AP Exam Review Flashcards: Types of Reactions & Solution Stoichiometry
1/85
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover key concepts and terms related to types of reactions, solution stoichiometry, gases, thermochemistry, kinetics, equilibrium, acids and bases, applications of thermodynamics, and electrochemistry.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
86 Terms
Strong Electrolyte
Substances that completely dissociate into ions in solution; includes strong acids, strong bases, and soluble ionic salts.
Weak Electrolyte
Substances that partially dissociate into ions in solution; typically includes weak acids and weak bases.
Nonelectrolyte
Substances that do not dissociate into ions in solution; includes insoluble ionic salts and covalent molecules.
Net Ionic Equation
An equation that shows only the species that participate in a reaction, omitting spectator ions.
Ideal Gas Law
A relation among the pressure (P), volume (V), temperature (T), and number of moles (n) of a gas, expressed as PV = nRT.
Endothermic Reaction
A reaction that absorbs heat from its surroundings, indicated by a positive change in enthalpy (ΔH).
Exothermic Reaction
A reaction that releases heat to its surroundings, indicated by a negative change in enthalpy (ΔH).
Le Chatelier's Principle
If a system at equilibrium is disturbed, it will shift in a direction that counteracts the disturbance.
Solubility Product Constant (Ksp)
An equilibrium constant that applies to the solubility of sparingly soluble ionic compounds.
Acid-Base Titration
A procedure used to determine the concentration of an acid or base by neutralizing it with a standard solution.
Gibbs Free Energy
A thermodynamic quantity used to predict the spontaneity of a reaction, with negative ΔG indicating a spontaneous reaction.
Redox Reaction
A reaction involving the transfer of electrons, where one species is oxidized (loses electrons) and another is reduced (gains electrons).
What items are all soluble in water
sodium, potassium, ammonium, and nitrate salts
strong acids
HCl, HBr, HI, HClO4, H2SO4, HNO3
strong bases
Group 1 & 2 hydroxides (Ex: NaOH, Ca(OH)2, Sr(OH)2, Ba(OH)2)
Net Ionic Equation Rules
Break apart strong acids, strong bases and soluble ionic salts
Do not break apart weak acids, weak bases, insoluble ionic salts, gases or liquids
when do real gases behave like ideal gases
low pressure and at high temperature
Heat released by the reaction =
heat absorbed by the solution
Heat absorbed by the solution =
mass x increase in temperature x specific heat
The solution is always
part of the surroundings
we assumed the solution was water with a specific heat of ____ and density of
4.184 J/g°C, 1.0 g/mL
First order
ln [A] vs t
first order graph
straight line
Second order
1/[A] vs t
Second order graph
gives a straight line
The rate of a reactant or product is determined by
the stoichiometry of a reaction
Represent an elementary reaction (one step reaction) as a rate law expression
stoichiometry
Rate laws for reactions that occur in more than one step must be determined by the
method of initial rates and data
The sum of the powers of the reactant concentrations in the rate law is the
overall order of the reaction
the proportionality constant in the rate law is called
the rate constant (k)
the rate constant (k) is dependent on
temperature
Units of rate constant (k) reflect
the overall reaction order (not always the same)
The rate-determining step in a mechanism is
the slow step and determines the rate law
@ equilibrium, the concentration of reactants and products remain
unchanged
The forward and reverse reactions rates are equal,
results in no observable change to the system
The equilibrium constant expression ONLY includes
gases and aqueous solutions
the equilibrium expression for Kc, Qc
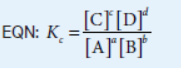
If you reverse a reaction, the K value is
the reciprocal of the forward reaction.
(Kreverse = 1/Kforward)
When the balanced equation for a reaction is multiplied by a factor of n
the equilibrium constant for the new reaction is the equilibrium constant for the original reaction raised to the nth power.
(Knew = (Koriginal)n
When two reactions with individual K values are combined
the K value for the overall reaction is K1 x K2
Reaction quotient (Q)
found the same way as K (law of mass action above) but uses initial concentrations instead of equilibrium concentrations
Q = K
the system is at equilibrium, no shift occurs
Q < K
the system shifts right to increase the products to reach equilibrium
Q > K
the system shifts left to decrease the products to reach equilibrium
Add a reactant
the reaction shifts right to use up the added reactant
Take away a reactant
the reaction shifts left to make more reactant
Add a product
reaction shifts left to use up the added product
Take away a product
the reaction shifts right to make more product
Increase the volume
decreases pressure. The reaction will shift in the direction to make more moles of gas to increase the pressure.
Decrease the volume
increases pressure. The reaction will shift in the direction to make less moles of gas to decrease the pressure
Common Ion Effect
solubility of a solid is lowered if the solution already contains ions common to the solid.
Q > Ksp
precipitation occurs
Q < Ksp
no precipitation occurs
The value of Kw is temperature dependent, so the pH of pure, neutral water will deviate from 7.0 at
temperatures other than 25°C.
Strong acid + strong base net ionic equation
H+ (aq) + OH- (aq) H2O (l)
Weak acid + strong base net ionic equation
HA (aq) + OH- (aq) A- (aq) + H2O (l)
Weak base + strong acid net ionic
B (aq) + H3O+ (aq) HB+ (aq) + H2O (l)
Henderson Hasselbach equation to calculate the pH when you have a concentration of both the weak acid & conjugate base (or weak base and conjugate acid)
pH = pKa + log([base]/[acid])
buffers
resists changes to pH when small amounts of acid or base are added
The BEST buffers have
equal concentrations of the weak acid & conjugate base (or weak base and conjugate acid) AND have a large initial concentration (larger buffer capacity)
If the concentrations are equal w buffer
pH = pKa
Equivalence point - moles of titrant =
moles of analyte originally present
analyte
the substance being measured or analyzed in a titration
titrant
the reagent added in a titration that reacts w/ analyte
Strong Acid + Strong Base, pH
7
Weak Acid + Strong Base, pH
> 7
Weak Base + Strong Acid, pH
<7
Half-way to the Equivalence point (Half-Equivalence point) is only for
titrations of weak acids or weak bases
liquid evaporating to a gas
+ΔS = increase in disorder
water freezing to ice
-ΔS = decrease in disorder
Spontaneous Reaction (thermodynamically favored)
products are favored
ΔG is negative & K > 1
Nonspontaneous Reaction, reactants are favored
ΔG is positive & K < 1
Equilibrium Gibbs Free energy
ΔG = 0 & K = 1
Thermodynamically favored (spontaneous) does not mean a reaction is
fast. Kinetics determines the speed of a reaction.
Loss of electrons is
oxidation
gain electrons is
reduction
Voltaic (Galvanic) Cell
spontaneous redox reaction (Ecell = +)
Concentration Cell
cell compartments are the cell (electrode & solution)
the lower concentration solution is in the anode and the higher concentration is in the cathode.
Electrolytic Cell
nonspontaneous redox reaction, must supply a voltage for the cell to operate
Anode
oxidation (mass of the electrode decreases)
Cathode
reduction (mass of the electrode increases)
concentration cell flow
anode to the cathode
concentration cell salt bridge
connects to anode & cathode and contains ions to maintain a balanced charge
The more positive half reaction STAYS
reduction
Hess law thermochem: Flip the half reaction that should be ___ and change the sign of ___
oxidation, E value
**Never multiply E by an integer even if you have to balance the half reaction!
hess law thermochem: