DNA vocabulary
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
4 mrs grieco
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
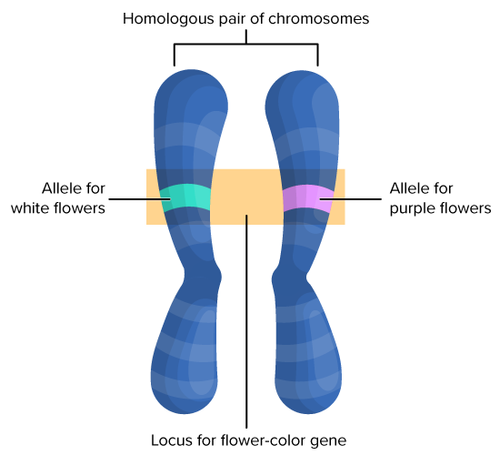
allele
A variant form of a gene.

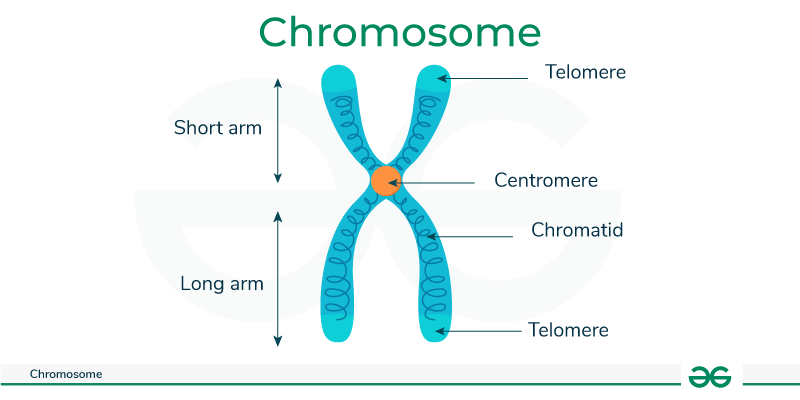
chromosome
A thread-like structure of nucleic acids and protein found in the nucleus of most living cells, carrying genetic information in the form of genes.
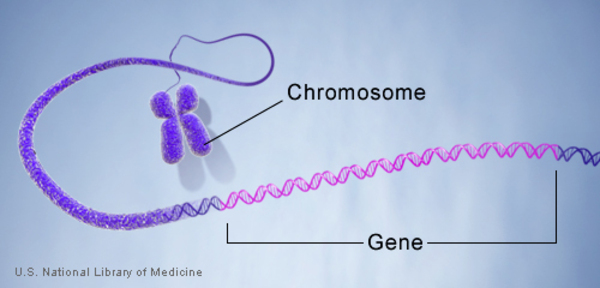
gene
A unit of heredity that is transferred from a parent to offspring and is held to determine some characteristic of the offspring.
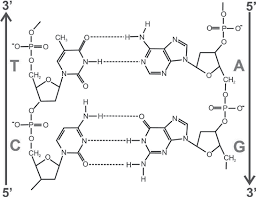
hydrogen bonds
A weak bond between two molecules resulting from an electrostatic attraction between a proton in one molecule and an electronegative atom in the other. Crucial for DNA structure.
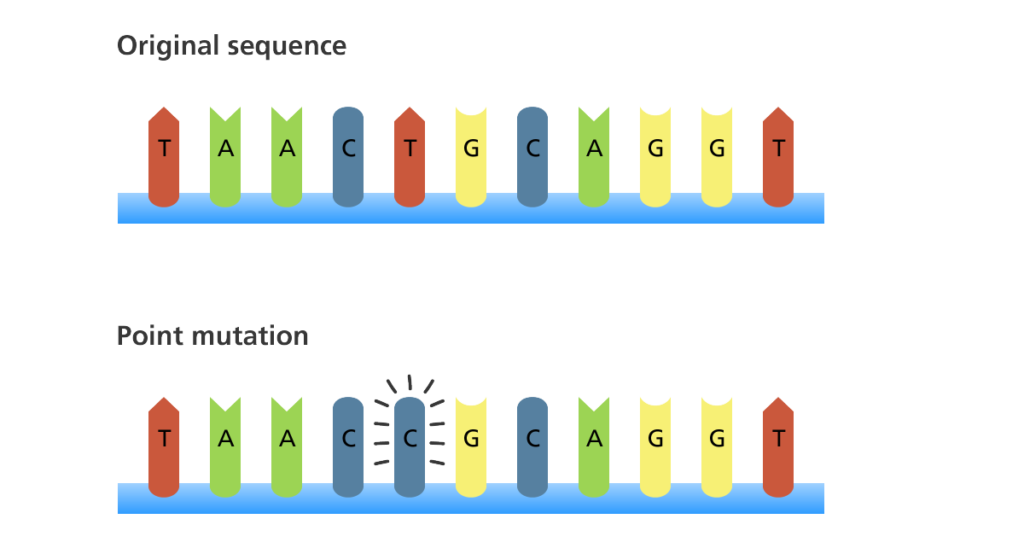
mutation
The changing of the structure of a gene, resulting in a variant form that may be transmitted to subsequent generations, caused by the alteration of single base units in DNA, or the deletion, insertion, or rearrangement of larger sections of genes or chromosomes.

nucleic acids
Complex organic substances present in living cells, especially DNA or RNA, whose molecules consist of many nucleotides linked in a long chain.
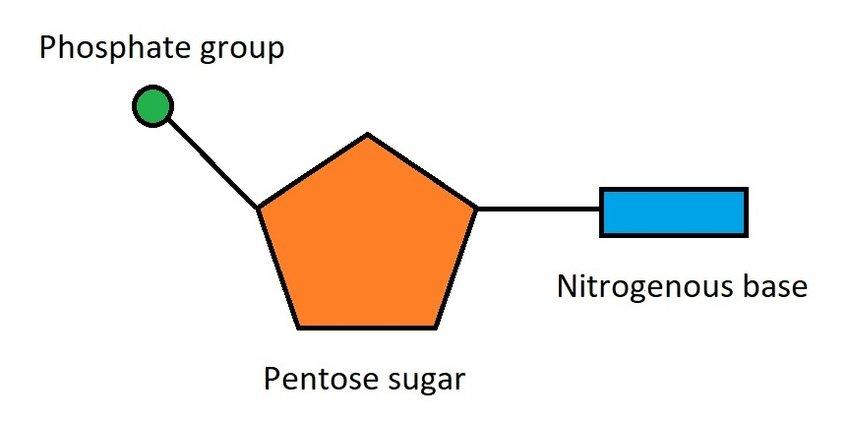
nucleotide
A compound consisting of a nucleoside linked to a phosphate group. Nucleotides form the basic structural unit of nucleic acids such as DNA.
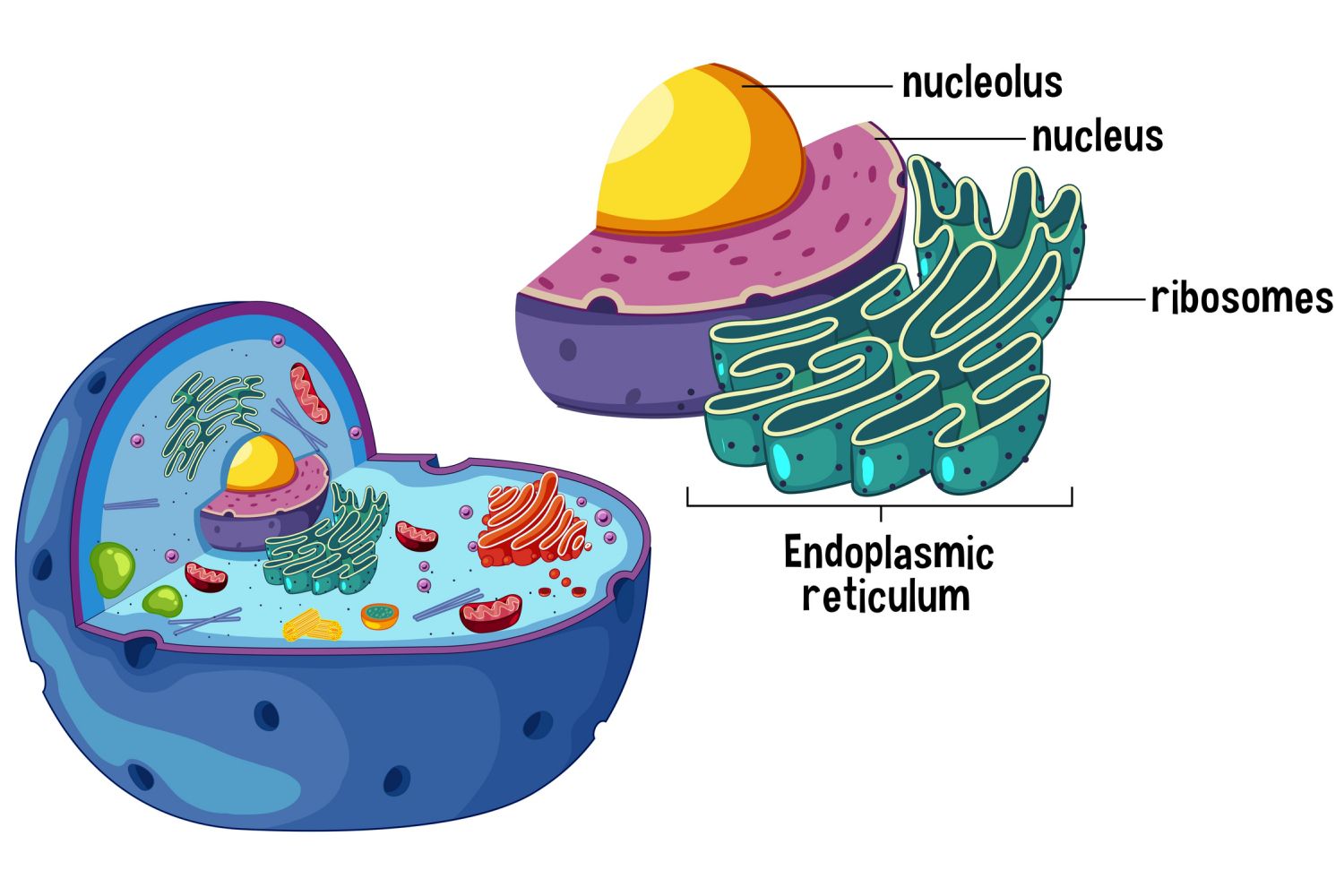
ribosome
A complex molecular machine found within all living cells that serves as the site of biological protein synthesis (translation).
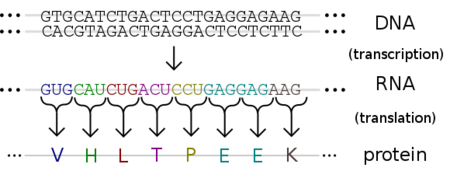
transcription
The process by which the genetic information in DNA is copied into RNA. This is a crucial step in the synthesis of proteins.
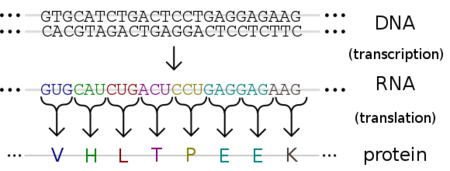
translation
The process by which ribosomes synthesize proteins by decoding messenger RNA (mRNA) into a polypeptide chain, involving transfer RNA (tRNA) and various enzymatic factors.
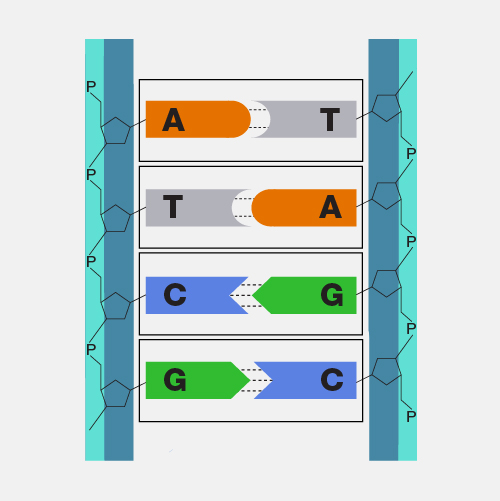
complementary pairs
Base pairs of DNA or RNA that match together, such as adenine with thymine (or uracil) and cytosine with guanine.
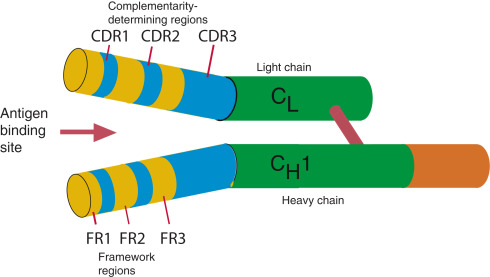
hypervariable region
A section of DNA that contains a high frequency of mutations, often used in genetic studies for identification purposes.
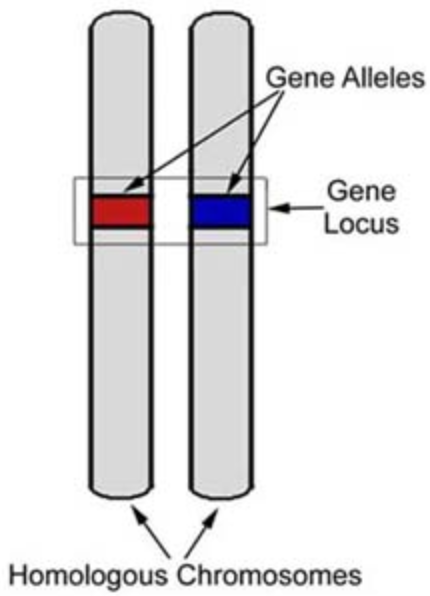
locus
A specific, fixed position on a chromosome where a gene or genetic marker is located.
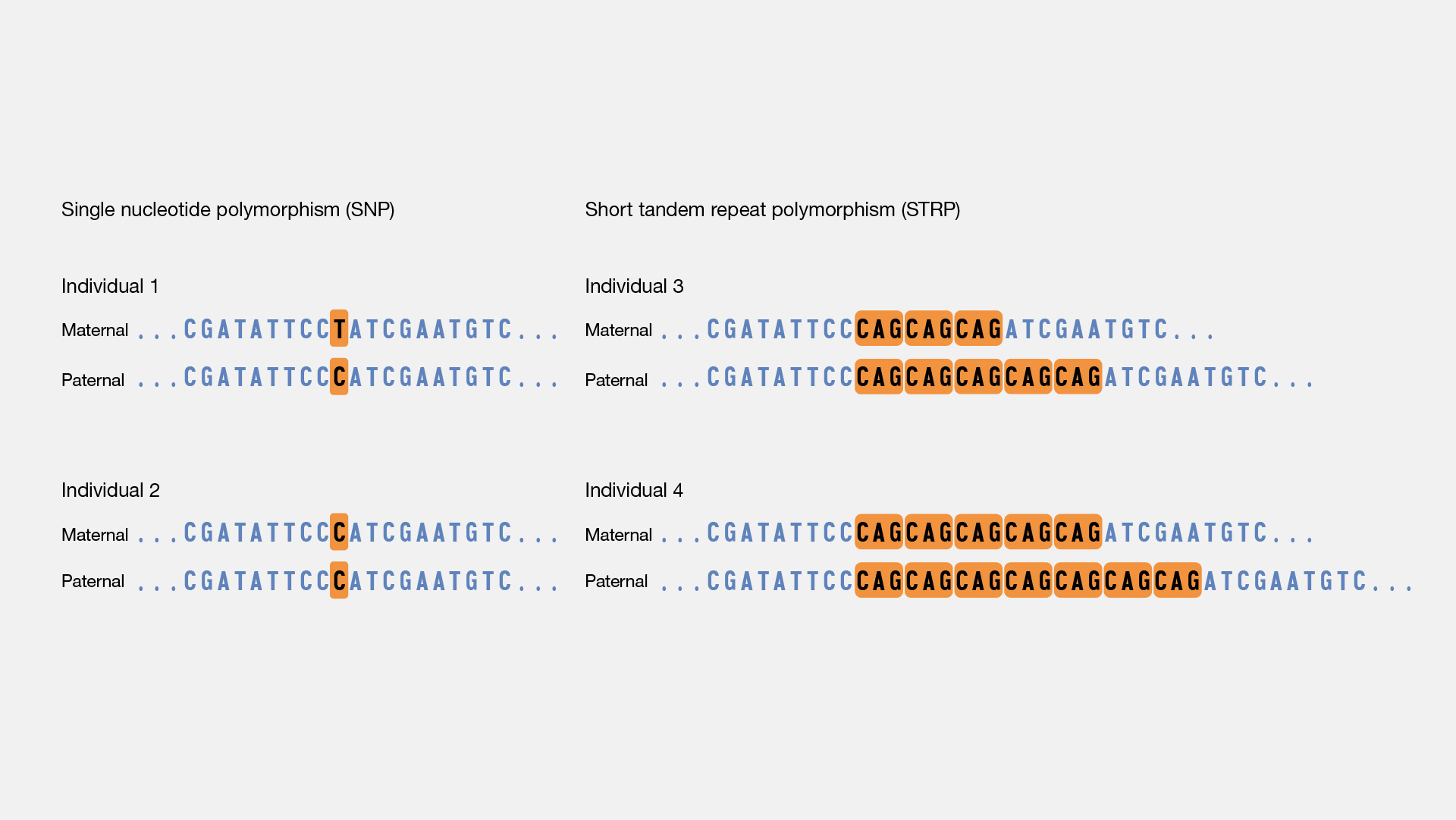
polymorphism
The occurrence of two or more different forms or alleles at a particular genetic locus in a population, contributing to genetic diversity.
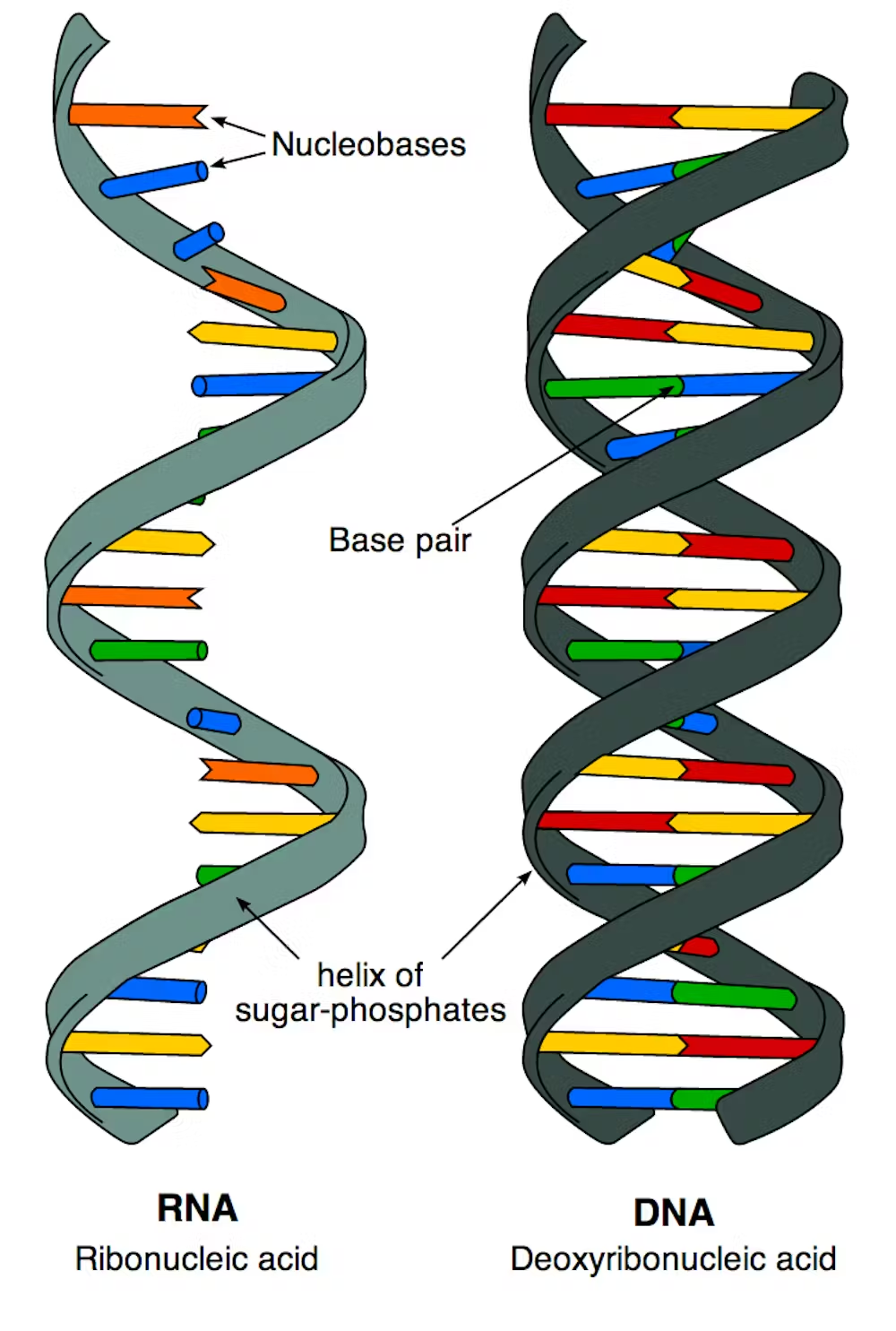
RNA
A nucleic acid similar to DNA, RNA is involved in protein synthesis and acts as a messenger between DNA and ribosomes. It can be single-stranded and includes types like mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA.
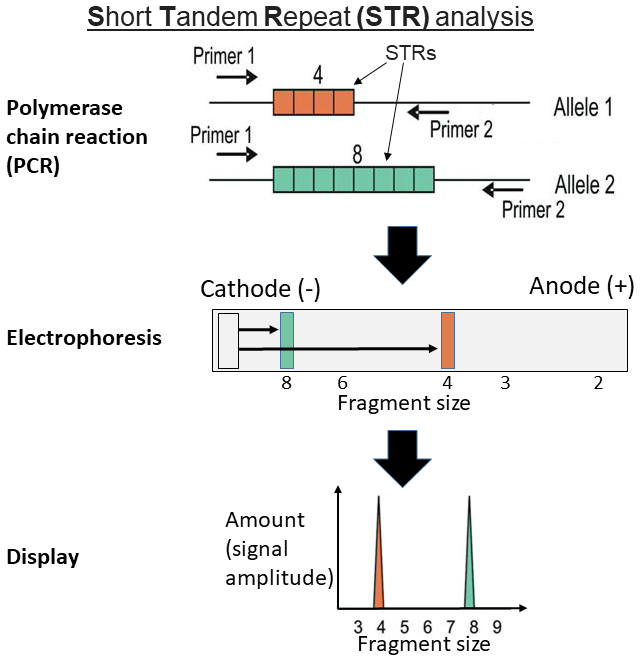
STR
Short Tandem Repeat, a type of genetic marker used in DNA profiling that consists of repeating sequences of 2-6 base pairs.
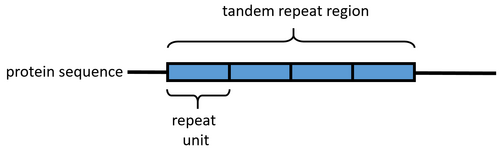
tandem repeat
a repetition of a sequence of DNA that occurs in consecutive cells, typically used in genetic profiling.
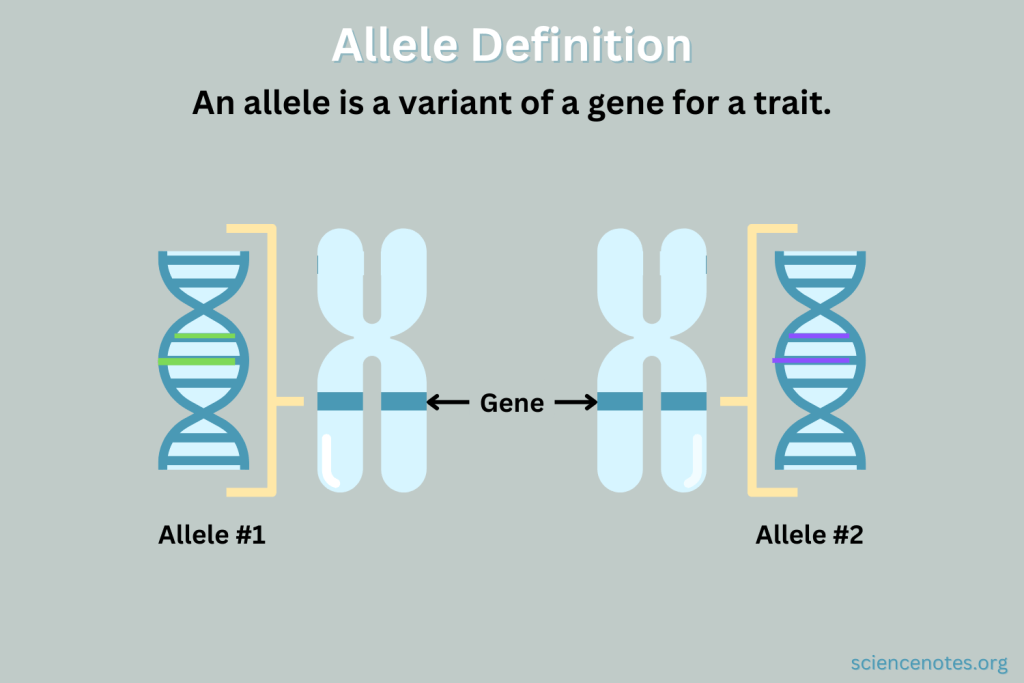
allele
A variant form of a gene.