Digestive & Circulatory Systems
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
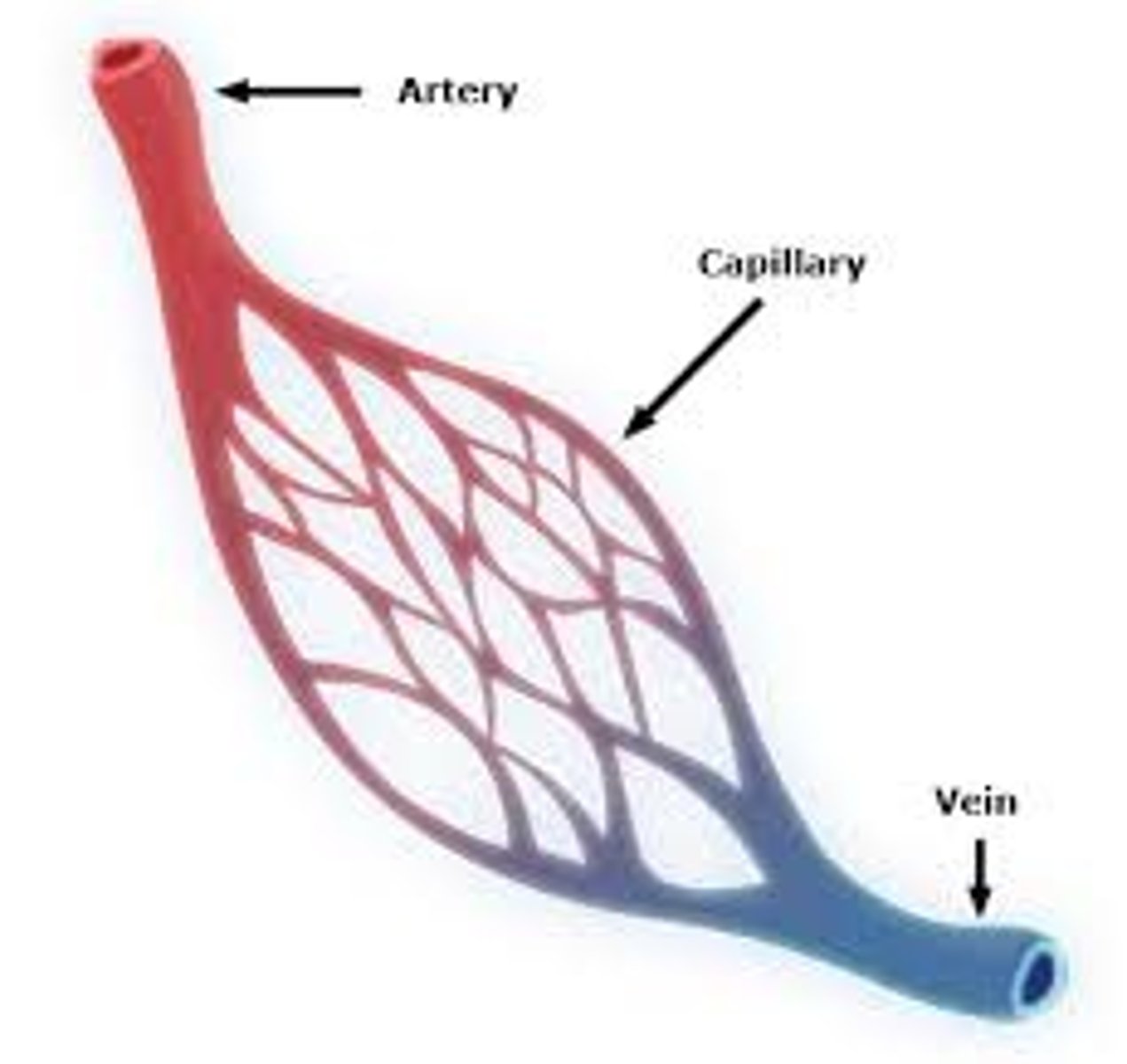
arteries
carry blood away from the heart
- thicker smooth muscle
veins
carry blood back to the heart
- larger lumen
- some have valves (to catch blood against gravity)
capillaries
allow exchange of cell nutrients & waste through blood
- 1 cell thick
myogenic
heart contracts w/o input from brain
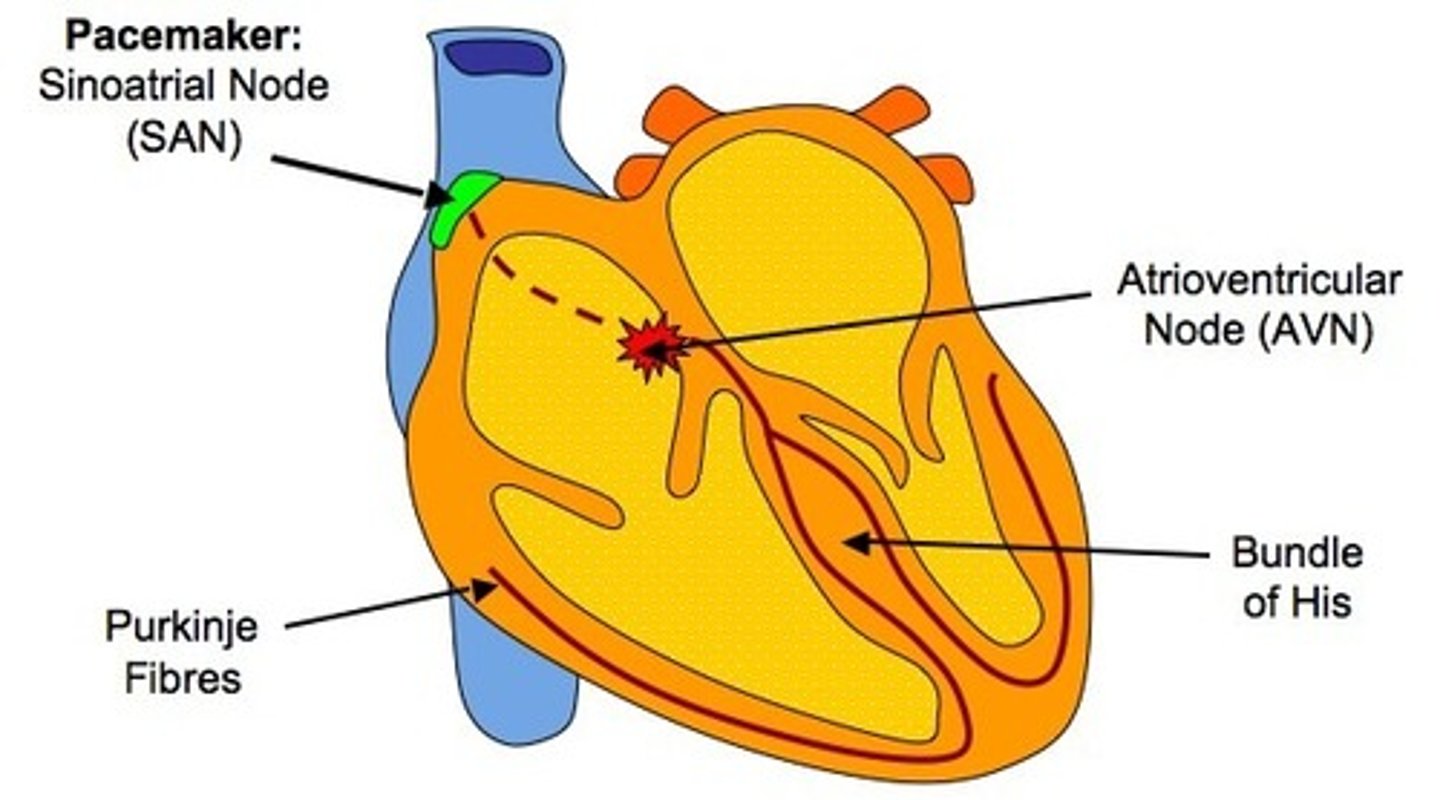
SA node
pacemaker (right atrium)
- directly signals atria to contract
- sends signal to AV node
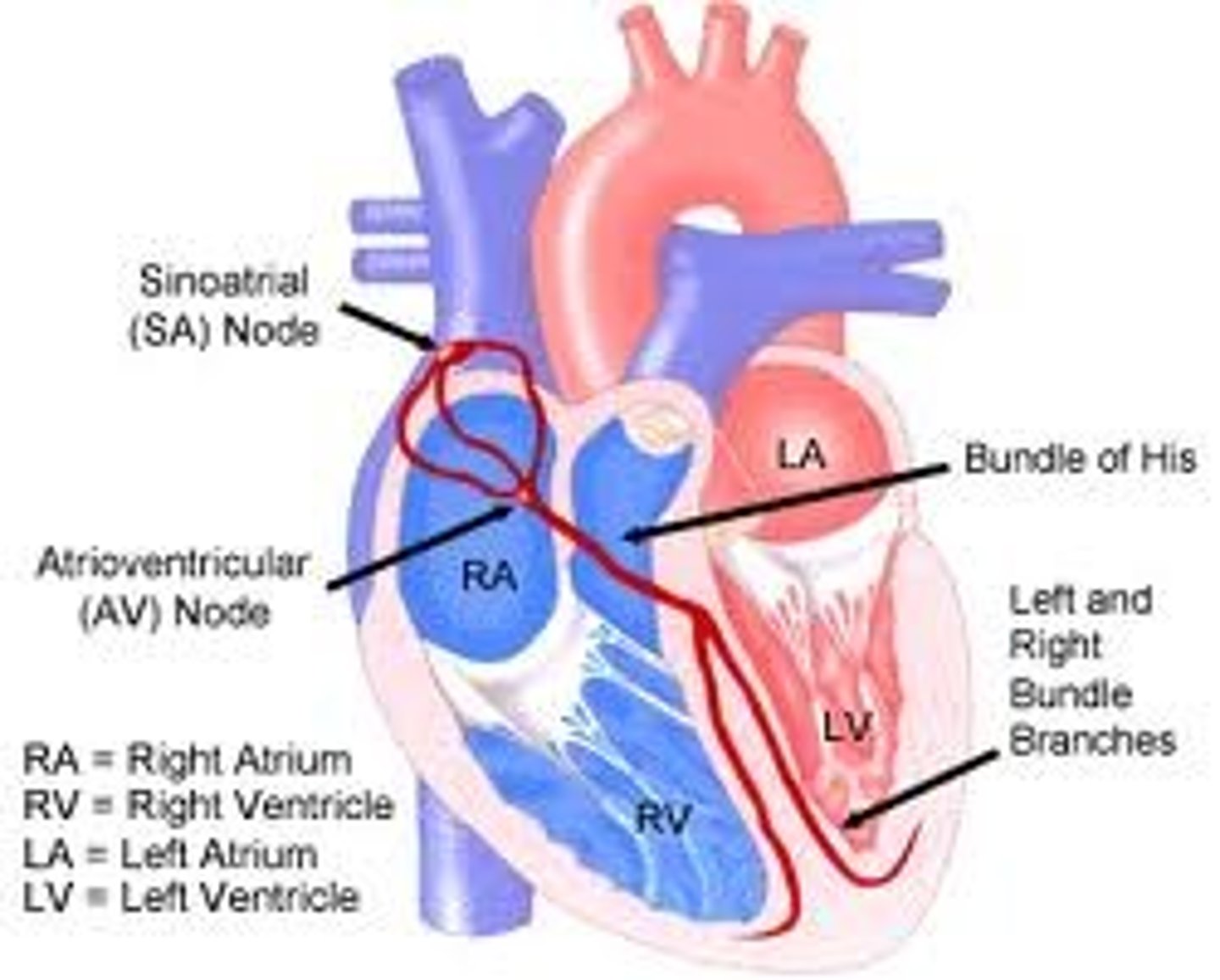
AV node
relays electrical impulses from SA node to Bundle of His
- right atrium, near AV valve
Bundle of His
relays electrical impulse from AV valve down the conducting fibers (septum), up walls of heart (Purkinje fibers)
- top of septum
- ventricles contract
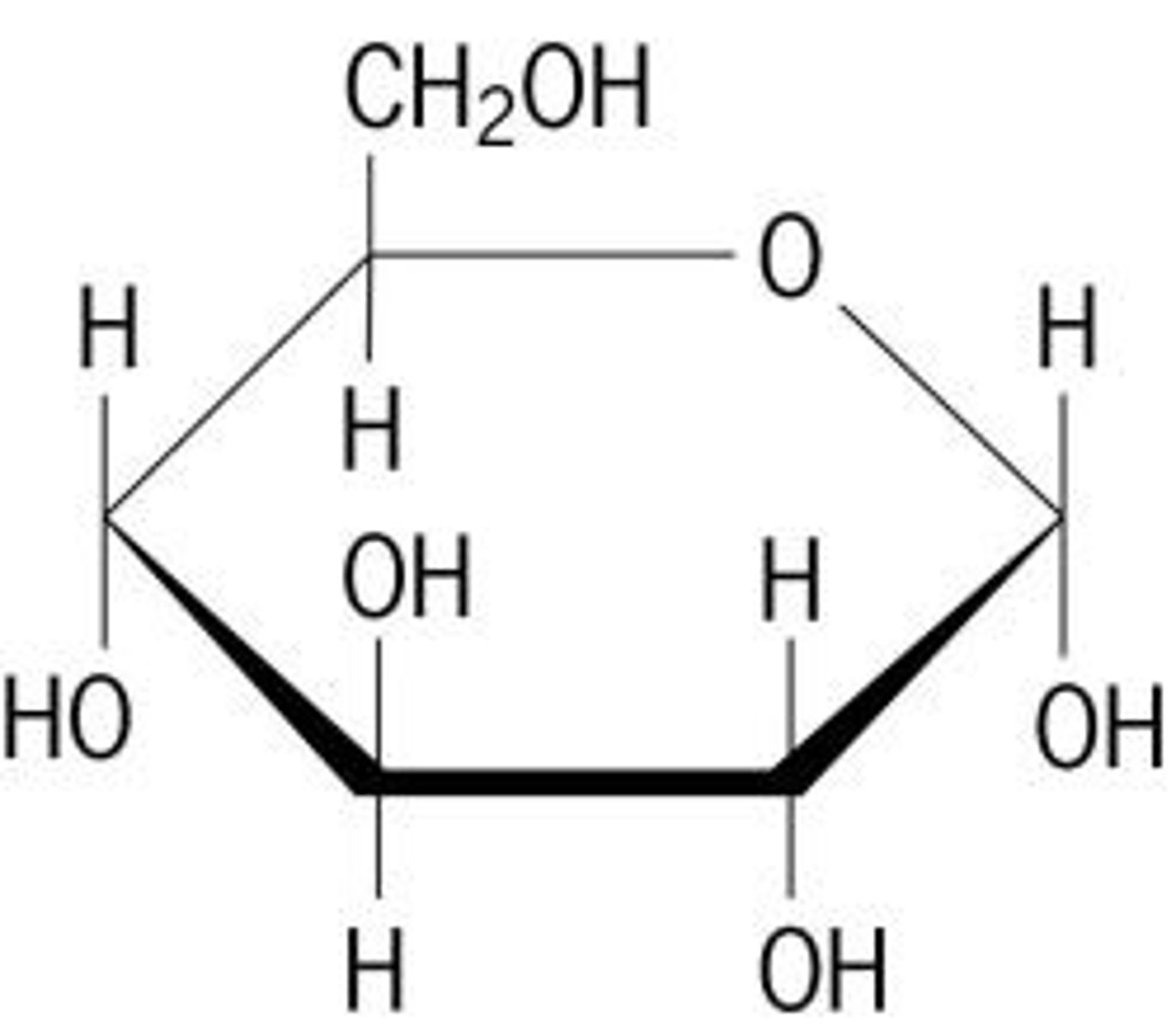
carbohydrates
mono: glucose, galactose, fructose:
di: sucrose, maltose, lactose
poly: amylose, glycogen, cellulose
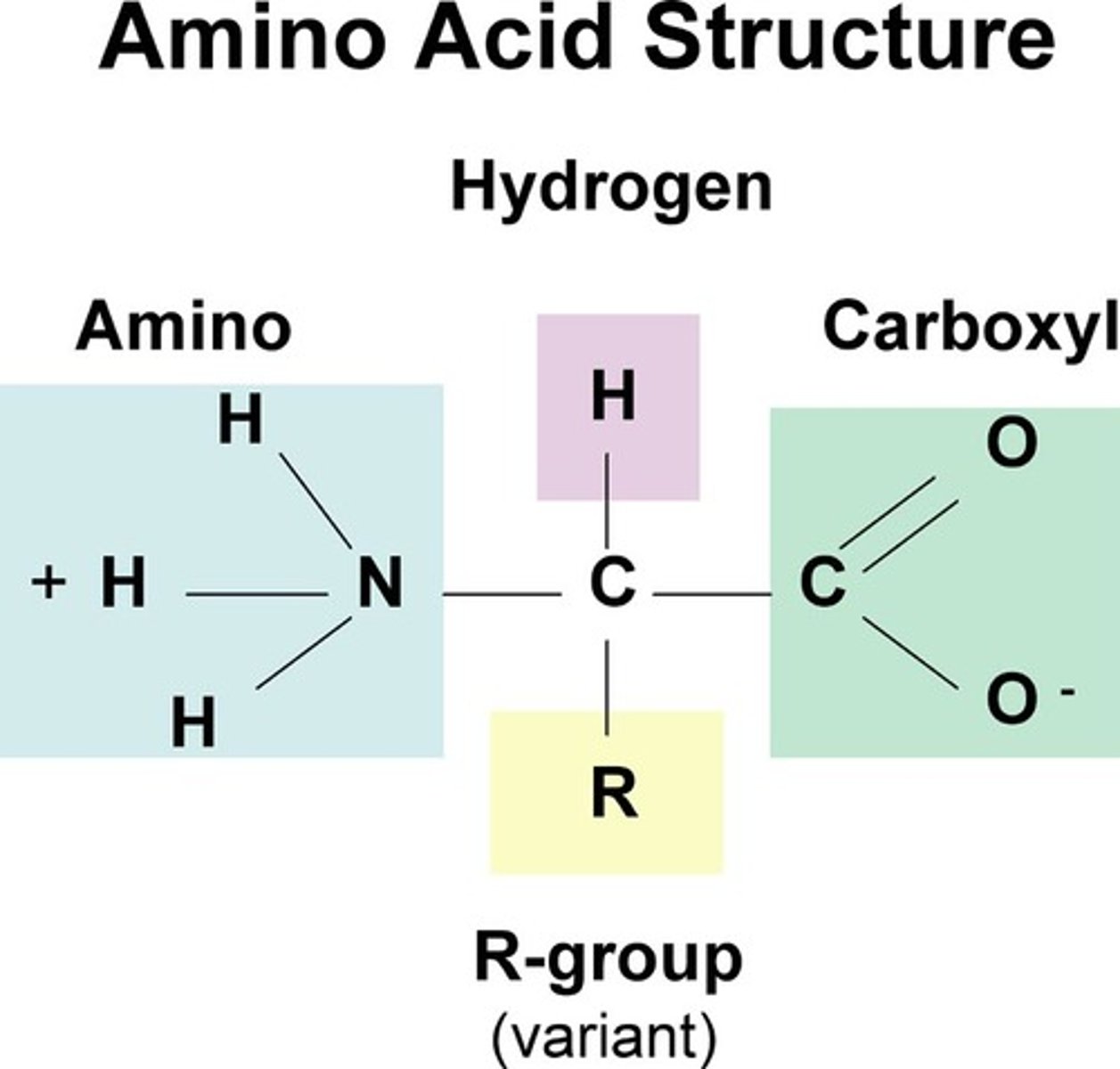
proteins
mono: amino acids
poly: polypeptides
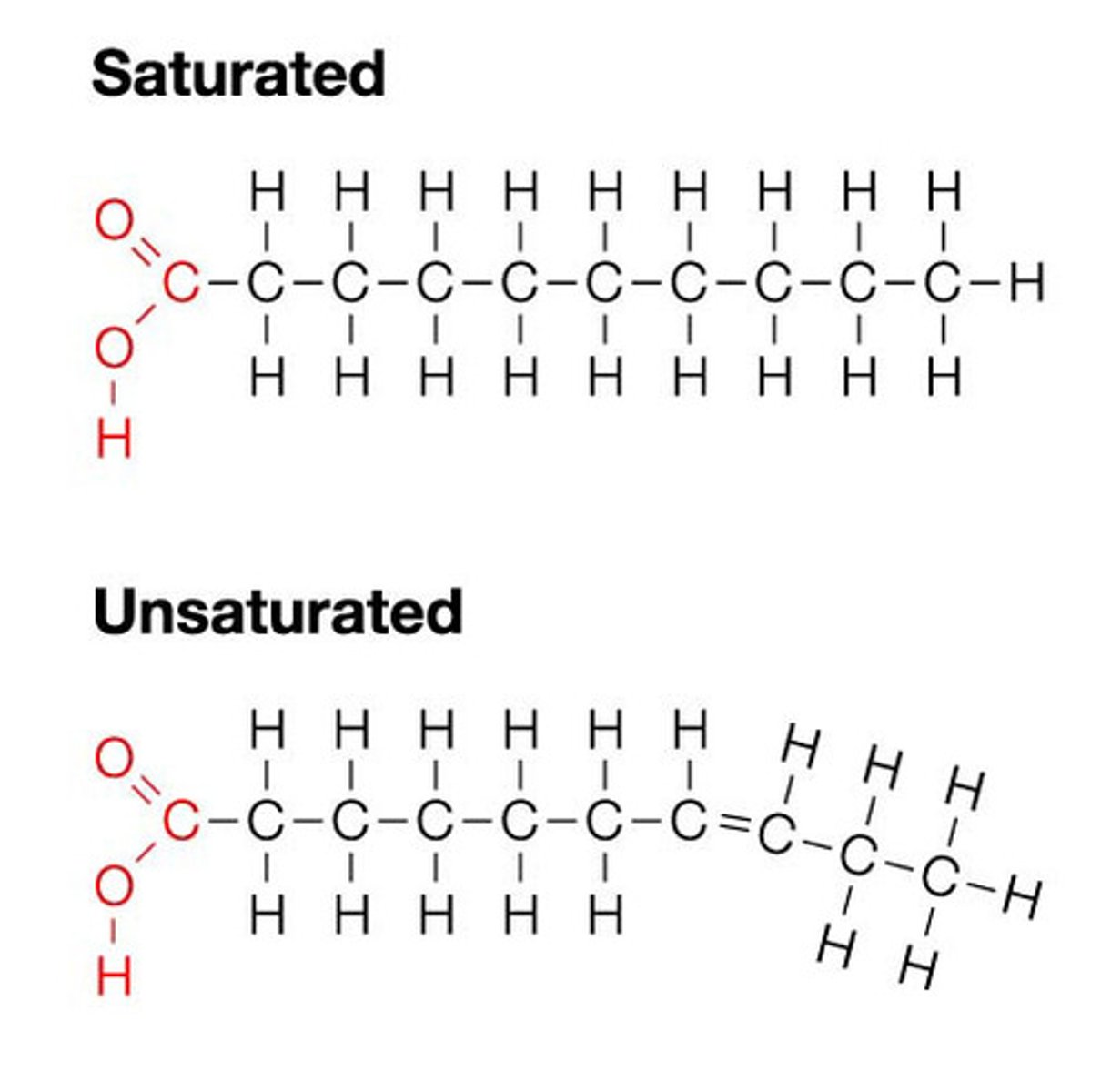
lipids
mono: glycerol, fatty acids
poly: triglycerides, phospholipids
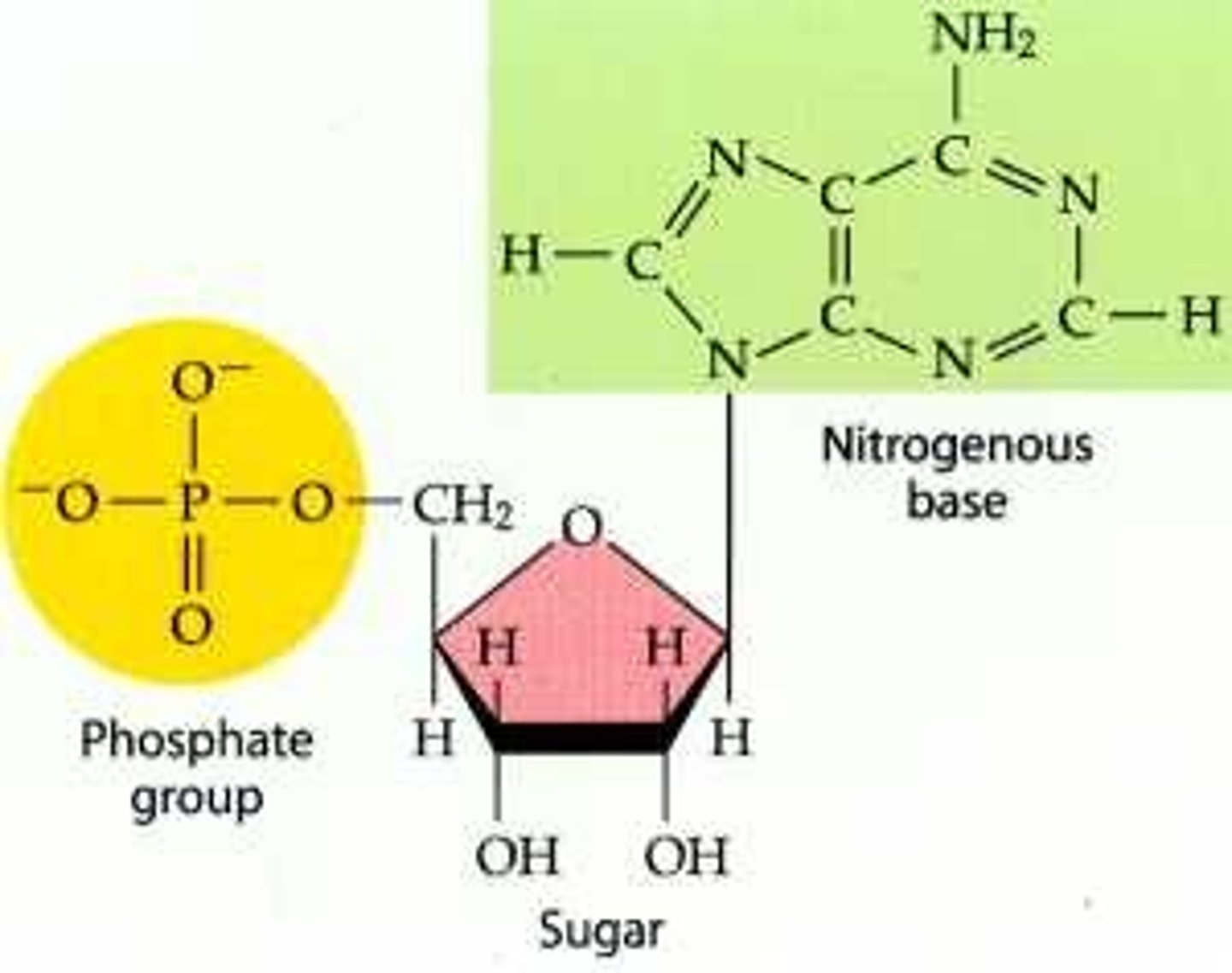
nucleic acids
mono: nucleotides
poly: DNA, RNA
salivary amylase
salivary gland enzyme that digests starch/glycogen -> smaller polysaccharides
pancreatic amylase
pancreas -> duodenum
digests smaller polysaccharides -> disaccharides
brush border
duodenum - made of villi (increase SA)
digest dimers -> monomers for absorption
pepsin
stomach enzyme, digests proteins -> smaller polypeptides
- hydrochloric acid (HCl) activates pepsinogen to convert to pepsin
trypsin
pancreas -> duodenum
smaller polypeptides -> dipeptides
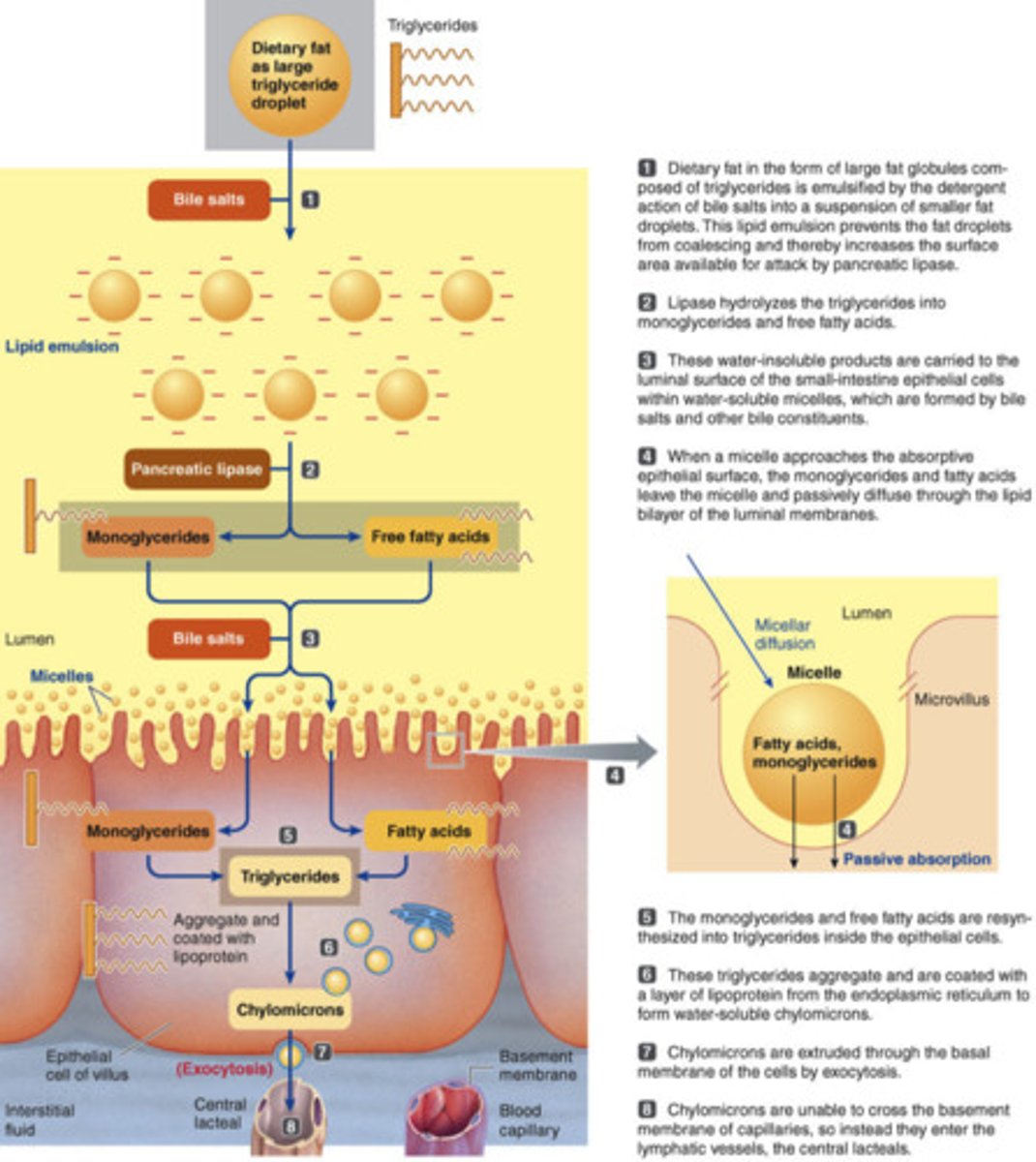
digestion of lipids
ALL OCCURS IN DUODENUM!!
- lipase (pancreas) hydrolyzes fat molecules
- bile salts (gallbladder) emulsify fat droplets
- absorbed by lacteal (in villus)
colon (large intestine)
absorption of water
effect of changing pH/temperature on enzymes
pH change, higher temp: denature (protein unfolds, PERMANENTLY losing structure/function)
lower temp: loss of kinetic energy
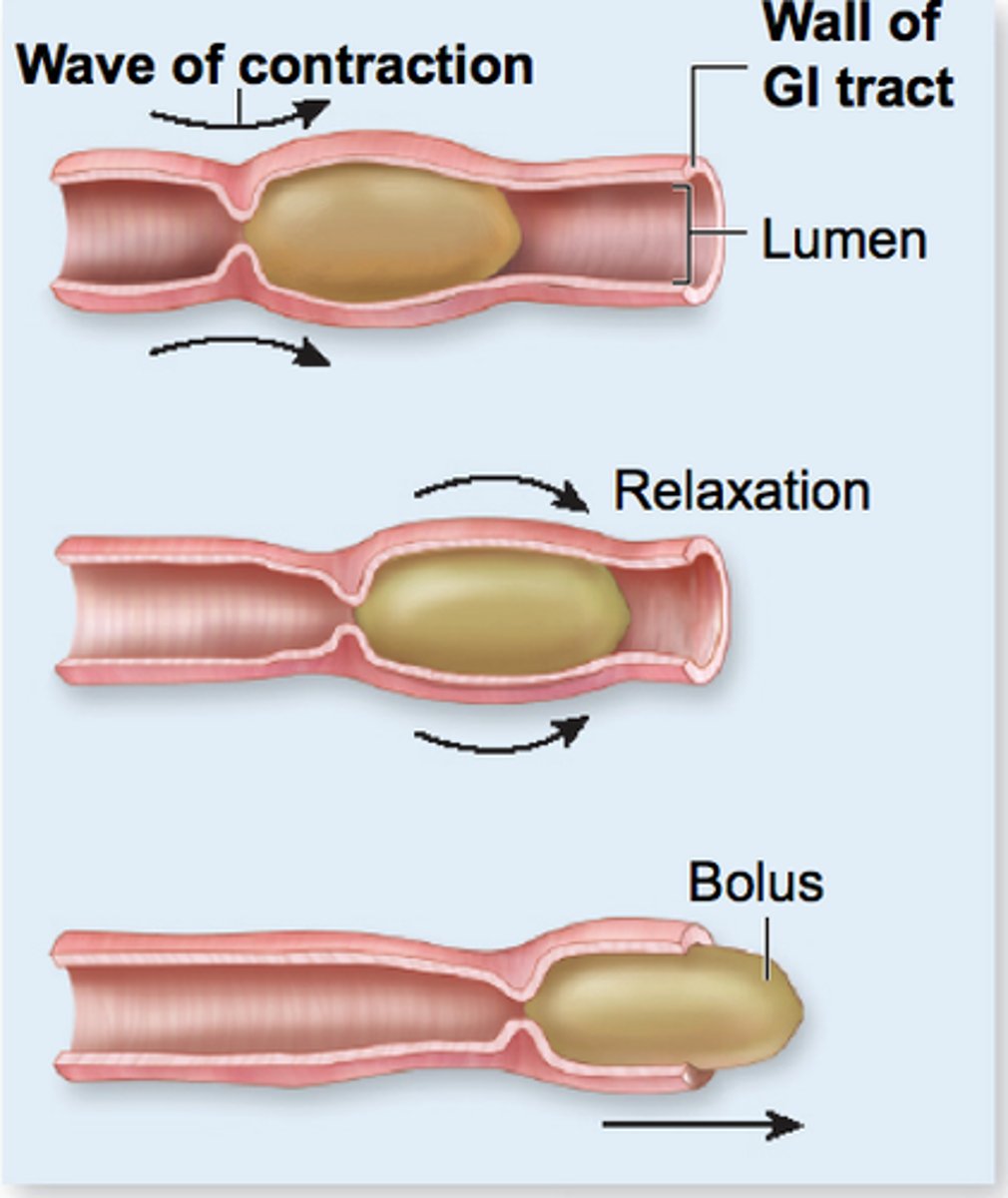
peristalsis
involuntary waves of smooth muscle contraction that push food thru digestive system
- 2 layers: lOngitudinal muscle Outside, cIrcular muscle Inside
ingestion
Intake of food
digestion
Breaking down food into monomers
absorption
cells take in monomers
assimilation
cell uses monomers to build new molecules/polymers
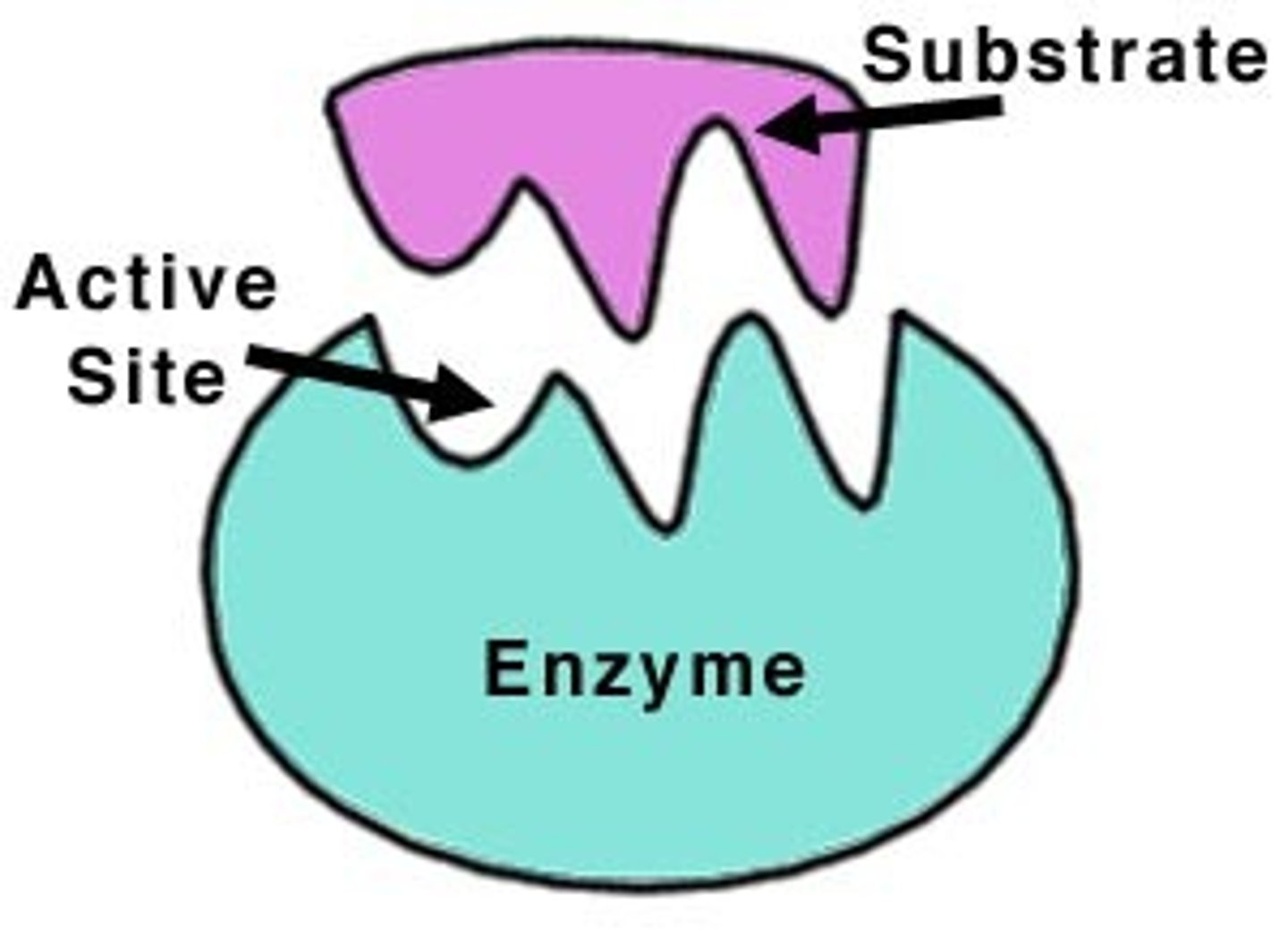
enzyme
protein catalyst that speeds up rate of reactions by lowering activation energy
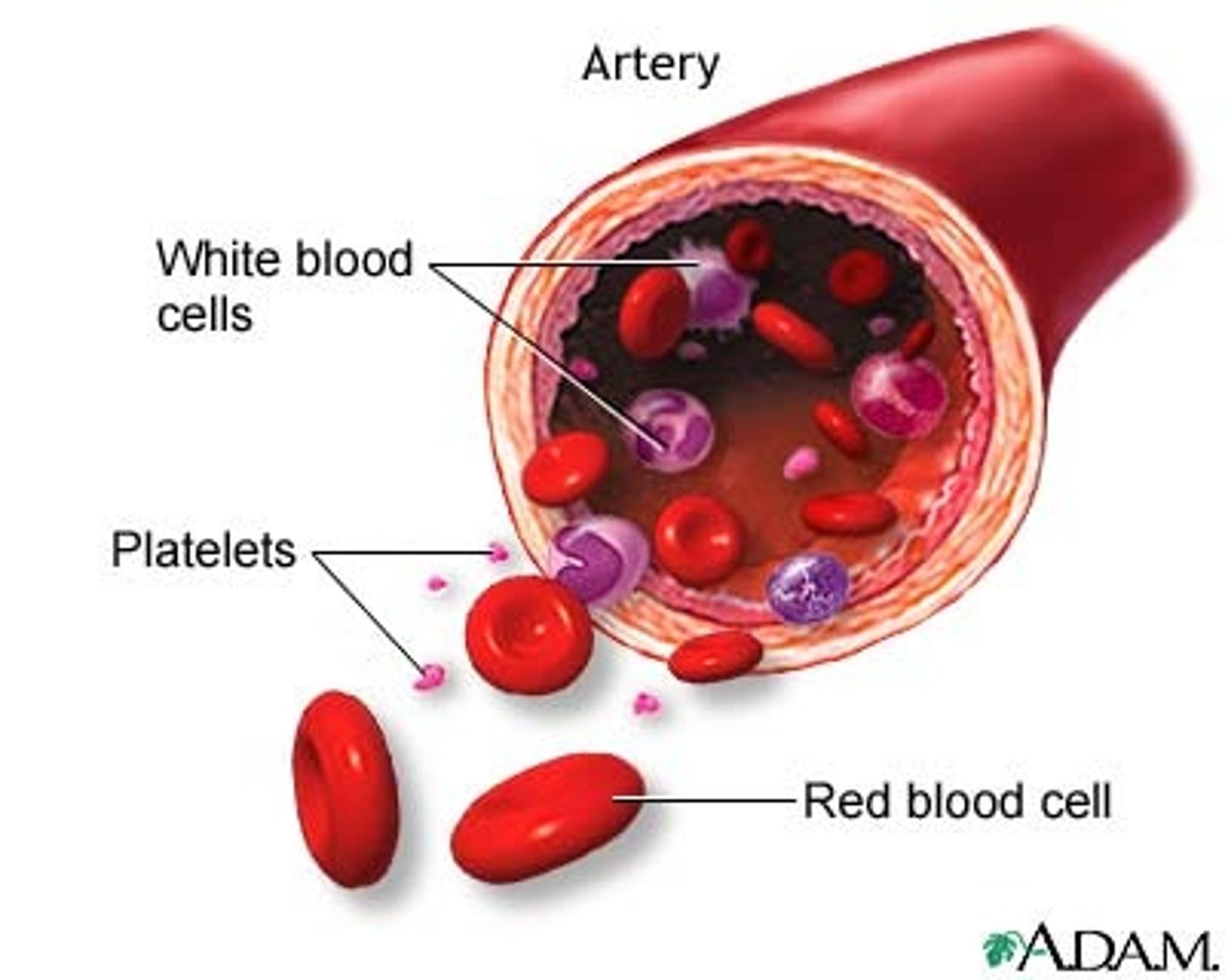
erythrocytes, leukocytes, thrombocytes
red blood cells (carry O2/CO2), white blood cells (fight infection), platelets (clotting)
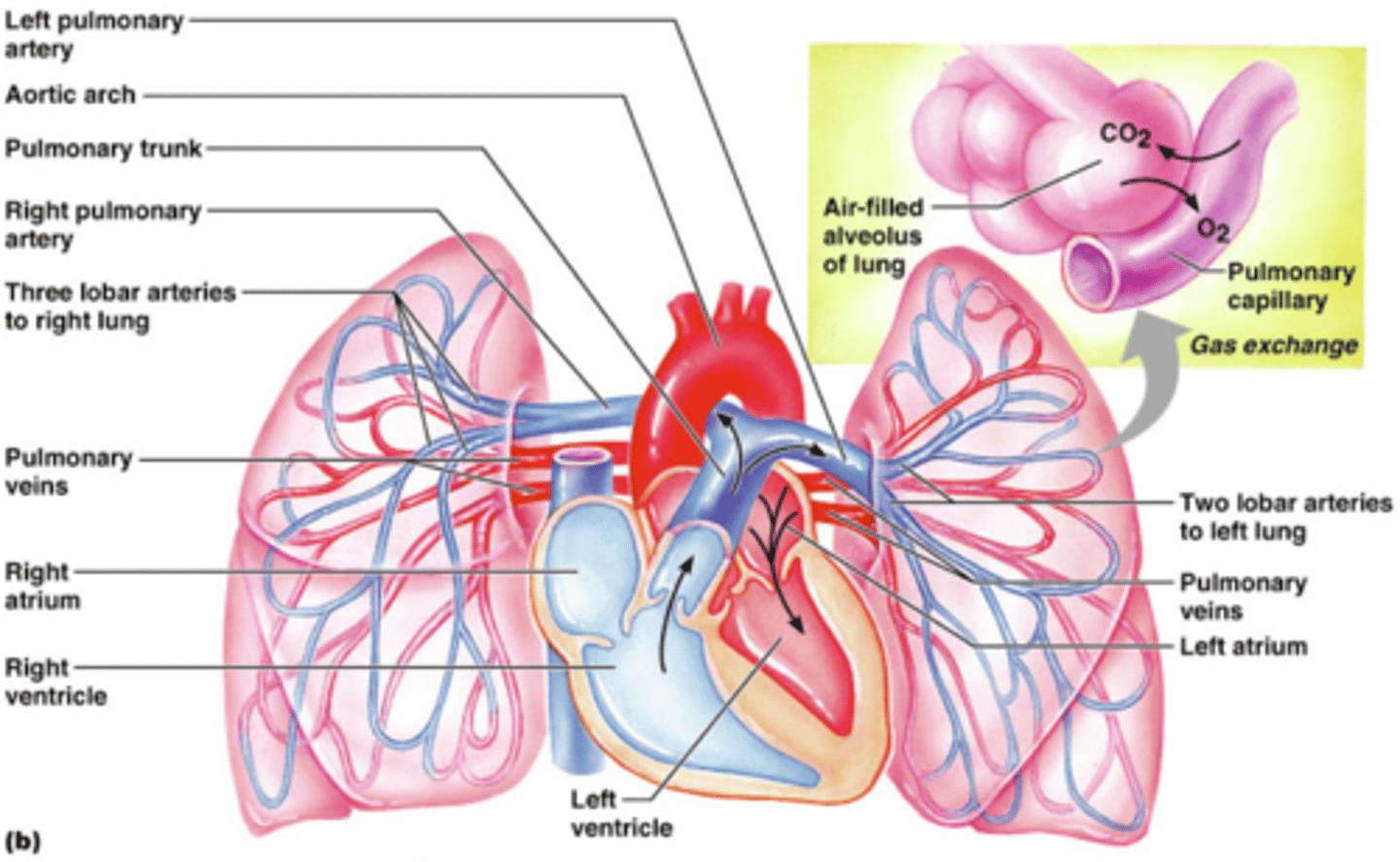
pulmonary arteries/veins
arteries take deoxygenated blood -> lungs
veins return oxygenated blood -> heart
(usually the other way around!!)
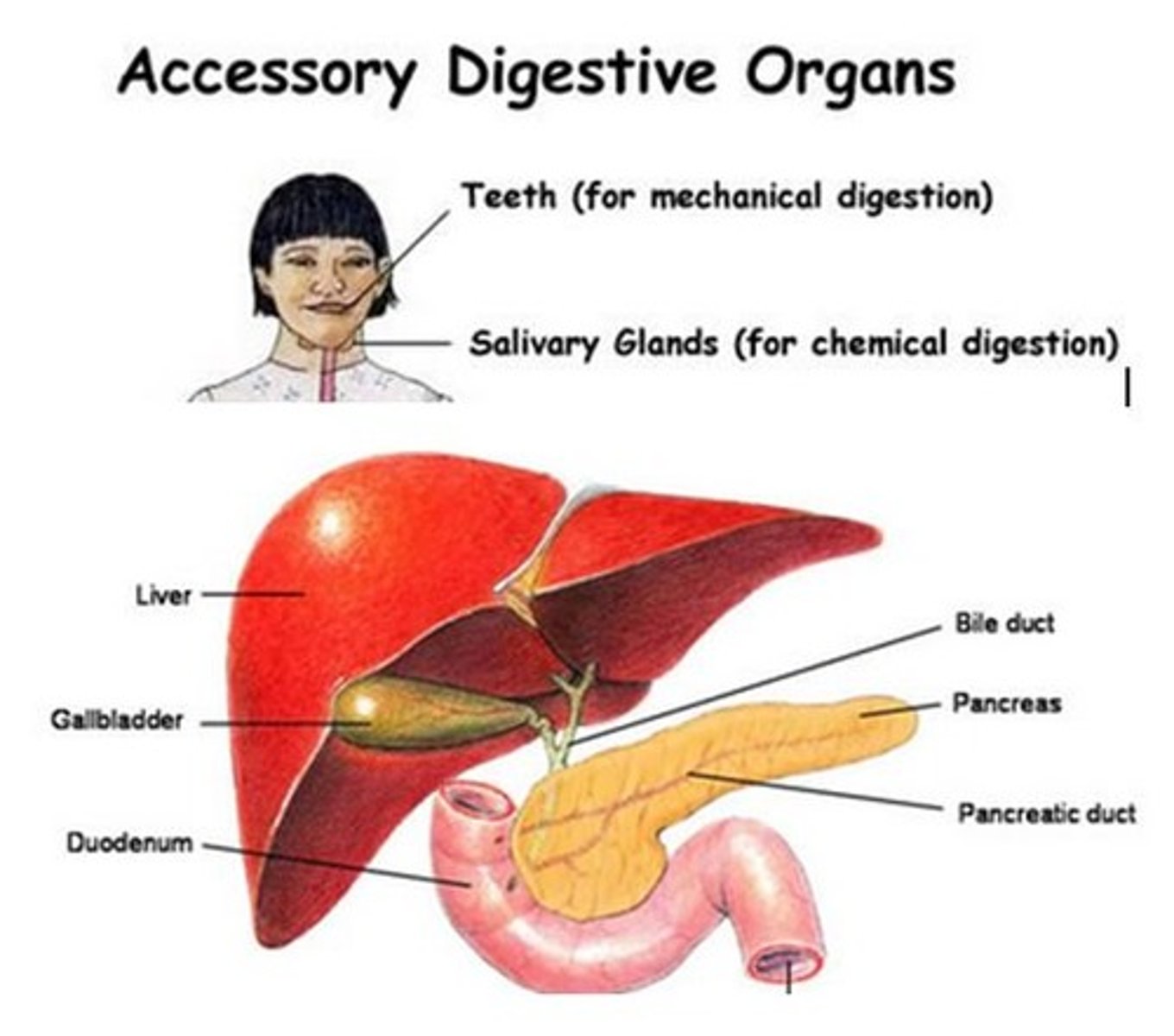
accessory organs of digestion
salivary glands: salivary amylase (starch -> smaller poly)
pancreas: trypsin (proteins), pancreatic amylase (carbs), lipase (fats)
liver: bile
gallbladder: stores bile -> bile salts (fats)
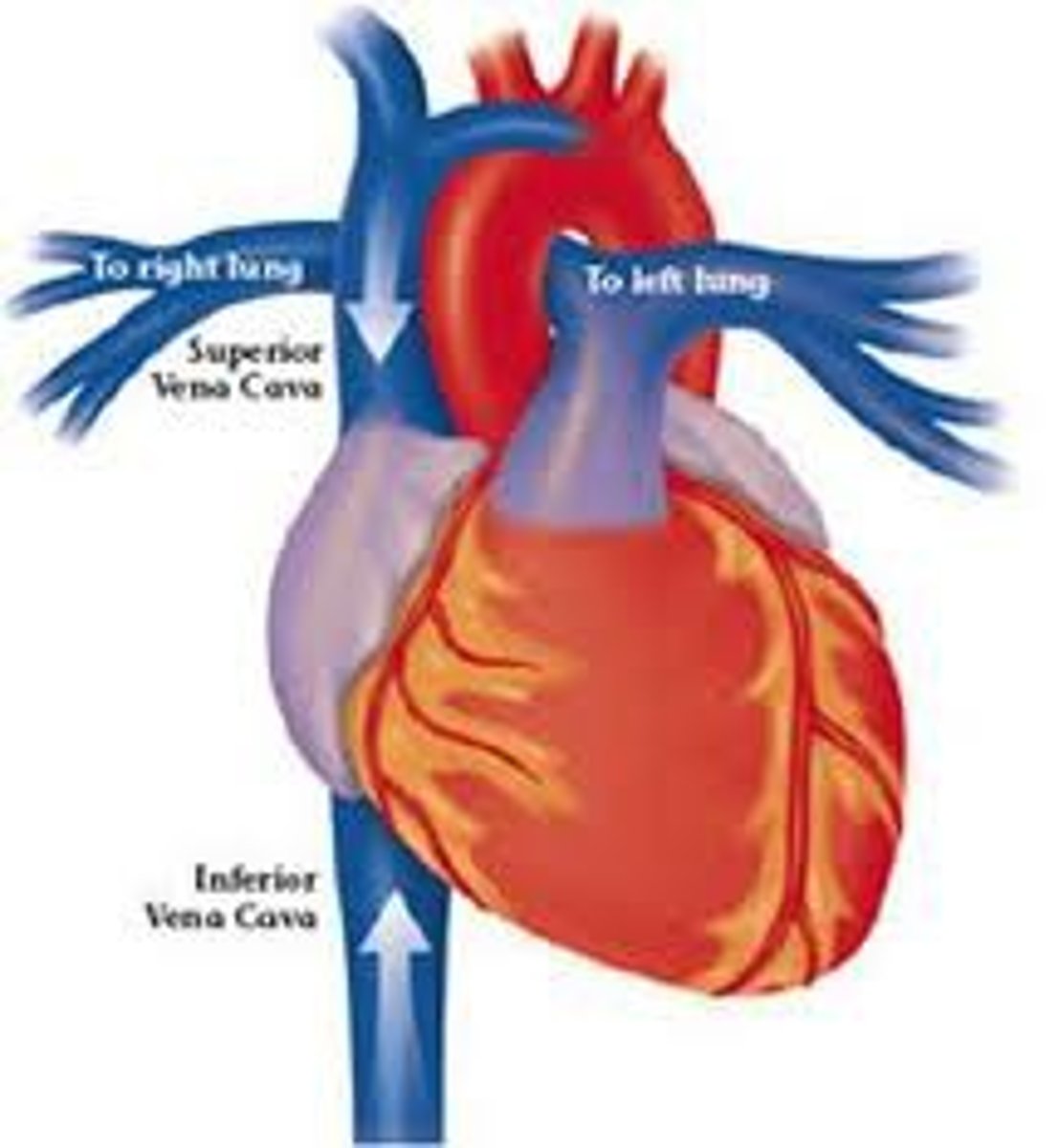
superior/inferior vena cava
superior: deoxygenated blood from upper body
inferior: deoxygenated blood from lower body (largest vein!)
...to right atrium
William Harvey
discovered heart was a pump, blood flows in a circle (one direction)
substances transported in blood
HEAT, enzymes, O2/CO2, antibodies, minerals/vitamins, glucose, hemoglobin, amino acids
oscilloscope
measures heartbeat, membrane potential - visualizes electric signals
systemic and pulmonary circulation
systemic: rest of body
pulmonary: lungs
villus
wall of small intestine (duodenum brush border) - increase SA for nutrient absorption
- columnar epithelial cells secrete dimerases
- microvilli increase SA
- goblet cells secrete mucus
- lacteal packed w/ white blood cells, absorbs fat
- capillaries absorb monomers -> liver
CHD (coronary heart disease)
narrowing of the coronary arteries (supply blood to heart)
- causes: high BP, high cholesterol, smoking, lack of exercise
- symptoms: chest pain, shortness of breath, heart attack
- treatment: exercise, quit smoking, medications (beta blockers), surgery (stent)
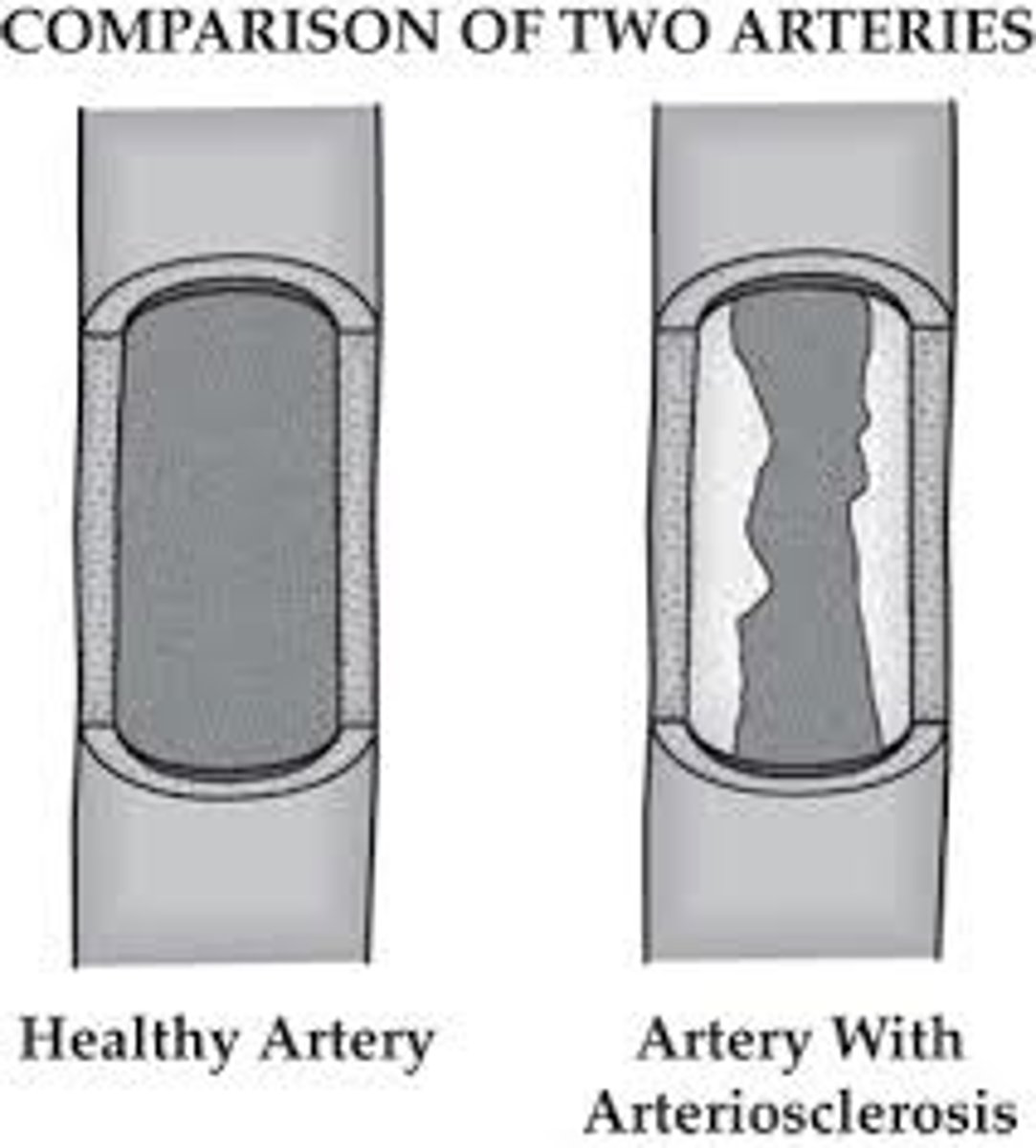
arteriosclerosis
hardening of the arteries
- caused by buildup of plaque (fats, cholesterol) -> calcification -> blood clot likely
- heart attack, stroke, pulmonary embolism
- treatment: treatment: exercise, diet, medications (blood thinners), surgery (stent)
factors that affect heart rate
sympathetic NS, adrenaline, exercise: HR increases, more O2 to muscles
parasympathetic NS: returns HR to normal
fever: HR increases as temperature increases, more white blood cell circulation, viruses less likely to survive