nervous system anatomy
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
66 Terms
what is the main role of the nervous system
control and coordinate body systems using electrical and chemical signals
what are the three main functions of the nervous system
sensory input, processing and motor output
what is the link between the nervous and endocrine system
together they maintain homeostasis
what are some key high brain functions
memory, emotional, reasoning, behaviour and consciousness
what are the two main nervous system cell types
neurons and glial cells
what is the function of a neuron
transmit information via electrical impulses
what is a synapse
junction where neurons communicate using neurotransmitters
what is the role of a glial cell
support, protect and maintain neurons
what is the role of a microglia
acts as a immune macrophage in CNS
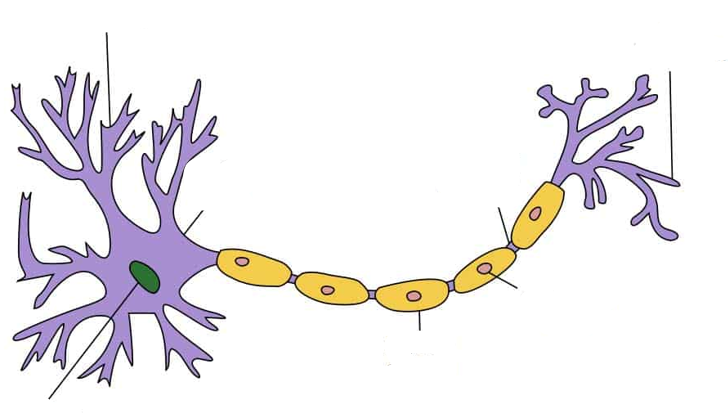
label the parts of the neuron
dendrites, cell body, myelin sheath, axon terminal
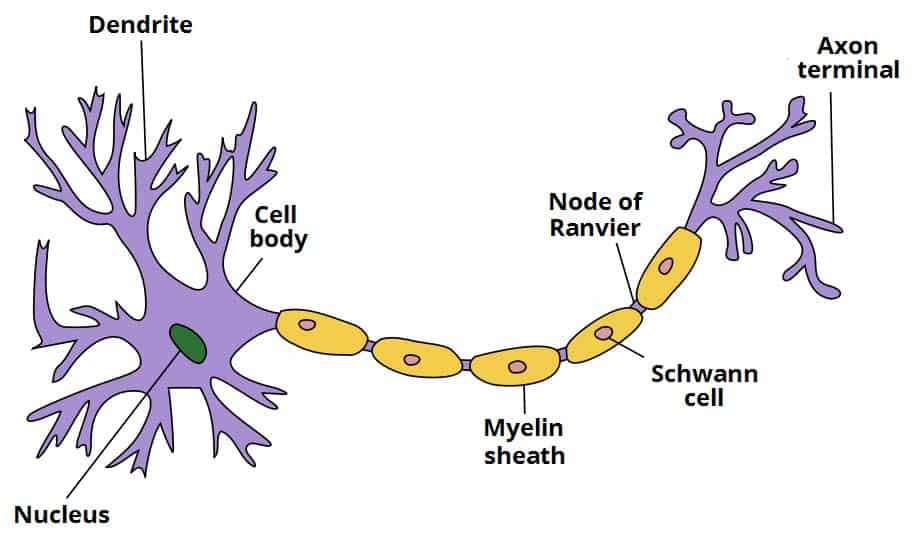
function of cell body
contains nucleus and organelles
function of dendrites
receive signals from other neurons
function of axon
long projection which carries electrical signal (i.e. action potential)
myelin function
fatty insulation layer which speeds up nerve transmission via saltatory conduction
function of nodes of ranvier
gaps in myelin that allow signal to jump to speed up conduction
function of axon terminals
connect to the next neuron or effector organ
what are the three types of neurons
sensory, relay and motor
what is the role of the sensory neuron
carry information to the CNS
what is the role of the relay neuron
connect sensory neuron to motor neuron
what is the function of the motor neuron
receives information from the CNS to the muscle/gland
what are the two main divisions of the nervous system
CNS and PNS
what does the CNS consist of
brain and spinal cord
what does the PNS consist of
Autonomic NS and Somatic NS
what is the meninges
protective layers surrounding the brain and spinal cord
what are the three meninge layers
dura mater, arachnoid mater and pia mater
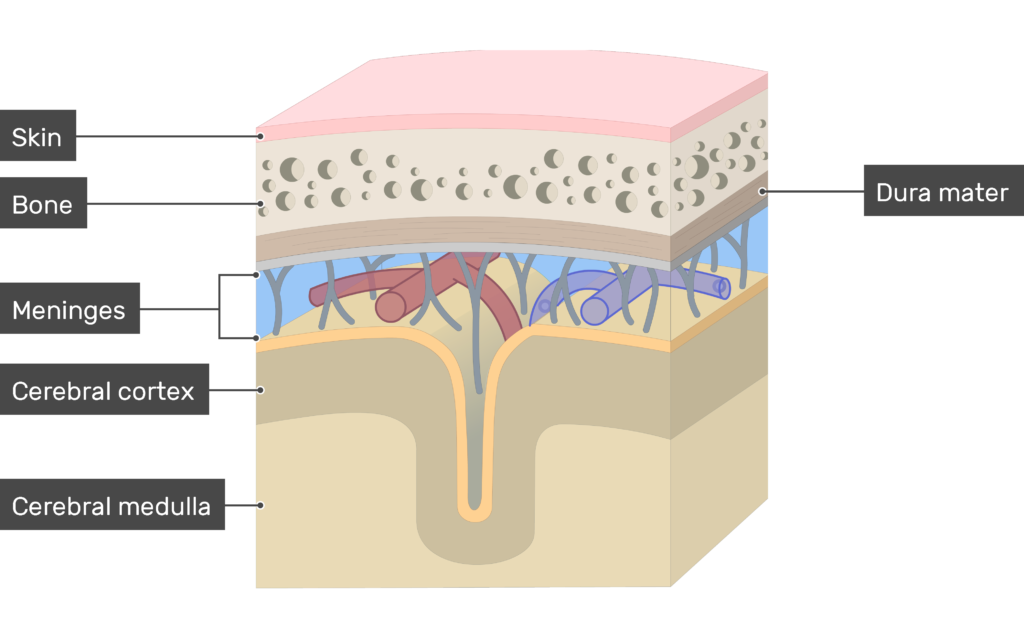
what is the dura mater
tough outer layer
what does the subarachnoid space contain
cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
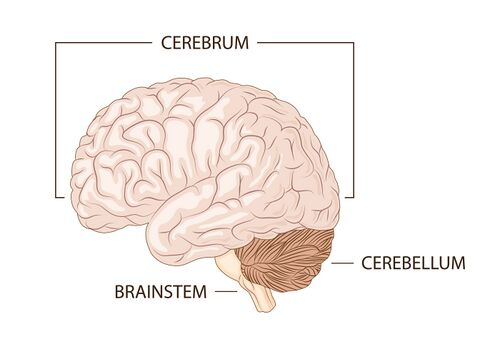
what is the function of the cerebrum
higher thinking, memory, voluntary movement and sensations
what does the brains hemispheres control
each control opposite sides of the body
what are the four brain lobes
frontal, occipital, parietal and temporal
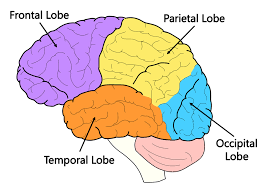
what is the function of the occipital lobe
vision
what are the two key areas of language and speech
wernicke’s and broca’s
what is wernickes area responsible for
language comprehension
what is broca’s area responsible for
speech production
what is the function of the hippocampus
memory formation
what is the function of the amygdala
emotion and fear responses
what is the Diencephalon
posterior part of the forebrain
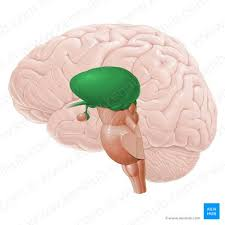
role of the diencephalon
relays sensory and motor signals to the cortex and helps maintain homeostasis
function of corpus callosum
connects left and right hemisphere
what is the function of the thalamus
sensory relay centre to cortex
what is the function of the hypothalamus
releases hormones, maintains temperature, hunger, sleep, behaviour control
what is the function of the pituitary gland
hormone releasing control centre
what is the function of the pineal gland
melatonin production, sleep regulation
what is the function of the cerebellum
balance, posture, coordination, fine movement control
what is the impact of a damaged cerebellum
lead to unsteady movement and poor coordination which can significantly impact daily living
what does the brain stem connect
brain to spinal cord
what does the brain stem control
vital involuntary functions such as breathing, heart rate etc
what is the function of the midbrain
dopamine reward system, where dopamine is produced
what is the role of pons
connects cerebrum, cerebellum and spinal cord to create a larger relay station for nerve signals
what is the role of the medulla oblongata
heart rate, blood pressure, breathing rate
what is the impact of a brain stem injury
can be life threatening
how many cranial nerves are there
12
how many layers are there to the spinal meninges
three layers
what are the three layers of the spinal meninge
dura, arachnoid and pia
what are the five difference areas of the spine
cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacrum and coccyx
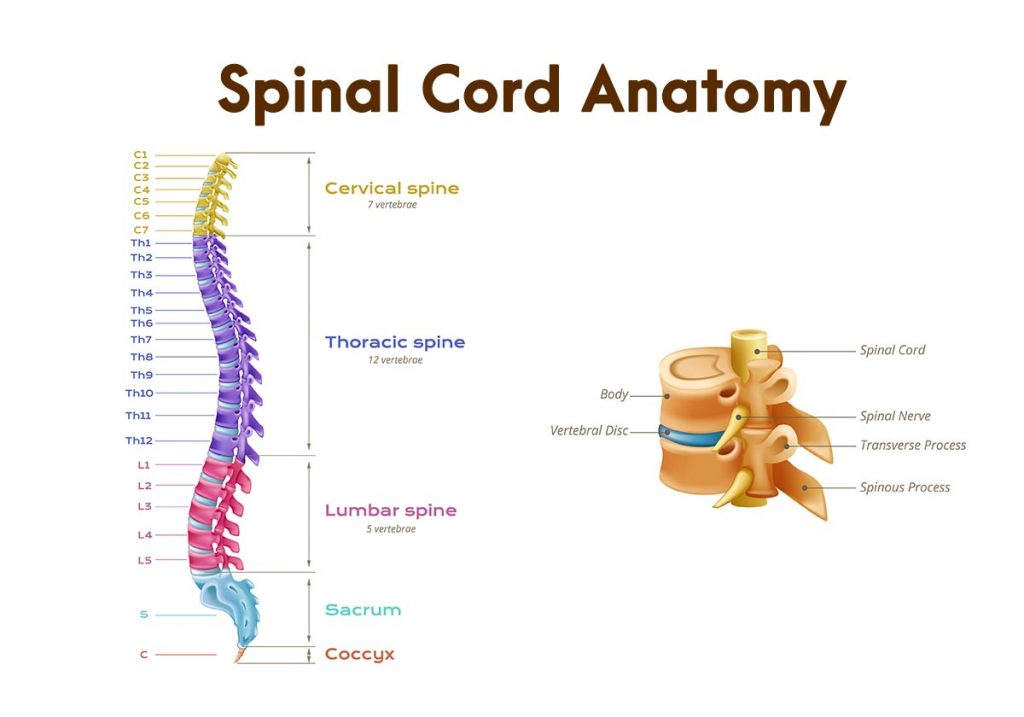
what is the function of the spinal cord
connect the CNS to the PNS
what is a reflex arc
rapid, automatic response to protect the body
what do reflexes required
receptor, sensory neuron, integration centre, motor neuron and effector (muscle or gland)
what is the integration system also known for
where processing occurs
what are the two divisions of the PNS
sensory and motor
what does the motor division of the PNS include
somatic and autonomic systems
what does the somatic system do
controls voluntary skeletal muscle
what does the autonomic system do
controls the heart, smooth muscle and glands
what are the branches of the ANS
sympathetic and parasympathetic
what is the role of the sympathetic NS
fight or flight
what is the role of the parasympathetic NS
rest and digest