Economics
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
Scarcity
the limited nature of society’s resources
Economics
the study of how society manages its scarce resources
Efficiency
the property of society getting the most it can from its scarce resources
Equality
the property of distributing economic prosperity uniformly among the members of society
Opportunity cost
whatever must be given up to obtain some item
Rational people
people who systematically and purposefully do the best they can to achieve their objectives
Marginal change
an incremental adjustment to a plan of action
Incentive
something that induces a person to act
Market economy
an economy that allocates resources through the decentralized decisions of many firms and households as they interact in markets for goods and services
Property rights
the ability of an individual to own and exercise control over scarce resources
Market failure
a situation in which a market left on its own does not allocate resources efficiently
Externality
the impact of one person’s actions on the well-being of a bystander
Market power
the ability of a single economic actor (or small group of actors) to have a substantial influence on market prices
Productivity
the quantity of goods and services produced from each unit of labor input
Inflation
an increase in the overall level of prices in the economy
Business cycle
fluctuations in economic activity, such as employment and production
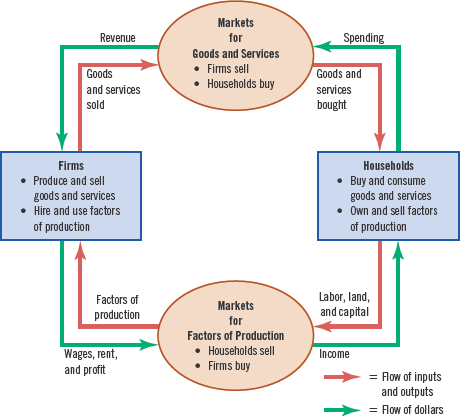
Circular-flow diagram
a visual model of the economy that shows how dollars flow through markets among households and firms
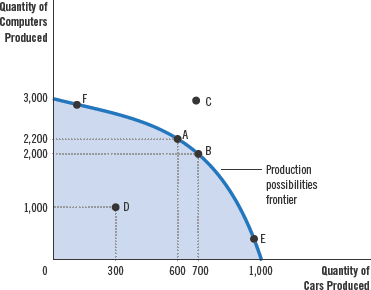
Production possibilities frontier
a graph that shows the combinations of output that the economy can possibly produce with the available factors of production and production technology
Positive statements
claims that attempt to describe the world as it is
Normative statements
claims that attempt to prescribe how the world should be
Market
a group of buyers and sellers of a particular good or service
Competitive market
a market in which there are many buyers and many sellers so each has a negligible impact on the market price
Quantity demanded
the amount of a good that buyers are willing and able to purchase
Law of demand
the claim that, other things being equal, the quantity demanded of a good falls when the price of the good rises
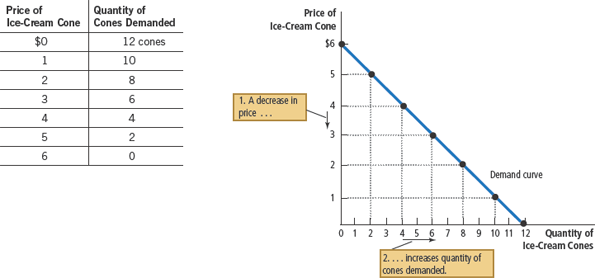
Demand schedule
a table that shows the relationship between the price of a good and the quantity demanded
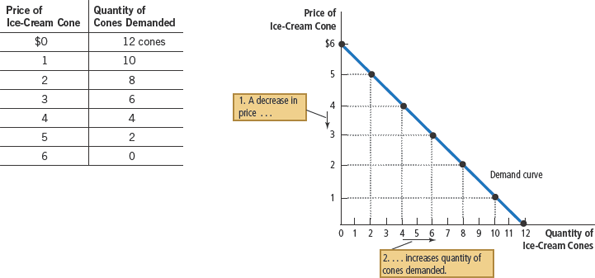
Demand curve
a graph of the relationship between the price of a good and the quantity demanded
Normal good
a good for which, other things being equal, an increase in income leads to an increase in demand
Inferior good
a good for which, other things being equal, an increase in income leads to a decrease in demand
Substitutes
two goods for which an increase in the price of one leads to an increase in the demand for the other
Complements
two goods for which an increase in the price of one leads to a decrease in the demand for the other
Quality supplied
the amount of a good that sellers are willing and able to sell
Law of supply
the claim that, other things being equal, the quantity supplied of a good rises when the price of the good rises
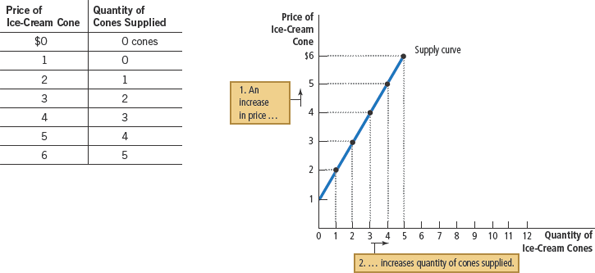
Supply schedule
a table that shows the relationship between the price of a good and the quantity supplied
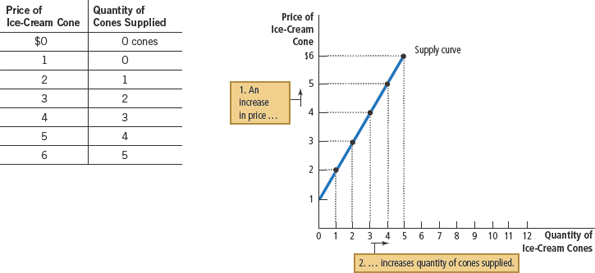
Supply curve
a graph of the relationship between the price of a good and the quantity supplied
Equilibrium
a situation in which the market price has reached the level at which the quantity supplied equals the quantity demanded
Equilibrium price
the price that balances the quantity supplied and the quantity demanded
Equilibrium quantity
the quantity supplied and the quantity demanded at the equilibrium price
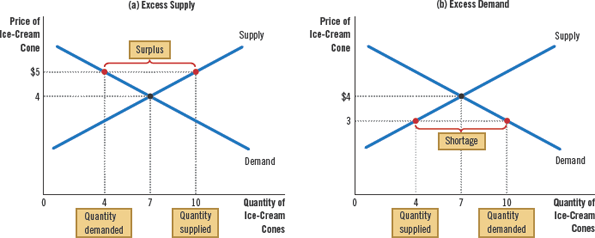
Surplus
a situation in which the quantity supplied is greater than the quantity demanded
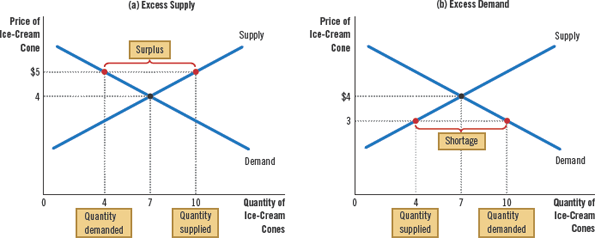
Shortage
a situation in which the quantity demanded is greater than the quantity supplied
Law of supply and demand
the claim that the price of any good adjusts to bring the quantity supplied and the quantity demanded of that good into balance
Elasticity
a measure of the responsiveness of the quantity demanded or quantity supplied to a change in one of its determinants
Price elasticity of demand
a measure of how much the quantity demanded of a good responds to a change in its price, calculated as the percentage change in quantity demanded divided by the percentage change in price

Total revenue
the amount paid by buyers and received by the sellers of a good, calculated as the price of the good times the quantity sold
Total revenue: P・Q
Income elasticity of demand
a measure of how much the quantity demanded of a good responds to a change in consumers’ income, calculated as the percentage change in quantity demanded divided by the percentage change in income
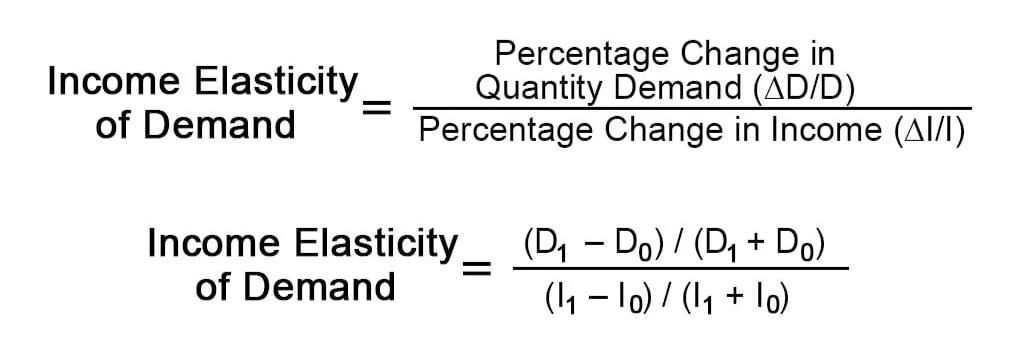
Cross-price elasticity of demand
a measure of how much the quantity demanded of one good responds to a change in the price of another good, calculated as the percentage change in the quantity demanded of the first good divided by the percentage change in the price of the second good

Price elasticity of supply
a measure of how much the quantity supplied of a good responds to a change in its price, calculated as the percentage change in quantity supplied divided by the percentage change in price

Price ceiling
a legal maximum on the price at which a good can be sold; price must stay BELOW the ceiling
Price floor
a legal minimum on the price at which a good can be sold; price must stay ABOVE the floor
Tax incidence
the manner in which the burden of a tax is shared among participants in a market
Welfare economics
the study of how the allocation of resources affects economic well-being
Willingness to pay
the maximum amount that a buyer will pay for a good
Consumer surplus
Value to buyers - Amount paid by buyers
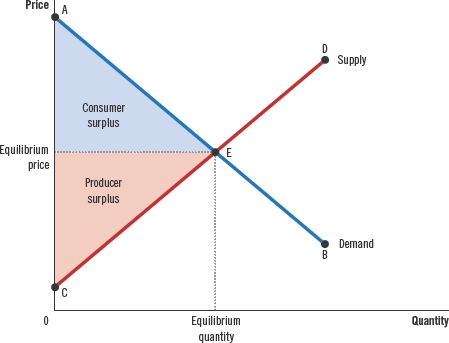
Cost
the value of everything a seller must give up to produce a good
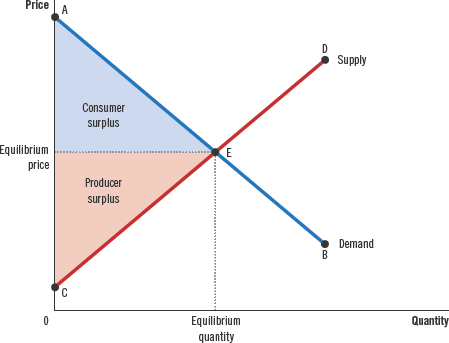
Producer surplus
Amount received by sellers - Cost to sellers
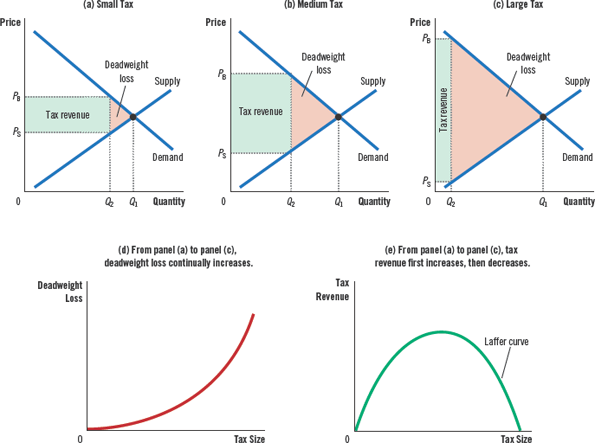
Deadweight loss
the fall in total surplus that results from a market distortion
Externality
the uncompensated impact of a person’s actions on the well-being of a bystander
Internalizing the Externality
altering incentives so that people take into account the external effects of their actions
Corrective tax
a tax designed to induce private decision makers to take into account the social costs that arise from a negative externality
Coase Theorem
the proposition that if private parties can bargain without cost over the allocation of resources, they can solve the problem of externalities on their own
Transaction costs
the costs that parties incur during the process of agreeing to and following through on a bargain
Absolute advantage
the ability to produce a good using fewer inputs than another producer
Comparative advantage
the ability to produce a good at a lower opportunity cost than another producer
World price
the price of a good that prevails in the world market for that good
Tariff
a tax on goods produced abroad and sold domestically
Unilateral vs Multilateral approach to free trade
Removing restrictions themselves vs doing it together with other countries
Excludability
the property of a good whereby a person can be prevented from using it
Rivalry in Consumption
the property of a good whereby one person’s use diminishes other people’s use
Private Goods
goods that are both excludable and rival in consumption
Public Goods
goods that are neither excludable nor rival in consumption
Common Resources
goods that are rival in consumption but not excludable
Club Goods
goods that are excludable but not rival in consumption
Free Rider
a person who receives the benefit of a good but avoids paying for it
Cost-Benefit Analysis
a study that compares the costs and benefits to society of providing a public good
Tragedy of the Commons
a parable that illustrates why common resources are used more than is desirable from the standpoint of society as a whole