topic 1
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
81 Terms
Systole definition
Phase of the heartbeat where the heart muscle contracts
Diastole
Phase of the heartbeat where beat where the heartbeat relaxes
Atrial systole
two atria contract increasing blood pressure
Increase in blood pressure causes the atrioventricular valves open and blood flows from atrium to ventricle
Semilunar valves are closed
Ventricular systole
ventricles contract increasing blood pressure
Increase in blood pressure causes the atrioventricular valves closed to prevent backflow
Increase in blood pressure causes semilunar valves open
Blood moves from the ventricles to the aorta and pulmonary artery
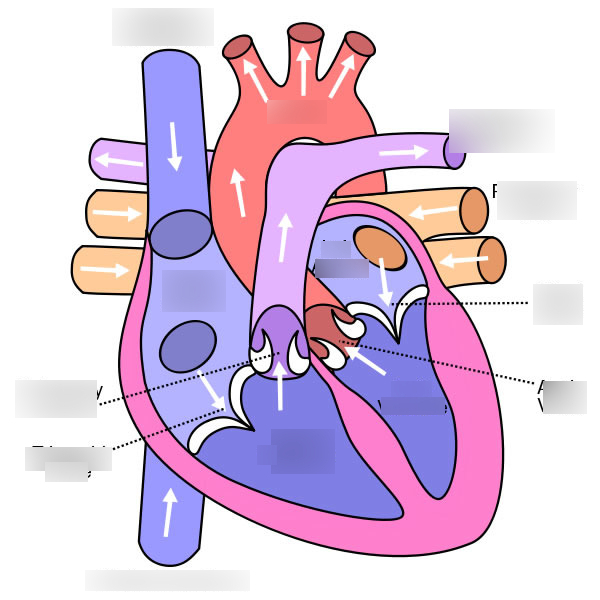
Label the heart
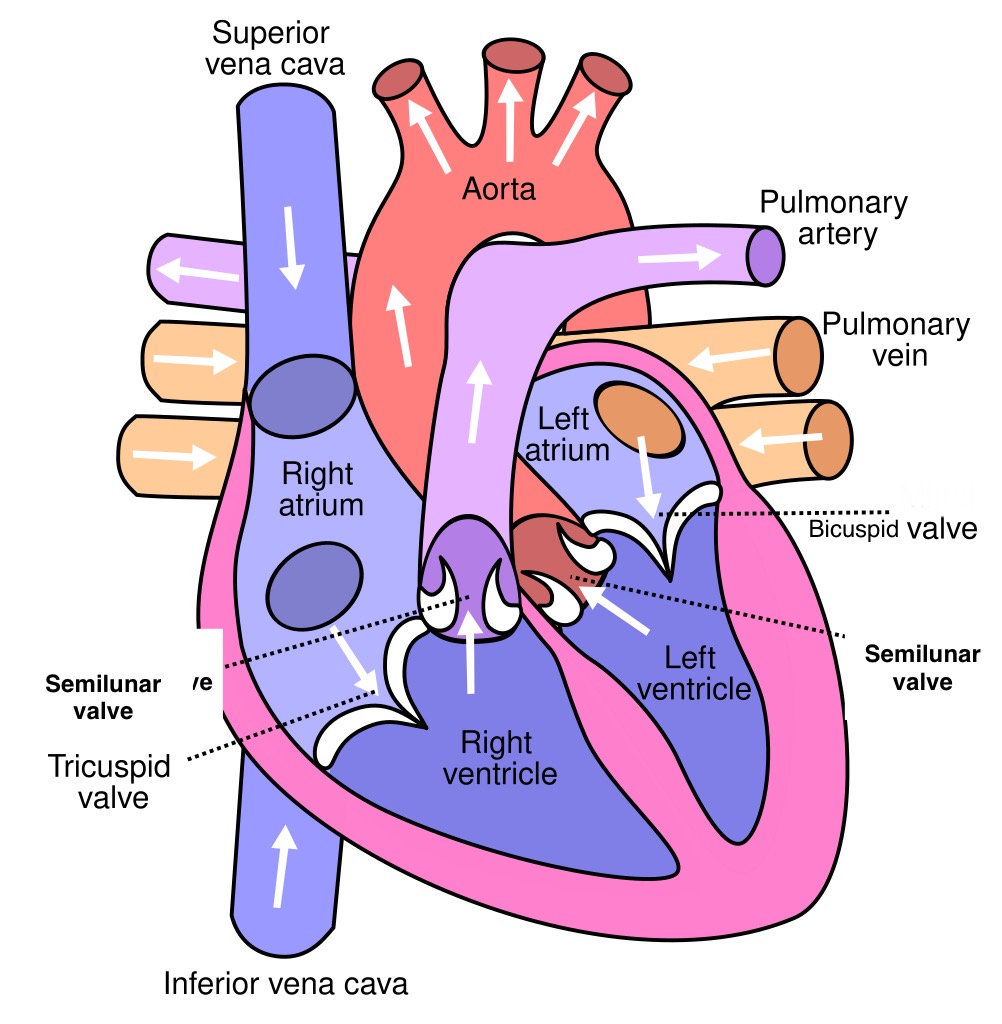
Pathway of blood through the heart
Body - vena cava - right atrium - tricuspid valve (open) - right ventricle - semi lunar valve (open) + tricuspid valve (close) - pulmonary artery - lungs (blood becomes oxygenated) - pulmonary veins - left atrium - bicuspid valve (open) - left ventricle - semi lunar (open) + bicuspid (close) - aorta - body
Cardiac muscle
Made up of cells connected by cytoplasmic bridges, which enables electrical impulses to pass through the tissue. It contains large numbers of mitochondria and myoglobin molecules.
Key differences between arteries and veins
Veins have
wider lumen
Thinner walls
Less collagen, smooth muscle and elastic fibres
Valves
Veins and arteries similarities
Walls of both vessels contain collagen, elastic fibres and smooth muscle. Both have a lumen
What makes up inner layer of arteries and veins
single layer of simple endothelial cells - flat + smooth so blood can flow
What makes up Middle layer of arteries and veins
Circularly arranged elastic fibres and smooth muscle
What makes up outer layer of arteries and veins
Collagen
What is endothelium
A type of epithelium that lines the interior surface of blood vessels. It is a thin layer of simple squamous cells called endothelial cells
What are elastic fibres
Allows the vessels to stretch and recoil so they don’t rupture when pressure comes in. NOT contracting as doesn’t require energy/ATP
What is smooth muscle
For constriction and dilation - relaxes to allow more blood flow to area and contracts to restrict blood flow. (Vasoconstriction + vasodilation)
What is collagen
For strength and durability, flexible, connective tissue
Features of capillaries
One cell thick
Join arterioles to venules
10 micrometres in diameter
Network of capillaries explained
blood pressure decreases as it moves from artery to arteriole to capillaries
Capillaries are 1 cell thick which slows blood down so gas exchange can happen
Once blood flows through capillaries its deoxygenated and moves into the venules and then veins
Why do veins have valves
low blood pressure so blood can backflow and veins make sure blood flows in 1 direction
Haemolymph
= a fluid equivalent to blood in most invertebrates
What is diffusion
Movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of ow concentration down a concentration gradient
Ficks law
Rate of diffusion is proportional to SA:V ratio x difference in conc / length of diffusion path
Open circulatory system
Consists of a heart that pumps haemolymph through short vessels and into a large cavity called haemocoel
Organism with an open circulatory system have:
low metabolic rate
Large SA:V
= sufficient diffusion rate between haemolymph and cells of O2/CO2
Closed circulatory system
Blood is fully enclosed within blood vessels at all times
Organisms with closed circulatory systems:
High metabolic rate + low SA:V
generate high pressure so blood travels faster, more efficient transport system
Overcomes limitations of diffusion
Single circulatory system
1 system
Higher BP than no blood vessels BUT not too high to damage capillaries
Not as efficient
Double circulatory system
2 systems
Pump 1: low blood pressure in lungs to protect capillaries in lungs
Pump 2: boosts the blood pressure for rapid and effective delivery of oxygen/glucose
Daphnia practical
place daphnia on cavity slide, using a few strands of cotton wool to immobilise the daphnia
Take heart rate fore using a microscope to observe the heart rate
Add caffeine solution to the daphnia and allow daphnia to acclimatise
Repeat for each caffeine conc 3x and calc a mean
Course of events that lead to atherosclerosis
endothelium is damaged
Damage triggers inflammatory response
White blood cells engulf (by phagocytosis) saturated fats or cholesterol
White blood cells become fatty, enlarged cells called foam cells
Atheroma formation i middle layer of artery
Calcium salts and fibrous tissue form plaque
Lumen narrows > raised blood pressure
Blood clotting process
thromboplastin release from damaged cells and platelets
Thromboplastin + Ca2+ salts + K+ causes cascade of events
Conversion of prothrombin to thrombin
Thrombin (enzyme) that causes conversion of (Soluble) fibrinogen to (insoluble) fibrin
Fibrin forms a tangled mesh to trap red blood cells and platelets to make a blood clot
What does atherosclerosis cause
increases risk of a blood clot forming coronary arteries, leading to a heart attack (myocardial infarction)
Or a blood clot forming in arterial es in brain, resulting in a stroke
What does a heart attack cause
lack of oxygen/glucose reaching heart muscle cells
Anaerobic respiration of affected heart muscle cells
Lactic acid production (pain)
Death of affected heart muscle cells
Carbohydrates
Group of substances used as both energy sources and structural materials
contain C, H, O with the general formula Cx(H2O)y
3 main groups of carbohydrates
monosaccharides
Disaccharides
Polysaccharides
Monosaccharides
simple sugars with the general formula (CH2O)n where n = 3-7
sweet taste
Cause sharp rise in blood sugar
Reducing sugars - ca be tested by Benedict’s
Disaccharides
“Double sugars” formed by 2 monosaccharides through condensation reactions forming glycosidic bonds
Polysaccharides
Large molecule formed from many monosaccharides joined together by glycosidic bonds formed through condensation reactions
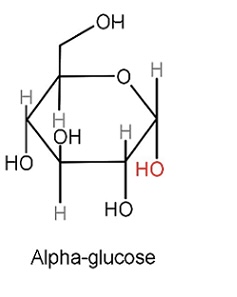
Structure of alpha glucose
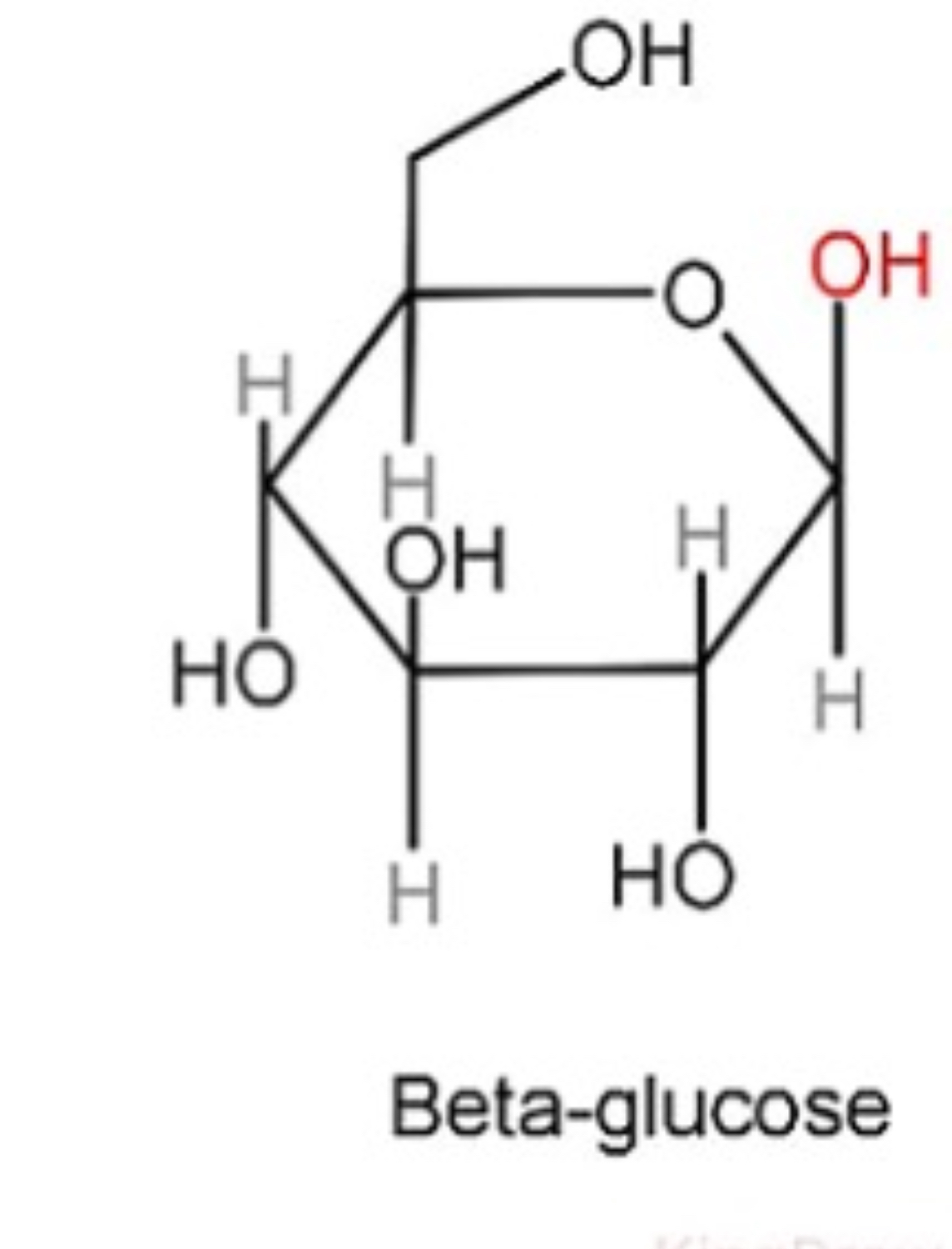
Structure of beta glucose
What are the properties of glucose
large molecule - transported via facilitated diffusion using channel proteins
Polar so hugely soluble in water
Main form in which carbs are transported around the body
3 important monosaccharides
glucose
Fructose
Galactose
Fructose
Very soluble and the main sugar in fruits and nectar. It’s sweeter than glucose.
Galactose
not as soluble as glucose
Important role in the production of glycolipids and glycoproteins
Ribose
a 5-carbon (pentose) monosaccharide present in RNA nucleotides
formula C5H10O5
Deoxyribose is the pentose sugar present in DNA nucleotides (- a O)
3 disaccharides
maltose
Sucrose
Lactose
Monosaccharides that make up maltose
Alpha glucose + alpha glucose
Monosaccharides that make up sucrose
Alpha-glucose and fructose
3 polysaccharides
starch
Glycogen
Cellulose
1,4 glycosidic bonds cause
Straight chains
1,6 glycosidic bonds cause
Branches
Propertie of glycogen and starch that name them good energy storage molecules
they are compact so can store lots of energy in a small area
They cannot dissolve so they have no osmotic effect on a cell
They cannot dissolve so they cannot move out of a cell
Amylose
Straight chain molecule that only contains 1,4 glycosidic bonds, forms a helix
Amylopectin
Branched has 1,4 and 1,6 glycosidic bonds
Glycogen functions
highly branched structure allows it to be hydrolysed very quickly to release glucose quickly for respiration
How is a triglyceride synthesised
The formation of 3x ester bonds during 3x condensation reactions between 1x glycerol and 3 fatty acids
Saturated lipids
no double carbon-carbon bonds in hydrocarbon chain
Solids at room temperature as due to shape they can form stronger intermolecular bonds and there is not enough energy at room temperature to break them
Unsaturated lipids
liquids at room temperature because they form weaker intermolecular bonds
1 or more double carbon-carbon bonds in their hydrocarbon chain
Properties of lipids
waterproof because the fatty tail is hydrophobic
Very compact
better for energy release than carbohydrates or proteins
Lipids are non-polar and insoluble in water and so good for storage
Conduct heat slowly therefore they provide thermal insulation
Risk factors for CVD
genetic predisposition
Diet high in saturated fats
Diet high in salt
Old age
Gender
High blood pressure
Smoking
Inactivity
Too much alcohol
How does genetic predisposition increase risk of CVD
alleles that result in high blood cholesterol levels
How diet high in saturated fats increases risk of CVD
Faster plaque development
How diet high in salt increases risk of CVD
Higher BP
How old age increases risk of CVD
Loss of elastic fibres in arteries > increase in BP
How high bp increases risk of CVD
Risk of damage to endothelium lining arteries
How gender (male) increases risk of CVD
Lack of protective oestrogen
How smoking increases risk of CVD
Toxins in blood that damage endothelium lining arteries
How inactivity increases risk of CVD
High BP
How too much alcohol increases risk of CVD
Toxins in blood that damage endothelium
Which type of cholesterol is linked to CVD
LDL
Treatments for CVD
antihypertensives
Statins
Anticoagulants
Platelets
Benefits and risks of anrihypertensives
Benefits: lowers bp
Risks: BP too low, dehydration
Benefits and risks of statins
Benefits: lowers blood cholesterol levels
Risks: liver damage, muscle pain, headache/dizziness
Risks and benefits of anticoagulants
Benefits: Reduces risk of blood clotting
Risks: uncontrolled bleeding
Risks and benefits of platelet inhibitors
BEnefits: reduces risk of blood clotting
Risks: uncontrolled bleeding
Types of antihypertensives
Beta blockers
Diuretics
ACE inhibitors
BMI
body mass index calculated by dividing weight in kg by height in metre squared. The value obtained is then compared to a chart.
Waist-to-hip ratio
Can be used to determine how likely a person is to get heart disease based on the distribution of fat in the body. A value above 1 = health risk
HDL
High density lipoprotein
‘Good’ cholesterol
Formed from unsaturated fats, protein and cholesterol and transports from body tissues to the liver
Reduces cholesterol levels and risk of atherosclerosis
LDL
low density lipoprotein
Bad cholesterol
Formed from saturated fats protein and cholesterol and transports cholesterol from the liver to the blood
This then causes cholesterol levels to increase and that’s why its linked to atherosclerosis
Vit C practical