Chemistry 211 - Exam 3 Prep (GMU, Dr. Fayissa)
1/67
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
Particle
Localized energy
Mass
Momentum
KE and PE
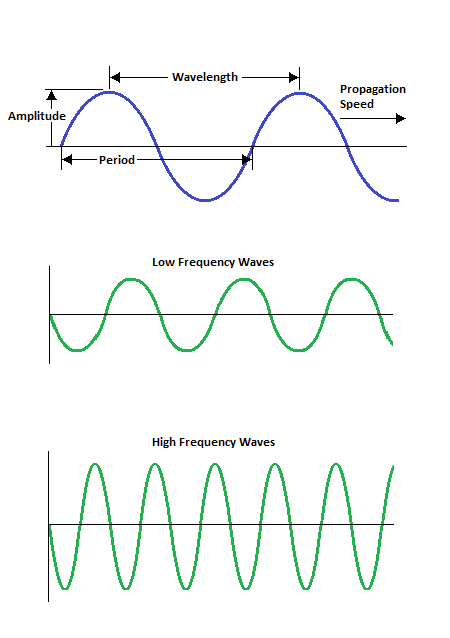
Wave
Continuous distribution of energy
Frequency (v)
Wavelength (λ)
Speed (c)
Amplitude (A)
When a wave hits a clear medium (like water)
it refracts because the speed of light changes which bends the path
When a particle hits a clear medium (like water)
the speed continues to change gradually
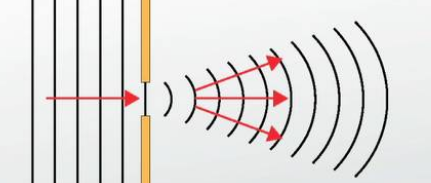
When a wave hits a small opening
it creates a semicircular wave coming out the other side (diffraction)
When a beam of particles hits a small opening
only what hit the opening go directly through to the other side, the rest is blocked
When a wave hits two small openings
it creates 2 semicircular waves thats can have both constructive and destructive interfrence with each other
Diffraction
Diffuses light/waves as it moves through a gap, leads to interference
Refraction
Bending light as it passes through something, think straw in water
Diffusion
Scattering light as it passes through something, think light through a prism = rainbow
Wavelength
Distance per cycle, λ
Frequency
Cycles per second, v
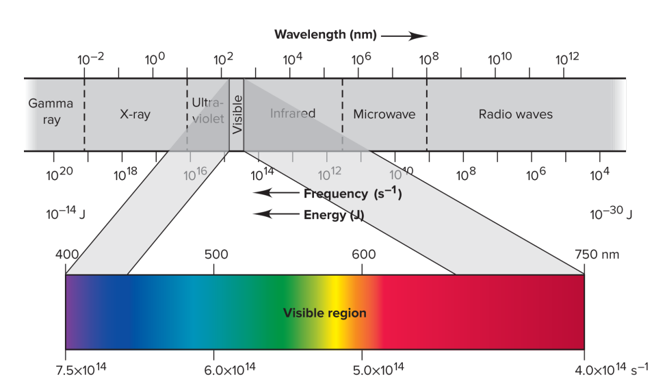
Electromagnetic Spectrum
This spectrum is the full range of electromagnetic radiation, organized by frequency or wavelength
Raging
Martians
Invaded
Venus
Using
X-ray
Guns
Blackbody Radiation
Visible light when a solid is heated to 1000K, color and intensity change with temperature
Temperature
is energy
Color
is determined by wavelength and frequency
Energy of a Photon Equation
E = nhv
AND
E = hc/λ
where,
n = postive integer
h = Planck’s constant
v = frequency
c = speed of light
λ = wavelength
Speed of Light
299,792,458 m/s
Plank’s Constant
6.626×10-23 J/s
Quantum Theory
LIMITs to how much energy something can emit or absorb
Quantized = fixed quantities for energy values
Change energy states either emit/absorb energy
Energy is directly proportional to
frequency of a wave
Energy is inversely proportional to
wavelength of a wave
Photoelectric Effect
Threshold frequency
Frequency determines whether electrons are released
No time lag
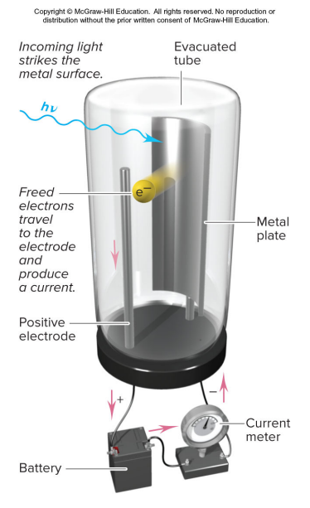
Energy of a Photon (Metal)
hv = Φ + (1/2)mv²
where:
hv = energy of a photon
Φ = binding energy of a electron to a metal surface, different for each metal
m = mass
v = velocity
Spectral Lines of Atomic Hydrogen
The line spectrum emitted by a hydrogen atom when an excited hydrogen atom returns to its ground state.
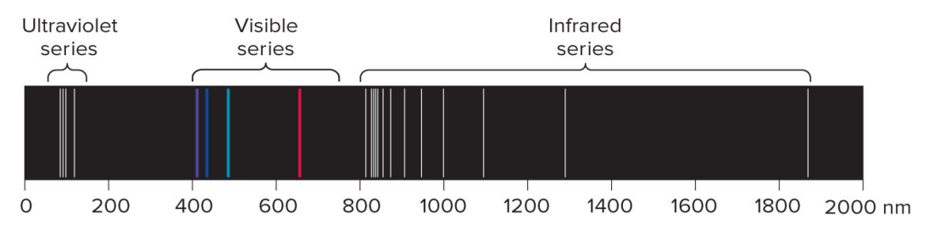
Rydberg Equation
A mathematical formula to determine the wavelength of light emitted by an electron moving between the energy levels of an atom. This equation doesn’t explain why line spectra occurs.
where:
n2 > n1
If n1 =
1: UV
2: Visible
3: Infrared
R = Rydberg constant, 1.0967×107 m-1
λ = wavelength
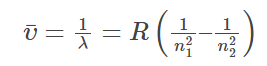
Issues with Rutherford
Positive nucleus is supposed to attract negative electrons, but it doesn’t
Contradicts classical physics
Supposed to be a continuous specrtra, like an ombre, not like the actual hydrogen line spectra
Bohr fixes Rutherford Issues
Planck + Einstein = quantized energy
Stationary states
Hydrogen only has certian energy levels, and they have fixed orbits
Higher level is further from nucleus, but further is less stable
1st orbit is ground state
Change of Energy of a Photon
EPhoton = EFinal - EInitial= hv
hv = energy of a photon
No energy emitted in stationary states
Jumping states emit or absorb photons
Higher than n=1 (ground state) is an excited state
Quantum Staircase
Space between levels get smaller as you get farther away from the nucleus
Highest frequency needed to go from n=1 to n=2
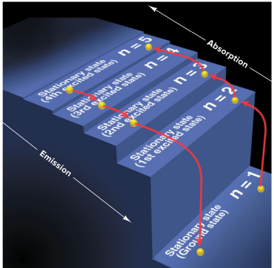
Photon Absorbtion
Lower energy level to higher energy level
EX: n=2 > n=4
Photon Emission
Higher energy level to lower energy level
EX: n=3 > n=1
Bohr Model Equation
where:
z = charge of nucleus
n = energy of ground state
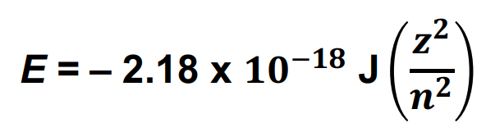
Matter/Energy Equation
e = mc²
where:
e = energy
m = mass
c = speed of light
De Broglie Wavelength
h = Plank’s Constant, 6.626×10-34 J*s
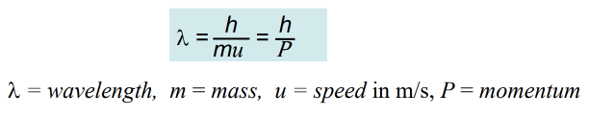
Heisenburg’s Uncertainty Principle
Can’t know both position and speed at the same time
If we know one, the other becomes less certain and vice versa
Quantum Mechanics
Wave nature of objects on the atomic scale
Schrodinger’s Wave Equation (Quantum Mechanics)
HΨ = EΨ
where:
H = Hamiltonian Operator (Total Energy of a System, KE + PE)
Ψ = Wave function is atomic orbital
E = Energy
Ψ² = Probabilty density, the measure of the probability of finding an electron in some tiny volume of the atom
Solveable for hydrogen, not for many-electron atoms
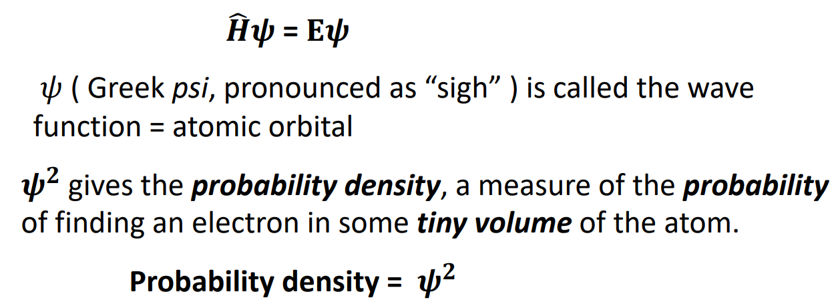
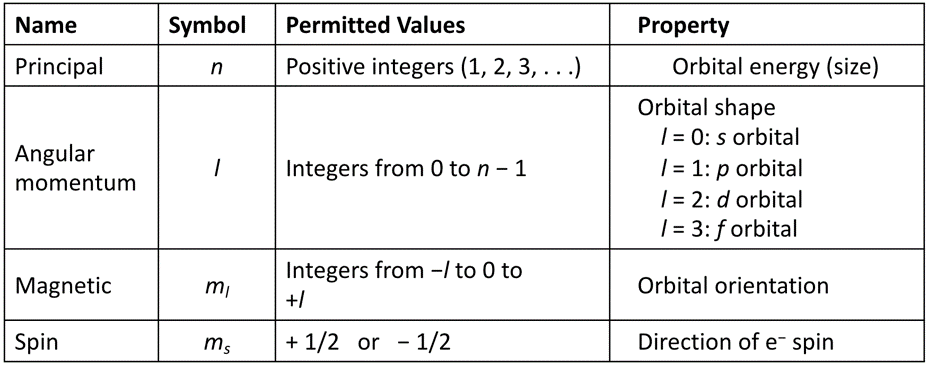
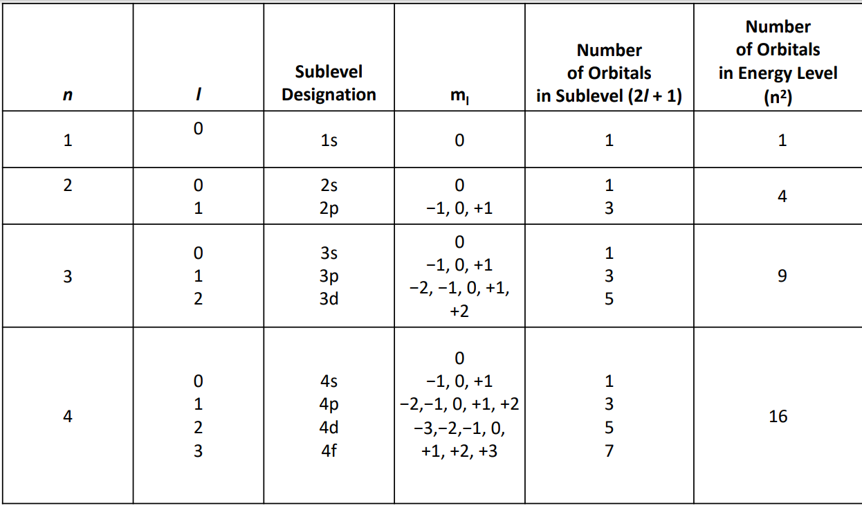
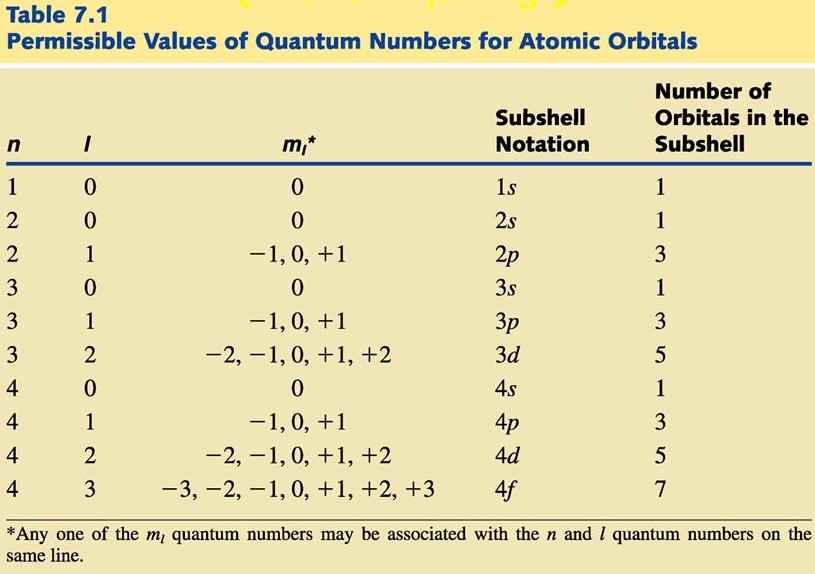
4 Quantum Numbers
Principle (n)
Always postive
Relative size and distance from nucleus
Energy
Angular Momentum (l)
Any number from 0 to (n-1)
Shape
Magnetic (ml)
-l
-l+1
0
l+1
l
Orientation
Spin (m2)
+1/2
-1/2
Direction of electron spin
n, l, m Chart
Pauli Exclusion Principle
Each atom is described completely by the four quantum numbers
No atom in an element will have the exact same 4 numbers
An atomic orbital can hold a maximum of two electrons and they have opposite spins.
Factors Affecting Atomic Orbital Energies
Nuclear charge
Shielding Effect
Orbital shape
As a element gets bigger the closer electrons get pulled more closely, while the farther away electrons are not pulled as tightly due to shielding and being farther away from the nucleus.
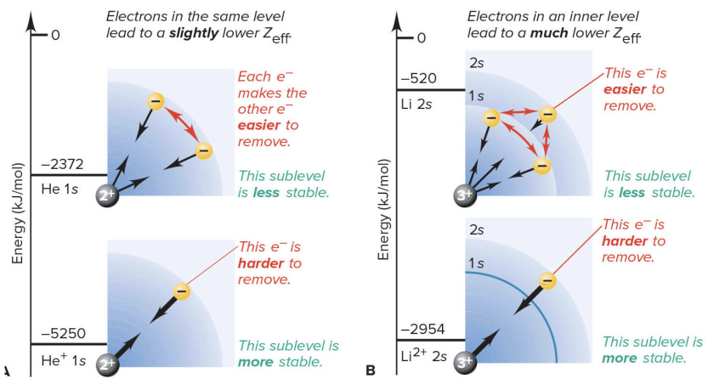
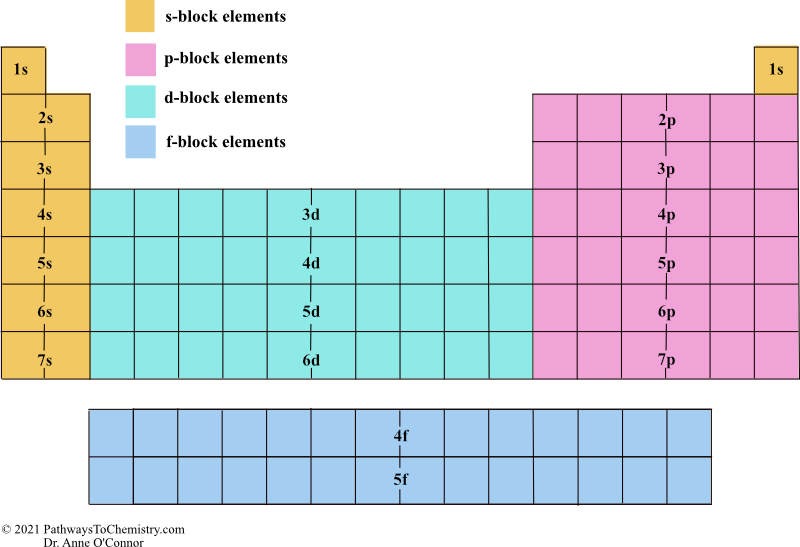
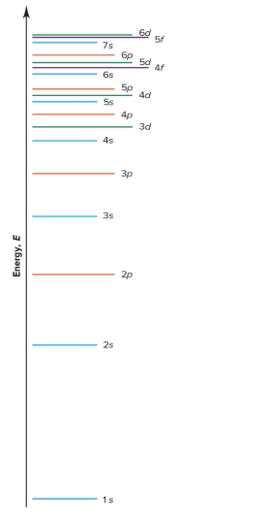
Sublevel Energy Levels
s < p < d < f in energy
Ground State Electron Configuration Example

Electron Configuration Chart
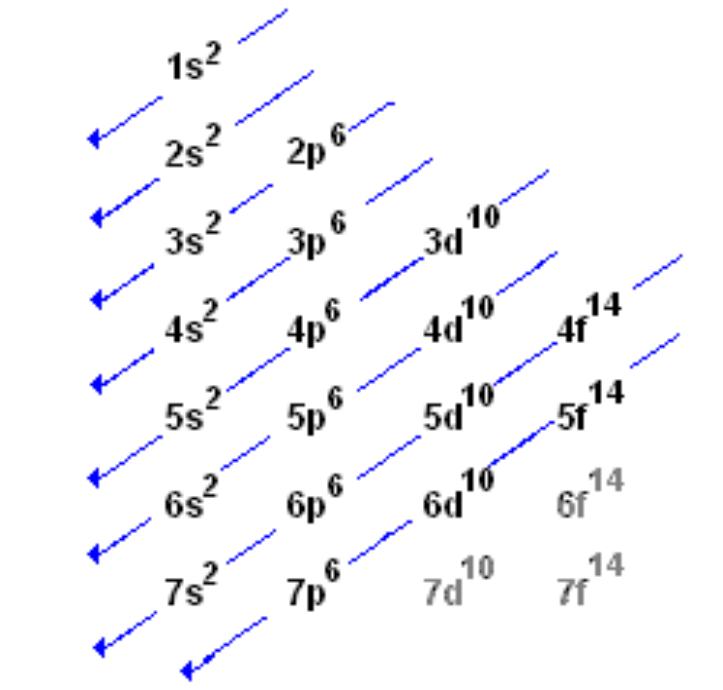
Ground State for Elements and Their Electrons
The most stable state for an element, which can be found from the periodic table (all elements are in these states on the periodic table)

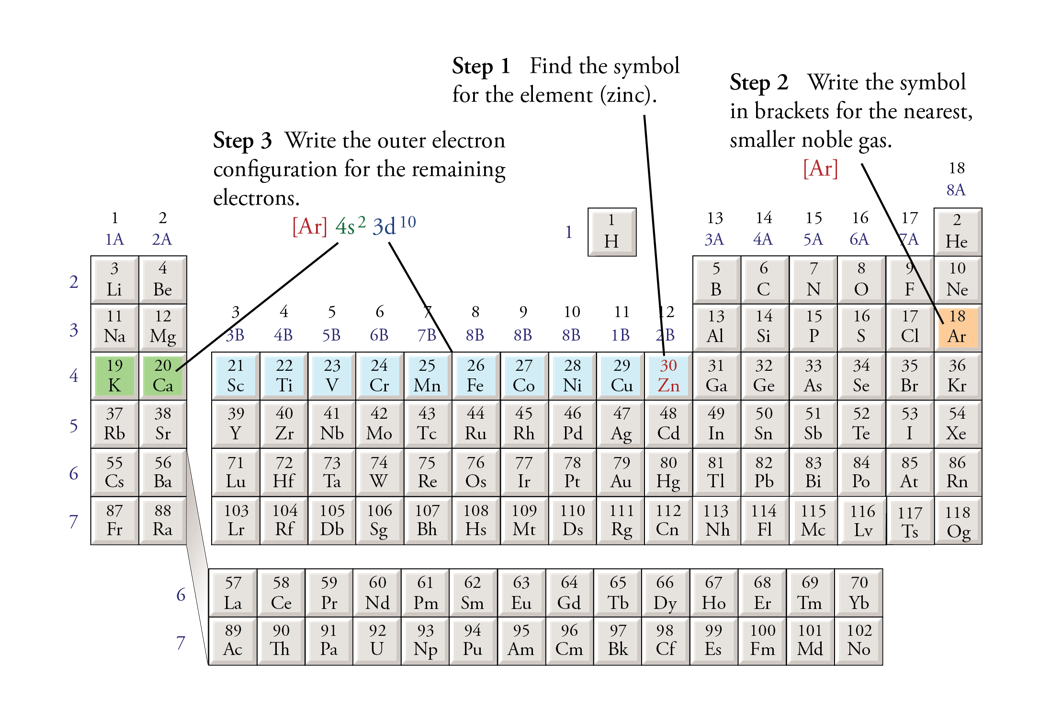
Condensed Electron Configuration
Find the element on the table
Write the symbol in brackets for the nearest, smaller noble gas
Subtract the amount of electrons for the noble gas from the element you are writing for
Write the electron config for those remaining atoms
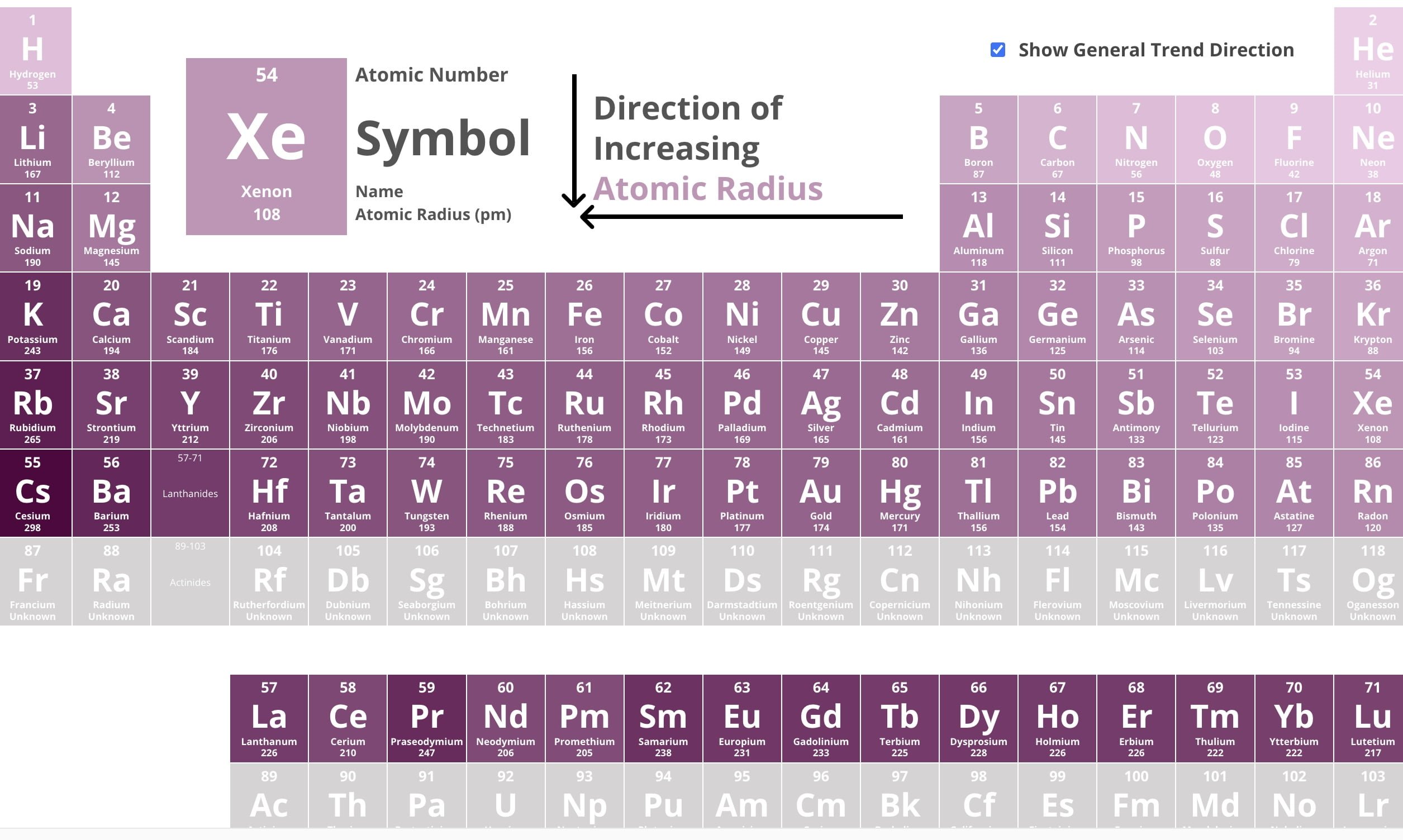
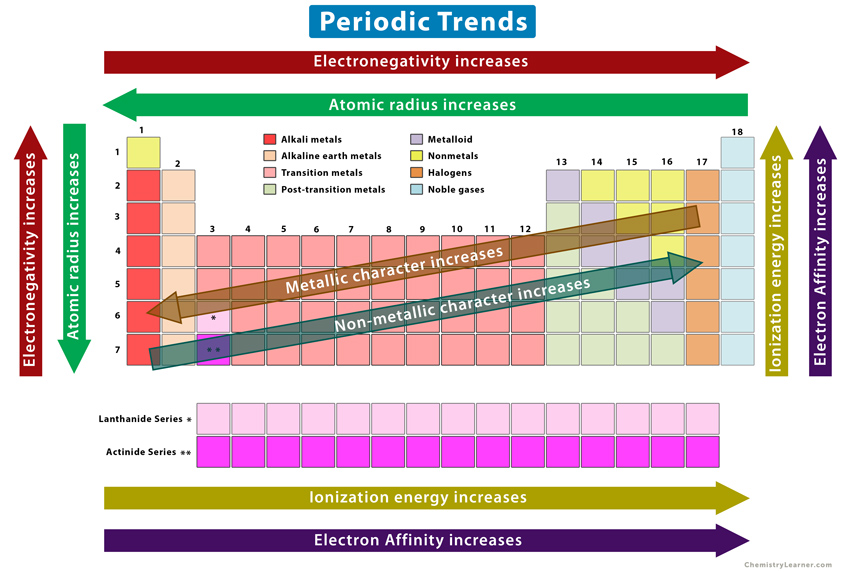
Atomic Radius Trend
Increases DOWN a column
Increases to the LEFT of a period
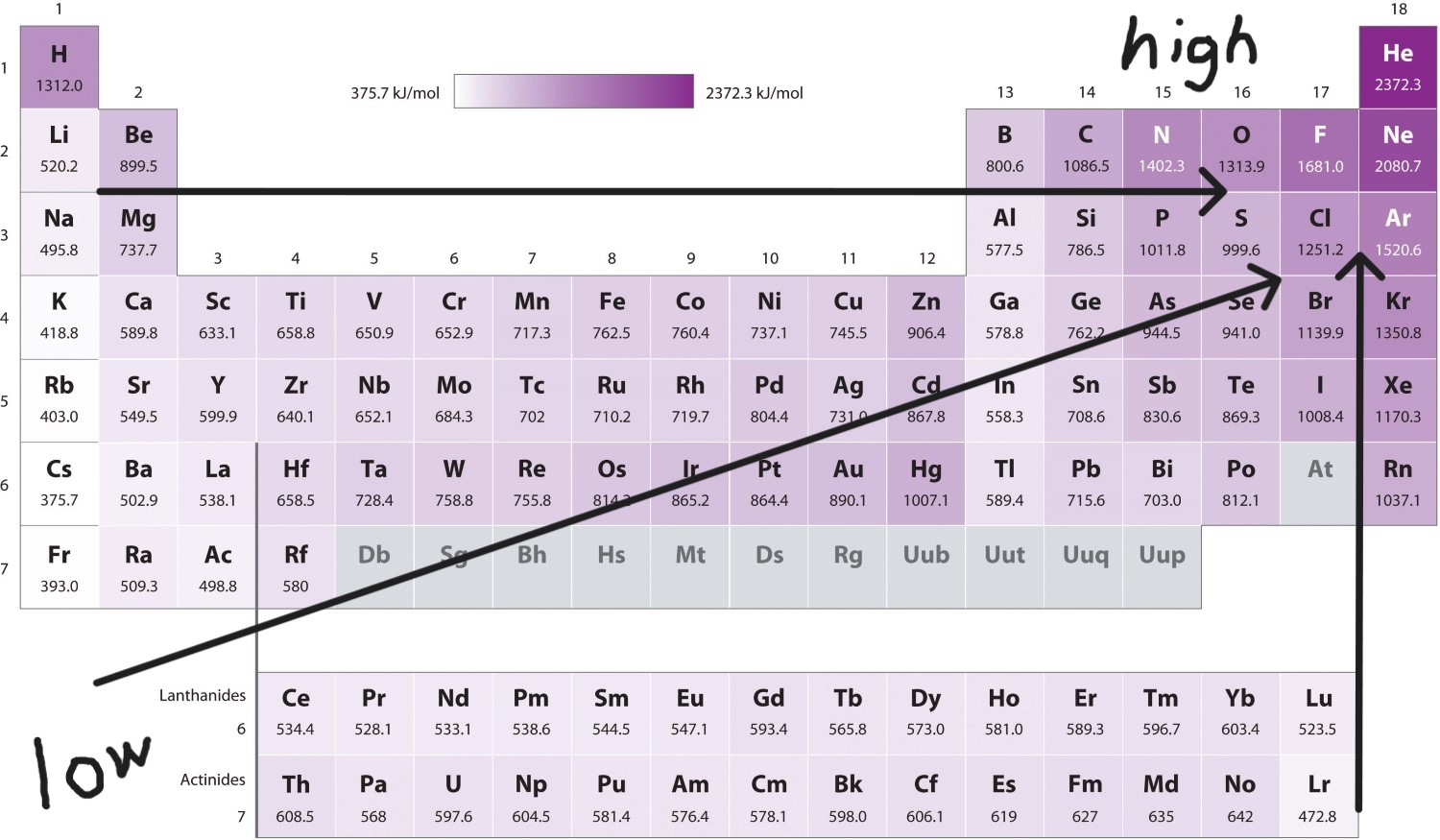
Ionization Energy Trend
Increases UP a column
Increases to the RIGHT of a period
Electron Affinity Trend
Increases UP a column
Increases to the RIGHT of a period
(with many exceptions for both)

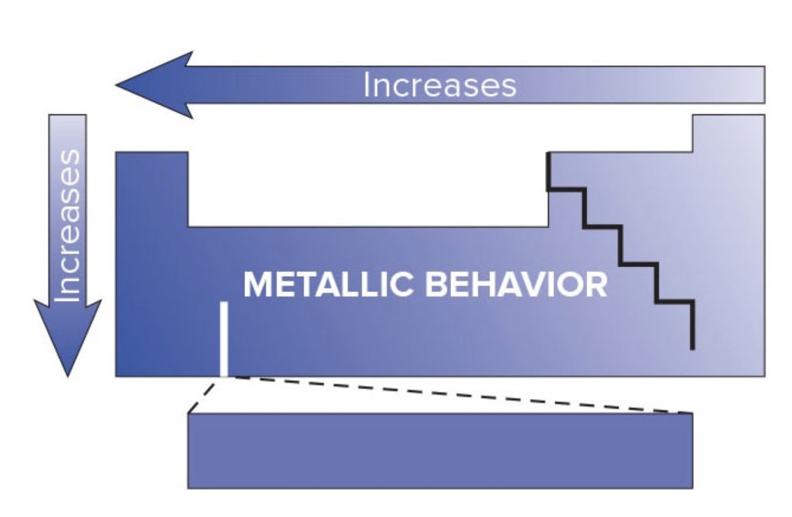
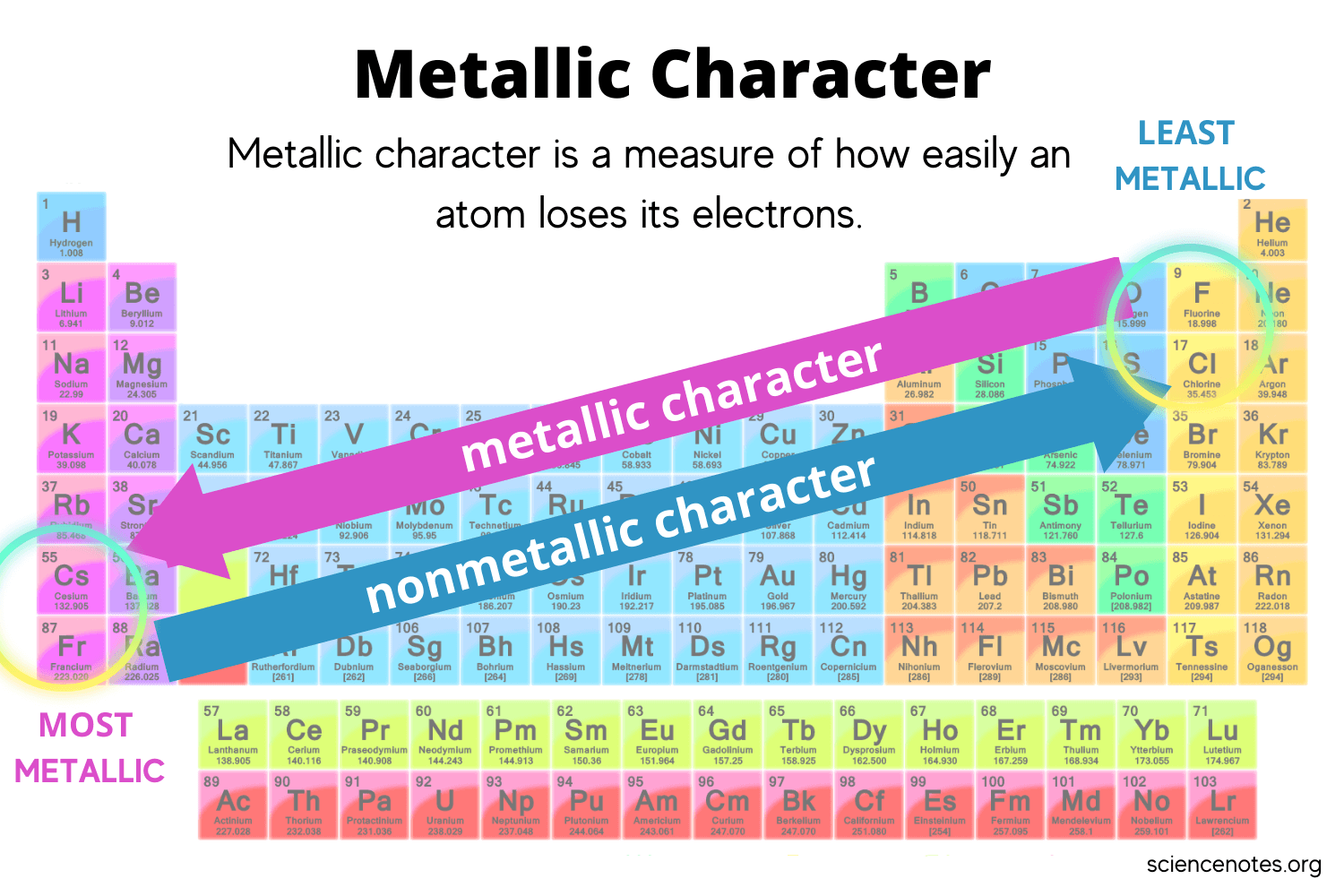
Metalic Behavior Trend
Increases DOWN a column
Increases to the LEFT of a period
Ionic Bonding
Bond between metal and nonmetal, the metal transfers an electron to the nonmetal, a strong bond
Covalent Bonding
Sharing of electrons between two nonmetals, a weak bond
Metallic Bonding
A type of chemical bond similar to a covalent bond. Atoms in metals are held together by forces caused by the valence electrons. Electrons float freely around metalic ion cores.
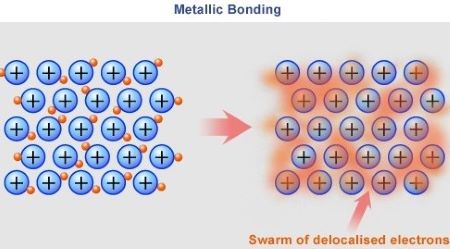
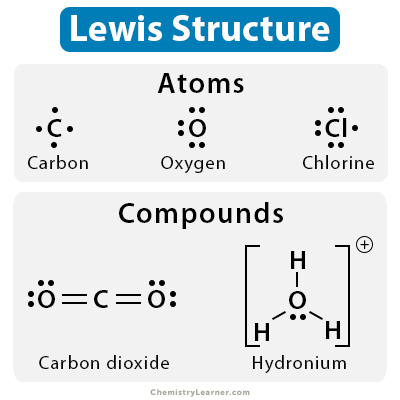
Lewis Dot Diagram
Representation of valence electrons.
- is a pair electron bond between two elements
= is a double pair electron bond between two elements
Each dot represents an electron
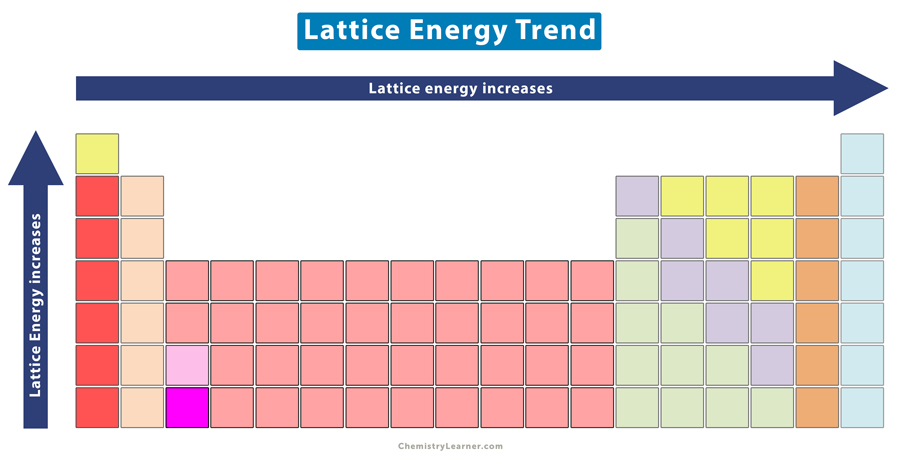
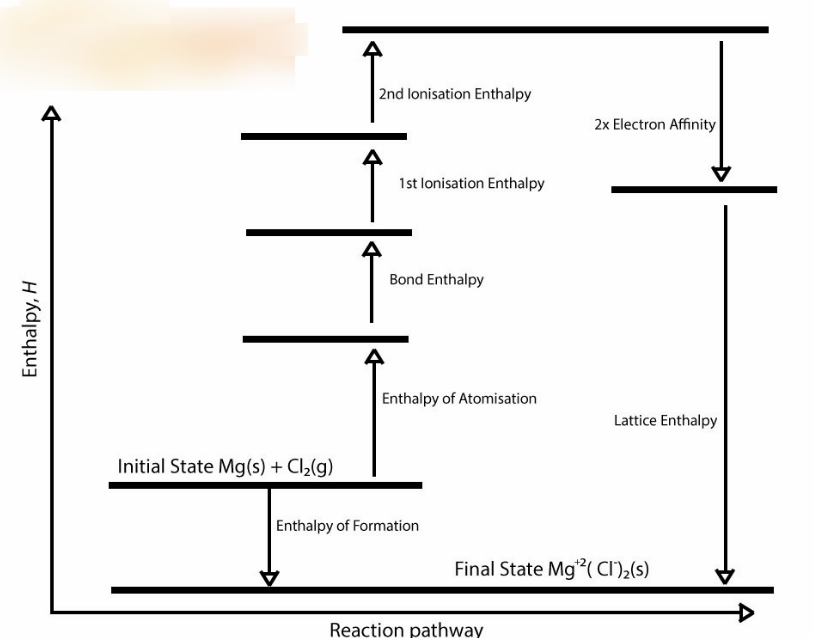
Lattice Energy Trend
Lattice energy: the energy required to separate 1 mol of an ionic solid into gaseous ions.
As ionic size increases, lattice energy decreases.
As ionic charge increases, lattice energy increases.
Coulomb’s Law
k(Q1*Q2 / r1 + r2)
where:
k = Coulomb’s constant
Q1 = Charge of particle 1
Q2 = Charge of particle 2
r1 = Particle 1 radius
r2 = Particle 2 radius
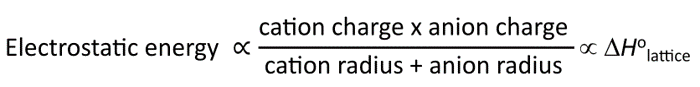
Covalent Bond Properties
Bond Order
The number of electrons being bonded.
EX:
Bond Order 1 = Single Bond
Bond Order 2 = Double Bond
Bond Order 3 = Triple Bond
Bond Energy
Energy needed to overcome the attraction between the nuclei and shared electrons. The stronger the bond, the higher the bond energy.
Higher bond order = more bond energy
Lower bond order = less bond energy
Bond Length
The distance between the nuclei of bonded atom
Higher bond order = shorter length (3)
Lower bond order = longer length (1)
Enthalpy of a Reaction
Change in H of Reaction = Change in H of Reactant Bonds - Change in H of Product Bonds
You basically subtract the H of products from the H of Reactants to find your H of the whole reaction
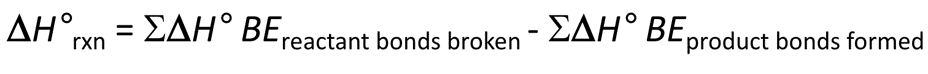
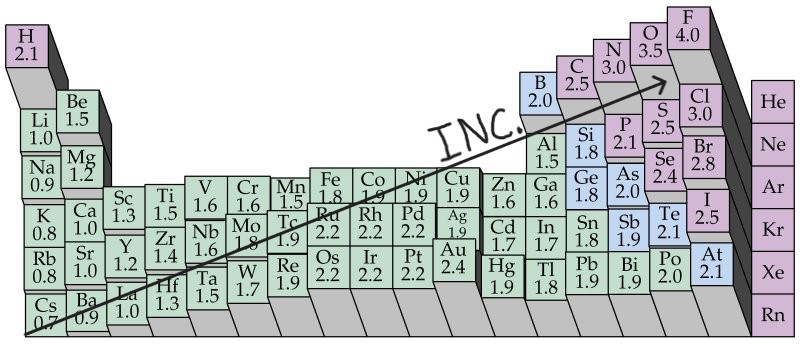
Electronegativity Trends
Increases UP a column
Increases to the RIGHT of a period
Bond Polarity / Ionic Character
The greater the difference in electronegativities between two bonded atoms, the greater the polarity / Ionic Character of the bond
Metallic and Non-Metallic Character
Diamagnetic Elements
Elements that have all of their electrons paired up in their electron configuration.
Paramagnetic (Non-Diamagnetic)
Elements that have one or more unpaired electrons in their electron configuration.
Quantum Numbers for Oribitals
S: l = 0, m1 = 0
P: l = 1, m1 = -1, 0, +1
D: l = 2, m1 = -2, -1, 0, +1, +2
F: l = 3, m1 = -3, -2, -1, 0, +1, +2, +3
Lattice Enthalpy Energy Diagram
All Periodic Table Trends
SPDF Blocks Periodic Table