long covid-19
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
what is long COVID?
WHO definition
usually within 3 months from the onset of COVID-19, with symptoms and effects that last for at least 2 months
symptoms cannot be explained by alternative diagnosis
no minimum symptoms required for diagnosis
occurs regardless of disease severity
new NASEM definition
LC is an infection-associated chronic condition (IACC) that occurs after SARS-CoV-2 and is present for at least 3 months as a continuous relapsing and remitting or progressive disease that affects one or more organ systems
SOB, cough, persistent fatigue, post-exertional malaise
can also manifest as single or multiple diagnosable conditions: interstitial lung disease, cardiovascular disease, POTS, chronic fatigue syndrome, fibromyalgia, etc
similar to MS in terms of different types
new or worsening preexisting conditions
ie. triggers preexisting conditions to become symptomatic that were previously asymptomatic
cardiovascular disease (covid can cause blood clots)
chronic kidney disease
POTS
diabetes
cognitive impairment
etc.
clinical presentation
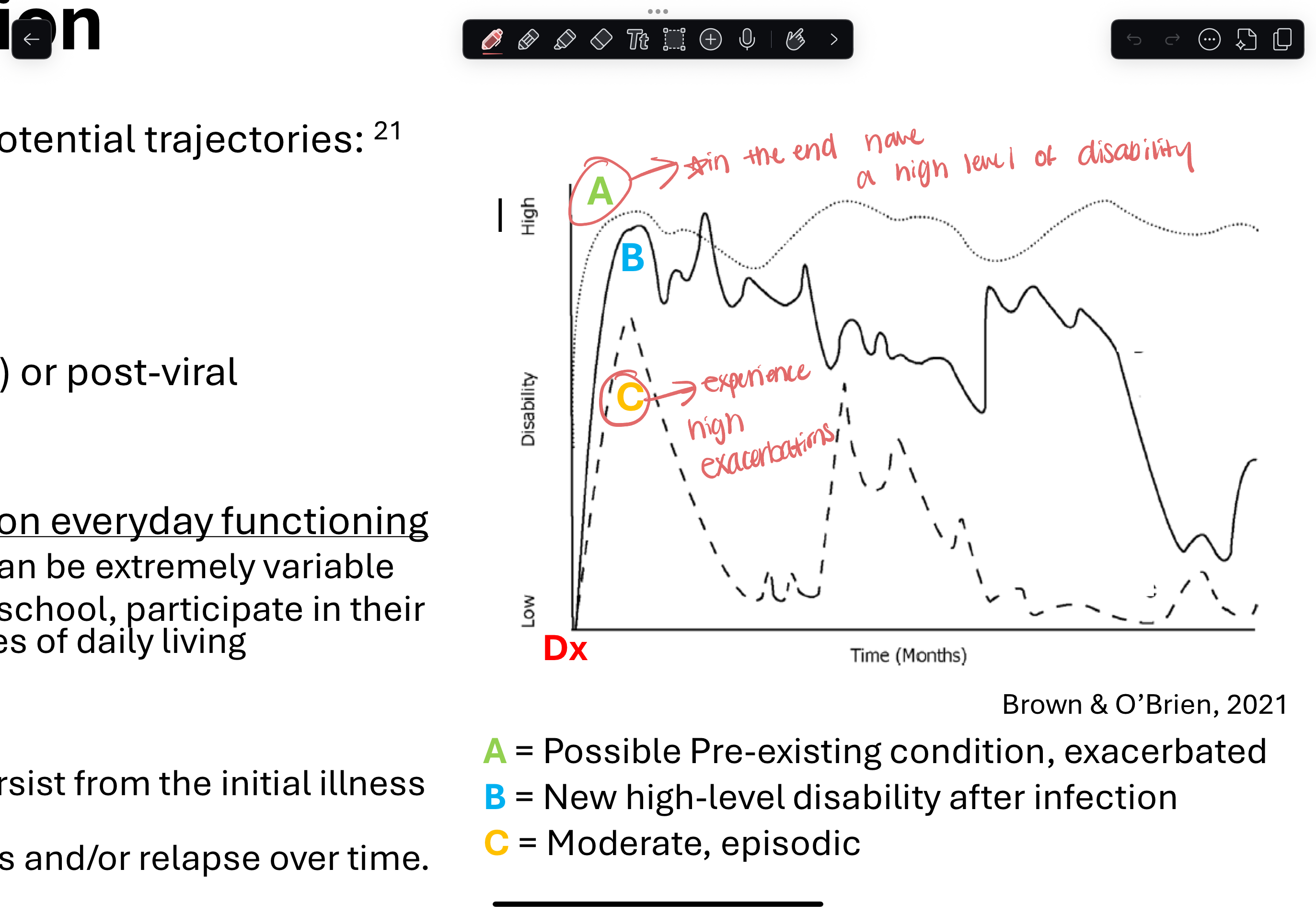
PCC can be characterized as 3 potential categories
multi-dimensional (pre-existing condition exacerbated)
fluctuating (high level of disability post infection)
episodic (moderate)
generally has impact on every day functioning → interferes with ability to work, attend school, participate in communities, and engage in ADLs
present for prolonged time frames and/or relapse over time
INSERT PIC
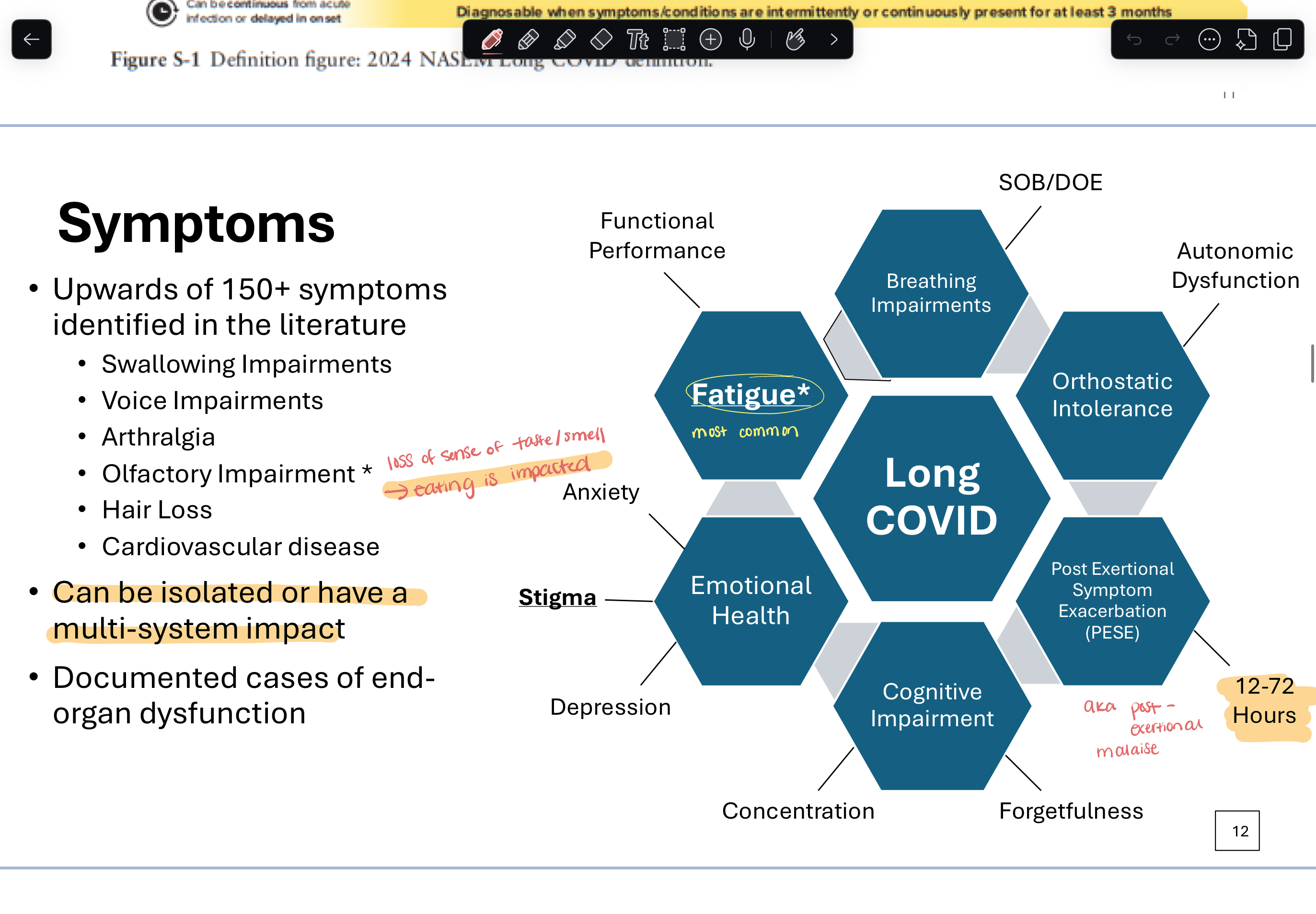
common symptoms
post exertional malaise
cognitive impairment
depression, anxiety
persistent fatigue (MOST COMMON)
difficulty concentrating
memory changes
headaches
sleep disturbance
SOB, cough
problems w/ taste and smell
INSERT PIC
symptoms cont.
no clear established link between medical and demographic characteristics and outcomes
some causal links noted that may increase risk of PCC:
female
older, younger
minority ethnicity
underlying health conditions
reinfections
pregnant
what is “safe” rehab
no standard protocol
4 concepts
avoiding acute events & symptom flare-ups → prevents further decline in functional performance
personalization
facilitating expectations (what does recovery look like?)
psychologically supportive → managing client’s expectations/emotions
avoid graded exercise therapy → do not want to over exert client
establish activity mgmt plan
“safe” rehab signs
pause session, reassess/proceed with caution
autonomic dysfunction
post exertional malaise
SEE a doctor/terminate session entirely
exertional oxygen desaturation (below 92%)
cardiac impairment
managing dysautonomia
postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome (POTS) → chronic condition that causes abnormal increase in HR when standing up/sitting up
common symptoms
difficulty standing still, fatigue, lightheadedness, nausea, brain fog, palpitations, SOB
how to treat:
exercise
lifestyle changes: hydration, adding salt, limiting alcohol
compression
stockings
abdominal binder
sleep
raising HOB
quality sleep
pacing
outcome measures
post-covid core outcome set (PC-COS)
fatigue
post-exertion symptoms
cognitive functioning
mental function
pain
work/occupational changes