Ionization
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
What determines the extent of ionization of a weak acid/base?
the intrinsic acidity/basicity (pKa) of the molecule and the pH of the environment
AKA pKa and pH
What do weak acids do?
Donate H+
What do weak bases do?
Accept H+
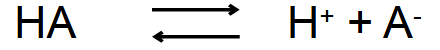
Which is ionized and which isn’t?
HA- Unionized
A- - Ionized
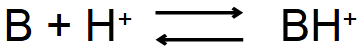
Which is ionized and which isn’t?
B- Unionized
BH+ - Ionized
What does the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation show us?
It helps us to determine the impact of the solution/environment pH and the drug pKa on the degree of ionization.
pka=pH?
50 % ionized and 50 % non-ionized
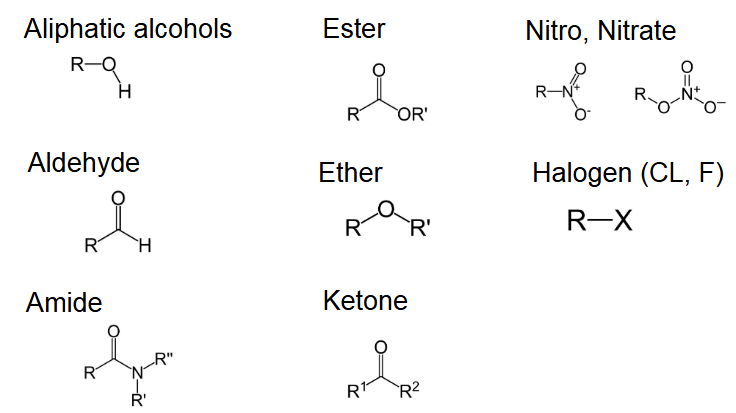
How do we know if it is an acid?
There are acidic groups and or have Acid/-ium
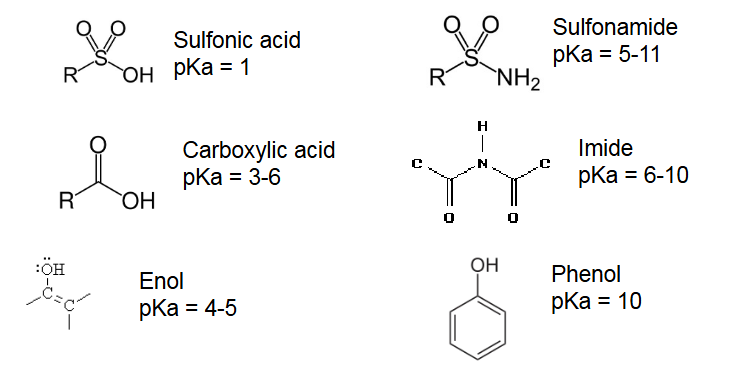
How do we know if it is a base?
There are basic groups and or have -ide/-ate
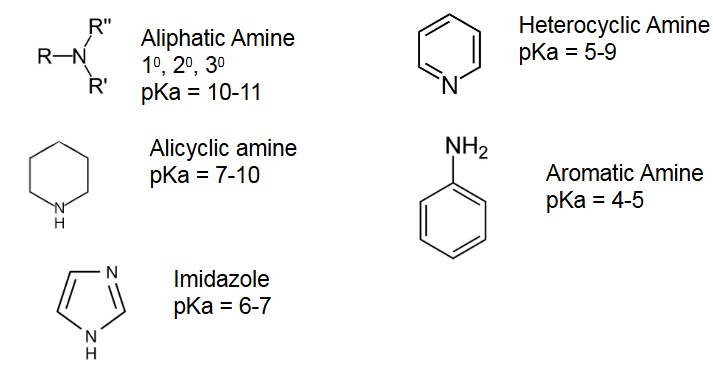
What are some examples of non-ionizable groups?
How are Drug salts made?
When ionized drug and ionized counterion have an ionic interaction with one another and crystallize.
How can salts form?
Strong Acid + Strong base
Weak Acids + Strong Base
Weak Base + Strong Acid
What is the pH Partition Hypothesis?
For Ionizable drugs, absorbed dose is determined by extent of unionized form at a given pH. The more lipid soluble form of a drug can permeate the cell membrane.
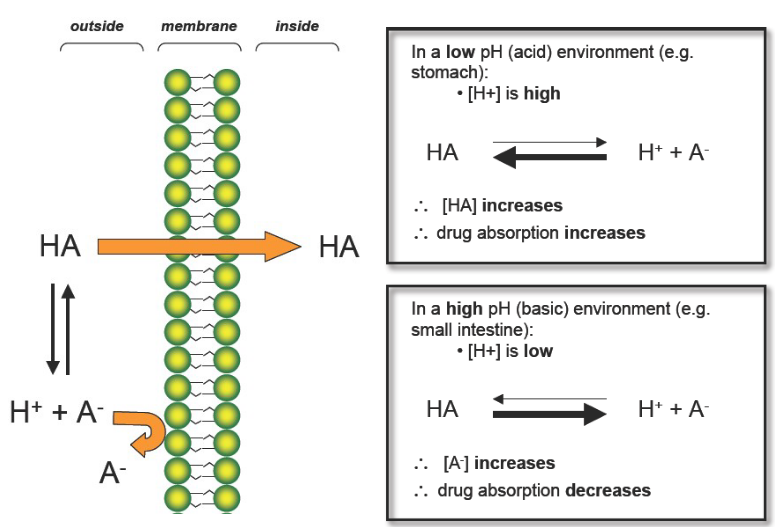
How does pH effect absorption of Acidic drugs?
In acidic Environments:
H+ is HIGH
HA increases (nonionized form)
Drug Absorption INCREASES
LIKE DISSOLVES LIKE!!!!!!!!!
In Basic environments:
H+ is LOW
A- increases (ionized form)
Drug Absorption DECREASES
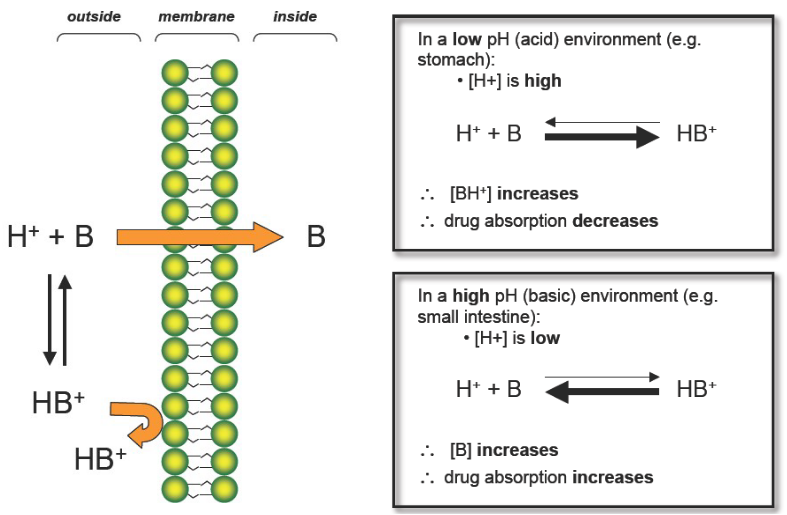
How does pH effect absorption of Basic drugs?
In acidic Environments:
H+ is HIGH
BH+ increases (ionized form)
Drug Absorption DECREASES
LIKE DISSOLVES LIKE!!!!!!!!!
In Basic environments:
H+ is LOW
B increases (nonionized form)
Drug Absorption INCREASES
LIKE DISSOLVES LIKE!!!!!!!!!
How does ionization affect solubility?
A drug in its ionic form is more readily soluble in Polar solvents compared to its un-ionized form. LIKE DISSOLVES LIKE!!!!!!!
The extent of drug ionization of a weak base or weak acid is dependent on the pH of the solution and the pKa of the drug.
Thus, the aqueous solubility will be affected by the pH of the solution and the pKa of the drug
Why do we need to drink an extra glass of water with sulfa drugs?
It is relatively insoluble and is mostly in unionized form in the kidneys and causes crystalluria leading to kidney damage.
What are some solutions to crystalluria?
Increasing urine flow by forced diuresis
Increasing urine pH by oral sodium bicarbonate
How does pH affect solubility?
In acidic pH:
Acids Increase the amount of non ionized form → DECREASES solubility
Bases increase the amount of ionized form → INCREASES solubility
In Basic pH:
Acids increase the amount of ionized form → INCREASES solubility
Bases increase the amount of nonionized form → DECREASES solubility
What is So?
Solubility of unionized form in the absence of ionized form
AKA Intrinsic Solubility
What is Si?
The solubility of the ionized form
What is our goal as pharmacists?
To avoid mixing potentially incompatible drugs
To avoid pH that may precipitate non-ionized forms
Incompatibilities of drugs:
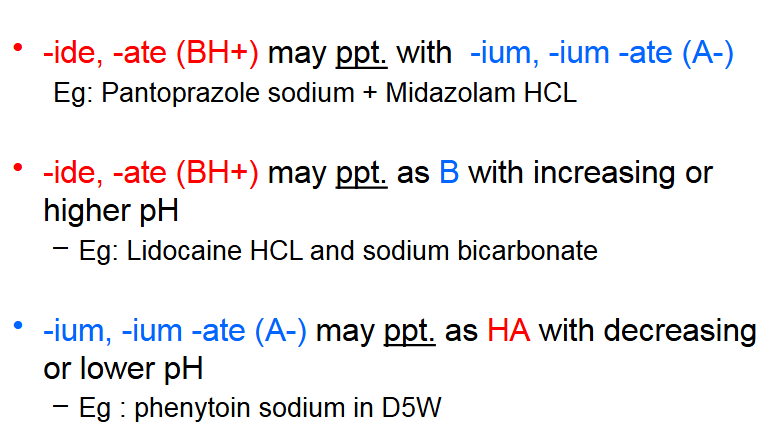
Weak acid + Strong base =
Equal molar species and dissolution of salt form yields pH > 7.0 solution
Weak Base + Strong Acid =
Equal molar species and dissolution of salt form yields pH < 7.0 solution
Weak Acid + Weak Base =
"Can" form ionic complexes with low solubility resulting in precipitation