34: Organs of Vision and CN II, III, IV, and VI
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
organs of vision
adnexa
eyeball (bulbus oculi)
Where are the bulbus oculi and adnexa located?
housed in the orbit
eyeball is embedded in fat
Adneza includes:
eyelids
ocular muscles
lacrimal apparatus
What are the differences between the body processes lateral to the orbit in cats and dogs?
cats: very close or fused
dogs: separated but joined together by the orbital ligament
optic axis
straight line passing through both poles
equator
line equidistant from the poles
tunics of the eye
external fibrous tunic
middle vascular tunic
internal nervous tunic
external fibrous tunic
exterior tunic of eyeball
gives form to and protects the eyeball
middle vascular tunic
middle tunic of the eyeball
blood vessels and smooth muscle, nutrition of the eyeball, and the regulation of the shape of the lens and size of the pupil
internal nervous tunic
internal tunic of the eyeball
translation of visual stimuli into nerve impulses
components of the external fibrous tunic
sclera
limbus
cornea
sclera
external fibrous tunic
white, fibrous tissue
covers outside of the eye
extends from the cornea to the optic nerve
cornea
forms ¼ of external fibrous tunic
outermost transparent layer of the eye
helps focus light and protect the eye
limbus
border between the cornea and sclera
innervation of the cornea
most densely innervated tissue
nerves are responsible for:
-sensation: touch, pain, temperature
-reflexes: blink reflex, tear production
-wound healing
components of the middle vascular tunic
AKA uvea
iris
ciliary body
choroid
pupil
anterior and posterior chamber
lens
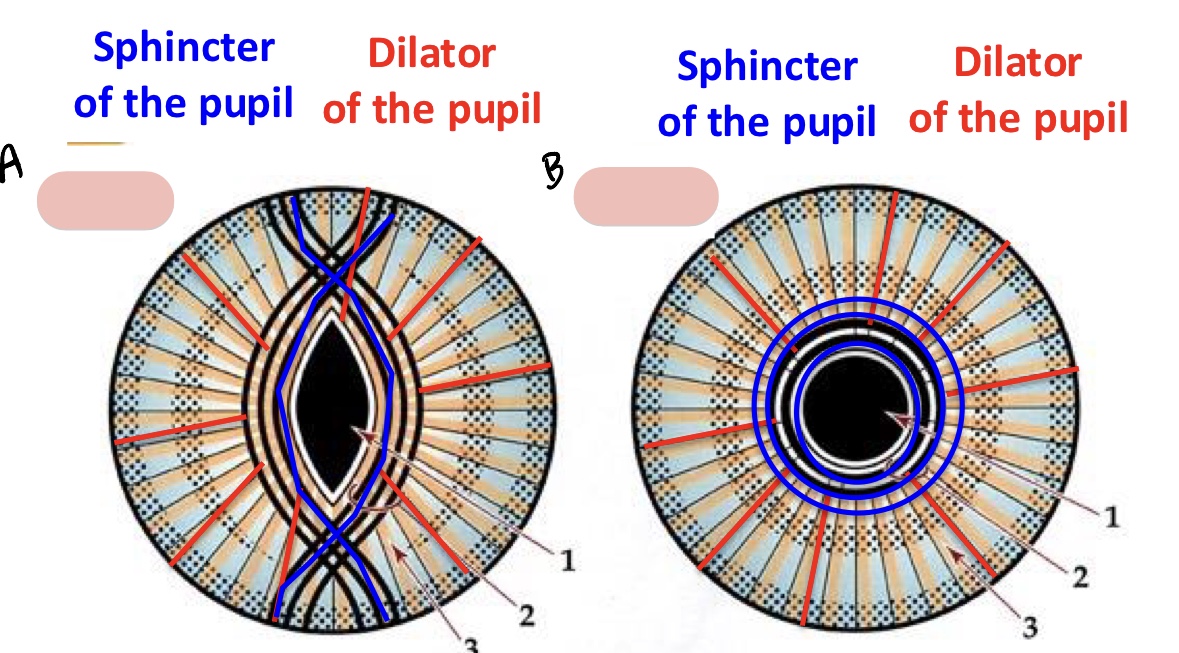
iris
adjusts size of pupil
divides the space between the lens and cornea into anterior and posterior chambers
contains two layers of smooth muscles
-sphincter of the pupil
-dilator of the pupil
anterior and posterior chambers
communicate through the pupil
both filled with aqueous humor
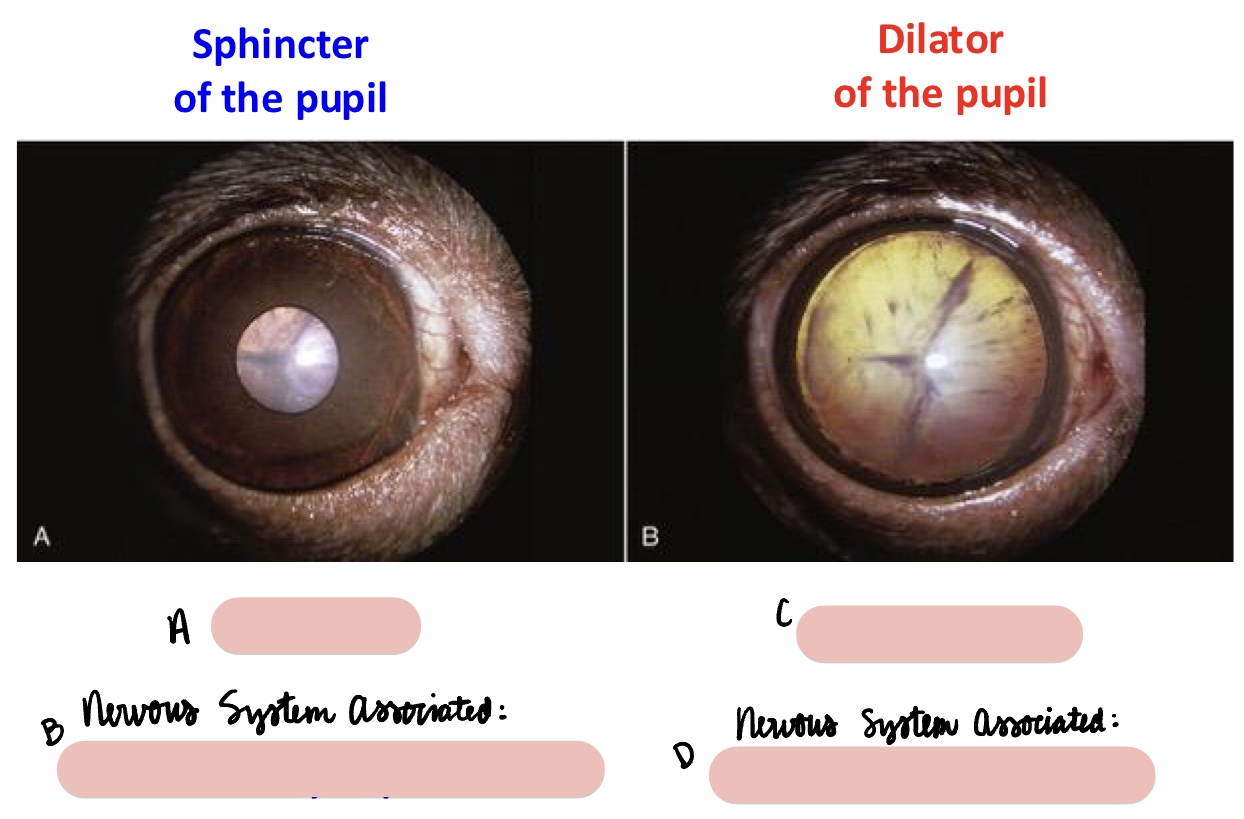
miosis
constricted pupil
GVE parasympathetic (CN III)
sphincter of the pupil
horner’s syndrome
mydriasis
dilated pupils
GVE sympathetic (CN III)
dilator of the pupil
ciliary body
suspends the lens and regulates its curvature
raised ring with ridges converging towards lens
smooth ciliary muscle
accommodation (ability of the eye to focus on near or distant objects by changing the shape of the lens
ciliary body reaction to far objects
sympathetic CN III innervation
smooth ciliary m. relaxes
zonular fibers tense
lens becomes more flat
ciliary body reaction to close objects
parasympathetic CN III innervation
smooth ciliary m. contracts
zonular fibers relax
lens becomes more spherical
choroid
dense network of blood vessels embedded in heavily pigmented connective tissue
tapetum lucidum
light reflecting area near optic nerve (black of eye, fundus)
internal nervous tunic components
retina
area centralis
optic disc
retina
light-sensitive receptor cells
area centralis
region of the retina with a higher concentration of photoreceptors
analogous to human macula, but does not have the concentration of cone receptors like humans
Why colors do dogs see?
limited to shades of blue and yellow
optic disc
“blind zone”
area where the axons of the 4th layer concentrate to leave the eye as optic nerve (CN II)
tapetum nigrum
dark, pigmented area of the fundus of the eye
eye chambers
anterior
posterior
vitreous
anterior chamber
between the cornea and iris, filed with aqueous humor
posterior chamber
between iris and ciliary body/lens, filled with aqueous humor
vitreous chamber
between ciliary body and retina, filled with vitreous humor
aqueous humor
role in the maintenance of intraocular pressure
produced by cells of the ciliary processes
glaucoma
disease of the eye in which the intraocular pressure is increased
intraocular pressure (IOP)
pressure within the eye
lens
soft, transparent tissue that sits posterior to the iris
helps focus incoming light to the retina
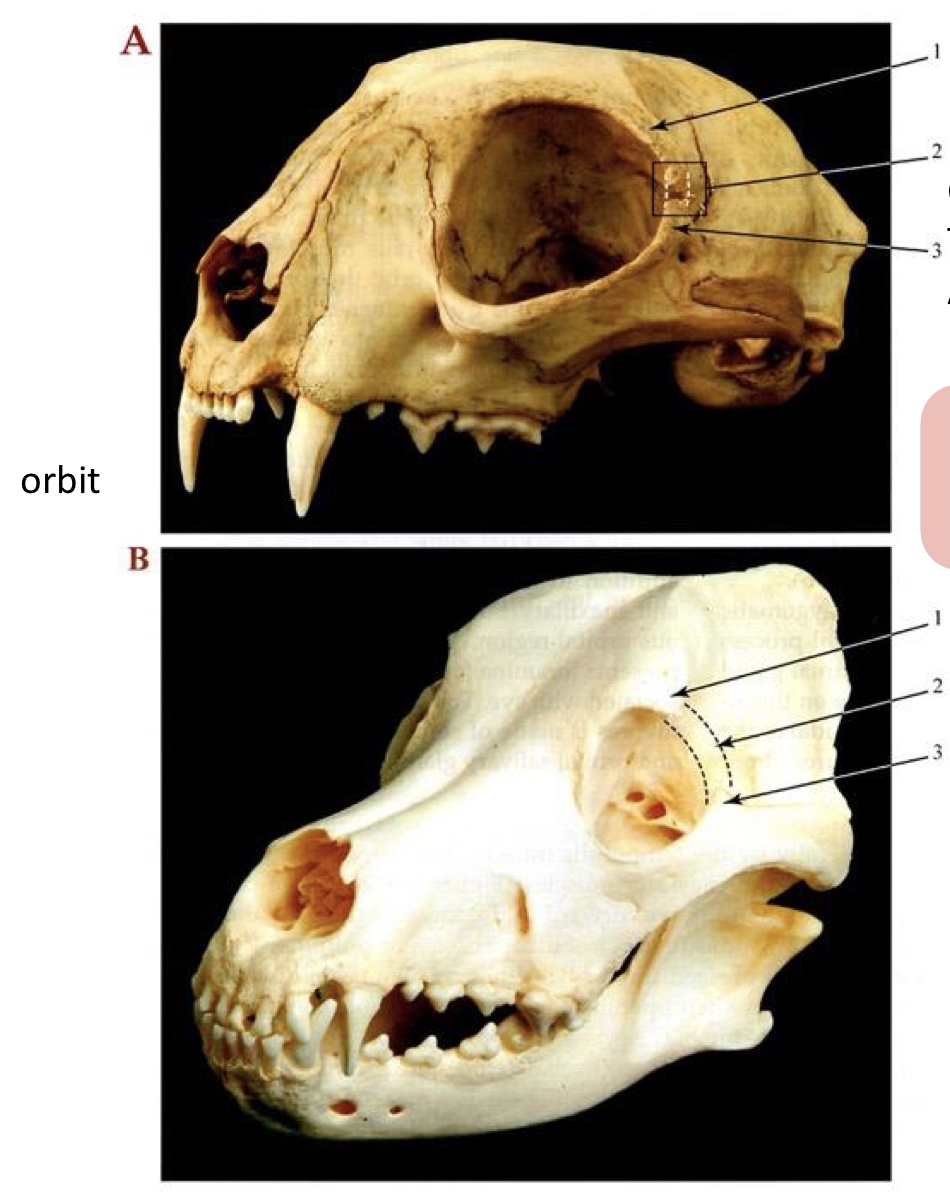
Name the structure(s) indicated by 1, 2, and 3.
zygomatic process of the frontal bone
orbital ligament
frontal process of zygomatic bone
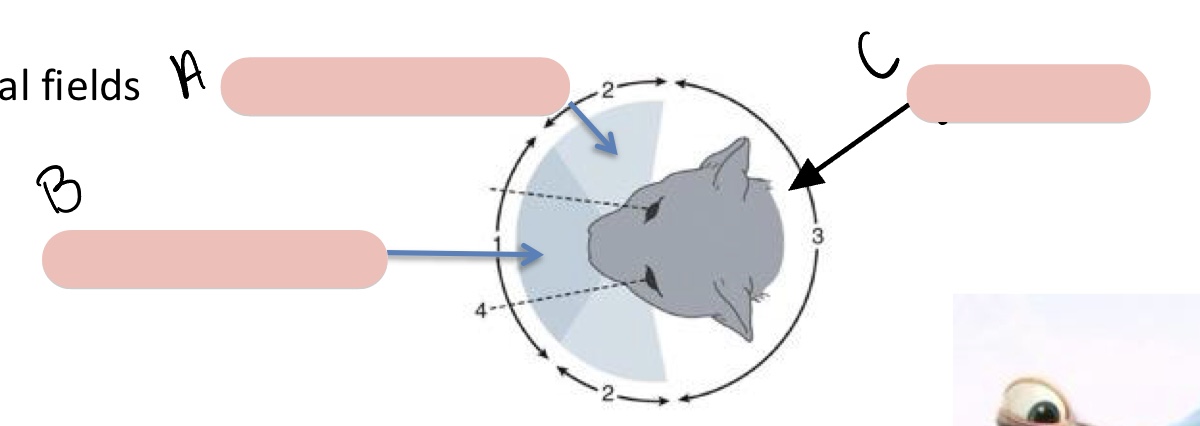
Name the structure(s) indicated by a, b, and c.
monocular vision
binocular vision
blind area
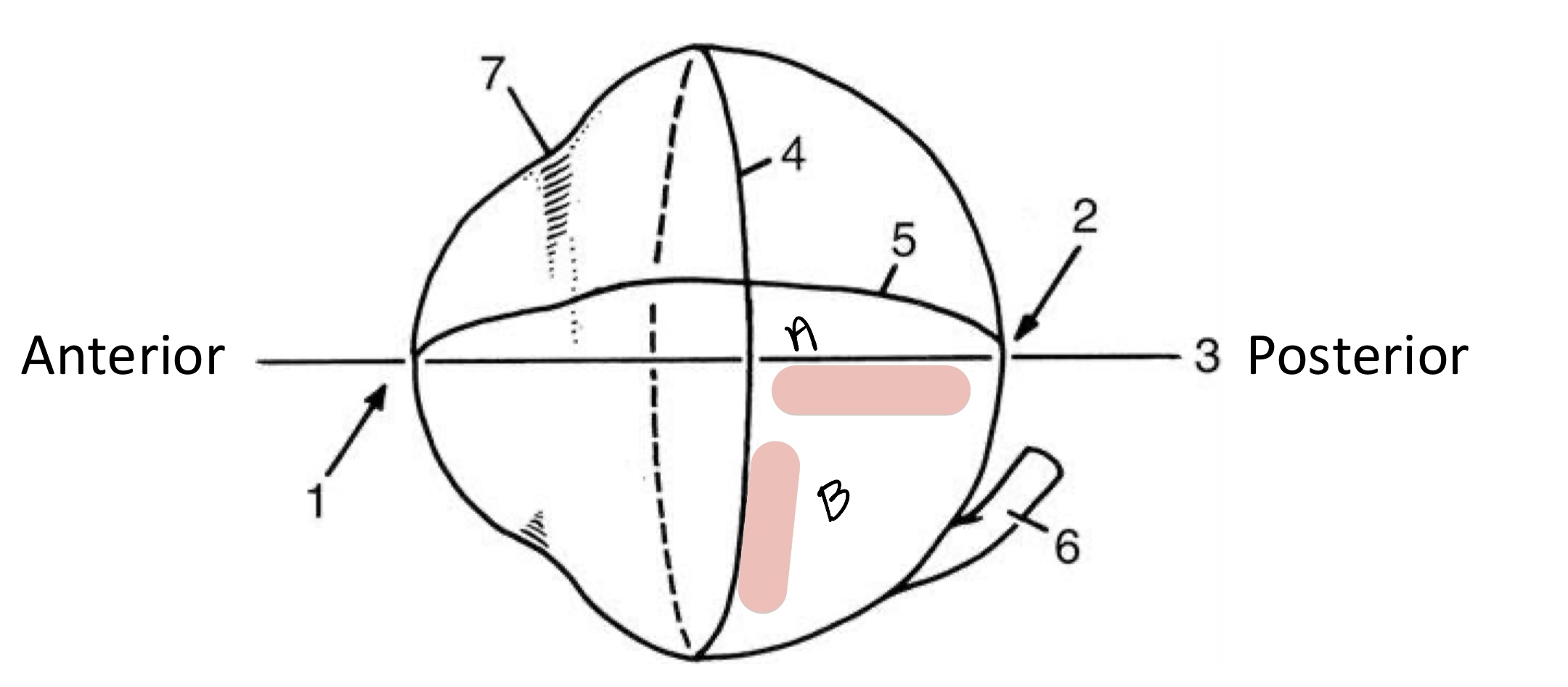
Name the structure(s) indicated by a and b.
optic axis
equator
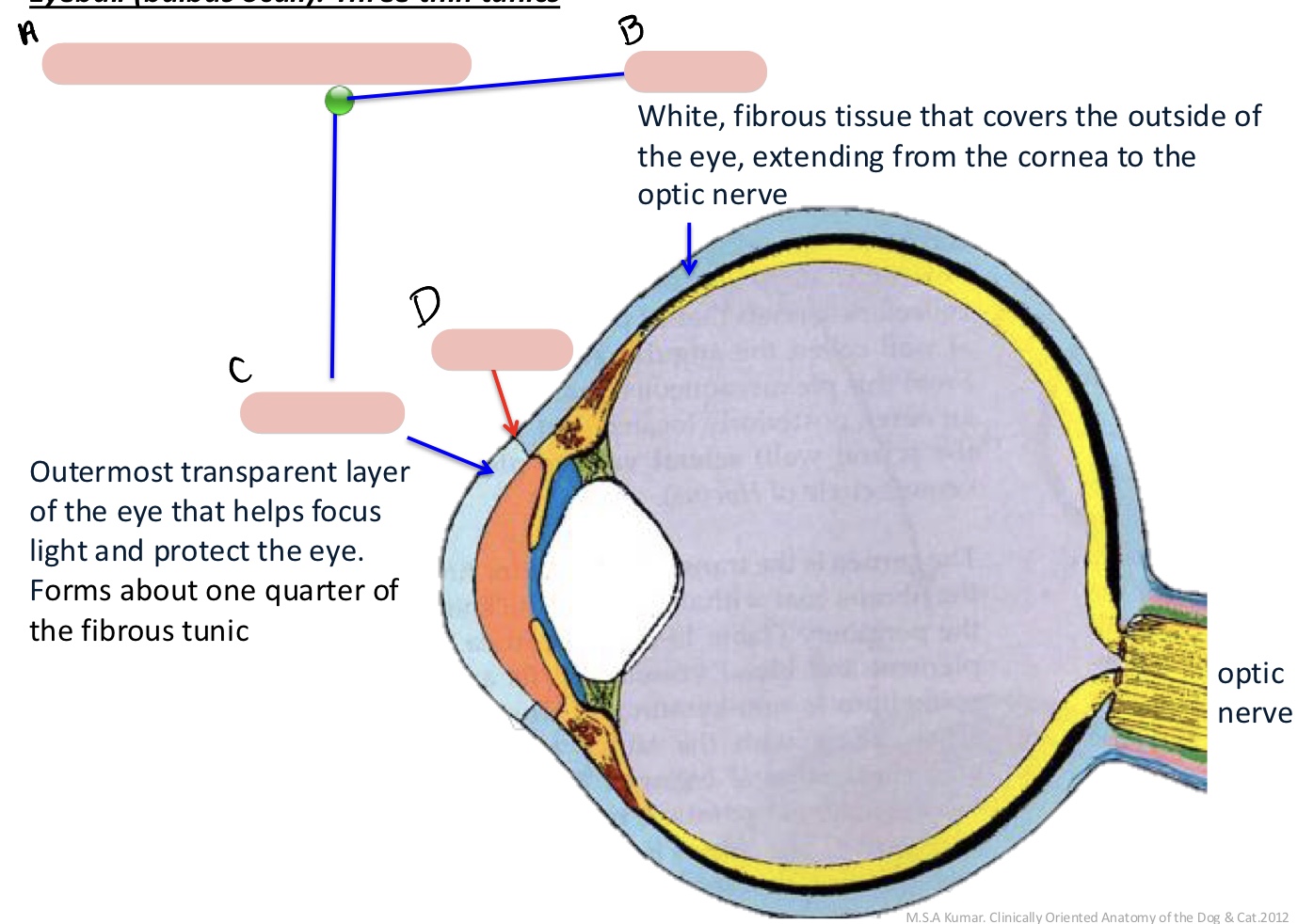
Name the structure(s) indicated by a, b, c, and d.
external fibrous tunic
sclera
cornea
limbus
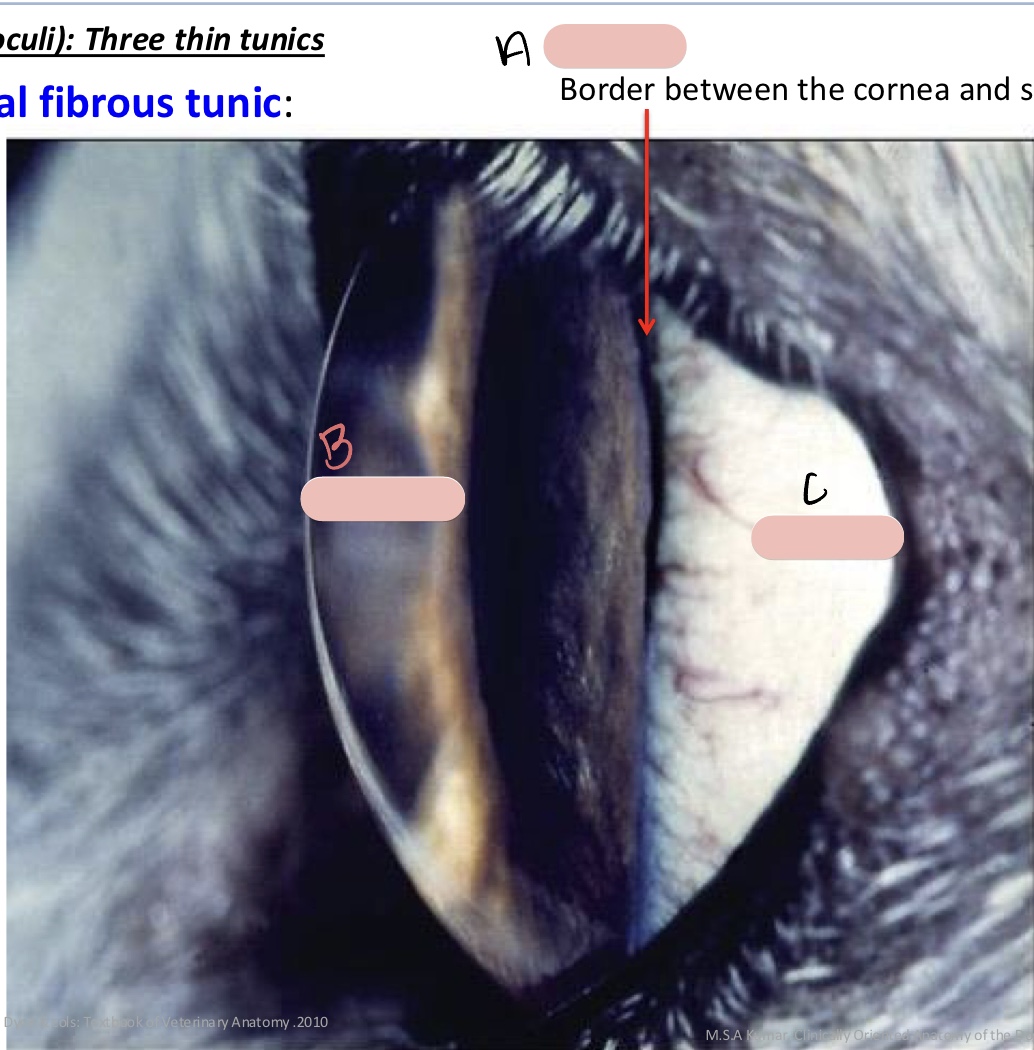
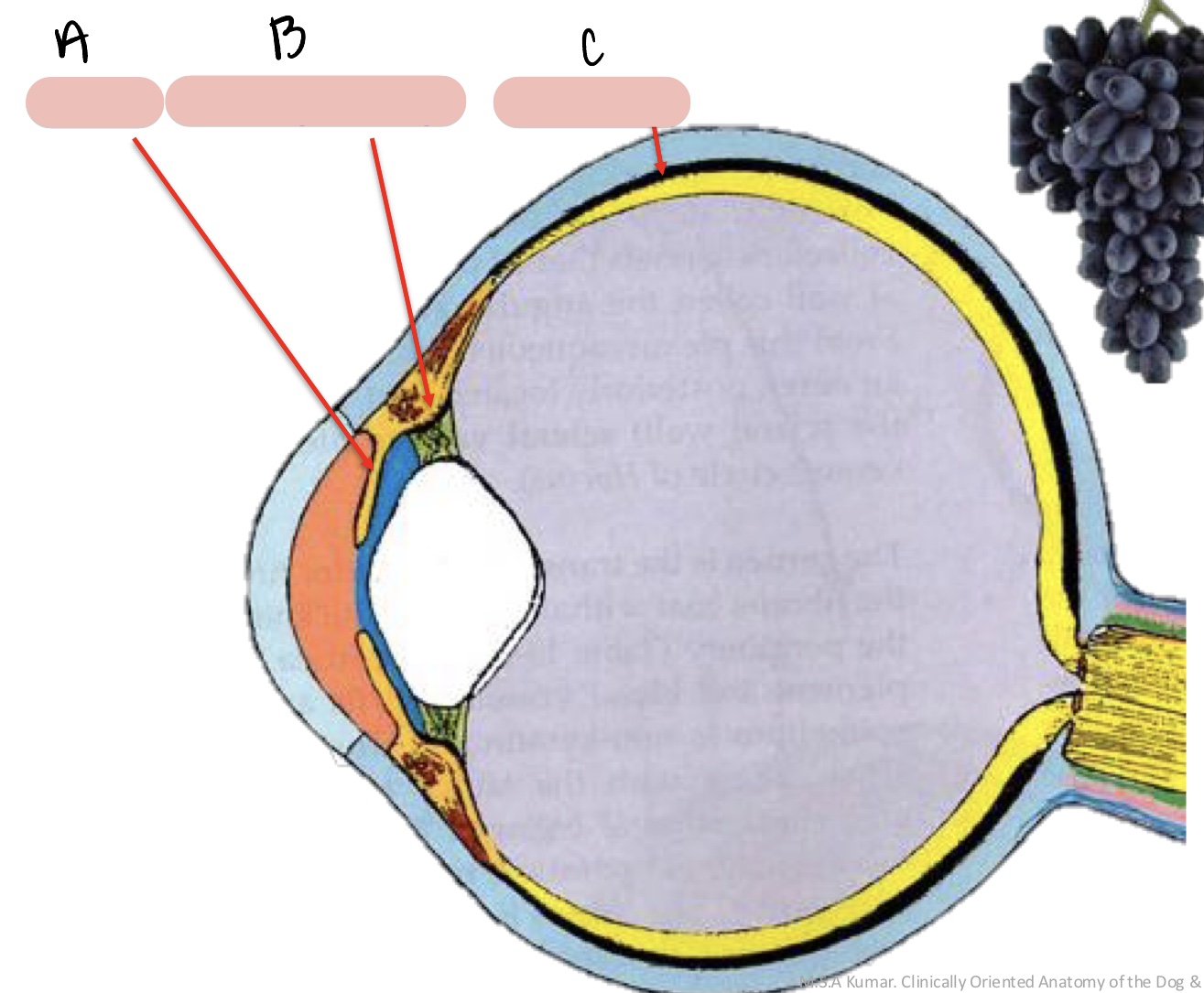
Name the structure(s) indicated by a, b, and c.
limbus
cornea
sclera
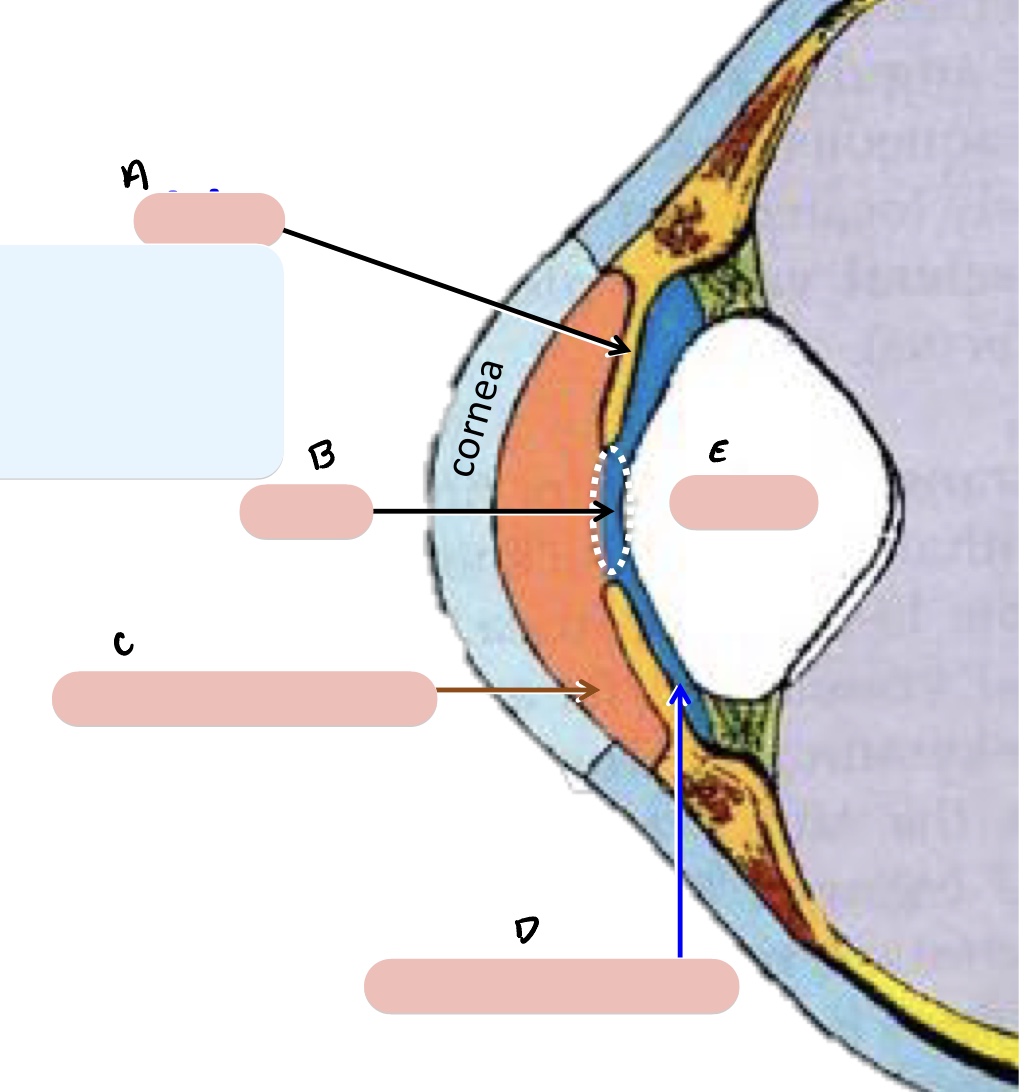
Name the structure(s) indicated by a, b, and c.
iris
ciliary body
choroid
Name the structure(s) indicated by a, b, and c.
iris
pupil
anterior chamber
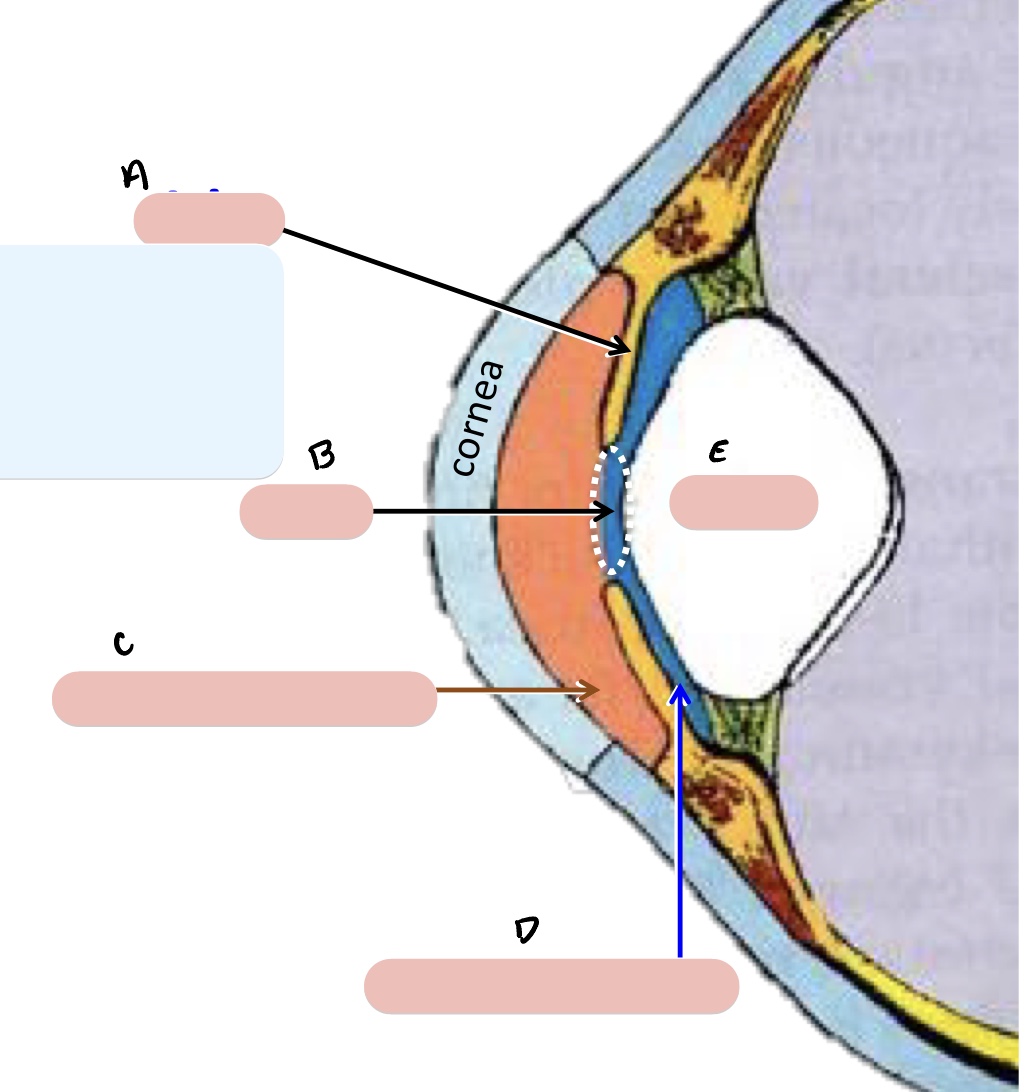
Name the structure(s) indicated by d and e.
posterior chamber
lens
Name the structure(s) indicated by a and b.
cat
dog
Name the structure(s) indicated by a, b, c, and d.
miosis
GVE sympathetic
mydriasis
GVE sympathetic
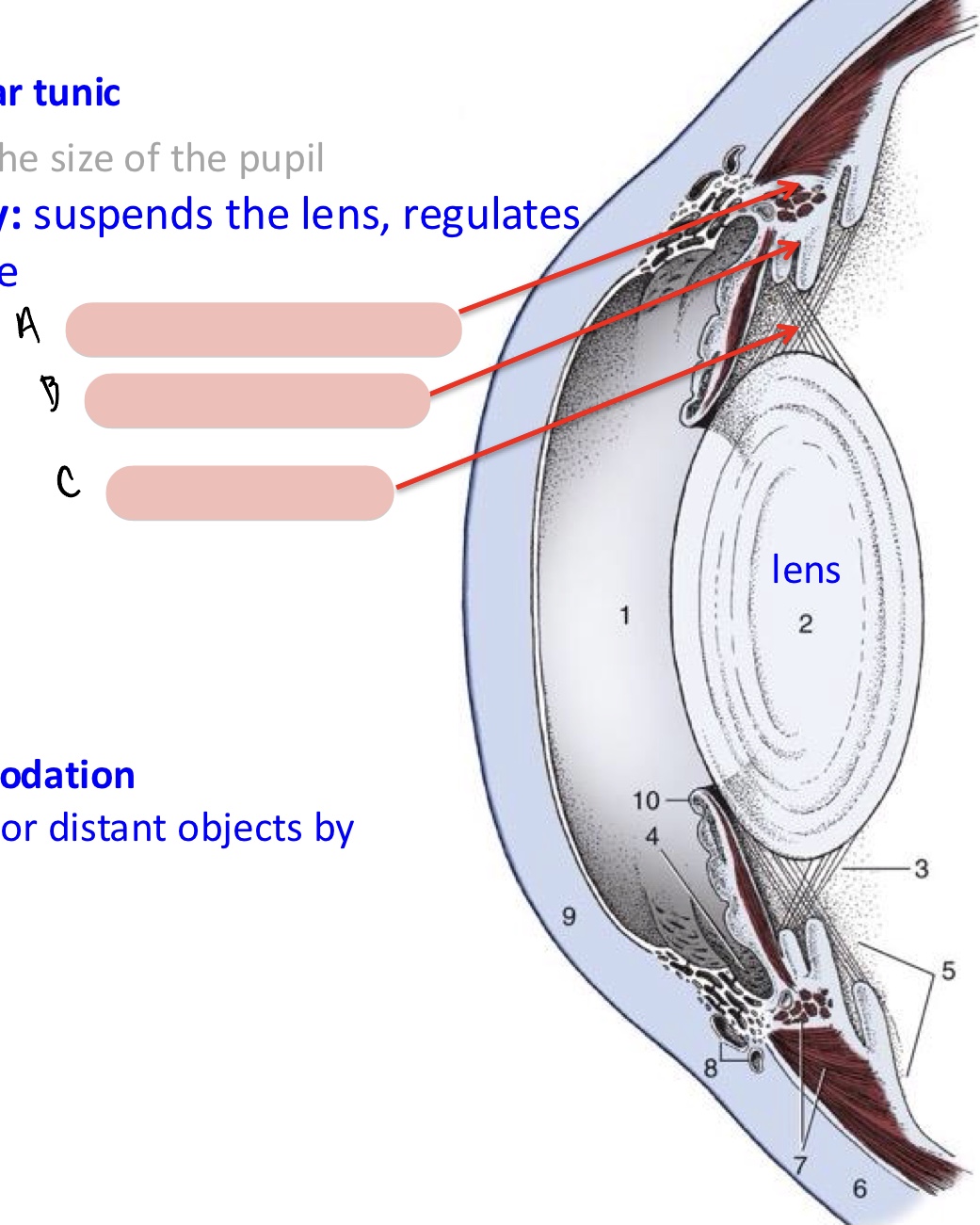
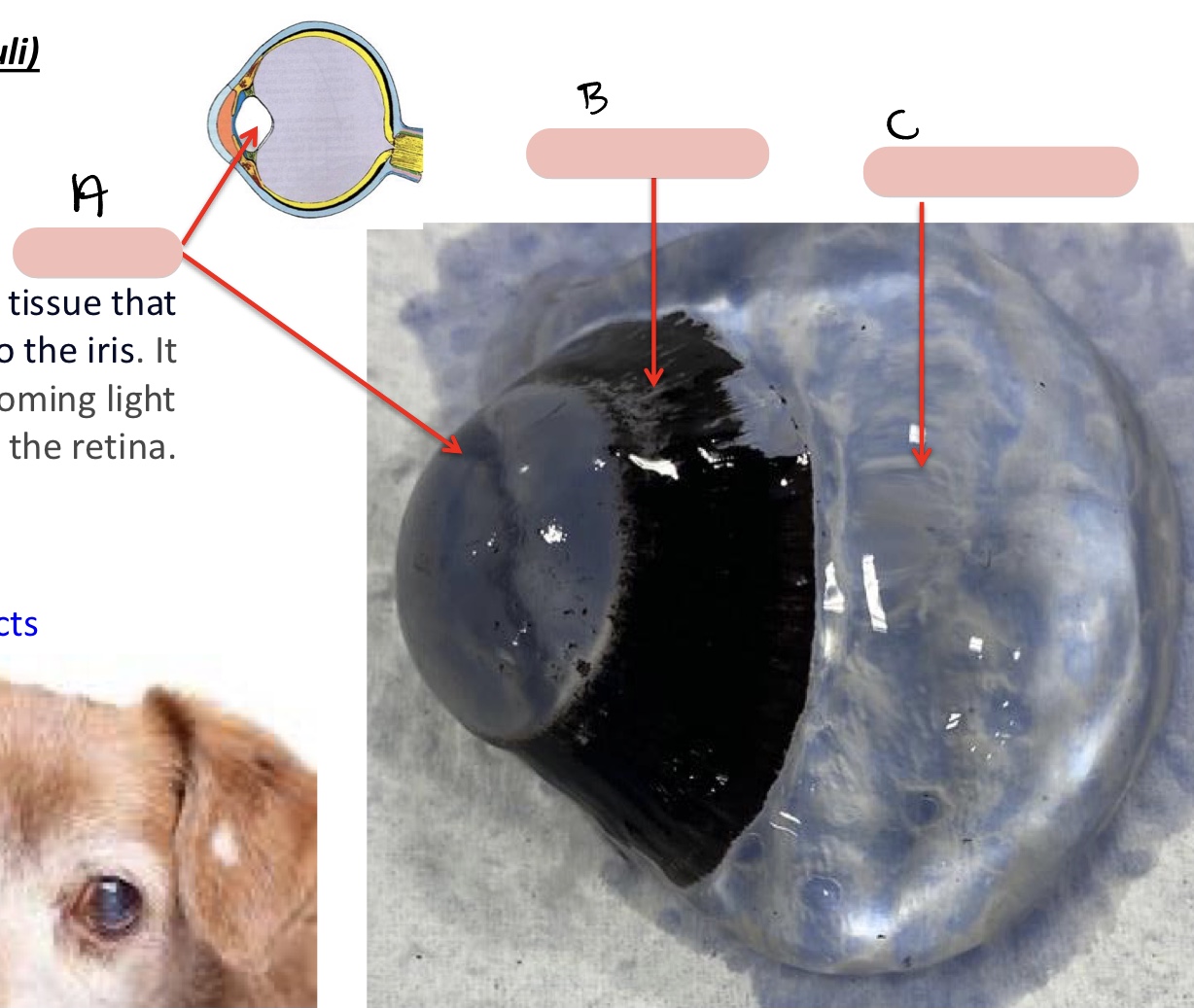
Name the structure(s) indicated by a, b, and c.
smooth ciliary m.
ciliary processes
zonular fibers
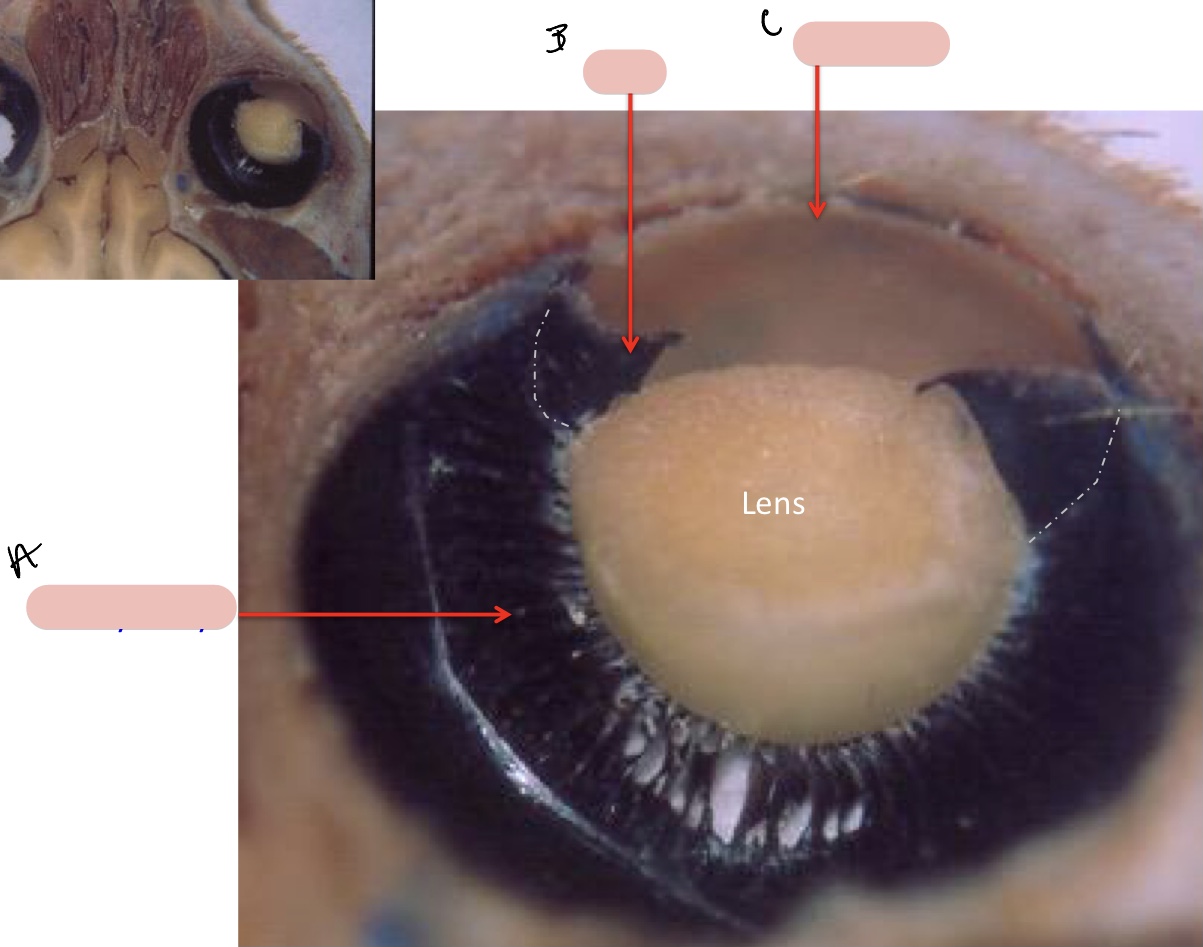
Name the structure(s) indicated by a, b, and c.
ciliary body
iris
cornea
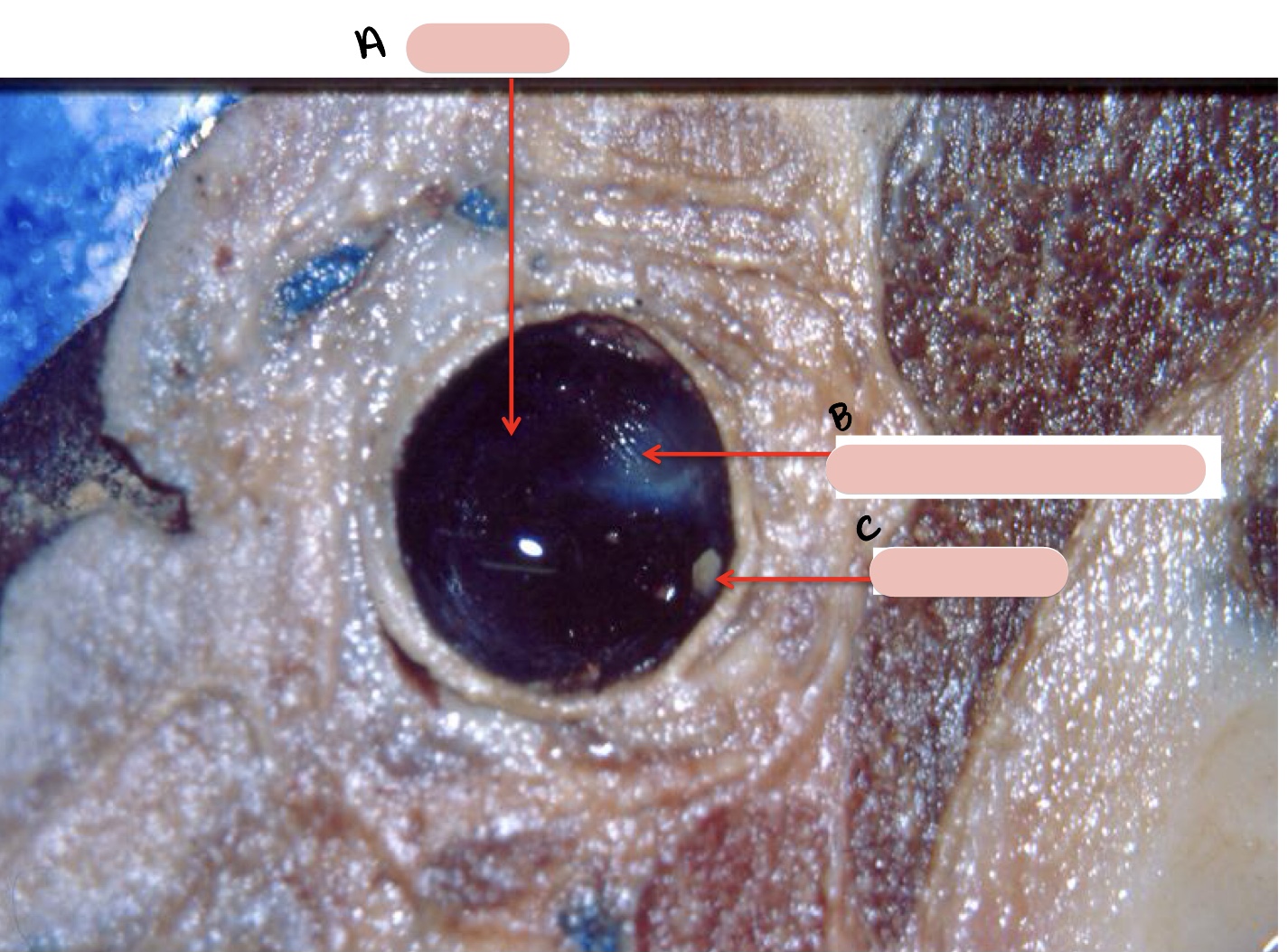
Name the structure(s) indicated by a, b, and c.
choroid
tapetum lucidum
optic disc
Name the structure(s) indicated by a, b, and c.
retina
choroid
sclera
Name the structure(s) indicated by d and e.
area centralis
optic disc
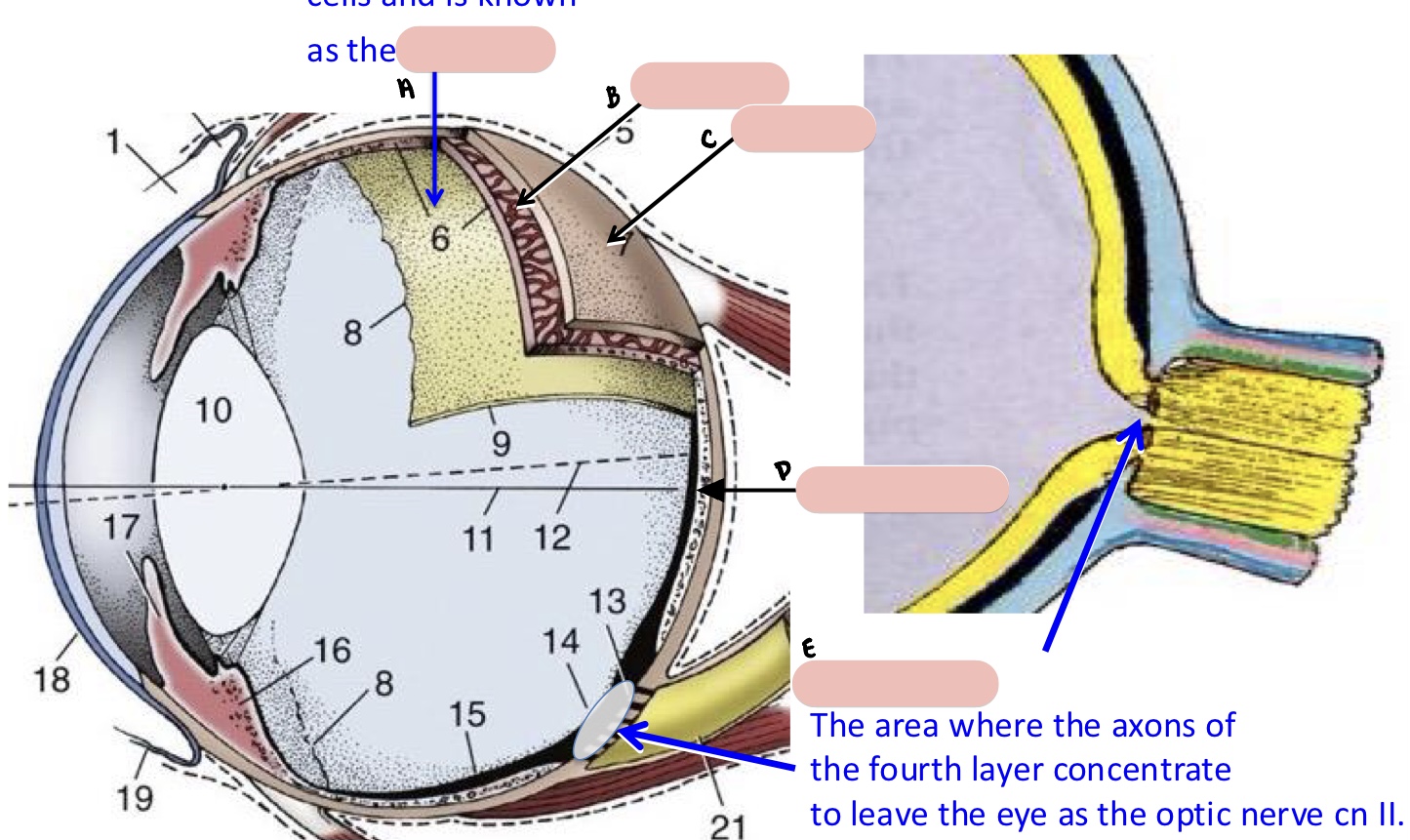
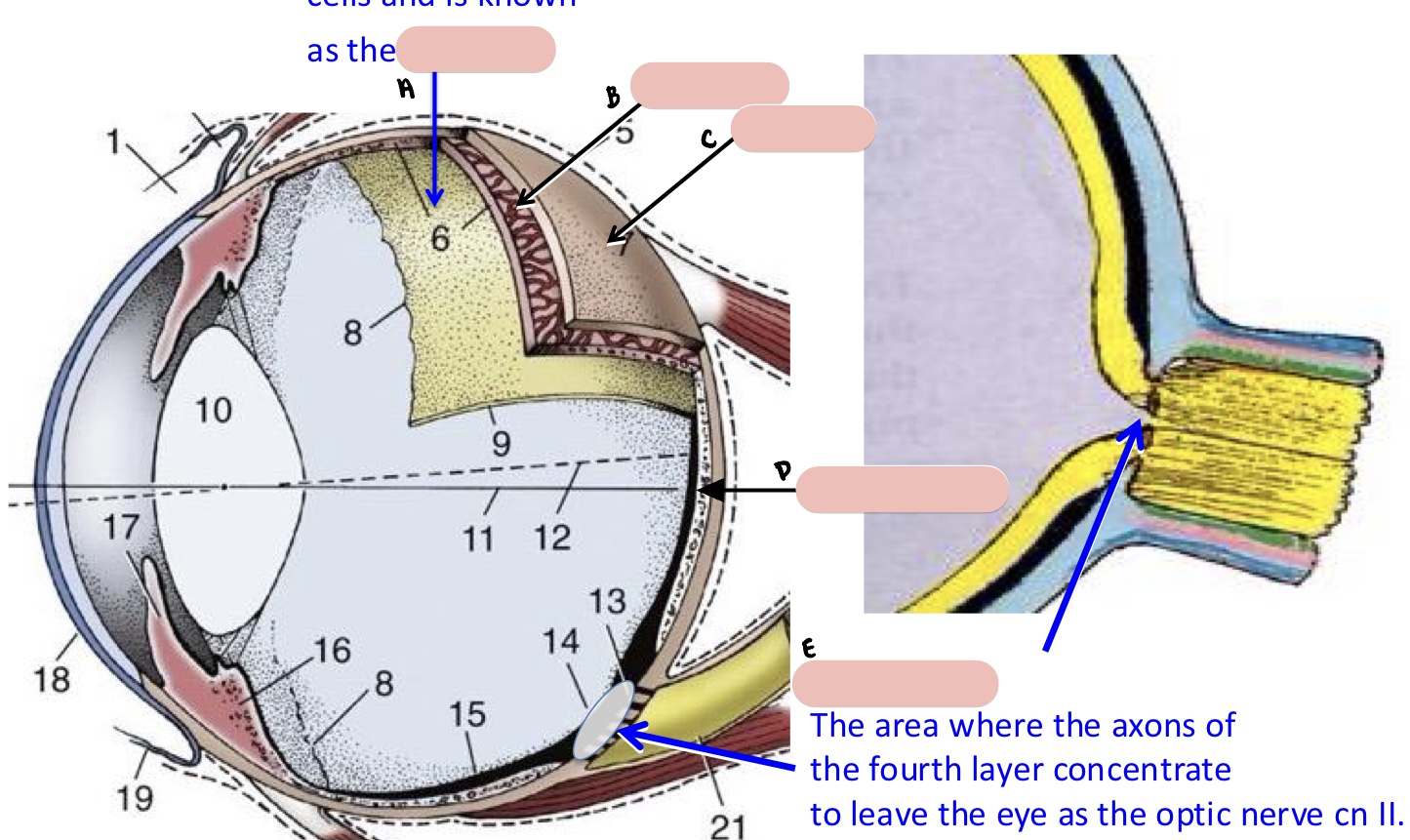
Name the structure(s) indicated by a, b, c, and d.
optic nerve
optic disc
tapetum nigrum
tapetum lucidum

Name the nerves and/or muscle damaged in images a, b, and c.
CN III, medial rectus
CN IV, dorsal rectus
CN VI, lateral rectus
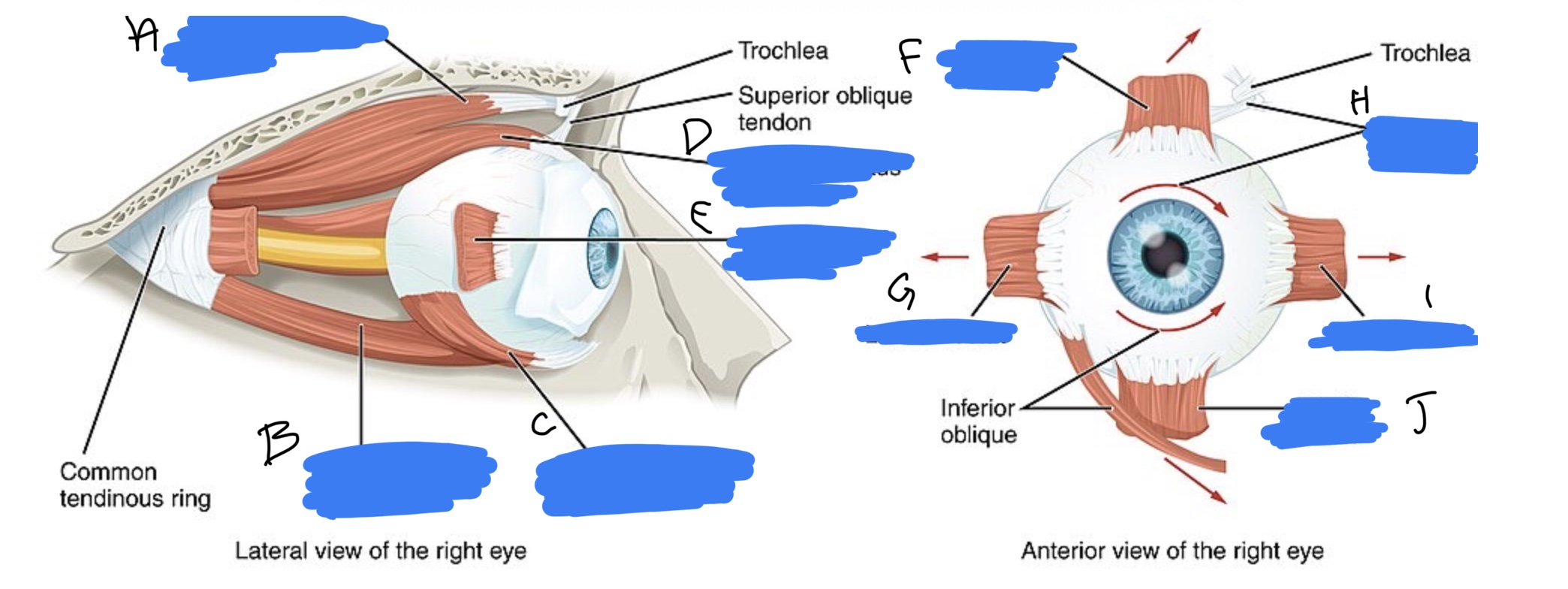
Name the structure(s) indicated by a, b, and c.
superior oblique m.
ventral rectus m.
inferior oblique m.
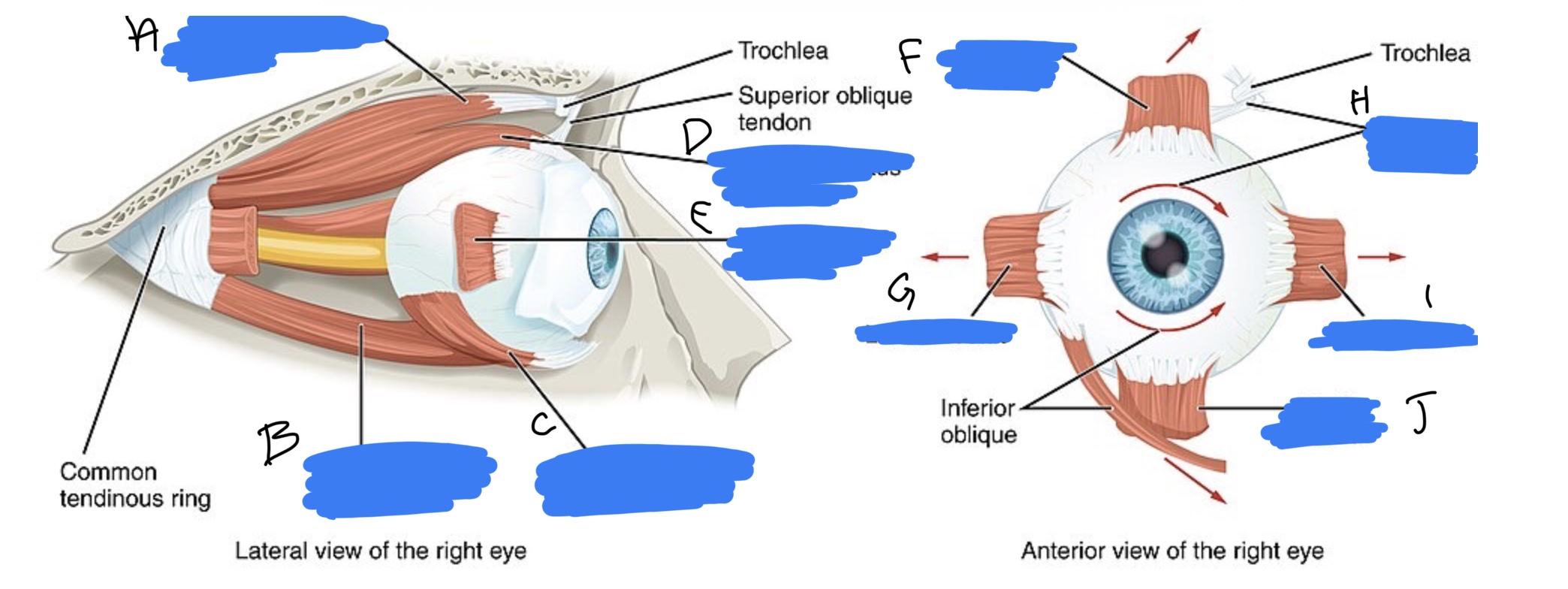
Name the structure(s) indicated by d, e, and f.
dorsal rectus m.
lateral rectus m.
dorsal rectus m.
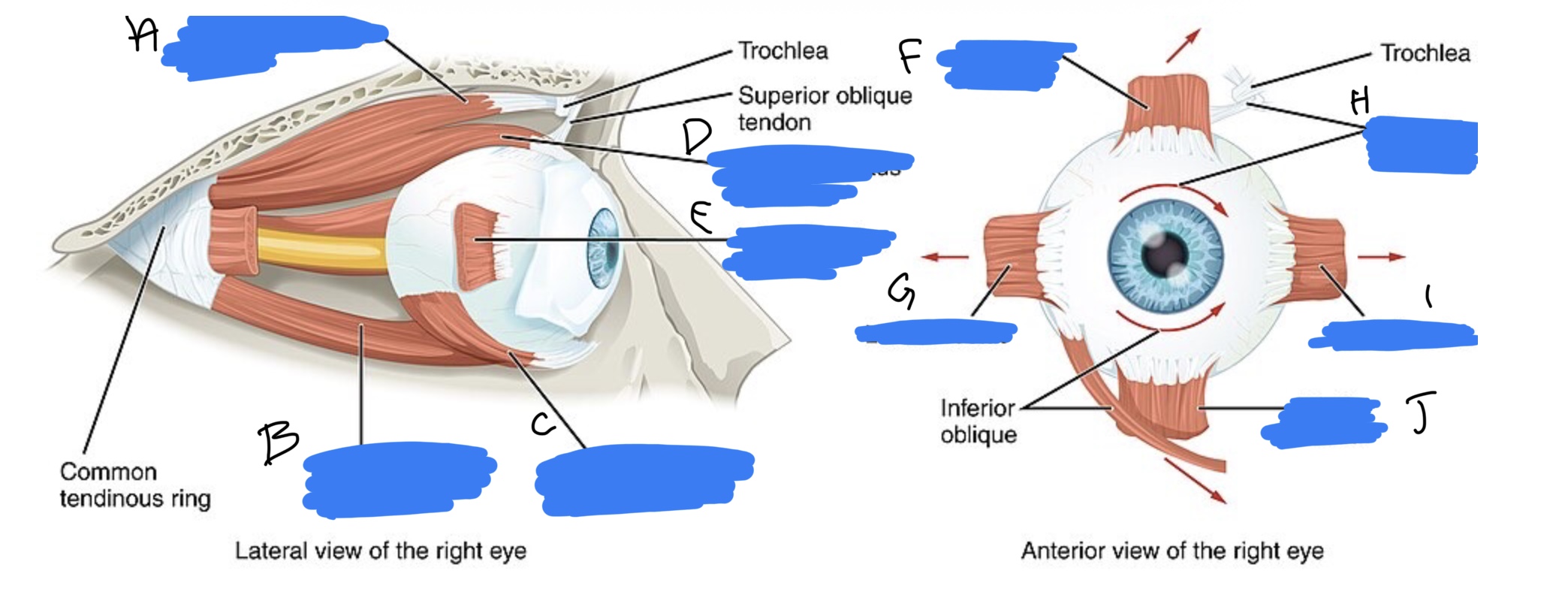
Name the structure(s) indicated by g, h, I, and j.
lateral rectus m.
superior oblique m.
medial rectus m.
ventral rectus m.
accessory (adnexa) organs of the eye
eyelids
tunica conjunctiva
lacrimal apparatus
extrinsic mm. of the eye
cranial nerves III, IV, and VI
orbital fascia