Lecture 3: Transcription
1/24
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
What is gene expression?
A. Replication of DNA into RNA
B. The transcription and translation of a gene into a protein
C. The conversion of a gene into its product, usually a protein via RNA
D. The removal of introns from a gene
C. The conversion of a gene into its product, usually a protein via RNA
Which of the following statements about gene expression is TRUE?
A. All genes are expressed in all cell types at all times
B. Only a subset of genes are expressed in a given cell at any given time
C. Genes are expressed only during embryonic development
D. Every gene is always transcribed, but not always translated
B. Only a subset of genes are expressed in a given cell at any given time
What is the main enzyme responsible for transcription?
A. DNA polymerase
B. Ligase
C. RNA polymerase
D. Helicase
C. RNA polymerase
In what direction is RNA synthesized during transcription?
A. 3’ to 5’
B. 5’ to 3’
C. Both directions
D. Depends on the gene
B. 5’ to 3’
What is the correct base pairing rule for RNA transcription?
A. A-T, G-C
B. A-U, G-C
C. A-U, G-C
D. A-G, C-T
C. A-U, G-C
The sequence of an RNA transcript is 5’ - GGUUACAUUC - 3’. What is the sequence of the coding strand?
A. 5’ - GAATGTAACC - 3’
B. 5’ - GGUUACAUUC - 3’
C. 5’ - GGTTACATTC - 3’
C. 5’ - GGTTACATTC - 3’
The sequence of an RNA transcript is 5’ - GGUACAUUC - 3’. What is the sequence of the template strand?
A. 5’ - GAATGTAACC - 3’
B. 5’ - GGUUACAUUC - 3’
C. 5’ - GGTTACATTC - 3’
D. 5’ - CCAATGTAAG - 3’
A. 5’ - GAATGTAACC - 3’
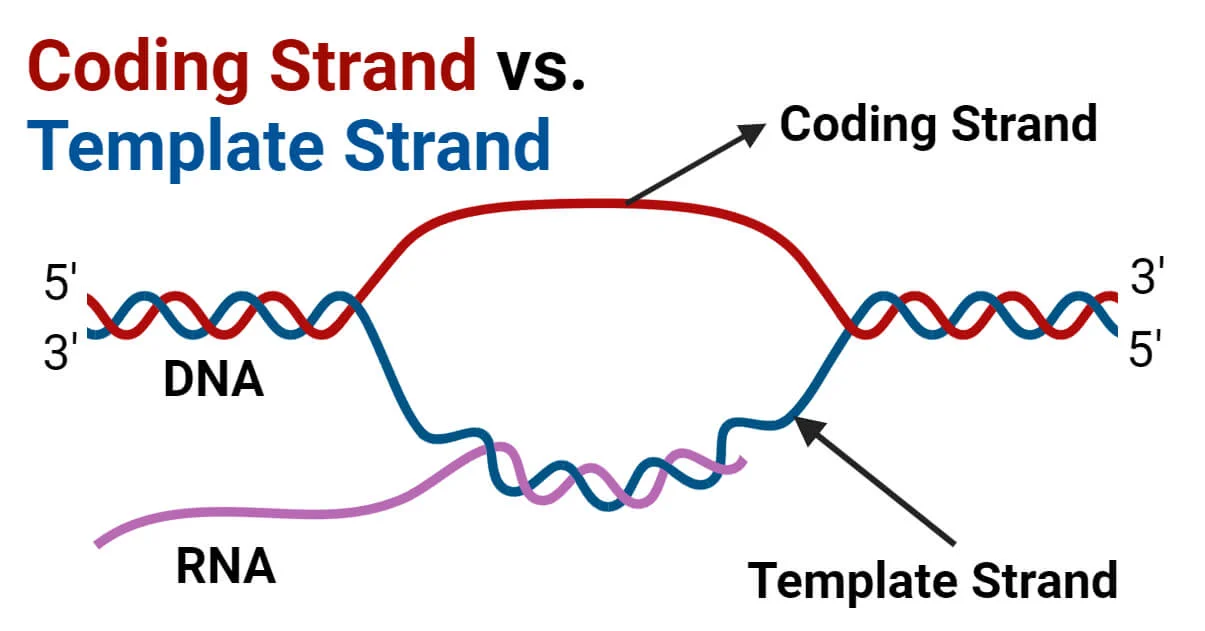
What is the coding strand?
A. The strand used as a template by RNA polymerase
B. The DNA strand that matches the mRNA sequence (except T for U)
C. The RNA strand made during transcription
D. The DNA strand that contains promoters and enhancer
B. The DNA strand that matches the mRNA sequence (except T for U)
What is the template strand?
A. The strand of DNA that RNA polymerase uses to synthesize RNA
B. The RNA transcript
C. The strand not read during transcription
D. The mRNA after splicing
A. The strand of DNA that RNA polymerase uses to synthesize RNA
Which of the following is a promoter sequence in prokaryotes?
A. -10 and -35 boxes
B. Start codon
C. Poly-A tail
D. Shine-Dalgarno sequence
A. -10 and -35 boxes
What determines the start point and direction of transcription?
A. Ribosome binding site
B. The promoter sequence
C. The terminator
D. The coding region
B. The promoter sequence
Transcription factors are proteins that:
A. Replicate DNA
B. Bind DNA to regulate transcription
C. Synthesize mRNA
D. Degrade introns
B. Bind DNA to regulate transcription
What is an enhancer?
A. A protein that terminates transcription
B. A gene sequence that gets translated
C. A DNA sequence that increases gene expression when bound by transcription factors
D. A segment of RNA that aids in translation
C. A DNA sequence that increases gene expression when bound by transcription factors
What is the role of a silencer?
A. Enhances transcription
B. Decreases transcription when bound by a transcription factor
C. Binds ribosomes
D. Activates promoters
B. Decreases transcription when bound by a transcription factor
What is a key difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic mRNA?
A. Only prokaryotic mRNA undergoes splicing
B. Only eukaryotic mRNA is translated
C. Eukaryotic mRNA is processed with a 5’ cap and poly-A tail
D. Prokaryotic mRNA is single-stranded
C. Eukaryotic mRNA is processed with a 5’ cap and poly-A tail
What is a 5’ cap?
A. A modified guanine nucleotide added to the beginning of eukaryotic mRNA
B. A protein complex that stabilizes DNA
C. An exon that initiates splicing
D. A sequence added to prokaryotic mRNA
A. A modified guanine nucleotide added to the beginning of eukaryotic mRNA
What is the function of the poly-A tail?
A. Initiates translation
B. Protects mRNA from degradation and aids in export from the nucleus
C. Recruits RNA polymerase
D. Signals intron remova
B. Protects mRNA from degradation and aids in export from the nucleus
What are introns?
A. Protein-coding regions
B. Non-coding sequences that are spliced out
C. RNA segments that form ribosomes
D. Binding sites for transcription factors
B. Non-coding sequences that are spliced out
What are exons?
A. DNA regulatory sequences
B. Introns that failed to be spliced
C. Coding sequences that remain in the mRNA
D. Silencers in eukaryotic genomes
C. Coding sequences that remain in the mRNA
Where does splicing occur?
A. Cytoplasm
B. Ribosome
C. Nucleus
D. Golgi apparatus
C. Nucleus
What is alternative splicing?
A. A way to remove RNA without a spliceosome
B. The random degradation of introns
C. The process by which different combinations of exons are joined
D. Mutation of RNA sequences
C. The process by which different combinations of exons are joined
Which of the following statements is FALSE about alternative splicing?
A. It increases protein diversity
B. It changes the order of exons
C. It can be regulated by cell type or conditions
D. It does not duplicate exons
B. It changes the order of exons
Which RNA type is translated into protein?
A. tRNA
B. rRNA
C. mRNA
D. miRNA
C. mRNA
Which of these RNAs are NOT translated?
A. mRNA
B. rRNA and tRNA
C. hnRNA
D. mature mRNA
B. rRNA and tRNA
What type of gene expression is typical of housekeeping genes?
A. Tissue-specific
B. Constantly expressed in most cells
C. Only expressed during growth
D. Only in prokaryotes
B. Constantly expressed in most cells