Chemistry Unit Test 2 BIG... (Includes organelles and their functions)
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
86 Terms
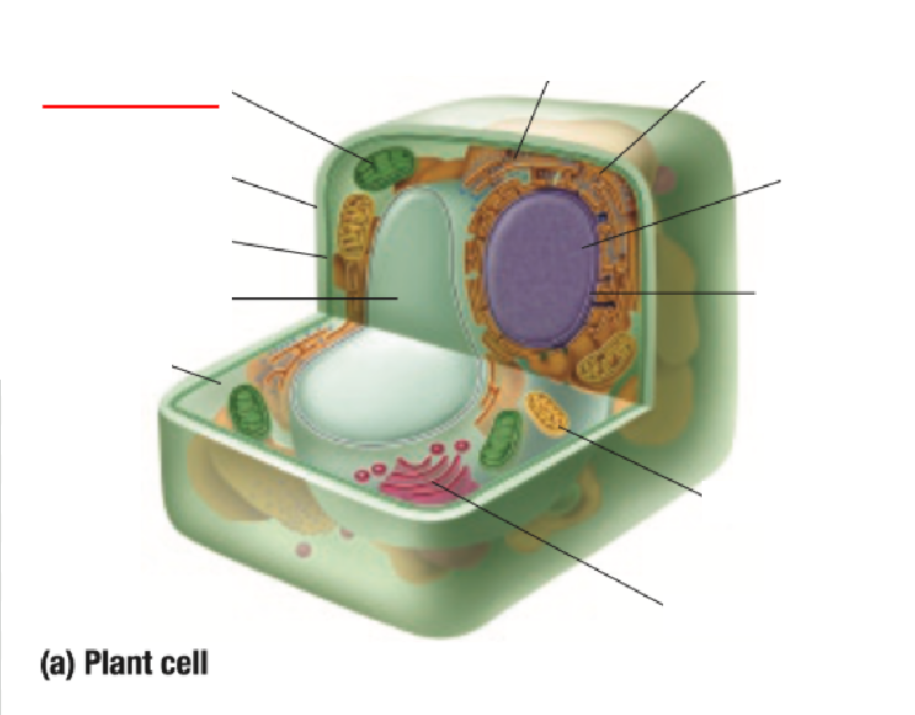
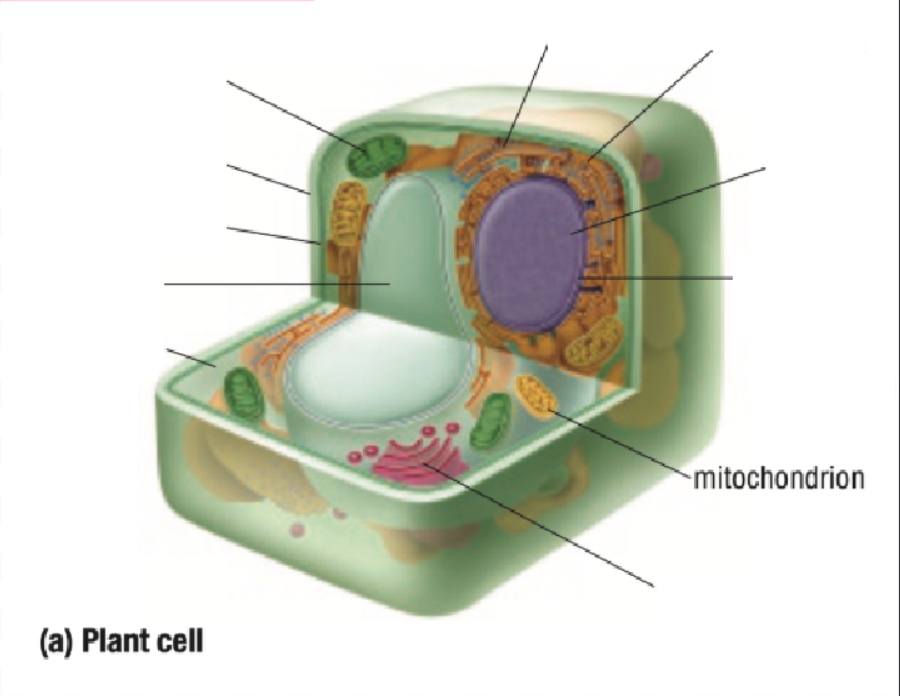
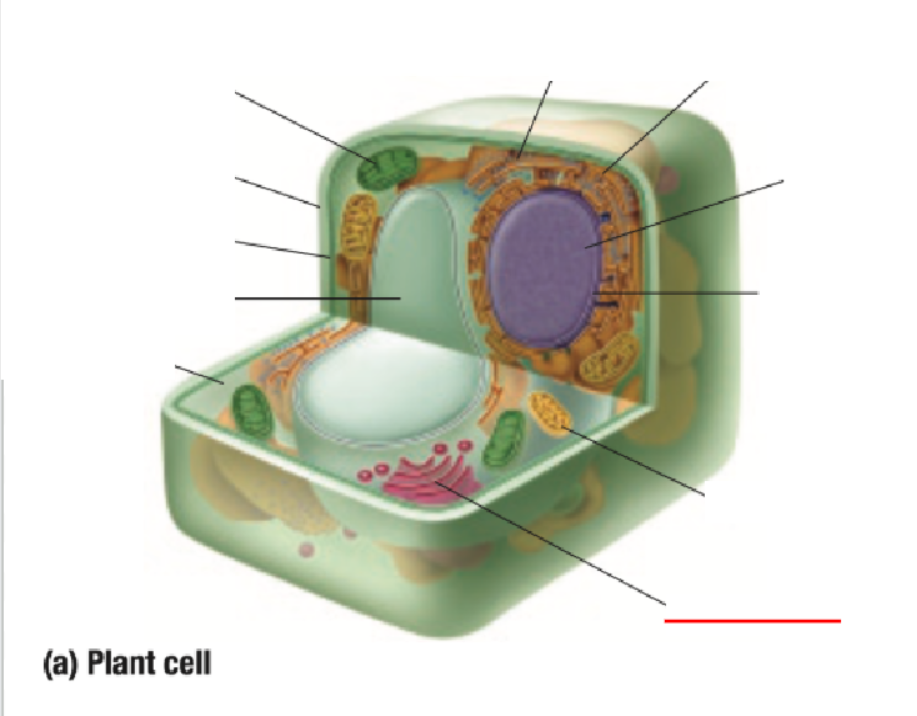
Cytoplasm
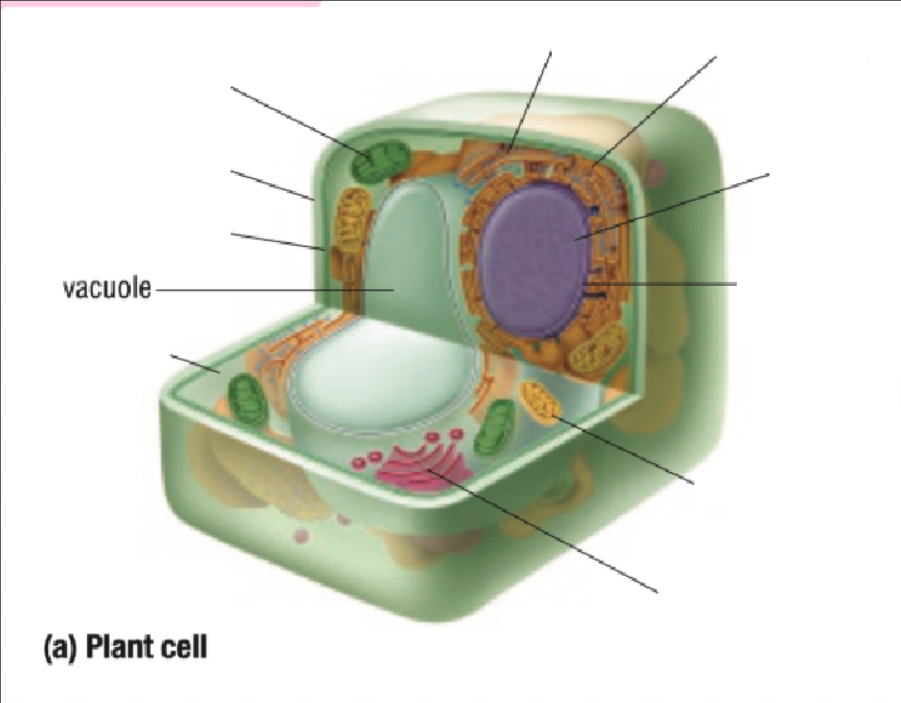
Vacuole
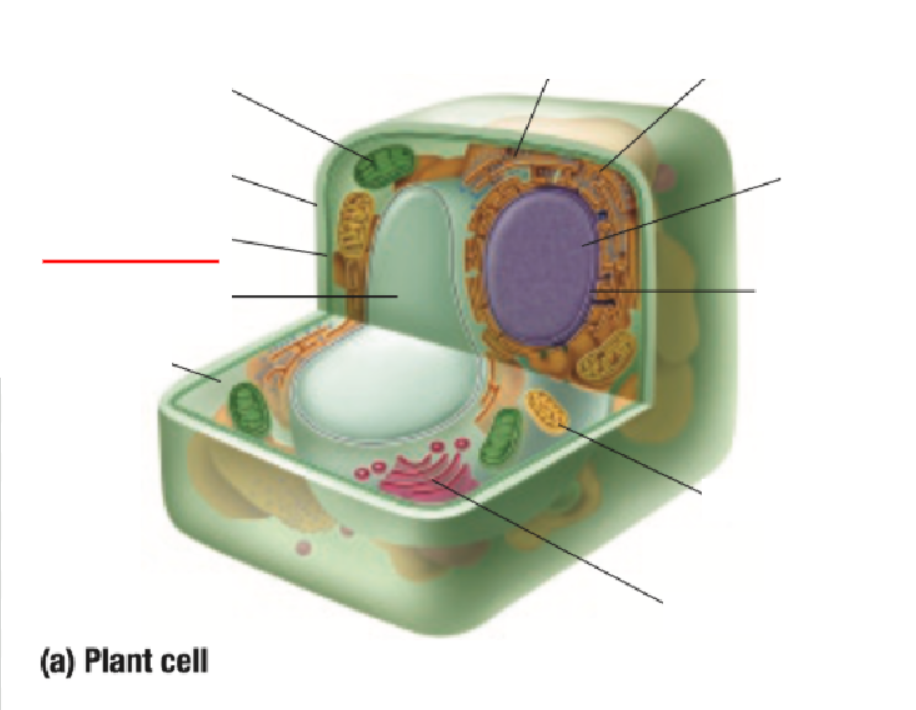
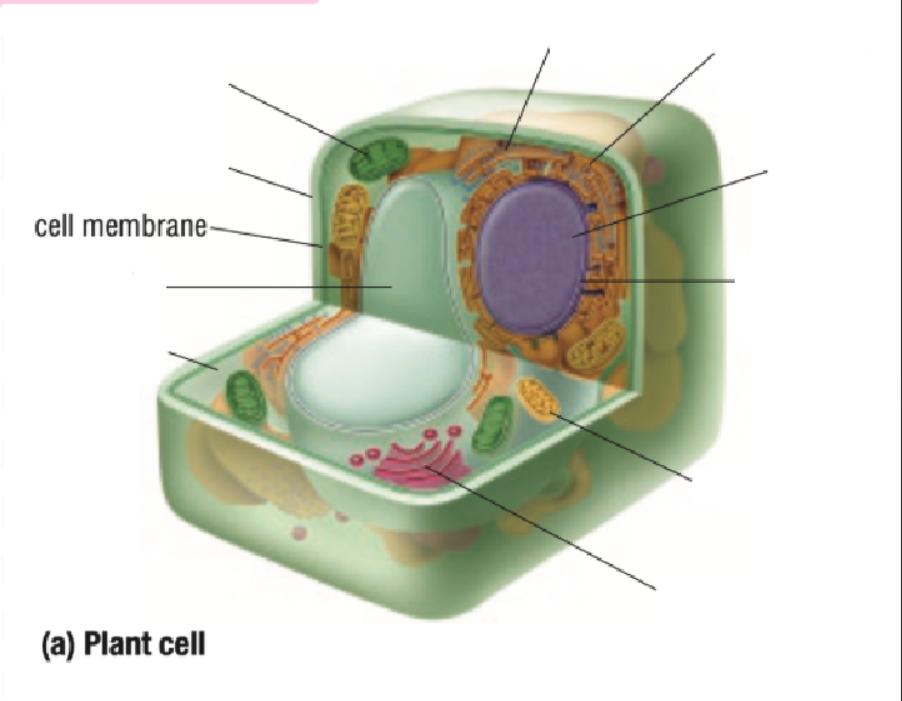
Cell Membrane
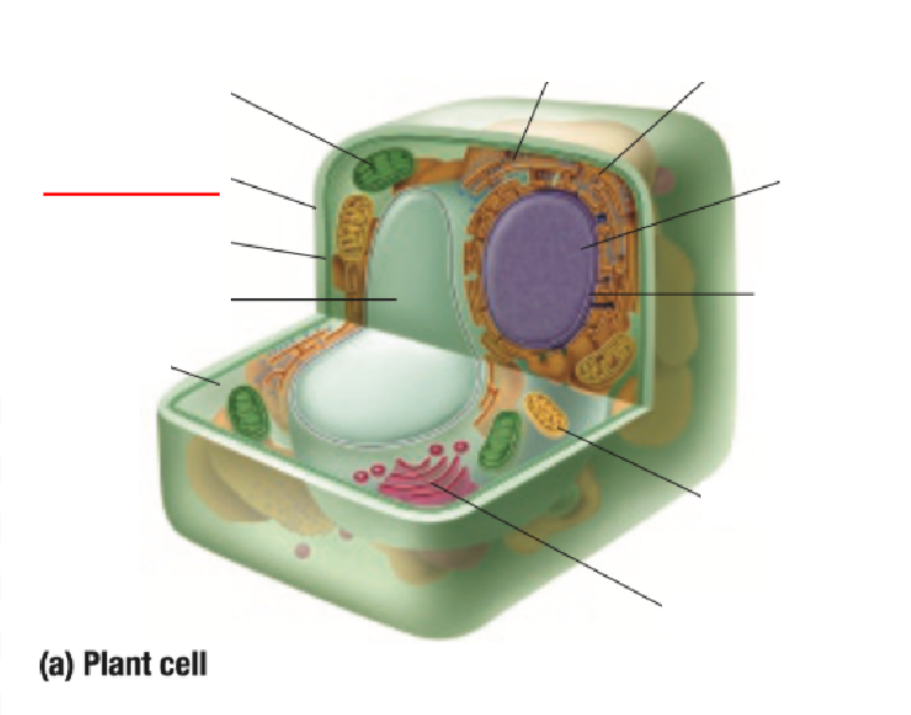
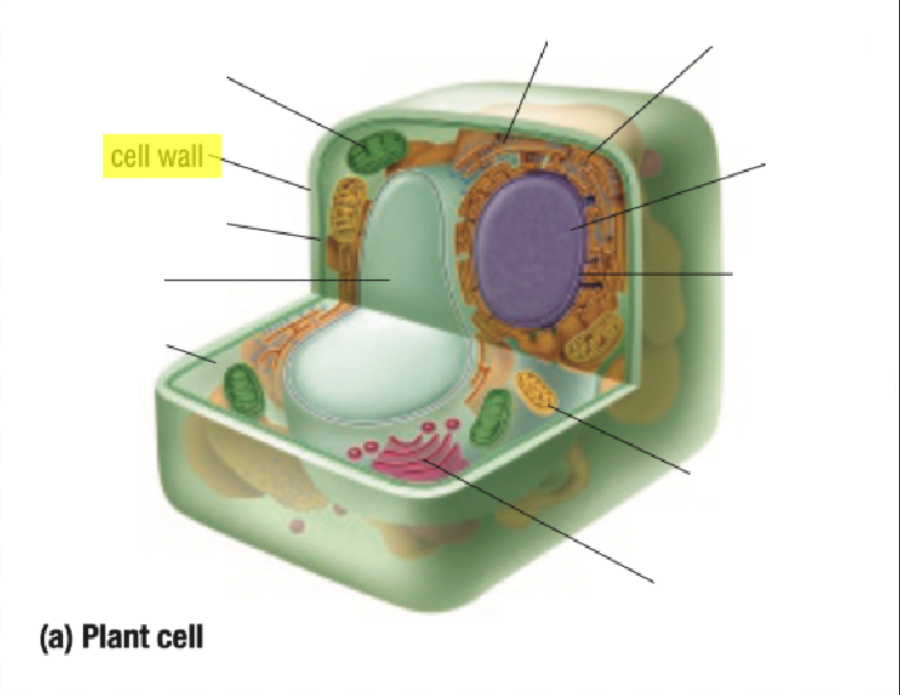
Cell Wall
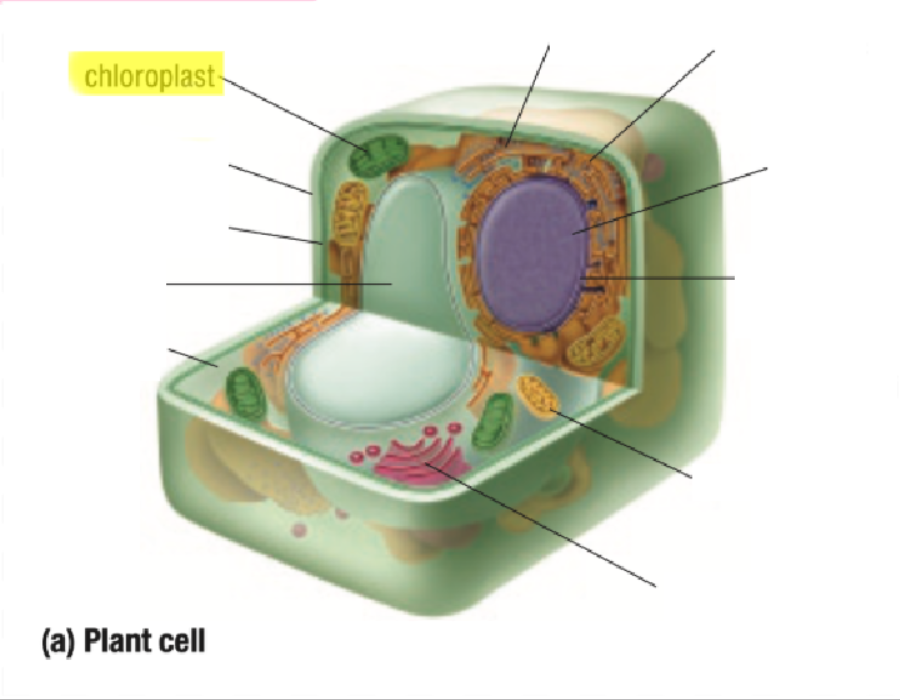
Chloroplast
Ribosome
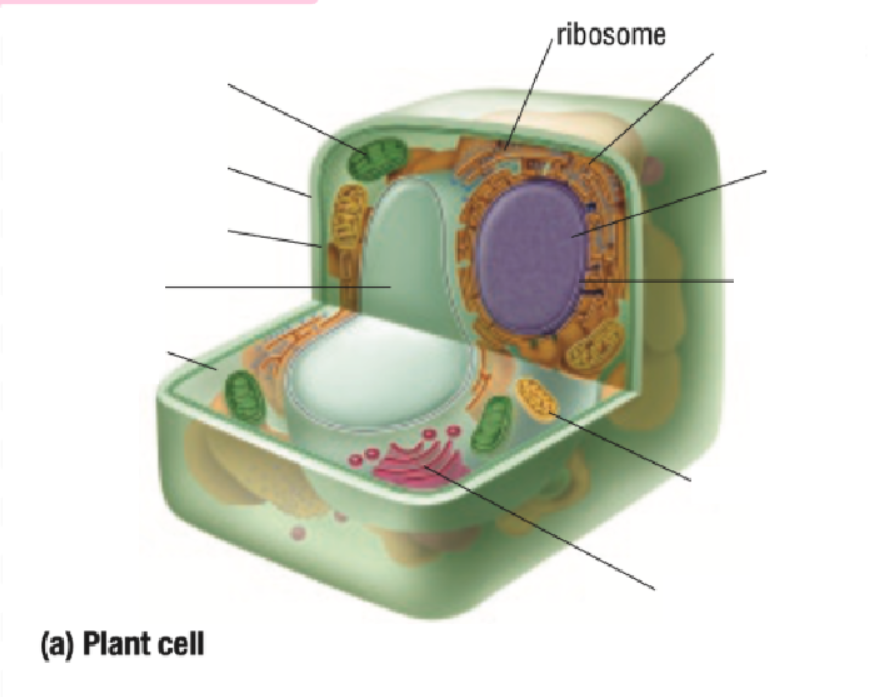
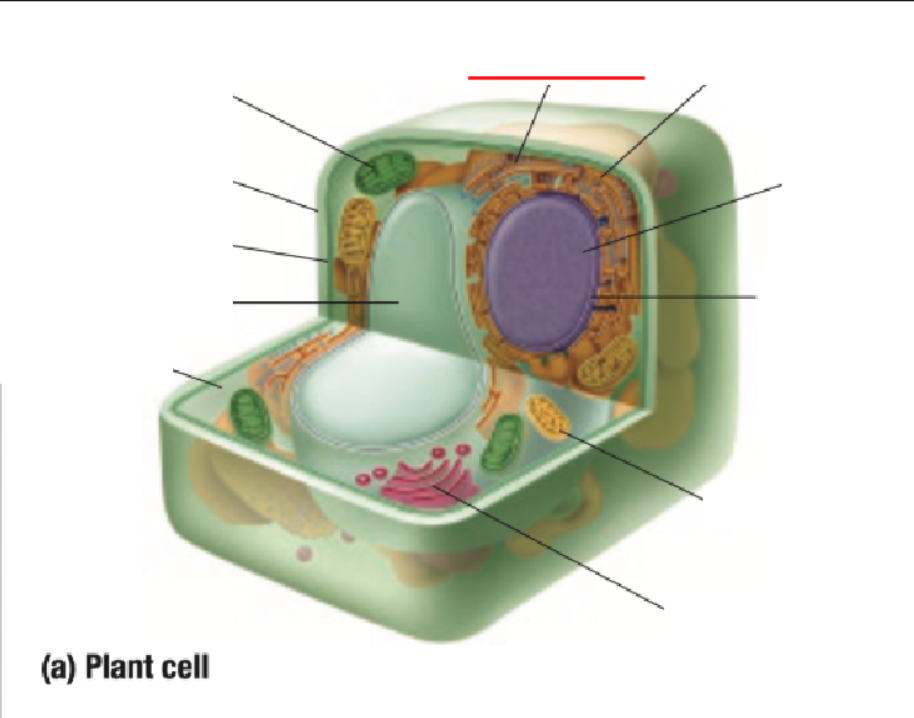
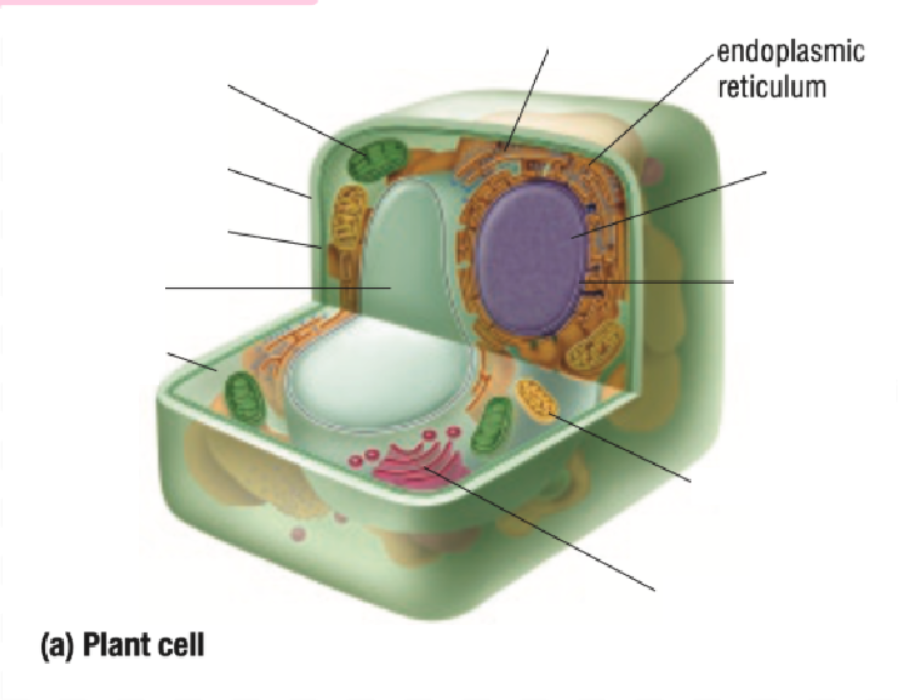
Endoplastic Recticulum
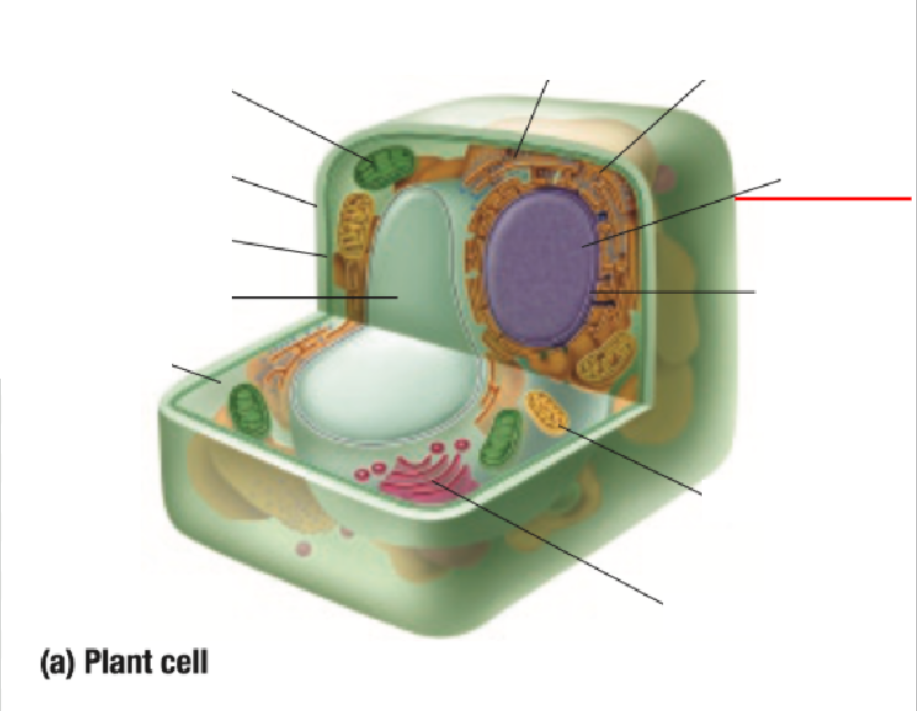
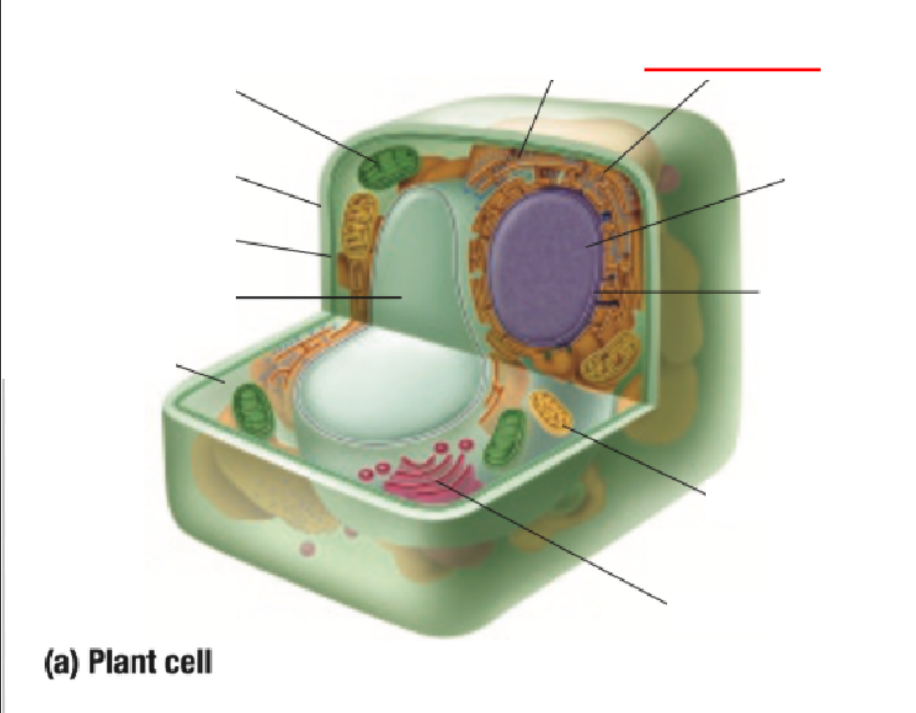
Nucleus
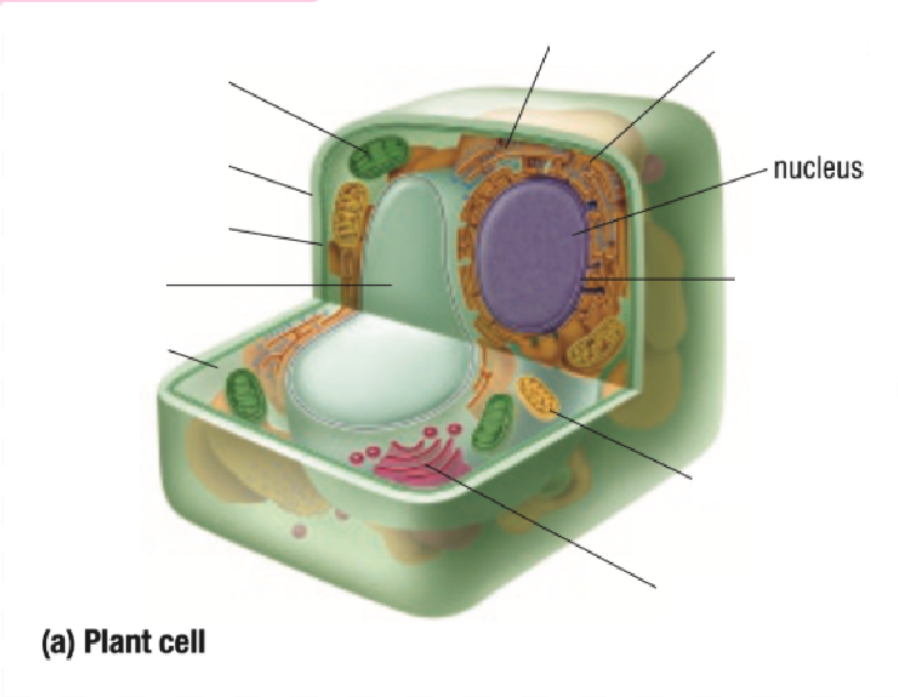
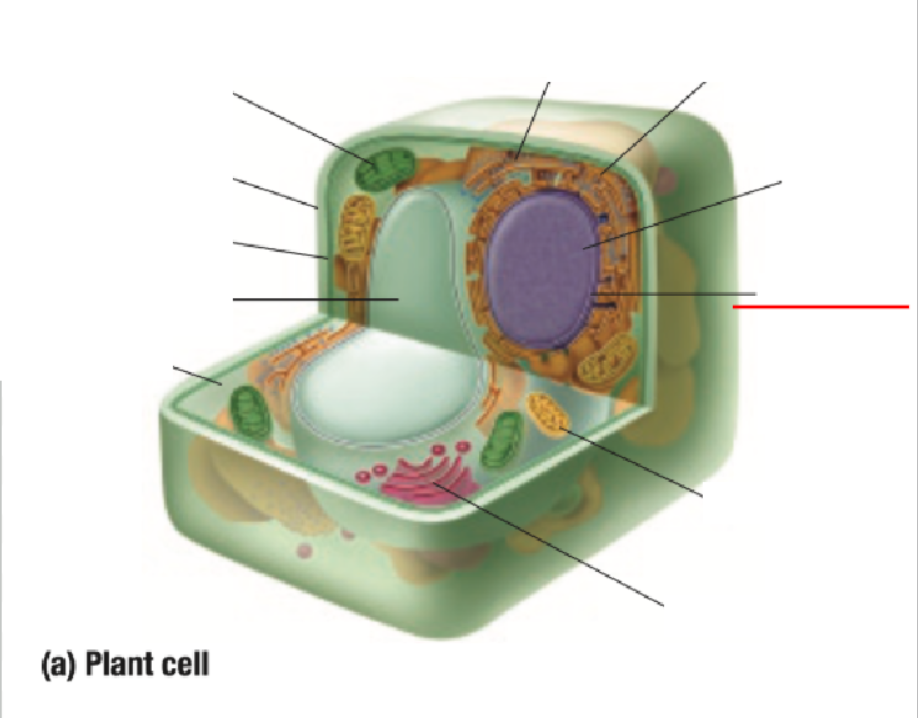
Nuclear Membrane
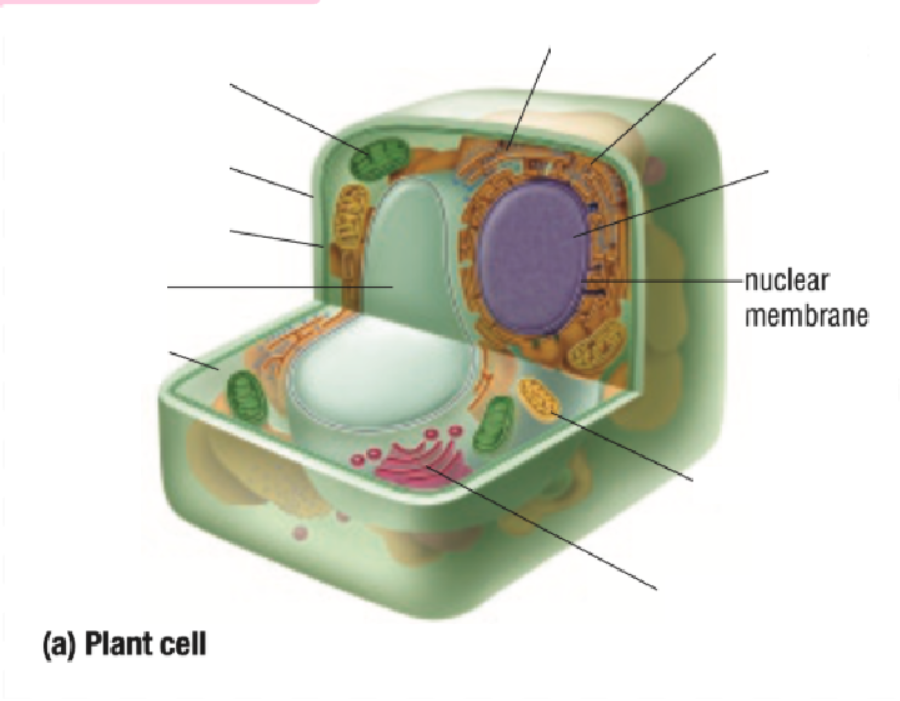
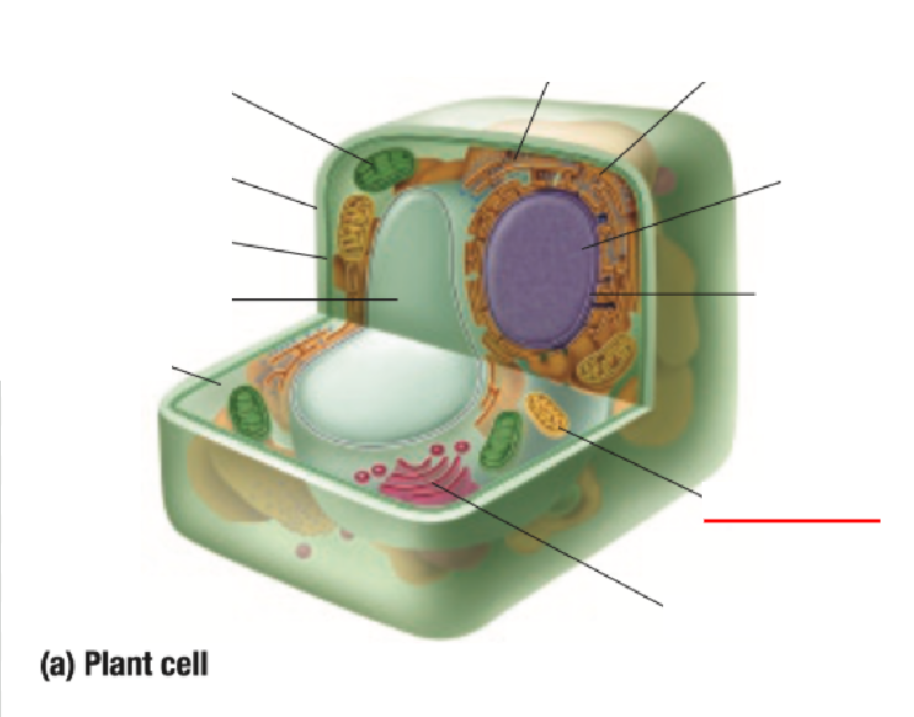
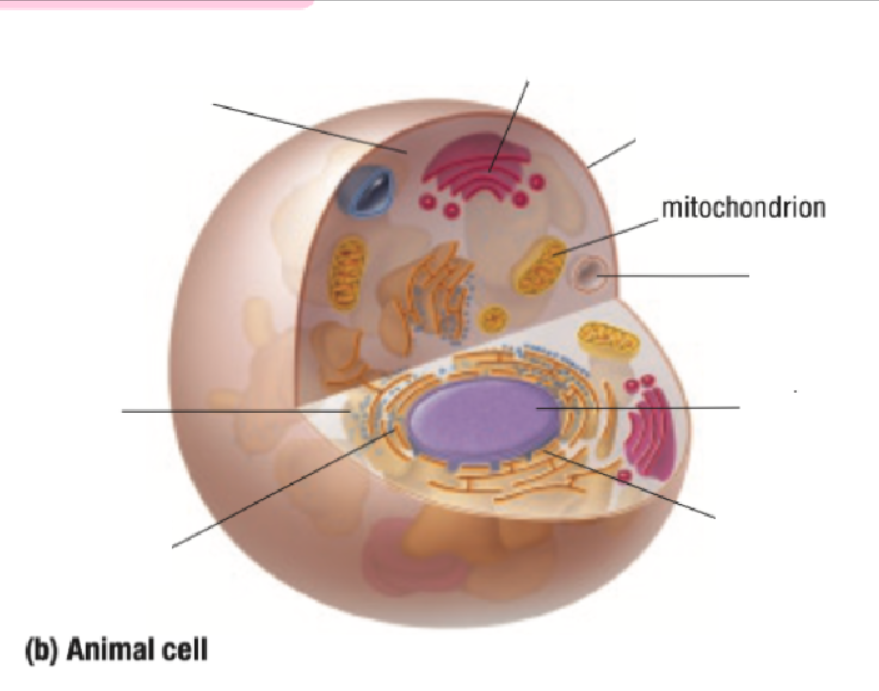
Mitochondria
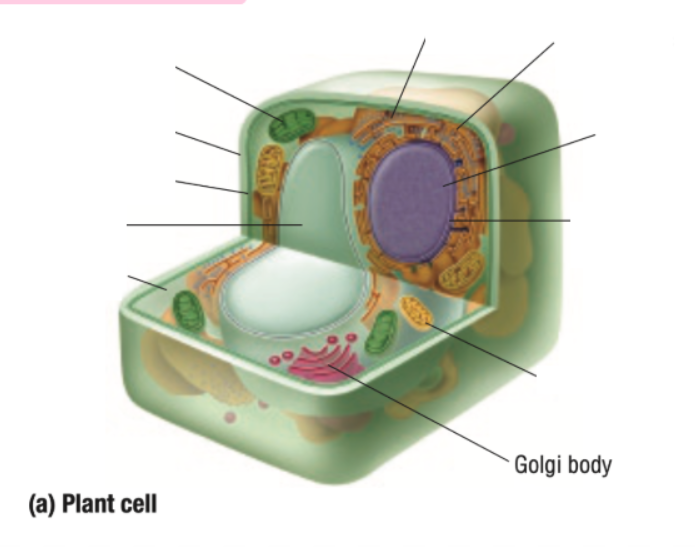
Golgi Body
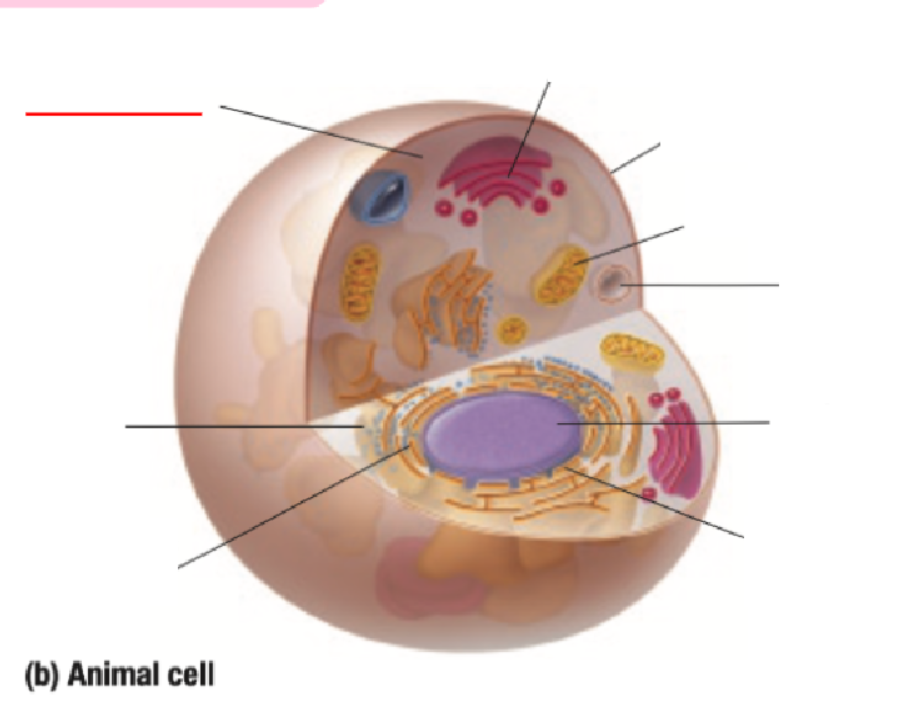
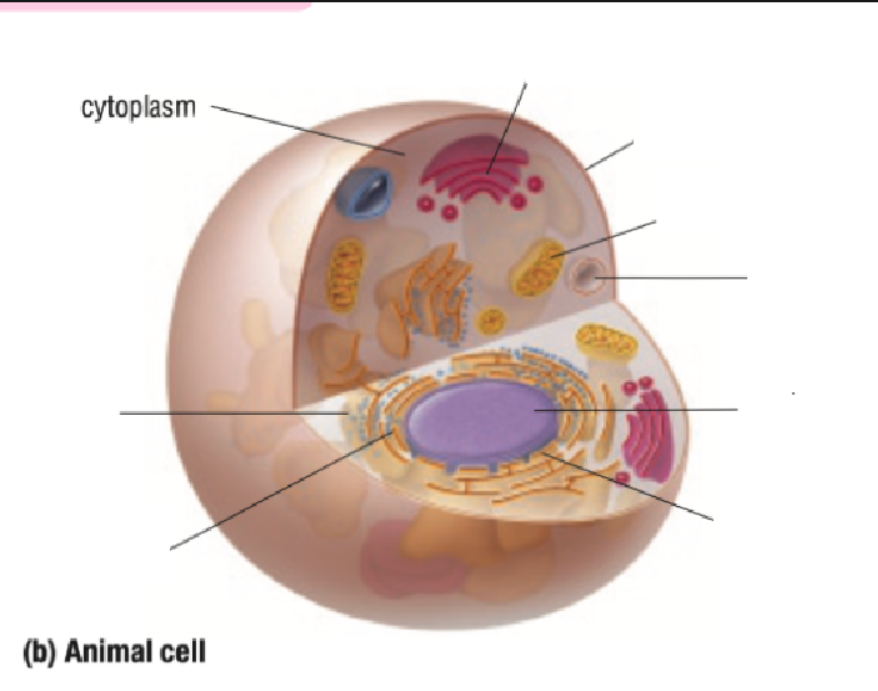
Cytoplasm
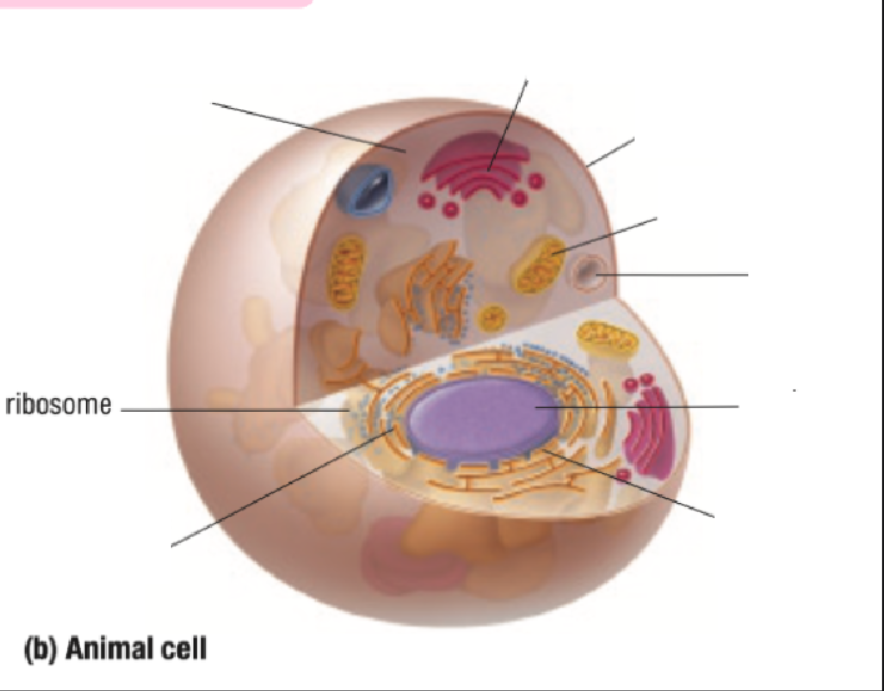
Ribosome
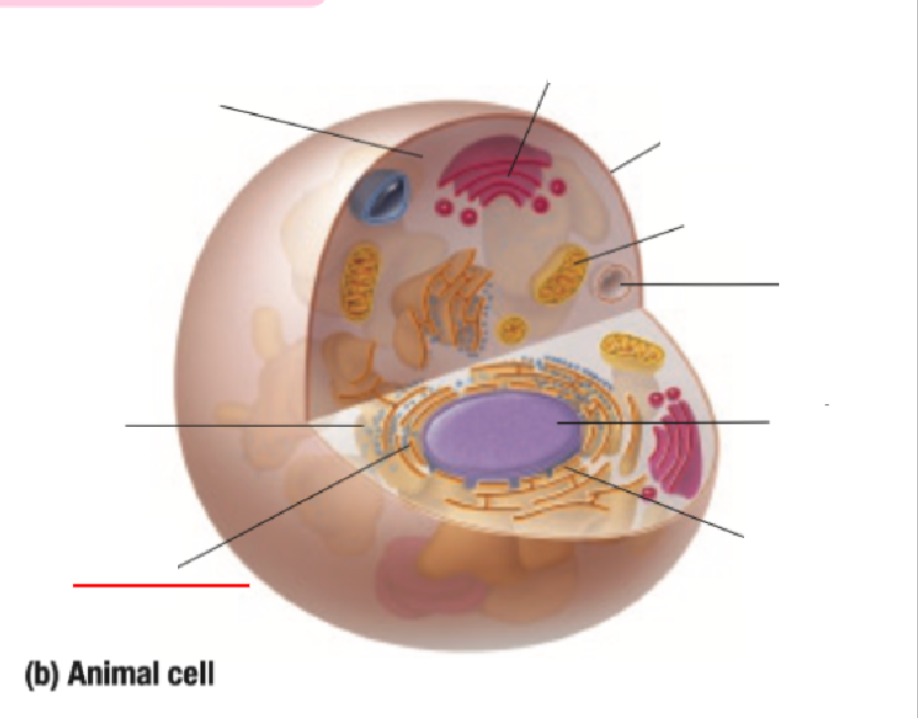
Endoplastic Recticulum
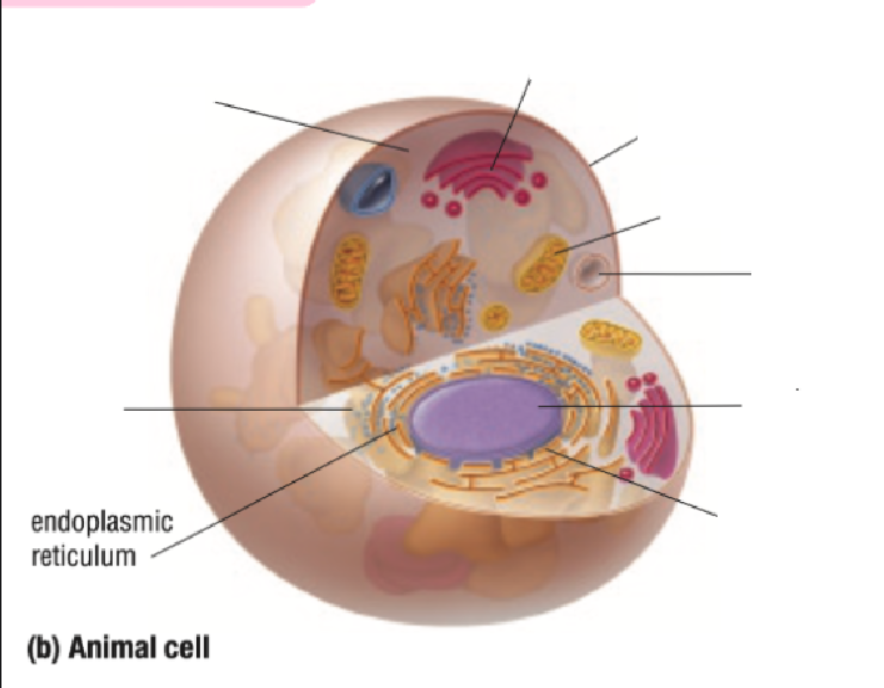
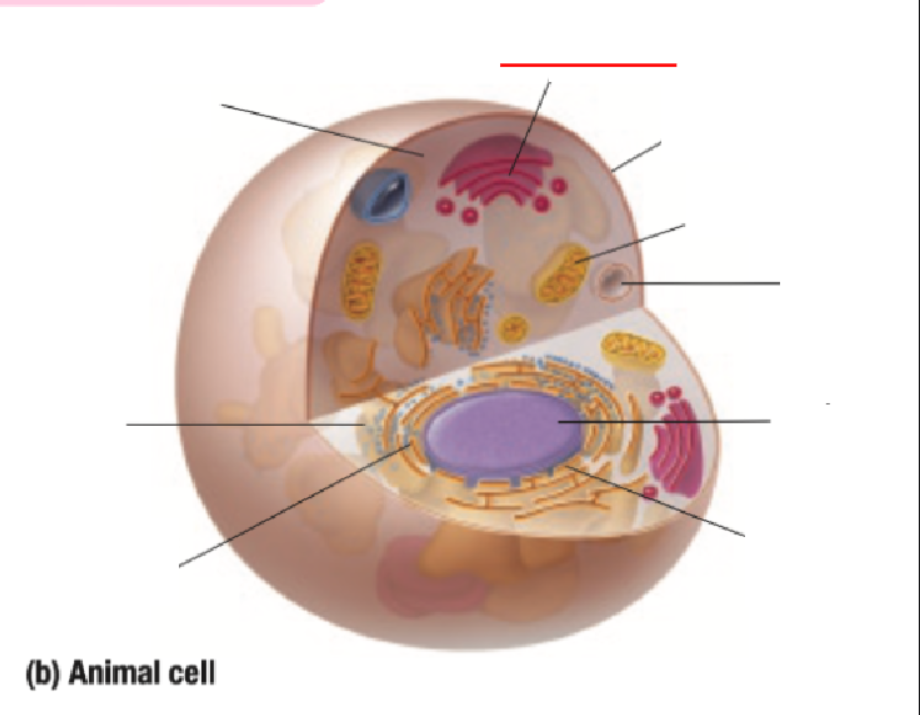
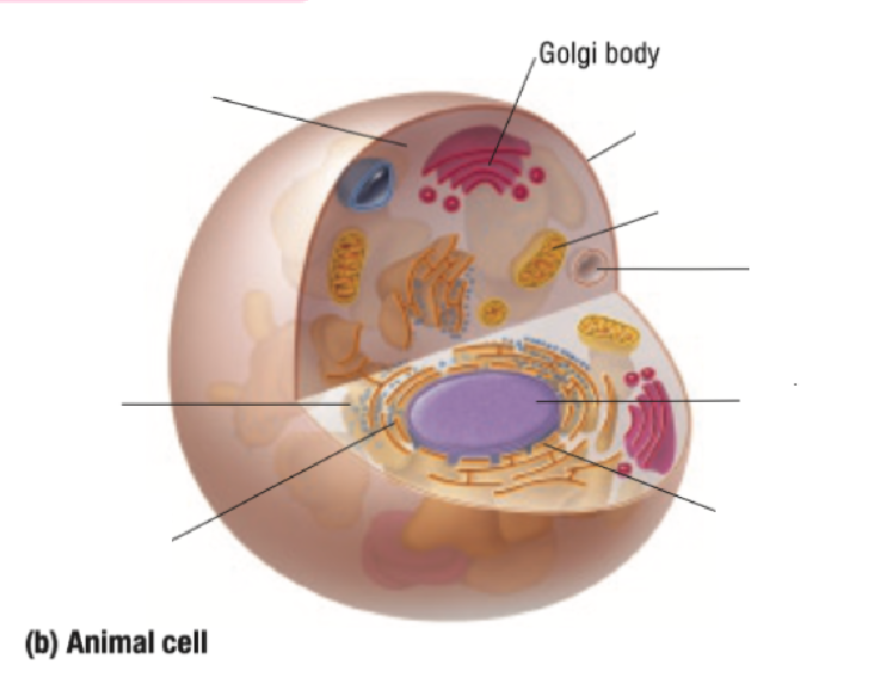
Golgi Body
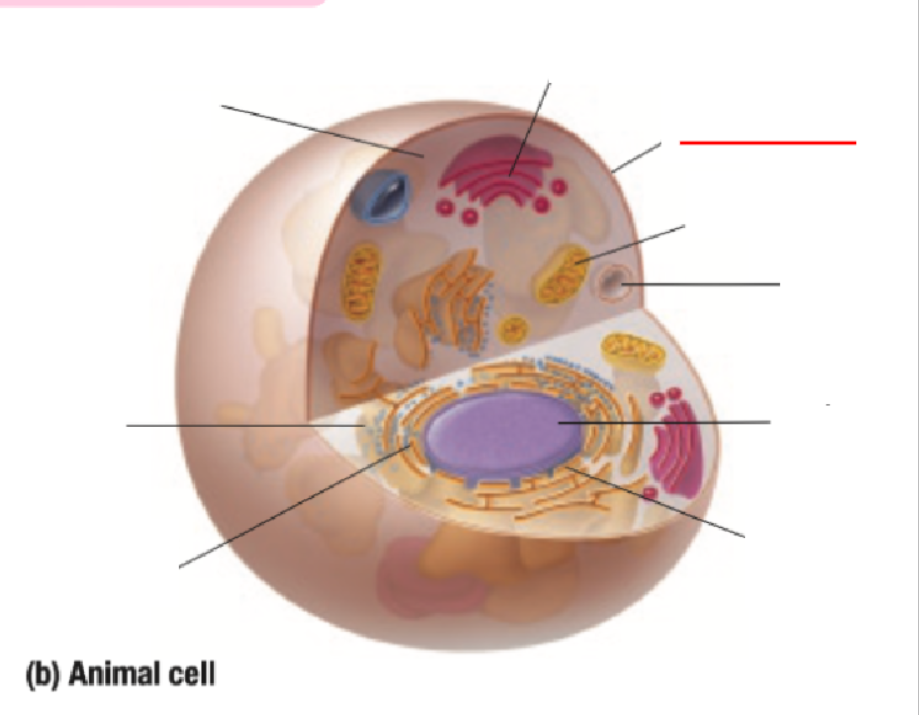
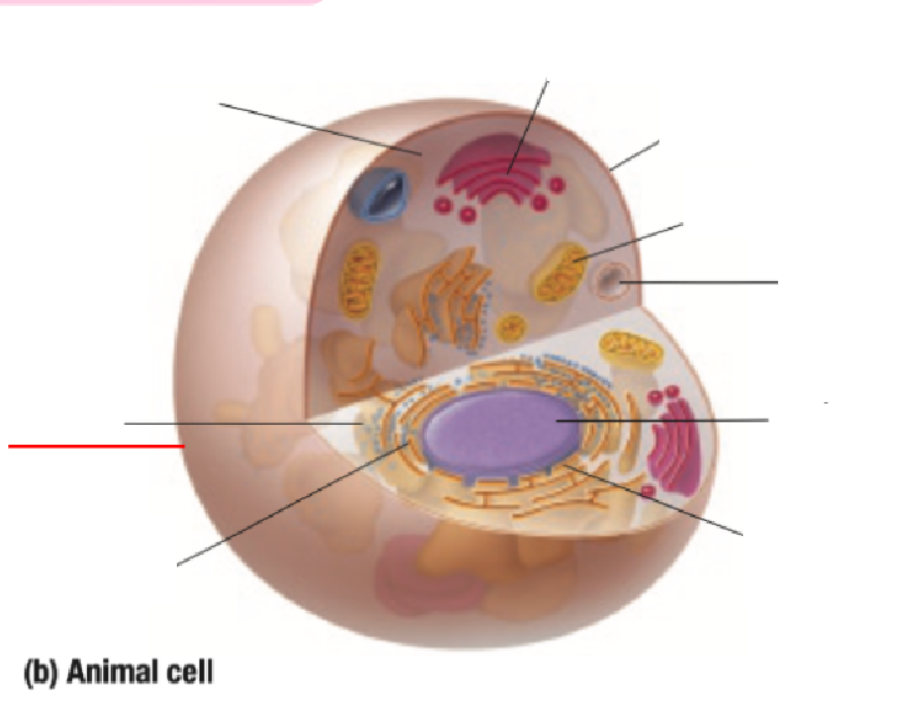
Cell Membrane
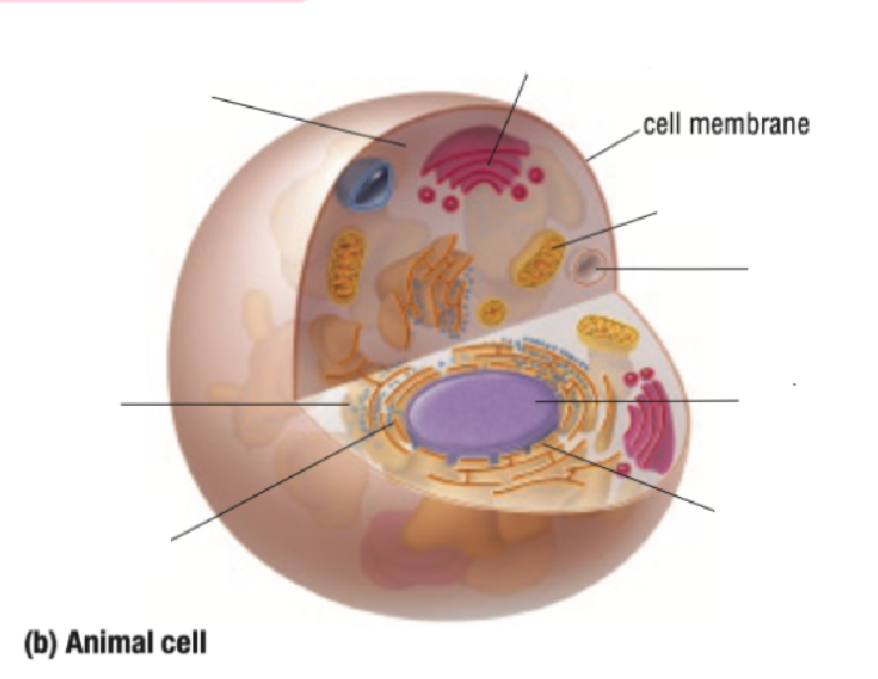
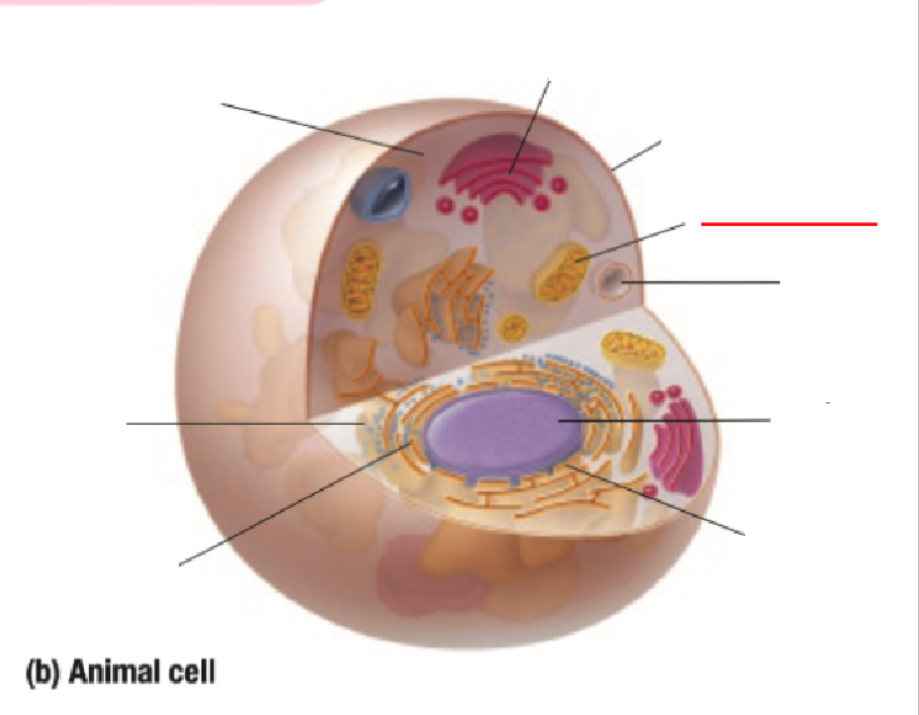
Mitochondria
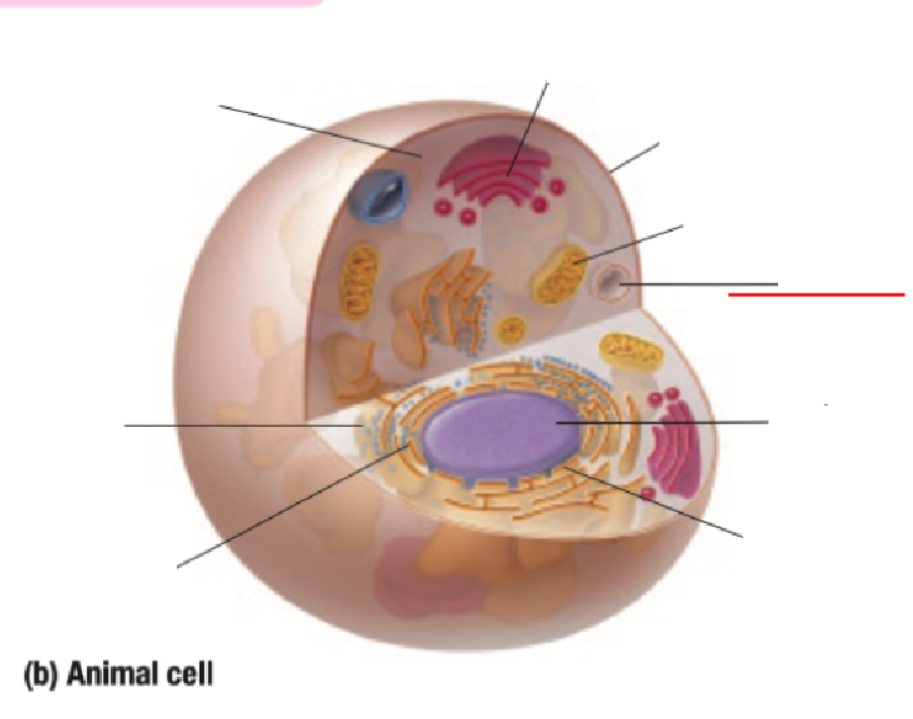
Vacuole
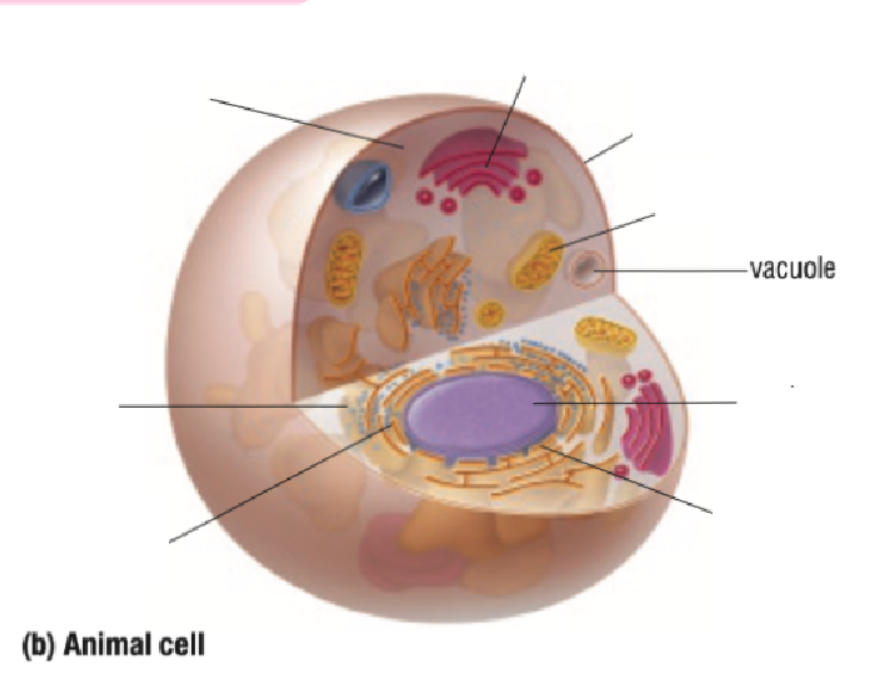
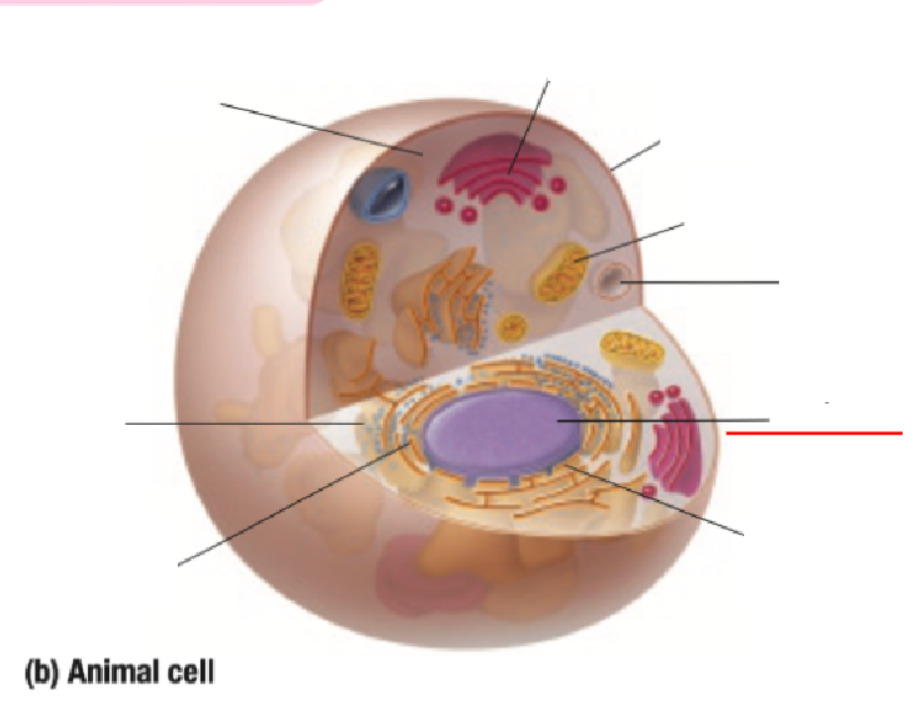
Nucleus
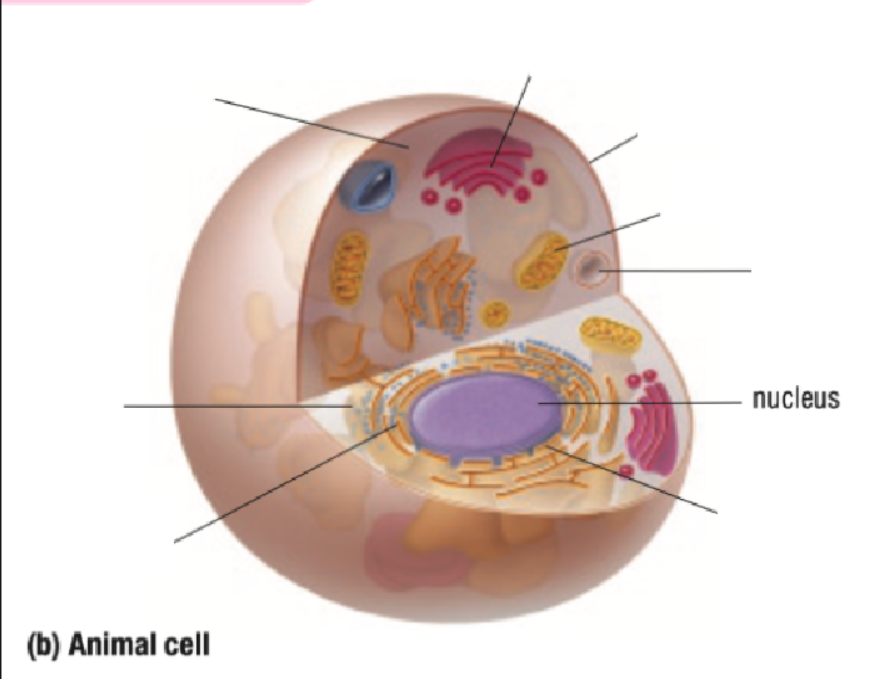
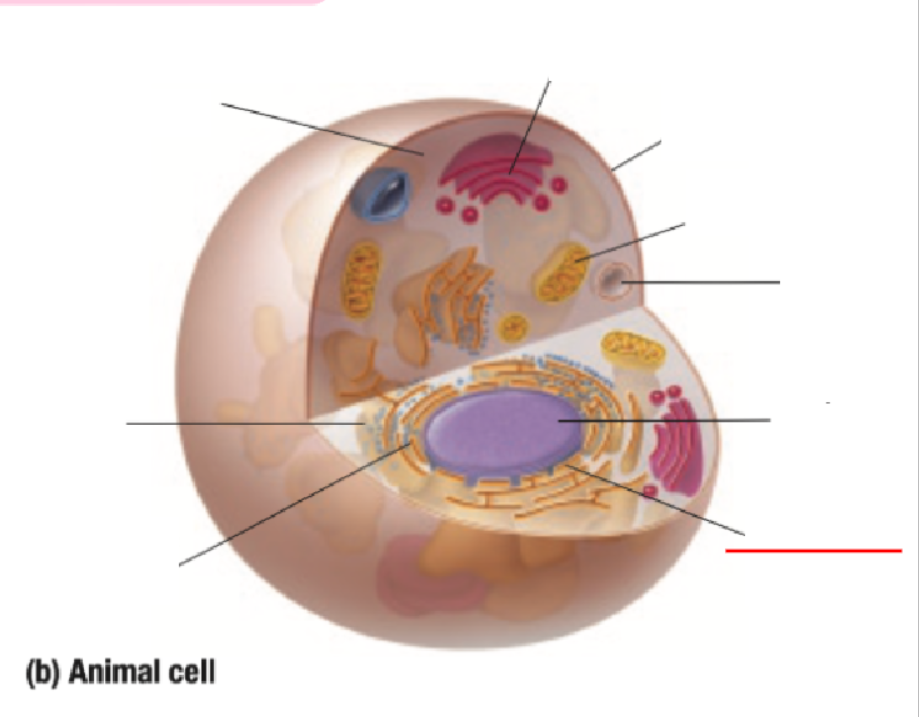
Nuclear Membrane
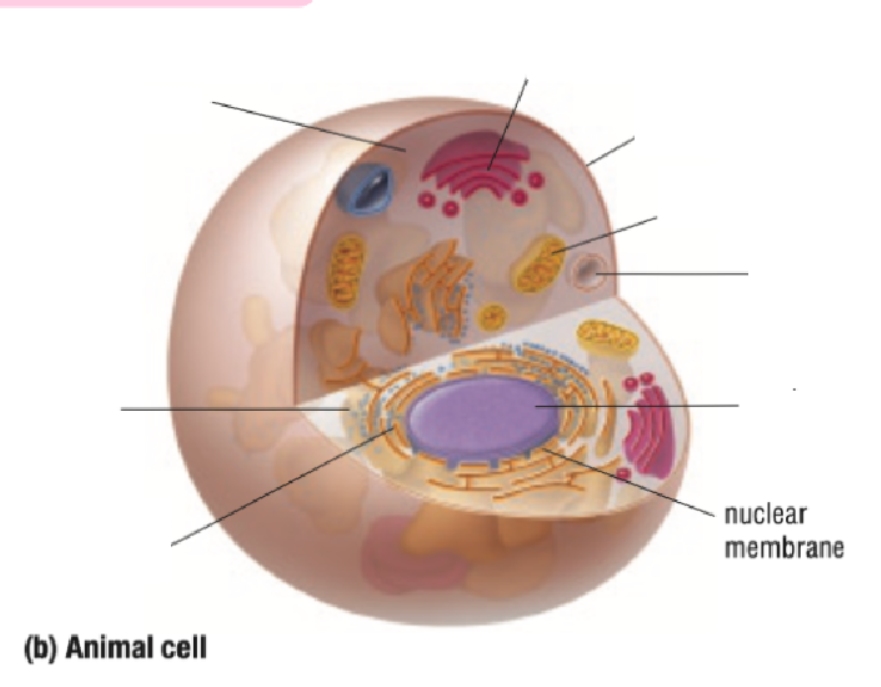
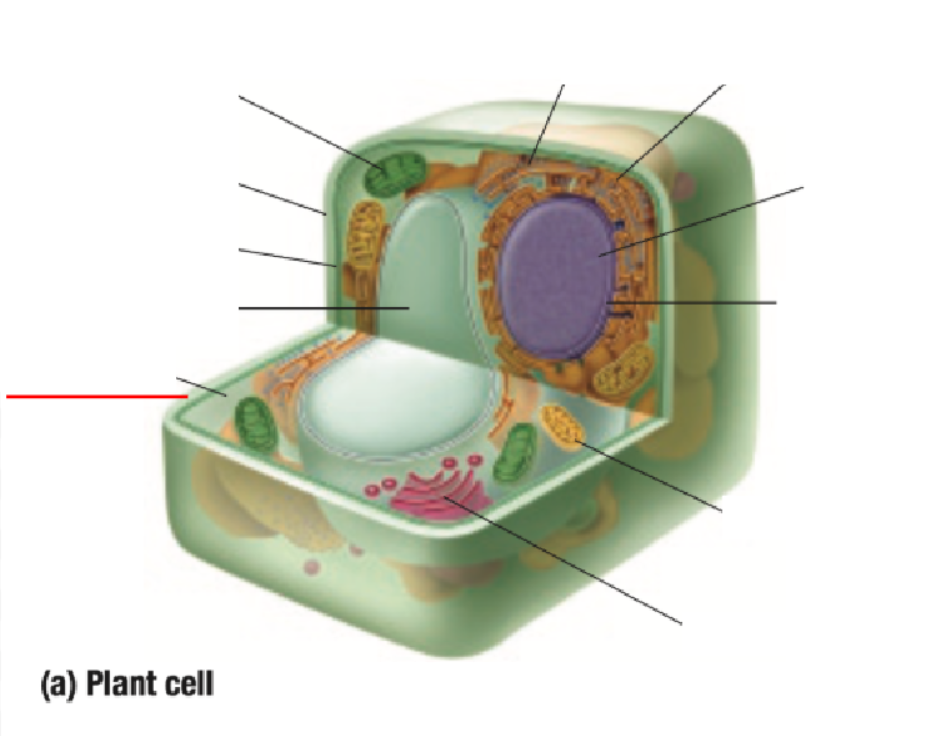
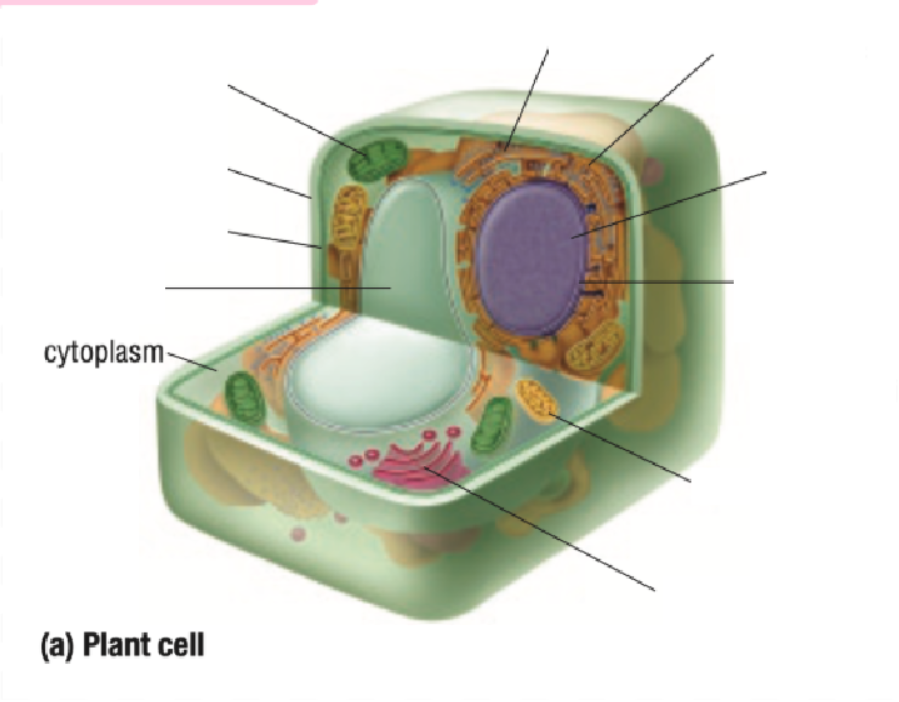
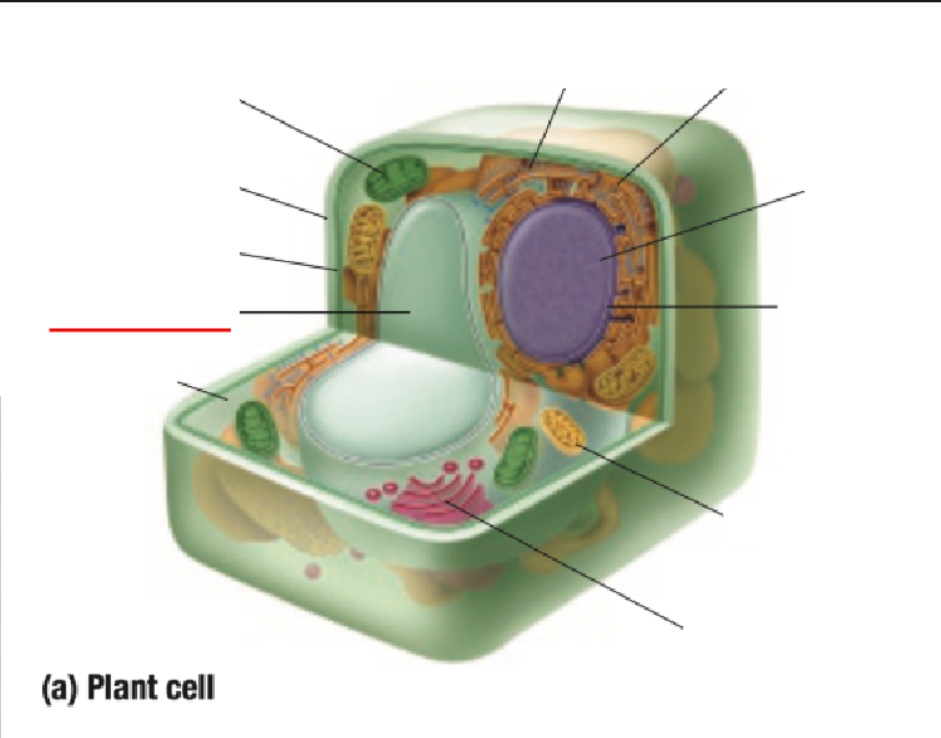
Cytoplasm Definition
All organelles are floating inside the cytoplasm
Made of mostly water, making it either jelly-like or liquid for organelles to move around inside of it
Endoplastic Reticulum Definition
Made of branching tubes and pockets
Continuous from the nuclear membrane to the cell membrane
Fluid-filled tubes transport materials through the cell
Ribosomes Definition
Protein Factory: Ribosomes are like tiny factories in a cell that make proteins. Proteins are important for the cell to work and grow
Ribosomes read the cell's DNA to know how to build the right proteins
You can find ribosomes floating in the cell’s cytoplasm or stuck on the endoplasmic reticulum.
Golgi Bodies Definition
Collect and process materials to be removed from the cell
Makes and secretes mucus
Vacuoles Definition
Single layer of membrane for a fluid-filled sac
Function depends on the type of cell
Some functions are:
containing some substances
removing unwanted substances from the cell
maintaining internal fluid pressure inside the cell
Takes up most space in plant cells
Cell Wall Definition
Outside the cell membrane of a plant cell
Made of cellulose
Gives support for cell shape
Protects cell from physical injury
Chloroplast
Contains chlorophyll pigment which gives leaves their green colour
Absorbs light energy to allow for photosynthesis
Photosynthesis: light energy from the Sun and carbon dioxide is used to make glucose (sugar) and oxygen
Prokaryotes
A cell that does NOT have a nucleus or other membrane-bound organelles
Eukaryotes
A cell that HAS a nucleus and other organelles, each surrounded by a thin membrane
Diffusion
Movement of particles from high concentration to low concentration
Osmosis
Movement of water from high concentration to low concentration
Digestive System Order
Digestive Tract:
Mouth
Esophagus
Stomach
Small Intestine
Big Intestine
Accessory Organs:
Liver
Pancreas
Gallbladder
What is the digestive tissue lined with?
Epithelial Tissue
Goblet Cells: make mucus. The mucus protects the digestive tube from digestive enzymes and helps food move easily.
The digestive tube also has layers of muscle tissue and nerves.
The esophagus is made up with what tissue? What is its function?
The muscular tube is made up of smooth muscle tissue, which contracts and relaxes to push food down. This is called peristalsis
The stomach consists of what type of tissue? What is it lined with?
The stomach lining contains cells that produce digestive enzymes and acids
Smooth muscle tissue contracts to mix the stomach contents.
Function of each intestine:
Small Intestine: (6 Metres)
Main area for digestion
Absorbs nutrients into the blood
Big Intestine: (1.5 Metres)
Absorbs water
Turns leftover waste into solid matter (feces)
Intestines have muscles that move food without thinking.
Liver Function
Liver makes bile, which helps us digest fats from food.
Pancreas Function
Pancreas makes insulin, which controls sugar levels in our blood after we eat food.
Circulatory: Pathway for the Blood
Deoxygenated Blood enters either from the
Superior or Inferior Vena Cava, depending on which part of the body it enters from
Right Atrium
Right Ventricle
Pulmonary Artery —> Lungs
=====
Pulmonary Vein
Left Atrium
Left Ventricle
Aorta —> Entire Body
What type of tissue is blood?
Blood is a connective tissue that flows through all of your body parts
4 main parts of the blood
Blood has FOUR components:
Red blood cells
White blood cells
Platelets
Plasma
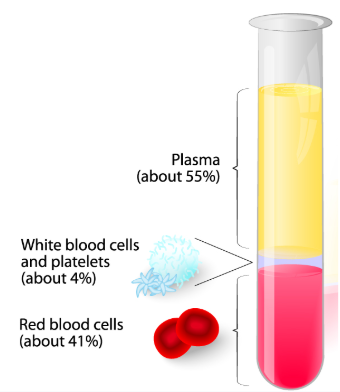
Red Blood Cell Function + Protein
Red blood cells carry oxygen to your body.
They look red because they have a protein called hemoglobin.
About 41%
White Blood Cell Function
These cells fight infections like bacteria and viruses.
They are less than 1% of your blood.
White blood cells are the only ones
with a nucleus (center).
Platelets Blood Cell Function
These are very small cells.
They help your blood clot (stops the bleeding by forming a plug or clog) for cuts or injuries.
They are also less than 1% of your blood.
Plasma Blood Cell Function
Plasma is a liquid with proteins.
It carries red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
Plasma makes up more than half of your blood.
The heart is made up of THREE tissues:
Cardiac muscle tissue: special muscle only found in the heart that contracts its muscle to pump blood around the body
Nerve tissue
Connective tissue
Capillaries in the body
The walls of capillaries are very thin, so things can pass in and out.
Oxygen and nutrients diffuse from the blood into body tissues.
Waste and carbon dioxide move from the tissues into the blood to be removed.
Respiratory Pathway/System:
nose
mouth (pharynx)
trachea + larynx (trachea)
two bronchi
lungs
bronchiole
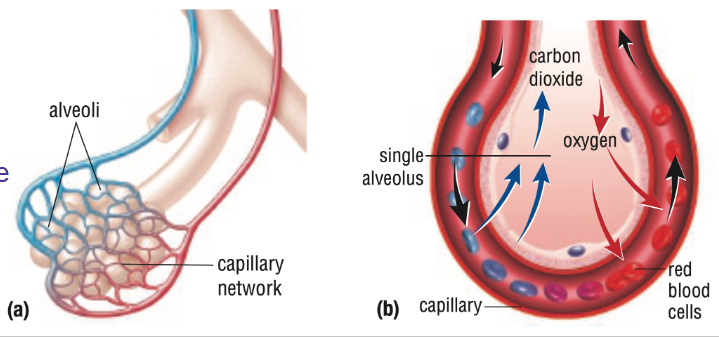
Alveoli
Tranchea and the bronchus are lined with what type of tissue?
Epithelial cells line the trachea and bronchi and produce mucus. Epithelial cells have cilia (hair-like projections) that help move mucus and filter out any bad or unknown materials.
What is gas exchange in terms of the capillaries and the alveoli?
Gas exchange:
When oxygen diffuses into capillaries and carbon dioxide diffuses into the alveoli
What happens to the diaphragm during breathing? List the two types.
Inhaling: The diaphragm contracts to allow air to be taken in
Exhaling: The diaphragm relaxes to release air outside
Nose Function
Thanks to the nose the air we breathe is clean, warm, and properly humidified before it reaches our lungs
Mouth Function
Even when the nose is the preferred pathway for breathing, this body part can also let the air in and filter some particles.
Larynx Function
It’s often called the "voice box." It helps you breathe and talk by using vocal cords to create sound.
Trachea Function
It’s often called the "windpipe," is like a special tube in your throat. Its job is to help you breathe and talk.
Bronchi Function
They are like the branches of a tree inside your lungs. They let the air go inside your lungs.
Cilia Function
Tiny hair-like structures on epithelial cells of the trachea and bronchi that move to keep airways clean by moving mucus and sweeping out dirt.
Bronchiole Function
They are like the smaller branches of a tree inside your lungs. They carry air to small air sacs at the end of the branch for breathing.
Alveoli Function
Tiny air sacs in your lungs where oxygen in your alveoli enter the blood and carbon dioxide from the blood enter your alveoli to be exhaled from the body.
Lungs Function
They extract the oxygen your body needs when you breath in. When you breathe out, they take out the carbon dioxide.
Diaphragm Function
It is a dome-shaped muscle that helps you breathe. It helps your lungs expand and fill with air and relaxes when it exhales the air out.
DIABETES Definition
Diabetes is a disease where the pancreas produces too much or too little insulin. A person with diabetes can experience weakness and dizziness due to too low or too high blood sugar levels
CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE Definition
Coronary arteries are the blood vessels that carry blood to the heart muscle. These arteries can become blocked with plaque.
Plaque is a sticky substance made of fat, cholesterol, calcium, and other things found in the blood.
Doctors can check for this problem with an X-ray called an angiogram.
HEART ATTACK Definition
Happens when coronary arteries get completely blocked by either a blood clot or plaque.
The muscle of the heart then loses blood, and the minerals and oxygen that the blood provides. The heart stops pumping and begins to die.
Tuberculosis Definition
A very contagious diseases. Happens when bacteria enters the body through breathing.
The bacteria will grow in your lungs, and may also spread to the rest of the body.
Lung Cancer Causes
Caused by first-hand or second-hand smoking.
Tobacco smoke contains many carcinogens: Chemicals that also affects the rest of the body’s function (Gives cancer)
SARS Definition
SARS (Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome) symptoms are similar to the flu.
OSTEOPOROSIS Definition
Causes the bone to lose tissue, and is very hard to notice unless checked by the bone density test. It does not cause pain directly, but makes bone fragile and easier to break.
MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS Definition
A disease that happens when the immune system does not work properly.
This disease damages a neuron’s myelin sheath in the brain and spinal cord.
PHYSICAL TRAUMA TO BRAIN Definition
When a fall or hit is done to the head. This causes the spinal cord to be damaged, and causes paralysis.
Brain Injuries, like concussions, are common in sports.
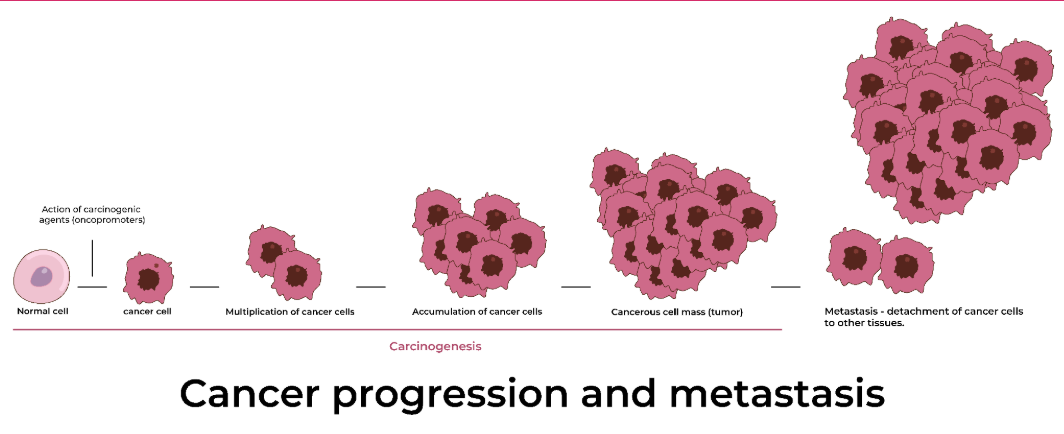
APOPTOSIS (CELL DEATH)
When a cell realizes it is damaged, it causes itself to self-destruct.
What is a tumor?
An abnormal mass of cells that can harm tissue. This leads to cancer
What is a Benign tumor?
A tumor that only affects the physical surrounding area of tissue, but not its functions.
What is a Malignant tumor?
A tumor that interferes the tissue’s function and surrounding area. A cancerous tumor.
What is metastasis?
The process where the primary tumor splits off and establishes a secondary tumor in another area of the body
What is Cellular Differentiation?
The process in which a stem cell becomes a specialized cell to perform a certain function
What is a stem cell?
An undifferentiated cell that can divide into specialized cells
What is an embryonic cell?
A stem cell that can differentiate into any type of specialized cell
What are tissue stem cells?
A stem cell that can only turn into a specialized cell that is based off what tissue it is in. (Ex: Nerve Tissue means Nerve Cells)
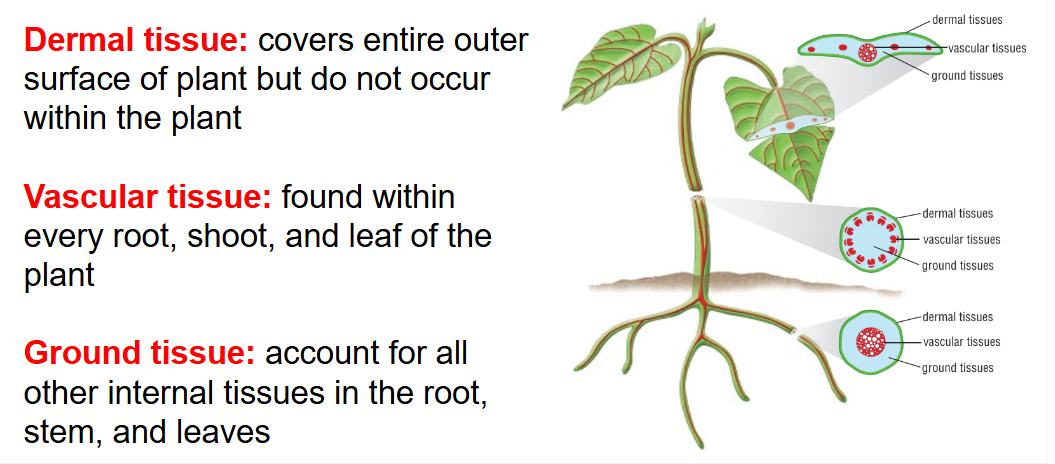
What does the shoot system include in a plant? + What is in the roots system?
Flower
Leaf
Fruit
Main Stem
Roots.
Flower system function?
Conducts photosynthesis and reproduces sexually. This includes the flower, leaf, and stem.
Root system function?
Anchors the main plant, while absorbing water and minerals, and stores food
What type of cell /tissue are root hairs? (Relating back to the -ology of skin)
Dermal Tissue Cells
What cell structure is responsible for photosynthesis? What does it consist of?
The chloroplast, which consists of thylakoids
What is a Meristematic Cell? (Recall stem cells)
undifferentiated plant cell that can divide & differentiate to form specialized cells
3 types of tissue in a plant.
Dermal
Ground
Vascular