Cell Transport - DP1 Biology
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
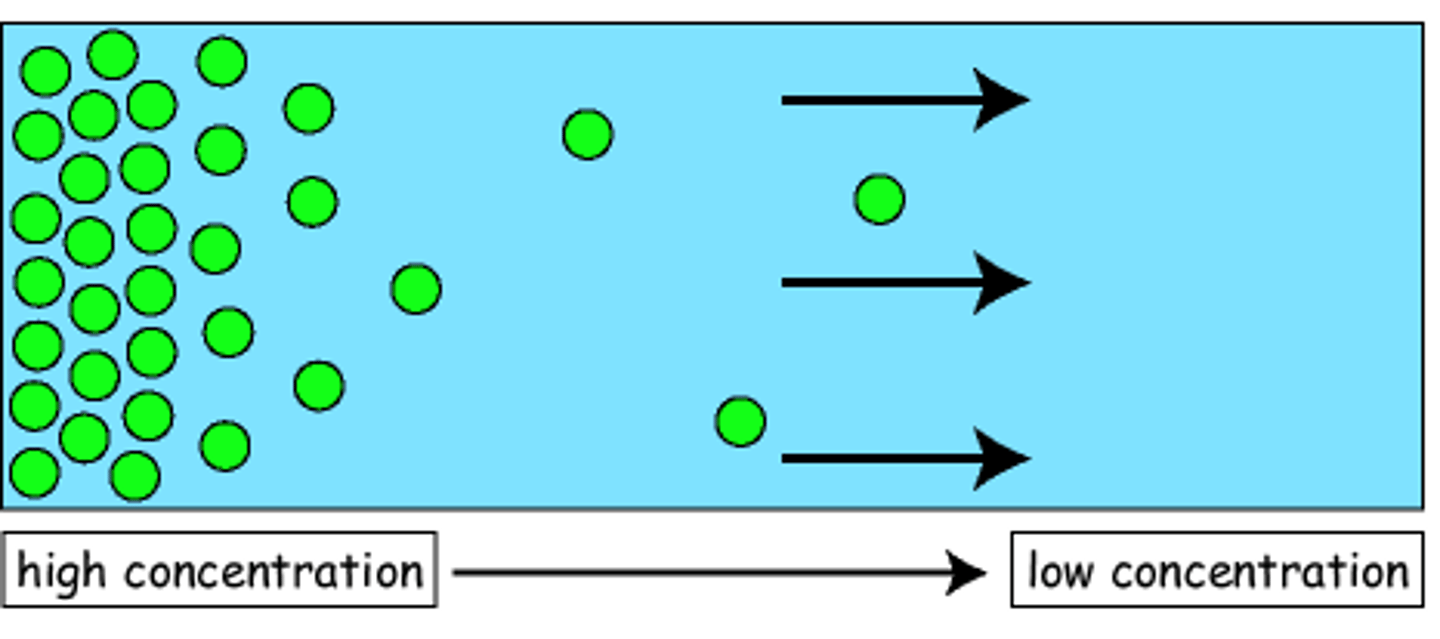
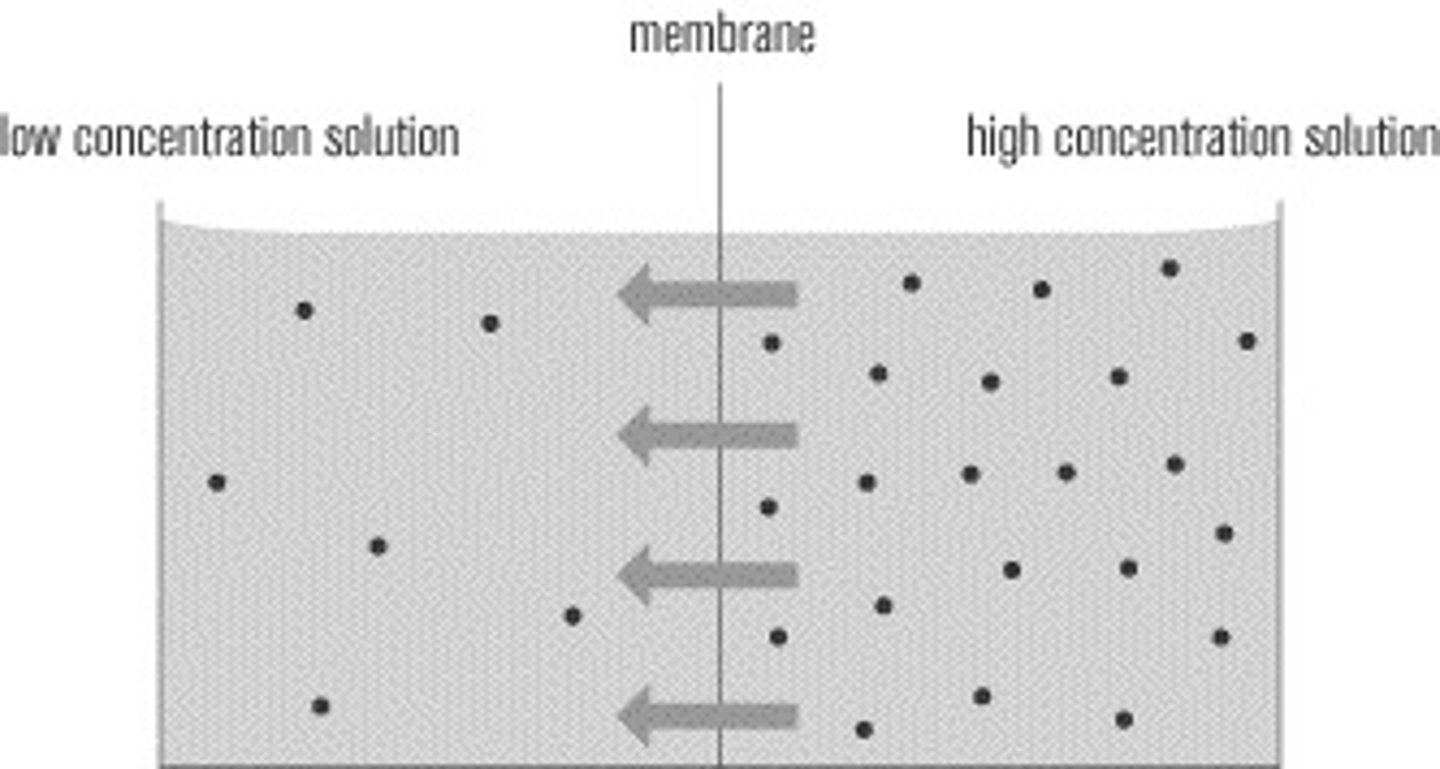
Diffusion (simple)
Net movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration.
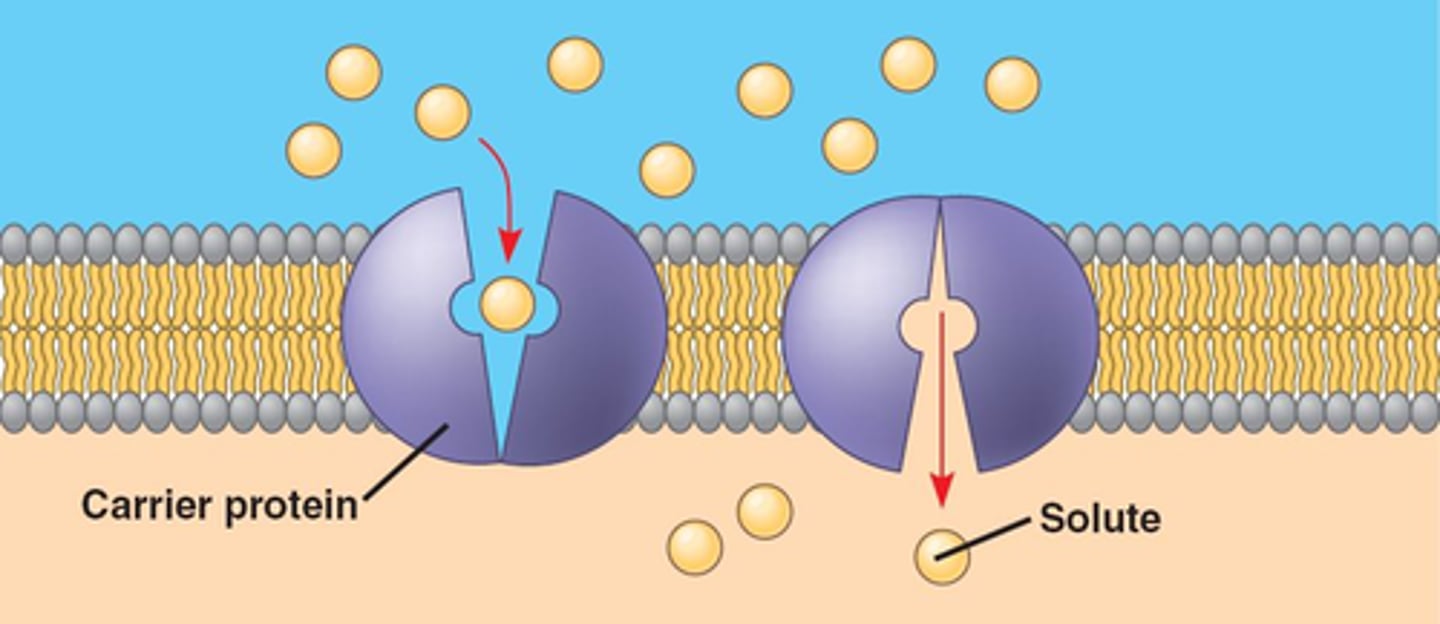
Facilitated Diffusion
Movement of specific molecules from high to low concentration across cell membranes through protein channels or carriers
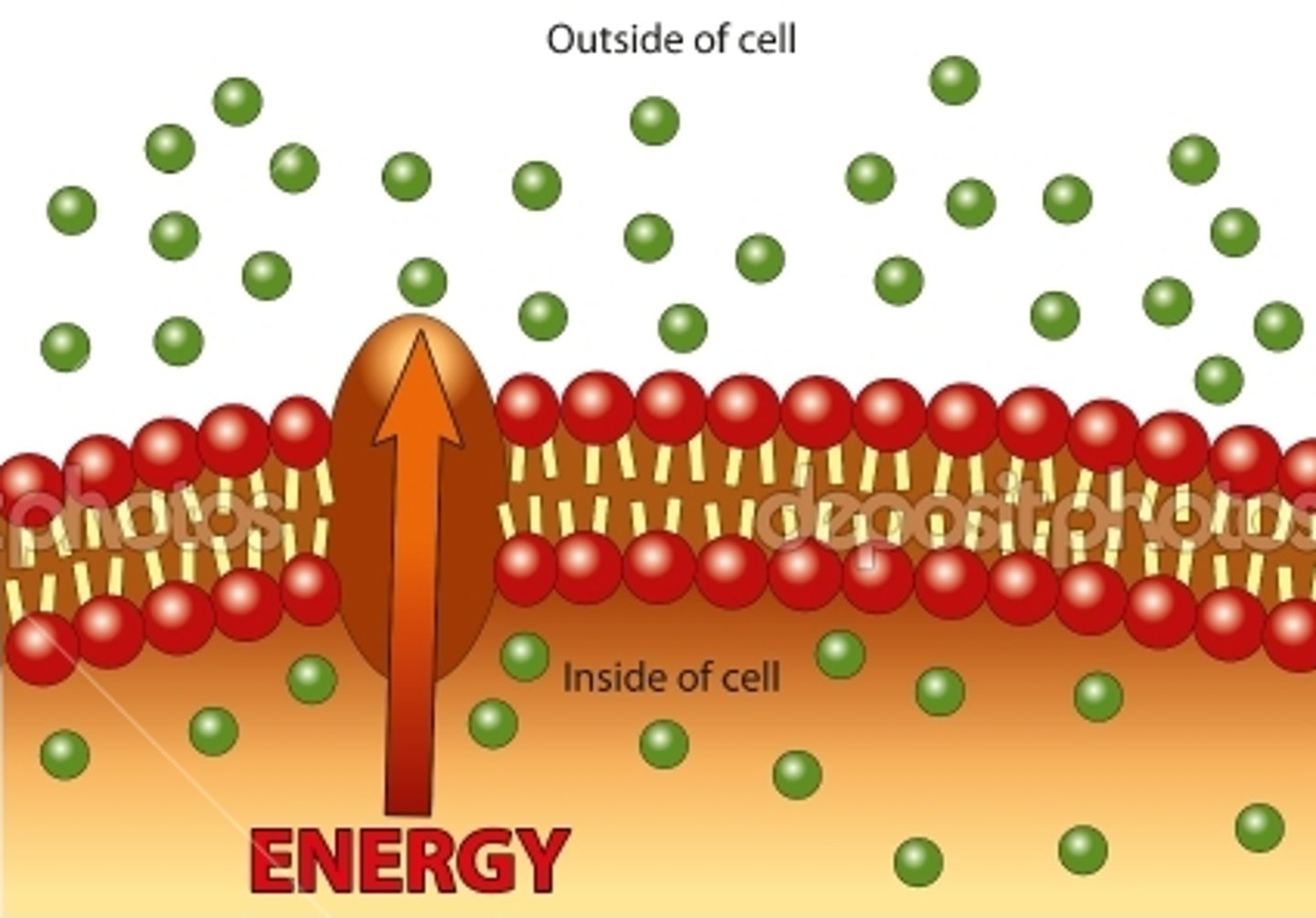
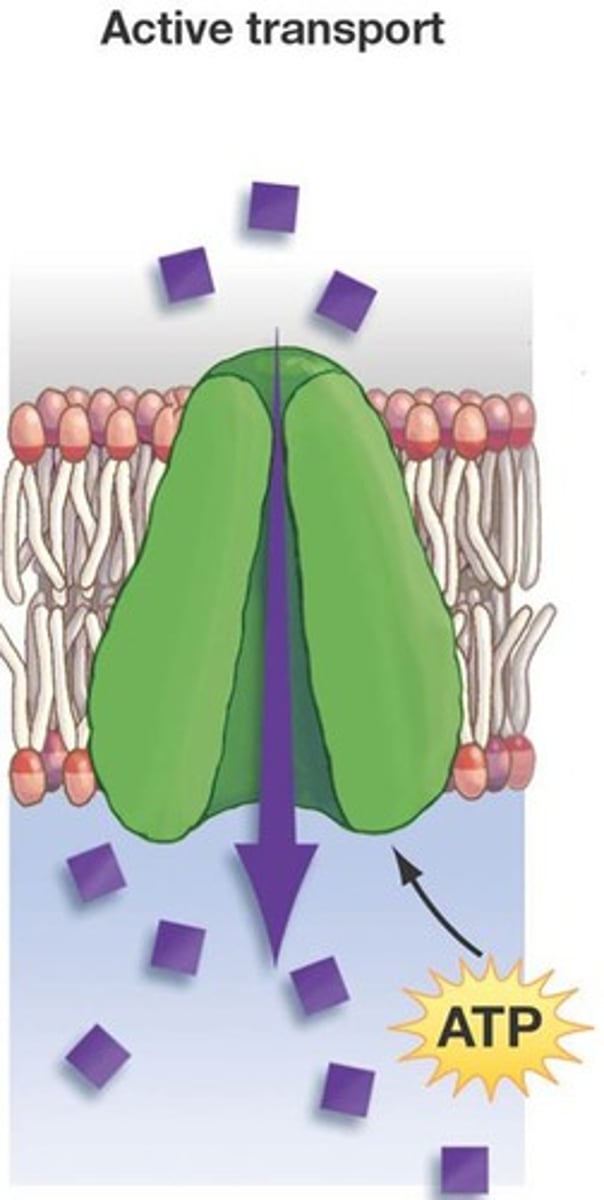
Active Transport
The movement of materials through a cell membrane using energy, proteins, and moving from low to high concentration.
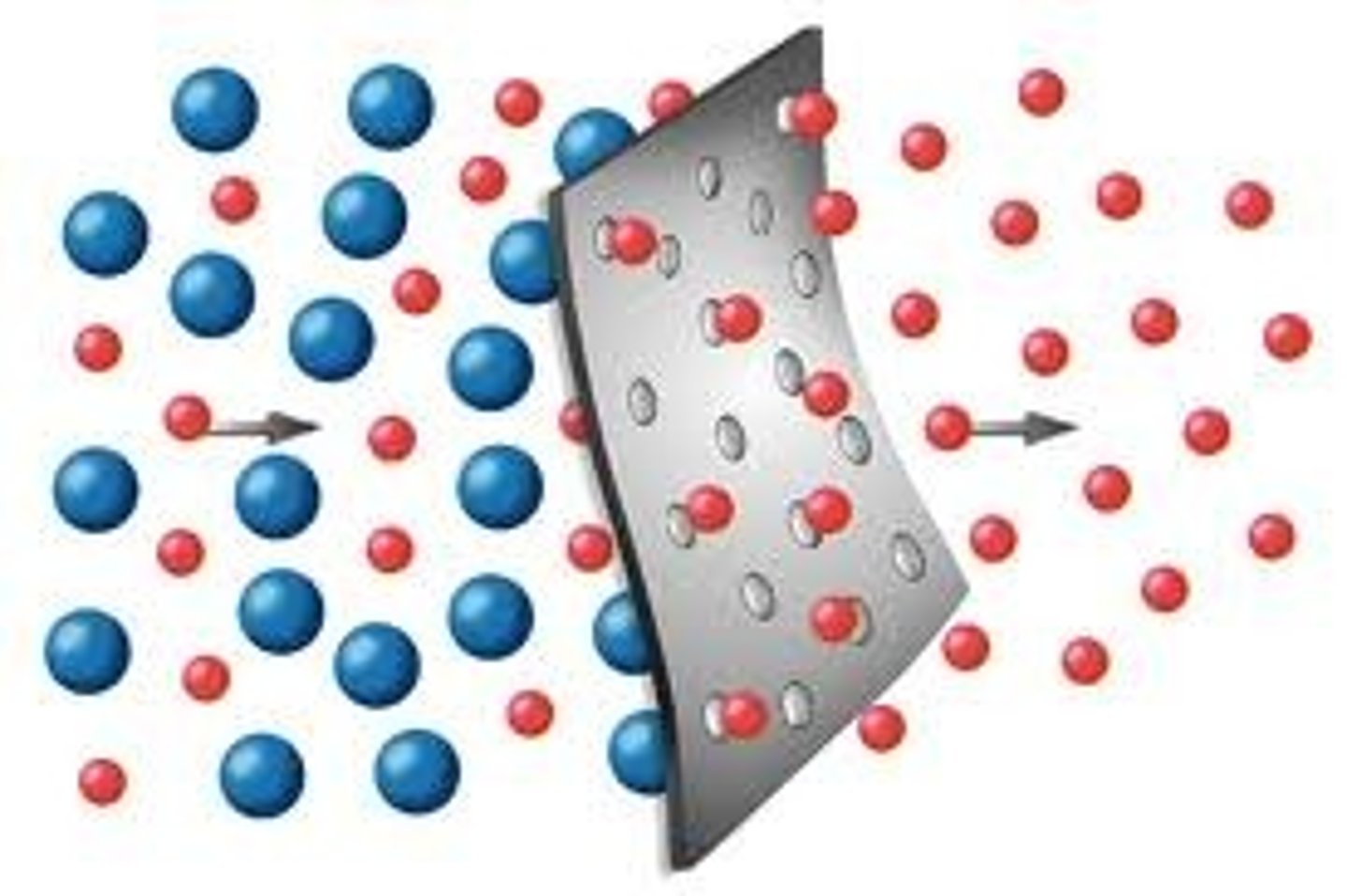
Selectively Permeable
Cell membranes that allow some substances to pass through, while not allowing others to pass.
Passive Transport
The movement of substances across a cell membrane without the use of energy by the cell and molecules moving from high to low concentration
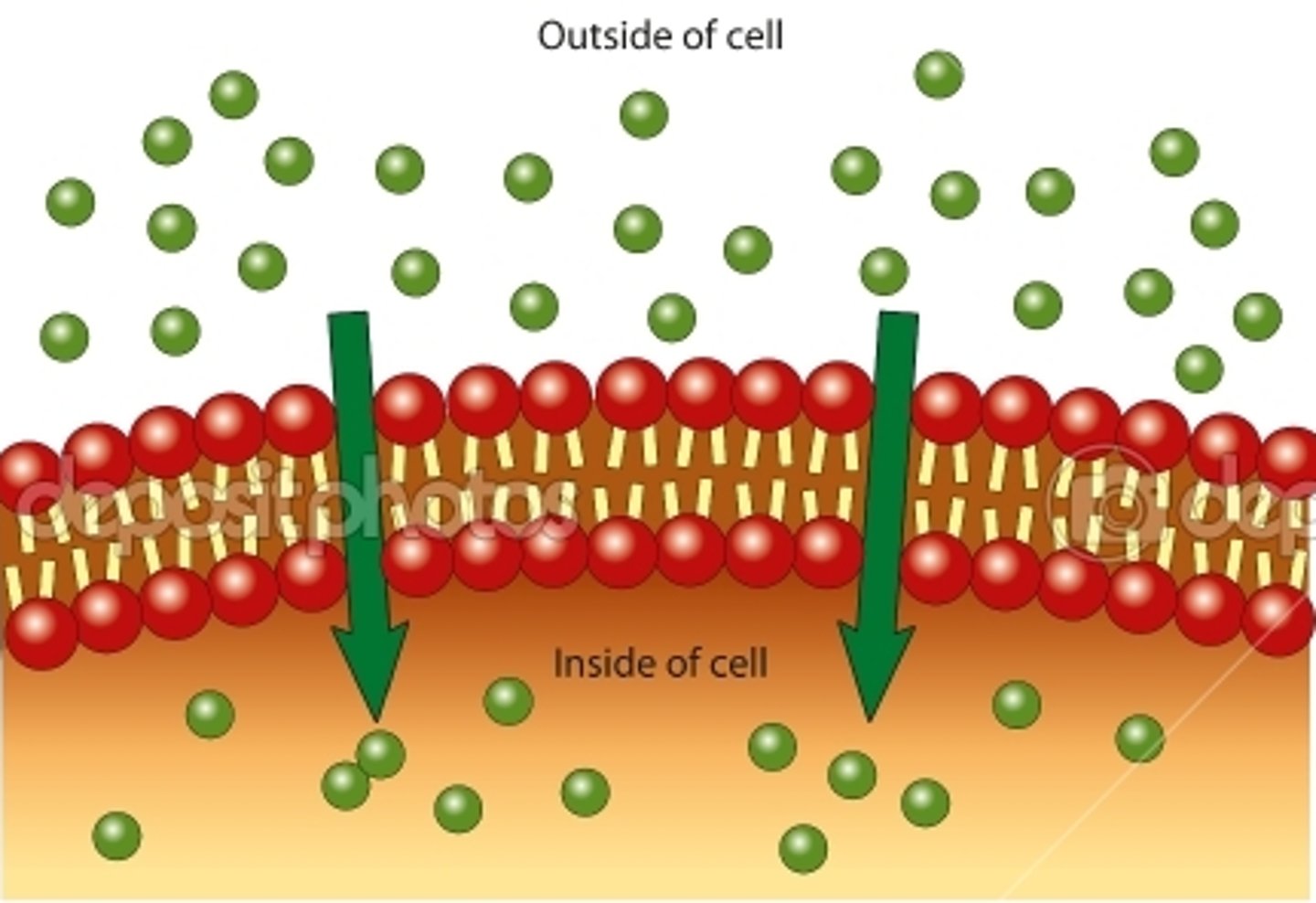
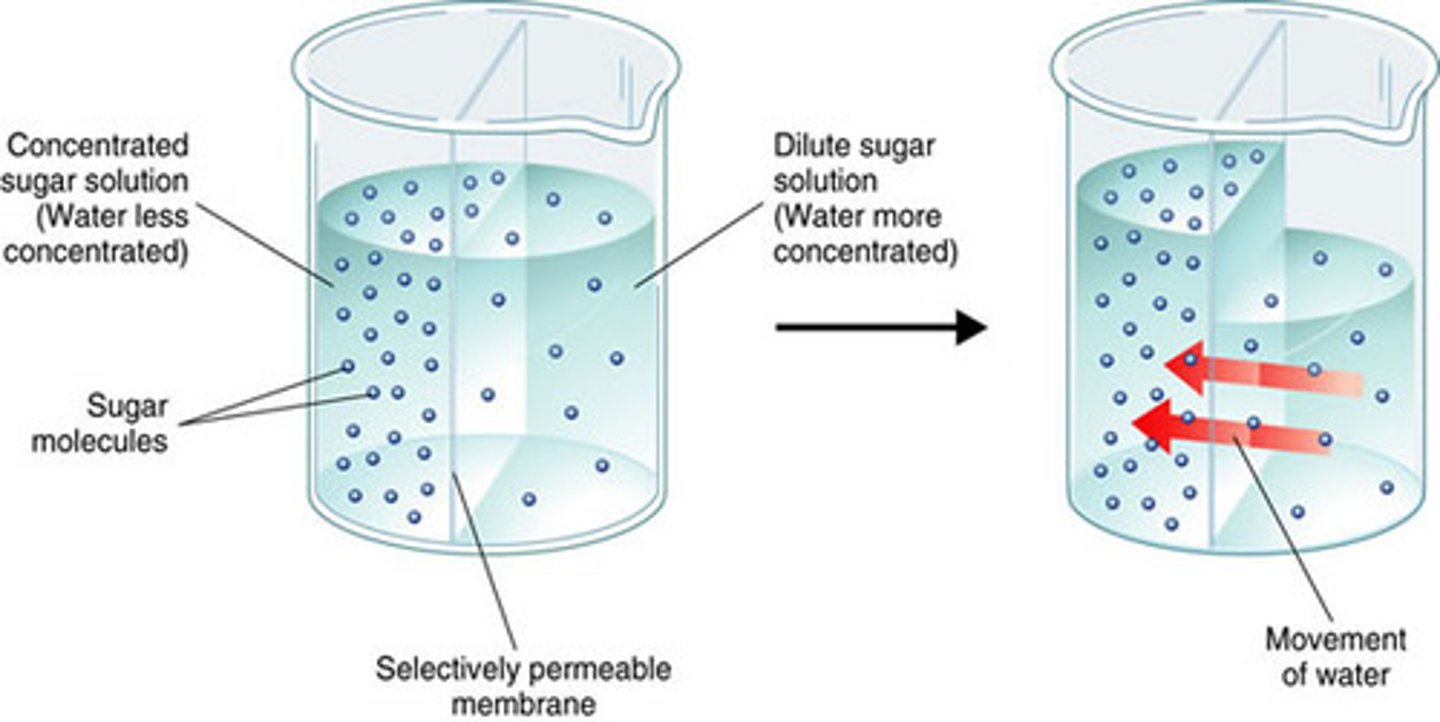
Osmosis
Passive diffusion of water from an area of low solute to an area of high solute through a selectively permeable membrane.
hypotonic environment
A cell placed in this environment GAINS water because there is less solute & more water around the cell.
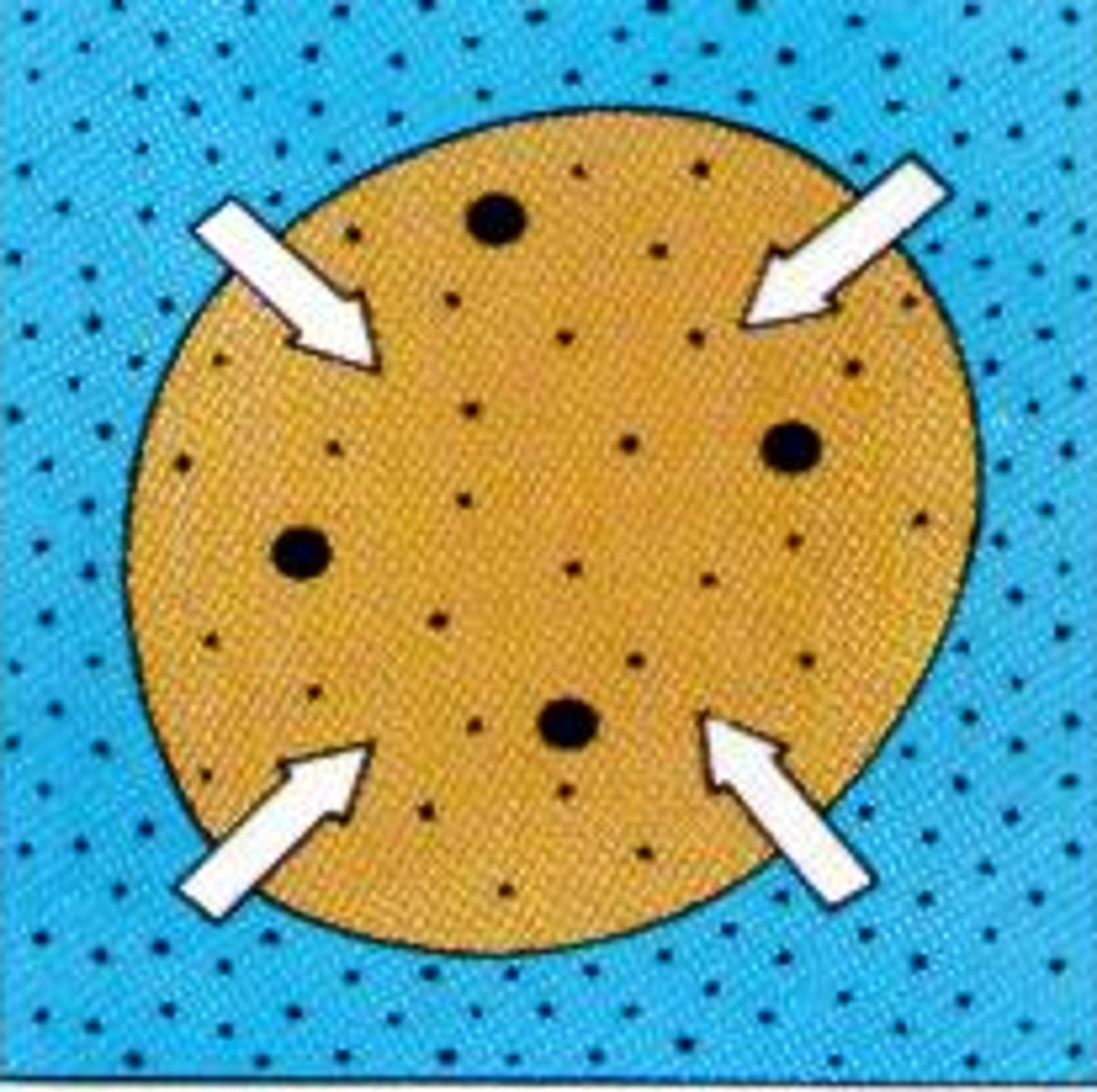
hypertonic environment
A cell placed in this environment LOSES water because there is more solute & less water around the cell.
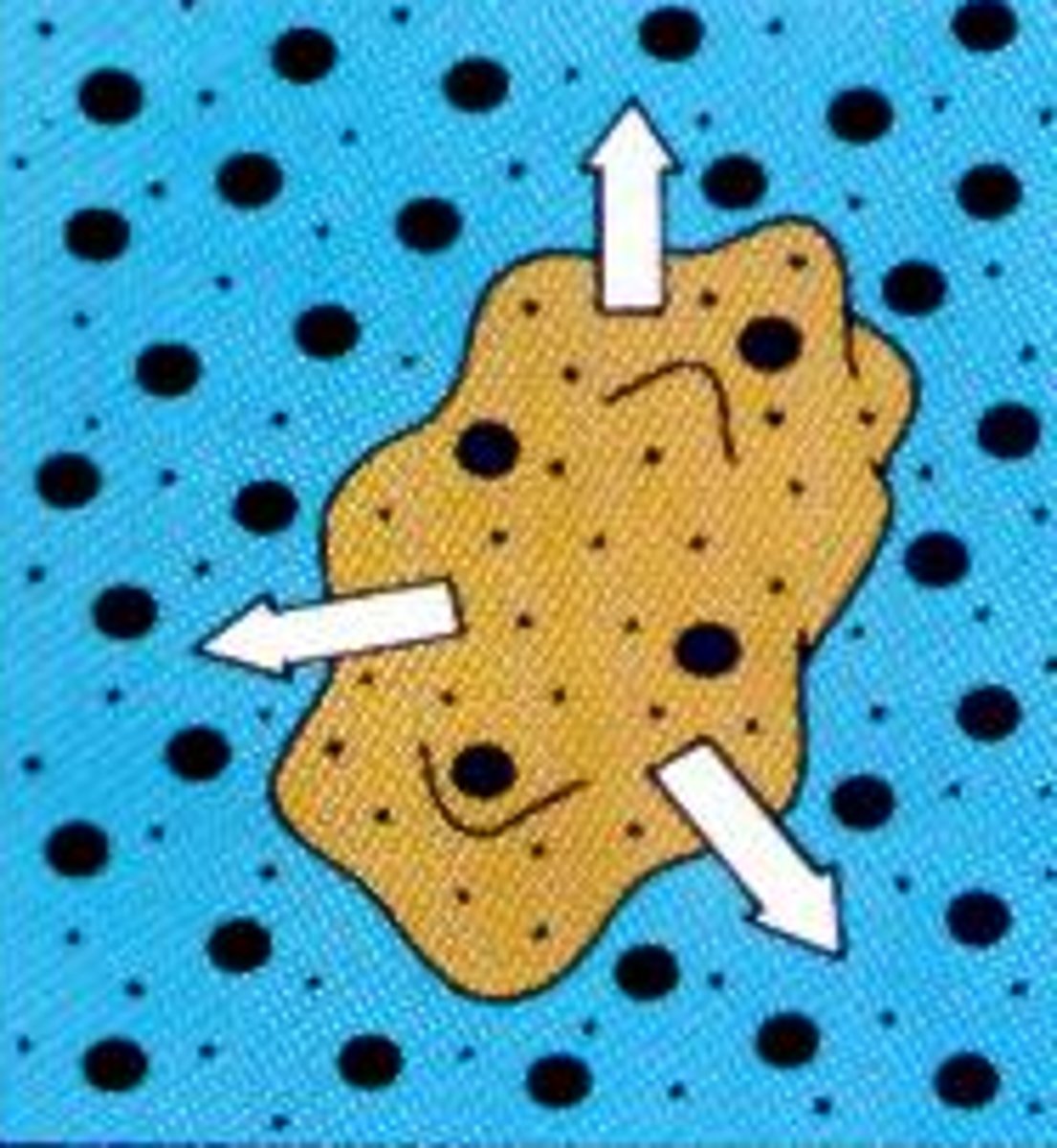

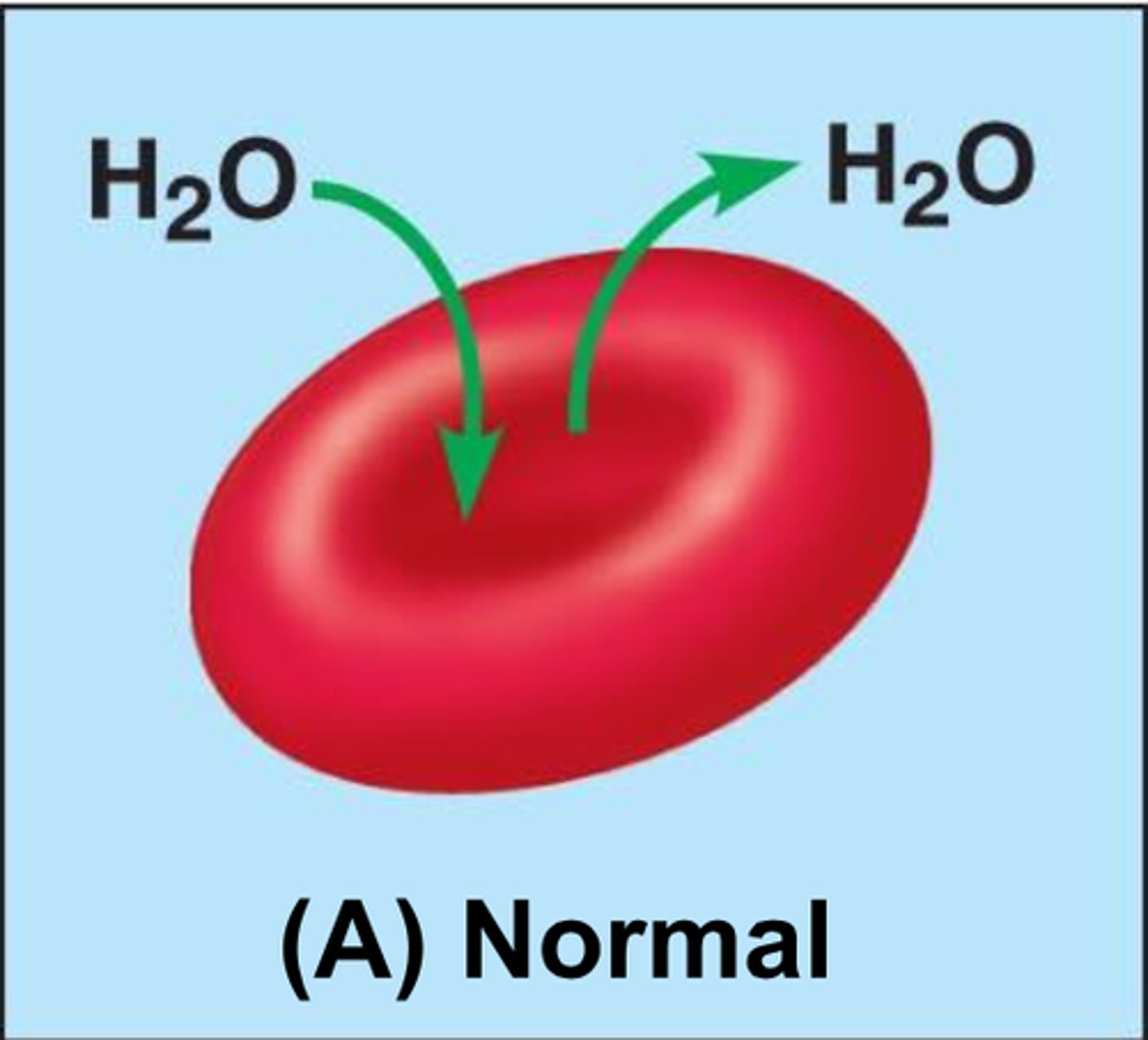
Isotonic
An equal balance of water moving in and out of the cell.
Integral Proteins
These structures (in purple) help move substances across a cell membrane during facilitated diffusion and active transport.
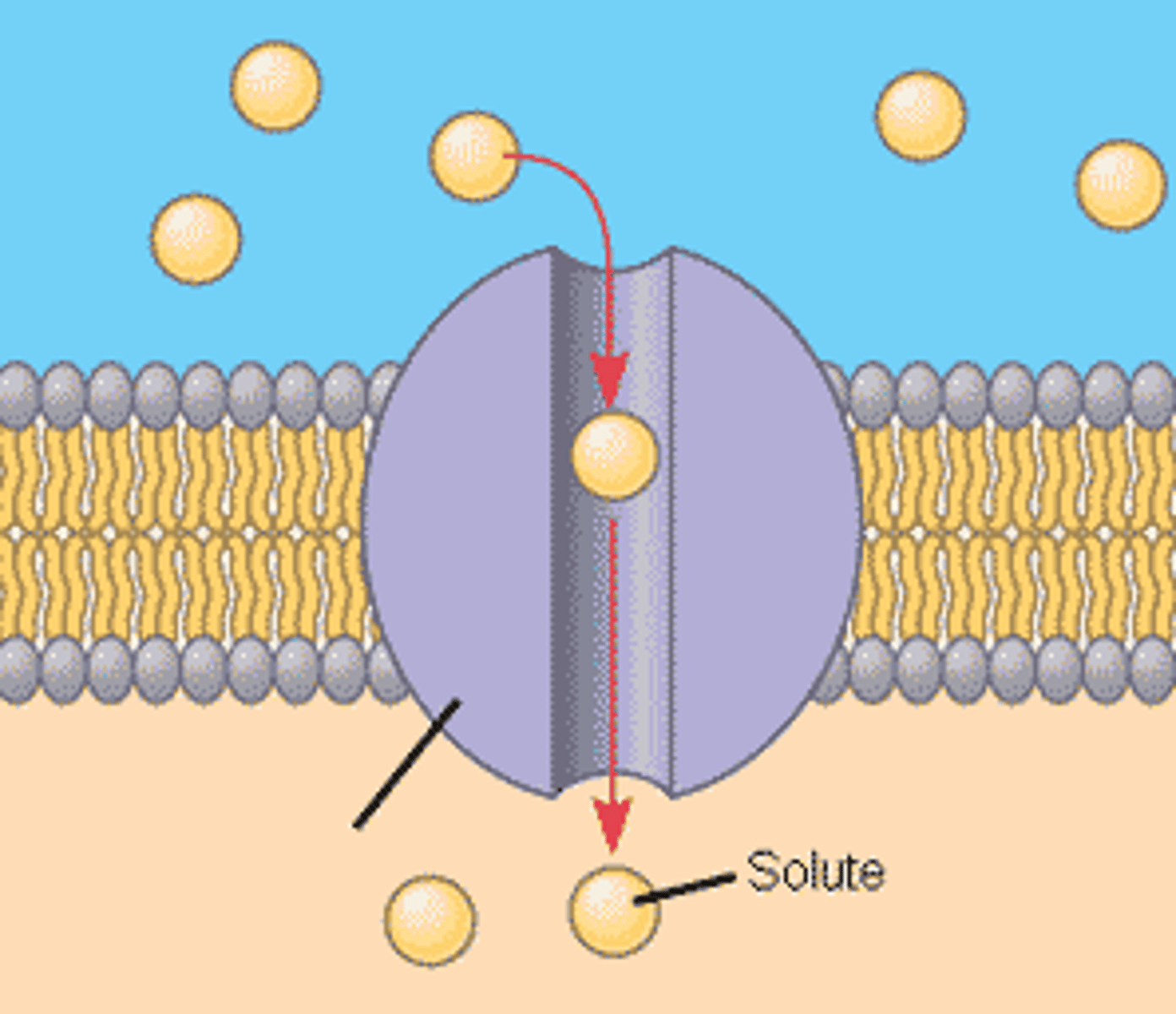
Equilibrium
No more NET movement occurs because the solute molecules are evenly spread out throughout a solvent. NO DIFFUSION occurs because there is no 'high' and 'low' however movement occurs equally in all directions.
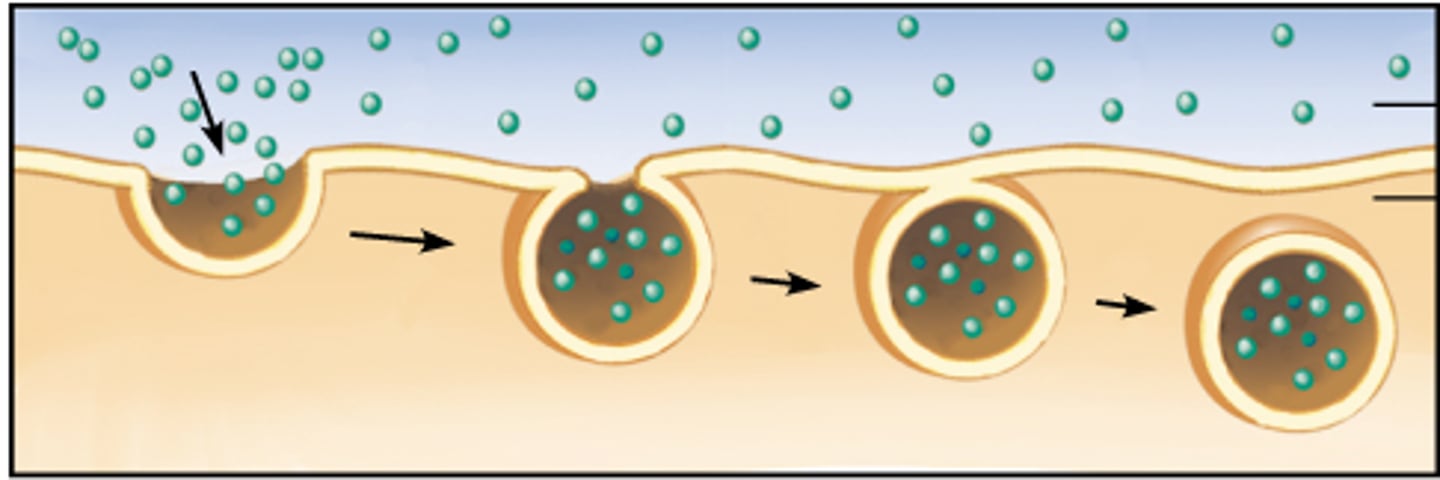
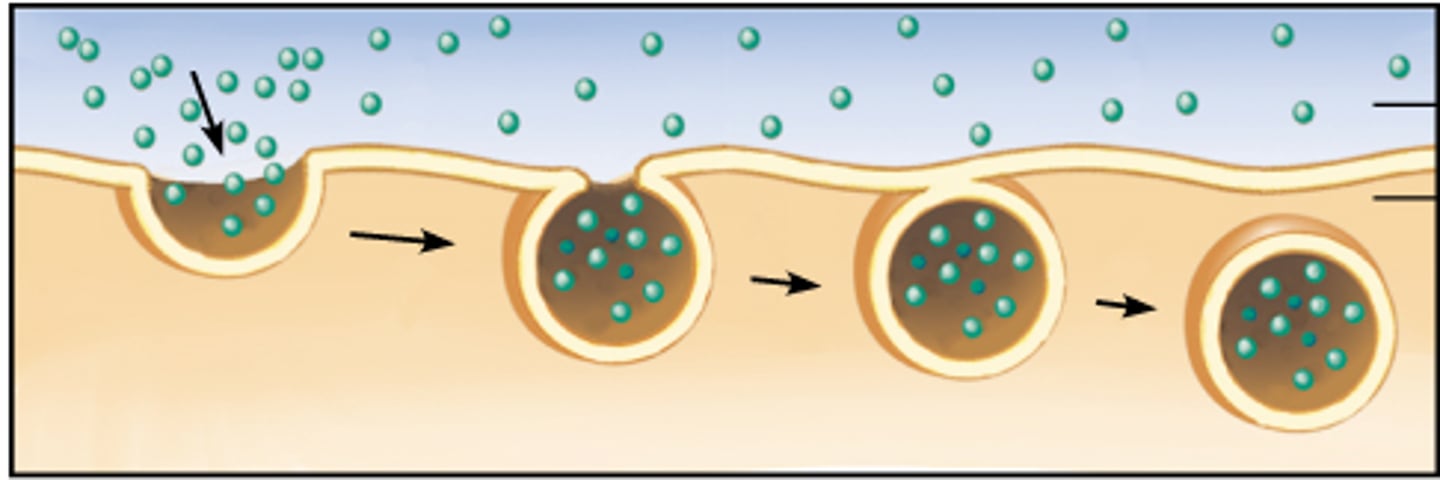
Endocytosis
A process when large materials ENTER a cell with a vesicle.
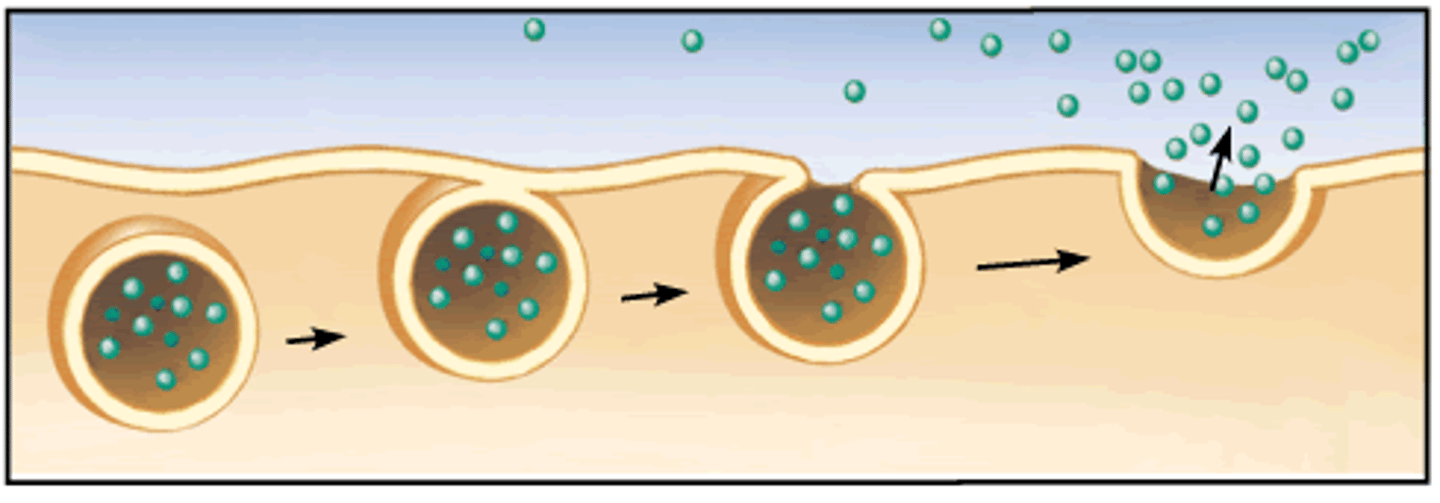
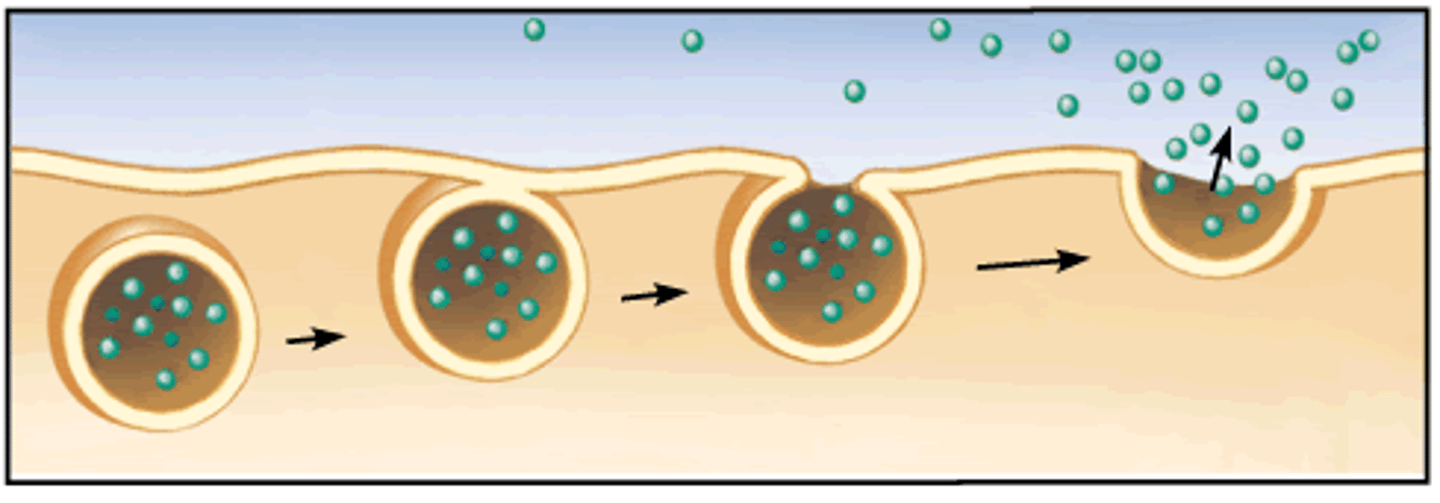
Exocytosis
A process when large materials EXIT a cell with a vesicle created by the rough ER or the golgi apparatus.
Solvent
The substance in which the solute dissolves

Solute
A substance that is dissolved in a solvent to create a solution.

Facilitated diffusion
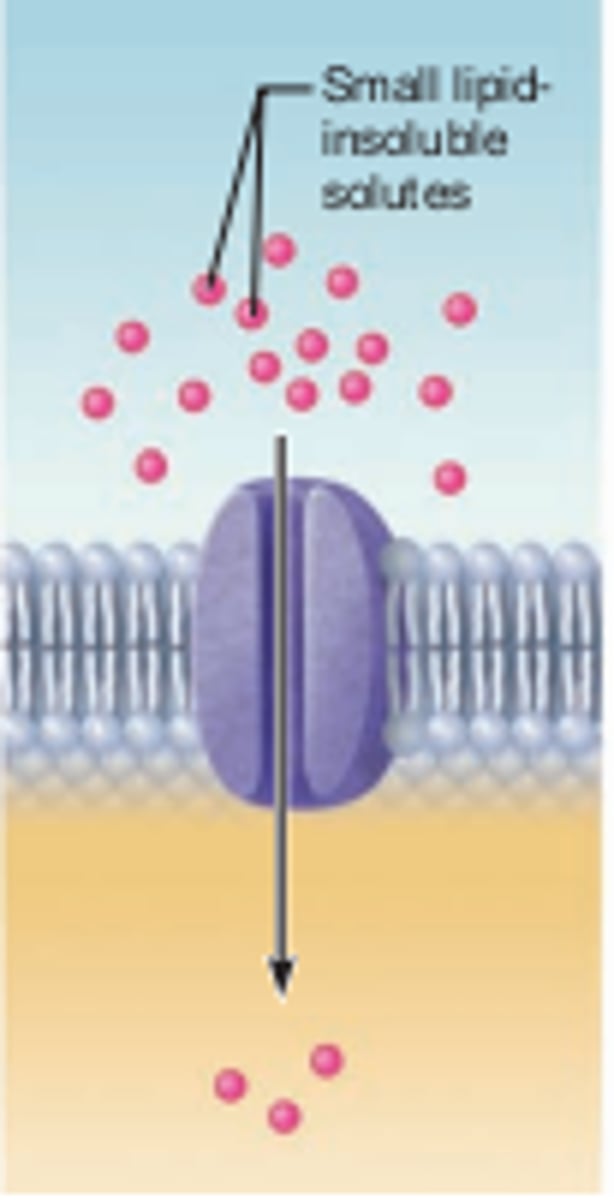
Active transport
Simple diffusion
Endocytosis
Exocytosis
Glycoprotein
A protein with one or more attached carbohydrates - used to identify the cell
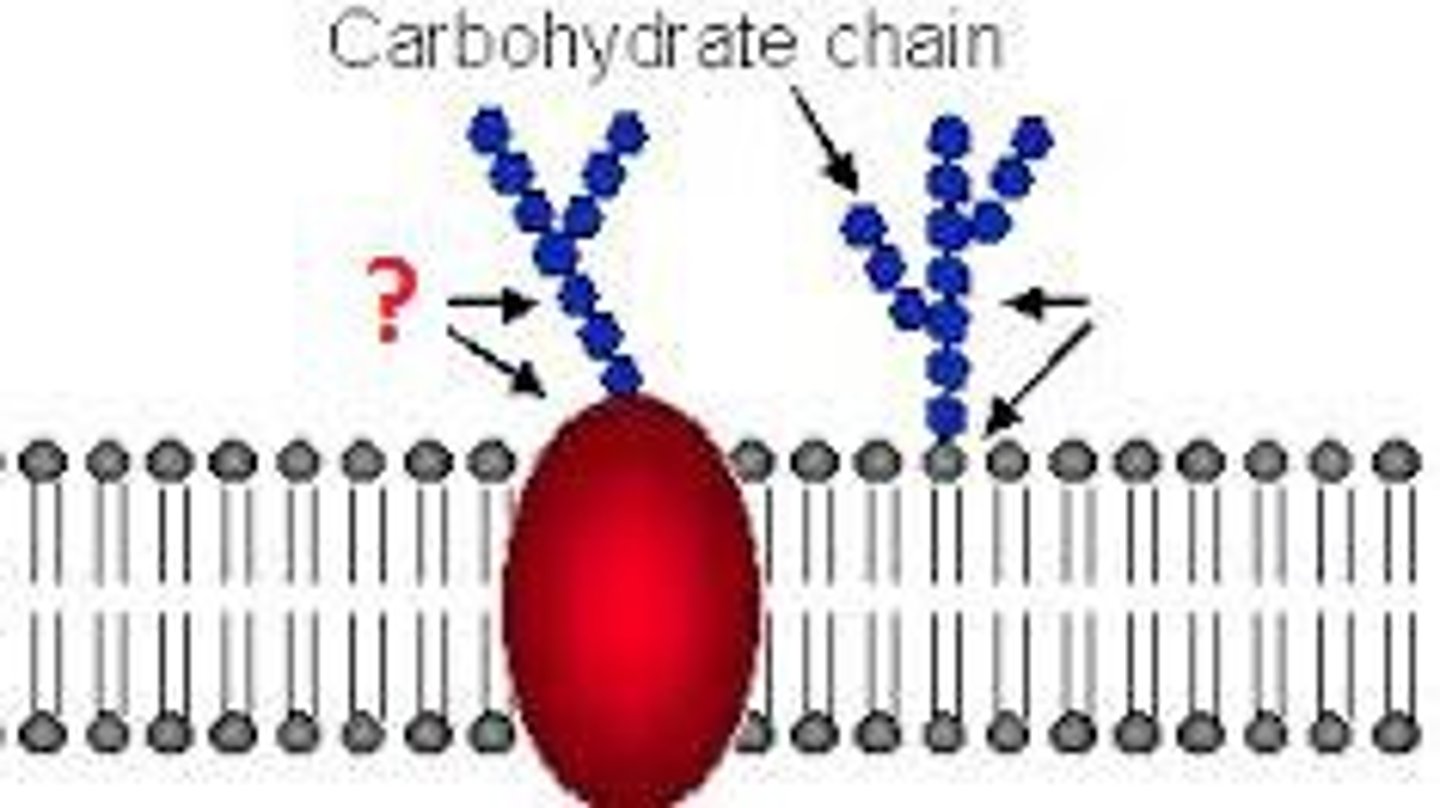
Glycolipid
A lipid with one or more attached carbohydrates - used to identify the cell
polar head
part of the phospholipid that is attracted to water (or is hydrophillic)
nonpolar tail
Part of the phospholipid that is not attracted to water (or is hydrophobic).
cholesterol
regulates the fluidity (and permeability) of the membrane because it regulates the spacing between phospholipids when temp changes
Osmolarity
Concentration of solutes on the inside of a cell. Determined by graphing the change in mass vs. environmental solute concentration and looking for the point where there is zero mass change
Na+/K+ pump
Integral protein (pump) that uses ATP to actively transport solutes from low to high concentration. The ATP is used to change the shape of the protein.