Chapter 11 Objectives
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
Genotype
The genetic constitution of an individual, specifically in relation to a particular trait.
Dominant Genetic Disorder
A disorder caused by a dominant allele, requiring only one copy of the allele for the disorder to be expressed.
Recessive Genetic Disorder
A disorder that occurs only when an individual has two copies of a recessive allele.
Sickle Cell Anemia
A genetic disorder characterized by the production of abnormal hemoglobin, leading to distorted (sickle-shaped) red blood cells.
Malaria Resistance
Individuals with sickle cell anemia exhibit increased resistance to malaria due to the altered shape of their red blood cells.
Pedigree
A diagram representing the familial relationships and inheritance patterns of traits across generations.
Complete Dominance
A form of inheritance where one allele completely masks the effect of another allele.
Incomplete Dominance
A form of inheritance where the phenotype of heterozygotes is intermediate between the phenotypes of the two homozygotes.
Codominance
A form of inheritance where both alleles are expressed equally in the phenotype.
Multiple Alleles
The presence of more than two alleles for a genetic trait in a population.
Blood Type
An example of multiple alleles, where ABO blood types are determined by three alleles: A, B, and O.
Sex-Linkage
Traits that are associated with genes located on sex chromosomes, often leading to different inheritance patterns in males and females.
Epistasis
A genetic interaction where the expression of one gene is modified or masked by another gene.
Polygenic Traits
Traits that are influenced by multiple genes, resulting in a wide range of phenotypes.
Environmental Factors
External factors that can influence gene expression and contribute to phenotypic variation.
Twin Studies
Research studies that compare traits in identical and fraternal twins to determine the influence of genetics versus environment.
Karyotype
A display of the full set of chromosomes in an individual, used for identifying chromosomal abnormalities.
Nondisjunction
The failure of homologous chromosomes or sister chromatids to separate properly during cell division, leading to an abnormal number of chromosomes.
Down Syndrome
A genetic disorder caused by an extra copy of chromosome 21, leading to characteristic facial features and developmental challenges.
Turner’s Syndrome
A chromosomal disorder in females caused by the presence of only one X chromosome (45, X) leading to various developmental issues.
Klinefelter’s Syndrome
A chromosomal disorder in males resulting from an extra X chromosome (47, XXY), often associated with infertility and other physical traits.
Fetal Tests
Medical procedures used during pregnancy to detect chromosomal abnormalities, such as amniocentesis or chorionic villus sampling (CVS).
A female member of a family
Circle
A male member of the family
Square
Carrier for the trait
Half-shaded shape
A person with the trait/disorder being tracked in a pedigree
Completely shaded shape
A person that does not have the trait/disorder and is not a carrier in a pedigree
Open shape
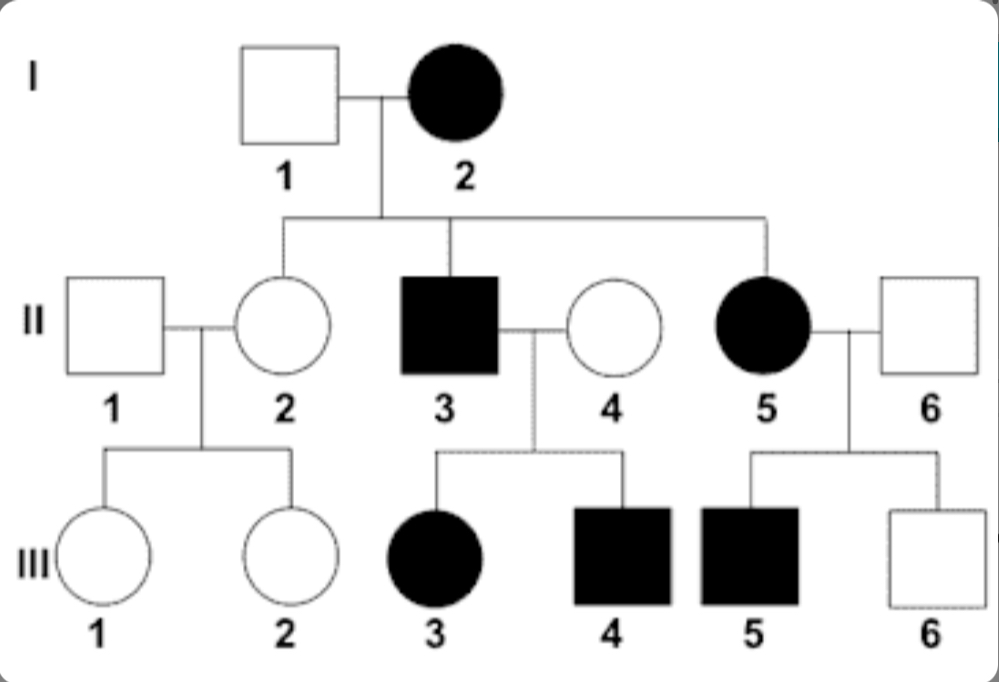
How many children did the couple in generation 1 have
3
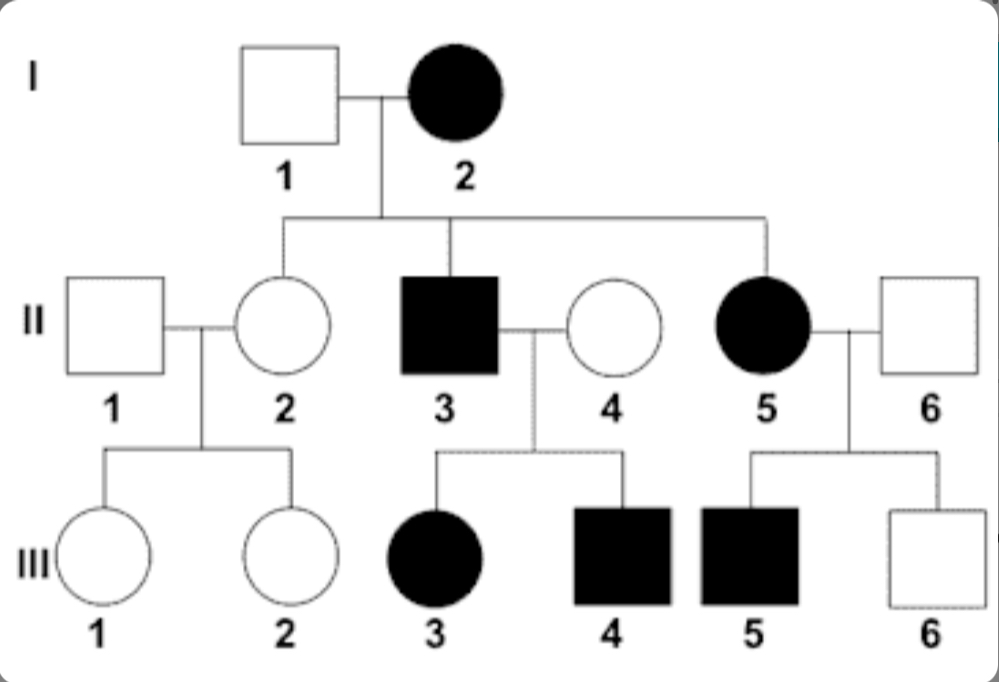
This pedigree shows a dominant trait. II-3 and II-4 plan to ahve another child. What is the chance their baby will have the trait?
50%
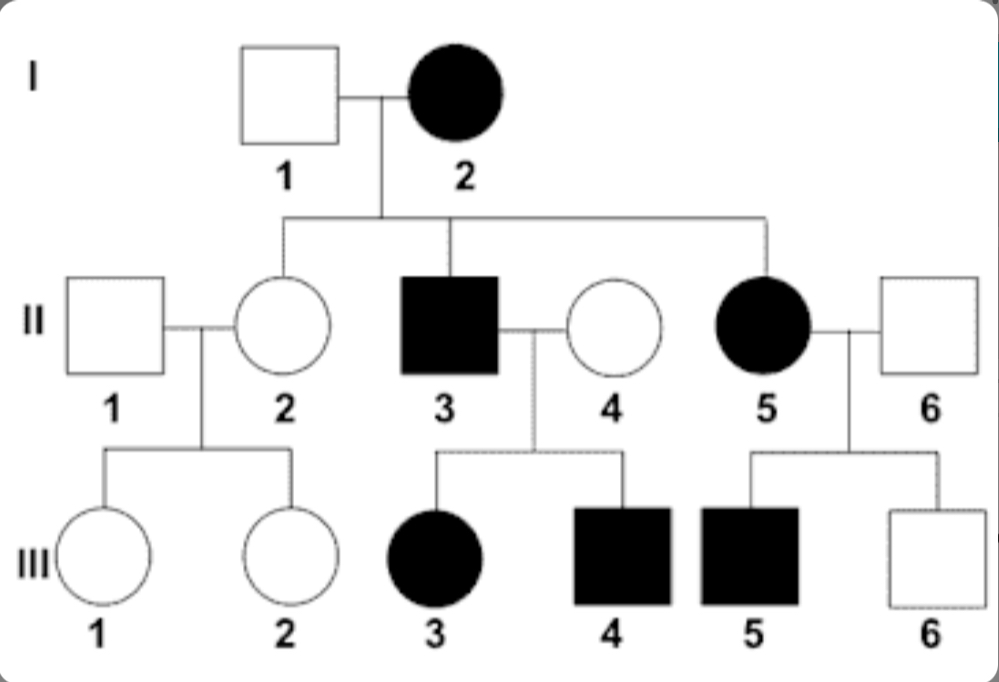
Is this a dominant or recessive trait?
Recessive
A chart tracking a particular trait through generations of the same family.
Pedigree
This type of inheritance is when both traits are dominant, so both are seen in the heterozygous phenotype
Codominance
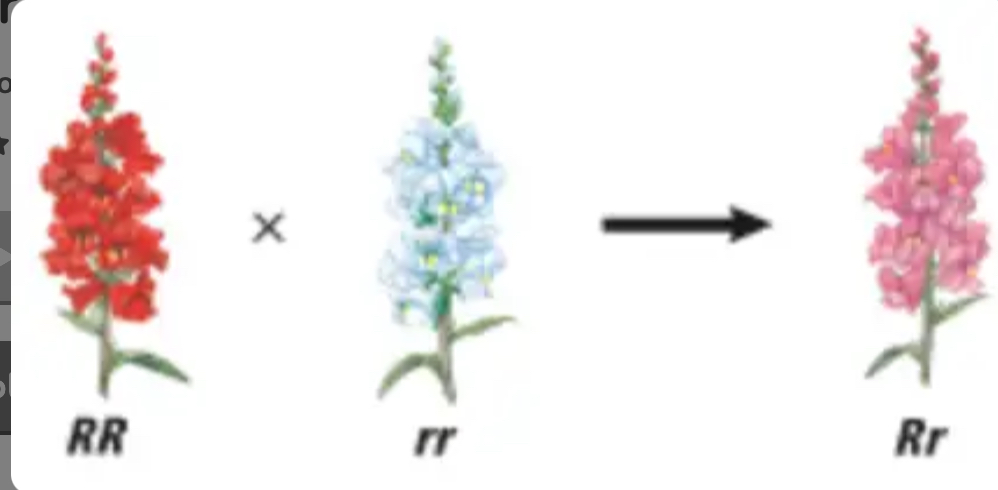
This would be an example of…
Incomplete dominance
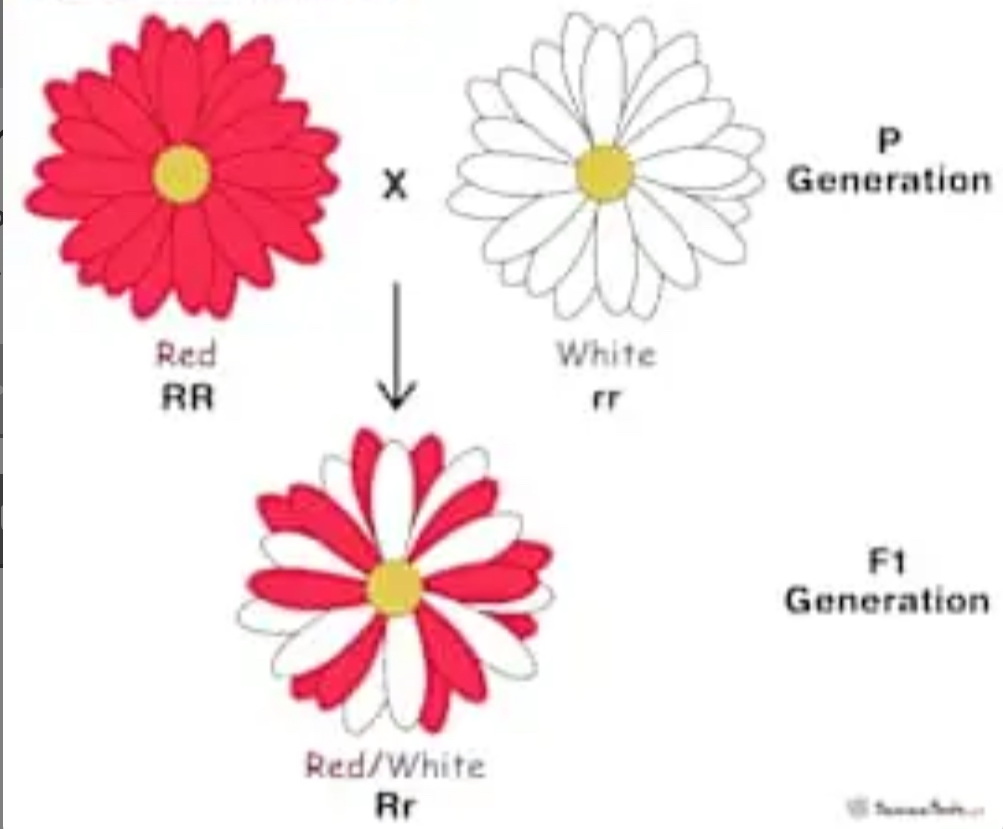
This would be an example of…
Codominance
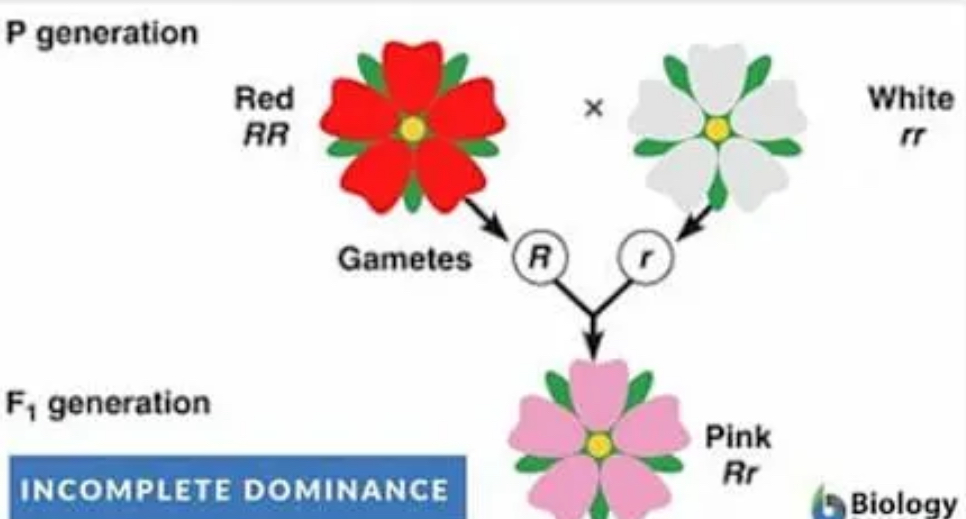
If tow pink flowered plants were crosses, what is the probability the offspring will have red flowers?
25%
When a black chinchilla (BB) is crossed with a white chinchilla (WW), all the offspring are grey (BW). If a grey chinchilla is crossed with a white chinchilla, how many offspring will be black?
0%
The gene for color blindness is located on the X chromosome. Because of this, color blindness is considered a…
Sex-linked trait
Hemophilia is a sex-linked recessive trait. What would the genotype be for a man that does not have hemophilia?
xHy
Hemophilia is a sex-linked recessive trait. If a man with hemophilia marries a woman that odes not have hemophilia (but is a carrier), what is the probability they will have a child with hemophilia?
50%
What is the genotype of someone that has heterozygous type A blood?
AO
A man that has heterozygous type A blood marries a woman that has type AB blood. What is the probability their child will have heterozygous type A blood?
25%
Why are men more likely to inherit a sex-linked disorder
Men have only one chromosome
A diagram of a person’s chromosomes, organizes by size, is called a…
Karyotype
A normal human karyotype should have ____ chromosomes.
46
Humans have ___ pairs of chromosomes
23
The first 22 pairs of chromosomes are called…
Autosomes
When one of the homologous chromosomes is missing
monosomy
When there is an extra copy of a chromosome present
Trisomy
What is the abnormality in the following karyotype
Trisomy 18
When a person inherits an extra 21st chromosome, it is called….
Down syndrome
Which of the following is not an example of a fetal test for chromosomal disorders= amniocentesis, chroionic villus sampling, blood sampling, nondisjunction
Nondisjunction
When chromosomes fail to separate correctly (either during meiosis I or meiosis II)
Nondisjunction
The protective ends of the chromosomes
Telomeres