Chapter 17 DBMS
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
Is data a source of competitive advantage?
YES - under the condition that it’s VRIS.
However, advantages based on capabilities and data that others can acquire easily will be short-lived
When might data not yield sustainable advantage?
publicly available
can be recreated
Are advantages based on analytics and modeling potentially sustainable? Why or why not?
YES - if they result in differentiation as opposed to just operational efficiency.
Advantages based on capabilities others can acquire will be short-lived
Database
Single table or a collection of related tables
Serves many applications by centralizing data and controlling redundant data
DBMS
Software for creating, maintaining, and manipulating data
◦ Known as database software
Interfaces between applications and physical data files
separates logical and physical views of data
solves problems of traditional file environment
controls redundancy
eliminates inconsistency
uncouples programs and data
enables organization to centrally manage data and data security
Data Hierarchy
BBFRFD
bit
0 and 1, up and down
byte
Collection of 8 bits, make up every character, number, or symbol
field
group of bytes
record
collection of related fields
file
collection of related records
database
collection of related files
Data warehouse
Stores current and historical data from many core operational transaction systems
Consolidates and standardizes information for use across enterprise
data cannot be altered
Data warehouse system will provide query, analysis, and reporting tools
Data marts
◦ Subset of data warehouse
◦ Summarized or highly focused portion of firm’s data for use by specific population of users
◦ Typically focuses on single subject or line of business
Relational DBMS
◦ Represent data as 2-D tables called relations or files
◦ Each table contains data on entity and attributes
Capabilities of DBMS
DDL, Dictionary and DML
What role do technology and timing play in realizing advantages from the data asset?
moving early can be the difference between a dominating firm and an also-ran
if more data brings more accurate modeling
advantages based on capabilities and data others can acquire will be short-lived
technology that cannot be easily replicated or imitated is KEY is distinguishing operationally effective tech from those efforts that can yield true strategic positioning
Why would a firm use a loyalty card?
What is the incentive for the firm?
What is the incentive for consumers to opt in and use loyalty cards?
What kinds of strategic assets can these systems create?
Loyalty card is a system that provides rewards and usage incentives
When customers use card, they give up info about themselves in exchange for a financial incentive
FIRM: collect personalized info about customer purchases and improve targeting
CUSTOMER: financial incentives; points or discounts
Switching costs
How can firms leverage customer data to better serve you and improve their performance?
product purchase reminder
new product/service availability
coupons/other incentives
product upgrades/offers
data security
be concerned
Big Data
Refers to the vast amount, volumes, and types of data that a company can collect and process using increasingly high-tech systems
measured in zettabytes (2 raised to the 70th power)
V3 in big data
Volume
Variety
Velocity
—> leads to complexity
3 more big data sources
Complexity
different standards, rules, and storage formats can exist with each asset type
Veracity
messiness/trustworthiness of the data. big data = less control over quality and accuracy
data cleansing is an important component
Value
unless we can turn big data into value, having access to it is useless
bottom line of big data
answers become a COMMODITY
real value lies in asking good questions
Data Analytics
using math and statistics to derive meanings from data in order to make better informed decisions
combo of computer technology, management science techniques, and statistics to solve real problems
Descriptive analytics
Essentially, deals with analysis of historic data
Dashboard, scorecards, and alerts
help summarize past events and tell us what happened (NOT why it happened or what might change)
Predictive analytics
use past data to model future outcomes
ex) predicting how customers will respond to a promotion event or advertising campaign
Descriptive analytics in excel
To summarize and organize data to make it easier to understand what has already occurred
Data visualization
Dashboards and scorecards
Descriptive statistics
hindsight
Predictive analytics in excel
enablers:
data mining
text mining/web mining
forecasting (ie. time series)
regression analysis
insight
Prescriptive analytics
Chooses techniques like optimization to help managers
answers the Q: “What should we do today in order to achieve a specific purpose”
ex) optimal allocation among stock investments to maximize ROI or minimize risk?
finds best possible decision
ex) excel solver; simulation
foresight
bottom line of data analytics
combining big data and effective analytics gives the company a key competitive advantage
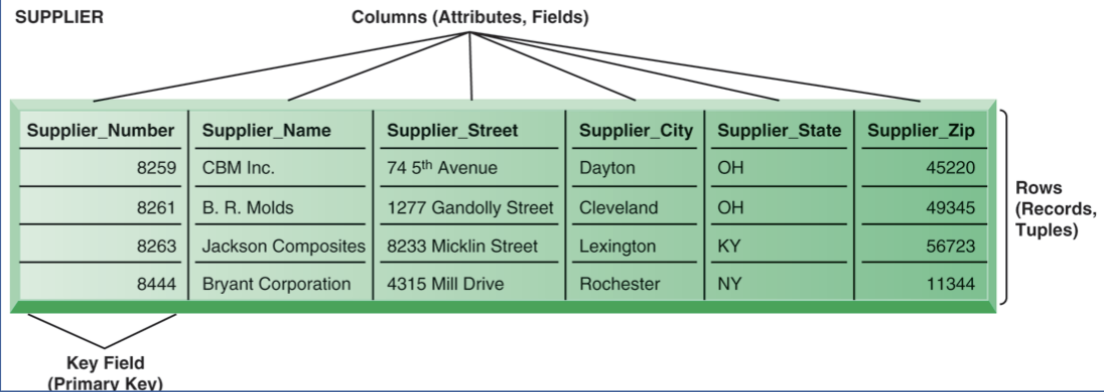
table: grid of columns and rows
rows/tuples: records for different entities
fields/columns: defines data table can hold (attribute for entity)
primary key: field in table used to uniquely identify a table
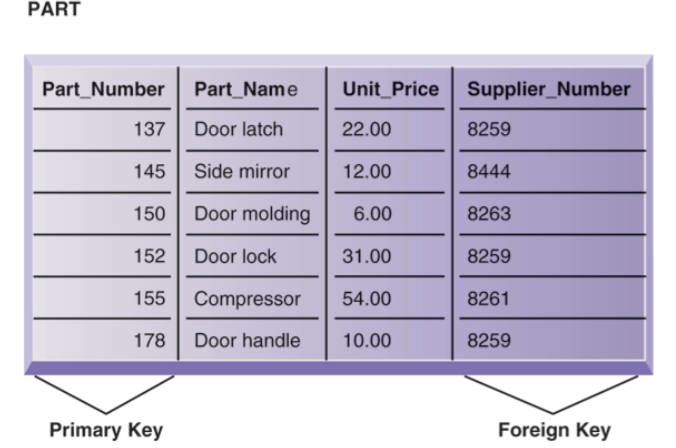
foreign key: primary key used in second table as look-up field to identify records from original table
data definition language (DDL)
specifies structure of database content, used to create tables and define characteristics of fields
data dictionary
automated or manual file storing definitions of data elements and their characteristics
data manipulation language
used to add, change, delete, retrieve data from database
SQL (structured query language)
Microsoft Access uses tools for generation SQL
Many DBMS have report generation capabilities for creating polished reports
entity-relationship diagram
used by database designers to document data model
illustrates relationships between entities
one-to-one
each instance in the relationship will have exactly one related instance
ex) every employee is assigned to one parking space
one-to-many
an instance on one side of the relationship can have many related instances, but an instance on the other side will have a maximum of one related instance
ex) a product line can contain many products
many-to-many
Instances on both sides of the relationship can have many related instances on the other side
ex) many students register for many courses
NOT ALLOWED bc redundancies
To break a many-to-many entity, introduce a third entity between
text mining
extracts key elements from lagre unstructred data sets
ex) stored emails
data quality
Most data problems stem from faulty input (GIGO)
data quality audit
◦ Structured survey of the accuracy and level of completeness of the data in an information system
Survey samples from data files, or
Survey end users for perceptions of quality
data cleansing
Software to detect and correct data that are incorrect, incomplete, improperly formatted, or redundant
Enforces consistency among different sets of data from separate information systems
attribute
describes the entity
ex) attributes date or grade belong to entity COURSE
entity
person, place, thing on which we store data
field
group of characters as words or number
record
group of related fields
file
group of records of the same type
database
group of related files
data redundancy
presence of duplicate data in multiple files
data inconsistency
same attribute has different values
rows/tuples/records
records for different entities
fields/columns/attributes
defines data table can hold (attribute for entity)
primary key
field in table used to uniquely identify a table
foreign key
primary key used in second table as look-up field to identify records from original table
cardinality of relationships
Relation has to be BI-DIRECTIONAL to make sense (from A to B and B to A)
Before new database in place, need to
identify and correct faulty data
establish better routines for editing data once database in operation