6.2 - Panic Disorder to BDD
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
Panic Disorder
Occurrence of panic attacks seems to come "out of the blue"
Panic Disorder
Recurrent, unexpected attacks and worry about additional attacks
Panic Disorder
Attacks are brief but intense
3
Panic Disorder:
Must be abrupt onset of ___ out of 13 symptoms (10 physical, 3 cognitive)
Unexpected Attacks
4+ Symptoms (like heart racing, sweating, dizziness, fear of dying)
1 month of Worry
Not Due to Substance
Not Another Disorder
Criteria for Panic Disorder:
Palpitations, pounding heart, or accelerated heart rate
Sweating
Trembling
Sensations of shortness of breath
Feelings of choking
Chest pain or discomfort
Nausea or abdominal distress
Feeling dizzy, unsteady, lightheaded, or faint
Panic Disorder Symptoms:
Agoraphobia
an anxiety disorder characterized by intense fear and anxiety related to places or situations where escape might be difficult or where help might not be available.
Fear of 2+ Situations
Escape Difficult
Provokes Fear
Avoidance/Help
Out of Proportion (Fear is excessive)
Lasts 6+ Months
Impairment
Criteria for Agoraphobia:
Public transport
Open spaces
Enclosed spaces
Standing in line/crowd
Outside home alone
Situations in Agoraphobia: (5)
Agoraphobia
Anxiety about being in places from which escape might be difficult or embarrassing:
Crowds
Theaters
Malls
Panic disorder without agoraphobia
________ is more common than panic disorder with agoraphobia
Agoraphobia
Twice as prevalent in women than in men
Agoraphobia
Average age onset is 23-34
1st panic attack
often occurs after periods of distress or a highly stressful life circumstance.
True
True or False.
It's important to note that many adults who experience a single panic attack DO NOT develop panic disorder.
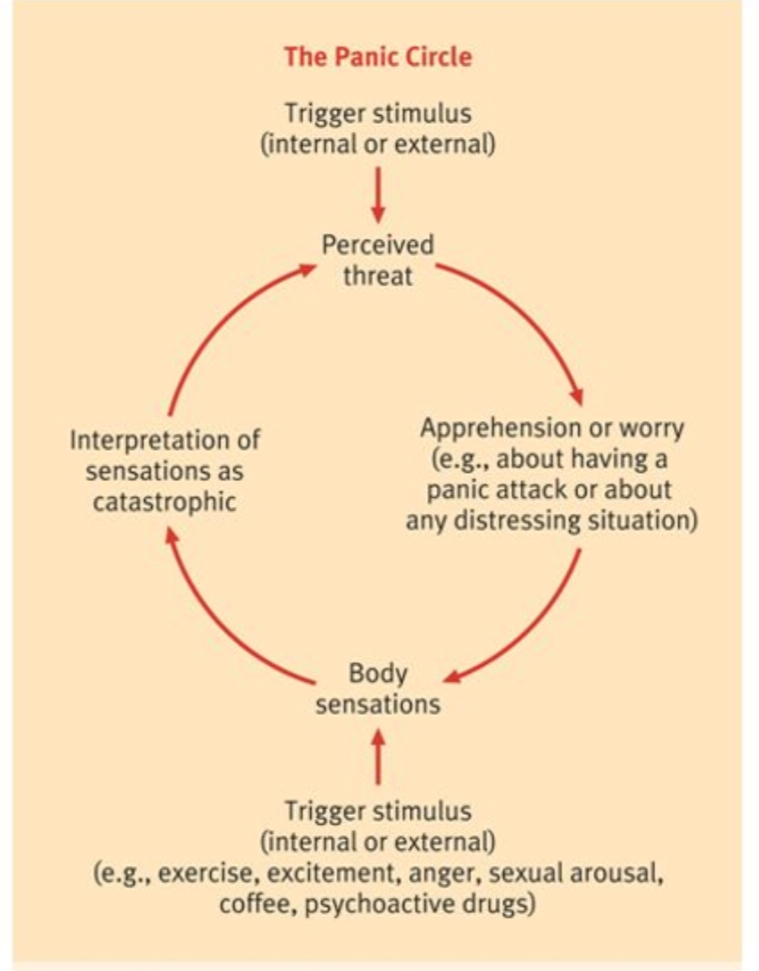
The Panic Circle:
Medications
Behavioral Treatments
Cognitive-Behavioral Treatments
Treatments for Agoraphobia:
Anxiolytics
Antidepressants
Medications for Agoraphobia:
Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD)
Chronic or excessive worry about multiple events and activities
Duration: Occurs more days than not for a 6-month period.
women
GAD is twice as common in _____
Excessive Worry (6+ Months)
Hard to control
3+ Symptoms
Causes Distress/Impairment
Criteria for GAD:
Restlessness/on edge
Easily fatigued
Concentration difficulty
Irritability
Muscle tension
Sleep disturbance
Symptoms for GAD: (6)
Conflict between id and ego
Perceptions of uncontrollability and unpredictability
Worry positive or negative
Automatic attentional bias toward threatening information in environment
Psychological Causal Factors of GAD:
Genetics
Neurotransmitters
CRH (Corticotropin-Releasing Hormone)
Biological Causal Factors of GAD:
Anxiolytic drugs
Buspirone
Cognitive-behavioral therapy
Treatments for GAD: (ABC)
Anxiolytic Drugs
medications primarily used to reduce anxiety.
They are also sometimes referred to as minor tranquilizers.
Buspirone
is an anxiolytic medication that belongs to a different class than benzodiazepines.
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder
Occurrence of unwanted and intrusive obsessive or distressing images
Usually accompanied by compulsive behaviors
Obsessive-Compulsive and related disorders
New category of disorders in DSM-5:
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder
Usually accompanied by compulsive behaviors performed to neutralize obsessive thoughts or images and/or prevent some dreaded event or situation
Contamination fears
Fears of harming oneself or others
Lack of symmetry
Pathological doubt
Obsessions: (CFLP)
Cleaning
Checking
Repeating
Ordering/arranging
Counting
Compulsions: (CCROC)
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder
affects both genders equally
boys
OCD
Also not uncommon in children: more frequent in ____
Mowrer
______ developed the two-process theory of avoidance learning
Two-Process Theory of Avoidance Learning
Neutral stimuli become associated with fearful thoughts via classical conditioning eliciting anxiety
Examples: touching doorknob, shaking hands
Two-Process Theory of Avoidance Learning
explains how fears and phobias are learned and maintained.
It combines classical and operant conditioning processes
Obsessions AND/OR Compulsions
Time-Consuming/Impairing (Obsessions/compulsions take up significant time OR cause distress/impairment.)
Criteria for OCD:
evolutionary
increase
Obsessions with contamination and dirt appear to have ________ roots
Attempting to suppress unwanted thoughts may _______ those thoughts
Genetics
Brain function abnormalities
Serotonin
Biological Causal Factors of OCD:
Serotonin
is strongly implicated in OCD.
Exposure and response prevention
Medications that affect neurotransmitter serotonin
Treatments of OCD:
Exposure and response prevention
most effective approach to obsessive compulsive disorder (OCD)
anxiety-producing obsession
compulsion
Exposure to ___________, prevention of ________ typically used
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder
Medications that affect neurotransmitter serotonin have also been found helpful
Body Dysmorphic Disorder
Obsessed with perceived or imagined flaw in appearance
Causes clinically significant distress
May focus on any body part
Somatoform disorders
BDD has been moved from _________ to OCD disorders because of its commonalities with it
skin
hair
nose
eyes
breasts/chest/nipples
stomach
face size/shape
Most common locations of complaints are:
heritability
self-schema
Causes of BDD still being researched.
There is some _________ and some issues with _______.
Preoccupation with Perceived Defects
Repetitive Behaviors
Clinically Significant Distress
Not Better Explained by Eating Disorder
Criteria for BDD:
both genders
adolescence
BDD:
Gender: BDD affects _____
Onset: Typically begins in ________.
similar behaviors and causes
shares body image distortions with eating disorders
BDD Relationship to OCD and Other Disorders:
Antidepressants
Cognitive-behavioral therapy
Treatments for BDD: (2)
Hoarding Disorder
Acquire and fail to discard limited value possessions (10-40% of OCD sufferers)
impulse-control disorders
Trichotillomania
Moved from ___________ to OCD-related disorders in DSM-5
Trichotillomania
Urge to pull out hair from any body location
Preceded by tension and followed by pleasure
Must cause clinically significant distress
Yoruba Culture of Nigeria
Koro in China
Taijin kyofusho in Japan
Cultural differences in Sources of Worry: (3)
Yoruba Culture of Nigeria
Sources of anxiety:
Creating and maintaining a large family
Fertility
Dreams that may indicate bewitchment
Somatic complaints that are atypical in Western society
Koro
In China, it is an anxiety that a body part is retracting into the body or shrinking
Taijin kyofusho (Japan)
Fear is about offending or embarrassing others, not self.
Is somewhat like social phobia in Western culture.