fatty acid oxidation
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
why is this needed
bc glucose isn’t the best storage molecule
adipocytes
fat cells, filled with lipid droplets that are small collections of fat
triacylglycerols
have 3 CH2 groups, each connected to a fatty acid via an ester linkage
fatty acid tails can be identical or not
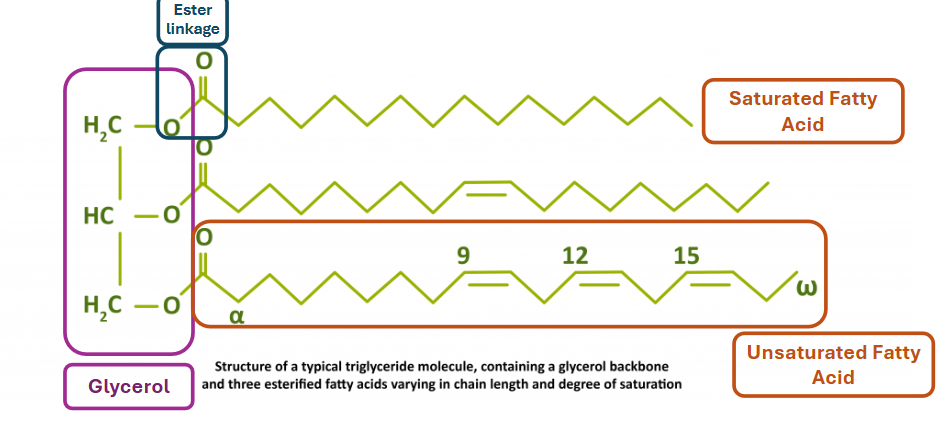
important enzyme
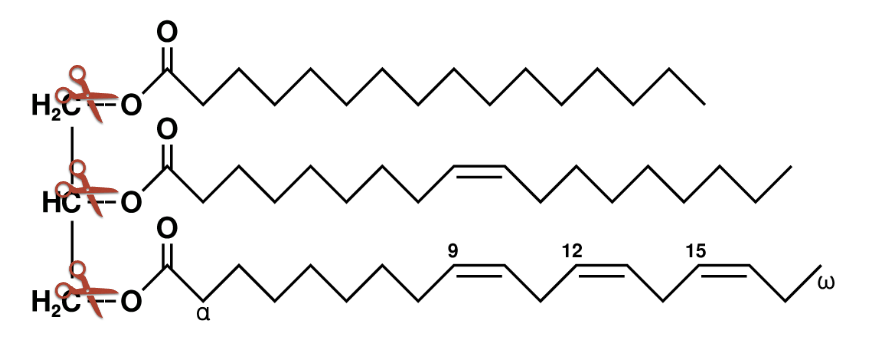
phospho/lipase - cleave glycerol and releases the tails as single fatty acids
works in a similar way to chymotrypsin
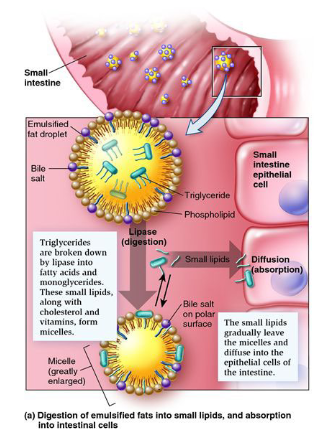
what happens to fats after being eaten
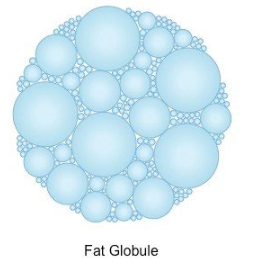
they’re grouped in the stomach as lipid droplets via the hphobic effect as large fat globules
enzymes can’t access the triacylglycerols
fat digestion steps
emulsification
lipases act and fats cross
remake triacylglycerols
package triacylglycerols into chylomicrons
lymphatic and circulatory system
step one of fat digestion - fat emulsification
the triacylglycerols are in the fat globules
body releases bile salts and their hphobic side binds to the fat globule so the hydrophilic is on the outside
separates lipid droplets into manageable sizes and makes them moveable
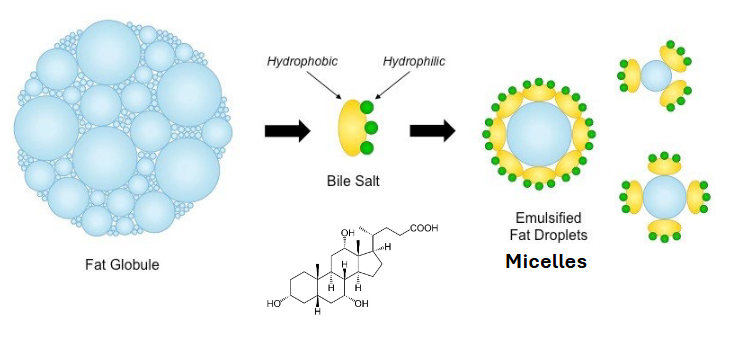
bile salts
are amphipathic - have hphilic and hphobic sides
hphobic sides binds to the fat globule so the hphilic is on the outside
allows for hphobic fat to be transported through our hphilic body
step 2 of fat digestion - lipases
now that the triacylglycerols are in smaller droplets, the lipases can access them and pull out indiv triacylglycerols
lipases cleave them into fatty acids and glycerol
both are then imported across small intestine cell membrane via diffusions
steo 3 and 4 of fat digestion
fatty acids are remade into triacylglycerols in the smooth ER
then packaged into a chylomicron for transport into the lymphatic system
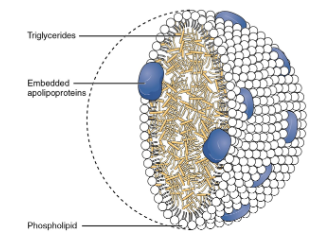
chylomicron
have a layer of phospholipids on the outside - hphobic tails interact with triacylglycerols and hphilic heads allow for movement throughout the body without clogging up blood cells
filled with triacylglycerols and has proteins imbedded in the phospholipid monolayer
step 5 of fat digestion
chylomicrons undergo exocytosis and enter the lacteal, then move throughout the lymphatic system and can enter the blood stream
in blood stream, lipases convert the triacylglycerates into fatty acids and glycerol again until they’re imported into a target
2 target cells for fat digestion
fat cells - converted back into triacylglycerate for longer term storage
muscle cells - oxidized for energy
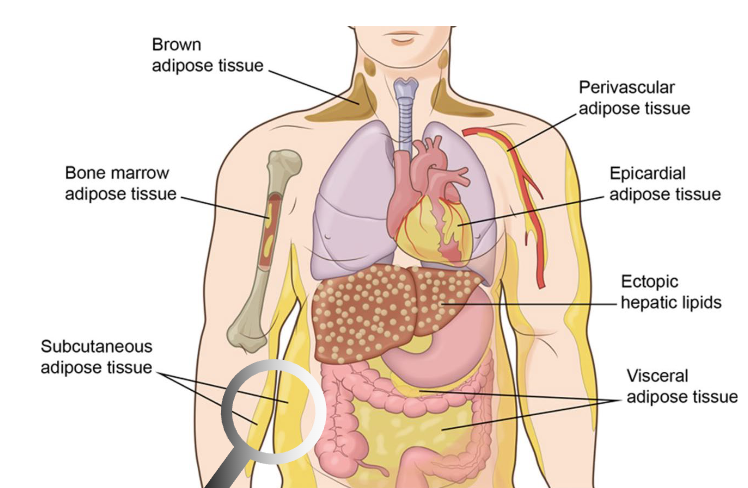
3 important types of fat
subcutaneous - fat storage, first to be lost in weight loss
visceral - fat under muscles, protects organs
brown - fat that runs etc, makes atp and heat
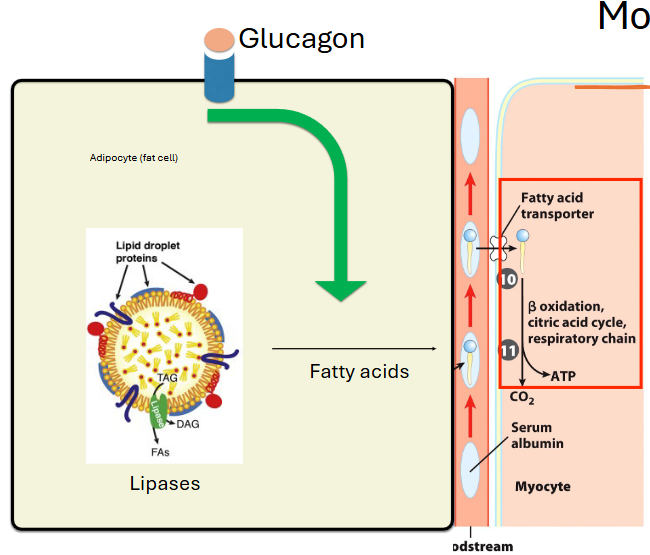
how to mobilize fat from fat cells for use
low blood sugar signals for glucagon hormone to be released, which binds to receptors on the surface of adipocytes and causes a signal cascade
cascade triggers activation of lipases on the surface of lipid droplets within the cell so they break down triacylglycerols
the fatty acids enter the blood stream and bind to albumin, then enter cells via a transporter and go to the mt
serum albumin
most plentiful rotein in blood plasma by mass
can carry 10 fatty acids and shields the hphobic tails from water
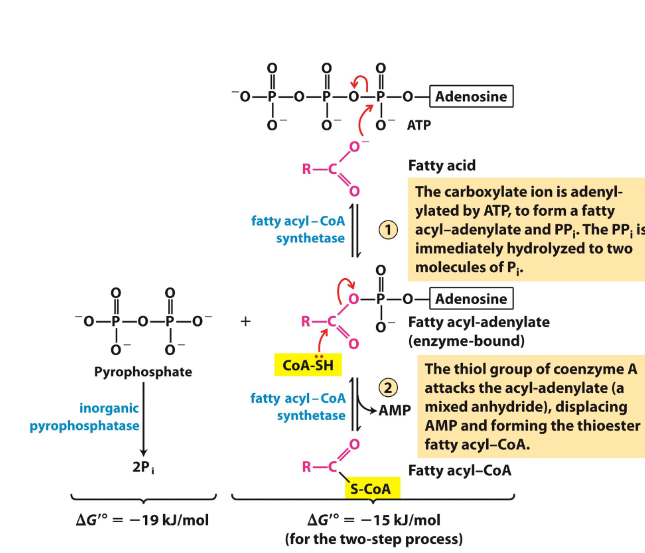
fatty acid oxidation: 1
before entering the mt, the fatty acids (no glycerols) need to be activated by fatty acyl-coa synthase - convert the fatty acid into fatty acyl-coa
uses atp and makes a high energy thioester bond - energetically favorable - and the other 2 phosphate groups are converted into Pi which is also favorable
turns atp → amp and uses coa bc amp and coa are both good lg
don’t need to know mech
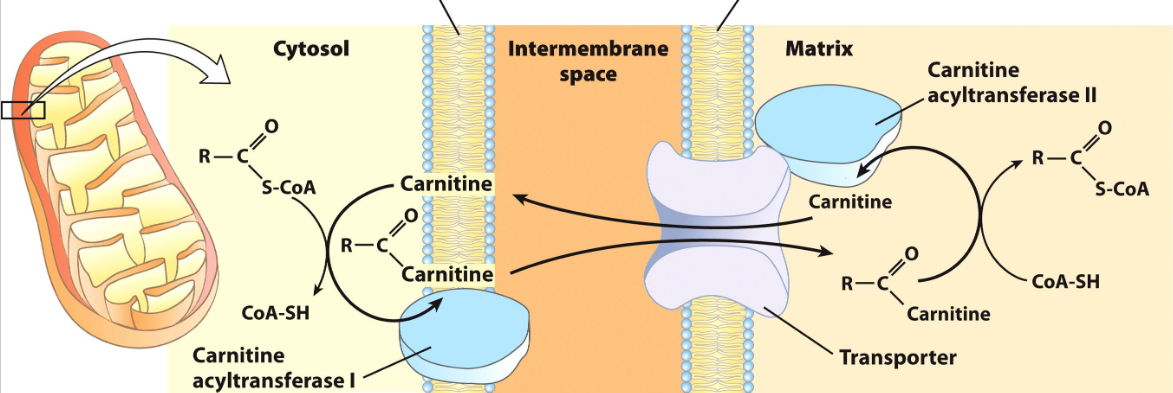
fatty acid oxidation: 2
entering the mt is the rate limiting step
fatty acids move from coa to carnitine acyl transferase i to cross the outer mt membrane (bc coa good lg) into the intermembrane space
then fatty acyl carnitine moves into the mt matrix through acyl carnitine transporter protein
fatty acyl transferred back onto a coa by carnitine acyl transferase ii
makes fatty acyl-coa now in the mt
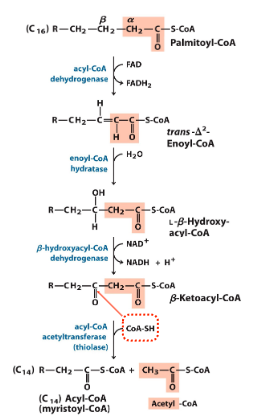
fatty acid oxidation: 3
beta oxidation
takes place in mt, goal is to fully oxidize c in fatty acid and does this by chopping fatty acid glycerols into acetyl coas (2C at a time) and adding a carbonyl (makes bond more unstable)
4 steps of beta oxidation
acyl coa dehydr → dehydr to gen 2x bond btwn alpha and beta C
enoyl coa hyratase → hydr to add water and make OH on beta C group
beta hydroxy acyl coa dehydr → dehydr to gen carbonyl on beta C
thiolase → acyl transfer so coa-sh nucleophilic attack and cleaves off acetyl-coa
acetyl-coa and fatty acid tail (-2C) are released
2C from fatty acid tail cleaved at a time
identical to last 3 steps of TCA (succinate → fumarate → malate → oaa)
if tail has X number of C
goes through X/2 rounds of beta oxidation, releases (X/2) + 1 acetyl coa
releases X/2 NADH+H and (X/2 - # 2x bonds) FADH2
uses 2((X/2)+1) coa - basically 2*acetyl coa
e- carriers to ATP
1 FADH2 = 1.5 ATP
1 NADH+H = 2.5 ATP
per 1 FADH2 or NADH+H, 0.5 O2 was used in ETC
to find total fatty acid to atp, just multiply w/ num made
acetyl coa to ATP
acetyl coa goes through etc and tca so:
Y acetyl coa → 3*Y NADH, Y FADH2, and Y GTP
GTP ~ ATP energy wise
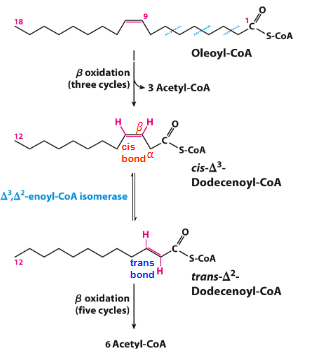
with unsaturated fatty acids
enzymes need trans double bond to work with BUT most naturally occurring 2x bonds are cis so need to isomerize and shift 2x bond up 1C to make it trans
skip the first step (so no FADH2 generated) and start at the second step
less saturated fatty acids = less energy bc make less FADH2 (bc the molec is already partially oxidized and less e- to harvest)
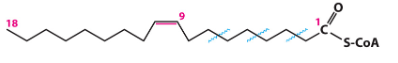
how are 2x bonds dealt with
beta oxidation occurs as normal (each round = blue squiggle) until reach point where beta C in 2x bond
d3, d2-enoyl-coa-isomerase isomerases to get the 2x bond btwn alpha and beta C so it can join the normal path at step 2
beta oxidation yield from one round
CX + coa + FAD + NAD+ + H2O → C(X-2) + acetyl-coa + fadh2 + nadh
overall beta oxidation equation
XC + Y O2 + Z ADP + ZPi + coa → Z ATP + Y H2O + some CO2
under starvation conditions, what happens
oaa is diverted to gng to make more glucose without being replenished from other sources
causes the tca cycle to slow bc dec oaa for fisrt step
inc [acetyl coa] bc not being used and free [coa] dec
causes fatty acid oxidation to dec
how does the body cope with the dec of free coa under starvation
generates ketone bodies that move around in body, which can by used by tissues for energy pdction and regens coa
tissues like brain and muscles and heart but NOT liver cause this happens there
forming ketone bodies
made in liver cell mt
don’t need to know struct
2 acetylcoas get smushed together to make acetoacetyl-coa (releases 1 coa-sh), which gets converted to beta-hydroxy-beta-methylglutaryl-coa when another acetyl-coa and water is added (releases 1 coa-sh). then gets turned into acetoacetate (releases 1 coa-sh) and converted into acetone and beta-hydroxybutyrate (using nadh and releasing co2)
acetone exhaled as waste
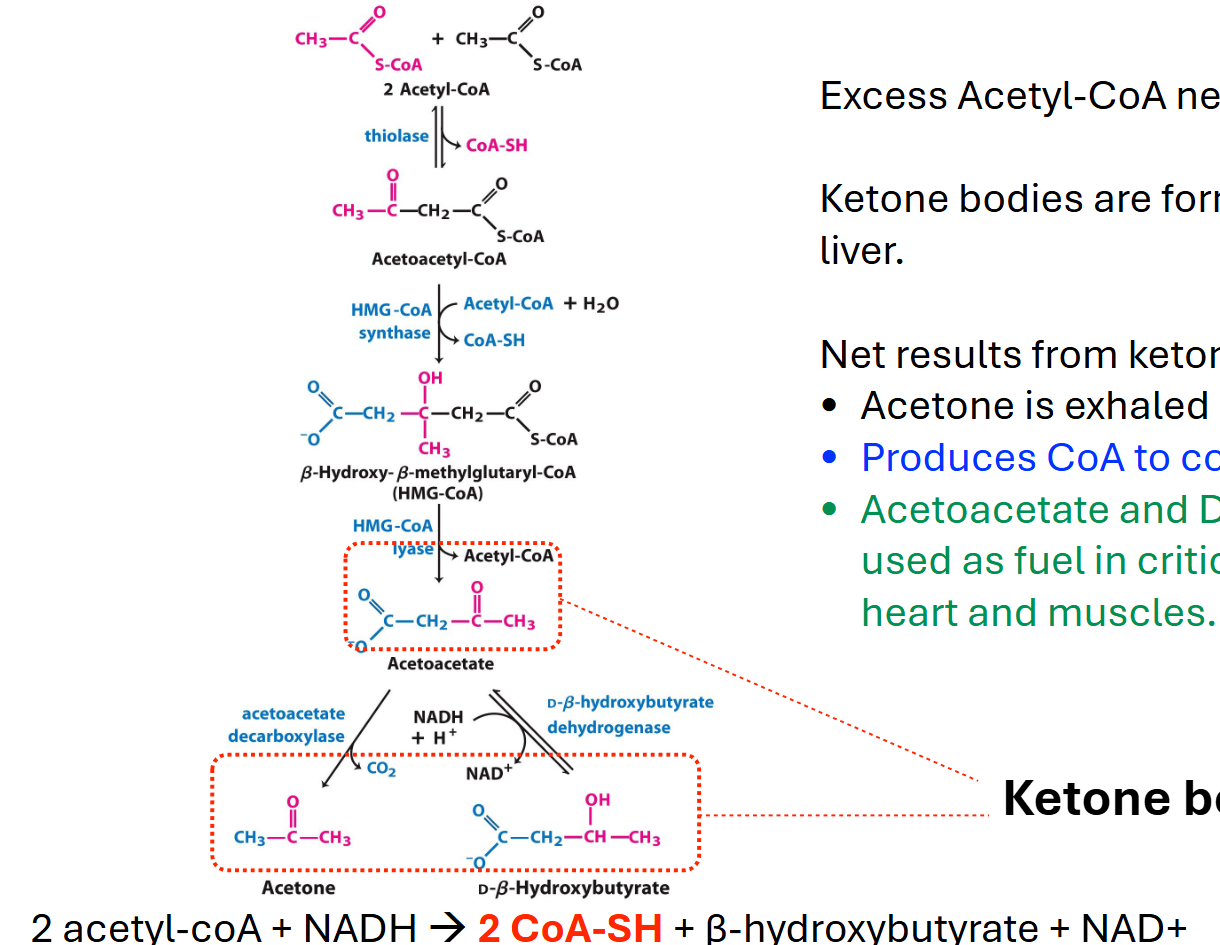
ketone bodies
acetoacetate, acetone, beta-hydroxybutyrate
hydroxybutyrate and acetoacetate can be used as fuel but acetone exhaled as waste
why ketone bodies?
beta-hydroxybutyrate can be converted back into acetoacetate
adding coa activates acetoacetate → acetoacetyl-coa
acetoacetyl-coa is cleaved by thiolase to make 2 acetyl-coa
that can enter the tca
allow for fatty acid oxidation in liver to cont and supply alt fuel