Biomaterials Test 2
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
biodegradable time frame
6 months
advantages of synthetic polymers:
no immune response, reproducible, wide range of properties
what is km?
the substrate concentration at half reaction rate
in 0 order reactions…
reaction concentration doesn’t matter
in 1st and 2nd order reactions…
concentration of reactants does matter
what are the modes of biodegradation?
surface erosion and bulk degradation
surface erosion is when
the material degrades from the surface in, becomes smaller as it happens, loses mass faster
bulk degradation is when…
more water infiltration, whole material is degraded.
ezymatic degradation is…
either bulk or surface,
enzymes do the degradation through reactions
enzymatic degradation is determined by..
location, concentration, and enzyme kinetics
biodegradation is
degradation that involves biological processes, such as bodily fluids, cell activities, or enzymes, and is influenced by biological environment
hydrophilic polymers degrade _______ than hydrophobic polymers (and why?)
faster, water can get in to break it down faster
amorphous degrades _____ than semi-crystalline
faster
polymers with high tg degrade _____ than polymers with low tg
slower
The ester bond is…
carbon double bonded to an oxygen, and bonded to an oxygen
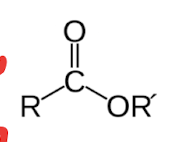
mechanisms of chemical degradation… (list three)
breaking cross links, removing pendant groups, breaking the backbone
hydrophobic polymers degrade by…
surface erosion
hydrophilic polymers degrade by…
bulk degreadation
polyanhydrides
hydrophobic, fast, non toxic
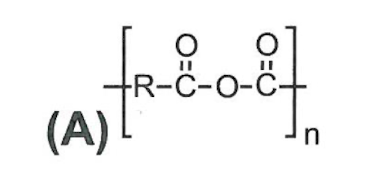
poly(ortho esters)
more hydrophobic, slower
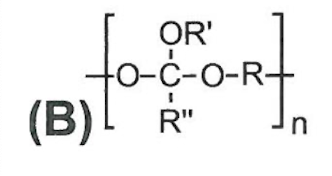
poly( alpha - hydroxy esters)
PLA, PGA, PLGA, broken down by hydrolysis
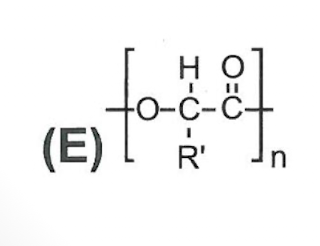
an ester bond next to a thioether group is ______ susceptible to degradation than an unmodified one.
more
_____ is a prerequisite for degredation to occur
water
poly(ortho esters), polyanhydrides, polyesters are ______ degradable polymers
hydrophobic
hydrolytic surface erosion/bulk degradation means…
degradation through water
all natural polymers degrade by…
enzymatic degradation
enzymatic degradation can be….
surface erosion or bulk degradation
for enzymatic degradation, surface erosion occurs in
hydrophobic and hydrophilic polymers
for enzymatic degradation, bulk degradation occurs in
hydrophilic polymers (where enzyme infiltrates and is evenly spread through bulk or the rate of enzymatic bond cleavage is slower than enzyme infiltration)