chapter 28
1/115
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
116 Terms
The gonads A. are the male testes and female ovaries. B. secrete xsex hormones. C. produce gametes. D. are dormant until puberty. E. All of the choices are correct.
E. All of the choices are correct.
A. testis.
B. scrotum.
C. penis.
D. bulbourethral gland.
E. prostate gland.
A. luteinizing hormone.
B. estrogen or testosterone.
C. follicle-stimulating hormone.
D. gonadotropin-releasing hormone.
E. androgens.
A. hypothalamus.
B. gonads.
C. anterior pituitary gland.
D. adrenal gland.
E. genitals.
A. ischial tuberosity and a posterior anal ellipse.
B. urethral orifice and a posterior pubic crest.
C. false pelvis and a posterior true pelvis.
D. urogenital triangle and a posterior anal triangle.
E. pubic quadralateral and a posterior anal rhombus.
A. anus.
B. pubic symphysis.
C. ischial tuberosity.
D. bulbospongiosus muscle.
A. chromosomes.
B. autosomes.
C. homologous chromosomes.
D. sex chromosomes.
A. polyploid.
B. diploid.
C. haploid.
D. monoid.
A. 12
B. 23
C. 46
D. 92
E. 2
A. two daughter cells that are diploid.
B. two daughter cells that are haploid.
C. four daughter cells that are diploid.
D. four daughter cells that are haploid.
A. Mitosis produces sex cells that are genetically identical to the parent cell, whereas meiosis produces somatic cells that are genetically different from the parent cell.
B. Mitosis produces sex cells that are genetically different from the parent cell, whereas meiosis produces somatic cells that are genetically identical to the parent cell.
C. Mitosis produces somatic cells that are genetically identical to the parent cell, whereas meiosis produces sex cells that are genetically different from the parent cell.
D. Mitosis produces somatic cells that are genetically different from the parent cell, whereas meiosis produces sex cells that are genetically identical to the parent cell.
The process by which double-stranded, homologous chromosomes exchange genetic material is known as
A. crossing over, and it occurs in interphase.
B. crossing over, and it occurs in mitosis.
C. crossing over, and it occurs in meiosis.
D. interphase, and it occurs in meiosis.
E. interphase, and it occurs in mitosis.
C. crossing over, and it occurs in meiosis.
A replicated chromosome consists of two identical structures known as
A. centromeres. B. sister chromatids. C. telomeres. D. haploids. E. tetrads.
B. sister chromatids.
A. prior to meiosis.
B. between meiosis I and meiosis II.
C. between anaphase I and telophase I.
D. between prophase I and prophase II.
E. between telophase II and cytokinesis.
When homologous replicated chromosomes pair up during meiosis, they form a
A. sister chromatid. B. tetrad. C. single-stranded chromosome. D. centromere.
B. tetrad.
A. the chemical reactions of oxidation and reduction take place.
B. the daughter cells receive only half as many chromosomes as the parent cell had.
C. one daughter cell is substantially reduced in size compared to the parent cell.
D. the size of chromosomes is reduced from double-stranded to single-stranded.
A. prophase I.
B. anaphase I.
C. interphase.
D. prophase II.
E. anaphase II.
The daughter cells that result from meiosis I are
A. diploid and contain single-stranded chromosomes.
B. diploid and contain double-stranded chromosomes.
C. haploid and contain single-stranded chromosomes.
D. haploid and contain double-stranded chromosomes.
D. haploid and contain double-stranded chromosomes.
A. Suspensory ligament
B. Ovarian ligament
C. Mesovarium
D. Broad ligament
E. Round ligament
A. Each ovary has an outer cortex and an inner medulla.
B. The ovaries are located lateral to the uterus.
C. The ovarian artery and vein join the ovary at its hilum.
D. The gametes develop from the ovarian germinal epithelium.
E. The tunica albuginea is deep to the germinal epithelium.
A. Secondary follicle
B. Primary follicle
C. Mature follicle
D. Primordial follicle
E. Polar follicle
A. Corona radiata
B. Zona pellucida
C. Corpus albicans
D. Corpus luteum
E. Antrum
A. prophase I.
B. anaphase I.
C. prophase II.
D. metaphase II.
E. metaphase I.
A. primary
B. secondary
C. primordial
D. polar
E. mature
A. secondary
B. primary
C. mature
D. primordial
E. oogonial
A. primordial oocytes within primordial follicles.
B. primary oocytes within primordial follicles.
C. primordial oocytes within secondary follicles.
D. primary oocytes within corpora lutea.
E. primordial oocytes within corpora albicans.
A. prophase I.
B. anaphase II.
C. prophase II.
D. metaphase II.
E. metaphase I.
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
E. 5
A. Luteal, follicular, ovulation
B. Follicular, luteal, ovulation
C. Follicular, ovulation, luteal
D. Ovulation, follicular, luteal
E. Ovulation, luteal, follicular
A. inhibin.
B. LH.
C. ovulin.
D. estrogen.
E. progesterone.
A. uterine lining cells, and it inhibits development of ovarian follicles.
B. follicular cells, and it inhibits FSH production.
C. the anterior pituitary, and it inhibits GnRH production.
D. the posterior pituitary, and it inhibits ovulation.
E. hypothalamic cells, and it inhibits LH production.
A. 1-5.
B. 6-14.
C. 15-28.
D. 8-18.
A. ampulla.
B. fornix.
C. isthmus.
D. infundibulum.
E. uterine part.
A. are extensions of the ovarian ligament.
B. line the ampulla of the uterine tube.
C. enclose the ovary at the time of ovulation.
D. are sloughed off during menstruation.
E. assist in the movement of sperm through the female reproductive tract.
A. vagina.
B. body of the uterus.
C. fundus of the uterus.
D. ampulla of the uterine tube.
E. uterine part of the uterine tube.
What is the correct order for the segments of the uterine tube, beginning at the ovary?
A. Infundibulum - isthmus - ampulla - uterine part
B. Uterine part - infundibulum - ampulla - isthmus
C. Ampulla - infundibulum - uterine part - isthmus
D. Infundibulum - ampulla - isthmus - uterine part
E. Uterine part - isthmus - ampulla - infundibulum
D. Infundibulum - ampulla - isthmus - uterine part
A. pseudostratified columnar epithelium.
B. simple columnar epithelium.
C. nonkeratinized squamous epithelium.
D. stratified cuboidal epithelium.
E. simple cuboidal epithelium.
A. Protection and support of developing embryo
B. Usual site of fertilization
C. Site of implantation
D. Muscle contraction for labor and delivery
E. Passageway for sperm
A. Round ligament
B. Transverse cervical ligament
C. Uterosacral ligament
D. Uterine ligament
E. Urogenital diaphragm
A. myometrium.
B. perimetrium.
C. endometrium.
D. serosa.
E. muscularis.
A. opening of the cervix into the vagina.
B. inferior portion of the central cavity.
C. bone that supports the uterus during pregnancy.
D. uterine tube attachment site.
E. primary suspensory ligament for the uterus.
A. skeletal muscle.
B. mucous membrane.
C. fibrous connective tissue.
D. loose connective tissue.
E. smooth muscle.
A. Fallopian tube
B. Vagina
C. Uterus
D. Isthmus
A. at the cervix.
B. near the fundus of the uterus.
C. at the superior end of the vagina.
D. near the vaginal orifice.
E. at the external urethral sphincter.
A. the first four days of menstruation.
B. a female's first menstrual cycle.
C. the stage immediately preceding menopause.
D. marked by a dramatic decline in androgen secretion.
E. the final phase of the uterine cycle.
A. Perimetrium
B. Basal layer of endometrium
C. Myometrium
D. Functional layer of endometrium
E. Epimetrium
A. ovulation.
B. the luteal phase of the ovarian cycle.
C. menstruation.
D. the follicular phase of the ovarian cycle.
E. proliferation.
A. Menstrual - proliferative - secretory
B. Proliferative - secretory - menstrual
C. Secretory - proliferative - menstrual
D. Menstrual - secretory - proliferative
E. Proliferative - menstrual - secretory
A. follicular
B. secretory
C. proliferative
D. menstrual
A. menstrual
B. proliferative
C. follicular
D. luteal
E. ovulation
A. Clitoris
B. Vestibular bulb
C. Mons pubis
D. Labia minora
E. Prepuce
A. Mons pubis
B. Clitoris
C. Labia majora
D. Labia minora
E. Vagina
A. lactiferous sinuses.
B. lactiferous ducts.
C. alveoli.
D. areolar glands.
E. Bartholin glands.
A. LH.
B. GnRH.
C. oxytocin.
D. prolactin.
E. progesterone.
A. anteverted
B. erect
A. attach the penis to the body wall.
B. produce erections.
C. regulate the temperature of the testes.
D. help the testes descend into the scrotum prior to birth.
E. move sperm along the ductus deferens.
A. septum.
B. raphe.
C. perineum.
D. tunica albuginea.
E. scrotal cord.
A. Raphe
B. Cremaster
C. Tunica vaginalis
D. Dartos muscle
E. Inguinal muscle
A. Tunica vaginalis
B. Perineal raphe
C. Spermatic cord
D. Tunica albuginea
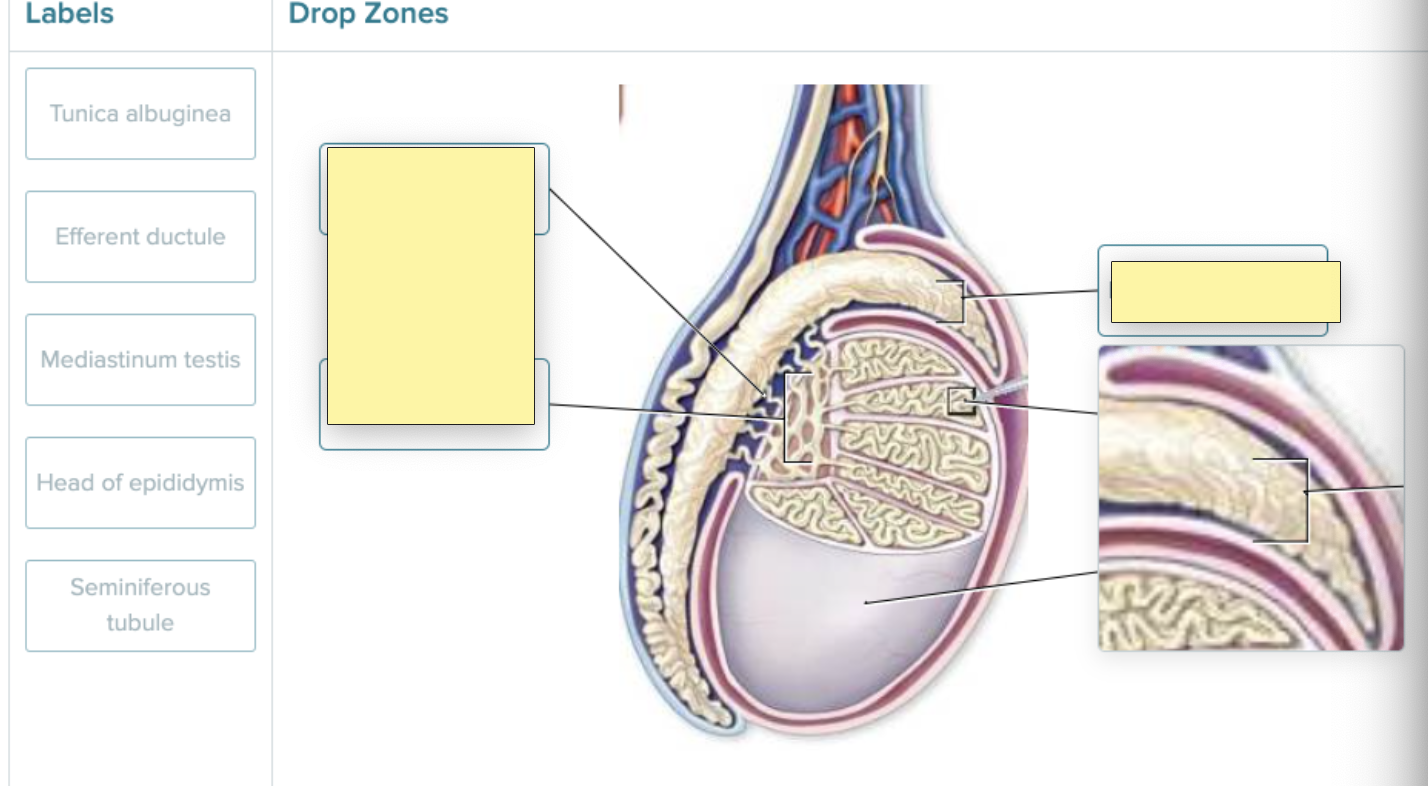
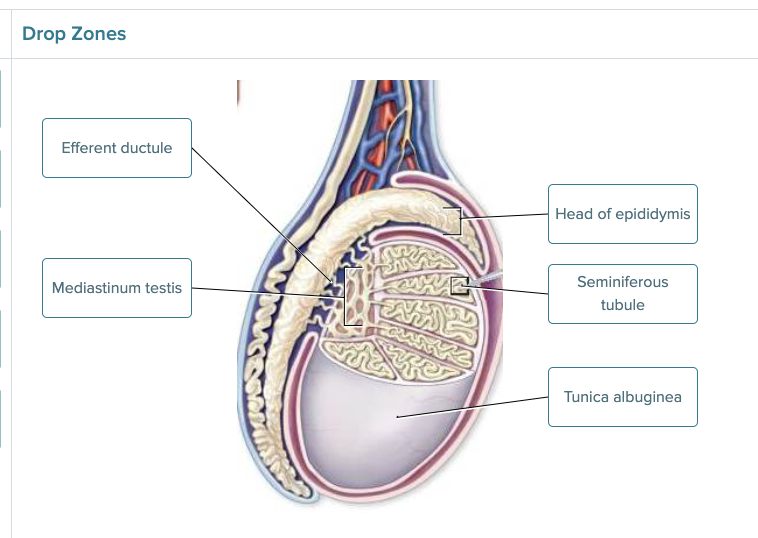
E. Mediastinum testis
A. rete testis.
B. seminiferous tubules.
C. epididymis.
D. seminal vesicles.
E. efferent ductules.
A. undergo mitosis to produce primary spermatocytes.
B. support and protect the developing sperm cells.
C. secrete testosterone.
D. convert fructose to glucose to nourish the sperm.
E. form the lining of the seminiferous tubules.
A. connective tissue septa.
B. interstitial spaces.
C. Leydig cells.
D. sustentacular cells.
E. leukocytes.
A. The process includes two meiotic divisions.
B. The final stage of the process is called spermiogenesis.
C. Mature spermatozoa are haploid (n\=23).
D. Spermatogenesis begins at birth and continues throughout a man's life.
E. The process takes place in the walls of the seminiferous tubules.
A. Acrosome cap
B. Head
C. Midpiece
D. Flagellum
E. Tail
The stages that appear during spermatogenesis are
a: spermatid
b: primary spermatocyte
c: spermatogonium
d: spermatozoon
e: secondary spermatocyte
What is the correct order of appearance of these stages?
A. b, e, c, d, a
B. c, e, d, a, b
C. c, b, e, a, d
D. a, c, b, e, d
E. d, b, c, e, a
C. c, b, e, a, d
A. testosterone.
B. nutrients to sustain the sperm.
C. enzymes to allow penetration into the oocyte.
D. mitochondria to provide energy for movement.
E. buffers to neutralize the acidity of the female reproductive tract.
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
E. 5
A. hypothalamic cells to secrete GnRH.
B. interstitial cells to secrete testosterone.
C. anterior pituitary cells to secrete FSH.
D. sustentacular cells to secrete testosterone.
E. spermatogenic cells to secrete ABP.
A. more gametes that are larger in size.
B. more gametes that are smaller in size.
C. fewer gametes that are larger in size.
D. fewer gametes that are smaller in size.
A. Epididymis
B. Rete testis
C. Ductus deferens
D. Seminiferous tubules
E. Efferent ductules
A. Glans
B. Corpora cavernosa
C. Tunica albuginea
D. Prepuce
E. Vestibular gland
A. receives sperm from the seminiferous tubules.
B. is the nerve plexus that supplies the testis.
C. is a venous network that cools the arterial blood traveling to the testis.
D. transports seminal fluid to the efferent ductules.
E. is the site of spermiogenesis.
The structures of the male reproductive tract are a: ductus deferens b: urethra c: epididymis d: ejaculatory duct e: ampulla
What is the order in which sperm passes through these structures from the testes to the penis?
A. a, b, c, e, d
B. c, a, e, d, b
C. a, c, e, b, d
D. c, a, b, d, e
E. d, a, c, e, b
B. c, a, e, d, b
A. ampulla and the proximal portion of the seminal vesicle.
B. ductus deferens and the ducts of the prostate gland.
C. ampulla and the distal portions of the bulbourethral glands.
D. ductus deferens and the ducts of the prostate gland and bulbourethral glands.
E. ampulla and the prostatic urethra.
A. Seminal vesicle
B. Bulbourethral gland
C. Prostate gland
D. Cowper's gland
E. Urethral gland
A. Seminal vesicle
B. Bulbourethral gland
C. Vestibular gland
D. Prostate gland
E. Urethral gland
A. Prostaglandin
B. Citric acid
C. Mucous
D. Seminalplasmin
E. Calcium
A. Epididymis
B. Bulbourethral gland
C. Prostate gland
D. Seminal vesicle
E. Corpus cavernosum
A. Seminal vesicles
B. Prostate glands
C. Bulbourethral glands
D. Areolar glands
A. Semen is composed of seminal fluid and sperm.
B. Seminal fluid is composed of semen and sperm.
C. Sperm are composed of seminal fluid within a cell membrane.
D. The three ingredients of ejaculate are sperm, semen, and prostate-specific antigen.
A. bulb
B. crus
C. glans
D. corpus cavernosum
E. body
A .semen pressure from the testes and ductus deferens.
B. muscle flexion of the penile muscles.
C. increased secretions of lymph into the spongy tissue.
D. blood filling the erectile bodies and compressing the veins.
E. ejaculatory muscles.
A. sympathetic, nitric oxide
B. sympathetic, norepinephrine
C. parasympathetic, nitric oxide
D. parasympathetic, norepinephrine
E. somatic, acetylcholine
A. peristalsis, and the internal urethral sphincter of the bladder relaxes.
B. peristalsis, and the internal urethral sphincter of the bladder contracts.
C. segmentation, and the external urethral sphincter contracts.
D. segmentation, and the external urethral sphincter becomes engorged with blood.
In males, the _________ region on the Y chromosome initiates male phenotypic development.
A. HRT B. AMH C. TDF D. SRY E. BPH
D. SRY
A. MDF
B. SRY
C. GRH
D. YXP
A. gender identity.
B. genetic sex.
C. phenotypic sex.
D. genotypic sex.
A. atrophy of the thermoregulatory center of the hypothalamus.
B. reduced levels of estrogen and progesterone.
C. increased production of androgens by the adrenal gland.
D. depletion of oocyte supply.
E. fluid retention that disrupts the osmotic balance of the body.
A. 2 months
B. 4 months
C. 6 months
D. 1 year
E. 18 months
A. becomes thicker
B. becomes thinner
C. does not change
A. Erectile dysfunction
B. Impotence
C. Decreased testosterone levels
D. Prostate enlargement
E. Termination of spermatogenesis
A. mesonephric
B. paramesonephric
C. metanephric
D. parametanephric
E. Wolffian
A. The superior ends of the mesonephric ducts
B. The anterior ends of the Wolffian ducts
C. The caudal ends of the paramesonephric ducts
D. The posterior ends of the gubernaculum
A. inhibin
B. estrogen
C. testosterone
D. AMH
E. TSH
A. clitoris.
B. vagina.
C. labia majora.
D. labia minora.
E. uterus.
A. scrotum.
B. scrotum and testes.
C. scrotum and root of the penis.
D. scrotum and dorsal side of the penis.
E. scrotum and ventral side of the penis.
A. ovarian follicular cells.
B. primary spermatocytes.
C. sustentacular cells.
D. interstitial cells.
E. paramesonephric cells.
A. 6
B. 12
C. 20
D. 32
E. 38
The daughter cells that result from meiosis I are
A. diploid and contain replicated chromosomes.
B. haploid and contain single chromosomes.
C. haploid and contain replicated chromosomes.
D. diploid and contain single chromosomes.
C. haploid and contain replicated chromosomes.