Macro unit 1-3
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
Factors of production
Land
2. Labor
3. Physical Capital
4. Entrepreneurship
PPC
production probabilities curve; max combos of 2 different goods that can be produced with fixed resources
what does a straight ppc instead of a curved one mean?
the products adapt to each other
absolute advantage
the ability of an individual or group to carry out a particular economic activity more efficiently than another individual or group.
produce more or using fewer resources
comparative advantage
produce at lower opportunity cost
input opportunity cost
the amount of one good that must be forgone to produce an additional unit of another good.
“it over”
output opportunity cost
the amount of output lost from producing an additional unit of a different good.
“other over”
Demand shifters
Tastes & preferences
Market size
Prices of related goods
Changes in income
expectation
price changes…
quantity, not demand
Prices of related goods types
substitudes and complements
changes in income
normal goods - people income rise, demand rise
inferior goods - income rise, so demand dec (ex: instant noodles)
product market
businesses r providing households with goods and resources
households are providing money to those businesses in the form of sales
factor market
resources (land labor capital entrepren) r going from households to the businesses
businesses provide households with wages, rent, internet, and profit
GDP + ways to calculate
Gross Domestic Product
Total value of all final goods and services produced within a country in a calendar year
-value added approach (adds contrib a countrys firms make to the final goods… ex. get for $8 sell for $15)
-income approach (rent, wages, interest, and profit with some adjustments)
-OUTPUT EXPENDITURE MODEL
Output Expenditure Model
look at sales that are in the product market —money that goes from households to businesses
C+I+G+Xn
C= Consumption ; I= Gross Investment (bus); G=Gov purchases; Xn = Net Exports (Exports - imports)
Per capita GDP
GDP divided by the pop of a country
used to determine a country’s standard of living
Unemployment rate formula
(Unemployed/Labor Force) x 100
Labor force formula
unemployed +employed
labor force participation rate formula
(Labor Force/Working age civilian pop) x 100
types of unemployment
frictional - in btwn jobs or looking for first
structural - changes in econ led to skills mismatch
cyclical - caused by overall economic downturn
NRU
natural rate of unemployment = frictional + structural
zero cyclical unemployment
CPI
tracks price changes in a market basket of products
(calc inflation)
GDP Deflator
tracks price changes in all products
first calculate nominal gdp (value of current year’s goods using current year’s prices so q x p )
(nominal/real) x 100
spending multiplier
formula to find out how much money the initial change in consumption can impact GDP
1/MPS or 1/(1-MPC)
ex: initial cost = $800
MPS = 0.2 so 1/0.2 =5 so
there is up to $4000 inc in GDP
tax multiplier
when the gov inc or dec taxes, and it changes the amount of disposable income consumers have
-MPC/MPS or -MPC/(1-MPC)
-0.8/0.2 = -4
10 million tax dec in taxes —> $40 million GDP inc
aggregate demand
the demand for all goods and services in the economy
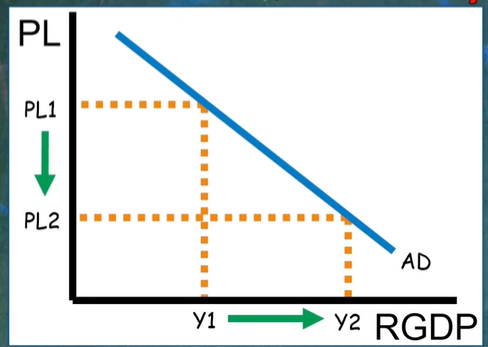
reasons for downward sloping aggregate demand
Wealth Effect (as prices fall, real wealth is inc —> cons inc consuming)
interest rate effect (as price levels fall interest rates also fall—> gross investment inc)
Net Exports Effect (lower price levels exports are cheaper for foregin countries—>exports will inc)
AGGREGATE DEMAND SHIFTERS
Consumer Spending
Gross Investment
Government Purchases
Net Exports
C + I + G + Xn
AGGREGATE SUPPLY SHIFTERS
Resource Prices (wages)
Productivity
Inflation Expectations
Business Taxes
Business Regulations
LRAS
long run aggregate supply
in the long run wages are flexible
LRAS SHIFTERS
Quantity of resources
Quality of resources
Productivity
Technology
Anything that shifts the PPC will shift the LRAS
Expansionary fiscal policy
fight unemployment by: inc gov spending and/or dec taxes
inc budget deficit or dec surplus
Contractionary Fiscal Policy
Fight Inflation By: Dec gov spending and/or inc taxes
dec budget deficit or inc surplus