Exam 5
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/104
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 3:45 PM on 12/5/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
105 Terms
1
New cards
Psychopathology
the study of psychological disorders, including their symptoms, etiology (causes), and treatment.
2
New cards
Psychological disorder
a condition characterized by abnormal thoughts, feelings, and behaviors.
> Behaviors, thoughts, and inner experiences that are atypical, dysfunctional, or dangerous are signs of psychological disorders.
> Behaviors, thoughts, and inner experiences that are atypical, dysfunctional, or dangerous are signs of psychological disorders.
3
New cards
Wakefield (1992):
Proposed a more influential concept in which he defines psychological disorders as a harmful dysfunction.
4
New cards
Dysfunction
occurs when an internal mechanism (e.g., cognition, perception, learning) breaks down and cannot perform its normal function.
5
New cards
For a dysfunction to be be classed as a disorder, it must also be harmful
leads to negative consequences for the individual or for others, as judged by the standards of the individual’s culture.
6
New cards
Diagnosis
appropriately identifying and labeling a set of defined symptoms
7
New cards
DSM-5 is the classification system used
by most mental health professionals.
8
New cards
Diagnostic features
overview of the disorder.
9
New cards
Diagnostic criteria
specific symptoms required for diagnosis.
10
New cards
Prevalence
percent of population thought to be afflicted.
11
New cards
comorbidity
the co-occurrence of two disorders
12
New cards
Supernatural perspective
psychological disorders attributed to a force beyond scientific understanding.
13
New cards
Psychosocial Perspective
> Emphasizes the importance of learning, stress, faulty and self-defeating thinking patters, and environmental factors.
> Views the cause of psychological disorders as a combination of biological and psychosocial factors.
> Views the cause of psychological disorders as a combination of biological and psychosocial factors.
14
New cards
Diathesis-Stress Model:
Integrates biological and psychosocial factors to predict the likelihood of a disorder.
> Diathesis + Stress → Development of a disorder
> Diathesis + Stress → Development of a disorder
15
New cards
Fear
an instantaneous reaction to an imminent threat.
16
New cards
Anxiety
apprehension, avoidance, and cautiousness regarding a potential threat, danger, or other negative content.
17
New cards
phobias
Involves excessive, distressing, and persistent fear or anxiety about a specific object or situation.
18
New cards
Acrophobia
heights
19
New cards
Aerophobia
flying
20
New cards
Arachnophobia
spiders
21
New cards
Claustrophobia
enclosed spaces.
22
New cards
Agoraphobia
Characterized by intense fear, anxiety, and avoidance of situations in which it might be difficult to escape or receive help if one experiences a panic attack.
23
New cards
Classical Conditioning.
Child is bitten by dog (US) → dogs become associated with biting (CS) → child experiences fear around dogs (CR).
24
New cards
Vicarious Learning.
Child observes cousin react with fear around spiders → child later expresses the same fears even though spiders have never presented any danger to him.
25
New cards
Verbal transmission of information.
> A child is continuously told that snakes are dangerous → child starts to fear snakes.
26
New cards
social anxiety disorder
Characterized by extreme and persistent fear or anxiety and avoidance of social situations in which the person could potentially be evaluated negatively by others, leading to serious impairments in life.
> Associated with lower educational attainment, lower earning, poor work performance, unemployment.
> Associated with lower educational attainment, lower earning, poor work performance, unemployment.
27
New cards
Safety behaviors
mental or behavioral acts that reduce anxiety in social situations by reducing the chance of negative social outcomes.
> comorbidity w alcohol use disorder
> comorbidity w alcohol use disorder
28
New cards
Behavioral inhibition
a consistent tendency to show fear and restraint when presented with unfamiliar people or situations.
29
New cards
Panic disorder
recurrent and unexpected panic attacks, along with at least one month of persistent concern about additional panic attacks, worry over the consequences of the attacks, or self-defeating changes in behavior related to the attacks.
> Comorbidity - anxiety disorders or major depressive disorder.
> Comorbidity - anxiety disorders or major depressive disorder.
30
New cards
Panic attack
a period of extreme fear or discomfort that develops abruptly and reaches a peak within 10 minutes.
31
New cards
Locus coeruleus
in the brainstem is possibly involved
> Major source of norepinephrine (neurotransmitter that triggers flight-or-flight response).
> Major source of norepinephrine (neurotransmitter that triggers flight-or-flight response).
32
New cards
Conditioning Theories
Panic attacks are classical conditioning responses to subtle bodily sensations resembling those normally occurring when one is anxious or frightened.
33
New cards
Cognitive Theories
Individuals with panic disorder are prone to interpret ordinary bodily sensations catastrophically, setting the state for panic attacks.
> In some patients, reducing catastrophic cognitions about sensations has proven to be as effective as medication in reducing panic attacks.
> In some patients, reducing catastrophic cognitions about sensations has proven to be as effective as medication in reducing panic attacks.
34
New cards
generalized anxiety disorder
A relatively continuous state of excessive, uncontrollable, and pointless worry and apprehension.
>Restlessness, difficulty concentrating, being easily fatigued, muscle tension, irritability, and sleep difficulties.
>Restlessness, difficulty concentrating, being easily fatigued, muscle tension, irritability, and sleep difficulties.
35
New cards
cognitive theories (anxiety disorder)
Worry represents a mental strategy to avoid more powerful negative emotions perhaps stemming from earlier unpleasant or traumatic experiences.
> Worrying acts a distraction from remembering painful childhood experiences.
> Worrying acts a distraction from remembering painful childhood experiences.
36
New cards
obsessive compulsive disorder
Involves thoughts and urges that are intrusive and unwanted (obsessions) and/or the need to engage in repetitive behaviors or mental acts (compulsions).
37
New cards
Obsessions
persistent, unintentional, and unwanted thoughts and urges that are highly intrusive, unpleasant, and distressing
38
New cards
common obsessions in OCD
> Concerns about germs and contamination
> Doubts
> Order and symmetry
> Aggressive or lustful urges
> Doubts
> Order and symmetry
> Aggressive or lustful urges
39
New cards
Compulsions
repetitive and ritualistic acts, typically carried out primarily as a means to minimize the distress that obsessions trigger or to reduce the likelihood of a feared event.
> Not performed out of pleasure.
> The person usually knows these obsessions and compulsions are irrational but suppressing them is extremely difficult.
> Not performed out of pleasure.
> The person usually knows these obsessions and compulsions are irrational but suppressing them is extremely difficult.
40
New cards
Body Dysmorphic Disorder
Involves a preoccupation with a perceived flaw in the individuals physical appearance that is either nonexistent or barely noticeable to other people.
41
New cards
Hoarding Disorder (OCD)
Involves great difficulty in discarding possessions, regardless of how valueless/useless they are, usually resulting in an accumulation
42
New cards
Why are hoarders unable to let go of items?
> They think items might be useful at a later time.
> Sentimental attachment to items.
> Sentimental attachment to items.
43
New cards
conditioning theories (OCD)
Symptoms of OCD are learned responses resulting from both classical and operant conditioning.
> Neutral stimulus + unconditioned stimulus → anxiety or distress.
> Once association has been acquired, encounters with the NS trigger anxiety and obsessive thoughts.
> Anxiety and obsessive thoughts continue until a strategy is identified to relieve it.
> Relief may be ritualistic behavior or mental activity that reduces anxiety.
> Compulsive acts become negatively reinforcing.
> Neutral stimulus + unconditioned stimulus → anxiety or distress.
> Once association has been acquired, encounters with the NS trigger anxiety and obsessive thoughts.
> Anxiety and obsessive thoughts continue until a strategy is identified to relieve it.
> Relief may be ritualistic behavior or mental activity that reduces anxiety.
> Compulsive acts become negatively reinforcing.
44
New cards
OCD Circuit
Several interconnected regions that influence perceived emotional value of stimuli and selection of behavioral and cognitive responses.
> Abnormalities in these areas may produce symptoms of OCD.
> Abnormalities in these areas may produce symptoms of OCD.
45
New cards
Orbitofrontal cortex
involved in learning and decision making.
provoked w negative stimuli
provoked w negative stimuli
46
New cards
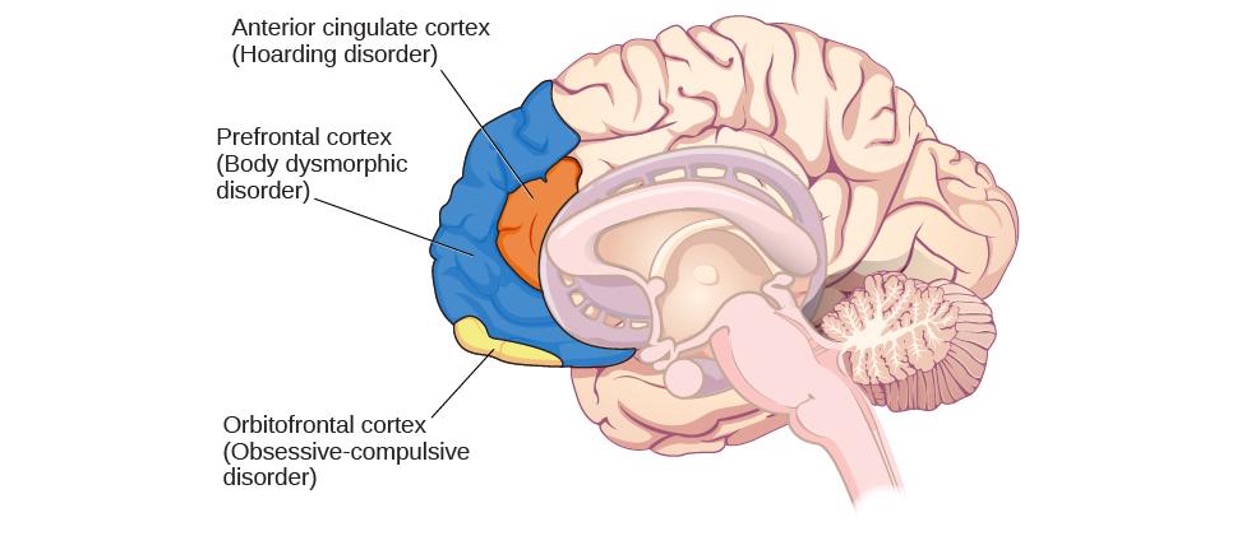
OCD in the brain
47
New cards
Anterior cingulate cortex
hoarding disorder
48
New cards
prefrontal cortex
body dysmorphic disorder
49
New cards
obitofrontal cortex
obsessive compulsive disorder
50
New cards
PTSD
Individual was exposed to, witnessed, or experienced the details of a traumatic experience (“actual or threatened death, serious injury, or sexual violence”)
51
New cards
symtoms of PTSD
> Intrusive and distressing memories of the event.
> Flashbacks – states during which individual relives the event and behaves as if it were occurring at that moment.
> Avoidance of stimuli connected to the event.
> Persistently negative emotional states.
> Feelings of detachment from others.
> Irritability.
> Proneness toward outbursts.
> Exaggerated startle response.
> Flashbacks – states during which individual relives the event and behaves as if it were occurring at that moment.
> Avoidance of stimuli connected to the event.
> Persistently negative emotional states.
> Feelings of detachment from others.
> Irritability.
> Proneness toward outbursts.
> Exaggerated startle response.
52
New cards
risk factors of PTSD
>Trauma experience.
Those involving harm by others carry greater risk than those that do not.
> Lack of immediate social support.
Social Support (comfort, advice, and assistance from relatives, friends, and neighbors) can reduce the risk of developing PTSD.
> Subsequent life stress.
Female gender.
> Low socioeconomic status.
Low intelligence.
> Personal history of mental disorders.
History of childhood adversity.
> Family history of mental disorders.
Personality characteristics – neuroticism and somatization (tendency to experience physical symptoms when one encounters stress).
> Possession of one or two short versions of a gene that regulates serotonin.
Those involving harm by others carry greater risk than those that do not.
> Lack of immediate social support.
Social Support (comfort, advice, and assistance from relatives, friends, and neighbors) can reduce the risk of developing PTSD.
> Subsequent life stress.
Female gender.
> Low socioeconomic status.
Low intelligence.
> Personal history of mental disorders.
History of childhood adversity.
> Family history of mental disorders.
Personality characteristics – neuroticism and somatization (tendency to experience physical symptoms when one encounters stress).
> Possession of one or two short versions of a gene that regulates serotonin.
53
New cards
conditioning theories of PTSD
> Traumatic event (UCS) → Extreme fear and anxiety (UCR).
> Cognitive, emotional, physiological, and environmental cues associated with the traumatic event become conditioned stimuli.
> Traumatic reminders (CS) → Extreme fear and anxiety (CR).
> Cognitive, emotional, physiological, and environmental cues associated with the traumatic event become conditioned stimuli.
> Traumatic reminders (CS) → Extreme fear and anxiety (CR).
54
New cards
Cognitive Theories of PTSD
1.Disturbances in memory for the event.
Poorly encoded memories of trauma can become fragmented, disorganized, and lacking in detail.
> Individuals cannot remember event in a way that gives meaning and context.
> May become haunted by these fragments involuntarily triggered by stimuli associated with the event.
2. Negative appraisals of the trauma and its aftermath (e.g., ”I deserve to be raped because I am stupid”).
> May lead to dysfunctional behavioral patterns that maintain symptoms and prevent changes in the problematic appraisals.
Poorly encoded memories of trauma can become fragmented, disorganized, and lacking in detail.
> Individuals cannot remember event in a way that gives meaning and context.
> May become haunted by these fragments involuntarily triggered by stimuli associated with the event.
2. Negative appraisals of the trauma and its aftermath (e.g., ”I deserve to be raped because I am stupid”).
> May lead to dysfunctional behavioral patterns that maintain symptoms and prevent changes in the problematic appraisals.
55
New cards
Mania
(extreme elation and agitation) is the main feature.
56
New cards
Seasonal pattern
applies to situations in which a person experiences the symptoms of major depressive disorder only during a particular time of year.
57
New cards
Peripartum onset (postpartum depression
major depression during pregnancy or in the four weeks following the birth.
58
New cards
Persistent depressive disorder (dysthymia)
– depressed moods most of the day nearly every day for at least two years, as well as at least two of the other symptoms of major depression.
59
New cards
bipolar disorder
Involves mood states that fluctuate between depression and mania.
60
New cards
Symptoms of Mania
> Excessively talkative.
> Excessively irritable.
> Exhibit flight of ideas – talk loudly and rapidly, abruptly switching from one topic to another.
> Easily distracted.
> Exhibit grandiosity – inflated but unjustified self-esteem and self-confidence.
> Show little need for sleep.
> Take on several tasks at once.
> Engage in reckless behaviors.
> Excessively irritable.
> Exhibit flight of ideas – talk loudly and rapidly, abruptly switching from one topic to another.
> Easily distracted.
> Exhibit grandiosity – inflated but unjustified self-esteem and self-confidence.
> Show little need for sleep.
> Take on several tasks at once.
> Engage in reckless behaviors.
61
New cards
Elevated levels of cortisol
are found in depression.
62
New cards
Cortisol activates the amygdala and
deactivates the prefrontal cortex (disturbances connected to depression).
63
New cards
Mood disorders often
involve imbalances in neurotransmitters.
(serotonin and norepinephrine.)
(serotonin and norepinephrine.)
64
New cards
Medications for depression
usually increase serotonin and norepinephrine
65
New cards
Medication for bipolar
Lithium, which blocks norepinephrine activity at the synapse.
66
New cards
Amygdala (mood disorders)
important in assessing the emotional significance of stimuli and experiencing emotions.
67
New cards
Prefrontal cortex
important in regulating and controlling emotions.
68
New cards
Cognitive theories suggest that depression
is triggered by negative thoughts, interpretations, self-evaluations, and expectations.
69
New cards
Aaron Beck (1960s)
Theorized that depression-prone people possess mental predispositions to think about most things in a negative way (depressive schemas).
70
New cards
Depressive schemas
contain themes of loss, failure, rejection, worthlessness, and inadequacy.
71
New cards
Hopelessness Theory
Specific negative thinking style → sense of hopelessness → depression.
72
New cards
Negative thinking
refers to a tendency to perceive negative life events as having stable (”It’s never going to change”) and global (“It’s going to affect my whole life”) causes.
73
New cards
Hopelessness
expectation that unpleasant outcomes will occur or desired outcomes will not occur, and there is nothing one can do to prevent such outcomes (seen as the primary cause of depression).
74
New cards
Rumination
repetitive and passive focus on the fact that one is depressed and dwelling on depressed symptoms, rather than distracting one’s self from the symptoms or attempting to address them in an active, problem-solving manner.
75
New cards
Hallucinations
perceptual experience that occurs in the absence of external stimulation. (Auditory hallucinations are most common).
76
New cards
Delusions
beliefs that are contrary to reality.
77
New cards
Paranoid delusions
belief that other people or agencies are plotting to harm them.
78
New cards
Grandiose delusions
belief that one holds special power, unique knowledge, or is extremely important.
79
New cards
Somatic delusions
belief that something highly abnormal is happening to one’s body.
80
New cards
Disorganized thinking
disjointed and incoherent thought processes.
81
New cards
Catatonic behaviors
decreased reactivity to the environment
82
New cards
Negative Symptoms
decreases and absences in certain behaviors, emotions, drives.
83
New cards
Avolition
lack of motivation to engage in self-initiated and meaningful activity.
84
New cards
Alogia
reduced speech output.
85
New cards
Asociality
social withdrawal.
86
New cards
Anhedonia
inability to experience pleasure.
87
New cards
Dopamine hypothesis
an overabundance of dopamine or too many dopamine receptors are responsible for the onset and maintenance of schizophrenia.
> Drugs that increase dopamine levels can produce schizophrenia-like symptoms.
> Medications that block dopamine activity reduce the symptoms.
> Drugs that increase dopamine levels can produce schizophrenia-like symptoms.
> Medications that block dopamine activity reduce the symptoms.
88
New cards
High levels of dopamine in the limbic system
hallucinations and delusions
89
New cards
Low levels of dopamine in the prefrontal cortex
negative symptoms
90
New cards
Brain Anatomy
> Enlarged ventricles.
> Reduced gray matter in the frontal lobes.
> Many show less frontal lobe activity when performing cognitive tasks.
> Reduced gray matter in the frontal lobes.
> Many show less frontal lobe activity when performing cognitive tasks.
91
New cards
Dissociative Disorders
Characterized by an individual becoming, split off, or dissociated, from their core sense of self - Memory and identity become disturbed.
92
New cards
Dissociative Amnesia
Inability to recall important personal information.
>Usually follows a stressful or traumatic experience.
>Usually follows a stressful or traumatic experience.
93
New cards
Dissociative fugue
individual suddenly wanders away from home, experiences confusion about their identity, and in some cases may adopt a new identity.
94
New cards
Depersonalization/Derealization Disorder
Characterized by recurring episodes of depersonalization, derealization, or both.
95
New cards
Depersonalization
feelings of “unreality or detachment from, or unfamiliarity with, one’s whole self or from aspects of the self”
96
New cards
Derealization
a sense of ”unreality or detachment from, or unfamiliarity with, the world, be it individuals, inanimate objects, or all surroundings”
97
New cards
Dissociative Identity Disorder
Individual exhibits two or more separate personalities or identities.
98
New cards
personality disorder
Characterized by a pervasive and inflexible personality style that differs markedly from the expectations of the individuals culture and causes distress or impairment.
99
New cards
Cluster A
Paranoid personality disorder
Schizoid personality disorder
Schizotypal personality disorder
Schizoid personality disorder
Schizotypal personality disorder
100
New cards
Cluster B
Antisocial personality disorder
Histrionic personality disorder
Narcissistic personality disorder
Borderline personality disorder
Histrionic personality disorder
Narcissistic personality disorder
Borderline personality disorder