116 infection 1
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
87 Terms
physical barriers
skin (keratin) and mucous membranes (nose, GI tract)
body defenses
phagocytosis, inflammatory mediators, interferons and interleukins, specific (memory) response, fever
interferons and IL
immunogenic proteins (cytokines) secreted by WBCs, stimulate immune responses
WBCs
eosinophil, basophil, monocyte, neutrophils, T, B and NK cells
secrete ILs
naive t cells and Th2 cells
th2
aid in immune response, communicates via IL
allergy first responders
T reg, cytotoxic, Th2 -secrete IL
neutrophils
up to 70% of WBCs -1st to site of damage -live up to 1 week -immature = band
lymphocytes
innate and adaptive (memory) -NK, B cells, T cells
monocytes
in blood, and macrophages in tissues -specific to tissues
eosinophils
allergy response -release enzymes/ chem mediators to destroy allergens and parasites
basophils
allergy response -pro inflammatory and anti-coagulating
boosters
boost memory, promoting active immunity
passive immunity
transferred from one person to another -fetus, meds
B cells
antigen presents itself and b cells clone (millions of copies, aka plasma cells) -antibodies secreted which circulate: immunoglobulins
immunoglobulins
most common IgG, secreted from B cells
antibodies fx
neutralize or mark for destruction (by phagocytic cells)
the next exposure
memory b cells always remember antigen and response is immediate and very fast during
t cell types
helper, cytotoxic, memory
t cells
t helper activates B cells, secrete cytokines -t memory cells develop post exposure and recognize antigen next time to respond fast
cytokines
interleukins, interferon, tumor necrosis factor, perforin
causes of decreased WBC
autoimmune disease, drug therapy, chronic infection/inflammation, immunodeficiencies, cancer
autoimmune disease
like IBD -systemic inflammation decreases synthesis and proliferation -depletion due to chronic inflammatory requirements
drug therapy
glucocorticoids (lower inflammatory process) -immunosuppressant drugs (biologics)
chronic infection/inflammation
mononucleosis, HIV -longterm infections = depletion due to chronic requirements
immunodeficiencies
look up during patient research -inborn errors
cancer
lymphomas, leukemias -destruction of production organs -interference with maturation of normal WBCs
causes an infection
host susceptibility, pathogenicity, port of entry
pathogenicity
organisms ability evade or overcome body defenses
pathogens
bacteria, viruses, fungi, parasites
virulence
the power to produce disease (covid 19 has high virulence)(potency) -even low numbers of pathogen are able to produce disease
port of entry
into the body past endogenous defenses
mechanisms of infection
strength in numbers and toxin production (raises ability to live in host environment)
prevention by decreasing numbers
80% of infections spread by hands (WASH) -streptococcus septicemia common in early 1990s
microflora
microorganisms present on/in human body -commensalism, mutualism (intestinal flora), parasitic relationship
intestinal flora
vitamin K and B formation -balance of good and bad
infectious disease
pathogens -host is negatively affected -parasitic relationship
opportunistic
affects one person but not another -any microorganism causing disease -eg. intestinal infection in an immuno suppressed host -common in high risk patients: chronic illness, elderly, newborn, drug tx, malnutrition
parasites
animals -3 main groups: protozoa (malaria), helmiths (tapeworm), arthropods (lice, ticks, mites, fleas) -not high numbers, not often in hospitals
fungi
eukaryotic (organized nucleus), freely reproduce -yeast and mold (candida albicans) -like dark, moist environments -severe disease is rare in a non compromised host
fungi disease
superficial: superficial mycoses (athletes foot, thrush, ringworm) -systemic: (lung, GI) rare serious and difficult to treat -prevention is key
viruses
no cell structure: protein coat and nuleic acid only (DNA or RNA) -retroviruses like HIV
-host needs to survive and replicate -more common and contagious than other pathogens
retroviruses
RNA only, requires reverse transcription into DNA (enzyme reverse trascriptase) -HIV (cause of aids)
virus host
must replicate and survive -must access host cell -may lyse host cell -eg HIV lyses host cell during replication -HPV alters host cell = oncogenic
common viral infections
covid 19, influenza, common cold, laryngitis
virus tx
symptom management: antivirals -immune system support: IVIG (boost immune response like interferons) -prevention: immunizations
bacteria
prokaryotes -no organized nucleus -contain DNA (small DNA bodies: plasmids) and RNA -reproduce autonomously -colonize affected areas: biofilms -like specific conditions -less contagious than viruses -commonly secrete toxin (exogenous pyrogens) = contribute to inflammation and disease process -gram negative or positive
bacteria tx
antibiotics -resistance is increasing
port of entry examples
direct content, inhalation, ingestion
direct contact
with the infected host -STIs, diseases causing a wound/rash (chickenpox)
inhalation
of airborne pathogens -resp diseases, colds, pathogens causing meningitis, childhood disease -chicken pox
ingestion
of contaminated foods -food poisoning -parasites (eggs) -food borne viruses (Hep A)
source of infection
nosocomial: acquired in hospital -community acquired: outside of hospital
emia suffix
for pathogen presence in blood -bacter____ = bacteria in blood
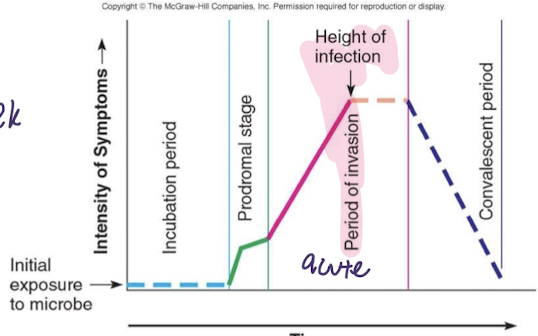
incubation
pathogen present and replicating -no symptoms -can infect others
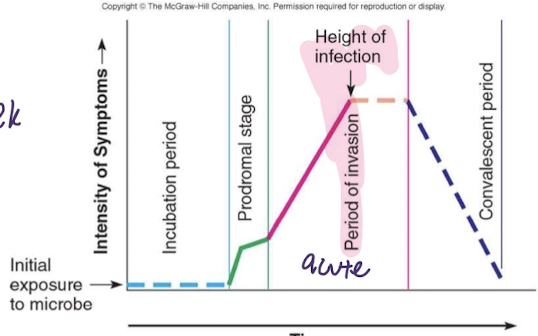
prodromal stage
initial symptoms: malaise, mild fever, headache, myalgia -generic in nature (hard to differentiate)
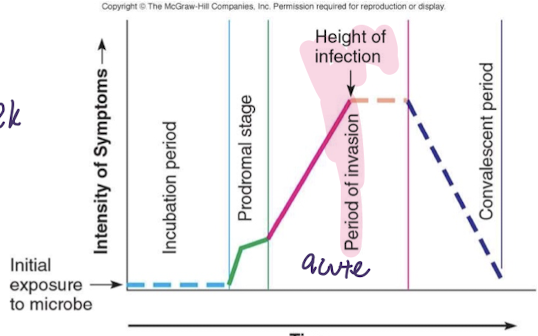
acute stage
maximum presence of pathogen, maximum response by host -maximum impact of infection -more specific and consistent symptoms
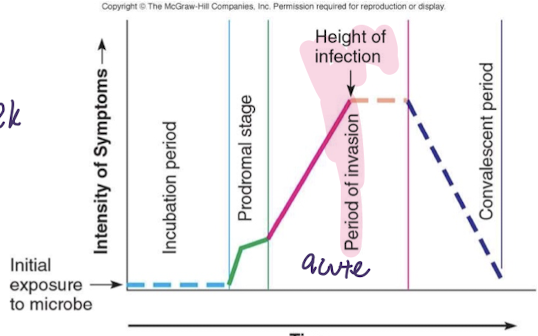
convalescent period
pathogen decreasing in numbers -progressive host repair of damages -recovery
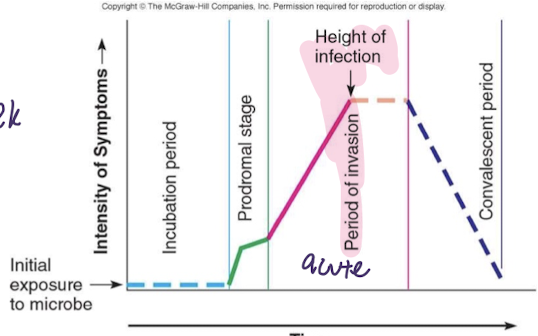
resolution
no signs of disease
1st step
where is the illness -based on health hx, and focused health assessment
immunization sched canada
part of assessing for something rare, should they already be protected against this?
common imunizations
DTaP, IPV, HPV
DTaP immunization
diptheria, tetanus, pertussis
IPV
polio virus immunization
HPV
human papillomavirus vaccine
botulism
less common due to prevention -gram + and anaerobic, neurotoxin (Ach block) -prevention with preservatives (potassium nitrate)
antitoxin HBAT
botulism tx -lowers binding of neurotoxin to ach receptors -need to treat in time
neurotoxin
Ach block -botulism does this -need for para, symp, and somatic NS fx -muscle paralysis
potassium nitrate salt
a way to prevent botulism -its a preservative
2nd step
identify what is causing illness -bacterial vs viral? CBC & diff, s&s, hx, culture from source
cbc
wbc, rbc, hemoglobin (HGB), hematocrit (HCT), PLT
diff
neutrophils, band neuts, lymphocytes
cbc and diff
to determine if bacterial or viral -part of identifying whats causing illness -24hrs
neutrophils
highest in bacterial infection -band _____ high in severe overwhelming infection
lymphocytes
T, B, NK? usually higher in viruses
culture tests
up to 72hrs -want to identify infection -blood culture, swaps, etc -on wounds -also sensitivity
sensitivity test
is it sensitive to this antibiotic or not
gram negative
thinner peptidoglycan, and has an outer membrane -ecoli, klebsiella, pseudomonas, salmonella, hib, cholera, syphillis, gonorrhea, nisseria M.
gram positive
thick peptidoglycan layer -staphylococci, streptococci (pneumococci), enterococci, listeria, c dif
tuberculosis
neither gram positive or negative
3rd step
antibacterial tx process -empiric or focal
abx empiric tx
based on suspected bacteria -evidence decision -broad spectrum may be used -starts ASAP -drug must reach target (ADME, patient compliance)
broad spectrum abx
effective at killing anything -both G + and -
abx focal tx
culture and sensitivity results used -tx initiated once results known -empiric tx maybe switched to focal -narrow spectrum abx better choice for that pathogen
streptococcus pyogenes
group A strep -bacterial pathogen -pharyngitis (sore throat) -incubation 2-4 days; highly infectious -post strep disease risk: glomerulonephritis, endocarditis (caused rheumatic fever)
streptococcus pyogenes symptoms
fever, sore throat, headache, malaise
variety of pathogens
an illness can be caused by