chapter 23: body mechanics, positioning, and moving
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
disuse syndrome
signs and symptoms that result from inactivity
gravity
force tht pulls objects to center of the earth
energy
capacity to do work. Used to move the body from place to place. Required to overcome the force of gravity.
balance
stead position with weight.
center of gravity
point at which the mass of an object is centered. For standing position is center of pelvis between umbilicus and pubic bone.
line of gravity
imaginary vertical line that passes through the center of gravity. Head to feet through center of the body.
base support
area on which an object rests. The feet are the base of support when a person is in a standing position.
alignment
parts of an object being in proper relationship to one another. The body is in good alignment in a position of good posture.
neutral position
the position of a limb that is turned neither toward nor away from the body’s midline
anatomic position
frontal and back views with arms at the sides and palms froward
functional position
position in which an activity is performed properly and normally. In the hand, the wrists are slightly dorsiflexed between 20 and 35 degrees and the proximal finger joints are flexed between 45 and 60 degrees, with the thumb in opposition and in alignment with the pads of the fingers
posture
the position of the body or the way in which it is held
muscle spasms
sudden, forceful, and involuntary muscle contractions
body mechanics
the efficient use of the musculoskeletal system
increases muscle effectiveness, reduces fatigue, and helps avoid repetitive strain injuries
repetitive strain injuries
disorders that result from cumulative trauma to musculoskeletal structures
ergonomics
a specialty field of engineering science devoted to promoting comfort, performance, and health in the workplace
functional mobility
an alignment that maintains the potential for movement and ambulation
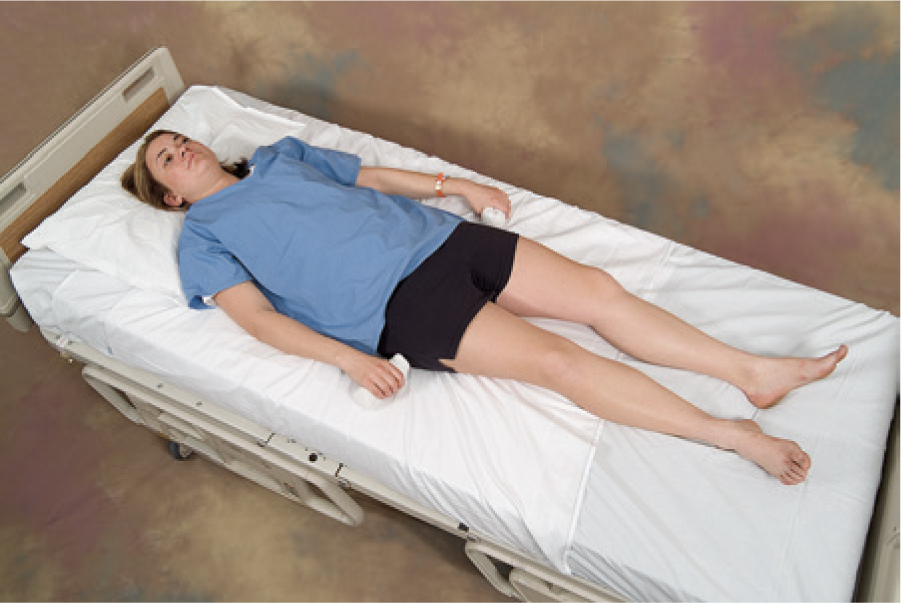
supine position
person lies on their back
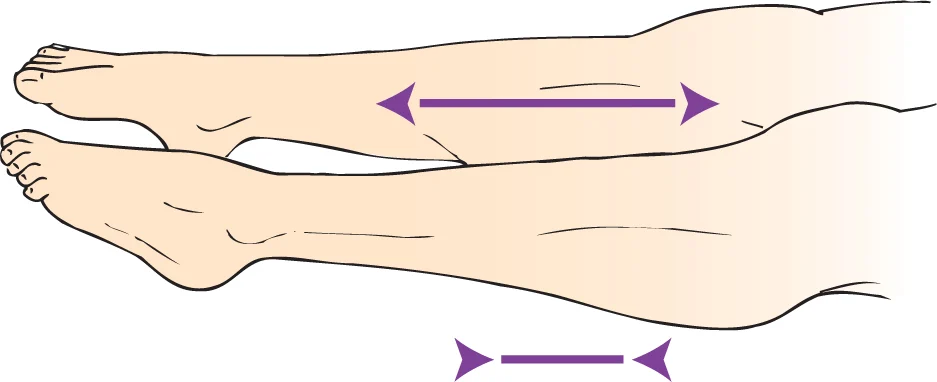
foot drop
permeant dysfunctional position caused by a shortening of the calf muscles and a lengthening of the opposing muscles on the anterior leg
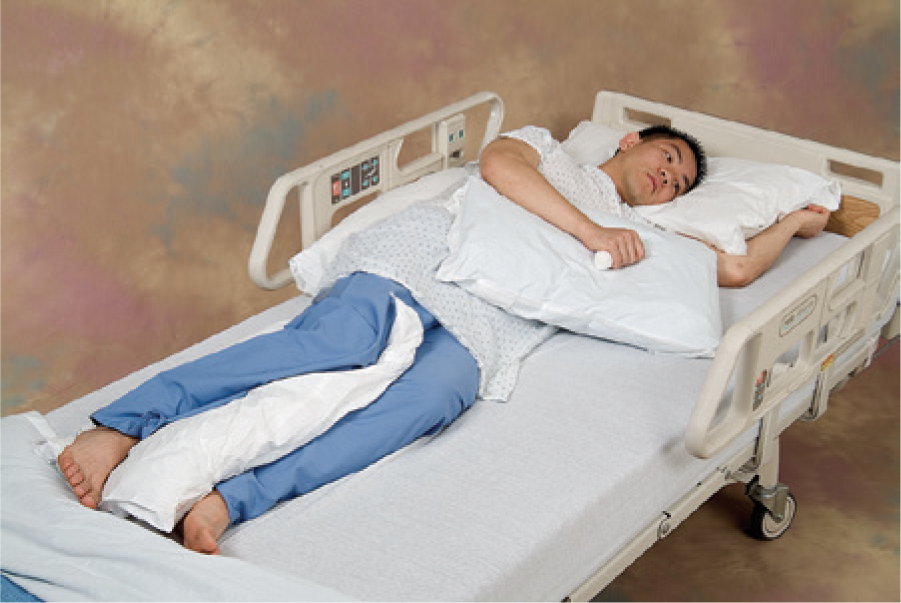
lateral position
a side laying position
lateral oblique position
a variation of the side lying position, client lies of the side with the top leg placed in 30 deg of hip flexion and 35 degrees of knee flexion
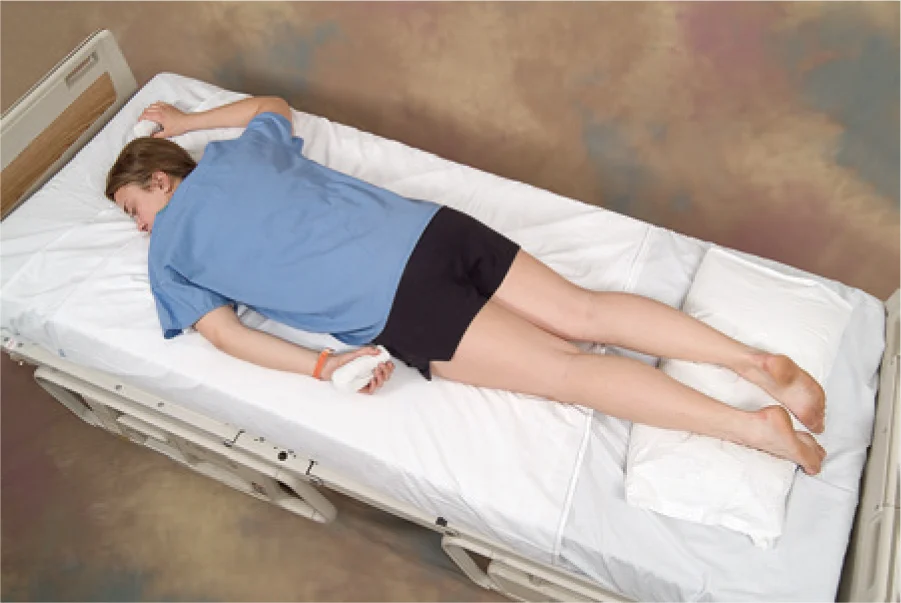
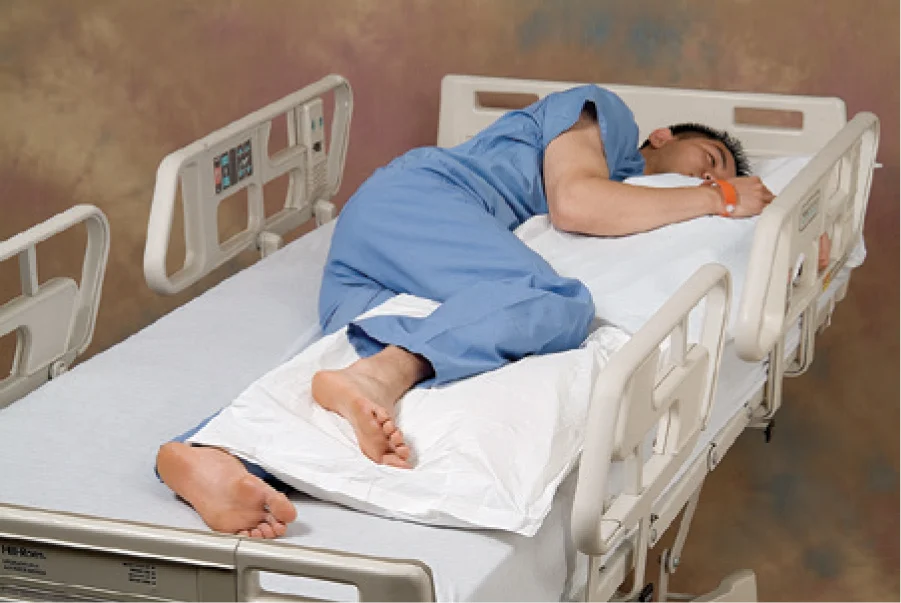
prone position
where client lies on the abdomen
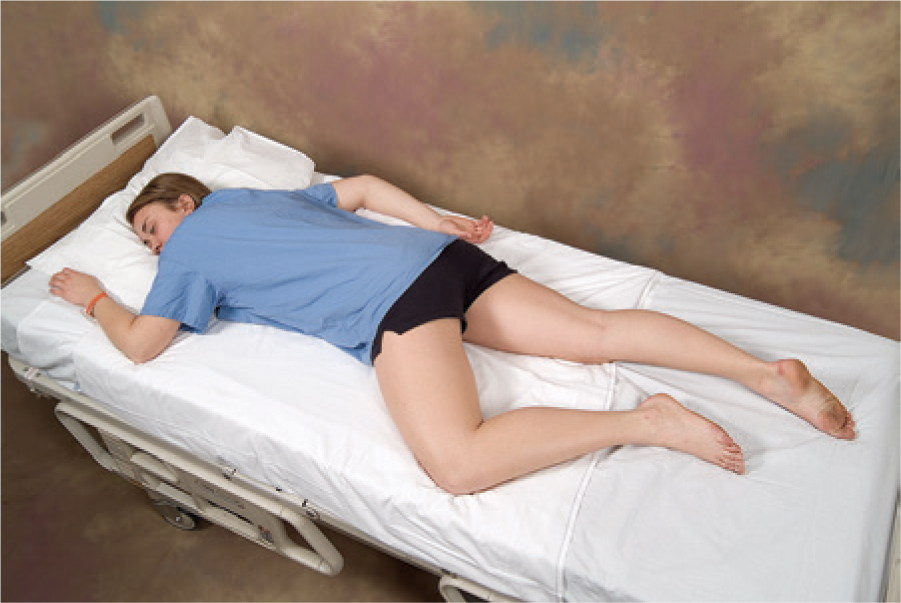
sims position
a semi-prone position
lies on left side with right knee drawn up toward the chest
used for observing rectum and vagina
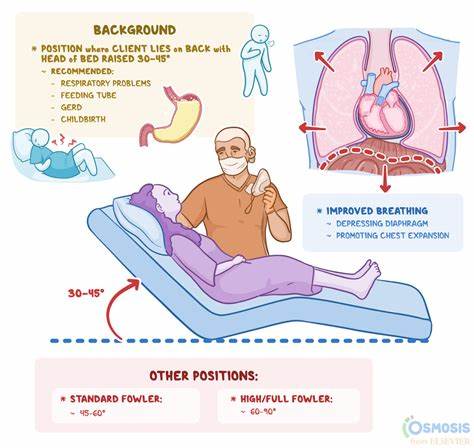
fowler position
a semi-sitting position
helps for breathing problems- exchange of greater volume of air
BUT can decrease blood flow to lower extremities (coccyx) increasing rick for pressure ulcers
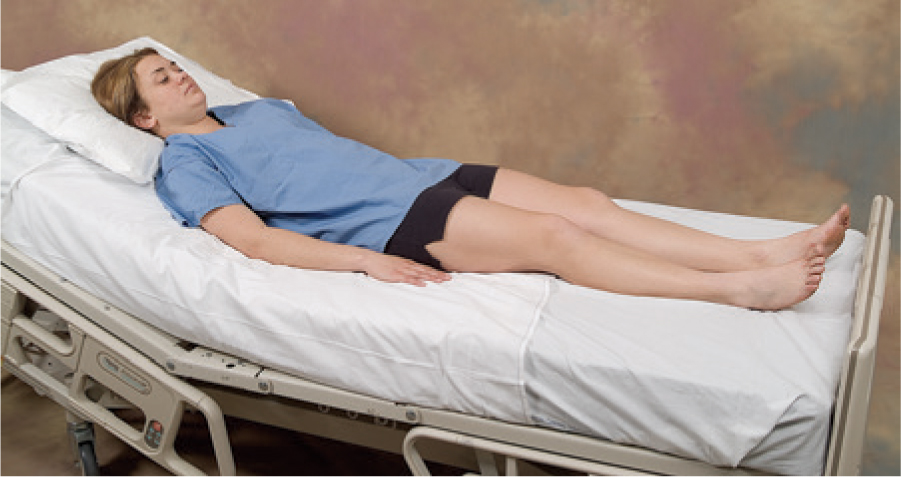
low fowler
head and torso are elevated to 30 deg
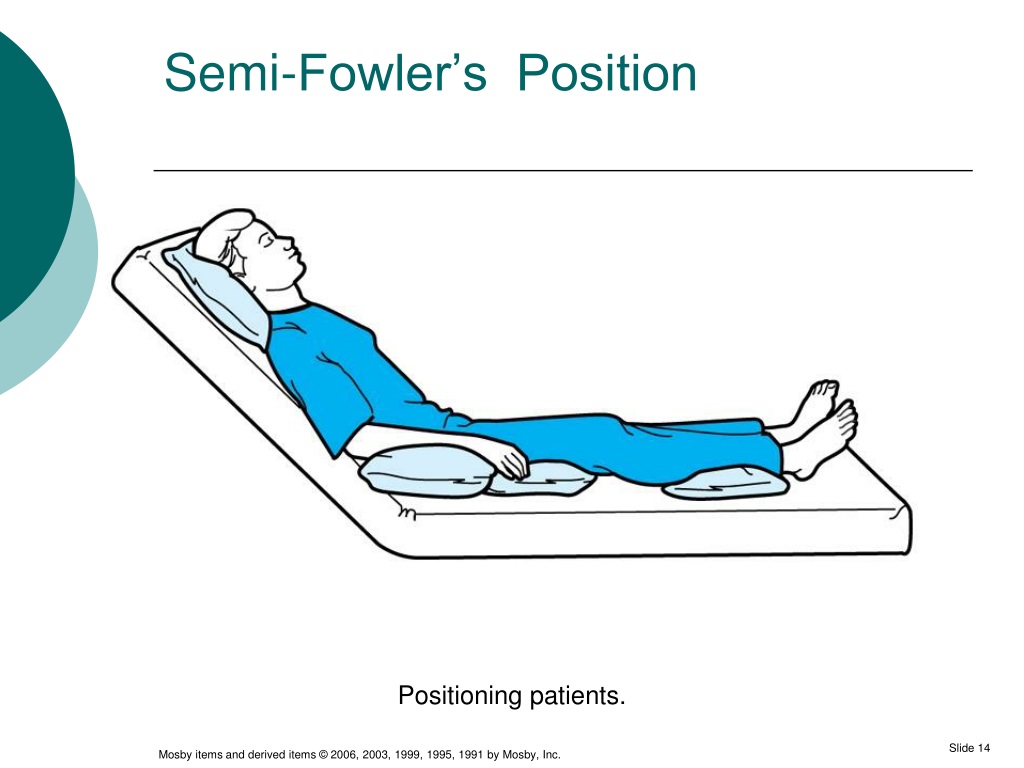
mid fowler (semi fowler)
elevation up to 45 deg
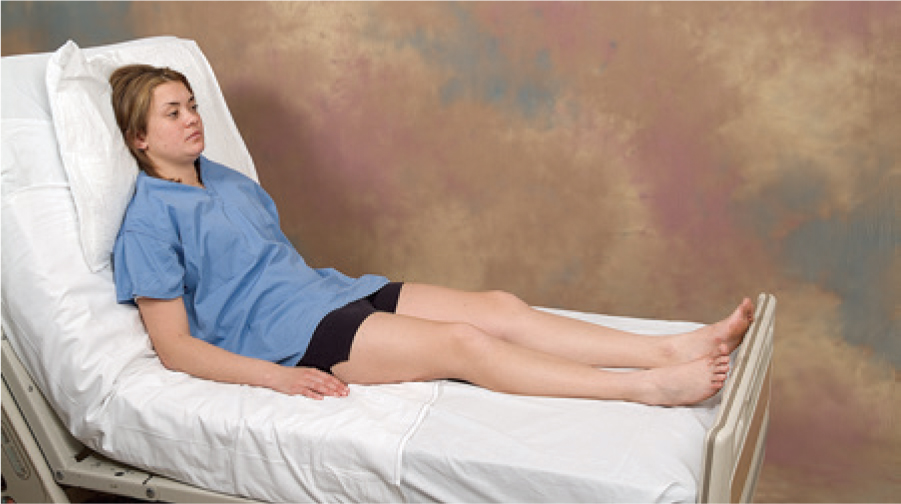

high fowler
elevation of 60-90 deg
bed board
a rigid structure placed under a mattress
contractures
permanently shortened muscles that resist stretching
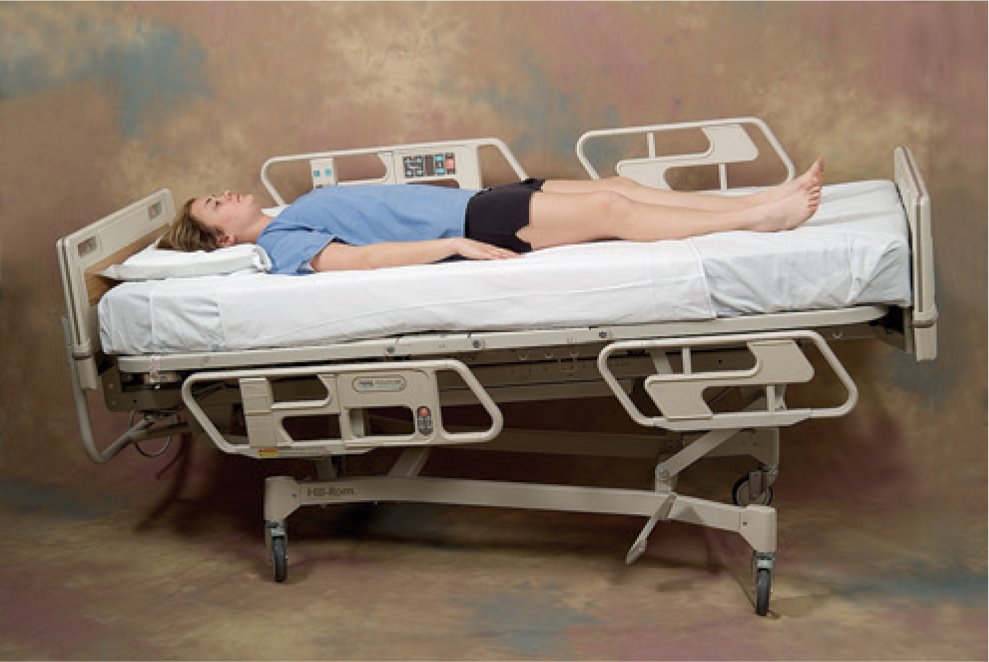
Trendelenburg position
head is lower than the feet
shearing
the force exerted against the surface and layers of the skin as tissues slide in opposite but parallel directions