Parasitic Diseases of Humans (2/9)
1/43
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Zhou Lecture 1 (Lecture 19)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
medical parasitology
study of eukaryotic parasites
common property: cant live outside host, easy spread through travel
7/8 tropical disease
studies of infections and diseases by:
protozoa: small singled celled
helminth worms: small to very big (10 meters)
Protozoa
kingdoms: animals; fungi; protista (algae and protozoa)
single celled, animal like
examples: amoebae, cilitates, flagellates, sporozoans
structure: cytoplasmic membrane, cytoplasm, usually w flagellum
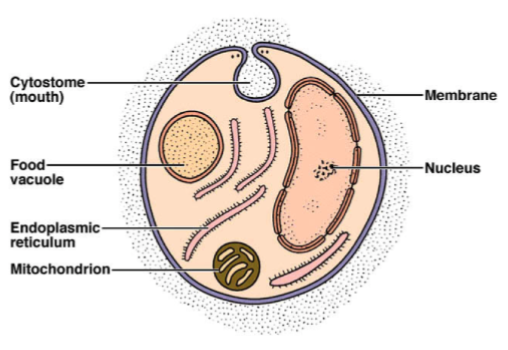
Life processes of protozoa
aquatic
obligate parasites
chronic/acute diseases:
amebiasis (amebic dysentery): entamoeba
sleeping sickness: trypanosoma bruci
chagas disease: trypanosoma cruzi
STD: trichomonas vaginalis
life cycle of protozoa
asexual reproduction: binary fission
sexual reproduction: conjugate; exchange DNA; segregate
Encystment
adverse conditions
cyst formation: round w protective coating, survive lack of food/water/high temperature
Classifications of protozoa (4 phyla)
amoebas, ciliates, flagellates, sporozoan
General properties of Infective amoebas
pseudopodia
trophozoite: actively growing
only binary fission
form cysts
major diseases: most not pathogenic
amebiasis
brain infection: naegleria, acanthamoeba
amoebiasis
entamoeba histolytica — intestinal disease
site of infection: intestinal mucosa
symptoms: mild diarrhea, dysentery (blood stools), abdominal pain, fever, fatigue, wt loss
tissue damage: cell ingestion due to enzymes dissolving tissue and ulcerations
severe cases of amoebiasis
liver, amoebic hepatitis
lung, pulmonary ameobiases
less freq: spleen, adrenals, kidney, skin brain
10% fatality rate
epidemiology of amoebiasis
tropical and subtropical disease:
US 0.1-0.5% infection rate
Tropical regions: 5-8%, sewage used as fertilizer
spread by asymptomatic chronic carriers
encystment stage completed in healthy carriers
active dysentery not infectious — cyst formation cannot occur
how is amoebiasis spread?
asymptomatic chronic carriers
encystment stage completed in health carriers
active dysentery: not infectious — cyst formation cant occur
Life Cycle of entamoeba histolytica
trophozoite: karyosome, nucleus, RBCs
mature cyst: chromatoidals, nucleus
excystment: nucleus
diagnosis and treatment of amoebiasis
diagnosis: ingested RBCs,4 nuclei in cysts, symptoms
treatment: drugs targeting parasite in feces and tissues
Iodoquinol, metronidazole, dehydroemetine, chlorquine
Naegleria fowleria(nf) and acantheamoeba (acanth)
amoebic infection of the brain
common, free living protozoans, accidental parasites
live in lakes, hot springs, swimming pools, hot tubs, moist soil
Pathogenesis of nf and treatment
killer amoeba
“primary amoebic meningoencephalitis”
invades nasal mucosa
amoeba burrows in, multiplies, migrates to brain
primary acute meningoencephalitis: rapid massive destruction of brain and spinal tissue
symptoms: hemorrhage, coma, death in a week
advances too fast for effective treatment:
amphotericin B,sulfadiazine, tetracycline, ampicillin if treated early can be helpful
pathogenisis of acanth
“granulomatous amoebic encephalitis”
invades broken skin, conjunctiva, lung and urogenitla epithelia
special risks: ppl w eye injuries or abrasions from contact lenses
course of infection longer than nf
balantidium coli is what type of organism? what disease and habitat is associated?
intestinal cilitate: movement, two nuclei (macro and micro), sexual and asexual production
disease: balantidiosis — infection in intestinal mucosa
natural habitat: large intestines of pigs, other domestic animals, primates (cysts in feces)
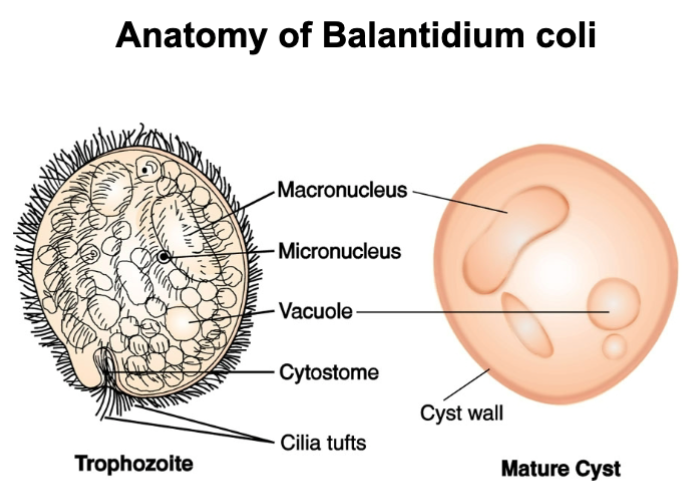
balantidium coli (infection/symptoms, treatment/prevention)
infection/symptoms: intestinal mucosa — irritation, injury, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, dysentery and abdominal colic
healthy indiv are resistant
treatment: oral tetracycline, then dodoquinol, nitrimidazine or metronidazole
prevention: prevent food or drink contamination with pig manure
Common feature of mastrigophorans and its diseases
long filamentous flagellas “flagellates”
mild diseases: trichomoniasis and giardiasis
debilitating: trypanosomiasis and leismaniasis
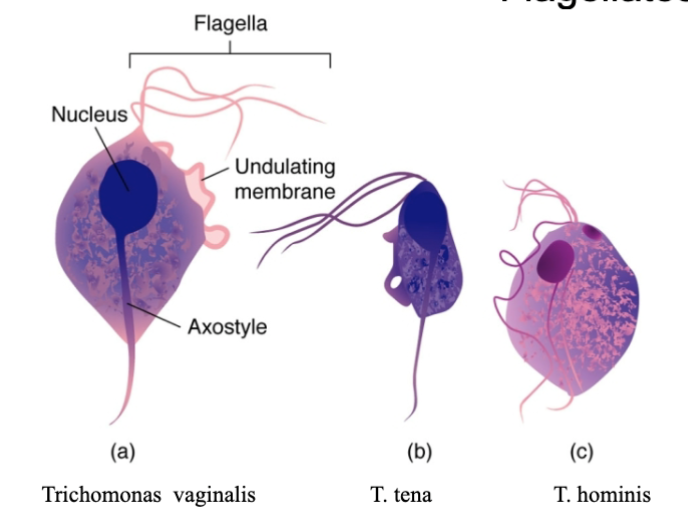
trichomonads
small pear shaped protozoa, w 4 flagella and undulating membrane. no cysts
pathogen: trichomonas vaginalis — trichomoniasis, a STD
reservoir: human urogenital tract: 50% asymptomatic
transit: sexual contact, communal bath, public facilities, mother to child
trichomoniasis (symptoms and treatment)
2nd most prevalent STD (most common chlamydia — bacteria)
symptoms:
females: foul smell, green to yellow vaginal discharge, vulvitis, cervicitis, urinary freq and pain
males: urethritis, milky discharge, prostate infection
treatment: oral and vaginal metronidazole, both partner have to be treated
what is giardiasis caused by? outbreaks? what do you treat it with?
giardia lamblia — prominent cause of diarrhea
most common flagellate isolated in clinical specimens
2 nuclei in trophozoites and 4 in cysts
outbreaks: traveler’s diarrhea, hikers, campers, drinking from fresh mountain streams, children in day care centers
Treatment: quinacrine, metronidazole
vector borne blood parasites
hemoflagellates (blood and tissue)
major species: trypanosoma, leishmania
life threatening disease spread by blood sucking insects with complicated life cycles
what are the developmental stages of hemoflagellates (look at table in notes)
amastigote: lacks free flagellum
promasitgote: single free anterior flagellum
epimastigote: flagellate stage, with both flagellum and an undulating membrane
trypomoastigote: large, fully formed stage of Trypanosoma
not all hemoflagellates have all stages
trypanosomiasis
trypanosoma:
trypanosoma brucei: african sleeping sickness
T. b. gambiense: West Africa
T. b. rhoesiense: East Africa
T. cruzi: Chagas disease
Vector: tsete flies
Infections by T. brucei
Tsetse flies get infected by feeding on infected reservoir hosts (antelope, lion, cow, goat, human)
Trypanosomes multiply in fly gut
migrate to salivary glands, develop into infectious stage
transfer into bite wounds on new hosts, to lymphatics and blood
what is the difference between rhodesian form and gambian form T.b infections?
rhodesian: T.b. rhoesiense — acute, effects brain in 3-4 wks
gambian: T.b. gambiense — chronic, may not affect the brain for several yrs
Pathology of Sleeping Sickness (T.b)
intermittent fever, enlarged spleen, swollen lymph nodes, joint pain
personality change, sleep disturbances (sleepy day, sleepless at night)
advanced neurological disorders:
muscular tremors, shuffling gait, slurred speech, epileptic seizures, paralysis
death: coma, secondary infections, heart damage
Treatment/prevention of T.b
chemotherapy admin before brain damage
expensive:
melarosprol-toxic arsenic based drug
difluroomethylornithine (DFMO) less toxic
control: insecticides (difficult)
sudan and zaire: 20-40% of population infected
Why can’t the immune system defeat trypanosomes?
they produce large #s of surface antigens in succession
antibodies produced by host fail to stop bugs with new antigen
hosts eventually overwhelmed
difficult to immunize: >100 antigenic variations
Chagas Disease
trypanosoma cruzi
insect host: kissing bugs with trypanosomes in the hind gut and discharge it in feces
central/south america and share habitat with humans
infection occur when bug defecates near bite wounds, incoulation by rubbing bug feces into wounds
pathology and treament for chagas disease
symptoms: fever, swelling lymph nodes, spleen, and liver
pathology: favored targets are heart muscle, large intestine —> heart enlarged —> death in 2 yrs
treatment: nifurtimox and benzonidazole admin early, side effects damaging
leishmaniasis
leishmania
cutaneous leishmanisis: capillary infections
trasmit among mammals by phlebotomine flies (sand)
endemic to equatorial regions
special risks: travelers and immigrants
death by destruction of tissues
leishmania life cycle
sand fly
promastigote stages in gut of sand fly
human/mammal
free and intracellular amastigotes in the spleen
apicocomplexan parasites
sporozoans: lack locomotor organelles in mature stage
sexual and asexual reproduction
human pathogens:
plasmodium: malaria
toxoplasma: toxoplasmosis (muscle aches/brain lesions/birth defects)
cryptosporidium: cryptosporidiosis (diarrhea)
what is malaria? cause? symptoms?
plasmodium, obligate intracellular sporozoan
dominant protozoan disease
exposure to bad air from swamps: mosquitoes
symptoms:
chills, fever at regular intervals, following by sweating (48-72hrs) due to synchronous rupturing of RBCs
anemia in children, organ ruptrure from accumulated cell debris (spleen, liver, kidneys)
long recovery: <5years
malaria species and transmission
P. malarae; P. vivax; P. falciparum; P. ovale
most severe: falciparum — persistent fever, rapid pulse, cough, weakness for weeks wo relief, high death rate in acute phase
transmission:
mostly by female anopheles mosquitoes
occasionally by sharing needles
blood transfusions
mother to child
asexual phase of plasmodium life cycle: exoerythrocytic development
injection of anticoag saliva into the capillar y
asexual plasmodium injection (sporozoites)
sporozoites reach liver and undergo schizogony (asexual division), generate daughter parasites (merozoites)
eruption of liver cells, release numerous mature merozoites into circulation
asexual phase of plasmodium life cycle: erythrocytic development
release merozoites invade RBCs, feed on Hb, producing cells called schizonts (filled w merozoites)
RBC burst releasing more merozoites
merozoites develop into macrogametocytes (female) and microgametocytes (male)
sexual phase of plasmodium life cycle: gametocyte phase
mosquitoes draw gametes into stomach
fertilization
diploid cells (oocyst) implants stomach wall and undergo multiple mitotic divisions, releasing sporozoites
sporozoites migrate to salivary glands and aval for next infection
hemoglobin C vs S warding off malaria
C: protection with no fitness cost
S: protection with a cost — sickle cell anemia in s/s individuals
malaria diagnosis and control
diagnosis: stained blood smear, antibodies, DNA-PCR analysis
control:
pesticides: DTT — resistance
treatment:
non-resistant strains: chloroquine has less toxic side fx
resistant strains: mefloquine, quinine
eliminate parasite from liver: primaquine or proguenil
toxoplasmosis exposure rate, symptoms
toxoplasma gondii — often exposed to us by cats
order coccidorida of the apicomplexa
exposure rate 90%
most cases: mild, sore throat, lymph node enlargement, low grade fever
Immunodef pts: brain lesions, fetal disruption of heart and lungs
toxoplasmosis in pregnant women
transmit to fetus 33% chance
still birth, liver failure, hydrocephalus, convulsions, retina dmg, blindness
summary of parasitic diseases of humans
Infective amoebas:
amoebiasis: entaomoeba histolytica
brain infections: nf and acanth
Intestinal Cilitates: balantidium coli
The Flagellates:
trichomoniasis: trichomonads
giardiasis-intestinal disease: giardia lamblia
trypanosomiasis: sleeping sickness
trypanosoma: chagas disease
leishmania: leishmaniasis
Apicomplexan parasites
plasmodium: malaria
toxoplasma gondii: toxoplasmosis