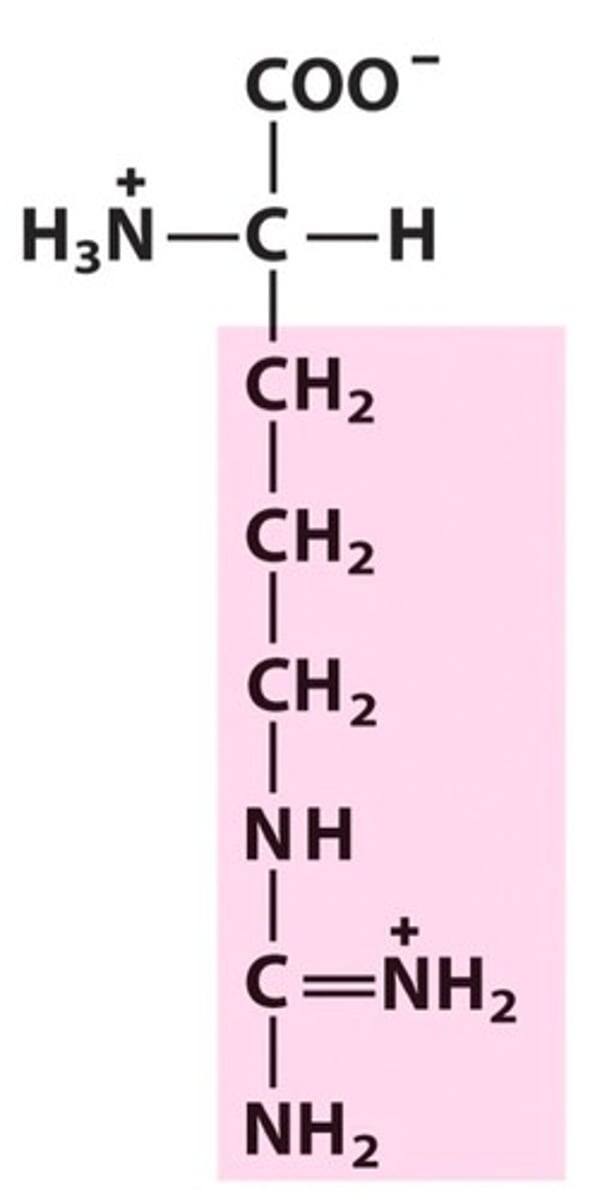
Histidine
Group C - Polar charged Amino Acids (Hydrophillic) (Basic)
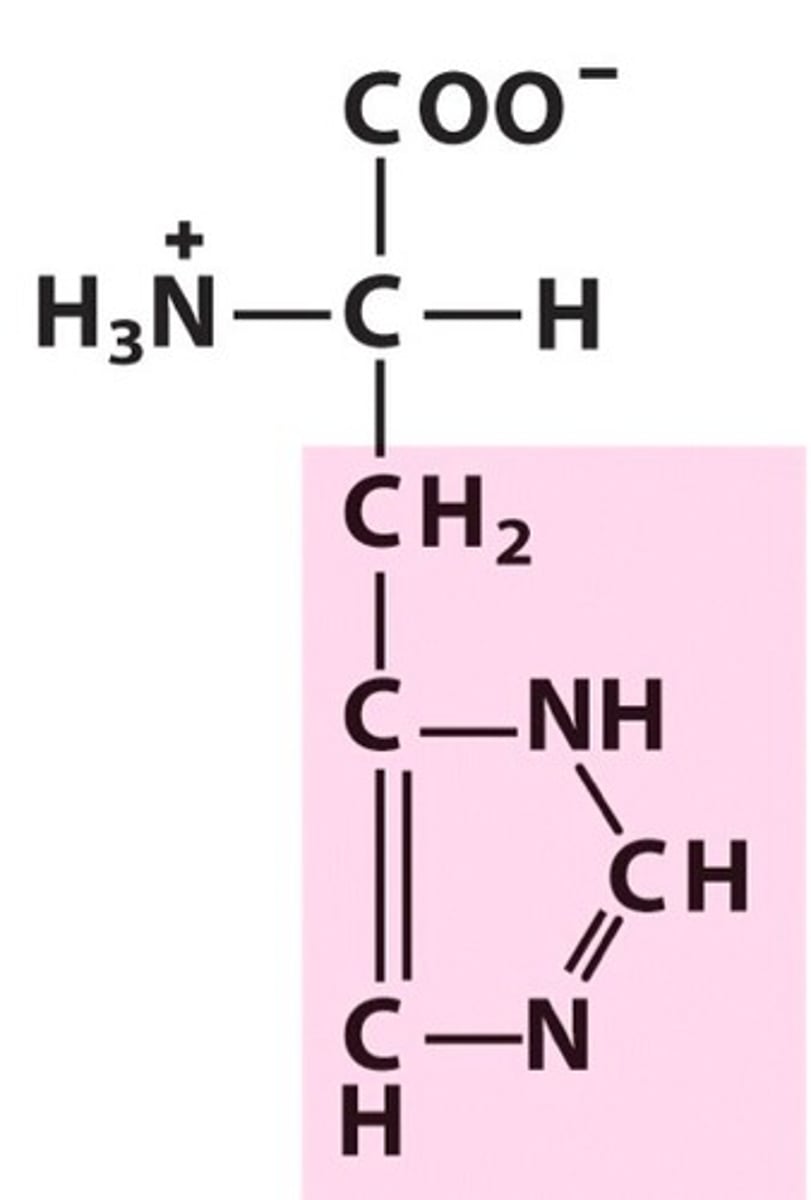
the most abundant elements in carbon based organisms
C, H, O, N, P, S
hydrocarbons
organic molecules consisting of only carbon and hydrogen
undergo reactions that release a large amount of energy
isomers
compounds with the same molecular formula but different structures and properties
structural isomers
have different covalent arrangements of their atoms
cis-trans isomers
have the same covalent bonds but differ in spatial arrangements
enantiomers
isomers that are mirror images
functional groups
components of organic molecules most commonly involved in chemical reactions
the seven functional groups
hydroxyl group (O-H)
carbonyl group (C-O)
carboxyl group(C-O-OH)
amino group (H-N-H)
sulfhydryl group (SH)
phosphate group (P-O-O-O)
methyl group (C-H-H-H)
adenine triphosphate
primary energy transferring molecule in the cell
adenosine attached to 3 phosphate group
macromolecules
large molecules composed of thousands of covalently connected atoms
polymer
a long molecule consisting of many similar building blocks
monomers
small building-block molecules
dehydration reaction
occurs when 2 monomers bond together through the loss of a water molecule
builds polymers
hydrolysis
a reaction that is essentially the reverse of a dehydration reaction
disassembles polymers
carbohydrates
sugars and the polymers of sugars
polysaccharides
macromolecules of carbohydrates
storage and structural roles
structure and function are determined by its sugar monomers and the positions of glycosidic linkages
monosaccharides
single sugars
usually have molecular formulas that are multiples of CH2O
how are monosaccharides classified
location of carbonyl group
number of carbons in the skeleton
what are sugars drawn as in aqueous solutions
rings
in non aqueous they are usually drawn linear
disaccharide
a dehydration reaction joins 2 monosaccharides
glycosidic linkage
the covalent bond between monosaccharides
starch
a storage polysaccharide of plants, consists entirely of glucose monomers
the simplest form of starch is amylose
stored mainly in granules within chloroplasts and other plastids
alpha glycosodic linkages
glycogen
a storage polysaccharide in animals
stored mainly in liver and muscle cells
cellulose
a structural polysaccharide comprising plant cell walls
beta glycosidic linkages
enzymes that digest starch cant hydrolyze beta linkages in cellulose
polymers with alpha glucose are what?
helical
polymers with beta glucose are what?
straight
allows h atoms on one strand to bond with oh groups on another strand
chitin
structural polysaccharide
found in the exoskeleton of arthropods
cells walls of many fungi
lipids
large biological molecule that does not form polymers
little or no affinity for water
consist mostly of hydrocarbons which form nonpolar covalent bonds
function of fats
energy storage
biologically important lipids
fats, phospholipids, and steroids
fats are made of what?
glycerol and fatty acids
glycerol
a three carbon alcohol with a hydroxyl group
fatty acid
carboxyl group attached to a long carbon skeleton
ester linkage
the bond between the fatty acids and glycerol in a fatty acid
triglyceride
3 fatty acids bonded to a glycerol
saturated fatty acids
have the maximum number of hydrogen atoms possible and no double bonds
solid at room temp
most animal fats are saturated
unsaturated fatty acids
have one or more double bonds
liquid at room temp
plant fats and fish fats are usually unsaturated
phospholipids
two hydrophobic fatty acids and a hydrophilic phosphate group are attached to glycerol
lipid bilayer structure in cell membranes
steroids
lipids characterized by a carbon skeleton consisting of 4 fused rings
common in animal cell membranes, regulates membrane fluidity
cholesterol is a steroid component in animal cells
protein functions
structural support, storage, transport, cellular communications, movement, and defense against foreign substances
enzymes
biological catalysts
8 common functions of proteins
enzymatic proteins
defensive proteins
transport proteins
storage proteins
hormonal proteins
receptor proteins
contractile and motor proteins
structure proteins
polypeptides
unbranched polymers built from the same set of 20 amino acids
protein
consists of one or more polypeptides
amino acids
monomer of polypeptides
organic molecules with carboxyl and amino groups
r groups differ in amino acids
how are amino acids linked
peptide bonds
carboxyl end (c-terminus) and amino end (n terminus)
primary structure
sequence of amino acids
secondary structure
consist of coils and folds of polypeptide chain due to hydrogen bonds
alpha helix and beta pleated sheet
tertiary structure
determined by interactions between R groups
can be hydrogen bonds, ionic, hydrophobic interactions, van der waals interactions, or strong covalent bonds called disulfide bridges
quaternary structure
results when 2 or more polypeptide chains form one macromolecule
collagen and hemoglobin
denaturation
loss of protein’s native structure
chaperonins
Protein molecules that assist the proper folding of other proteins
nucleotides
monomers of nucleic acids
nitrogenous base, sugar, and phosphate group
nucleoside
sugar and nitrogenous base
phosphodiester bond
the bond that nucleotides build
sugar phosphate backbone - OH group on 3’ carbon of one nucleotide and the next phosphate on the 5’ carbon
double helix
two polynucleotides spiraling
antiparallel
backbones run in opposite directions
purine
2 carbon rings
adenine and guanine
pyrimidines
one carbon ring
cytosine, uracil, thymine
complementary pairing
purines will pair with pyrimidines
A to T
C to G