Physics IA1
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
Properties of a vector
Magnitude & Direction
Projectile motion
Horizontal and vertical motion are independent of each other
Horizontal motion
Excluding air resistance, projectiles have no force acting on them horizontally, so horizontal velocity does not change until impact.
Projectiles
Objects flying through the air with no propulsion of their own
Normal force
The force acting upon an imaginary line drawn perpendicular to the surface
Tension
The pulling force transmitted along a rope, string, cable or chain on an object
Inclined planes
An inclined plane is a consists of a surface that is sloped (i.e. raised at an angle to the horizontal). The higher this angle to the horizontal, the higher the force directed down and parallel to it.
Uniform Circular Motion
UCM is when an object is moving in a circle at a constant speed.
Centripetal force (Fc - N)
The force acting on an object travelling in a circle that constantly either pulls or pushes the object towards the centre of motion. (F = mv^2/r)
Centripetal acceleration (ac - m/s^2)
The acceleration experienced by any object moving in a circular path directed towards the centre of motion
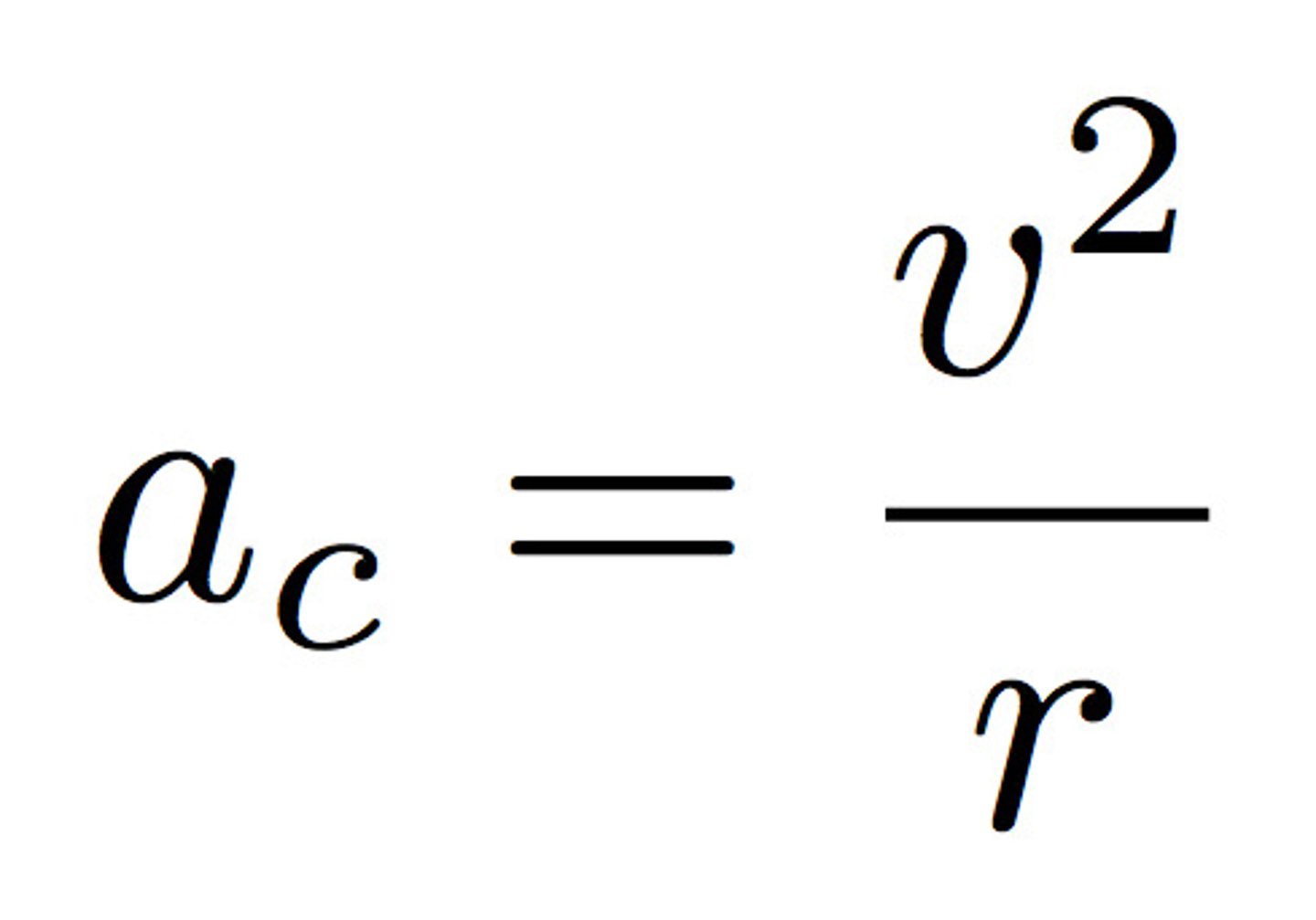
Average speed (v - m/s)
the rate of change of distance calculated by the formula: av speed = d/t (scaler quantity)
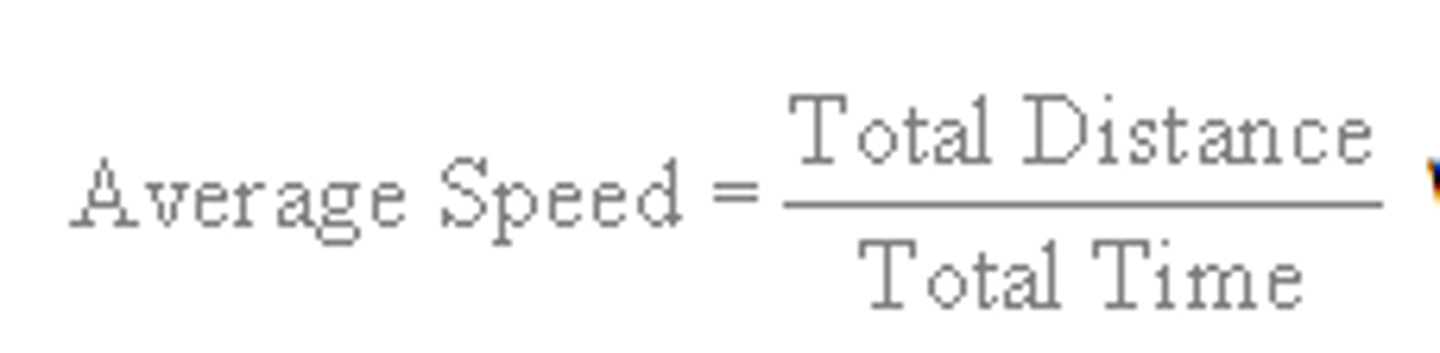
Period (T - s)
The time taken to complete one revolution calculated by the formula: period = t/no. of revolutions
Tangential velocity (v - m/s)
The linear velocity of an object undergoing circular motion
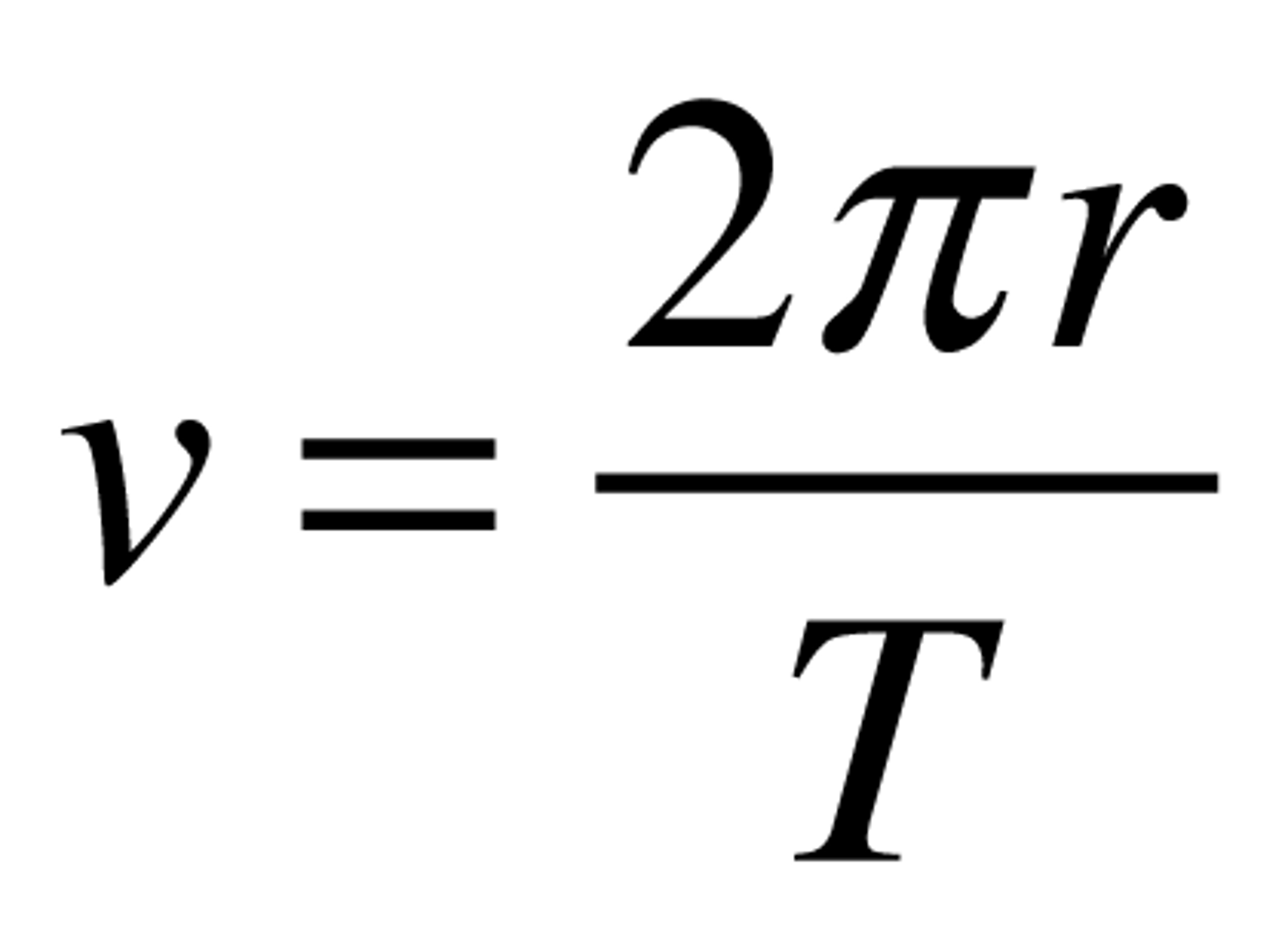
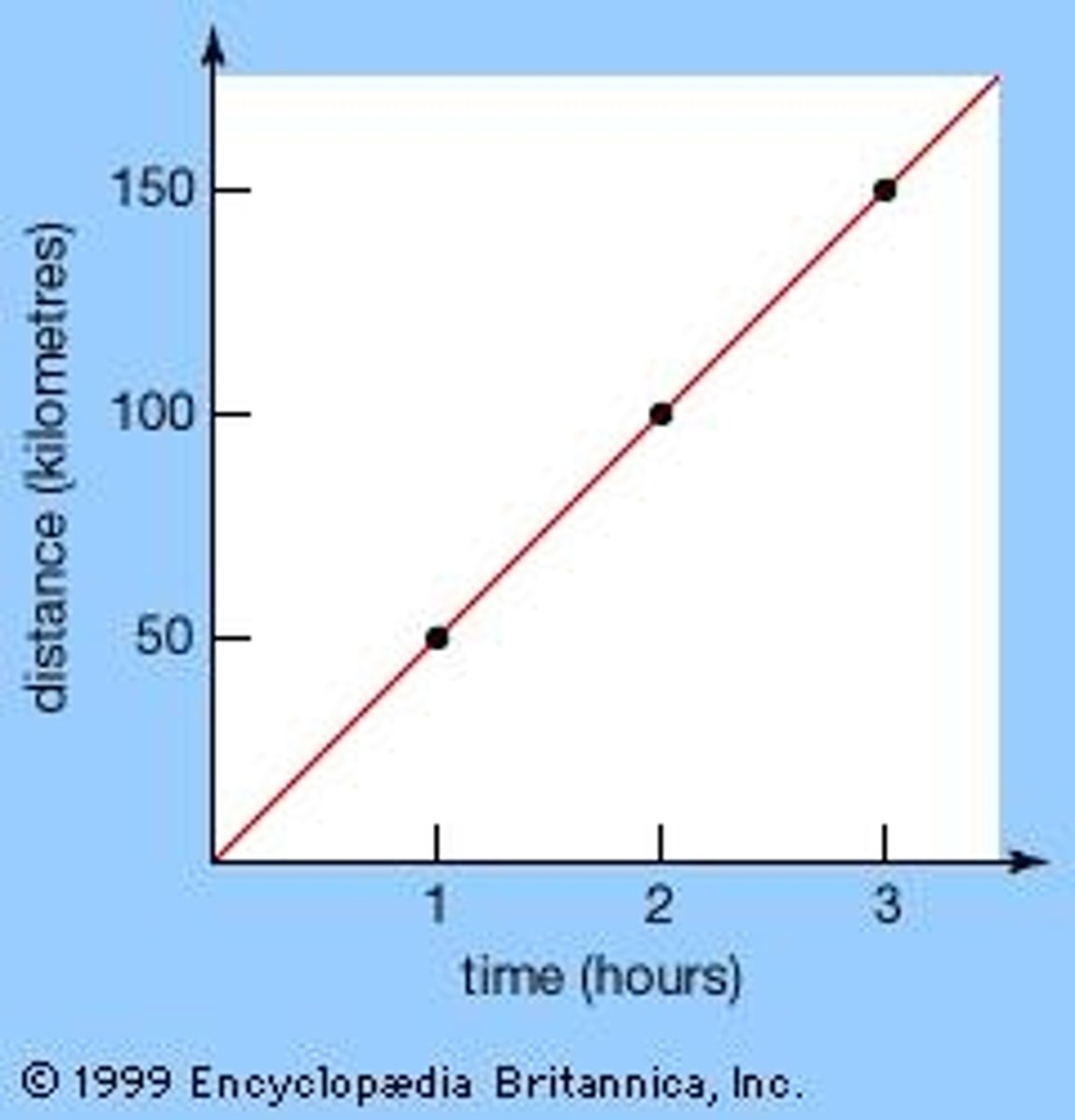
Linear relationship
A linear relationship is represented as a straight line when graphed (can be directly or indirectly proportional)
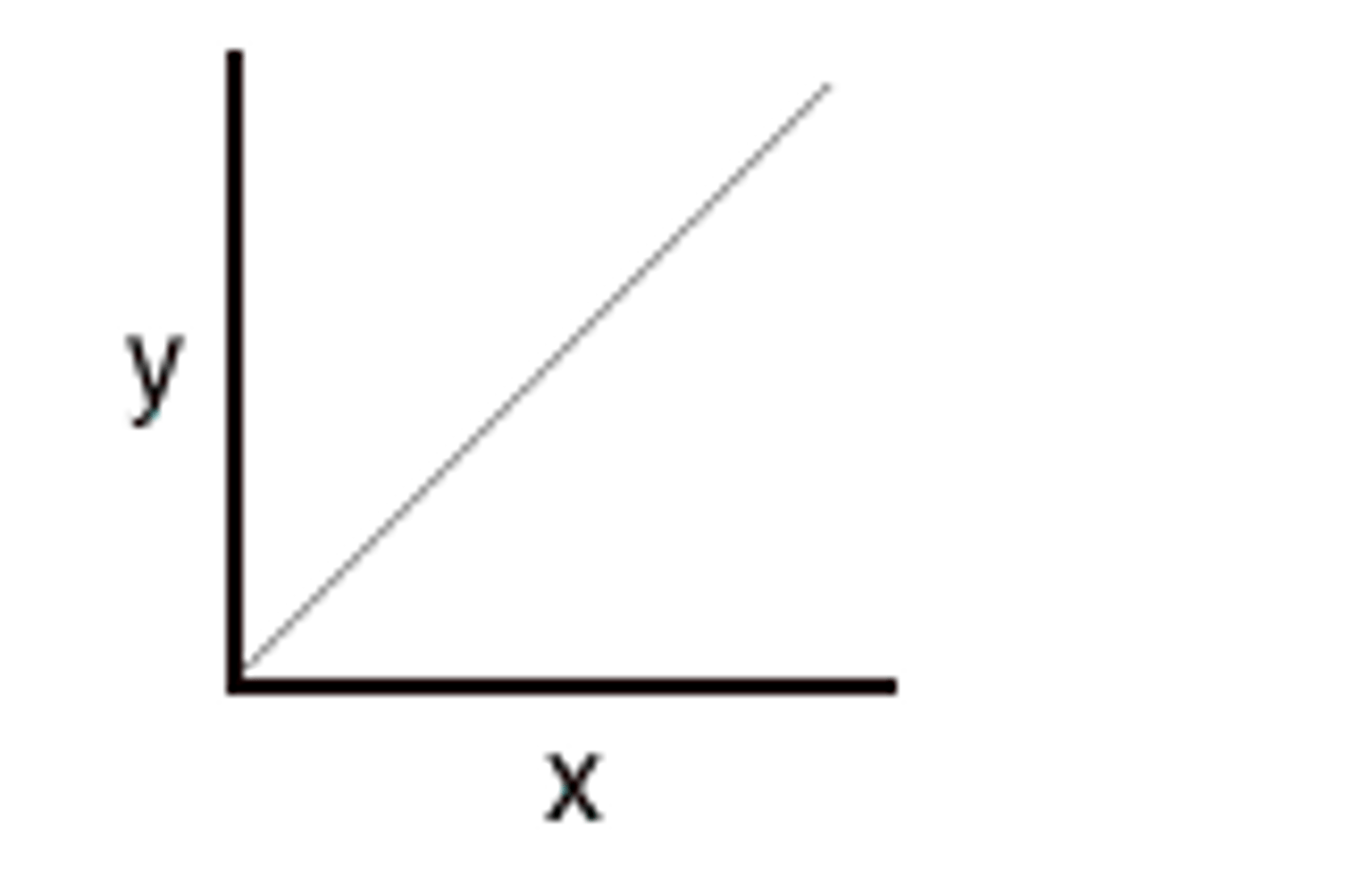
Directly proportional relationship
A linear relationship that goes through the origin when graphed
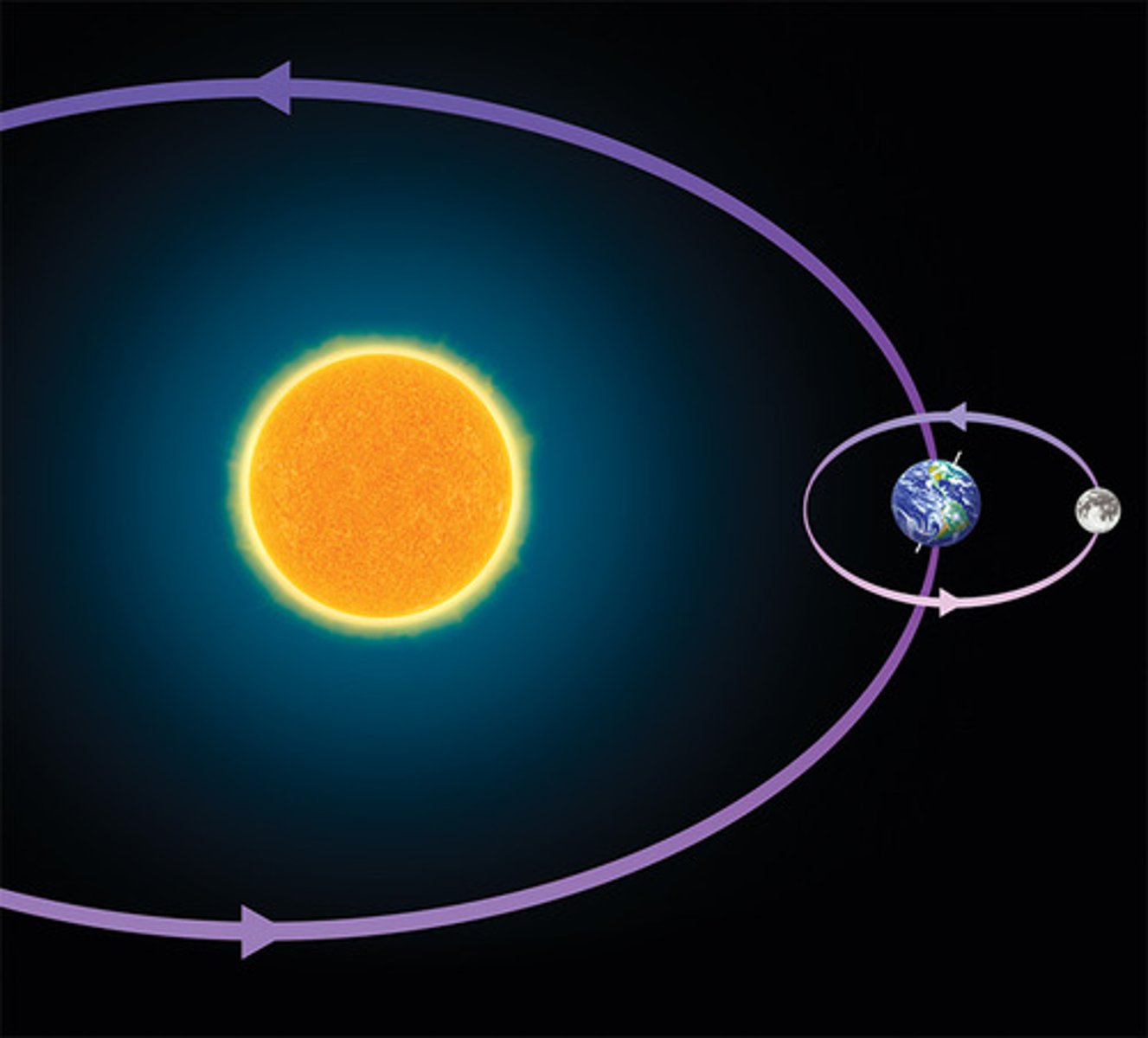
The Earth's path around the sun
Approximately uniform circular motion
Force Strength of Gravity
Extremely weak force compared to the others e.g. electromagnetism
Newton's 1st Law
(Law of Inertia) an object in motion tends to stay in motion & an object at rest stays at rest unless acted upon by an outside force.
Newton's 2nd Law
Force = mass x acceleration (F = ma)
Newton's 3rd Law
For every action force there is an equal and opposite reaction force
Gravity
A force of attraction between objects that is due to their masses.
Newton's Law of of Universal Gravitation
states that every particle of matter in the universe attracts every other particle with a force. This force is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
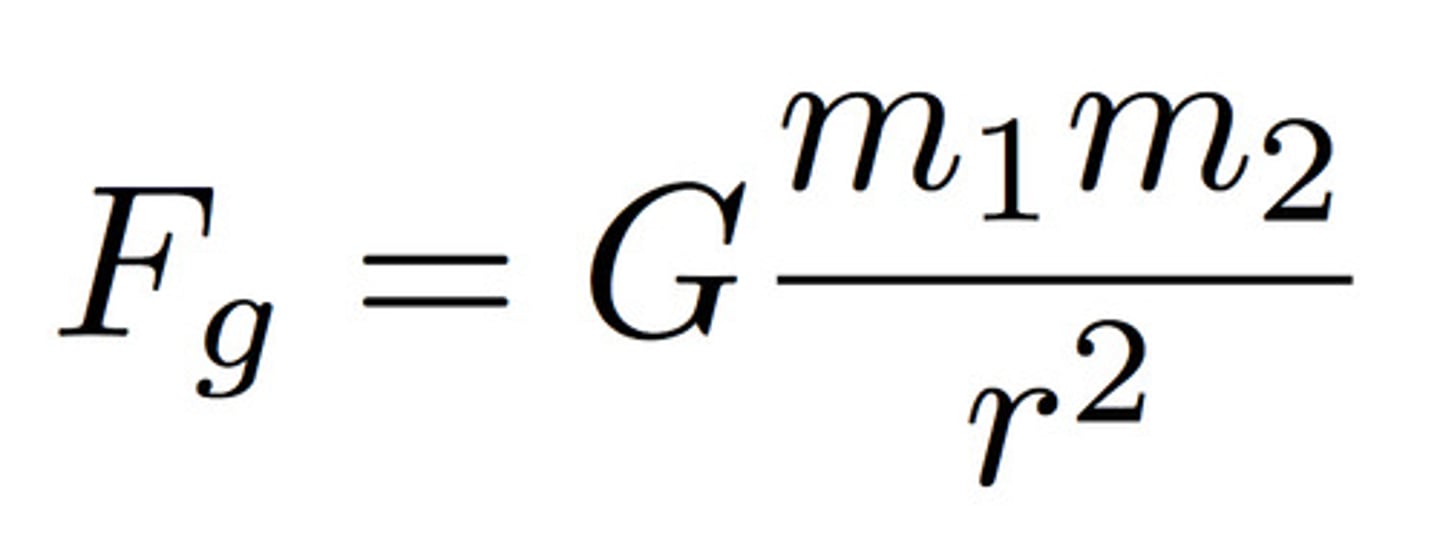
Gravitational Field
The region of space surrounding a body in which another body experiences a force of gravitational attraction.
Gravitational field direction
Towards the direction of the net gravitational force
1st Law of Planetary Motion (Law of Orbits)
All planets move about the sun in elliptical orbits, having the sun as one of their foci
2nd Law of Planetary Motion (Law of Areas)
A radius vector joining any planet to the sun sweeps out equal areas in equal lengths of time
3rd Law of Planetary Motion (Law of Periods)
The square of the sidereal period of a planet is directly proportional to the cube of its mean distance from the Sun (T^2 { r^3)
Sidereal period
The time it takes for a planet to complete 1 orbit of another body relative to the stars
Kepler's ratio
T² / a³ = constant
Coulomb's Law
Electric force between charged objects depends on the distance between the objects and the magnitude of the charges.
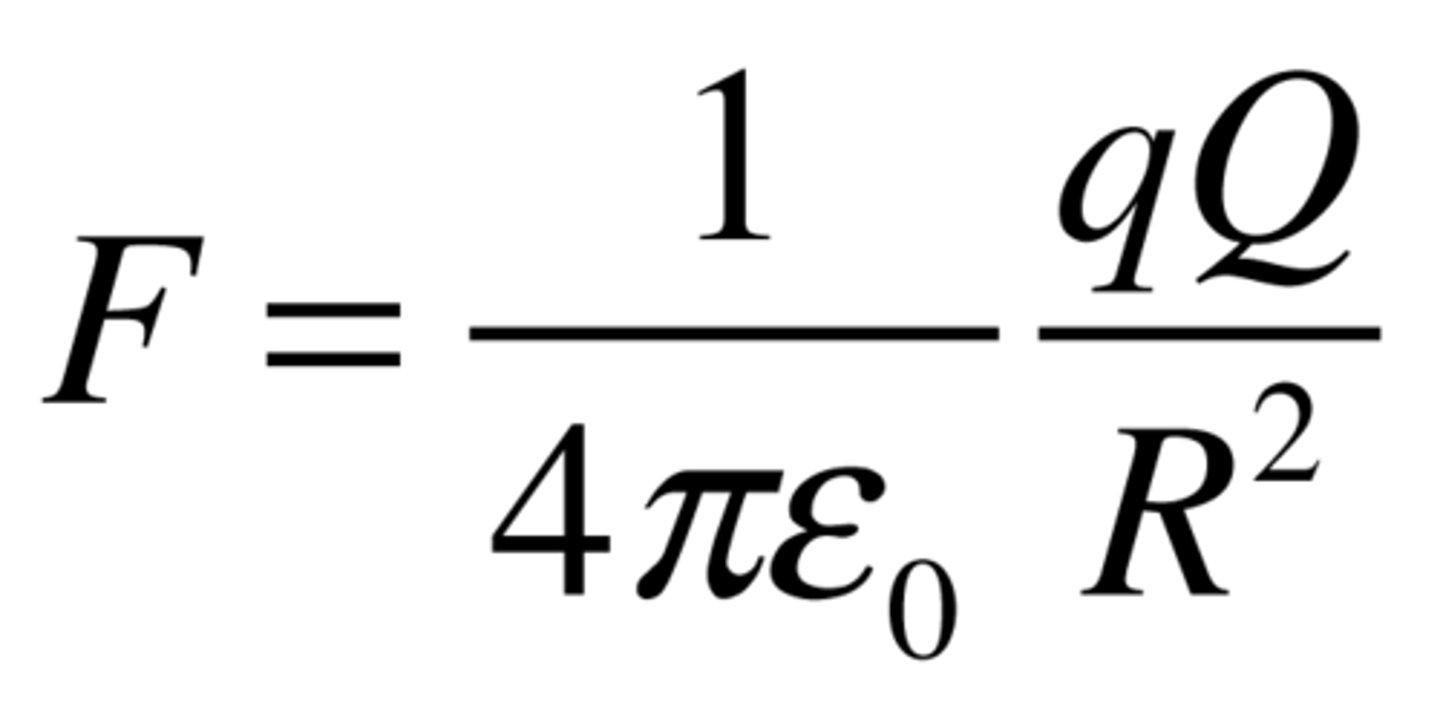
Electric Field
A region of space near an electrically charged particle or object within which a force would be exerted on other electrically charged particles or objects
Parabolic relationship
Graphs that have the same shape on either side of a turning point 'y is proportional to x2'
Inverse-square relationship
As the x value doubles the y value is divided by 4 (y α 1/x^2)
Inverse relationship
A relationship in which one variable decreases when another variable increases or when x is doubled y is halved (y α 1/x)