Respiratory Histology
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
parasympathetic effects on respiratory system
bronchoconstriction
mucous secretion
vasodilation
sympathetic effects on respiratory system
bronchodilation
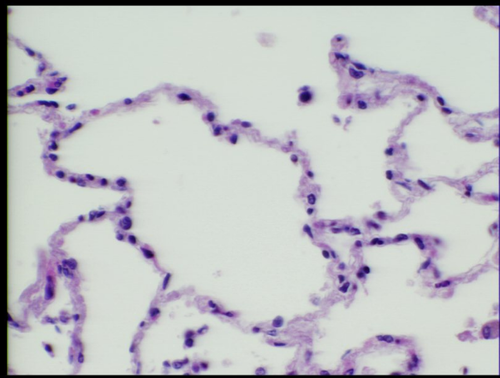
alveolar-capillary barrier
site of O2 and CO2 exchange between distal airspaces and pulmonary vasculature
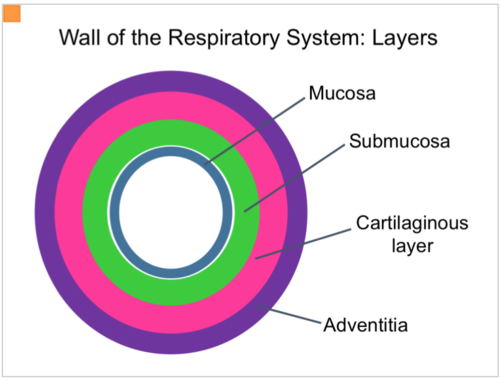
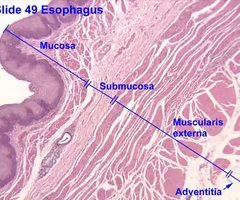
histological - 4 layers of respiratory system
mucosa - epithelium and supporting lamina
submucosa
cartilage and/or muscle (Trachea)
adventitia
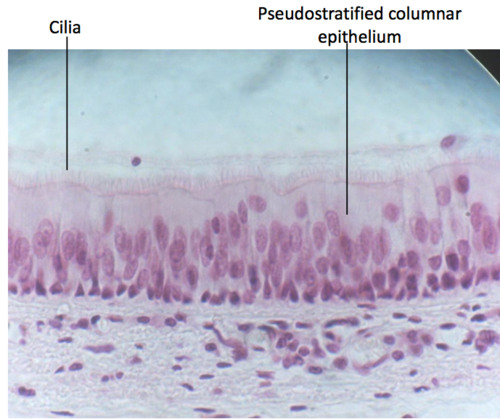
trachea histology
pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium
what are the gaps between trachea cartilage filled with
trachealis muscles
fibroelastic tissue
what are the respiratory mucosa and submucosa adopted to do
warm and moisten air to trap foreign particles in mucous
mucosa histology
ciliated pseudistratified columnar epithelium with goblet cells
lamina propria underneath epithelium contains elastic blood vessels
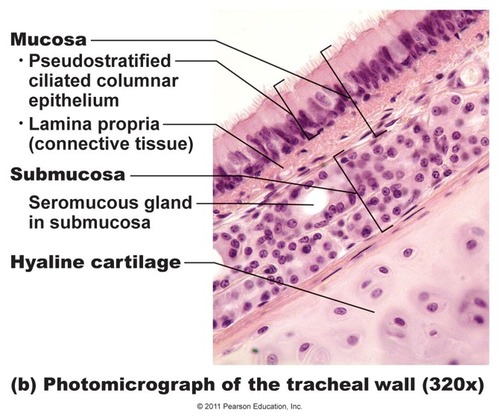
what humidifies the inspired air in submucosa
watery secretions from serous glands
how does the submucosa trap foreign particles
mucus
transported up towards the pharynx by cilia on epithelium
keeps lungs free of particles and bacteria
Adventitia (histology of esophagus)
connects and supports trachea
contains nerves, vessels and adipose tissue
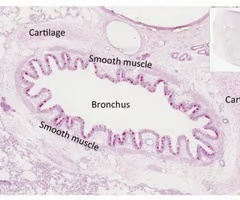
Bronchi histology
Pseudostratified columnar epithelium --> simple columnar cells
Irregular cartilage plates
Fewer seromucous glands
Smooth muscle is prominent
Has abundant elastic fibers
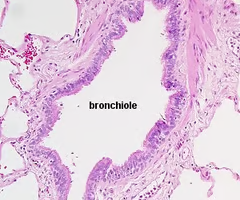
bronchiole histology
-lumen lined with ciliated simple columnar epithelium to ciliated simple cuboidal epithelium
-layer of smooth muscle
respiratory bronchiole histology
Cuboidal ciliated columnar epithelium with interspaced club cells
Sparse smooth muscle layer
lack cartilage
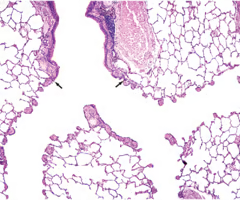
alveoli histology
simple squamous epithelium
type 1 large flattened cells
type 2 little round cells that secrete surfactant