mid term-science MYP4 '25
1/43
Earn XP
Description and Tags
science note cards
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
DNA
DNA stores genetic information, directs protein production, and is passed from parents to offspring. It replicates during cell division and controls traits and functions in living organisms.
nucleotide
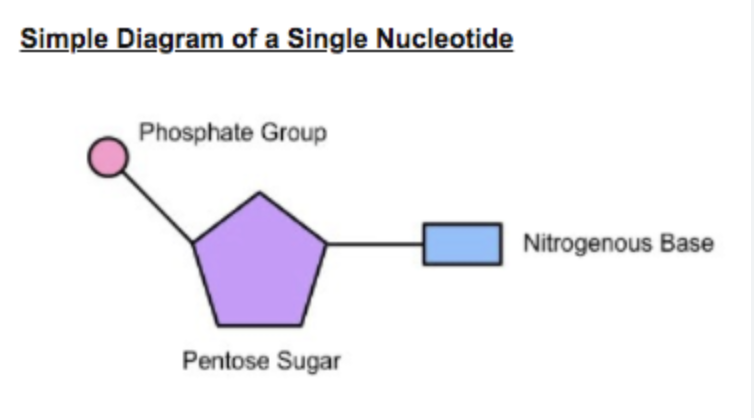
Building block of DNA; phosphate, sugar, nitrogenous base.
gene
DNA segment coding for a protein
genome
Complete set of an organism’s DNA.
chromosome
DNA coiled around proteins in the nucleus.A chromosome packages and organizes DNA so it can fit in the nucleus and be copied correctly during cell division.
RNA polymerase
Enzyme that makes RNA from DNA.RNA polymerase does unwind DNA locally to read the template and synthesize RNA,
transcription
DNA → mRNA in the nucleus.
translation
mRNA → protein at the ribosome.
mRNA
Carries genetic info from DNA to ribosome.
tRNA
Transfers amino acids to ribosome.
codon
3-nucleotide sequence on mRNA coding for an amino acid.
anticodon
3-nucleotide sequence on tRNA matching mRNA codon.
amino acid
Building block of proteins.
polypeptide
Chain of amino acids forming a protein
protein
Made of one or more polypeptides; essential for cell function.
mutation
Change in DNA sequence
mutagen
Agent (e.g., radiation, chemicals) that causes mutations.
somatic (mutation)
Occurs in body cells, not passed to offspring.
gametic (mutation)
Occurs in sperm/egg cells, passed to offspring.
frameshift mutation
Insertion/deletion shifts reading frame.
DNA fingerprinting
Identifies individuals using unique DNA patterns. (STR)
PCR
Amplifies small DNA samples.
gel electrophoresis
Separates DNA by size to compare samples.
reproductive cloning
Creating genetically identical organisms.
gene editing
Altering DNA (e.g., CRISPR, plasmids).
plasmid
Small DNA molecule used in genetic engineering. (only found in bacterium)
CRISPR
Tool for precise gene editing.
GMO
(Genetically Modified Organism): Organism with altered genes.
transgenic organism
Organism with DNA from another species.
Draw and label the three parts of a DNA nucleotide. (Day 1)
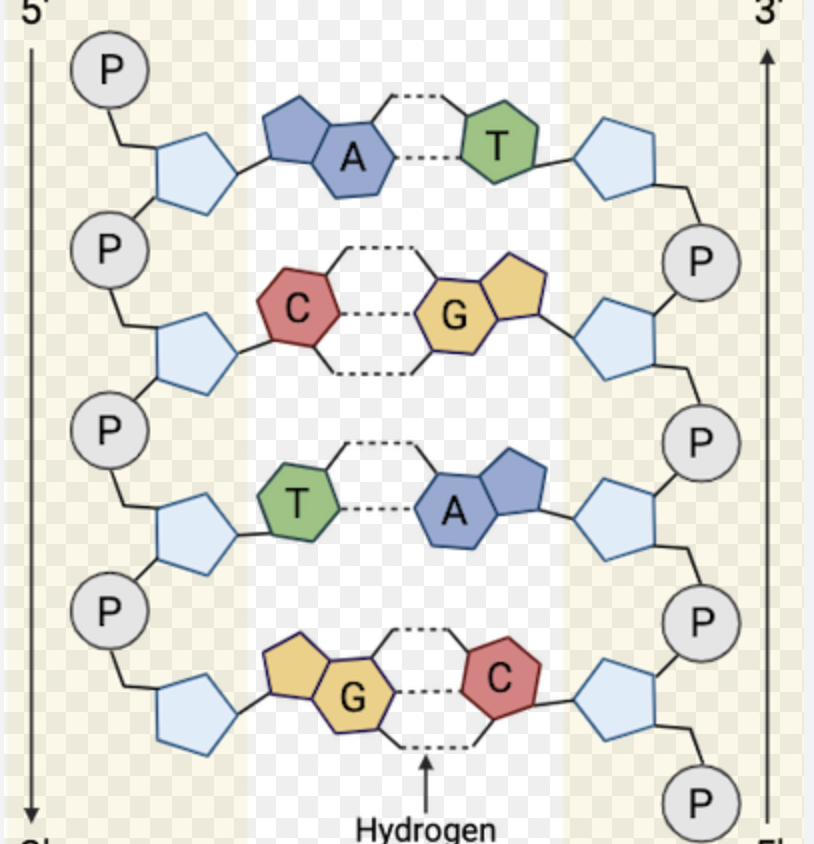
Draw and label a double-stranded DNA molecule with two different base pairs. (Day 2)
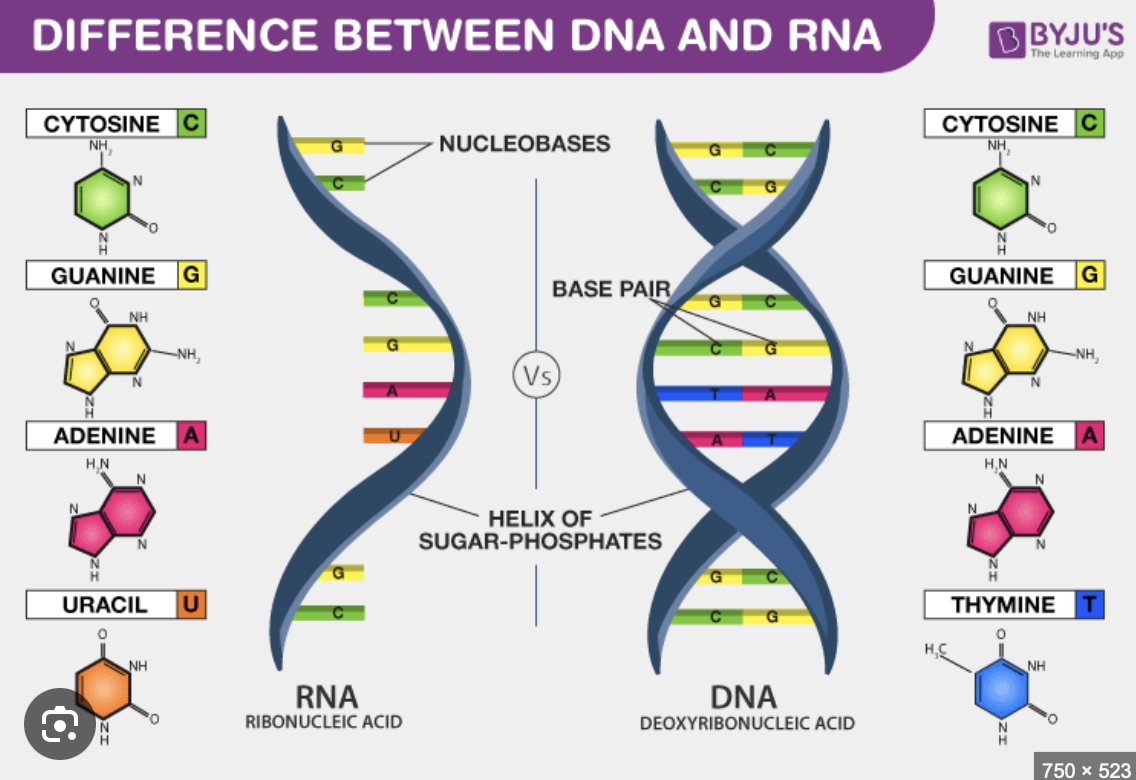
Compare and contrast the structures and functions of DNA and 3 different types of RNA. (Day 3)
Explain how and where DNA is transcribed into mRNA. (Day 3)
Where?
DNA is transcribed into mRNA in the nucleus (eukaryotes) or cytoplasm (prokaryotes).
How?
RNA polymerase makes a copy of DNA into mRNA.
The mRNA is built by matching bases (A → U, T → A, C → G).
When done, mRNA leaves the nucleus to make proteins.
Describe the relationship between amino acids, polypeptides, and proteins. (Day 4)
Amino acids are linked together to form polypeptides, which are chains of amino acids. Polypeptides fold into specific shapes to become functional proteins, which perform various tasks in the body.
Explain how and where the code carried by mRNA is translated to make proteins. (Day 4 & 5)
The mRNA code is translated into proteins at the ribosome in the cytoplasm. The ribosome reads the mRNA, and tRNAbrings amino acids to form a protein.
Transcribe and translate a DNA sequence into the amino acid sequence of a polypeptide/protein. (Days 4 and 5)
The DNA sequence 3' - TAC GGA TCG - 5' transcribes to mRNA 5' - AUG CCU AGC - 3'. This translates to the amino acids Met-Pro-Ser.
Outline the three major types of mutagens and give an example of each type. (Day 6)
Physical mutagens, like UV radiation, damage DNA. Chemical mutagens, such as tobacco smoke, alter DNA structure. Biological mutagens, like the HPV virus, can cause mutations.
Distinguish between the potential consequences of somatic versus gametic mutations. (Day 6)
Determine the effects of a base substitution (mutation) vs. a frameshift mutation (insertion or deletion) on the resulting mRNA, polypeptide/protein, and health of the organism. (Day 6)
Base substitution: Small change, may cause disease (one amino acid change).
Frameshift mutation: Larger changes, usually harmful (entire protein altered).
Explain some of the uses of DNA fingerprinting. (Day 8)
Crime Scene Investigation
Paternity Testing
Identification of Missing Persons
Genealogy and Ancestry Testing
Wildlife Conservation
Outline the goals and processes of PCR and gel electrophoresis. (Day 8)
PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) aims to amplify (make many copies of) a specific DNA segment, while gel electrophoresis separates these amplified DNA fragments (or any DNA) by size, allowing visualization and analysis
Analyze the results of DNA fingerprinting to determine the paternity of a child or to determine which suspect’s DNA was found at a crime scene. (Day 9)
who’s da daddy?

Outline how animals have been reproductively cloned. (Day 11)
Somatic Cell is taken, nucleus is inserted into an egg, and (stimulate the egg thingy) the embryo is implanted in a surrogate mother.
The result is an identical clone of the original animal.
Outline how genomes have been edited using gene cloning, plasmids, and CRISPR. (Day 11)
gene cloning to amplify DNA, plasmids as carriers for editing tools (like CRISPR components), and CRISPR-Cas9 to precisely cut DNA at target sites, enabling gene knockout (via error-prone repair) or knock-in (using a DNA template for precise insertion/replacement)