CMS III: PEDS - EXAM #2 (BOLD/UNDERLINE ALL)
1/196
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
197 Terms
Choanal Atresia
Bilateral: Noisy breathing, Cyanosis with feeding that improved with crying
Unilateral: Later in life, unilateral discharge or obstruction
Dx: Attempted catheter from nose to oropharynx
Tx:
-Oral airway placement
-Gavage feedings
-Surgery, Puncture, or stenting
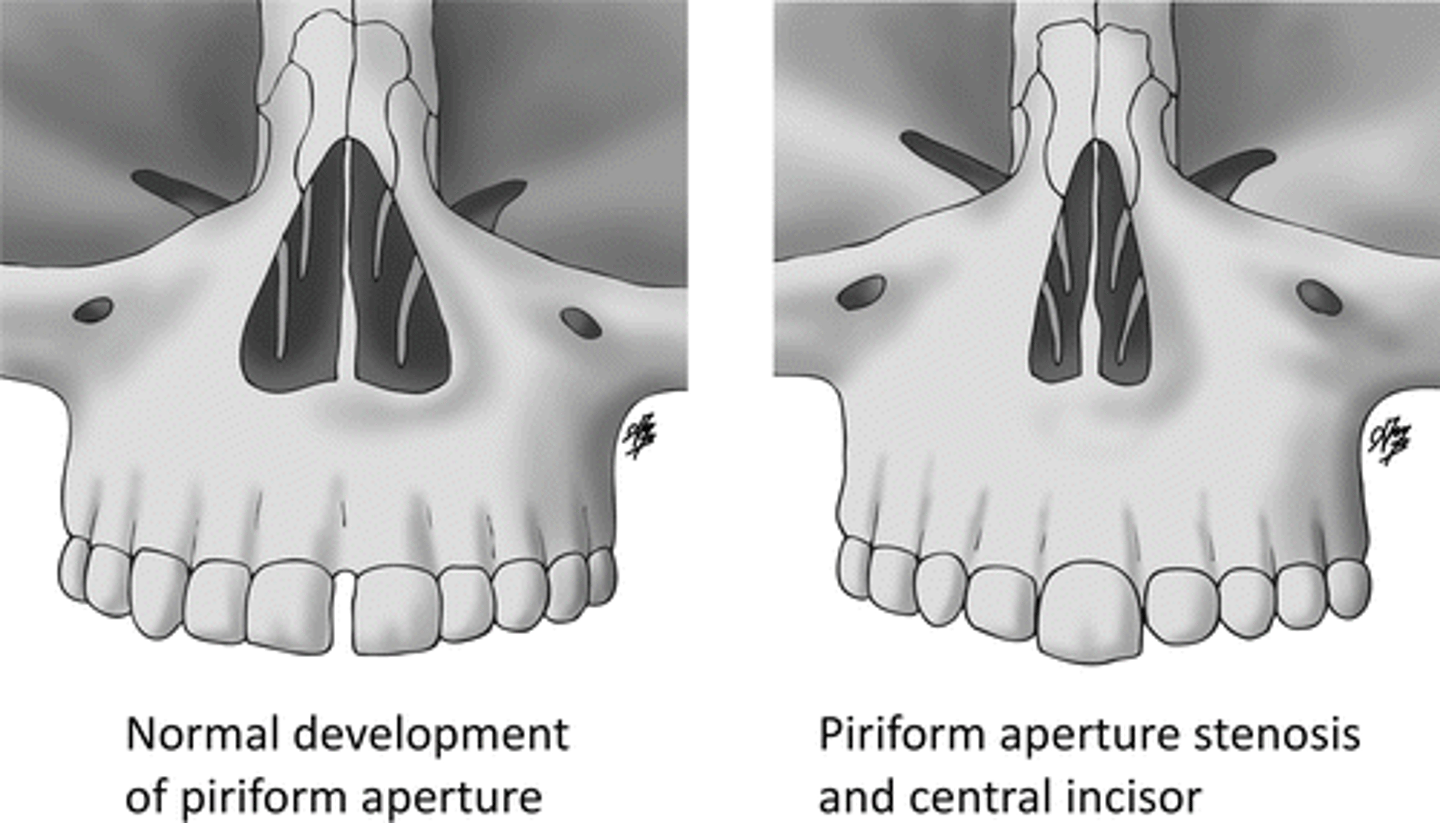
Pyriform Aperture Stenosis
Dz: Bony overgrowth at anterior bony opening
Sx:
-Noisy breathing
-Respiratory distress worsened with feeding, better when crying
Seen with:
-Craniosynostosis
-Pituitary anomalies
Dx: CT confirms
Tx: Nasal stenting or tracheostomy/surgery
Nasal Foreign Body
What is at the top of your differential when a child presents with unilateral, foul-smelling nasal discharge?
Lingual Ankyloglossia
Dz: Restriction of tongue movement caused by prominent lingual frenulum (usually in Males***)
- "Tongue Tied"
Sx: Exacerbates/forces mouth breathing causing sleeping issues
Tx: Frenectomy
Lingual Thyroid
Dz: Failure of thyroid tissue to descend into neck from tongue base
Complication: Airway obstruction
Tx: Surgery, and TH replacement
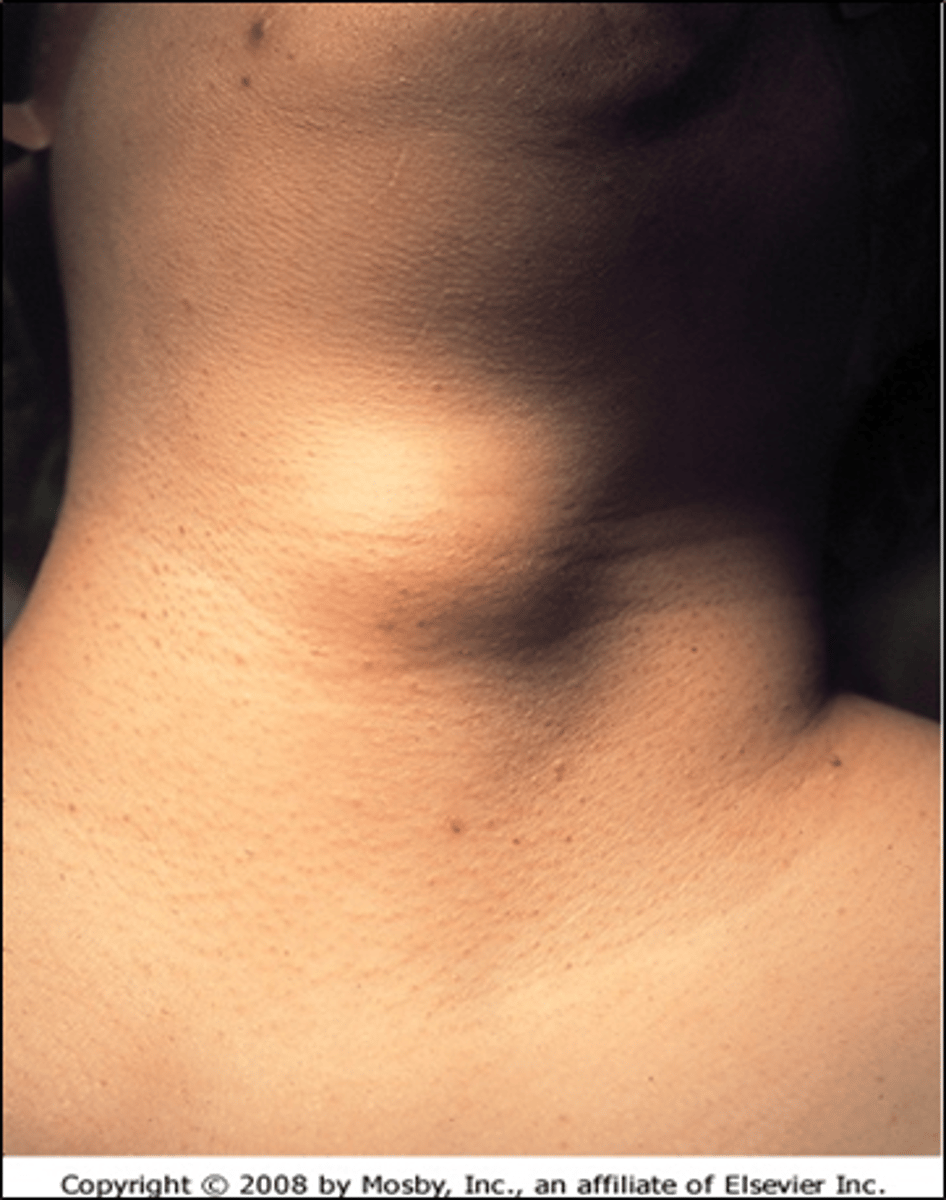
Thyroglossal Duct Cysts
Dz: Midline cystic mass in neck
Sx:
- Asymptomatic if not infected
- Swelling/airway compromise with infection
- Vertical motion of mass with swallowing and tongue protrusion (PATHOGNOMONIC!!)
Tx: Surgery
Laryngeal Lesions
Sx:
-Inspiratory stridor
-Hoarseness
-Aphonia
-Feeding disorders
NOTE: Expiratory stridor is typically tracheal in origin***
Laryngomalacia
Dz: Collapse of supraglottic structures during inspiration
- **Congenital anomaly of the larynx**
Sx:
-Dyspnea, Tachypnea, Cyanosis
-Feeding difficulties
-Apnea
- **cause of stridor in infants**
Tx:
-Self resolves in 12-18 months
-Surgery if severe or not self limiting
Laryngomalacia!!
(NOTE: Also M/C cause of stridor in infants)
What is the M/C congenital anomaly of the larynx?
Subglottic Stenosis
Dz: Narrowing of Cricoid lumen
Presentation:
- **Recurrent Croup**
- Biphasic stridor in newborn if severe
Dx: Visualization
Tx:
-Self-limiting normally
-Surgery if symptomatic
Laryngeal Webs
Dz: Incomplete separation of vocal folds
Sx: Respiratory distress and unsual cry
Tx: Surgery
Laryngeal Atresia
Sx: Asphyxia at birth
Tx: Emergent tracheostomy
Tracheal Atresia
Sx: Respiratory distress
Tx:
-Tracheostomy
-Intubate esophagus to trachea of TEF is present
Tracheal Stenosis
Sx:
-Complete/near complete cartilage rings
-Sternal retractions
-Dyspnea
-Stridor
-Monophonic wheeze that doesn't respond to bronchodilators
Dx: Bronchoscopy
Tx: Surgery
Tracheomalacia
Dz: Flaccidity of trachea during breathing leading to collapse
Sx: Expiratory stridor
Tx: Self-limits in 6-12 months
- Surgery otherwise
Bronchomalacia
Dz: Weak cartilage causing collapse of bronchus on expiration
Primary: Due to cartilaginous ring malformation
Secondary: Due to extrinsic compression
Dx: Bronchoscopy
Congenital Lobar Emphysema
Dz: Over inflation of lobe with increased number of alveoli
M/C Lobe: Left Upper Lobe***
CXR: -Distention of affected lobe
-Mediastinal shift
-Compression/atelectasis of nonaffected lung
Tx: Lobectomy
CI: Needle Aspiration
Pulmonary Hypoplasia
Sx:
-Respiratory Distress
-Hypoxia
-Hypercarbia
Associations:
-Premature Rupture of Membranes (PROM)
-Premature delivery
Tx: Mechanical ventilation until lungs develop
Pulmonary Arteriovenous Fistulas
Sx:
-R to L shunting of blood into pulmonary veins and left heart
-Dyspnea
-Hemoptysis
-Exercise intolerance
Associations: ***Rendu-Osler-Weber syndrome***
Tx:
-Ablation by angiography
-Surgical removal
Bronchopulmonary Sequestration
Dz: Nonfunctioning mass of lung tissue lacking normal communication to tracheobronchial tree, receives its blood supply from systemic circulation
*Intralobar: Contained within the normal lung (M/C)
- Dx later in life
Tx: lobectomy
Extralobar: Seperate from normal lung with own pleura
- Dx in utero
Tx: resection
Bronchogenic Cysts
Dz: Cysts along tracheobronchial tree
- **LOWER respiratory anomaly**
Sx:
-Respiratory distress/airway compromise
-Cough/Wheeze
-Dyspnea/stridor
-Retractions
-Rales
Dx:
-CT or MRI to confirm
-CXR shows Round water density mass or air trapping
Tx: Lobectomy
Kyphoscoliosis
Cause: Most cases idiopathic
Sx:
> 50º restrictive changes can be seen on PFT’s and patients can have hypoventilation
> 90º can have associated cardiopulmonary compromise
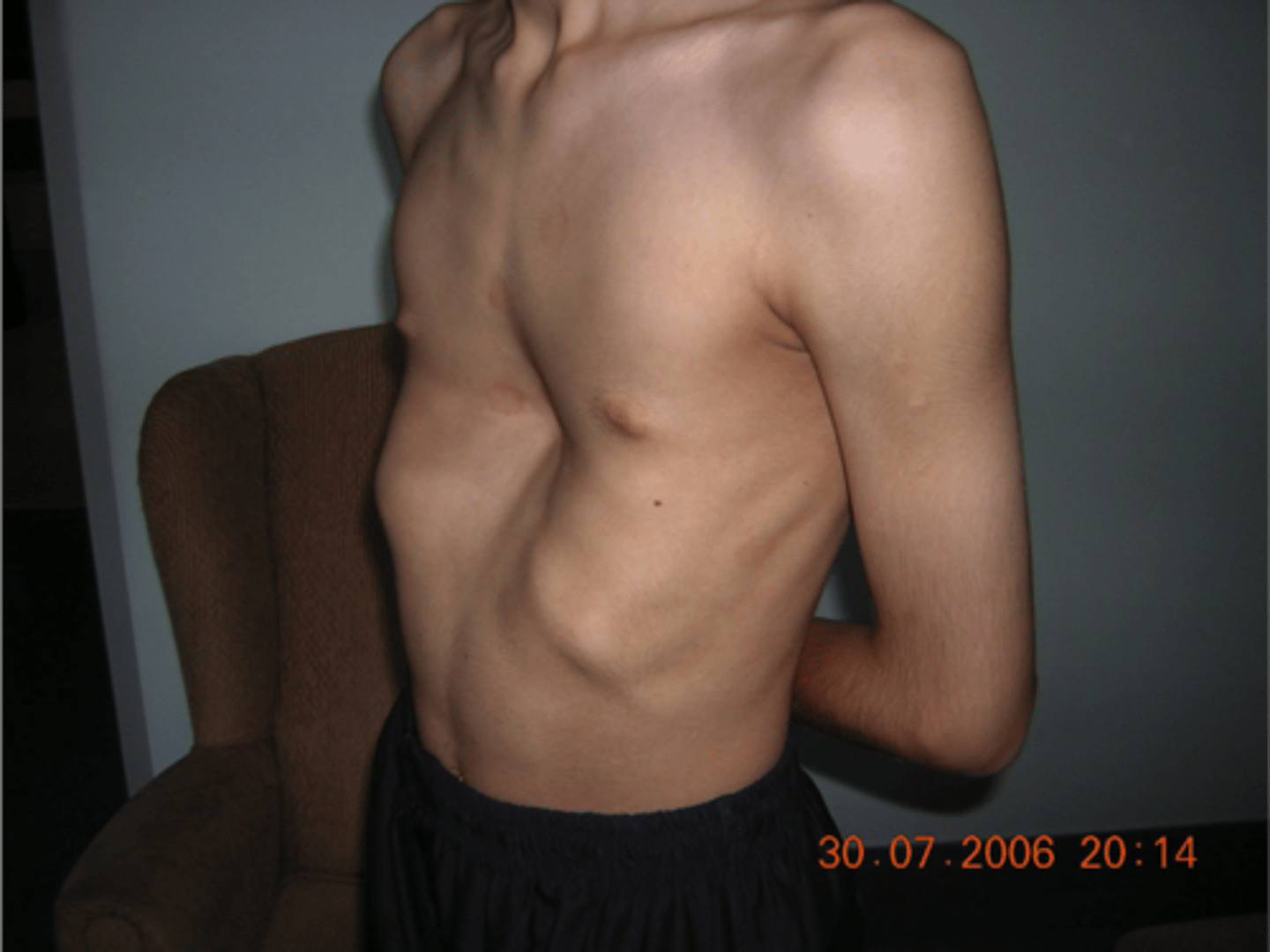
Pectus Excavatum
Sx:
◦Inward bowing of the midsternum
◦Congenital, familial or acquired
◦PFT = normal
◦Show restriction with severe pectus deformity
Tx: Surgical correction à usually cosmetic
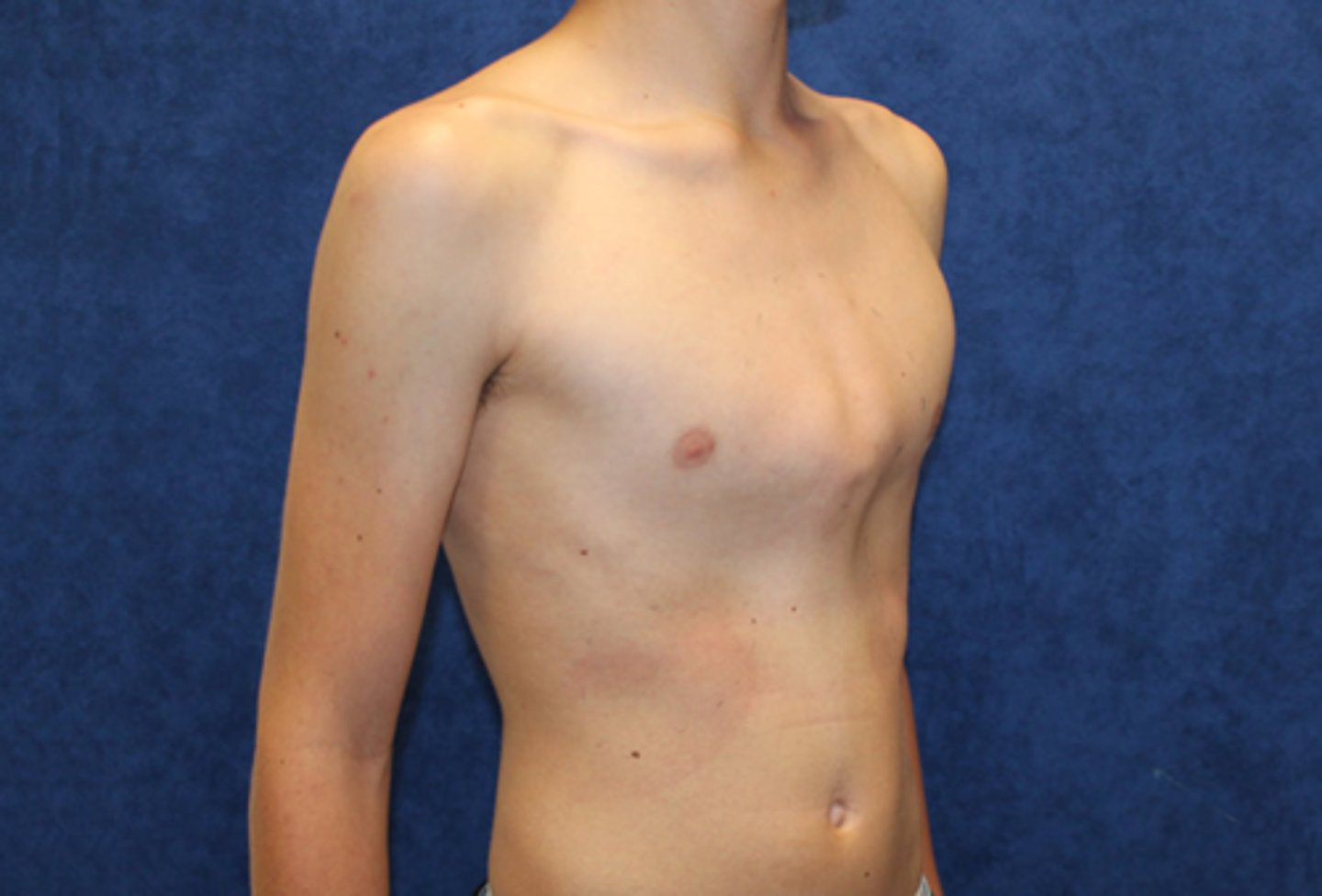
Pectus carinatum
Sx:
◦ Protrusion of the sternum
◦ Rarely causes problems
Tx: Surgical correction à almost always cosmetic
Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia (CDH)
Location: ***LEFT-side Posterolateral (M/C)
Sx:
-Respiratory distress
-Barrel chest
-Scaphoid Abdomen
Dx: CXR (Loops of bowel in chest w/ mediastinal shift)
Tx: Intubate, NG with suction, and Surgery
Laryngotracheobronchitis (Croup)
Etiology: Parainfluenza
Sx:
-Barky cough
-Hoarseness
-Stridor
Dx: ***Steeple sign*** on XR
Tx:
-No improvement = ***ER, Racemic Epinephrine (Gold Standard)***
- ***Multiple doses of racemic epi = ADMIT***
-Dexamethasone
Spasmodic Croup
Child wakes up in the night with a barking cough and stridor
BUT they are fine the next day
- NOT infectious, and likely with ***GER***
Acute Bronchitis
Demographic: **Older children, typically post viral URI**. Acute inflammation of the tracheobronchial tree, generally self-limited & with eventual complete healing & return of function.
Sx: Dry hacking cough that becomes productive aboot day 3 and dissapears around day 5
- Rhinorrhea
- Rhonchi
Labs:
- PFT showing airway obstruction
- CXR showing increased pulmonary markings
Tx: Supportive
- Nasal saline + Suction
- Check for other causes
Chronic Bronchitis
Cause
◦ Cough lasting >4 weeks
Top 3 causes
◦ Asthma
◦ Protracted bacterial bronchitis (PBB)
◦ Non-specific cough
◦Immune Deficiencies/Anatomic abnormalities/Cystic Fibrosis
◦Cigarette smoke exposure/other environmental exposure
◦Bronchiectasis/Upper airway infection with post-nasal discharge
◦ Foreign Body Aspiration
Acute Bronchiolitis
Demo: Younger kids/infants
Etiology:
- **RSV**
- **< 18 months of age**
- Peak < 6 months
- **hospitalization for children <2 years old**
Sx:
-Tachypnea, Cough, Rhinorrhea, **Wheezing**
-Shallow, rapid respirations
Severity Predictor:
***O2 saturation while feeding***
Dx: CXR with hyperinflation of lungs (DDx: **Asthma**)
Tx: Supportive
- Saline and Nasal Suction
- Albuterol
Acute Bronchiolitis
Treatment
If on room air with stable O2 and:
<6 months: <60 breaths/min
6-11 months: <55 breaths/min
>12 months: <45 breaths/min
Pneumonia
MC overall: Viral (**RSV**) < 5 y/o***
MC if <5yo: S. Pneumoniae (M/C), S Aureus, and S. Pyogenes
MF if >5 yo: Mycoplasma Pneumonia and Chlamydia Pneumonia
Pneumonia
Sx:
-Fever + Cough
-Respiratory distress
Bacterial: IF >15000 WBC and/or fever > 39ºC (102.2ºF)
Viral: Low-grade fever, Nonproductive cough, Tachypnea with wheezing, Diffuse crackles
Strep. pneumoniae (Pneumonia)
________________: "Rust Colored Sputum"
**cause of “typical” bacterial pneumonia**
◦ Abrupt infection with fever, cough, tachypnea, malaise, and emesis
◦ DEC breath sounds, localized crackles
◦ Fever recurring + effusion still present = think empyema = thoracentesis with evaluation
Tx: Amoxicillin
A. Strep. pneumoniae (Pneumonia)
B. S. pyogenes (Pneumonia)
C. S. aureus (Pneumonia)
S. pyogenes (Pneumonia)
______________:
◦ Pneumonia usually after rash disease
◦ Complications = Abscess & empyema
Tx: PCN
A. Strep. Pneumoniae (Pneumonia)
B. S. pyogenes (Pneumonia)
C. S. aureus (Pneumonia)
S. aureus (Pneumonia)
_______________: Not common, but has serious complications
Complications
◦ Pneumatoceles, pneumothoraxes, abscess and empyema are common
◦ Recent URI = **influenza**
◦ Fever, cough, tachypnea
◦CXR = pneumotoceles
Tx: Nafcillin or Vancomycin (MRSA)
A. Strep. Pneumoniae (Pneumonia)
B. S. pyogenes (Pneumonia)
C. S. aureus (Pneumonia)
Mycoplasma Pneumonia
atypical pneumonia
Sx:
-Fever, Malaise, HA, Sore throat, Nonproductive cough
-"CXR looks worse then the pt"
-Splenomegaly, Bullous myringitis, Pharyngitis, AMS
Tx:
-Azithromycin
-Tetracycline
A. Mycoplasma Pneumonia
B. Chlamydophila Pneumoniae
Chlamydophila Pneumoniae
Demo: >5 yo
Sx: Fever, Malaise, HA, Sore throat, Nonproductive cough
-Common cause of epidemic pneumonia
Tx: Azithromycin, improves quickly (48-72 hours)
A. Mycoplasma Pneumonia
B. Chlamydophila Pneumoniae
Tuberculosis (TB)
**Infected by household or close contact**
-Screen all patients at 1st contact & every 6 months thereafter for their 1st year of life
- If risk factors are positive – screen for TB
- If recently immigrated – screen 8-12 weeks after immigration & then repeat in 6 months; 2 negatives = negative
Tuberculosis (TB)
15 mm: No risk factors
10 mm: High incidence population
5 mm: Immunosuppressed
(NOTE: Measure on INDURATION not erythema)
Tuberculosis (TB)
CXR:
- Cavitations (Caseating granulomas)
- MIliary infiltrates
- **Isolated Hilar or Mediastinal Adenopathy**
- Segmental hyperinflation or atelectasis
- Alveolar consolidations
- Interstitial densities
- Pleural effusions
Tuberculosis (TB)
Tx:
- Isoniazid and Rifampin x 9 MONTHS
Recall:
- Rifampin will turn your fluids orange (Urine/tears)
- Both may cause hepatotoxicity
- Give Pyridoxine (Vit B6) with Isoniazid to prevent peripheral neuropathy
Pertussis (Whooping Cough)
Etiology: Bordetella Pertussis (G-)
Sx: Paroxysmal cough with prolonged, high pitched, crowing inspiratory whoop, post-tussive emesis
- 3 stages (Catarrhal, Paroxysmal, Convalescent)
Clinical Suspicion: **LOW threshold for suspicion in young infants**
Pertussis (Whooping Cough)
Dx: Sputum Cult GOLD STANDARD
Tx: Ideal within 1st week of Sx. Pts don't come in until paroxysmal phase.
- Admit to hospital if severe or <3 mo
- Macrolides (Azith = < 1 month)
- Trimethoprim-Sulfa ≥ 2 months old
When to hospitalize:
◦ <4 months of age
◦ CBC with diff = WBC >30,000 cell/microL
◦ Any age with significant complications
Bronchiectasis
Dz: IRREVERSIBLE focal bronchial dilation, usually accompanied by chronic infection & associated with diverse conditions, some congenital or hereditary
Cause: Obstruction/Poor Drainage
***Cystic Fibrosis (M/C)***, FB, Infection
Sx:
-Persistent cough with early morning sputum
-Productive cough increased with exercise/position change
-Sinusitis
-Clubbing
-Moist rales/rhonchi
-Hemoptysis later
Bronchiectasis
Labs: Culture (H. Flu common infection)
-CXR (bronchovascular markings/atelectasis)
-CT
-PFTs (Obstructive pattern)
Tx:
-Abx/Tx underlying dz
-Physiotherapy
-Surgery to remove affected lobe/area
-Vaccines
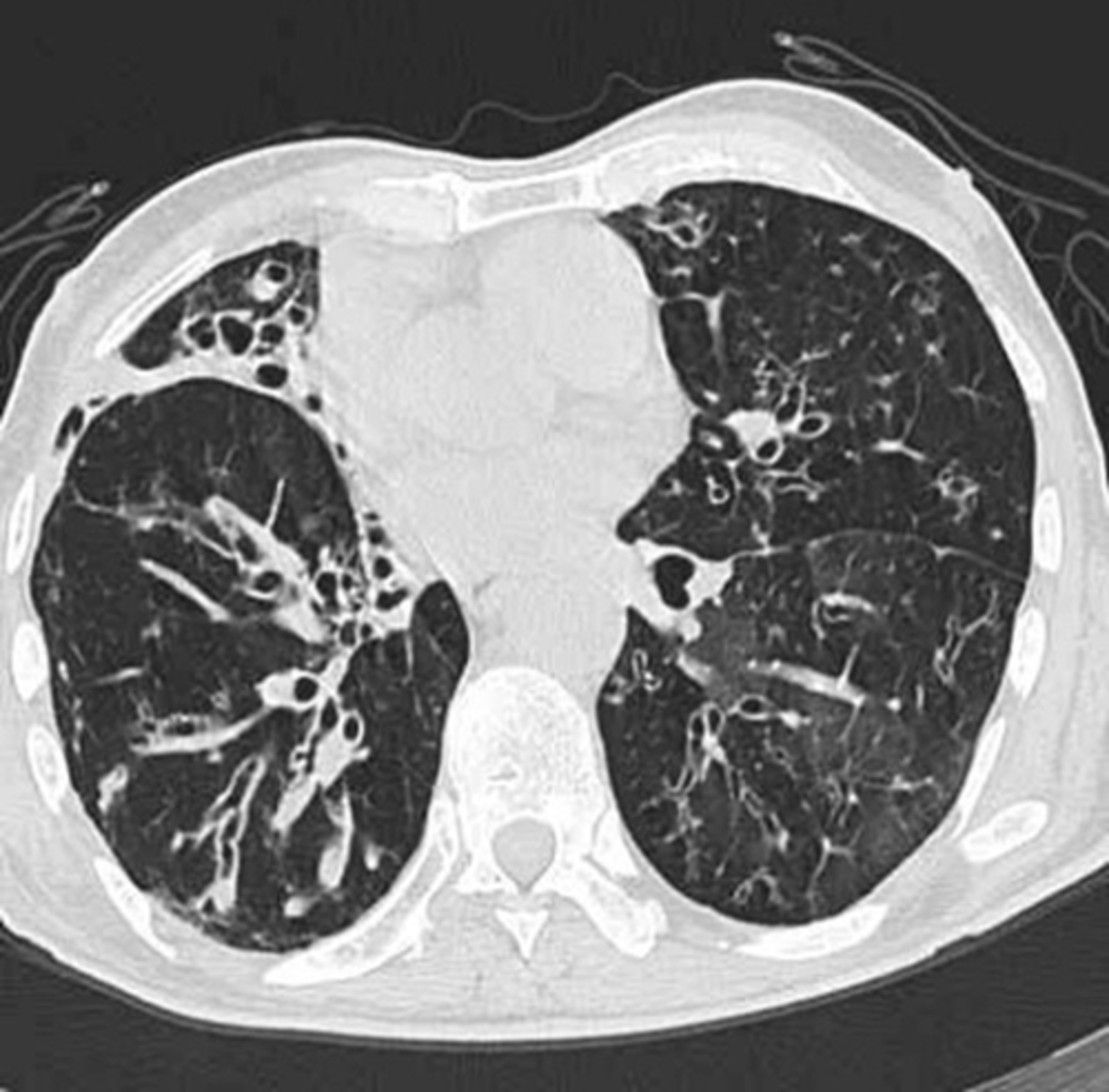
Cystic Fibrosis (CF)
When Dz do you suspect with a positive sweat chloride test (>60 mEq/L)?
(NOTE: Normal is 10-35 mEq/L)
Cystic Fibrosis (CF)
Cause
- Inherited Dz of the exocrine gland
- Respiratory & GI system
- Defect in the gene produces ABNL thick, sticky mucus
- Lung infection: Pseudomonas (M/C)
- Obstruct the pancreas = malabsorption
Clinical Features
**Delayed Meconium** = Meconium Ileus presents at birth
◦ Rectal prolapse
◦ COPD
◦ Abnormally high sweat electrolytes
◦ Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency
Dx: d508 chromosomal analysis
Foreign Body Aspiration
Cause
**aspirated objects are seeds, nuts, popcorn, coins, hot dogs, small toys, balloons, jewelry**
Clinical Features
◦ Choking, coughing, wheezing, dyspnea or stridor
◦ Most lodge in the mainstem Bronchi
Dx Testing
◦ Atelectasis on end-expiratory CXR is indicative of a "Drowned Lung."
Dx delayed often until aspiration is witnessed
Asthma
A child has had a **coughing/wheezing** without other Sx for > 3 weeks without improvement, especially at night/seasonal/in response to specific exposure (cold, exercise, laughing, etc). What Dz should this make you suspicious for?
Asthma
Dx:
1. Variable expiratory airflow limitations (spirometry)
2. Reversible obstruction (Albuterol helps)
3. Exclusion of alternative dx
Asthma
Quick-relief:
1. SABA (Albuterol)
2. Anticholinergics (Ipratroprium Bromide)
3. ICS
Long-term:
1. ICS (Advair, Pulmicort, etc)
2. LABA (Salmeterol, Formoterol)
3. Methylxanthines (Theophylline)
4. Leukotriene Modifiers (Montelukast)
(NOTE: ICS are MOST EFFECTIVE as anti-inflammatories for asthma, and will not have systemic adverse effects if given inhaled.)
Asthma
Tx:
**Corticosteroids (Oral and IV)
◦ **anti-inflammatory agents for Tx of asthma**
SE:
◦Osteoporosis
◦Cataracts
◦Hyperglycemia
◦Weight Gain
◦Thinning of Skin
◦Striae
◦Growth Restriction
**Inhaled corticosteroids are not associated with these risks at moderate dose**
Asthma
Long-term Tx for ___________ if they:
1. Have had more than 3 episodes of wheezing over a 1 year period
2. Have recurrent episodes lasting more than 1 day
3. Have episodes that are affecting sleep
4. Have risk factors for the development of asthma
Intermittent Asthma
________________:
-Sx < 2x weekly
-Nighttime Sx < 2x monthly
-SABA Use < 2x weekly
-No interferance with normal activity
-FEV1 > 80%, FEV1/FVC > 80%
-Exacerbation < 1x yr
A. Intermittent Asthma
B. Mild Persistent Asthma
Mild Persistent Asthma
_______________:
-Sx > 2x weekly, not daily
-Nighttime Sx 3-4x monthly
-SABA Use > 2x weekly
-Minor interferance with normal activity
-FEV1 > 80%, FEV1/FVC > 80%
-Exacerbation > 2x yr
A. Intermittent Asthma
B. Mild Persistent Asthma
Moderate Persistent Asthma
_____________:
-Sx daily
-Nighttime Sx >1 x weekly, not nightly
-SABA Use daily
-Interferance with normal activity
-FEV1 60-80%, FEV1/FVC 75-80%
-Exacerbation > 2x yr
A. Moderate Persistent Asthma
B. Severe Persistent Asthma
Severe Persistent Asthma
________________:
-Sx continuously
-Nighttime Sx nightly
-SABA Use multiple times daily
-Severe interference with normal activity
-FEV1 < 60%, FEV1/FVC < 75%
-Exacerbation > 2x yr
A. Moderate Persistent Asthma
B. Severe Persistent Asthma
Asthma
Tx Progression:
1. SABA
2. SABA + Low dose ICS
3. SABA + Medium dose ICS
4. SABA + Medium dose ICS + LABA
5. SABA + High dose ICS
NOTE: LABA/LTRA/Theophylline are alternatives to Medium dose ICS or LABA
Hemoptysis
Cause:
◦**infection, foreign body, bronchiectasis**
◦Vasculitis, congenital heart or lung defects, pulmonary embolism, idiopathic
Clinical Features:
◦Fever, Chills
◦Illicit drug usage
◦Hematuria
◦Telangiectasia
◦Clubbing
Hemoptysis
Dx Testing:
◦Localize the source
◦Coffee grounds = GI
◦Bright red, rust colored, frothy, mixed with sputum = Lungs
◦CXR = Some are normal
◦Chest CT if diagnosis unclear
◦Bronchoscopy with lavage = hemosiderin
◦Consider ECHO if BAL positive
◦Consider lung biopsy
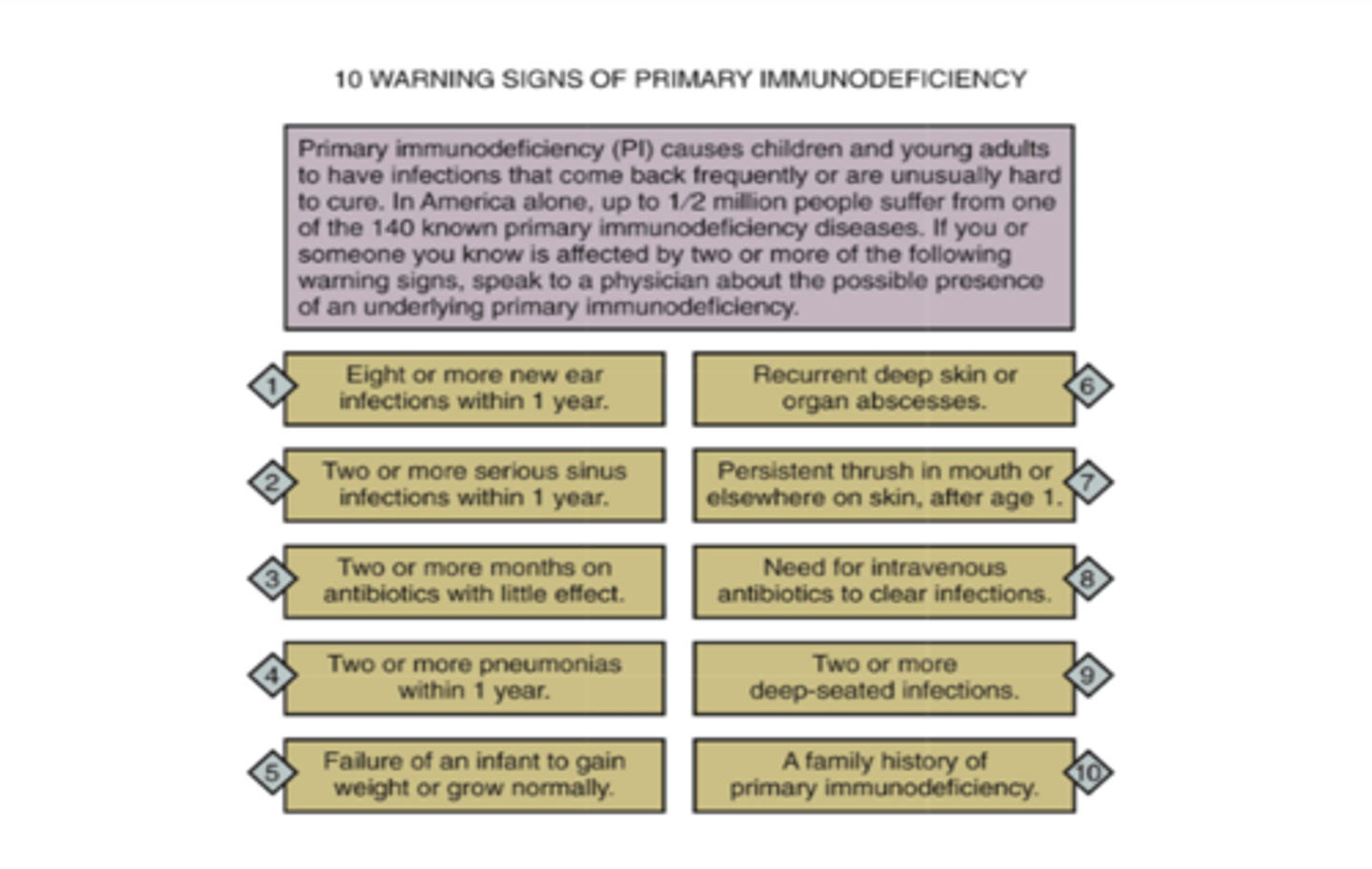
Primary Immunodeficiency
10 warning signs of ____________:
A. Primary Immunodeficiency
B. Secondary Immunodeficiency
Combined B/T cell disorders
______________:
1. Severe Combined Immunodeficiency (SCID)
2. Ataxia-Telangiectasia
3. Bloom Syndrome
4. Nijmegen Breakage Syndrome
A. Combined B/T cell disorders
B. T cell disorders
C. B cell disorders
T cell disorders
__________: DiGeorge Syndrome
A. Combined B/T cell disorders
B. T cell disorders
C. B cell disorders
B cell disorders
___________: Can't make Abs
- X-linked Agammaglobulinemia (Bruton's)
- Common Variable Immunodeficiency (CVID)
- Hyper-IgM syndrome
- X-linked lymphoproliferative syndrome (Duncan's)
- Transient Hypogammaglobulinemia of infancy
A. Combined B/T cell disorders
B. T cell disorders
C. B cell disorders
B cell disorders
Clinical Features:
◦Recurrent Sinopulmonary Infections
◦Bacterial = S. pneumonia, H. influenza, S. Aureus (no IgG or IgM)
◦Viral = Enterovirus (no IgA)
◦Protozoal = Giardia (No IgA or IgE)
A. Combined B/T cell disorders
B. T cell disorders
C. B cell disorders
DiGeorge Syndrome
Dz: 22q11 microdeletion causing T-cell immunodeficiency
Sx:
-VSD
-ToF
-Thymic/Parathyroid dysgenesis (hypocalcemia/seizures)
-Developmental/speech delays
Cardiac
Abnormal facies
Thymic hypoplasia
Cleft lip/palate
Hypocalcemia
22 - Chromosome
Severe Combined Immunodeficiency (SCID)
Dz: Autosomal recessive/X-linker disorder of B & T-cells immunity disturbance (weak NK cells)
Sx:
-Recurrent infections/opportunistic infections
-Chronic diarrhea
-Failure to thrive
-Death between 12-24 mo
- Think "Bubble boy"
Tx: Bone marrow transplantation/Hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT)
Ataxia-Telangiectasia
Dz: Autosomal recessive dz causing B and T cell deficiency
Sx:
-Cerebellar ataxia
-Abnormal eye movements
-Oculocutaneous telangiectasis
Complications: Lymphomas/leukemias (HIGH RISK FOR CANCER)
Tx: None, 25 yr lifespan avg
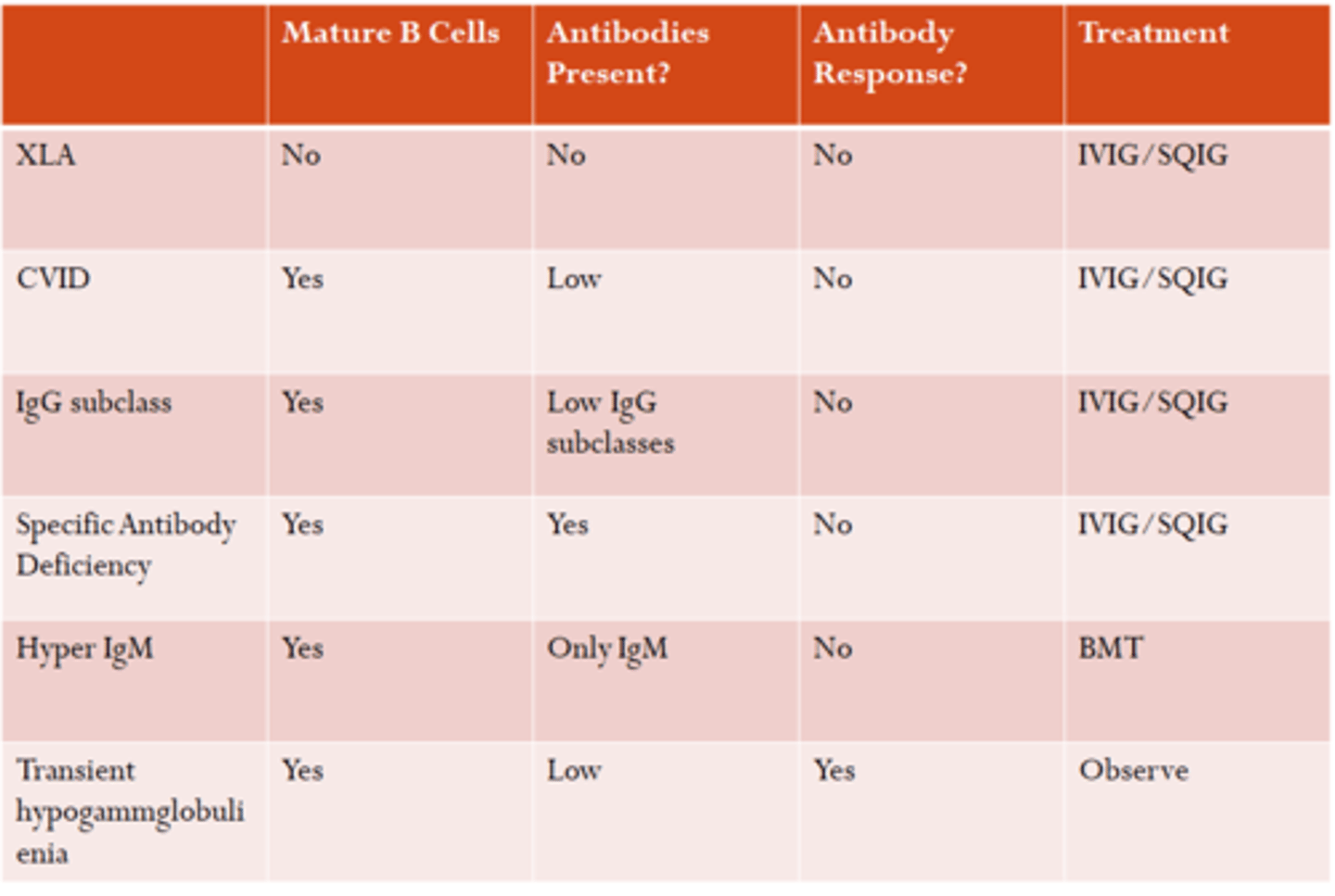
X-linked agammaglobulinemia
"Bruton's Agammaglobulinemia"
Dz: Mutation of BTK (Bruton tyrosine kinase) = B cell arrest before maturation
Sx: Extra-susceptible to encapsulated organisms (Strep, H. Flu, Meningococcus, Staph., Giardia, etc)
Dx: Flow cytometry (no B cells/Abx)
Tx: IVIG
Common Variable Immunodeficiency (CVID)
Dz: Mature B cells unable to differentiate to plasma cells
Sx:
-Recurrent sinopulm infections of encapsulated bacteria (Bronchiectasis)
-Sarcoid-like dx
-Sprue-like illness (Diarrhea, steatorrhea, Malabsorption)
Dx: Flow cytometry (Mature B cells present, low Abx level)
Tx: IVIG
X-Linked Hyper IgM Syndrome
Dz: Inability for B cells to switch from IgM to other abx
- T cells are unable to interact with macrophages (**CD40L Defect**)
Sx: Sinopulm. bacterial infections/PCP
Dx: Flow cytometry (Low CD40L)
Tx: BMT (Bone marrow transplant), IVIG, SQIG,
- Bactrim for PCP prophylaxis
Transient Hypogammaglobulinemia of Infancy
Dz: Natural Hypogammaglobuliemia occuring when mothers Abx wean (Delayed IgG production by baby)
How to Differentiate between:
-X-Linked Agammaglobulinemia syndrome
-Common Variable Immunodeficiency
-Hyper IgM syndrome
-Transient Hypogammaglobulinemia of newborn
1. Kostmann syndrome
2. Severe chronic Neutropenia
3. Cyclic Neutropenia
1. _____________: Mutation of HAX1 gene, Neutropenia
2. _____________: Mutation of PMN elastase
3. _____________: PMN levels increase/decrease over time (Q3-6 wks)
A. Kostmann syndrome
B. Severe chronic Neutropenia
C. Cyclic Neutropenia
(NOTE: These are all phagocytic disorders)
Leukocyte Adhesion Deficiency
Dz: WBC can't leave vasculature to migrate into tissue (mainly PMNs)
LAD I:
-Recurrent bacterial infections, Increased PMNs
-ABSENT PUS FORMATION
-Impaired wound healing
LAD II:
-Absence of fucosylated carbohydrate ligans on hematopoietic cells
-Defective rolling of WBCs
-Less severe/fewer infections then LAD I
-Intellectual disabiliites, small stature, depressed nasal bridge
LAD III: Autosomal recessive integrin defect
-LAD I + Bleeding
-Most severe!
Job Syndrome (Hyper IgE Syndrome)
Dz: "Hyper IgE Syndrome." IgE elevated, sometimes (Not always high apparently)
Sx:
-Recurrent abscesses
-Eczema
-Scoliosis
-Delayed primary teeth
-Fx
-Pneumatoceles
-Coarse facies (Asymmetric jaw, broad nose, prominent forehead, triangular jaw)
Chediak-Higashi
Dz: Impaired lysosome degranulation
Sx:
-Cutaneous/sinopulm infections
-Oculocutaneous albinism
-Intellectual disabilities
-Peripheral neuropathy
-GIANT GRANULES ON PERIPHERAL SMEAR
Tx: Bone marrow transplant
Chronic Granulomatous Disease
Dz: **X-linked** inability to generate "Respiratory burst"
Sx:
- Recurrent abscesses
- Walled off granuloma formation
Dx: Dihydrohodamine oxidation test with flow cytometry (DHR)
Tx: Interferon, Abx
Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)
Cause:
-Acquired thru Vertical Transmission
-Also can acquire through breast milk & during delivery
-If NO antiretroviral med is given, mom has 25% chance of transmitting the infection to the child
Tx:
-6 weeks of antiretroviral therapy (Zidovudine)
-Bactrim/Sulfa given at 6 wks old for PCP prophylaxis
-Follow CD4 levels Q4mo
Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)
Vaccinations: Receive ALL vaccines; EXCEPT Live Virus Vaccines
(Live Vaccines: MMR, Varicella, BCG, Oral Polio, Intranasal Flu (Flumist), Small Pox)
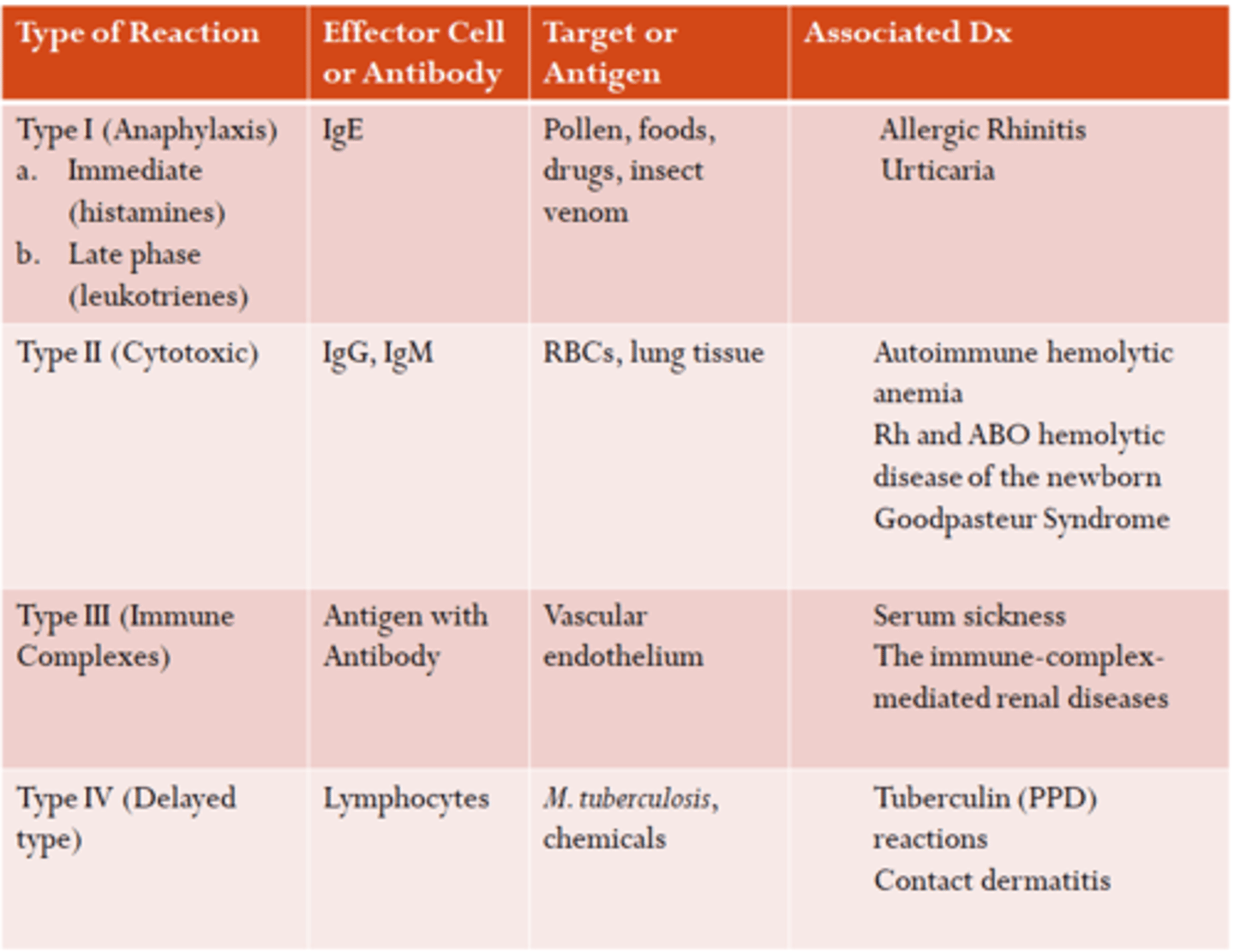
Type 1
What are the 4 types of hypersensitivities?
_______: Anaphylaxis/Allergies (IgE mediated) -- Acute vs late phase
A. Type 1
B. Type 2
C. Type 3
D. Type 4
Type 2
What are the 4 types of hypersensitivities?
___________: Cytotoxic (Body-Anti = Abx dependent) -- Foreign antigens/blood transfusion rxns
A. Type 1
B. Type 2
C. Type 3
D. Type 4
Type 3
What are the 4 types of hypersensitivities?
___________: Immune Complex rxn -- Immune Complexes deposited and stimulate inflammation (Serum sickness, Arthus rxn, Lupus)
A. Type 1
B. Type 2
C. Type 3
D. Type 4
Type 4
What are the 4 types of hypersensitivities?
__________: Delayed (Cell-mediated) -- >24 hrs later, PPD rxn or contact dermatitis (Poison IV)
A. Type 1
B. Type 2
C. Type 3
D. Type 4
What are the 4 types of hypersensitivities?
Anaphylaxis/Anaphylactoid
(NOTE: Anaphylactoid is not IgE mediated. It is d/t mast cell degranulation.)
Dz: Indistinguishable from each other
- Reactions occur within 5-30 minutes after antigen exposure
Multisystemic symptoms = cutaneous M/C
◦Angioedema and urticarial
◦ Respiratory symptoms (Wheeze, SOB)
◦ Cardiac (Hypotension)
◦ GI (Abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting)
Tx: Epinephrine!!!
Dennie's Lines
Lines from inner canthus that traverse the lower lid margin -- Indicates allergic rhinitis
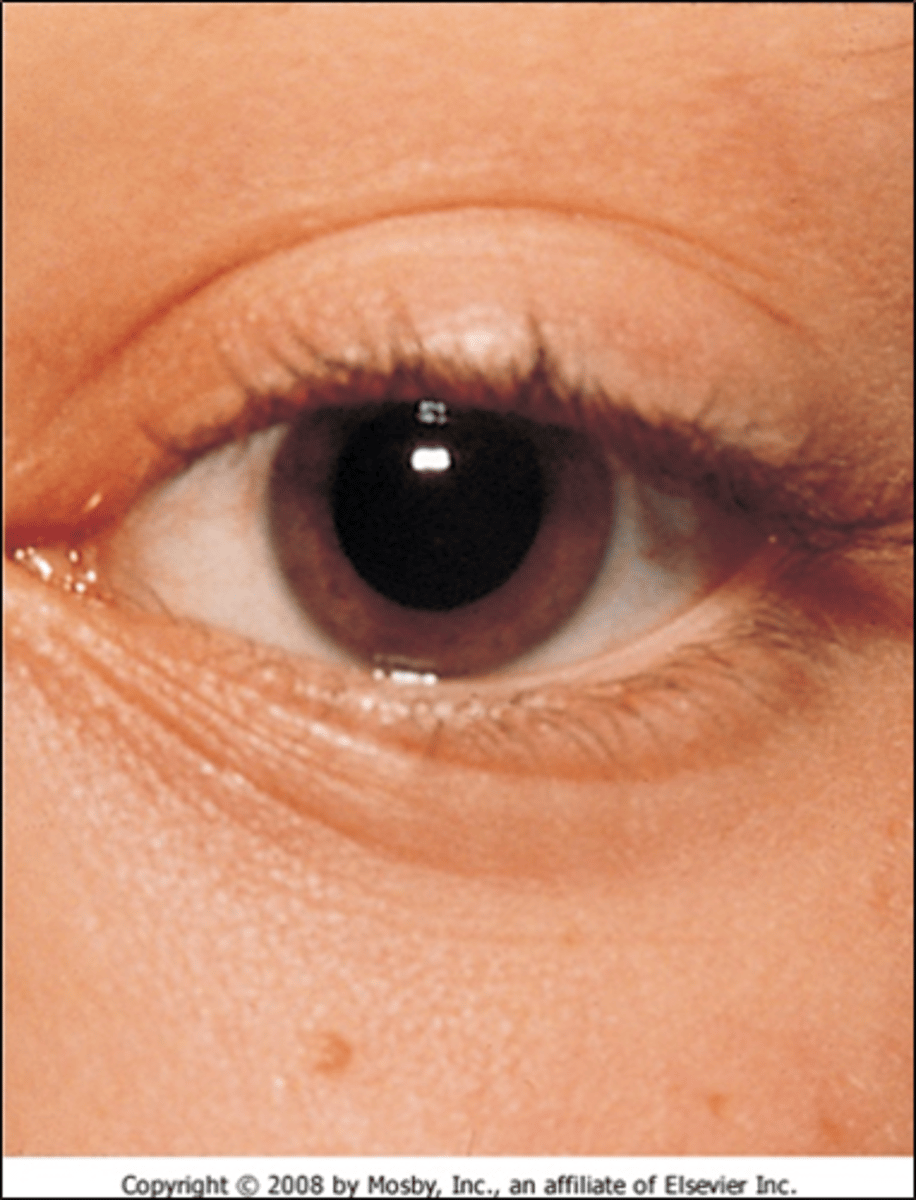
Allergic Conjunctivitis
Cause:
◦Inflammation of conjunctiva
◦IgE mediated response and Mast Cell degranulation
◦Increased vascular permeability
Clinical Features:
◦Conjunctival Injection (Erythema) + edema (chemosis) + Folliculitis (papillary edema)
Common Allergens:
◦Cats
◦Smoke
◦Pollen
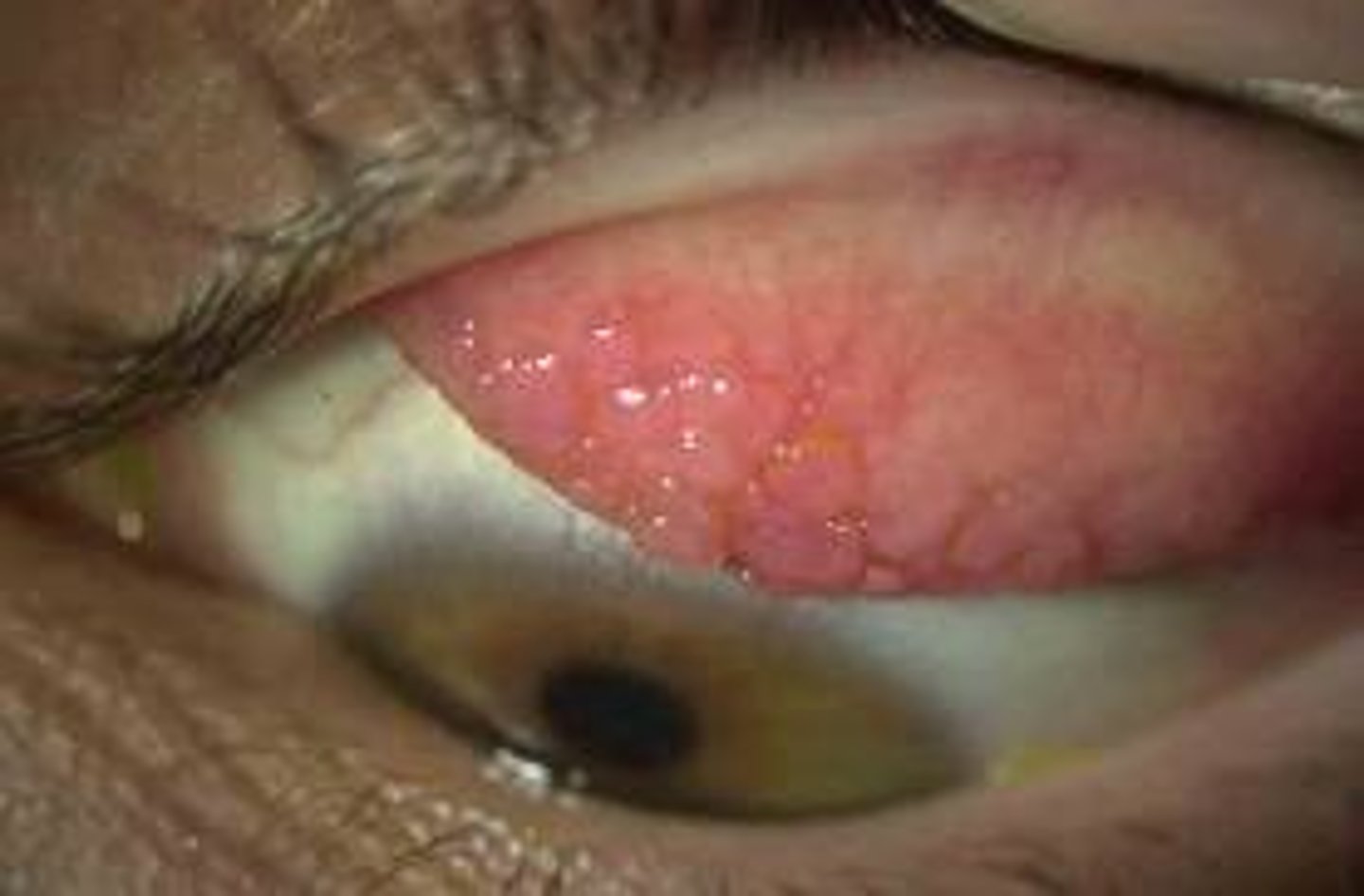
Allergic Rhinitis
S&S:
◦Nasal Itching à Transverse Nasal Crease = "Nasal Salute"
◦Mouth Breathing = High arched palate
◦Dental Malocclusion/overbite
◦Infraorbital congestion (dark circles à Allergic shiners)
◦Watery/mucoid rhinorrhea & postnasal drainage
◦Sneezing
◦Cobble stoning of posterior pharyngeal wall
◦Pale/violaceous nasal mucosa
◦Swollen nasal turbinate
Allergic Rhinitis
Dx Testing:
◦Nasal smear for eosinophils
◦Serum Total IgE
◦Allergy Skin test
◦Radioallergosorbant assay test (RAST)
Tx:
◦Avoiding offending agent
◦Antihistamines
◦Nasal cromolyn
◦Nasal Corticosteroids (Flonase, Nasonex, Nasacort, etc)
◦Immunotherapy
Atopic Dermatitis
Clinical Features:
◦ Itch --> Scratch --> Rash
◦ Chronic Pruritis
Physical Features:
◦ Dry Skin + scratch marks
◦ Erythematous papules, vesicle, plaques, lichenifiction
◦ Symmetrical Distribution
◦ Infants = cheeks, trunk, hands, feet, extremities (Extensor surface)
◦ Children = hands, feet, extremities (Flexural)
Atopic Dermatitis
Tx:
- Moisturizers: Aquaphor, Petrolatum, Eucerin, Cetaphil, Neutroderm, Lacticare, Keri
- Creams: Eucerin, Cetaphil, Cerave
- Lotions: Neutroderm, Lacticare, Keri
- Antihistamines: Hydroxyzine, Cetrizine
- Steroids: Desonide, Fluticasone, Mometasone, Flurocinolone
- Abx: Cephalexin, Dicloxacillin
Food Intolerance
___________: ABNL physiologic response to an ingested food, not immunologic
◦ Lactase deficiency: Bloating, Abdominal pain, Diarrhea
◦ GB Disease: ABD pain d/t fat indigestion
◦ Pancreatic Insufficiency: Malabsorption
◦ Bacterial Food Poisonings: Vomiting and Diarrhea
◦ Tyramine in aged cheese and/or MSG: HA
◦ Caffeine: Tachycardia and Nervousness
A. Food Intolerance
B. Food Allergy
IgE Mediated
Food allergy
1. __________ Oral Allergy syndrome, anaphylaxis, Urticaria/angioedema
A. IgE Mediated
B. Mixed IgE Mediated
C. Non-IgE Mediated
Mixed IgE Mediated
Food allergy
2. ______________: Atopic dermatitis, Allergic eosinophilic esophagitis/gastroenteritis
A. IgE Mediated
B. Mixed IgE Mediated
C. Non-IgE Mediated
Non-IgE Mediated
Food allergy
3. _____________: Proctocolitis or Enterocolitis (Cow milk hypersensitivity)
A. IgE Mediated
B. Mixed IgE Mediated
C. Non-IgE Mediated
delayed introduction of foods
**AAP no longer supports ________________.
**Introduce high allergy foods between ages 4-11 months regardless of risk of allergies**
Live Vaccines
- MMR**
- OPV
- Varicella**
- Yellow Fever
- Rotavirus (Oral)**
- Nasal Flu (Flumist)**
- Smallpox
- BCG
- Oral typhoid
A. Live Vaccines
B. Inactivated Vaccine
YES! There are NO CONTRAINDICATIONS to simultaneous administration of routine vaccines.
(Live vax must be given 4 weeks apart)
Can I give multiple vaccinations at a time?