Mos 2181 -- Organizational Behavior
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
Def: Organizational Behavior
Field of study devoted to understanding, explaining and improving the attitudes and behaviors of individuals and groups in organizations
Relationship between OB and HRM
OB is identifying solutions through research whilst HRM is the application of such findings
Who is Fredrick Taylor?
He proposed the idea of efficiency through scientific experiment and measure:
Scientific management
Optimal and efficient work processes
Focus on scientific method
Who is Max Weber?
He proposed a focus on organization and specialized work:
Bureaucracy
Specialization — strict chain of command, formal rules/procedures, decision making from high ranking people of the organization
What were the Hawthorne Studies?
A study which identified the limitation to the classical approach to management
What was the Human relations Movement?
Recognized that needs, attitudes, and social influences within groups affect behavior
What is the contemporary management theory?
There is not one best, universal principle… it depends on an employee’s needs
What are examples of Inimitable resources that help a firm maintain a competitive advantage?
History (time to develop)
Numerous small decision (Management, training, etc)
Socially complex resources (trust, teamwork, organization)
What is the Rule of 1/8th
At best, 1/8th (12%) of organizations will do what is required to build profits by putting people first
What are the Ways of Knowing?
Method of Experience
past experience
Methods of Intuition
Common sense
Method of authority
Higher up tells you something is true
Method of Science
research
What is the research practice gap?
The gap between research findings and the amount of research applied to the organization by HR management
What is a theory?
Collection of assertations that specify how/why variables are related and the conditions under which they should be related
What is a hypothesis?
Written prediction that specifies relationships between variables
What is a correlation?
statistical relationship between two variables
Can be positive or negative
Can range from 0 to (-+)1
0.1 = weak
0.3 = moderate
0.5 = strong
What are conditions for causation?
The two variables are correlated
No alternate explanation exists for the correlation
Correlation does NOT = Causation
What is meta analysis?
A method that combines the results of multiple studies by calculating a weighted average correlation across studies
More participants = weighted higher
Evidence-based management
Making the best decisions using the best available evidence from multiple sources
Def: Job Performance
Employee behaviors that either contribute positively or negatively to the accomplishment of organizational goals
What are the 3 aspects of Job Performance?
Task Performance (required)
Citizenship behavior (voluntary)
Counterproductive Behavior (hinders performance)
What are the types of Task Performance?
Def: teams
two or more people who work interdependently over some time period to accomplish common goals related to some task-oriented purpose
Team Characteristics:
Team types
team interdependence
team composition
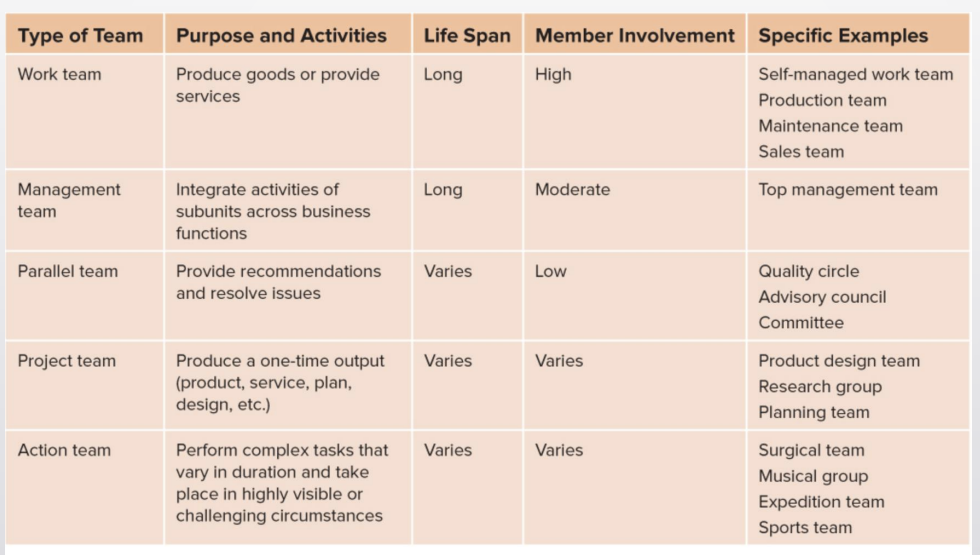
Team Types
Work teams — relatively permanent teams in which members work together to produce goods or provide services
production teams members work together to assemble vehicles
management teams — relatively permanent teams that participate in managerial-level tasks that affect the entire organization
parallel teams —teams composed of members from various jobs within the org that meet to provide recommendations about important issues that run parallel to the org’s production process
project teams — teams formed to take on one-time tasks, most of which tend to be complex and require input from members from different functional areas
action teams —teams of limited duration that perform complex tasks in contexts that tend to be highly visible and challenging
a team of nurses and surgeons work together to complete a surgery, etc
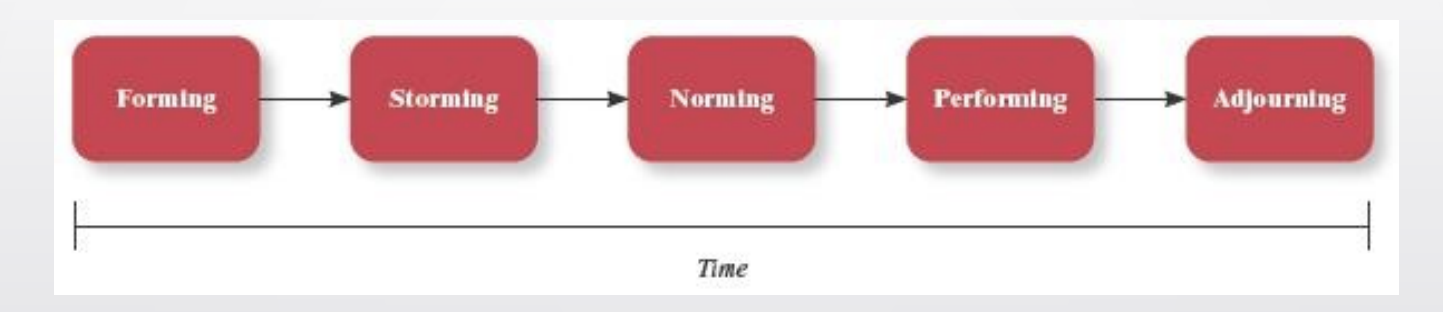
What is the five-stage model of team development?
Forming — members get a feel for what is expected of them, what behaviors are out of bounds, who is in charge
storming — members remain committed to the ideas they bring with them to the team, and conflict may result
norming —members begin to cooperate; norms and expectations develop
performing —members are comfortable in their roles, the team makes progress towards goals
adjourning — members separate, disperse from team
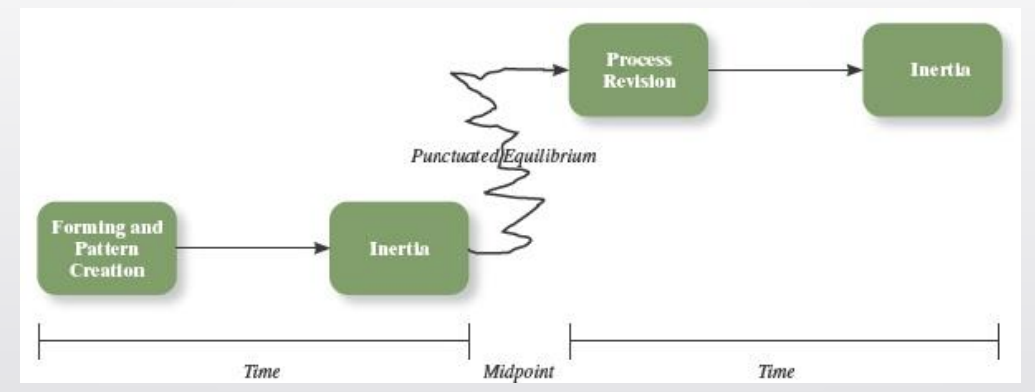
What is the punctuated equilibrium model?
Time (first half) — members make assumptions and establish a pattern of behavior that lasts for the first half of the project’s life
Midpoint —members realize that they must change their approach to the task in order to complete it on time
Time (second half) — the new framework dominates team behavior until task completion
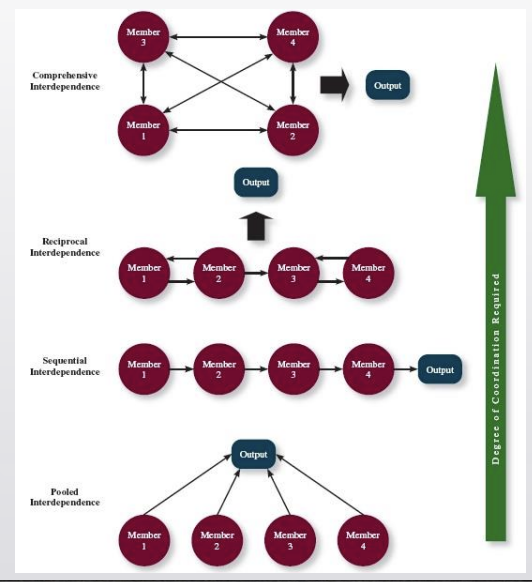
Team Interdependence:
The ways in which members of a team are linked to one another
3 general types of team interdependence:
task interdependence
goal interdependence
outcome interdependence
Task interdependence
Degree to which team members interact with and rely on other members for information, materials, and resources needed to accomplish work for the team
four types of task interdependence
pooled
sequential
reciprocal
comprehensive
Goal interdependence:
degree to which team members have a shared vision of the team’s goal and align their individual goals with that vision
Outcome interdependence:
degree to which team members share equally in feedback and rewards that result from the team achieving its goals
Team Composition:
Mix of the various characteristics that describe the individuals who work in a team
5 aspects of team composition:
member roles
member ability
member personality
team diversity
team size
member roles:
Team task roles: behaviors that directly facilitate accomplishment of team tasks
initiator-contributor — proposes new ideas
devil’s advocate — offers challenges to the team’s status quo
energizer — motivates the team to strive to do better
Team-building roles: behaviors that influence the quality of the team’s social climate
encourager — praises the contributions of other team members
compromiser — attempts to find the halfway point to end conflict
follower — accepts the ideas of teammates
Individualistic roles: behaviors that benefit the individual at the expense of the team
recognition seeker — brags and calls attention to themselves
slacker — acts cynically or nonchalantly, or goofs off
Member ability:
additive tasks — in these tasks, abilities of all members add up to determine team performance
e.g. fighting fires
disjunctive tasks — in these tasks, the most able member has the most influence on team performance
e.g. finding an error in a computer program
conjunctive tasks — in these tasks, the least able members has the most influence on team performance
e.g. packaging boxes on an assembly line
Member personality: